Detecting Methylation Changes Induced by Prime Editing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Plasmids Used for CRISPR and Prime Editing
2.2. HEK293T Cells
2.3. gDNA Isolation and Sequencing of Cas9-Edited and PE2-Edited Cells
2.4. Methylation Sequence
2.5. Methylation Analysis
2.6. Calculation of Differentially Methylated Regions
2.7. Gene Ontology and KEGG Analysis of Differentially Methylated Regions
3. Results
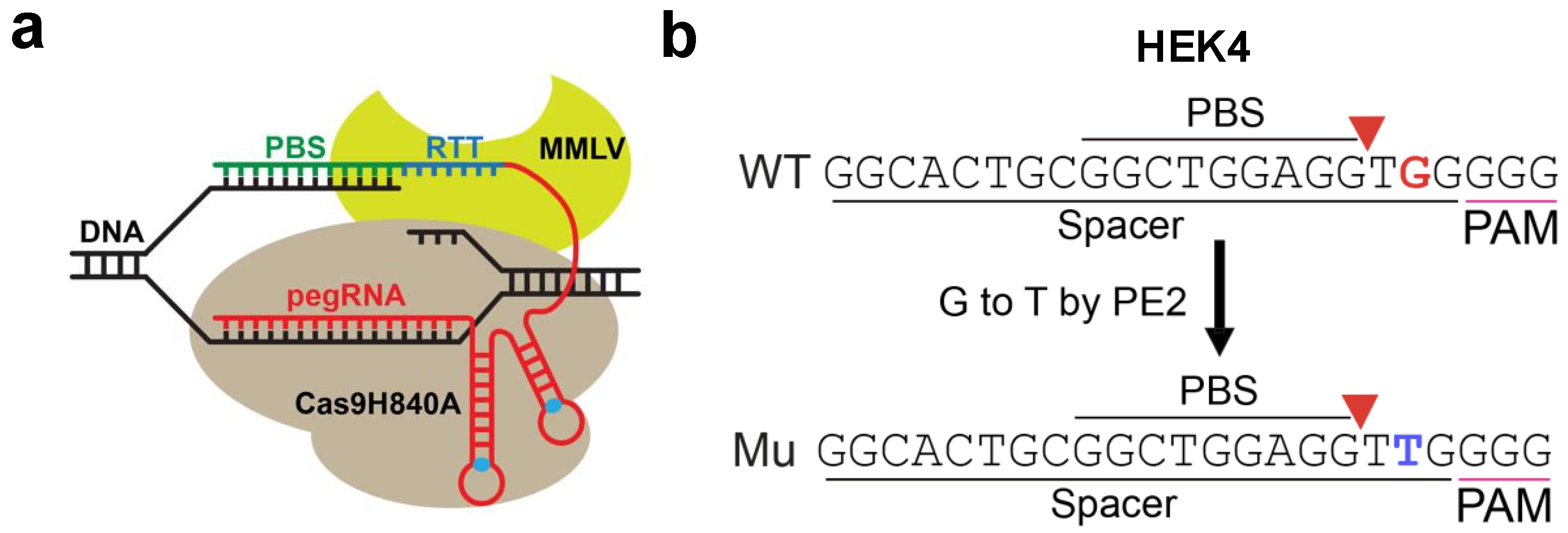
3.1. Cas9- and PE2-Based Editing of HEK293T Cells
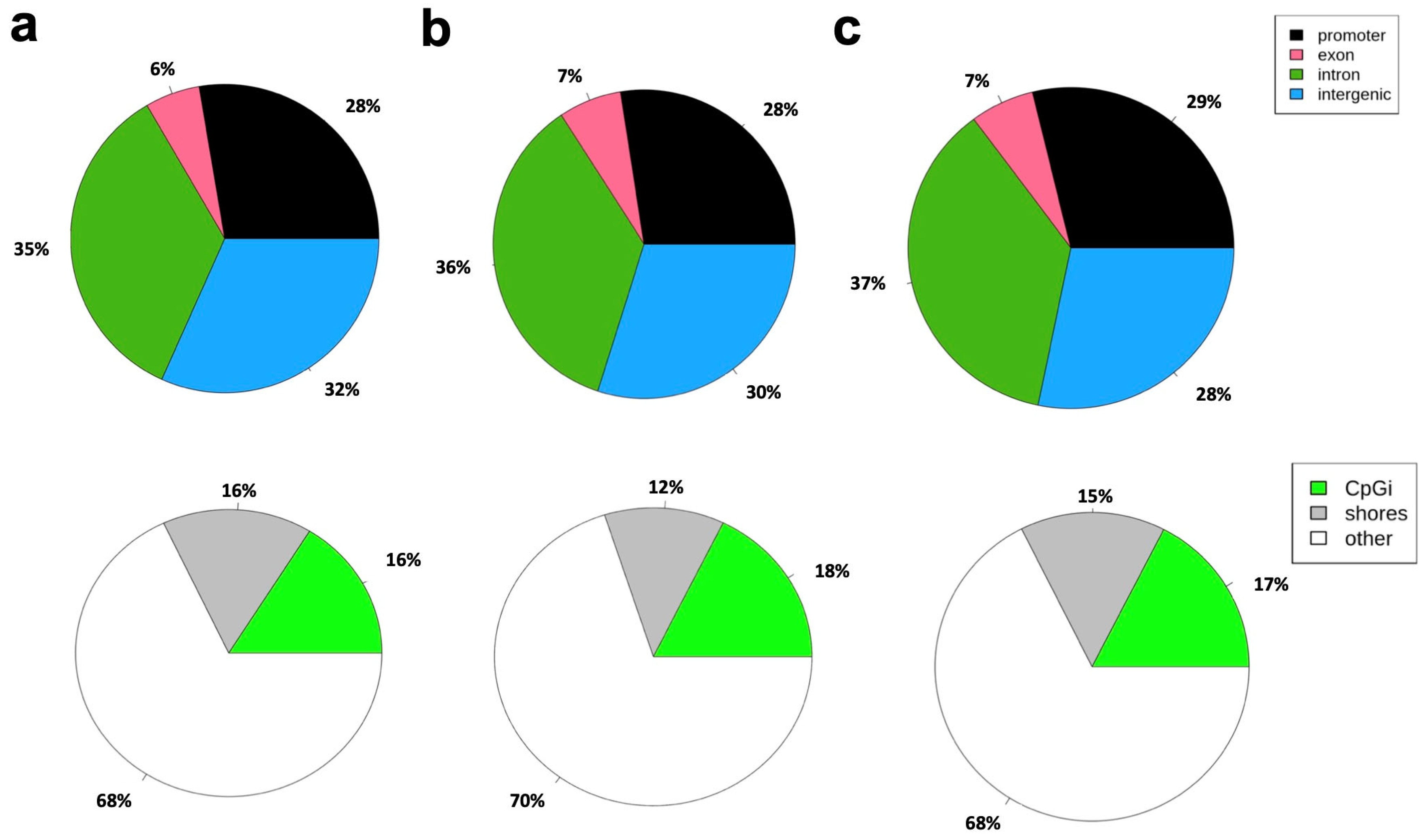
3.2. Whole-Genome Bisulfite Sequencing for a Genome-Wide Evaluation of CpG Methylation Patterns
3.3. Differentially Methylated Regions
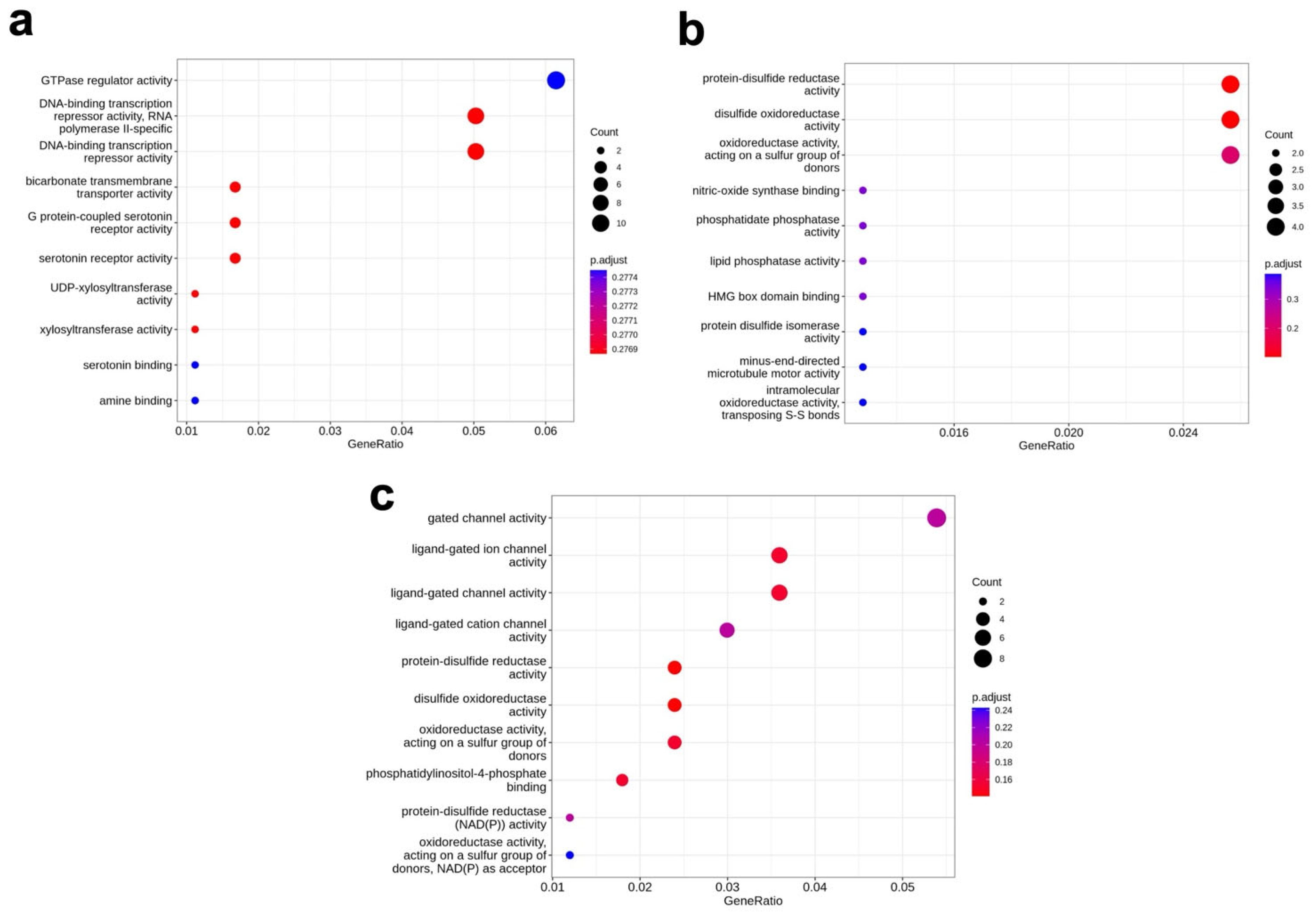
3.4. Molecular Function
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anzalone, A.V.; Randolph, P.B.; Davis, J.R.; Sousa, A.A.; Koblan, L.W.; Levy, J.M.; Chen, P.J.; Wilson, C.; Newby, G.A.; Raguram, A.; et al. Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA. Nature 2019, 576, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doman, J.L.; Raguram, A.; Newby, G.A.; Liu, D.R. Evaluation and minimization of Cas9-independent off-target DNA editing by cytosine base editors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doman, J.L.; Pandey, S.; Neugebauer, M.E.; An, M.; Davis, J.R.; Randolph, P.B.; McElroy, A.; Gao, X.D.; Raguram, A.; Richter, M.F.; et al. Phage-assisted evolution and protein engineering yield compact, efficient prime editors. Cell 2023, 186, 3983–4002.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Oyler-Castrillo, P.; Ravisankar, P.; Ward, C.C.; Levesque, S.; Jing, Y.; Simpson, D.; Zhao, A.; Li, H.; Yan, W.; et al. Improving prime editing with an endogenous small RNA-binding protein. Nature 2024, 628, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirincione, A.; Simpson, D.; Yan, W.; McNulty, R.; Ravisankar, P.; Solley, S.C.; Yan, J.; Lim, F.; Farley, E.K.; Singh, M.; et al. A benchmarked, high-efficiency prime editing platform for multiplexed dropout screening. Nat. Methods 2024. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.Q.; Liu, P.; Ponnienselvan, K.; Suresh, S.; Chen, Z.; Kramme, C.; Chatterjee, P.; Zhu, L.J.; Sontheimer, E.J.; Xue, W.; et al. Genome-wide profiling of prime editor off-target sites in vitro and in vivo using PE-tag. Nat. Methods 2023, 20, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farris, M.H.; Texter, P.A.; Mora, A.A.; Wiles, M.V.; Mac Garrigle, E.F.; Klaus, S.A.; Rosfjord, K. Detection of CRISPR-mediated genome modifications through altered methylation patterns of CpG islands. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiner-Garden, M.; Frommer, M. CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 1987, 196, 261–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Liang, S.Q.; Zheng, C.; Mintzer, E.; Zhao, Y.G.; Ponnienselvan, K.; Mir, A.; Sontheimer, E.J.; Gao, G.; Flotte, T.R.; et al. Improved prime editors enable pathogenic allele correction and cancer modelling in adult mice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.H.; Miller, S.M.; Geurts, M.H.; Tang, W.; Chen, L.; Sun, N.; Zeina, C.M.; Gao, X.; Rees, H.A.; Lin, Z.; et al. Evolved Cas9 variants with broad PAM compatibility and high DNA specificity. Nature 2018, 556, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casini, A.; Olivieri, M.; Petris, G.; Montagna, C.; Reginato, G.; Maule, G.; Lorenzin, F.; Prandi, D.; Romanel, A.; Demichelis, F.; et al. A highly specific SpCas9 variant is identified by in vivo screening in yeast. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slaymaker, I.M.; Gao, L.; Zetsche, B.; Scott, D.A.; Yan, W.X.; Zhang, F. Rationally engineered Cas9 nucleases with improved specificity. Science 2016, 351, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
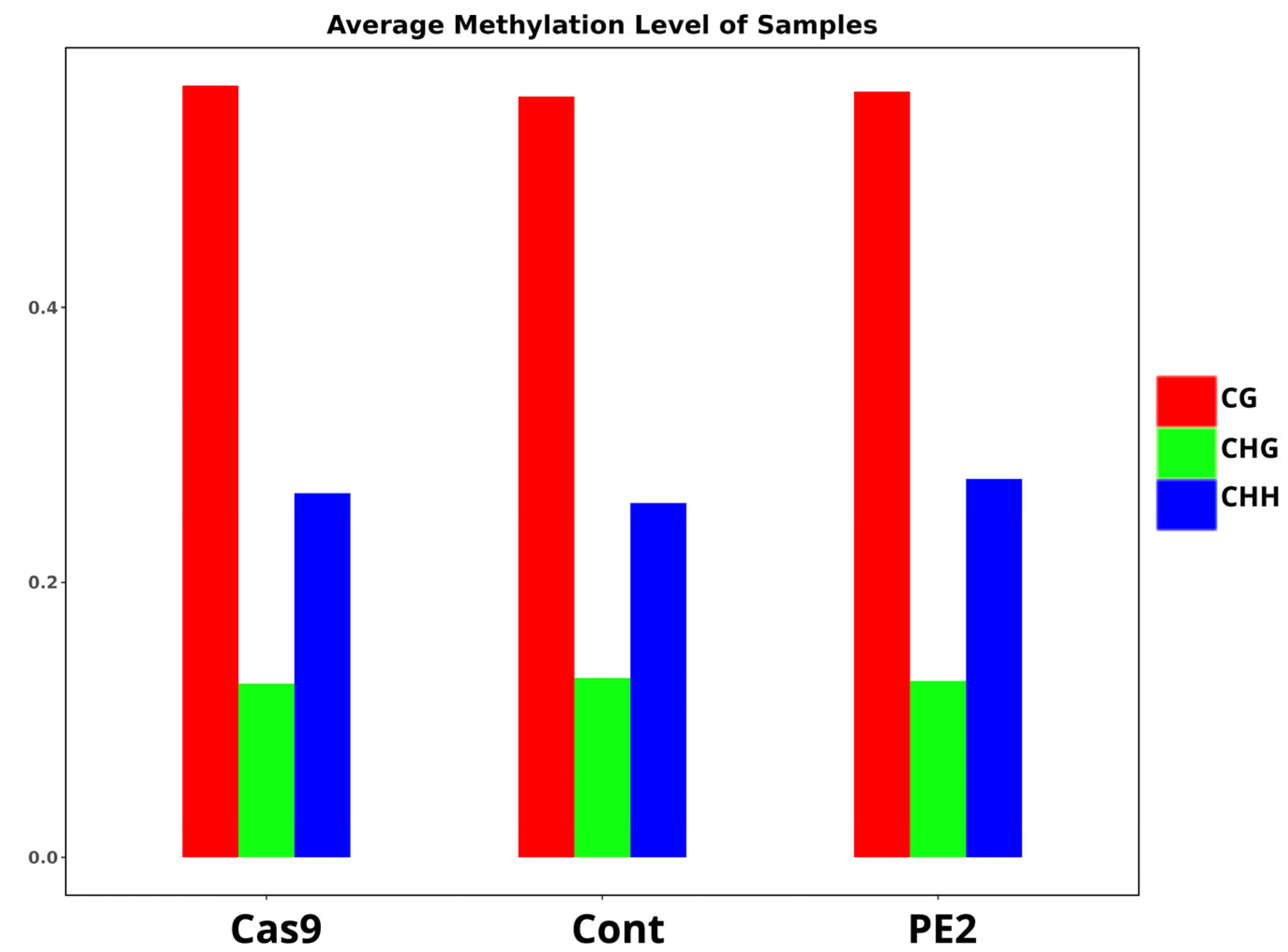
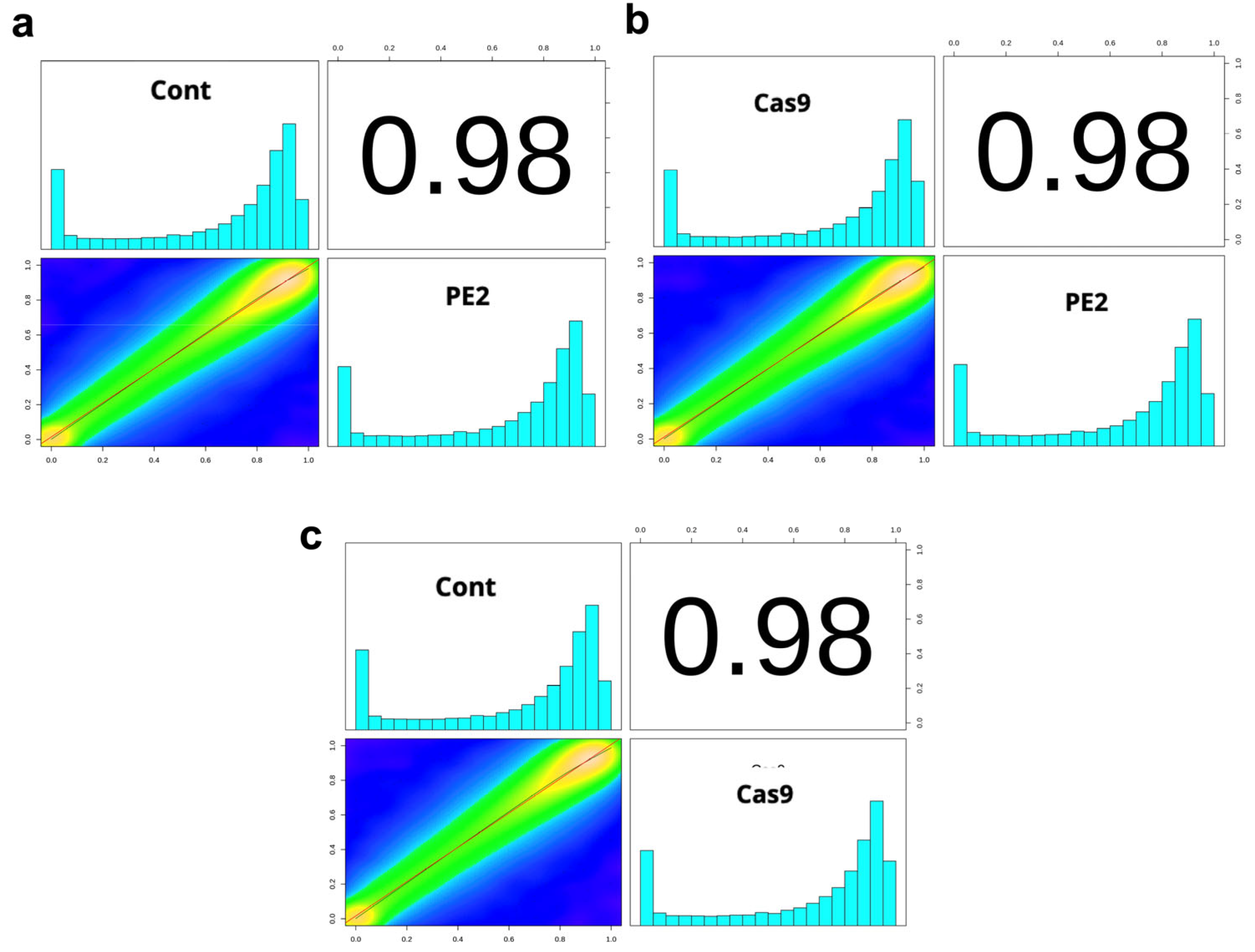
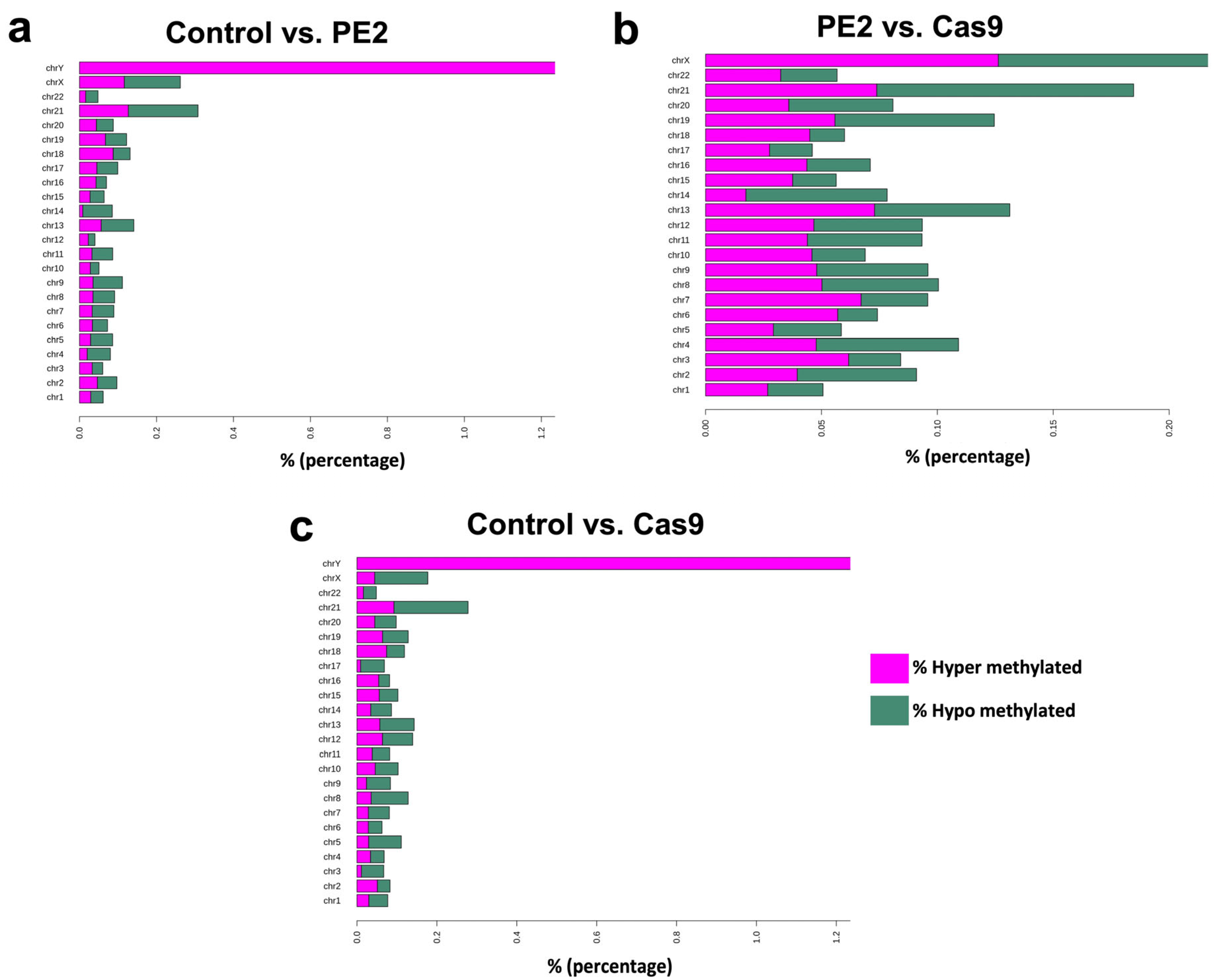

| Sample | CG_Sites | CG_Level | CHG_Sites | CHG_Level | CHH_Sites | CHH_Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cas9 | 8261436 | 0.561295 | 10172 | 0.126323 | 1102 | 0.264732 |
| Cont | 8028686 | 0.553411 | 10523 | 0.130532 | 1084 | 0.257863 |
| PE2 | 8339041 | 0.556807 | 9706 | 0.128426 | 1083 | 0.275219 |
| ID | Reads | Bases | Q20_Bases | Q20 (%) | Q30_Bases | Q30 (%) | GC_Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cas9 | 81731140 | 12259671000 | 11162724275 | 91.05 | 10046972287 | 81.95 | 42.35 |
| Cont | 72604456 | 10890668400 | 9980473084 | 91.64 | 9079741803 | 83.37 | 41.47 |
| PE2 | 80107718 | 12016157700 | 10956798055 | 91.18 | 91.189860376079 | 82.06 | 42.85 |
| Sample | C | mC | mC % | CG | mCG | mCG % | CHG | mCHG | mCHG % | CHH | mCHH | mCHH % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cas9 | 1438567163 | 122870303 | 8.54 | 252777071 | 119342131 | 47.21 | 387118516 | 1220866 | 0.32 | 798671576 | 2307306 | 0.29 |
| Cont | 1571793335 | 133611308 | 8.50 | 269031122 | 129803533 | 48.25 | 422583066 | 1309668 | 0.31 | 880179147 | 2498107 | 0.28 |
| PE2 | 1428845943 | 121996982 | 8.54 | 249947085 | 118476765 | 47.40 | 384145186 | 1217365 | 0.32 | 794753672 | 2302852 | 0.29 |
| Group | Total_Regions | Total_DMRs | Hyper_DMRs | Hyper_DMRs (%) | Hypo_DMRs | Hypo_DMRs (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cont_vs_Cas9 | 373527 | 538 | 0.14 | 220 | 0.06 | 318 |
| Cont_vs_PE2 | 379227 | 493 | 0.13 | 221 | 0.06 | 272 |
| Cas9_vs_PE2 | 371483 | 478 | 0.13 | 261 | 0.07 | 217 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cosiquien, R.J.S.; Whalen, I.J.; Wong, P.; Sorensen, R.J.; Shetty, A.V.; Liang, S.-Q.; Steer, C.J. Detecting Methylation Changes Induced by Prime Editing. Genes 2025, 16, 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070825
Cosiquien RJS, Whalen IJ, Wong P, Sorensen RJ, Shetty AV, Liang S-Q, Steer CJ. Detecting Methylation Changes Induced by Prime Editing. Genes. 2025; 16(7):825. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070825
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosiquien, Ronin Joshua S., Isaiah J. Whalen, Phillip Wong, Ryan J. Sorensen, Anala V. Shetty, Shun-Qing Liang, and Clifford J. Steer. 2025. "Detecting Methylation Changes Induced by Prime Editing" Genes 16, no. 7: 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070825
APA StyleCosiquien, R. J. S., Whalen, I. J., Wong, P., Sorensen, R. J., Shetty, A. V., Liang, S.-Q., & Steer, C. J. (2025). Detecting Methylation Changes Induced by Prime Editing. Genes, 16(7), 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070825








