MODY5 and 17q12 Microdeletion Syndrome: Phenotype Variability, Prenatal and Postnatal Counseling
Abstract
1. Renal Cysts and Diabetes Syndrome: One of the Inherited Forms of Diabetes
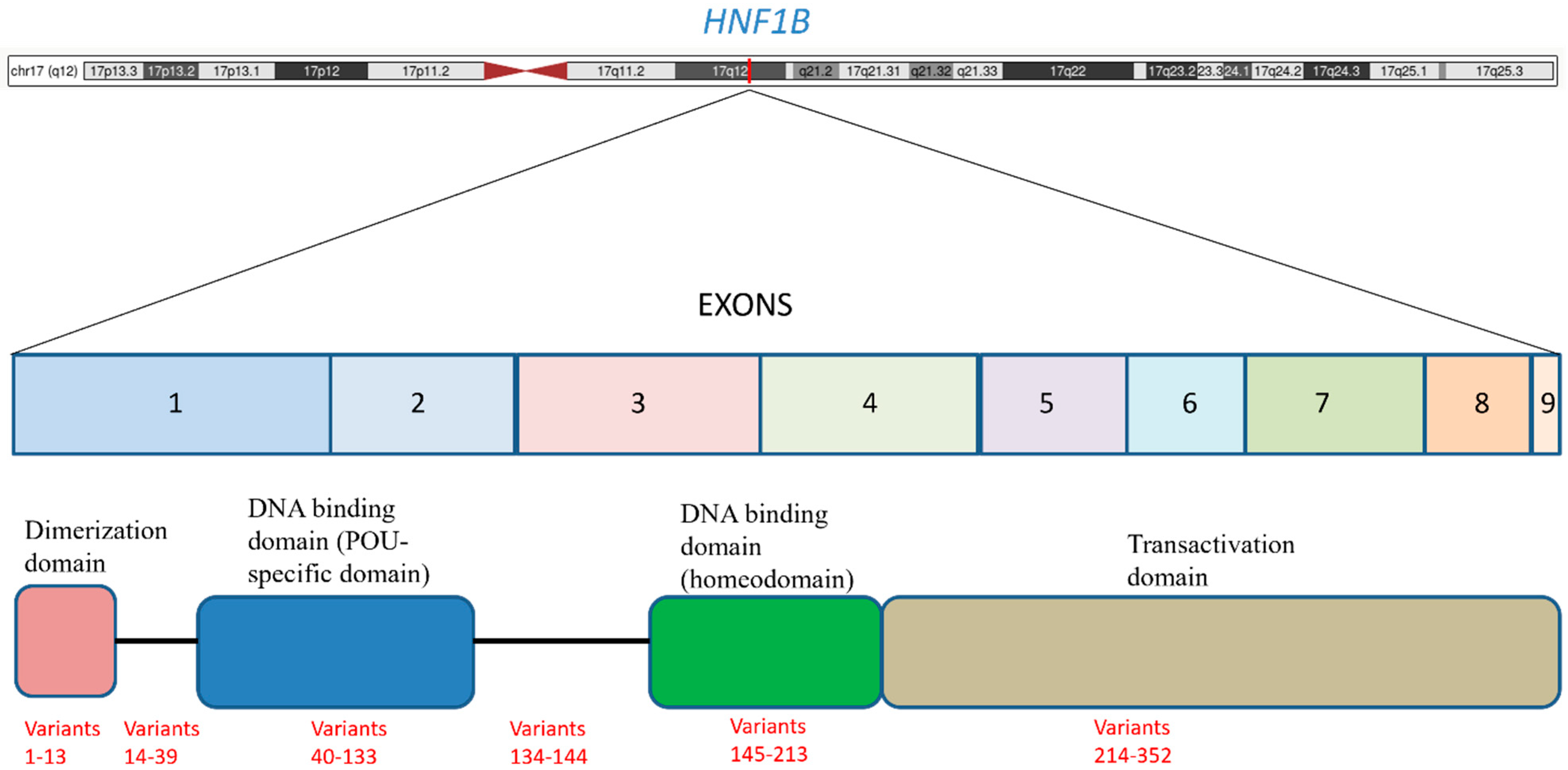
2. The Major MODY5 Associated Gene: HNF1B
3. 17q12 Deletions
4. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young
5. Renal Manifestations
- 1.
- Cystic kidney disease: Bilateral cortical and medullary cysts (sometimes resembling ADPKD) are frequent. Many patients show multiple kidney cysts on imaging, even if renal function is preserved [19].
- 2.
- Renal hypodysplasia/agenesis: Unilateral or bilateral small kidneys, hyperechogenic kidneys on ultrasound, or solitary kidney are common. Up to 30–40% have renal hypoplasia or agenesis [20].
- 3.
- Tubulointerstitial kidney disease (ADTKD): Some patients develop slowly progressive cystic kidney disease with tubulointerstitial fibrosis. HNF1B-related ADTKD is now recognized as a common monogenic CKD cause [21].
- 4.
- Congenital anomalies of the kidney/urinary tract (CAKUT): A range of structural anomalies can occur (horseshoe kidney, duplex collecting systems, hydronephrosis) [8].
- 5.
- Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: Partial nephrogenic DI (polyuria and dilute urine) are occasionally described [8].
- 6.
- Electrolyte disturbances: Chronic renal magnesium wasting leads to hypomagnesemia in many patients. Hypokalemia is also reported. Hyperuricemia/gout can occur at a young age [22].
- 7.
- End-stage renal disease (ESRD): Cystic kidney disease can lead to renal failure, often developing in adolescence/adulthood but not in childhood [23]. In one series, 8 of 10 patients had cystic kidney disease and several required transplant; kidney disease may precede or outpace the onset of the diabetes [4]. The progression to ESRD appears to be less in patients with 17q12 deletions compared to patients with HNF1B point variants [13].
6. Neurodevelopmental Disorders
7. Gastrointestinal Features
8. Eye Defects and Hearing Loss
9. Other Congenital Defects
10. Prenatal Counseling
11. Postnatal Counseling
- 1.
- Extended evaluation of both renal morphology and function, including the diagnosis of hypomagnesemia
- 2.
- Endocrinologic follow-up for MODY5
- 3.
- Neurodevelopmental assessment in children with 17q12 deletions
- 4.
- Ultrasound screening for heart and genital defects
- 5.
- Eye examination and audiological evaluation
- 6.
- Liver function tests
- 7.
- Genetic counseling for follow-up care coordination, the identification of eventual less common clinical signs, and providing information about recurrence risk.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Khairi, R.; Vallier, L. The role of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 beta in disease and development. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18 (Suppl. 1), 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattersall, R.B. Mild familial diabetes with dominant inheritance. Q J. Med. 1974, 43, 339–357. [Google Scholar]
- Horikawa, Y.; Iwasaki, N.; Hara, M.; Furuta, H.; Hinokio, Y.; Cockburn, B.N.; Lindner, T.; Yamagata, K.; Ogata, M.; Tomonaga, O.; et al. Mutation in hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 beta gene (TCF2) associated with MODY. Nat. Genet. 1997, 17, 384–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, S.; Palha, A.; Bogalho, P.; Silva-Nunes, J. Maturity-onset diabetes of the young secondary to HNF1B variants (HNF1B-MODY): A series of 10 patients from a single diabetes center. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Gong, Y.; Patel, V.; Karner, C.M.; Fischer, E.; Hiesberger, T.; Carroll, T.J.; Pontoglio, M.; Igarashi, P. Mutations of HNF-1-beta inhibit epithelial morphogenesis through dysregulation of SOCS-3. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20386–20391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornfeld, J.-W.; Baitzel, C.; Konner, A.C.; Nicholls, H.T.; Vogt, M.C.; Herrmanns, K.; Scheja, L.; Haumaitre, C.; Wolf, A.M.; Knippschild, U.; et al. Obesity-induced overexpression of miR-802 impairs glucose metabolism through silencing of Hnf1b. Nature 2013, 494, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delvecchio, M.; Pastore, C.; Giordano, P. Treatment Options for MODY Patients: A Systematic Review of Literature. Diabetes Ther. 2020, 11, 1667–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzi, C.; Dordoni, C.; Econimo, L.; Delbarba, E.; Grati, F.R.; Martin, E.; Mazza, C.; Savoldi, G.; Rampoldi, L.; Alberici, F.; et al. Variable Expressivity of HNF1B Nephropathy, From Renal Cysts and Diabetes to Medullary Sponge Kidney Through Tubulo-interstitial Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 2341–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Han, K.H.; Ahn, Y.H.; Kang, H.G.; Ha, I.S.; Cheong, H.I. Genotype and Phenotype Analyses in Pediatric Patients with HNF1B Mutations. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, A.J.; Hansen, S.; Selzer, R.R.; Cheng, Z.; Regan, R.; Hurst, J.A.; Stewart, H.; Price, S.M.; Blair, E.; Hennekam, R.C.; et al. Discovery of previously unidentified genomic disorders from the duplication architecture of the human genome. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 1038–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamani, S.C.S.; Erez, A.; Shen, J.; Li, C.; Roeder, E.; Cox, S.; Karaviti, L.; Pearson, M.; Kang, S.L.; Sahoo, T.; et al. spectrum associated with recurrent genomic rearrangements in chromosome 17q12. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 18, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.Y.; Yang, J.; Jiang, S.; Du, G.L. HNF1β, LHX1, and GGNBP2 deletion contributed to kidney and reproductive dysfunction in 17q12 deletion syndrome: Evidence from a case report. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1391804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois-Laforgue, D.; Cornu, E.; Saint-Martin, C.; Coste, J.; Bellanné-Chantelot, C.; Timsit, J. Diabetes, associated clinical spectrum, long-term prognosis, and genotype/phenotype correlations in 201 adult patients with hepatocyte nuclear factor 1B (HNF1B) molecular defects. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1436–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anık, A.; Çatlı, G.; Abacı, A.; Böber, E. Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY): An update. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 28, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timsit, J.; Bellanné-Chantelot, C.; Dubois-Laforgue, D.; Velho, G. Diagnosis and management of maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Treat. Endocrinol. 2005, 4, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellanné-Chantelot, C.; Clauin, S.; Chauveau, D.; Collin, P.; Daumont, M.; Douillard, C.; Dubois-Laforgue, D.; Dusselier, L.; Gautier, J.F.; Jadoul, M.; et al. Large genomic rearrangements in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1beta (TCF2) gene are the most frequent cause of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 5. Diabetes 2005, 54, 3126–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitou, C.; Francois, H.; Bellanne-Chantelot, C.; Noel, C.; Jacquet, A.; Clauin, S.; Beaudreuil, S.; Damieri, H.; Hebibi, H.; Hammoudi, Y.; et al. Maturity onset diabetes of the young: Clinical characteristics and outcome after kidney and pancreas transplantation in MODY3 and RCAD patients: A single center experience. Transpl. Int. 2012, 25, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bantounas, I.; Rooney, K.M.; Lopes, F.M.; Tengku, F.; Woods, S.; Zeef, L.A.H.; Lin, I.H.; Kuba, S.Y.; Bates, N.; Hummelgaard, S.; et al. Human pluripotent stem cell-derived kidney organoids reveal tubular epithelial pathobiology of heterozygous HNF1B-associated dysplastic kidney malformations. Stem Cell Rep. 2024, 19, 859–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clissold, R.L.; Hamilton, A.J.; Hattersley, A.T.; Ellard, S.; Bingham, C. HNF1B-associated renal and extra-renal disease—An expanding clinical spectrum. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madariaga, L.; García-Castaño, A.; Ariceta, G.; Martínez-Salazar, R.; Aguayo, A.; Castaño, L. Variable phenotype in HNF1B mutations: Extrarenal manifestations distinguish affected individuals from the population with congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract. Clin. Kidney J. 2018, 12, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, K.U.; Alper, S.L.; Antignac, C.; Bleyer, A.J.; Chauveau, D.; Dahan, K.; Deltas, C.; Hosking, A.; Kmoch, S.; Rampoldi, L.; et al. Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease: Diagnosis, classification, and management—A KDIGO consensus report. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhave, J.C.; Bech, A.P.; Wetzels, J.F.; Nijenhuis, T. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1β-associated kidney disease: More than renal cysts and diabetes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bockenhauer, D.; Jaureguiberry, G. HNF1B-associated clinical phenotypes: The kidney and beyond. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2016, 31, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois-Laforgue, D.; Bellanné-Chantelot, C.; Charles, P.; Jacquette, A.; Larger, E.; Ciangura, C.; Saint-Martin, C.; Rastel, C.; Keren, B.; Timsit, J. Intellectual disability in patients with MODY due to hepatocyte nuclear factor 1B (HNF1B) molecular defects. Diabetes Metab. 2017, 43, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clissold, R.L.; Shaw-Smith, C.; Turnpenny, P.; Bunce, B.; Bockenhauer, D.; Kerecuk, L.; Waller, S.; Bowman, P.; Ford, T.; Ellard, S.; et al. Chromosome 17q12 microdeletions but not intragenic HNF1B mutations link developmental kidney disease and psychiatric disorder. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symmank, J.; Gölling, V.; Gerstmann, K.; Zimmer, G. The transcription factor LHX1 regulates the survival and directed migration of POA-derived cortical interneurons. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 1644–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiyonobu, T.; Inoue, N.; Morimoto, M.; Kinoshita, T.; Murakami, Y. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor deficiency caused by mutations in PIGW is associated with West syndrome and hyperphosphatasia with mental retardation syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 2014, 51, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, A.; Chan, S.C.; Igarashi, P. Role of transcription factor hepatocyte nuclear factor-1β in polycystic kidney disease. Cell Signal. 2020, 71, 109568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nittel, C.M.; Dobelke, F.; König, J.; Konrad, M.; Becker, K.; Kamp-Becker, I.; Weber, S. Review of neurodevelopmental disorders in patients with HNF1B gene variations. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1149875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffargue, F.; Bourthoumieu, S.; Llanas, B.; Baudouin, V.; Lahoche, A.; Morin, D.; Bessenay, L.; De Parscau, L.; Cloarec, S.; Delrue, M.-A.; et al. Towards a new point of view on the phenotype of patients with a 17q12 microdeletion syndrome. Arch. Dis. Child. 2015, 100, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laliève, F.; Decramer, S.; Heidet, L.; Baudouin, V.; Lahoche, A.; Llanas, B.; Cochat, P.; Tenenbaum, J.; Lavocat, M.P.; Eckart, P.; et al. School level of children carrying a HNF1B variant or a deletion. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 28, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-De-Luca, D.; SGENE Consortium; Mulle, J.G.; Simons Simplex Collection Genetics Consortium; Kaminsky, E.B.; Sanders, S.J.; GeneSTAR; Myers, S.M.; Adam, M.P.; Pakula, A.T.; et al. Deletion 17q12 is a recurrent copy number variant that confers high risk of autism and schizophrenia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 87, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vas, M.G.; Kopp, J.L.; Heliot, C.; Sander, M.; Cereghini, S.; Haumaitre, C. Hnf1b controls pancreas morphogenesis and the generation of Ngn3+ endocrine progenitors. Development 2015, 142, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldorsen, I.S.; Vesterhus, M.; Raeder, H.; Jensen, D.K.; Søvik, O.; Molven, A.; Njølstad, P.R. Lack of pancreatic body and tail in HNF1B mutation carriers. Diabet. Med. 2008, 25, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettunen, J.L.T.; Parviainen, H.; Miettinen, P.J.; Färkkilä, M.; Tamminen, M.; Salonen, P.; Lantto, E.; Tuomi, T. Biliary Anomalies in Patients With HNF1B Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotalova, R.; Dusatkova, P.; Cinek, O.; Dusatkova, L.; Dedic, T.; Seeman, T.; Lebl, J.; Pruhova, S. Hepatic phenotypes of HNF1B gene mutations: A case of neonatal cholestasis requiring portoenterostomy and literature review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 2550–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckwerth, J.A.; Dahl, A.R.; Pittock, S.T.; Kumar, S.; Rosen, C.B.; Grothe, R.M.; Furuya, K.N. Liver Transplantation and Development of Diabetes in an Adolescent Male with HNF1B Disease. JPGN Rep. 2021, 2, e085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Zeng, N.; Wen, X.; Zhu, P.; Li, W. A rare combination of MODY5 and duodenal atresia in a patient: A case report. BMC Med. Genet. 2020, 21, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, M.; Vestergaard, E.M.; Graakjaer, J.; Petkov, Y.; Bache, I.; Fagerberg, C.; Kibaek, M.; Svaneby, D.; Petersen, O.B.; Brasch-Andersen, C.; et al. 17q12 deletion and duplication syndrome in Denmark-a clinical cohort of 38 patients and review of the literature. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2016, 170, 2934–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raile, K.; Klopocki, E.; Holder, M.; Wessel, T.; Galler, A.; Deiss, D.; Müller, D.; Riebel, T.; Horn, D.; Maringa, M.; et al. Expanded clinical spectrum in hepatocyte nuclear factor 1b-maturity-onset diabetes of the young. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 2658–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oram, R.A.; Edghill, E.L.; Blackman, J.; Taylor, M.J.; Kay, T.; Flanagan, S.E.; Ismail-Pratt, I.; Creighton, S.M.; Ellard, S.; Hattersley, A.T.; et al. Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1β (HNF1B) gene are common with combined uterine and renal malformations but are not found with isolated uterine malformations. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 203, 364.e1–364.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, E.; Tran, M.; Robevska, G.; Ayers, K.; van der Bergen, J.; Gopalakrishnan Bhaskaran, P.; Haan, E.; Cereghini, S.; Vash-Margita, A.; Margetts, M.; et al. Functional genomics analysis identifies loss of HNF1B function as a cause of Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2023, 32, 1032–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, L.; Gimelli, S.; Gervasini, C.; Carella, M.; Baban, A.; Frontino, G.; Barbano, G.; Divizia, M.T.; Fedele, L.; Novelli, A.; et al. Recurrent microdeletion at 17q12 as a cause of Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser (MRKH) syndrome: Two case reports. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2009, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, K.; Chapla, A.; Chandramohan, A.; Singh, C.J.; Thomas, N.; Jebasingh, F.K. Diabetes Mellitus With Renal and Müllerian Anomalies. AACE Clin. Case Rep. 2021, 8, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeri, S.; Devers, P.L.; Kaiser-Rogers, K.A.; Moylan, V.J., Jr.; Torchia, B.S.; Horton, A.L.; Wolfe, H.M.; Aylsworth, A.S. Deletion of hepatocyte nuclear factor-1-beta in an infant with prune belly syndrome. Am. J. Perinatol. 2010, 27, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.L.; Gandomi, S.K.; Parra, M.; Lu, I.; Gau, C.L.; Dasouki, M.; Butler, M.G. Clinical report of a 17q12 microdeletion with additionally unreported clinical features. Case Rep. Genet. 2014, 2014, 264947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verscaj, C.P.; Velez-Bartolomei, F.; Bodle, E.; Chan, K.; Lyons, M.J.; Thorson, W.; Tan, W.H.; Rodig, N.; Graham, J.M., Jr.; Peron, A.; et al. Characterization of the prenatal renal phenotype associated with 17q12, HNF1B, microdeletions. Prenat. Diagn. 2024, 44, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Pan, L.; Chen, K.; Tan, R. Prenatal ultrasound features and genetic analysis for 17q12 microdeletion syndrome. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban J. Cent. South Univ. Med. Sci. 2021, 46, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Vasileiou, G.; Hoyer, J.; Thiel, C.T.; Schaefer, J.; Zapke, M.; Krumbiegel, M.; Kraus, C.; Zweier, M.; Uebe, S.; Ekici, A.B.; et al. Prenatal diagnosis of HNF1B-associated renal cysts: Need to differentiate intragenic variants from 17q12 microdeletion syndrome? Prenat. Diagn. 2019, 39, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iafusco, F.; Meola, S.; Pecoraro, C.; Mazzaccara, C.; Iafusco, D.; Tinto, N. Prenatal diagnosis of HNF1b mutation allows recognition of neonatal dysglycemia. Acta Diabetol. 2021, 58, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, R.N.; Patel, K.A.; Kettunen, J.L.; Männistö, J.M.; Støy, J.; Beltrand, J.; Polak, M.; ADA/EASD PMDI; Vilsbøll, T.; Greeley, S.A.; et al. Systematic Review of Treatment of Beta-Cell Monogenic Diabetes. medRxiv 2023. medRxiv:2023.05.12.23289807. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Terakawa, A.; Chujo, D.; Yasuda, K.; Ueno, K.; Nakamura, T.; Hamano, S.; Ohsugi, M.; Tanabe, A.; Ueki, K.; Kajio, H. Maturity-Onset diabetes of the young type 5 treated with the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist: A case report. Medicine 2020, 99, e21939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variant | Type | Variant | Type | Variant | Type | Variant | Type | Variant | Type | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | c.3G>T | N | 2 | c.18delG | N | 3 | c.22delC | N | 4 | c.25C > T | N | 5 | c.30_33delAGAA | N |
| 6 | c.34C>T | M | 7 | c.36_38delCCT | D | 8 | c.46delC | N | 9 | c.58G>A | M | 10 | c.61dupG | N |
| 11 | c.70delG | N | 12 | c.73G>T | M | 13 | c.79G>C | M | 14 | c.107C>T | M | 15 | c.110dupC | N |
| 16 | c.118G>A | M | 17 | c.121_122insAG | N | 18 | c.130G>A | M | 19 | c.130G>T | N | 20 | c.143delT | N |
| 21 | c.148C>T | M | 22 | c.179C>G | M | 23 | c.182T>G | M | 24 | c.187delC | N | 25 | c.188_191 dupATAC | N |
| 26 | c.206_207delAC | N | 27 | c.207_211 delCGCCA | N | 28 | c.211_217 delAAGGGCC | N | 29 | c.226G>T | M | 30 | c.231C>G | M |
| 31 | c.232G>T | M | 32 | c.234G>C | N | 33 | c.239C>G | M | 34 | c.241G>T | N | 35 | c.244G>A | M |
| 36 | c.248G>A | M | 37 | c.252delC | N | 38 | c.263C>T | M | 39 | c.264_265delAC | N | 40 | c.274C>T | M |
| 41 | c.280delG | N | 42 | c.281_284 dupAGCT | N | 43 | c.286C>T | N | 44 | c.301G>T | N | 45 | c.305A>G | M |
| 46 | c.313G>A | M | 47 | c.322delG | N | 48 | c.324_340del17 | N | 49 | c.329T>G | M | 50 | c.335G>C | M |
| 51 | c.335_342 delGGATGCTC | N | 52 | c.344+2_344+5 delTAGG | S | 53 | c.344+2T>C | S | 54 | c.344+2T>G | S | 55 | c.345-4C>T | S |
| 56 | c.345-1G>A | S | 57 | c.345-1G>T | S | 58 | c.353delC | N | 59 | c.354T>G | Sy | 60 | c.356G>A | N |
| 61 | c.364G>T | M | 62 | c.367A>T | N | 63 | c.372G>T | M | 64 | c.374T>C | M | 65 | c.377A>G | M |
| 66 | c.386_392 delTGCAGCA | N | 67 | c.388C>T | N | 68 | c.390_395 delGCAACA | D | 69 | c.391C>T | N | 70 | c.393A>T | M |
| 71 | c.395A>G | M | 72 | c.395A>C | M | 73 | c.398A>G | M | 74 | c.406C>G | M | 75 | c.406C>T | N |
| 76 | c.412G>A | M | 77 | c.434T>A | M | 78 | c.434delT | N | 79 | c.436A>G | M | 80 | c.439C>G | M |
| 81 | c.439C>T | N | 82 | c.441G>T | M | 83 | c.443C>T | M | 84 | c.443C>G | M | 85 | c.451T>C | M |
| 86 | c.452C>G | M | 87 | c.454delC | N | 88 | c.457C>A | M | 89 | c.460C>T | M | 90 | c.466A>G | M |
| 91 | c.471delC | N | 92 | c.472_473 insTGCAGCCC | N | 93 | c.473C>A | M | 94 | c.475C>G | M | 95 | c.476C>T | M |
| 96 | c.477delT | N | 97 | c.478A>G | M | 98 | c.481A>T | N | 99 | c.484delA | N | 100 | c.487delC | N |
| 101 | c.490A>C | M | 102 | c.493C>T | M | 103 | c.493C>G | M | 104 | c.494G>A | M | 105 | c.494G>C | M |
| 106 | c.495_496delTG | N | 107 | c.499G>A | M | 108 | c.499_504 delGCTCTG insCCCCT | I | 109 | c.503T>C | M | 110 | c.505T>C | M |
| 111 | c.508A>C | M | 112 | c.512G>A | N | 113 | c.513G>C | M | 114 | c.513G>A | N | 115 | c.516C>G | N |
| 116 | c.517G>A | M | 117 | c.517G>C | M | 118 | c.523A>T | N | 119 | c.526C>T | N | 120 | c.529C>T | N |
| 121 | c.530G>A | M | 122 | c.534delG | N | 123 | c.541C>T | N | 124 | c.542G>A | M | 125 | c.542_544+16 del19 | D |
| 126 | c.544C>T | N | 127 | c.544+1G>A | S | 128 | c.544+1G>C | S | 129 | c.544+1G>T | S | 130 | c.544+2dupT | S |
| 131 | c.544_544+3 delCGTA | S | 132 | c.544+3_544+6 delAAGT | S | 133 | c.544+4A>C | S | 134 | c.578T>C | M | 135 | c.589A>C | M |
| 136 | c.656C>T | M | 137 | c.662A>T | M | 138 | c.674A>C | M | 139 | c.684C>G | M | 140 | c.694C>T | M |
| 141 | c.695delG | N | 142 | c.698G>A | M | 143 | c.703C>T | M | 144 | c.704G>A | M | 145 | c.708C>T | Sy |
| 146 | c.712T>C | M | 147 | c.713G>T | M | 148 | c.715G>C | M | 149 | c.715_717 delGGG | D | 150 | c.716G>A | M |
| 151 | c.716G>T | M | 152 | c.717dupG | N | 153 | c.717delG | N | 154 | c.719_720dupCC | N | 155 | c.721G>A | M |
| 156 | c.722C>T | M | 157 | c.727delC | N | 158 | c.728A>C | M | 159 | c.731A>G | M | 160 | c.737T>C | M |
| 161 | c.742C>G | M | 162 | c.742C>T | N | 163 | c.750C>A | N | 164 | c.755G>A | M | 165 | c.758A>C | M |
| 166 | c.766C>T | M | 167 | c.780G>C | M | 168 | c.781A>G | M | 169 | c.786_787dupGG | N | 170 | c.791T>C | M |
| 171 | c.791dupT | N | 172 | c.793G>A | M | 173 | c.799G>C | M | 174 | c.809+1G>A | S | 175 | c.810-4C>G | S |
| 176 | c.810-2A>C | S | 177 | c.810-1G>A | S | 178 | c.810-1G>C | S | 179 | c.818G>A | M | 180 | c.823C>T | N |
| 181 | c.826C>G | M | 182 | c.826C>T | N | 183 | c.827G>A | M | 184 | c.840dupC | N | 185 | c.840delC | N |
| 186 | c.840_844 delCTCCA | N | 187 | c.850delC | N | 188 | c.853G>A | M | 189 | c.854G>A | M | 190 | c.856C>G | M |
| 191 | c.857T>G | M | 192 | c.857T>C | M | 193 | c.860G>T | M | 194 | c.865A>G | M | 195 | c.865A>C | M |
| 196 | c.865_870 delAACTTGinsGT | I | 197 | c.867C>G | M | 198 | c.869T>A | N | 199 | c.882_888 delCCGTGTC | N | 200 | c.883C>T | M |
| 201 | c.884G>A | M | 202 | c.884G>C | M | 203 | c.886G>T | M | 204 | c.895T>G | M | 205 | c.904A>G | M |
| 206 | c.905delA | N | 207 | c.906C>A | M | 208 | c.908G>A | M | 209 | c.910A>G | M | 210 | c.913A>G | M |
| 211 | c.913A>T | N | 212 | c.928C>T | M | 213 | c.931C>T | N | 214 | c.940G>A | M | 215 | c.944T>C | M |
| 216 | c.949G>A | M | 217 | c.949delG | N | 218 | c.953dupA | N | 219 | c.967dupA | N | 220 | c.972_973delCA | N |
| 221 | c.981C>G | M | 222 | c.982_986 delCCTCT | N | 223 | c.983delC | N | 224 | c.988C>T | M | 225 | c.1000T>A | M |
| 226 | c.1006delC | N | 227 | c.1006dupC | N | 228 | c.1006C>A | M | 229 | c.1006C>G | M | 230 | c.1006C>T | M |
| 231 | c.1007A>G | M | 232 | c.1024T>C | M | 233 | c.1025C>T | M | 234 | c.1027C>T | M | 235 | c.1033A>G | M |
| 236 | c.1045+1G>A | S | 237 | c.1045+12T>C | S | 238 | c.1046-15T>A | S | 239 | c.1046-2A>G | S | 240 | c.1046delG | N |
| 241 | c.1048dupG | N | 242 | c.1052_1059 delGCTACAGC | N | 243 | c.1054T>A | M | 244 | c.1055A>G | M | 245 | c.1055dupA | N |
| 246 | c.1060C>T | N | 247 | c.1084T>C | M | 248 | c.1085C>T | M | 249 | c.1099A>G | M | 250 | c.1101T>C | Sy |
| 251 | c.1103_1116del14 | N | 252 | c.1107+1G>T | S | 253 | c.1107+2T>A | S | 254 | c.1107+2T>C | S | 255 | c.1108-42G>T | S |
| 256 | c.1108-2A>G | S | 257 | c.1108-2A>T | S | 258 | c.1108G>T | S | 259 | c.1108G>A | M | 260 | c.1117G>C | M |
| 261 | c.1127C>T | M | 262 | c.1128_1129 insCCCCC | N | 263 | c.1130G>T | M | 264 | c.1132dupC | N | 265 | c.1133A>C | M |
| 266 | c.1136C>T | M | 267 | c.1136C>A | N | 268 | c.1138delG | N | 269 | c.1144C>T | N | 270 | c.1147C>T | N |
| 271 | c.1156C>T | M | 272 | c.1196delA | N | 273 | c.1206+1G>C | S | 274 | c.1206+5G>C | S | 275 | c.1207-1G>C | S |
| 276 | c.1211_1212delCA | N | 277 | c.1217C>T | M | 278 | c.1235delC | N | 279 | c.1235dupC | N | 280 | c.1253A>T | M |
| 281 | c.1253A>C | M | 282 | c.1282C>T | N | 283 | c.1299delC | N | 284 | c.1302delC | N | 285 | c.1309+48C>T | S |
| 286 | c.1309+54C>T | S | 287 | c.1310-2A>G | S | 288 | c.1310-1G>A | S | 289 | c.1310C>T | M | 290 | c.1312dupC | N |
| 291 | c.1325T>C | M | 292 | c.1333_1334delGC | N | 293 | c.1339+1G>A | S | 294 | c.1339+2dupT | S | 295 | c.1339+3_1339+6 delAAGT | S |
| 296 | c.1339+5G>A | S | 297 | c.1339+5G>C | S | 298 | c.1340-276T>C | S | 299 | c.1340-3C>G | S | 300 | c.1340-1G>A | S |
| 301 | c.1351T>A | M | 302 | c.1360C>T | N | 303 | c.1360_1361 delCA | N | 304 | c.1363_1364 delAG | N | 305 | c.1367T>C | M |
| 306 | c.1370C>T | M | 307 | c.1373T>G | M | 308 | c.1390G>C | M | 309 | c.1395C>G | M | 310 | c.1397_1412del16 | N |
| 311 | c.1401delA | N | 312 | c.1406_1413 dupTGCAGCCC | N | 313 | c.1408C>T | N | 314 | c.1414G>A | M | 315 | c.1446_1459del14 | N |
| 316 | c.1447C>T | N | 317 | c.1460T>C | M | 318 | c.1462C>T | N | 319 | c.1474G>A | M | 320 | c.1484T>A | M |
| 321 | c.1489delC | N | 322 | c.1492C>T | N | 323 | c.1501A>G | M | 324 | c.1501+1G>A | S | 325 | c.1501+1G>T | S |
| 326 | c.1501+4A>G | S | 327 | c.1501+5G>C | S | 328 | c.1501+7G>A | S | 329 | c.1502-6G>A | S | 330 | c.1502-2A>G | S |
| 331 | c.1502-2A>T | S | 332 | c.1535-48C>T | S | 333 | c.1535-23C>T | S | 334 | c.1538A>G | M | 335 | c.1540G>A | M |
| 336 | c.1543C>T | M | 337 | c.1547delA | N | 338 | c.1563G>C | M | 339 | c.1580G>A | M | 340 | c.1594A>G | M |
| 341 | c.1610C>A | M | 342 | c.1623+1G>A | S | 343 | c.1623+2T>C | S | 344 | c.1624-1G>A | S | 345 | c.1640C>T | M |
| 346 | c.1654-2A>T | S | 347 | c.1657C>A | M | 348 | c.1768+1G>A | S | 349 | c.1768+1G>T | S | 350 | c.1768 + 3G>A | S |
| 351 | c.1769-3C>T | S | 352 | c.1769-1G>A | S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fontana, P.; Costabile, C.; Falco, M.; Barillari, M.R.; Lonardo, F. MODY5 and 17q12 Microdeletion Syndrome: Phenotype Variability, Prenatal and Postnatal Counseling. Genes 2025, 16, 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091002
Fontana P, Costabile C, Falco M, Barillari MR, Lonardo F. MODY5 and 17q12 Microdeletion Syndrome: Phenotype Variability, Prenatal and Postnatal Counseling. Genes. 2025; 16(9):1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091002
Chicago/Turabian StyleFontana, Paolo, Claudia Costabile, Mariateresa Falco, Maria Rosaria Barillari, and Fortunato Lonardo. 2025. "MODY5 and 17q12 Microdeletion Syndrome: Phenotype Variability, Prenatal and Postnatal Counseling" Genes 16, no. 9: 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091002
APA StyleFontana, P., Costabile, C., Falco, M., Barillari, M. R., & Lonardo, F. (2025). MODY5 and 17q12 Microdeletion Syndrome: Phenotype Variability, Prenatal and Postnatal Counseling. Genes, 16(9), 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091002





