Comparative Transcriptome and Metabolome Analyses Provide New Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Taproot Development and Bioactive Compound Biosynthesis in Ficus hirta vahl
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Transcriptomic Analysis
2.3. Widely Targeted Metabolomic Analysis
2.4. Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Integrative Analysis
2.5. RT-qPCR Analysis
3. Results
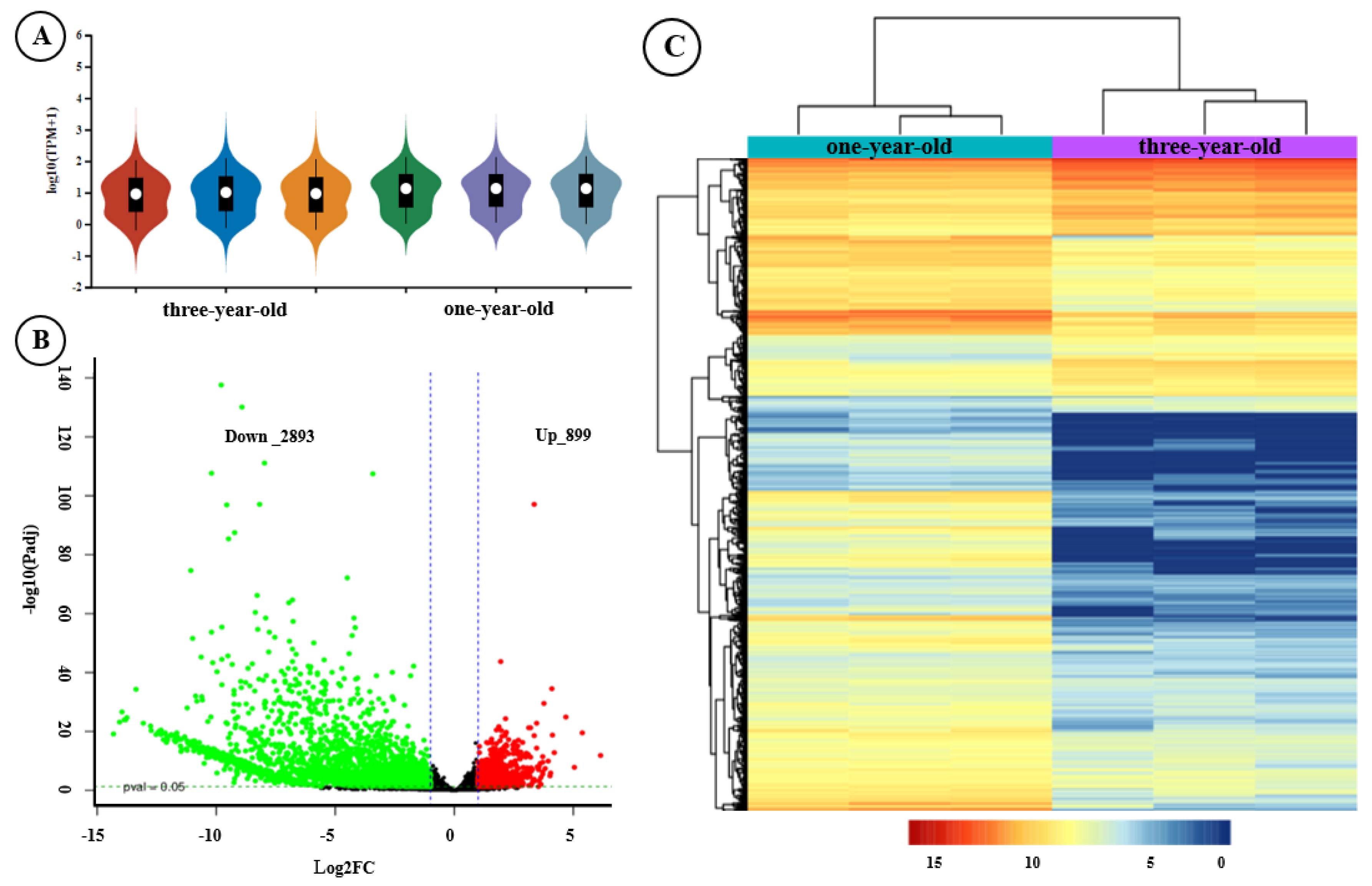
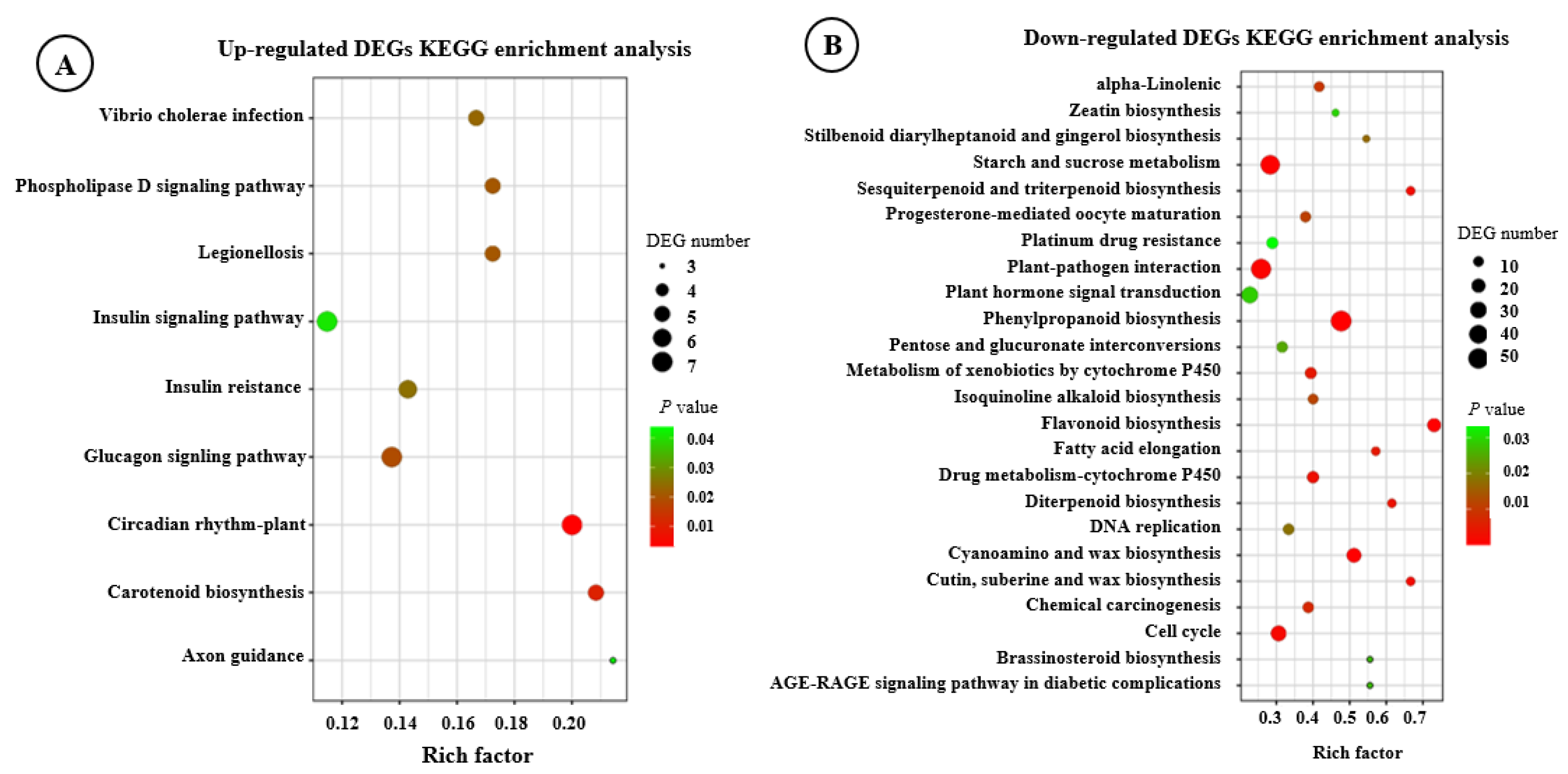
3.1. Transcriptome Analysis of F. hirta Taproots
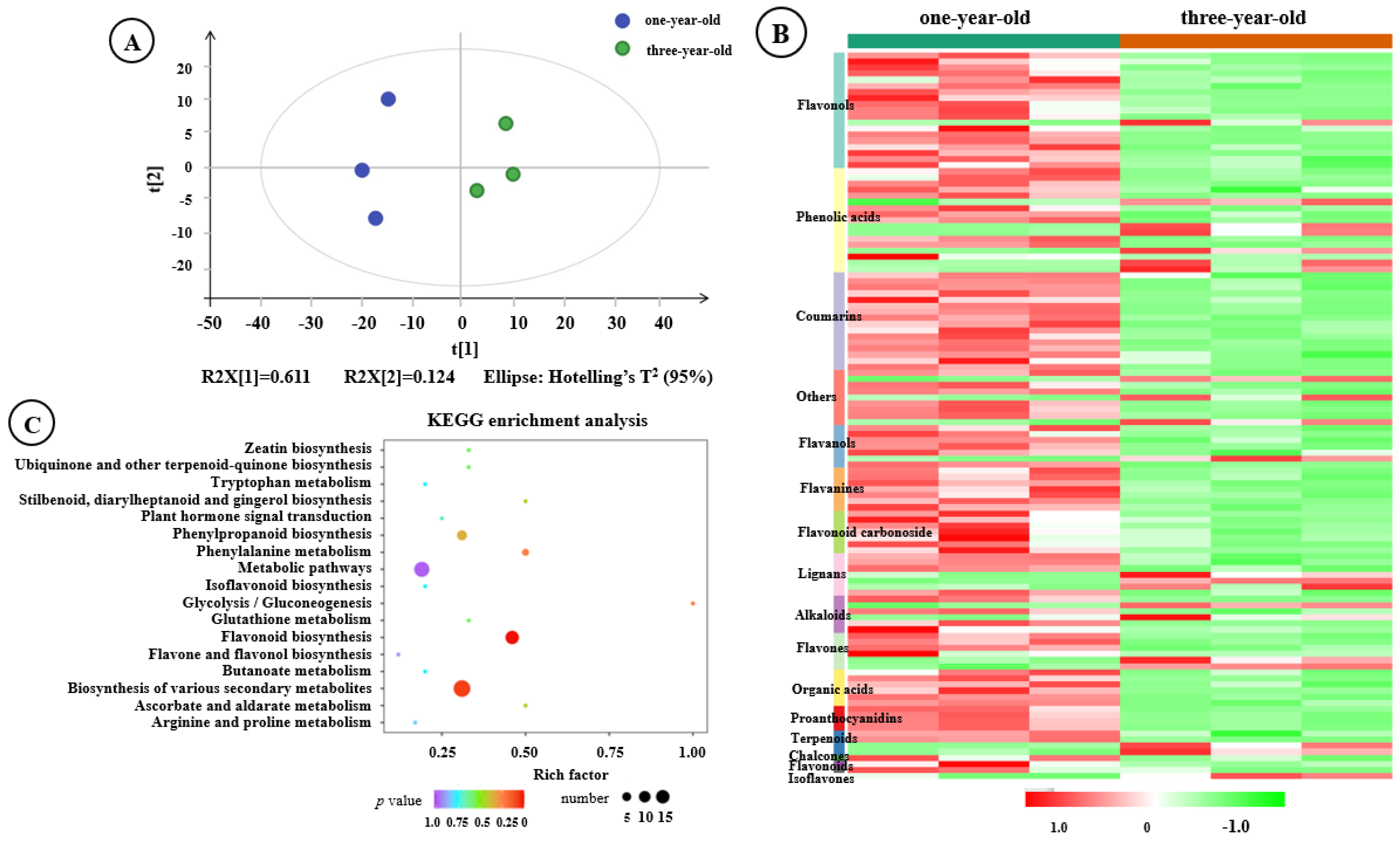
3.2. Metabolome Analysis of F. hirta Taproots
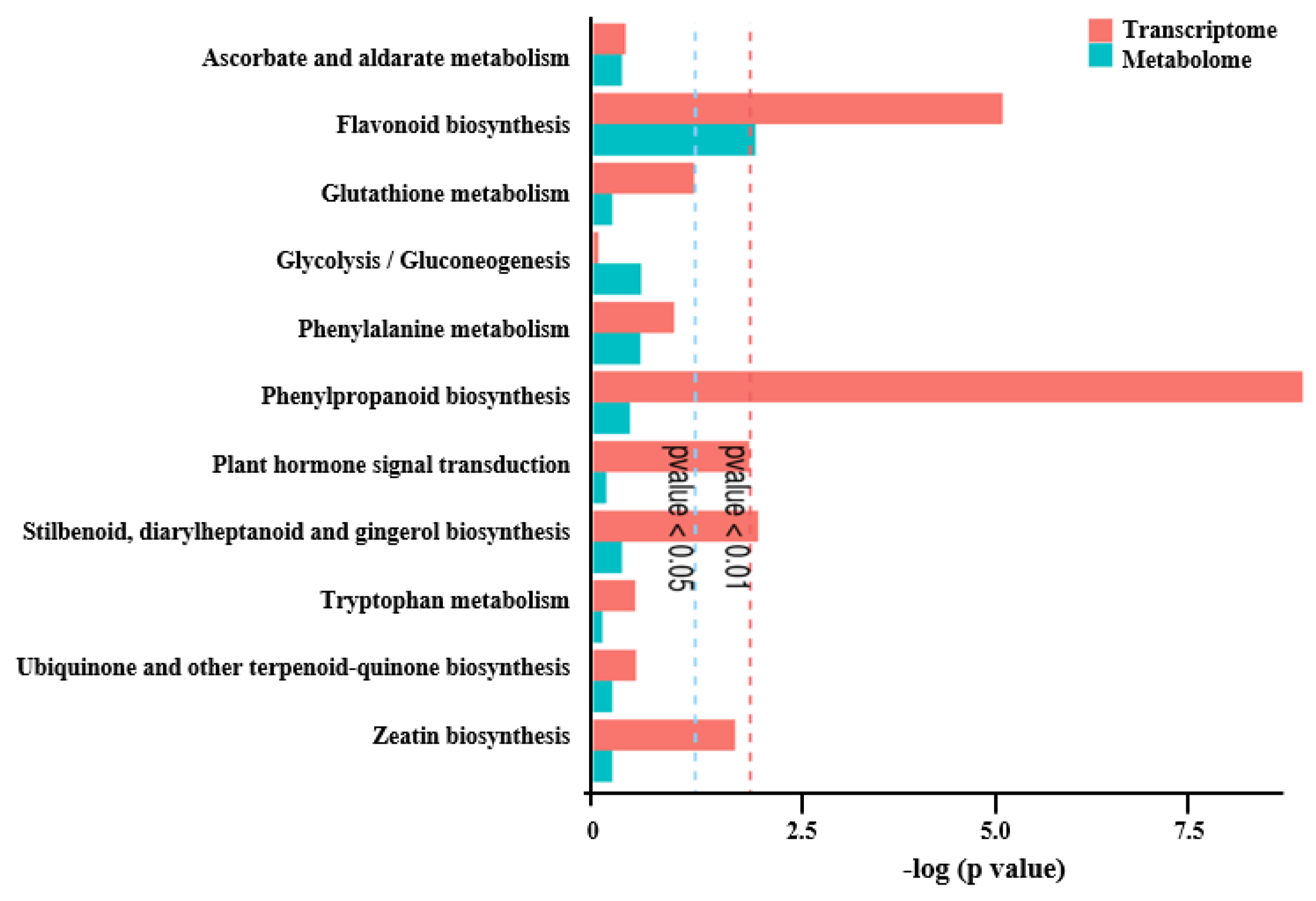
3.3. Integrated Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis
3.4. Validation of the Expression Level of DEGs by RT-qPCR
4. Discussion
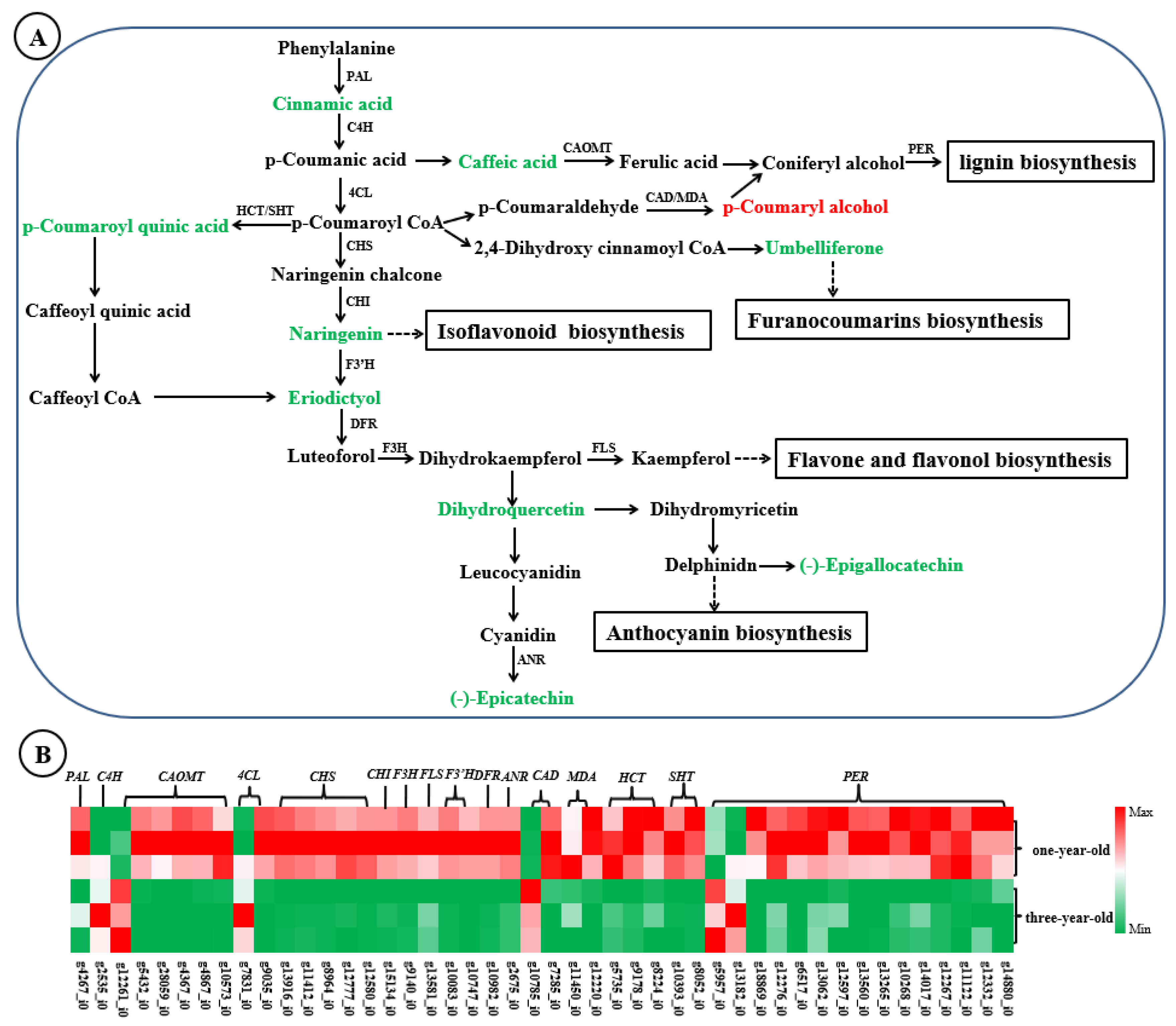
4.1. Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis Pathway Plays a Dual Role Both in Taproot Development and Accumulation of Bioactive Compounds in F. hirta
4.2. Effect of Plant Hormone Signal Transduction and Lignin on Taproot Development in F. hirta
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, Y.N.; Yan, Q.; Li, W.X.; He, J.J.; Luo, P.; Zhang, H.L. Research progress on chemical composition, extraction process and pharmacological effects of Ficus hirta Vahl. J. Pharm. Res. 2024, 43, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, T.; Zhou, F.; Chen, H.; Jian, L.; Yang, Y.; Xia, F.; Xiang, S.; Zhou, B.; Li, S. Ficus hirta Vahl. ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through regulating lipid metabolism and gut microbiota. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 3474723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Peng, X.; Chen, J.; Wan, C. Antioxidant, antifungal activities of ethnobotanical Ficus hirta Vahl. and analysis of main constituents by HPLC-MS. Biomedicines 2022, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; Chen, Q.; He, X.; So, S.; Lo, Y.; Fan, L.; Xu, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Chemical quantification and antioxidant assay of four active components in Ficus hirta root using UPLC-PAD-MS fingerprinting combined with cluster analysis. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.Y.; Kong, J.; Liu, G.W.; Wu, Z.J.; Li, S.Y.; Liu, J.T.; Yan, D.G.; Huang, Y.M.; Ma, E.Y. Quality evaluation and determination of psoralen, bergamot lactone and apigenin in Radix Fici Hirtae. Pharm. Today 2019, 29, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.J.; Liu, H.; Shi, J.J.; Shang, M.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Liu, G.X.; Xu, F.; Cai, S.Q. Study on quality standard of Fici Hirtae Radix. Chin. Trad. Herb. Drug 2017, 48, 782–791. [Google Scholar]
- Bourgaud, F.; Hehn, A.; Larbat, R.; Doerper, S.; Gontier, E.; Kellner, S.; Matern, U. Biosynthesis of coumarins in plants: A major pathway still to be unravelled for cytochrome P450 enzymes. Phytochem. Rev. 2006, 5, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.T.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, B.Z.; Yuan, Y.J. Advances in biosynthesis of scopoletin. Microb. Cell Fact. 2022, 21, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamat, F.; Olry, A.; Munakata, R.; Koeduka, T.; Sugiyama, A.; Paris, C.; Hehn, A.; Bourgaud, F.; Yazaki, K. A coumarin-specific prenyltransferase catalyzes the crucial biosynthetic reaction for furanocoumarin formation in parsley. Plant J. 2014, 77, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munakata, R.; Olry, A.; Karamat, F.; Courdavault, V.; Sugiyama, A.; Date, Y.; Krieger, C.; Silie, P.; Foureau, E.; Papon, N.; et al. Molecular evolution of parsnip (Pastinaca sativa) membrane-bound prenyltransferases for linear and/or angular furanocoumarin biosynthesis. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villard, C.; Munakata, R.; Kitajima, S.; Velzen, S.K.; Schranz, M.E.; Larbat, R.; Hehn, A. A new P450 involved in the furanocoumarin pathway underlies a recent case of convergent evolution. New Phytol. 2021, 231, 1923–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larbat, R.; Kellner, S.; Specker, S.; Hehn, A.; Gontier, E.; Hans, J.; Bourgaud, F.; Matern, U. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of psoralen synthase, the first committed monooxygenase of furanocoumarin biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 542–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.S.; Teng, Y.X.; Li, J.; Yan, Y.J. Recent advances in the biosynthesis of coumarin and its derivatives. Green. Chem. Eng. 2024, 5, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yu, Y.; Shi, R.; Xie, G.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, G.; Qin, M. Organ-specific metabolic shifts of flavonoids in Scutellaria baicalensis at different growth and development stages. Molecules 2018, 23, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.H.; Wang, C.Q.; Liu, J.H.; Li, X.W.; Wang, X.; Shang, M.Y.; Cai, S.Q.; Zhu, S.; Komatsu, K. Comparative studies of saponins in 1-3-year-old main roots, fibrous roots, and rhizomes of Panax notoginseng, and identification of different parts and growth-year samples. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 67, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, C.H.; Huang, J.; Li, G.Y.; Liu, X.H.; Sun, S.Q.; Wang, J.H. Rapid discrimination of cultivated Codonopsis lanceolata in different ages by FT-IR and 2DCOS-IR. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1069, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Yang, J.; Cao, B.; Xue, Y.; Gao, P.; Liang, H.; Li, G. Growth years and post-harvest processing methods have critical roles on the contents of medicinal active ingredients of Scutellaria baicalensis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 158, 112985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.Z.; Wang, X.P.; Gao, W.C.; Li, Z. Comparison of contents of psoralen, apigenin and bergapten in the root of Ficus hirta vahl from different origins. Clin. J. Chin. Med. 2022, 14, 124–126. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, R.T.; Liu, J.M.; Chen, L.K.; Han, Z.Z.; Lu, Y.Y.; Chen, W.D.; Chen, W.W. Investigation on the production status of Lingnan herbal medicine in Guangdong province. J. Guangzhou Univ. Trad. Chin. Med. 2020, 37, 1836–1843. [Google Scholar]
- Motte, H.; Vanneste, S.; Beeckman, T. Molecular and environmental regulation of root development. Annu. Rev. Plant. Biol. 2019, 70, 465–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsui, Y.; Shimomura, M.; Komatsu, K.; Namiki, N.; Shibata-Hatta, M.; Imai, M.; Katayose, Y.; Mukai, Y.; Kanamori, H.; Kurita, K.; et al. The radish genome and comprehensive gene expression profile of tuberous root formation and development. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Fu, L.; Tie, W.; Yan, Y.; Wu, C.; Dai, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, W. Highly dynamic, coordinated, and stage-specific profiles are revealed by a multi-omics integrative analysis during tuberous root development in cassava. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 7003–7017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, S.; Xu, P.; Zhu, S.; Ye, M.; Chen, C.; Wu, X.; Liang, W.; Pu, J. Integrative analysis of the transcriptome and metabolome reveals the developmental mechanisms and metabolite biosynthesis of the tuberous roots of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum. Molecules 2023, 28, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.D.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gong, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, S.; Xiong, L.; Luo, J. A novel integrated method for large-scale detection, identification, and quantification of widely targeted metabolites: Application in the study of rice metabolomics. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, T. Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Mol. Plant 2010, 533, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.S.; Lin, Q.H.; Chen, W.F.; Lu, Z.B.; Yu, X.G.; Shi, X.X.; Chen, G.; Cai, W.J. Study on introduction and cultivation techniques of Ficus hirta. For. Environ. Sci. 2022, 38, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, D.X.; Li, Y.Q.; Bai, M.; He, H.J.; Liang, G.X.; Wu, H. Correlation between the dynamic accumulation of the main effective components and their associated regulatory enzyme activities at different growth stages in Lonicera japonica Thunb. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 96, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wen, K.S.; Ruan, X.; Zhao, Y.X.; Wei, F.; Wang, Q. Response of plant secondary metabolites to environmental factors. Molecules 2018, 23, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, G.G.; Xue, Y.L. Physiological role and regulation of phenylpropanoid metabolism in plant. Plant Physiol. Commun. 1988, 3, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.W.; Lu, J.Q.; Lin, H.; Pang, Y.; Tang, M.L.; Yu, M.P. Advances in the study on the chemical composition, pharmacological effect and clinical application of Radix Fici Simplicissimae. J. Liaoning Univ. TCM 2020, 22, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Lu, S. Identification and characterization of flavonoid biosynthetic enzyme genes in Salvia miltiorrhiza (Lamiaceae). Molecules 2018, 23, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, T.; Inokuchi, T.; Fujioka, S.; Kimura, Y. Phenolic compounds and flavonoids as plant growth regulators from fruit and leaf of Vitex rotundifolia. Z. Naturforsch. 2004, 59C, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Pan, L.; Yang, T.; Wang, W.; Li, C.; Chen, B.; Shen, Y. Metabolomic and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) analyses reveal the important function of flavonoids in Amygdalus pedunculata Pall leaves with temporal changes. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 648277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Li, L.B.; Gan, F.Q.; Huang, R.S. Growth evaluation of Ficus hirta Vahl planted under Pinus massoniana forest. Hunan Agric. Sci. 2020, 9, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, M.X.; Gao, Y.; Cen, X.M.; Tian, M.J.; Huang, G.L.; Mo, Z.H.; Lan, W.M.; Wu, L.J. Study on the growth characters and the best harvest time of Ficus simplicissima Lour planted under Pinus massoniana Lamb. Forst. J. Green. Sci. Technol. 2023, 25, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.J.; Zhao, Y.; He, S.L.; Meng, J.; Lu, Y.C.; Shi, H.N.; Liu, C.L.; Hao, B.; Tang, Q.Y.; Zhang, S.Y.; et al. Integrated metabolome and transcriptome analyses reveal the molecular mechanism underlying dynamic metabolic processes during taproot development of Panax notoginseng. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Yang, J.L.; Hao, B.; Lu, Y.C.; Qian, Z.L.; Li, Y.; Ye, S.; Tang, J.R.; Chen, M.; Long, G.Q.; et al. Comparative transcriptome and metabolome analyses provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying taproot thickening in Panax notoginseng. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.M.; Zhang, L.M.; Guan, Y.A.; Wang, Z.L. Endogenous hormone concentration in developing tuberous roots of different sweet potato genotypes. Agric. Sci. China 2006, 5, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; van-Lammeren, A.A.; Vermeer, E.; Vreugdenhil, D. The role of gibberellin, abscisic acid, and sucrose in the regulation of potato tuber formation in vitro. Plant Physiol. 1998, 117, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, J.; Serrani-Yarce, J.C.; Chen, F.; Baxter, D.; Venables, B.J.; Dixon, R.A. Role of bifunctional ammonia-lyase in grass cell wall biosynthesis. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 16050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firon, N.; LaBonte, D.; Villordon, A.; Kfifir, Y.; Solis, J.; Lapis, E. Transcriptional profiling of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) roots indicates down-regulation of lignin biosynthesis and up-regulation of starch biosynthesis at an early stage of storage root formation. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Samples | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Clean Bases | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | GC Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| one-year-old-1 | 58,846,288 | 58,355,866 | 8,569,908,235 | 98.05 | 94.29 | 46.94 |
| one-year-old-2 | 52,592,982 | 52,199,062 | 7,605,999,070 | 98.21 | 94.80 | 46.56 |
| one-year-old-3 | 54,274,762 | 53,825,646 | 7,875,174,914 | 98.03 | 94.31 | 46.93 |
| three-year-old-1 | 41,074,490 | 40,674,184 | 5,941,654,993 | 98.00 | 94.28 | 46.17 |
| three-year-old-2 | 48,135,216 | 47,776,358 | 6,984,940,329 | 98.14 | 94.54 | 46.90 |
| three-year-old-3 | 45,302,458 | 44,878,188 | 6,566,856,537 | 97.93 | 93.99 | 46.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, M.; Liang, C.; Peng, Y.; He, H.; Wei, F.; Hu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Tang, C.; Li, G.; Li, L. Comparative Transcriptome and Metabolome Analyses Provide New Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Taproot Development and Bioactive Compound Biosynthesis in Ficus hirta vahl. Genes 2025, 16, 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070784
Tang M, Liang C, Peng Y, He H, Wei F, Hu Y, Lin Y, Tang C, Li G, Li L. Comparative Transcriptome and Metabolome Analyses Provide New Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Taproot Development and Bioactive Compound Biosynthesis in Ficus hirta vahl. Genes. 2025; 16(7):784. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070784
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Meiqiong, Chunying Liang, Yude Peng, Hong He, Fan Wei, Ying Hu, Yang Lin, Chunfeng Tang, Gang Li, and Linxuan Li. 2025. "Comparative Transcriptome and Metabolome Analyses Provide New Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Taproot Development and Bioactive Compound Biosynthesis in Ficus hirta vahl" Genes 16, no. 7: 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070784
APA StyleTang, M., Liang, C., Peng, Y., He, H., Wei, F., Hu, Y., Lin, Y., Tang, C., Li, G., & Li, L. (2025). Comparative Transcriptome and Metabolome Analyses Provide New Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Taproot Development and Bioactive Compound Biosynthesis in Ficus hirta vahl. Genes, 16(7), 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070784






