Integrating Imaging and Genomics in Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Novel Diagnostic Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Molecular Genetic Analysis
2.3. Radiographic Analysis
2.3.1. Measurement of Width and Height
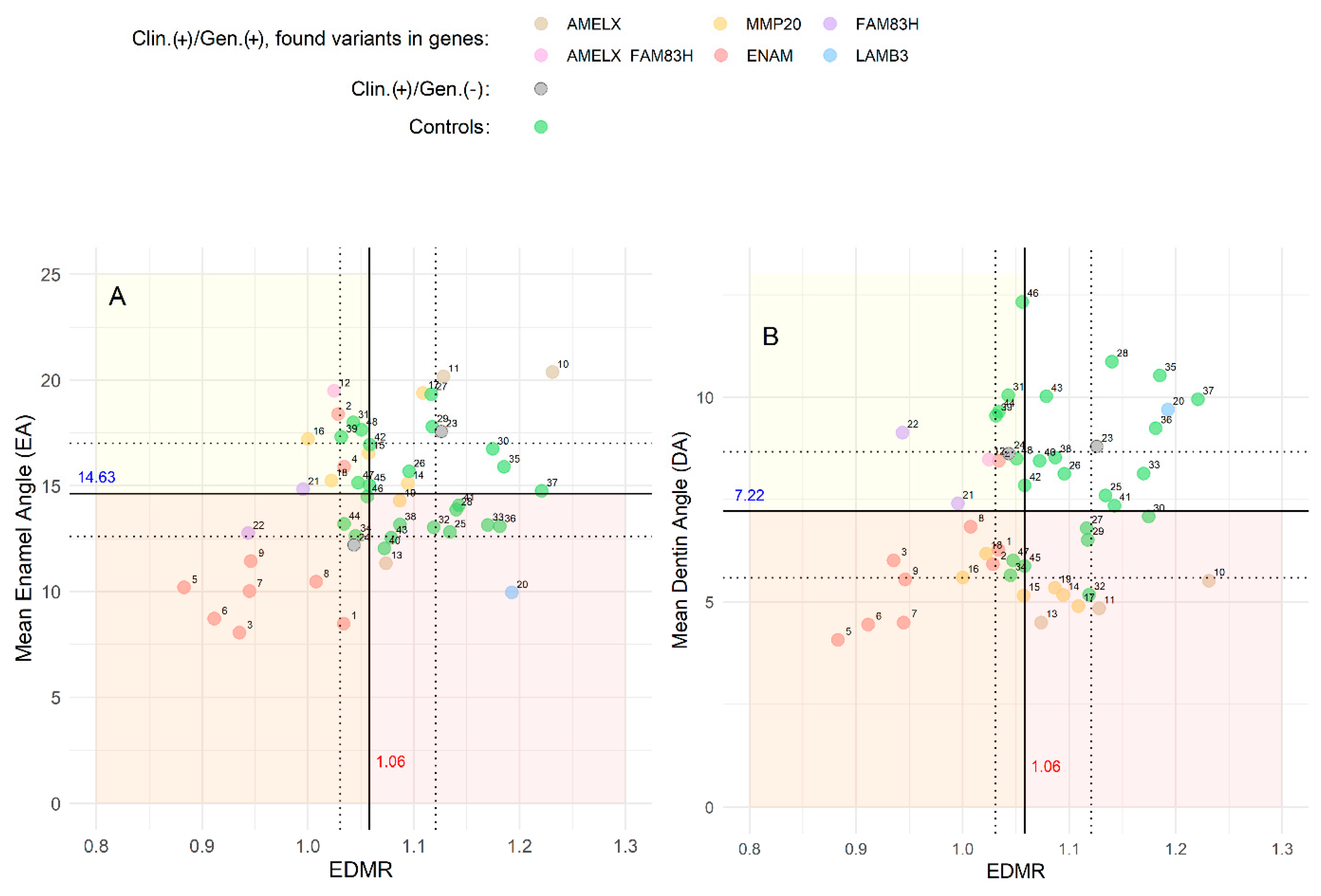
2.3.2. Measurement of Enamel Angle, Dentine Angle, and Enamel–Dentine Mineralization Ratio
2.4. Statistics Analysis and Model Performance
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Molecular Analysis
3.3. Radiographic Analysis
3.4. Statistics Analysis and Model Training
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Witkop, C.J. Amelogenesis imperfecta, dentinogenesis imperfecta and dentin dysplasia revisited: Problems in classification. J. Oral Pathol. 1988, 17, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, P.J.; Aldred, M.; Bloch-Zupan, A. Amelogenesis imperfecta. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2007, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.E.L.; Poulter, J.A.; Antanaviciute, A.; Kirkham, J.; Brookes, S.J.; Inglehearn, C.F.; Mighell, A.J. Amelogenesis imperfecta: Genes, Proteins, and Pathways. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulos, G.; Smith, C.E.L.; Poulter, J.A.; Murillo, G.; Silva, S.; Lamb, T.; Berry, I.R.; Brown, C.J.; Day, P.F.; Soldani, F.; et al. Spectrum of pathogenic variants and founder effects in amelogenesis imperfecta associated with MMP20. Hum. Mutat. 2021, 42, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlic, A.; Petelin, M.; Battelino, T. Phenotype and enamel ultrastructure characteristics in patients with ENAM gene mutations g.13185-13186insAG and 8344delG. Arch. Oral Biol. 2007, 52, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldred, M.J.; Savarirayan, R.; Crawford, P.J. Amelogenesis imperfecta: A classification and catalogue for the 21st century. Oral Dis. 2003, 9, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagerström, M.; Dahl, N.; Nakahori, Y.; Nakagome, Y.; Bäckman, B.; Landegren, U.; Pettersson, U. A deletion in the amelogenin gene (AMG) causes X-linked amelogenesis imperfecta (AIH1). Genomics 1991, 10, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.T. Enamel Phenotypes: Genetic and Environmental Determinants. Genes 2023, 14, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.S.; Aldred, M.J.; Crawford, P.J.; Wright, N.J.; Hart, T.C.; Wright, J.T. Amelogenesis imperfecta phenotype-genotype correlations with two amelogenin gene mutations. Arch. Oral Biol. 2002, 47, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruyucu, M.; Bayram, M.; Tuna, E.B.; Gencay, K.; Seymen, F. Clinical findings and long-term managements of patients with amelogenesis imperfecta. Eur. J. Dent. 2014, 8, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauch, S.; Hahnel, S. Restorative Treatment in Patients with Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Review. J. Prosthodont. 2018, 27, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodalal, Z.; Trebeschi, S.; Nguyen-Kim, T.D.L.; Schats, W.; Beets-Tan, R. Radiogenomics: Bridging imaging and genomics. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 1960–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.N.; Köhler, S.; Bauer, S.; Seelow, D.; Horn, D.; Mundlos, S. The Human Phenotype Ontology: A tool for annotating and analyzing human hereditary disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 83, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. ACMG Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IBM SPSS Statistics. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/products/spss-statistics (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining; AAAI Press: Portland, OR, USA, 1996; pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance (PERMANOVA). In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; Balakrishnan, N., Colton, T., Everitt, B., Piegorsch, W., Ruggeri, F., Teugels, J.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y. Discovering the False Discovery Rate. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2010, 72, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B.; Whitney, D.R. On a Test of Whether One of Two Random Variables Is Stochastically Larger than the Other. Ann. Math. Stat. 1947, 18, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.K. Random Decision Forests. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–16 August 1995; Volume 1, pp. 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, C.; Clayton-Matthews, A. Multinomial logistic regression. Nurs. Res. 2002, 51, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. In R Foundation for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2024; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 8 June 2024).
- Zhang, H.; Hu, Y.; Seymen, F.; Kuruyucu, M.; Kasimoglu, Y.; Wang, S.K.; Wright, J.T.; Havel, M.W.; Zhang, C.; Kim, J.W.; et al. ENAM mutations and digenic inheritance. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e00928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leban, T.; Trebušak Podkrajšek, K.; Kovač, J.; Fidler, A.; Pavlič, A. An Intron c.103-3T>C Variant of the AMELX Gene Causes Combined Hypomineralized and Hypoplastic Type of Amelogenesis Imperfecta: Case Series and Review of the Literature. Genes 2022, 13, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasse, B.; Karayigit, E.; Mathieu, E.; Jung, S.; Garret, A.; Huckert, M.; Morkmued, S.; Schneider, C.; Vidal, L.; Hemmerlé, J.; et al. Homozygous and compound heterozygous MMP20 mutations in amelogenesis imperfecta. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kang, J.; Seymen, F.; Kuruyucu, M.; Gencay, K.; Shin, T.J.; Hyun, H.K.; Lee, Z.H.; Hu, J.C.; Simmer, J.P.; et al. Analyses of MMP20 Missense Mutations in Two Families with Hypomaturation Amelogenesis Imperfecta. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urzúa, B.; Martínez, C.; Ortega-Pinto, A.; Adorno, D.; Morales-Bozo, I.; Riadi, G.; Jara, L.; Plaza, A.; Lefimil, C.; Lozano, C.; et al. Novel missense mutation of the FAM83H gene causes retention of amelogenin and a mild clinical phenotype of hypocalcified enamel. Arch. Oral Biol. 2015, 60, 1356–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirjian, A.; Goldstein, H.; Tanner, J.M. A New System of Dental Age Assessment. Hum. Biol. 1973, 45, 211–227. [Google Scholar]
- Tonni, I.; Iannazzi, A.; Piancino, M.; Costantinides, F.; Dalessandri, D.; Paganelli, C. Asymmetric molars’ mesial rotation and mesialization in unilateral functional posterior crossbite and implications for interceptive treatment in the mixed dentition. Eur. J. Orthod. 2017, 39, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.K.; Zhang, H.; Chavez, M.B.; Hu, Y.; Seymen, F.; Kuruyucu, M.; Kasimoglu, Y.; Colvin, C.D.; Kolli, T.N.; Tan, M.H.; et al. Dental malformations associated with biallelic MMP20 mutations. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuéllar Rivas, E.; Pustovrh Ramos, M. The role of enamelysin (MMP-20) in tooth development: Systematic review. Rev. Fac. Ondontol. Univ. Antioq. 2016, 27, 154–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinakis, N.M.; Svingou, M.; Veltra, D.; Kekou, K.; Sofocleous, C.; Tilemis, F.N.; Kosma, K.; Tsoutsou, E.; Fryssira, H.; Traeger-Synodinos, J. Phenotype-driven variant filtration strategy in exome sequencing toward a high diagnostic yield and identification of 85 novel variants in 400 patients with rare Mendelian disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2021, 185, 2561–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


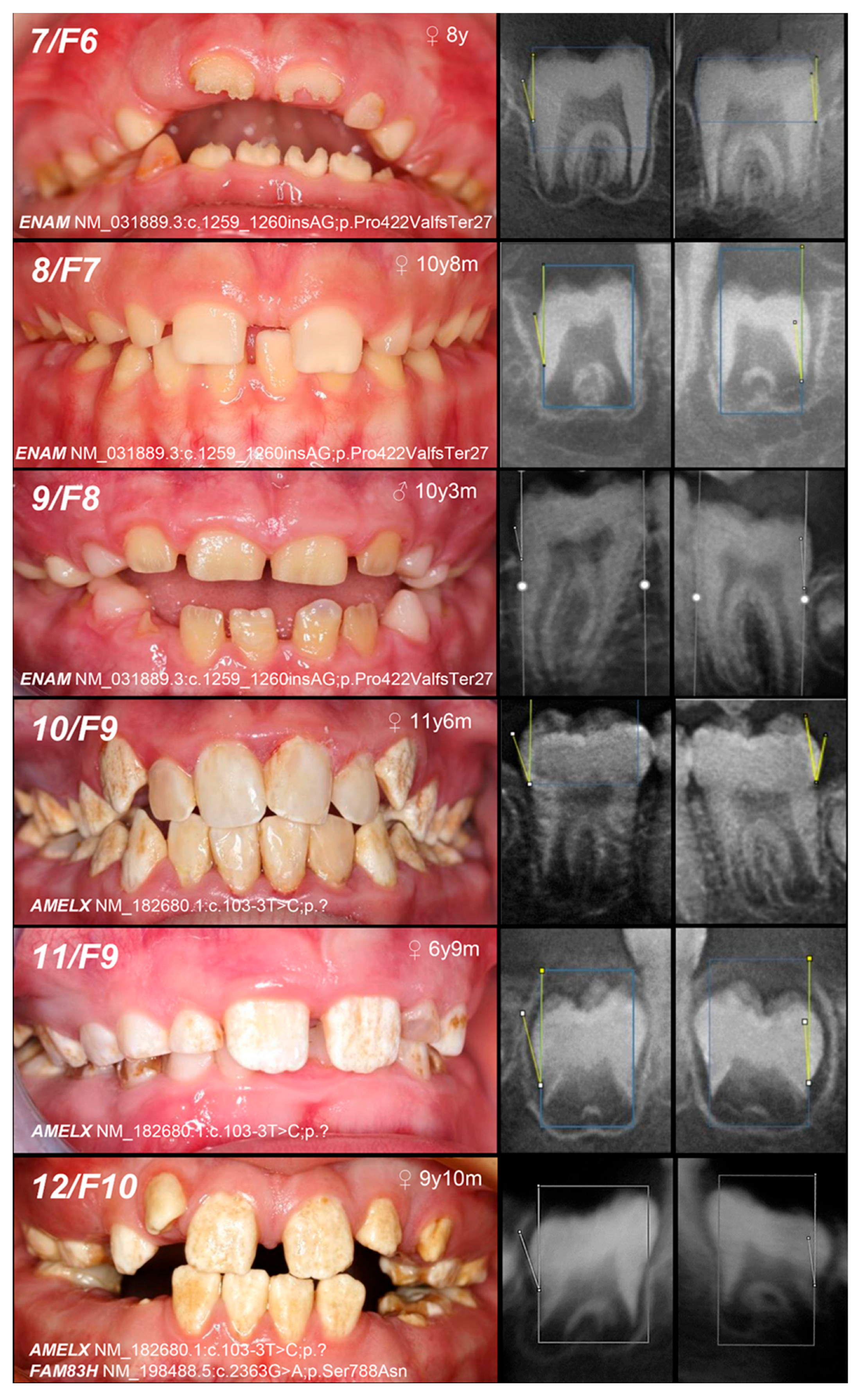
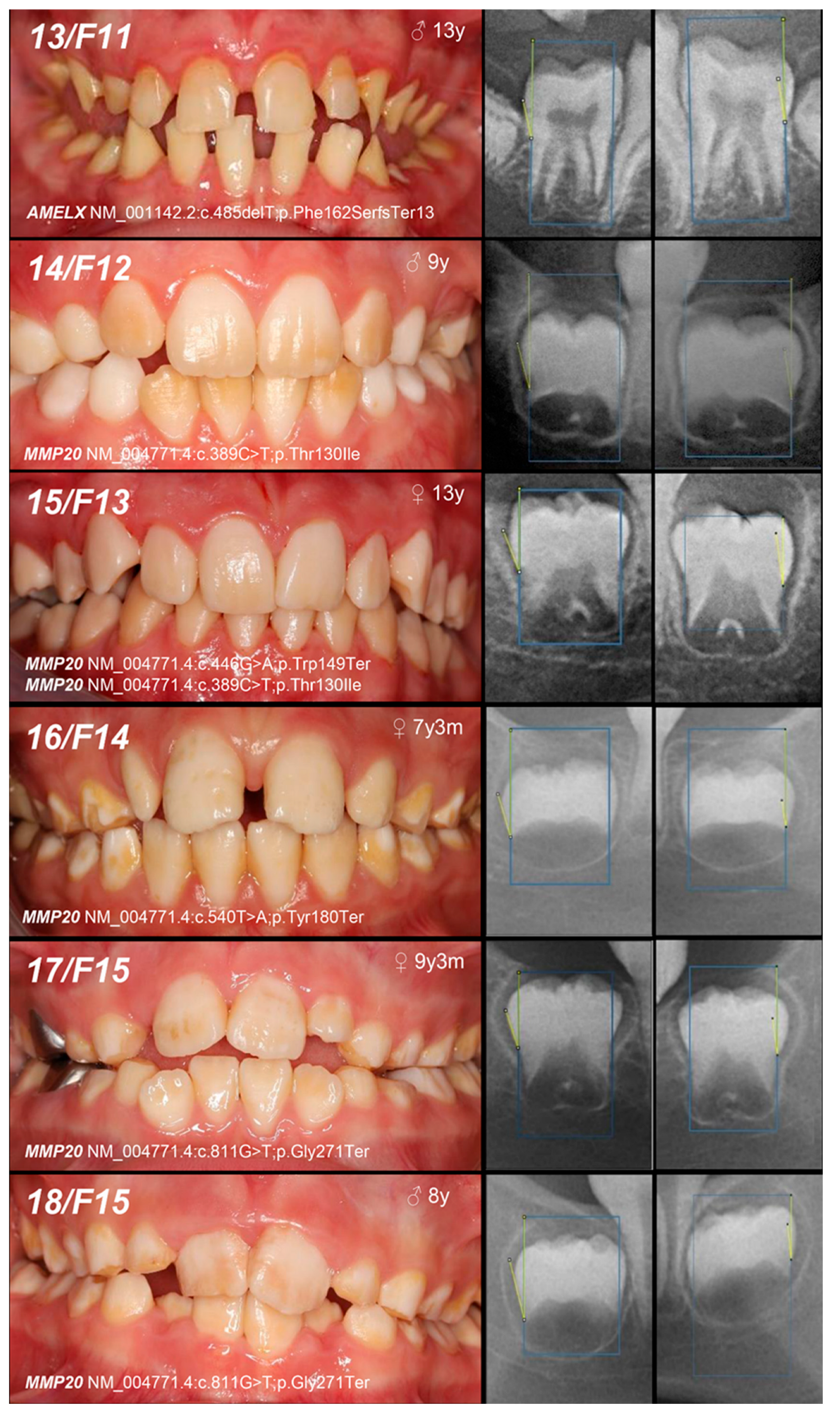
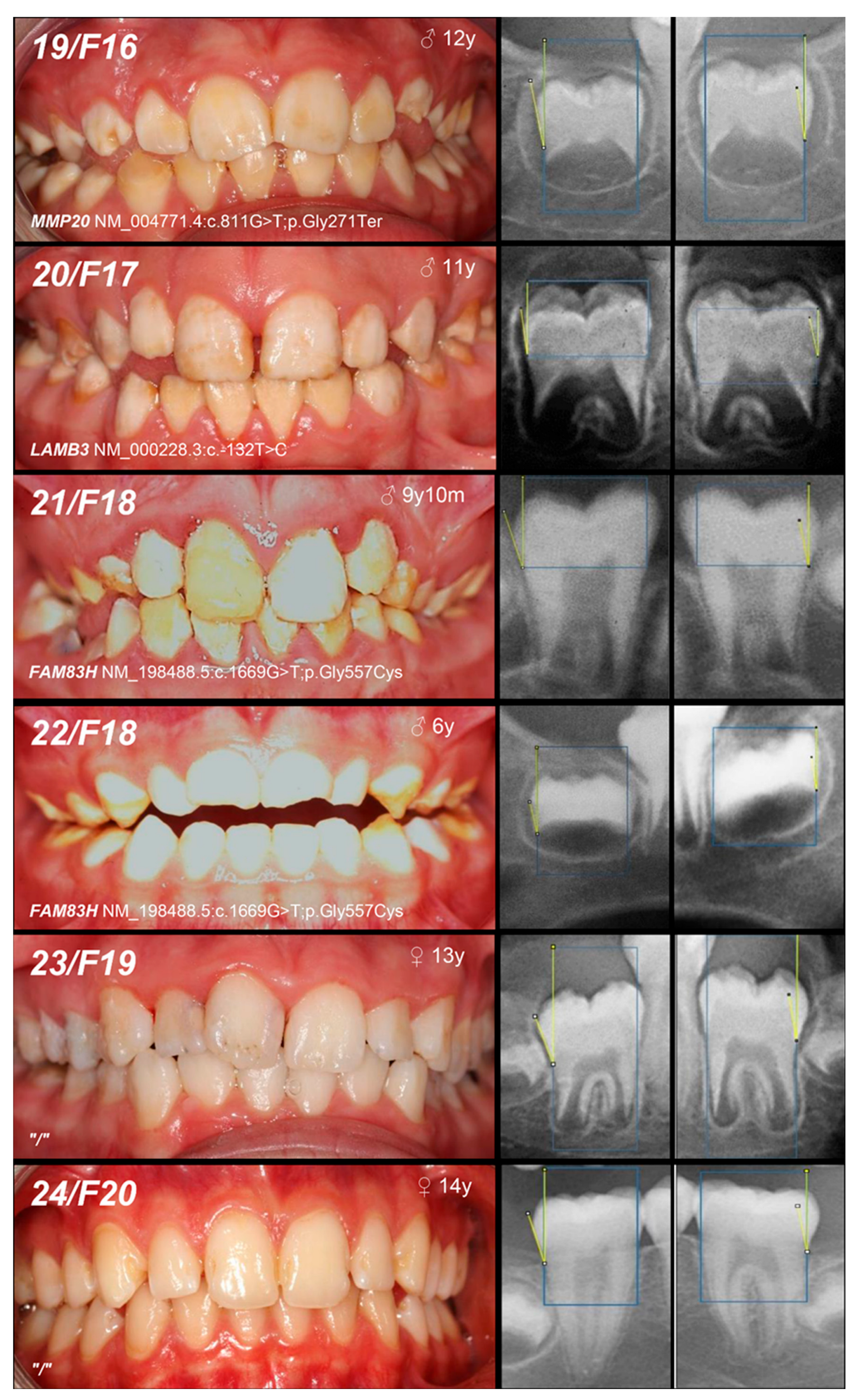

| Patient (n) Family (n) | Phenotype | OMIM, Mode of Inheritance, Gene Affected | Gene Variant | Zyg. | Protein Outcome | References | Fam. Segreg. | ACMG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1, F1 | Hypoplastic (localized) | IB, AD, ENAM | c.92T>C | +/− | p.Leu31Pro | novel | Mo (AC) Fa (U) | likely pathogenic (PP1:moderate, PM5:moderate, PM2:moderate) |
| 2, F2 | c.306G>A | +/− | p.Trp102Ter | novel | Mo (AC) FaS (U) | likely pathogenic (PVS1:very strong, PM2:moderate) * | ||
| 3, F3 | Hypoplastic (generalized) | c.588+1del | +/− | p.? | [25] | Mo (U) Fa (AC) | pathogenic (PS4:strong, PVS1:strong, PM2:moderate) | |
| 4, F4 | Hypomineralized (hypoplastic) | IB, AD, ENAM | c.1259_1260insAG | +/− | p.Pro422Val fsTer27 | [5] | Mo (AC) FaS (U) | pathogenic (PS4:strong, PVS1:strong, PM2:moderate) GnomAD: 0.0002517 |
| 5, 6, F5 | Hypoplastic (generalized—recessive trait; localized, pitting, grooving—dominant trait) | IC, AR/AD, ENAM | −/− | [25] | MoFa (UC) | |||
| 7, F6 | MoFaS (UC) | |||||||
| 8, F7 | MoFa (UC) | |||||||
| 9, F8 | MoFa (UC) | |||||||
| 10, 11, F9 | Hypomineralized (heterogeneity) | IE, XLD, AMELX | c.103-3T>C | +/− | p.? | [26] | Mo(U) Fa (AC) | likely pathogenic (PP1:strong, PM2:moderate)* |
| 12, F10 | +/− | Mo (AC) Fa (NA) | ||||||
| and IIIA, AD, FAM83H | c.2363G>A | +/− | p.Ser788Asn | [26] | benign (BA1:stand-alone, BS2:strong, BP4:supporting, BP6:strong) | |||
| 13, F11 | Hypoplastic (heterogeneity) | IE, XLD, AMELX | c.485delT | 0/− | p.Phe162SerfsTer13 | novel | MoS (A) Fa (NA) | likely pathogenic (PVS1:very strong, PM2:moderate) |
| 14, F12 | Hypomineralized (pigmented hypomature) | IIA2, AR, MMP20 | c.389C>T | −/− | p.Thr130Ile | [27] | MoFa (UC) | likely pathogenic (PP5: strong, PM2: moderate) GnomAD: 0.001747 |
| 15, F13 | +/− | Mo (U) Fa (NA) | ||||||
| and c.446G>A | +/− | and p.Trp149Ter | novel | likely pathogenic (PVS1:very strong, PM2:moderate) GnomAD: 0.00000398 |
| Patient (n) Family (n) | Phenotype | OMIM, Mode of Inheritance, Gene Affected | Gene Variant | Zyg. | Protein Outcome | References | Fam. Segreg. | ACMG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16, F14 | Hypomineralized (pigmented hypomature) | IIA2, AR, MMP20 | c.540T>A | +/− | p.Tyr180Ter | [28] | Mo (UC) Fa (U) | likely pathogenic (PVS1: very strong, PM2: moderate) GnomAD: 0.00000707 |
| 17, 18, F15 | c.811G>T | +/− | p.Gly271Ter | novel | Mo (AC) Fa (U) | likely pathogenic (PVS1: very strong, PM2: moderate) | ||
| +/− | ||||||||
| 19, F16 | +/− | Mo (UC) Fa (U) | ||||||
| 20, F17 | Hypoplastic (pitted) | IA, AD, LAMB3 | c.-132T>C | +/− | / | novel | Mo (AC) Fa (U) | VUS (PM2: moderate, BP7: supporting) |
| 21, 22, F18 | Hypomineralized (hypocalcified) | IIIA, AD, FAM83H | c.1669G>T | +/− | p.Gly557Cys | [29] | MoFa (NA) | benign (BA1: stand-alone, BS1: strong, BS2: supporting, BP4: supporting, BP6: supporting) * |
| +/− |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leban, T.; Fidler, A.; Trebušak Podkrajšek, K.; Pavlič, A.; Tesovnik, T.; Jenko Bizjan, B.; Vrhovšek, B.; Šket, R.; Kovač, J. Integrating Imaging and Genomics in Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Novel Diagnostic Approach. Genes 2025, 16, 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070822
Leban T, Fidler A, Trebušak Podkrajšek K, Pavlič A, Tesovnik T, Jenko Bizjan B, Vrhovšek B, Šket R, Kovač J. Integrating Imaging and Genomics in Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Novel Diagnostic Approach. Genes. 2025; 16(7):822. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070822
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeban, Tina, Aleš Fidler, Katarina Trebušak Podkrajšek, Alenka Pavlič, Tine Tesovnik, Barbara Jenko Bizjan, Blaž Vrhovšek, Robert Šket, and Jernej Kovač. 2025. "Integrating Imaging and Genomics in Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Novel Diagnostic Approach" Genes 16, no. 7: 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070822
APA StyleLeban, T., Fidler, A., Trebušak Podkrajšek, K., Pavlič, A., Tesovnik, T., Jenko Bizjan, B., Vrhovšek, B., Šket, R., & Kovač, J. (2025). Integrating Imaging and Genomics in Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A Novel Diagnostic Approach. Genes, 16(7), 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070822






