Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns in Herbaceous Peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) Based on Transcriptome Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Transcriptome Data
2.2. Indices of Codon Usage
2.3. Neutrality Plot
2.4. ENC Plot
2.5. Determination of Optimal Codons
2.6. Correspondence Analysis
2.7. PR2-Bias Plot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nucleotide Contents of Genes in P. lactiflora


3.2. Relative Synonymous Codon Usage Analysis of the P. lactiflora Genome
| Parameters | GC12 | GC3 | GCall | ENC | CAI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC3 | −0.03** | ||||
| GCall | 0.737** | 0.590** | |||
| ENC | 0.100** | −0.053** | 0.034** | ||
| CAI | −0.107** | 0.330** | 0.124** | −0.405** | |
| Axis1 | 0.159** | 0.758** | 0.610** | 0.022** | 0.293** |
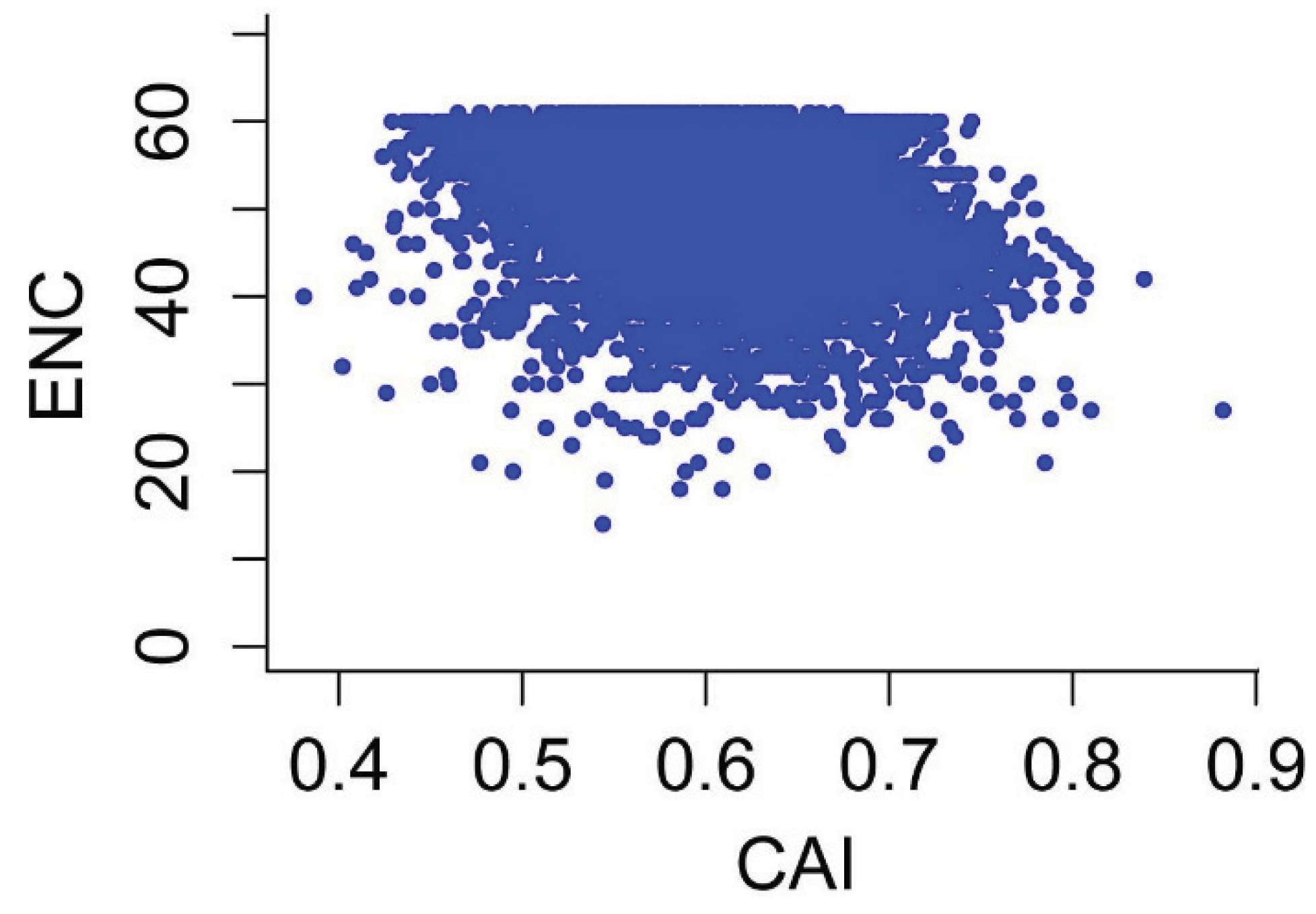
3.3. Determination of Codon Usage Bias Based on ENC
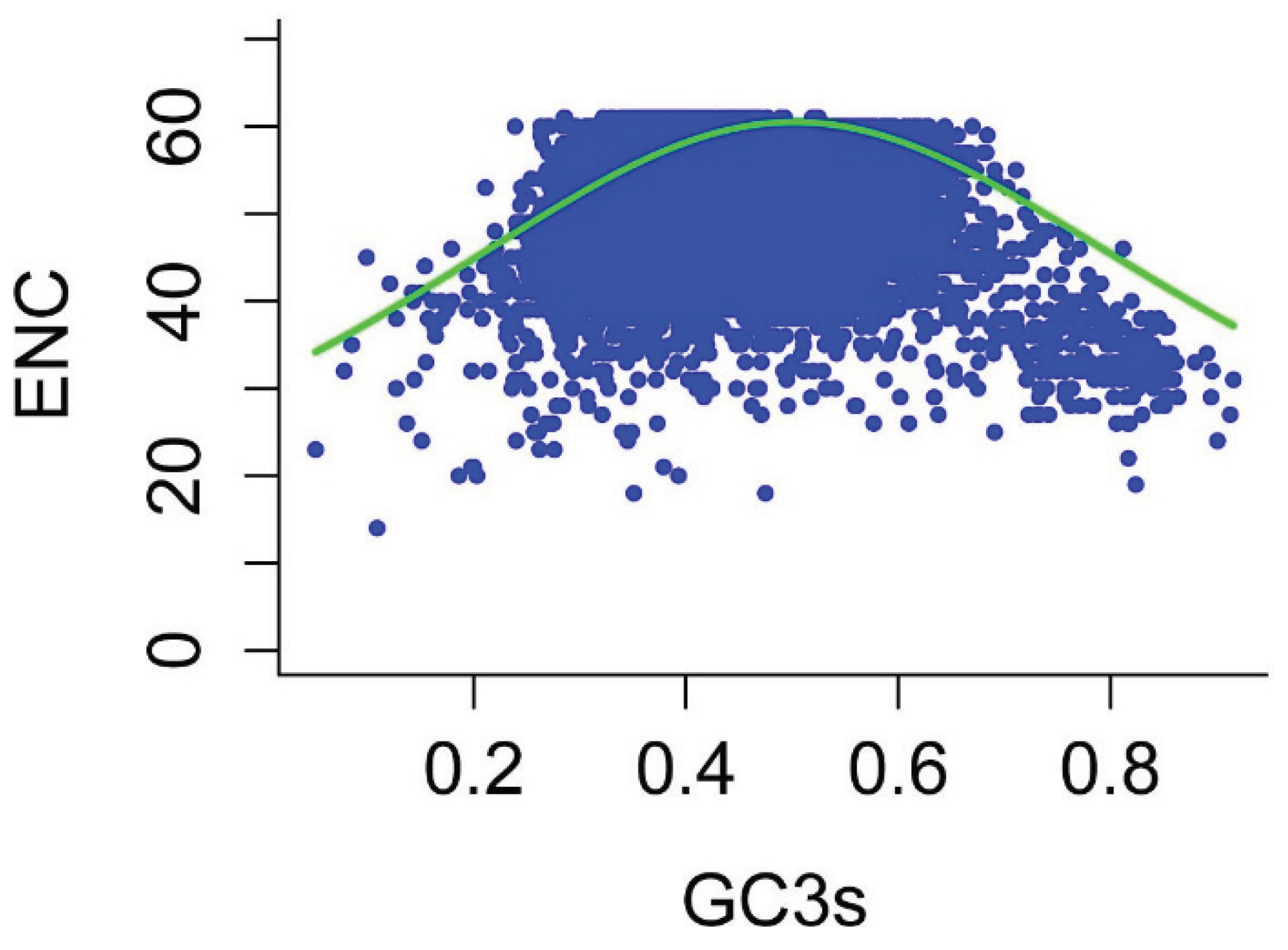
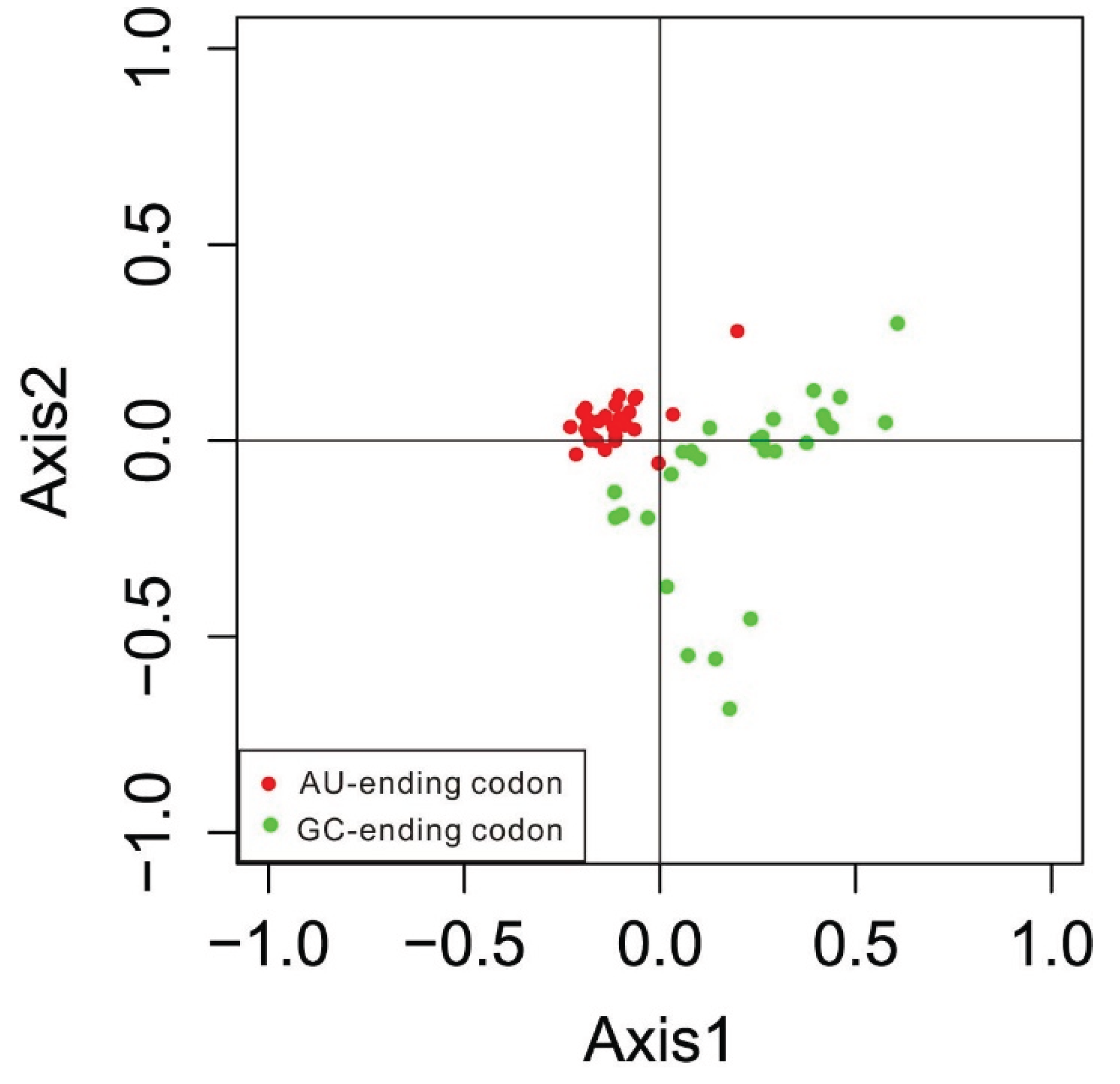
3.4. Correspondence Analysis

3.5. PR2-Bias Plot Analysis
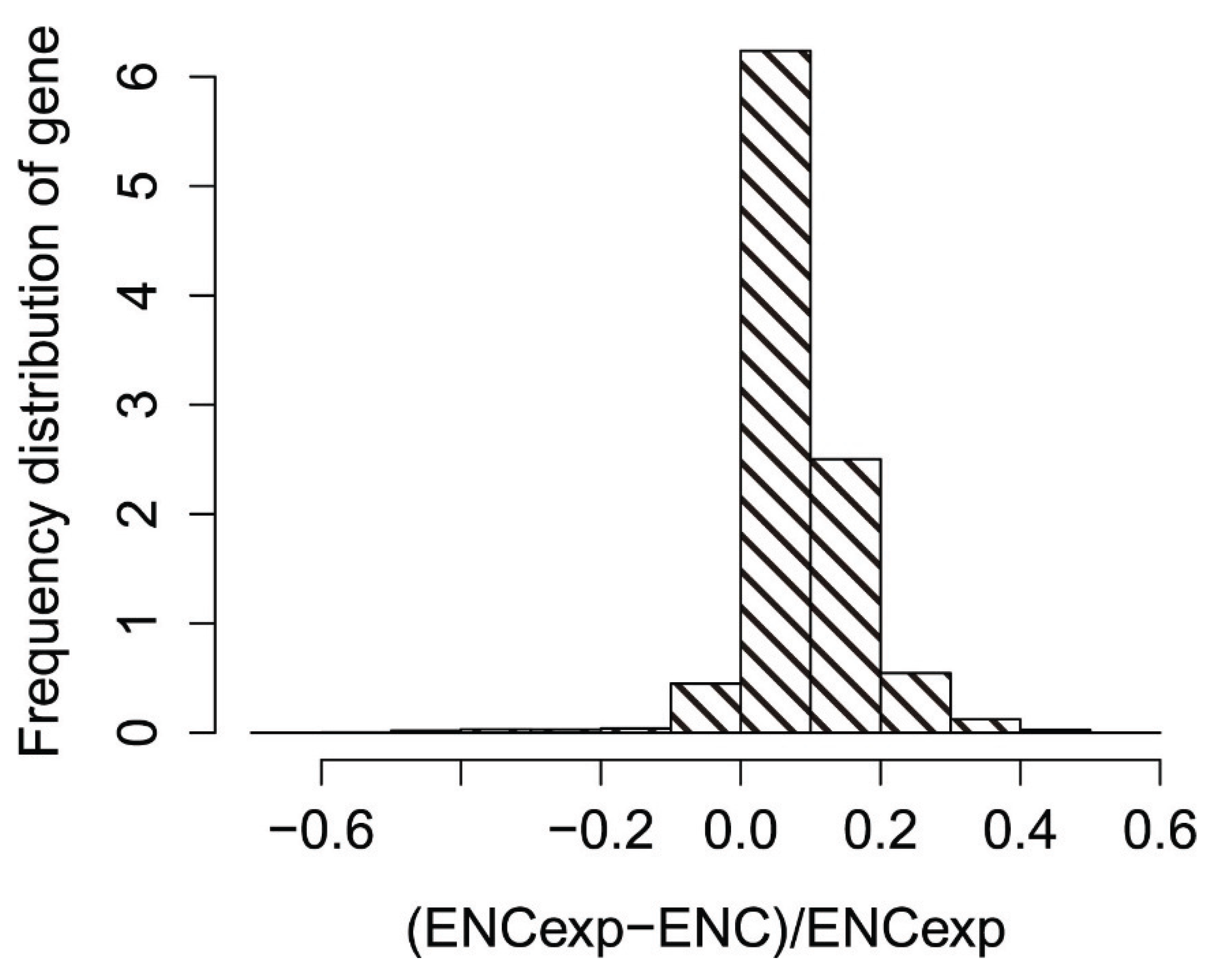
3.6. Effects of Gene Expression Level and Encoded Protein Length on Synonymous Codon Usage Bias

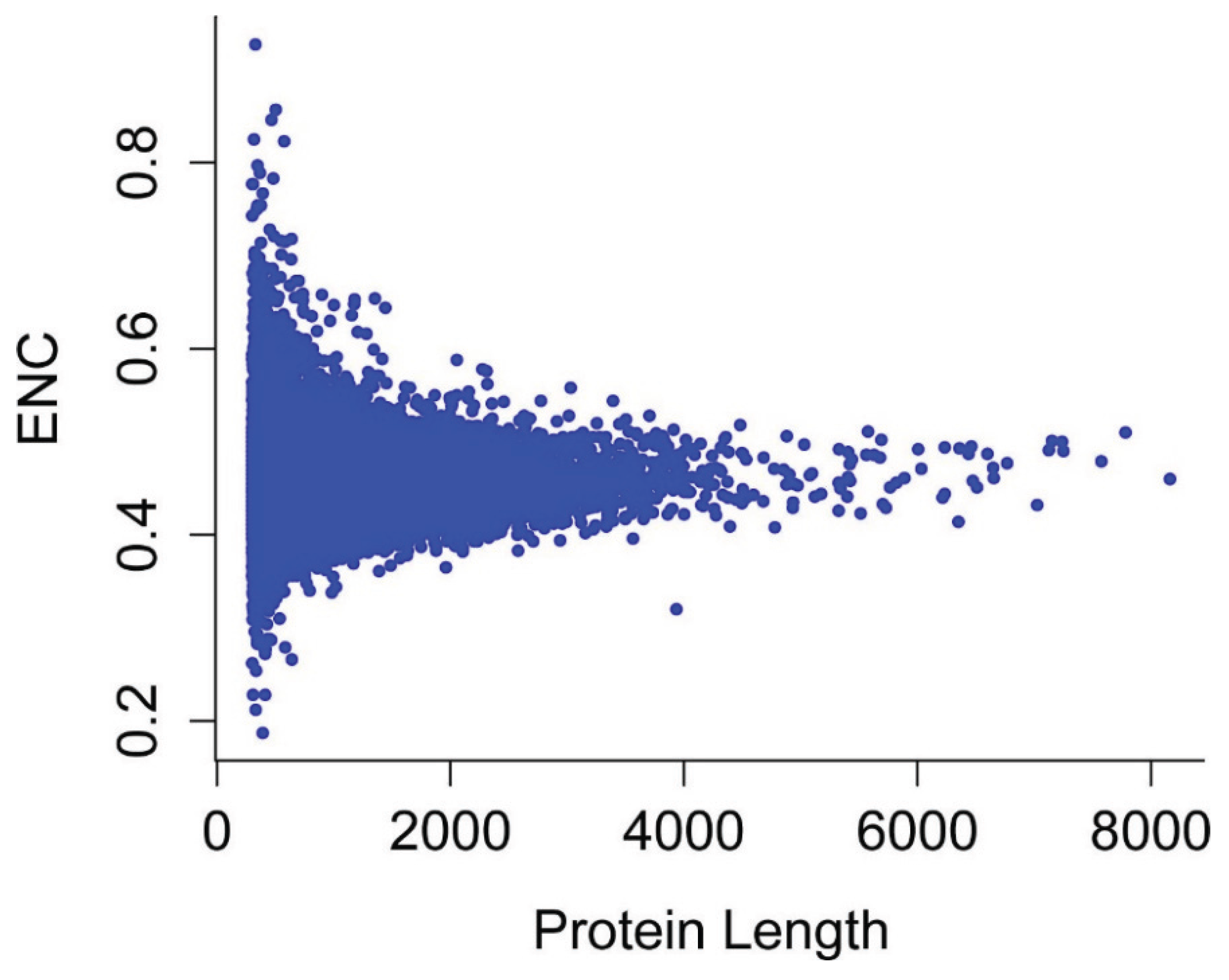
3.7. Optimal Codons
| AA | Codon | High RSCU(N) | Low RSCU(N) | AA | Codon | High RSCU(N) | Low RSCU(N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ala | GCA | 1.245(3868) | 1.296(10,358) | Leu | CUA | 0.637(1889) | 0.510(3679) |
| GCC* | 0.888(2761) | 0.610(4878) | CUC | 1.036(3071) | 0.662(4778) | ||
| GCG | 0.471(1464) | 0.305(2439) | CUG | 0.757(2244) | 0.671(4848) | ||
| GCU* | 1.396(4338) | 1.789(14,297) | CUU* | 1.343(3981) | 1.621(11,707) | ||
| Arg | AGA* | 1.582(2545) | 1.939(8781) | UUA | 0.838(2486) | 0.893(6449) | |
| AGG | 1.478(2378) | 1.552(7025) | UUG | 1.389(4119) | 1.643(11,862) | ||
| CGA | 0.831(1338) | 0.641(2901) | Lys | AAA | 0.911(6111) | 0.925(13,915) | |
| CGC | 0.582(936) | 0.481(2177) | AAG | 1.089(7299) | 1.075(16,161) | ||
| CGG | 0.648(1042) | 0.492(2228) | Met | AUG | 1.000(4764) | 1.000(10,846) | |
| CGU | 0.880(1416) | 0.895(4054) | Pro | CCA* | 1.376(3278) | 1.458(8919) | |
| Asn | AAC | 0.882(3785) | 0.627(6592) | CCC* | 0.779(1855) | 0.590(3608) | |
| AAU | 1.118(4801) | 1.373(14,443) | CCG | 0.606(1444) | 0.383(2340) | ||
| Asp | GAC | 0.742(3791) | 0.529(7071) | CCU | 1.239(2953) | 1.569(9600) | |
| GAU | 1.258(6427) | 1.471(19,638) | Ser | AGC* | 0.807(2057) | 0.573(4176) | |
| Cys | UGC* | 0.949(1812) | 0.748(2950) | AGU | 1.031(2628) | 1.074(7834) | |
| UGU* | 1.051(2005) | 1.252(4937) | UCA* | 1.218(3105) | 1.427(10,405) | ||
| Gln | CAA | 1.086(3875) | 1.099(10,044) | UCC* | 0.961(2450) | 0.670(4885) | |
| CAG | 0.914(3259) | 0.901(8230) | UCG* | 0.620(1580) | 0.431(3144) | ||
| Glu | GAA | 1.038(6811) | 1.112(18,684) | UCU | 1.365(3481) | 1.826(13,318) | |
| GAG | 0.962(6315) | 0.888(14,916) | Thr | ACA* | 1.198(2842) | 1.316(7458) | |
| Gly | GGA* | 1.195(3801) | 1.270(10,495) | ACC | 1.047(2485) | 0.745(4221) | |
| GGC | 0.733(2333) | 0.546(4515) | ACG | 0.491(1166) | 0.365(2069) | ||
| GGG | 0.849(2699) | 0.779(6443) | ACU | 1.263(2997) | 1.574(8922) | ||
| GGU | 1.223(3890) | 1.405(11,615) | Trp | UGG | 1.000(2675) | 1.000(5315) | |
| His | CAC | 0.871(2065) | 0.609(3419) | Tyr | UAC* | 0.917(2611) | 0.702(4462) |
| CAU | 1.129(2679) | 1.391(7818) | UAU* | 1.083(3082) | 1.298(8257) | ||
| Ile | AUA* | 0.765(2676) | 0.730(5857) | Val | GUA* | 0.711(2143) | 0.642(5096) |
| AUC* | 0.939(3286) | 0.632(5066) | GUC | 0.801(2412) | 0.569(4523) | ||
| AUU | 1.296(4532) | 1.638(13,133) | GUG* | 1.106(3331) | 0.930(7389) | ||
| Phe | UUC* | 0.939(4017) | 0.665(6011) | GUU | 1.382(4163) | 1.859(14,764) | |
| UUU* | 1.061(4535) | 1.335(12,077) |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ikemura, T. Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1985, 2, 13–34. [Google Scholar]
- Hershberg, R.; Petrov, D.A. Selection on codon bias. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.M.; Li, W.H. An evolutionary perspective on synonymous codon usage in unicellular organisms. J. Mol. Evol. 1986, 24, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulmer, M. The selection-mutation-drift theory of synonymous codon usage. Genetics 1991, 129, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Angellotti, M.C.; Bhuiyan, S.B.; Chen, G.; Wan, X.F. CodonO: Codon usage bias analysis within and across genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.M.; Bailes, E.; Grocock, R.J.; Peden, J.F.; Sockett, R.E. Variation in the strength of selected codon usage bias among bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.M.; Tuohy, T.M.; Mosurski, K.R. Codon usage in yeast: Cluster analysis clearly differentiates highly and lowly expressed genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986, 14, 5125–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Sun, X.; Lu, Z. Synonymous codon usage in environmental chlamydia UWE25 reflects an evolutional divergence from pathogenic chlamydiae. Gene 2006, 368, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duret, L.; Mouchiroud, D. Expression pattern and, surprisingly, gene length shape codon usage in Caenorhabditis, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4482–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafay, B.; Sharp, P.M. Synonymous codon usage variation among Giardia lamblia genes and isolates. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1484–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ghosh, T.C.; Gupta, S.K.; Majumdar, S. Studies on codon usage in Entamoeba histolytica. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInerney, J.O. Replicational and transcriptional selection on codon usage in Borrelia burgdorferi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 10698–10703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishihara, M.; Nakatsuka, T. Genetic engineering of flavonoid pigments to modify flower color in floricultural plants. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: A revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.Q.; Jiang, Y.; Ning, C.L.; Meng, J.; Lin, S.; Ding, W.; Tao, J. Transcriptome sequencing of a chimaera reveals coordinated expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes mediating yellow formation in herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.). BMC Genomics 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iseli, C.; Jongeneel, C.V.; Bucher, P. ESTScan: A program for detecting, evaluating, and reconstructing potential coding regions in EST sequences. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 1999, 99, 138–148. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, F. The “effective number of codons” used in a gene. Gene 1990, 87, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuglsang, A. The “effective number of codons” revisited. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 317, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.M.; Li, W.H. The codon adaptation index—A measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 1281–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peden, J.F. CodonW. PhD Thesis, University of Nottingham, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sueoka, N. Directional mutation pressure and neutral molecular evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 2653–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Luo, X.; Cai, X. Analysis of codon usage pattern in Taenia saginata based on a transcriptome dataset. Parasit. Vectors 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenacre, M.J. Theory and Applications of Correspondence Analysis; Academic Press: London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Noboru, S. Near homogeneity of PR2-bias fingerrints in the human genome and their implications in phylogenetic analyses. J. Mol. Evol. 2001, 53, 469–476. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, G.M.; Holmes, E.C. The extent of codon usage bias in human RNA viruses and its evolutionary origin. Virus Res. 2003, 92, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueoka, N. Translation-coupled violation of Parity Rule 2 in human genes is not the cause of heterogeneity of the DNA G + C content of third codon position. Gene 1999, 238, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naya, H.; Romero, H.; Carels, N.; Zavala, A.; Musto, H. Translational selection shapes codon usage in the GC-rich genome of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. FEBS Lett. 2001, 501, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Bhattacharyya, T.; Ghosh, T.C. Synonymous codon usage in Lactococcus lactis: Mutational bias versus translational selection. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2004, 21, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, C.; Govindarajan, S.; Minshull, J. Codon bias and heterologous protein expression. Trends Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, R.D.; Freeland, S.J.; Landweber, L.F. A simple model based on mutation and selection explains trends in codon and amino-acid usage and GC composition within and across genomes. Genome Biol. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, Y.; Kawamata, K.; Haraguchi, T.; Chikashige, Y. Codon usage bias is correlated with gene expression evels in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Genes Cells 2009, 14, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, A.; Saxonov, S.; Gilbert, W. Regularties of context-dependent codon bias in eukaryotic genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comeron, J.M.; Kreitman, M.; Aguade, M. Natural selection on synonymous sites is correlated with gene length and recombination in Drosophila. Genetics 1999, 151, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Carlini, D.B.; Baines, J.F.; Parsch, J.; Braverman, J.M.; Tanda, S.; Stephan, W. RNA secondary structure and compensatory evolution. Genes Genet. Syst. 1999, 74, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Oresic, M.; Dehn, M.; Korenblum, D.; Shalloway, D. Tracing specific synonymous codon-secondary structure correlations through evolution. J. Mol. Evol. 2003, 56, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vinogradov, A.E. Intron length and codon usage. J. Mol. Evol. 2001, 52, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabe, A.; Miyashita, N.T. Patterns of codon usage bias in three dicot and four monocot plant species. Genes Genet. Syst. 2003, 78, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saul, A.; Battistutta, D. Codon usage in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1988, 27, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milhon, J.L.; Tracy, J.W. Updated codon usage in Schistosoma. Exp. Parasitol. 1995, 80, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, A.; Yamao, F.; Osawa, S. The genome of Mycoplasma capricolum. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1987, 34, 29–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Tao, J. Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns in Herbaceous Peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) Based on Transcriptome Data. Genes 2015, 6, 1125-1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6041125
Wu Y, Zhao D, Tao J. Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns in Herbaceous Peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) Based on Transcriptome Data. Genes. 2015; 6(4):1125-1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6041125
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yanqing, Daqiu Zhao, and Jun Tao. 2015. "Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns in Herbaceous Peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) Based on Transcriptome Data" Genes 6, no. 4: 1125-1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6041125
APA StyleWu, Y., Zhao, D., & Tao, J. (2015). Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns in Herbaceous Peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) Based on Transcriptome Data. Genes, 6(4), 1125-1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes6041125





