Genome Annotation and Catalytic Profile of Rhodococcus rhodochrous IEGM 107, Mono- and Diterpenoid Biotransformer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture
2.2. Whole Genome Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
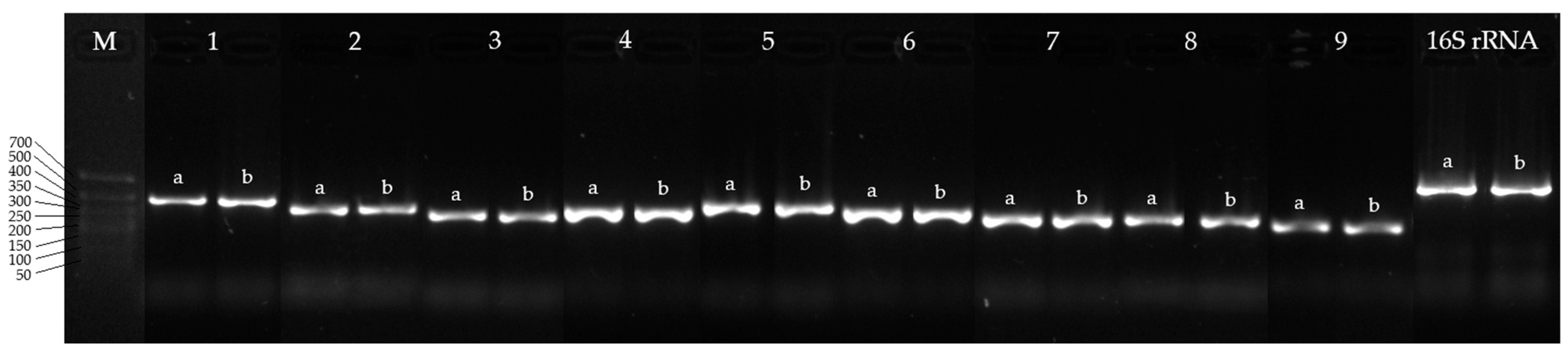
2.4. PCR and Electrophoresis of Amplicons
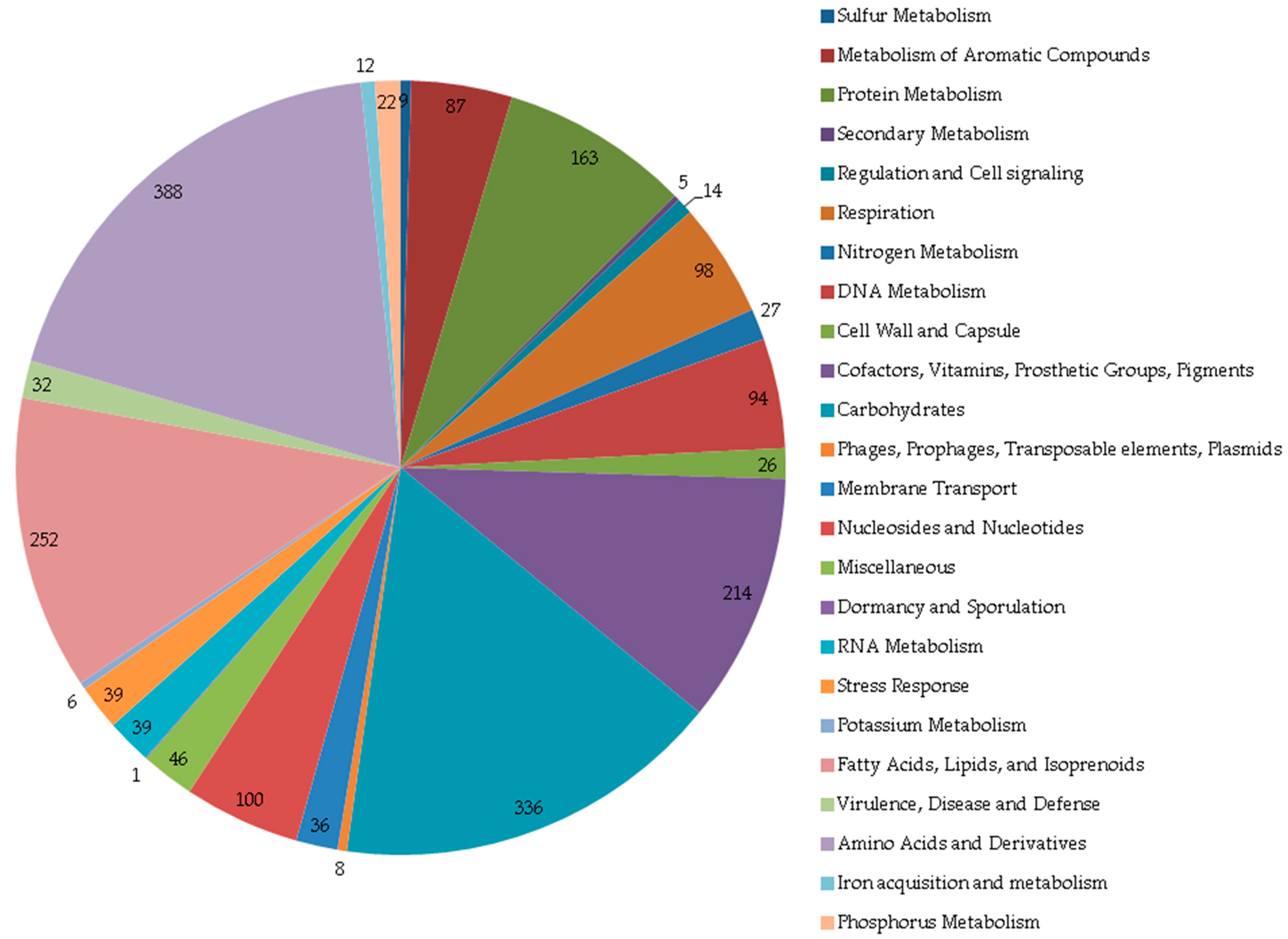
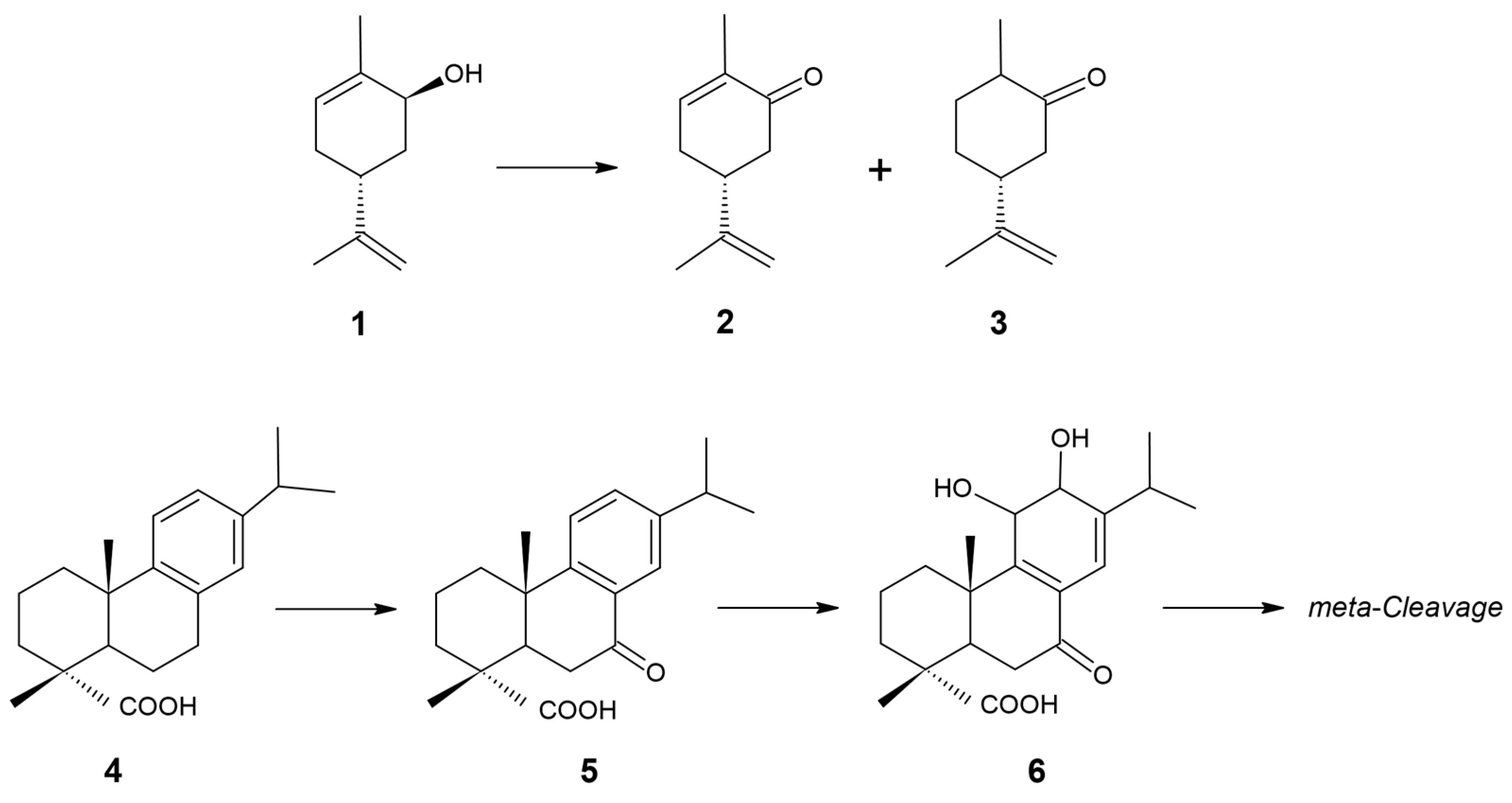
3. Results and Discussion

4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDS | Coding sequence |
| CYP450 | Cytochrome P450 |
| R. | Rhodococcus |
References
- Maltseva, P.Y.; Plotnitskaya, N.A.; Ivshina, I.B. Transformation of Terpenoids and Steroids Using Actinomycetes of the Genus Rhodococcus. Molecules 2024, 29, 3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubovska, J.; Meškys, R. Characterization of 1,8-Cineole Degradation Encoding Operon from Rhodococcus sp. TMP1. Chemija 2016, 27, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf, M.J.; van der Ven, C.; Barbirato, F.; Eppink, M.H.M.; de Bont, J.A.M.; van Berkel, W.J.H. Stereoselective Carveol Dehydrogenase from Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 26296–26304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Werf, M.J.; Overkamp, K.M.; de Bont, J.A.M. Limonene-1,2-Epoxide Hydrolase from Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14 Belongs to a Novel Class of Epoxide Hydrolases. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 5052–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giang, P.D.; Churchman, L.R.; Stok, J.E.; Soo, R.M.; De Voss, J.J. CYP108N12 Initiates p-Cymene Biodegradation in Rhodococcus globerulus. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2022, 730, 109410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giang, P.D.; Churchman, L.R.; Buczynski, J.B.; Bell, S.G.; Stok, J.E.; De Voss, J.J. CYP108N14: A Monoterpene Monooxygenase from Rhodococcus globerulus. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 752, 109852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltseva, P.Y.; Plotnitskaya, N.A.; Chudinova, A.A.; Ilyina, I.V.; Salakhutdinov, N.F.; Ivshina, I.B. Search for Rhodococcus Strains—Active Biotransformers of Monoterpenoids. Microb. Biotechnol. Fundam. Appl. Asp. Collect. Sci. Pap. 2024, 16, 351–360. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, K.M.; Grishko, V.V.; Ivshina, I.B. Highly Efficient Biodegradation of Ecotoxic Dehydroabietic Acid by Resting Cells of Rhodococcus rhodochrous IEGM 107. Microbiology 2022, 91, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Sun, R.; Feng, R.; Zhu, H.; Li, X. Recent Advances of Terpenoids with Intriguing Chemical Skeletons and Biological Activities. Chin. J. Chem. 2025, 43, 443–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustamova, N.; Huang, G.; Isokov, M.; Movlanov, J.; Farid, R.; Buston, I.; Xiang, H.; Davranov, K.; Yili, A. Modification of Natural Compounds through Biotransformation Process by Microorganisms and Their Pharmacological Properties. Fitoterapia 2024, 179, 106227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, K.K.; Khanuja, S.P.S.; Ahmad, A.; Santha Kumar, T.R.; Gupta, V.K.; Kumar, S. Antimicrobial Activity Profiles of the Two Enantiomers of Limonene and Carvone Isolated from the Oils of Mentha spicata and Anethum sowa. Flavour Fragr. J. 2002, 17, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Han, H.; Li, B.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, Y. Fumigant Toxicity and Physiological Effects of Spearmint (Mentha spicata, Lamiaceae) Essential Oil and Its Major Constituents against Reticulitermes Dabieshanensis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 171, 113894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muftic, M. Essay on Antibiotic Properties of Abietyl Compounds. Q. J. Crude Drug Res. 1970, 10, 1301–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriks, M.; Ekman, R.; Von Weissenberg, K. Bioassay of Some Resin and Fatty Acids with Fomes annosus. Acta Acad. Abo. 1979, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Lei, R.; Ding, S.-W.; Zhu, S. Skewer: A Fast and Accurate Adapter Trimmer for next-Generation Sequencing Paired-End Reads. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Nurk, S.; Bankevich, A.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.; Korobeynikov, A.; Lapidus, A.; Prjibelsky, A.; Pyshkin, A.; Sirotkin, A.; Sirotkin, Y.; et al. Assembling genomes and mini-metagenomes from highly chimeric reads. In Research in Computational Molecular Biology, Proceedings of the 17th Annual International Conference, RECOMB 2013, Beijing, China, 7–10 April 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Göker, M. TYGS Is an Automated High-Throughput Platform for State-of-the-Art Genome-Based Taxonomy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Carbasse, J.S.; Peinado-Olarte, R.L.; Göker, M. TYGS and LPSN: A Database Tandem for Fast and Reliable Genome-Based Classification and Nomenclature of Prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Auch, A.F.; Klenk, H.-P.; Göker, M. Genome Sequence-Based Species Delimitation with Confidence Intervals and Improved Distance Functions. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefort, V.; Desper, R.; Gascuel, O. FastME 2.0: A Comprehensive, Accurate, and Fast Distance-Based Phylogeny Inference Program. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2798–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, J.S. Estimating Phylogenetic Trees from Distance Matrices. Am. Nat. 1972, 106, 645–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreft, Ł.; Botzki, A.; Coppens, F.; Vandepoele, K.; Van Bel, M. PhyD3: A Phylogenetic Tree Viewer with Extended phyloXML Support for Functional Genomics Data Visualization. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2946–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.-H.; Ha, S.; Lim, J.; Kwon, S.; Chun, J. A Large-Scale Evaluation of Algorithms to Calculate Average Nucleotide Identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid Annotations Using Subsystems Technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overbeek, R.; Olson, R.; Pusch, G.D.; Olsen, G.J.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Parrello, B.; Shukla, M.; et al. The SEED and the Rapid Annotation of Microbial Genomes Using Subsystems Technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D206–D214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettin, T.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Olsen, G.J.; Olson, R.; Overbeek, R.; Parrello, B.; Pusch, G.D.; et al. RASTtk: A Modular and Extensible Implementation of the RAST Algorithm for Building Custom Annotation Pipelines and Annotating Batches of Genomes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Kloosterman, A.M.; Charlop-Powers, Z.; Van Wezel, G.P.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. AntiSMASH 6.0: Improving Cluster Detection and Comparison Capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W29–W35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG Tools for Functional Characterization of Genome and Metagenome Sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, F.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Lee, J.; Eusebi, A.; Niewielska, A.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Lopez, R.; Butcher, S. The EMBL-EBI Job Dispatcher Sequence Analysis Tools Framework in 2024. Nucleic Acids Res 2024, 52, W521–W525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.A.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2--a Multiple Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelli, C.; Laird, M.R.; Williams, K.P.; Fraser University Research Computing Group, S.; Lau, B.Y.; Hoad, G.; Winsor, G.L.; Brinkman, F.S. IslandViewer 4: Expanded Prediction of Genomic Islands for Larger-Scale Datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W30–W35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltseva, P.Y.; Plotnitskaya, N.A.; Krivoruchko, A.V.; Beletskiy, A.V.; Rakitin, A.L.; Mardanov, A.V.; Ivshina, I.B. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Genome of Rhodococcus rhodochrous IEGM 1362, an (−)-Isopulegol Biotransformer. Genes 2024, 15, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.L.; Goodfellow, M. Rhodococcus (Zopf 1891) Emend. Goodfellow, Alderson and Chun 1998a. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Springer: London, UK, 2012; pp. 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Overbeek, R.; Begley, T.; Butler, R.M.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Chuang, H.-Y.; Cohoon, M.; de Crécy-Lagard, V.; Diaz, N.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.; et al. The Subsystems Approach to Genome Annotation and Its Use in the Project to Annotate 1000 Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 5691–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Wei, X.; Wan, C.; Zhao, W.; Song, R.; Xin, S.; Song, K. Exploring the Biological Pathways of Siderophores and Their Multidisciplinary Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Molecules 2024, 29, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerson, S.R.; Rimando, A.M. A Plethora of Polyketides: Structures, Biological Activities, and Enzymes; ACS Symposium Series: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; pp. 2–14. [Google Scholar]
- Xingrong, L.; Gorish, B.M.T.; Qaria, M.A.; Hussain, A.; Abdelmula, W.I.Y.; Zhu, D. Unlocking Ectoine’s Postbiotic Therapeutic Promise: Mechanisms, Applications, and Future Directions. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivshina, I.; Bazhutin, G.; Tyumina, E. Rhodococcus Strains as a Good Biotool for Neutralizing Pharmaceutical Pollutants and Obtaining Therapeutically Valuable Products: Through the Past into the Future. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 967127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janocha, S.; Schmitz, D.; Bernhardt, R. Terpene Hydroxylation with Microbial Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenases. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2015, 148, 215–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryle, M.J.; Stok, J.E.; De Voss, J.J. Reactions Catalyzed by Bacterial Cytochromes P450. Aust. J. Chem. 2003, 56, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.E.; Ahmed, F.; Antoniou, T. Microbial Transformations of Steroids. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1993, 21, 1077–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecelão, C.S.R.; Van Keulen, F.; Da Fonseca, M.M.R. Development of a Reaction System for the Selective Conversion of (–)-trans-Carveol to (–)-Carvone with Whole Cells of Rhodococcus erythropolis DCL14. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2001, 11, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, M.P.; Warren, R.L.; Hsiao, W.W.L.; Araki, N.; Myhre, M.; Fernandes, C.; Miyazawa, D.; Wong, W.; Lillquist, A.L.; Wang, D.; et al. The Complete Genome of Rhodococcus sp. RHA1 Provides Insights into a Catabolic Powerhouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2006, 103, 15582–15587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C.A.; Wyndham, R.C. Characterization of Tdt Genes for the Degradation of Tricyclic Diterpenes by Pseudomonas diterpeniphila A19-6a. Can. J. Microbiol. 2002, 48, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.J.; Martin, V.J.J.; Mohn, W.W. A Cytochrome P450 Involved in the Metabolism of Abietane Diterpenoids by Pseudomonas abietaniphila BKME-9. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 3631–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddocks, S.E.; Oyston, P.C.F. Structure and Function of the LysR-Type Transcriptional Regulator (LTTR) Family Proteins. Microbiology 2008, 154, 3609–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivshina, I.B.; Luchnikova, N.A.; Maltseva, P.Y.; Ilyina, I.V.; Volcho, K.P.; Gatilov, Y.V.; Korchagina, D.V.; Kostrikina, N.A.; Sorokin, V.V.; Mulyukin, A.L.; et al. Biotransformation of (–)-Isopulegol by Rhodococcus rhodochrous. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Feature | Value |
|---|---|
| Size, bp | 5,730,104 |
| GC content, % | 67.8 |
| N50, bp | 190,984 |
| L50 | 10 |
| Number of contigs | 118 |
| Number of CDSs | 5555 |
| Number of RNAs | 56 |
| Genome coverage | 357× |
| Subject Type Strain | dDDH, % | G + C Content Difference, % | ANI, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| R. rhodochrous NBRC 16069 | 79.90 | 0.43 | 97.98 |
| R. rhodochrous NCTC10210 | 79.70 | 0.36 | 97.94 |
| R. rhodochrous EP4 | 83.50 | 0.11 | 98.21 |
| R. pyridinivorans TG9 | 60.60 | 0.24 | 95.12 |
| R. pyridinivorans DSM 44555 | 59.10 | 0.04 | 95.02 |
| R. gordoniae NCTC 13296 | 41.70 | 0.10 | 90.74 |
| Coding Element | Number of Clusters |
|---|---|
| Non-ribosomal peptide synthetase | 10 |
| Terpene | 3 |
| β-lactone | 2 |
| Terpene precursor | 1 |
| Ectoine | 1 |
| Non-ribosomal peptide metallophores | 1 |
| Non-α poly-amino acids like ε-polylysin | 1 |
| T1 polyketide synthase | 1 |
| Gene No. | Protein ID | Function | Contig ID | Gene Localization | Size, bp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | fig|1829.162.peg.2180 | Cytochrome P450 | JAJNCP010000006.1 | 99283–98072 | 1212 |
| 2 | fig|1829.162.peg.2317 | Cytochrome P450 | JAJNCP010000006.1 | 238491–237112 | 1380 |
| 3 | fig|1829.162.peg.3629 | Cytochrome P450 | JAJNCP010000012.1 | 67604–68950 | 1347 |
| 4 | fig|1829.162.peg.4187 | Putative cytochrome P450 hydroxylase | JAJNCP010000016.1 | 90221–88989 | 1233 |
| 5 | fig|1829.162.peg.4655 | Putative cytochrome P450 hydroxylase | JAJNCP010000022.1 | 10812–9490 | 1323 |
| 6 | fig|1829.162.peg.4855 | Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase | JAJNCP010000025.1 | 31024–29690 | 1335 |
| 7 | fig|1829.162.peg.4867 | Putative cytochrome P450 hydroxylase | JAJNCP010000025.1 | 41056–42348 | 1293 |
| 8 | fig|1829.162.peg.4920 | Putative cytochrome P450 | JAJNCP010000026.1 | 37768–36389 | 1380 |
| 9 | fig|1829.162.peg.5314 | Putative cytochrome P450 hydroxylase | JAJNCP010000037.1 | 20577–18217 | 2361 |
| Gene No. | Upstream Transcriptional Regulators | Proteins Participating in Electron Transfers and Redox Reactions | Mobile Elements and Transposases | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AraC family | 1,2-dihydroxycyclohexa-3,5-diene-1-carboxylate dehydrogenase; oxidoreductase FAD-binding domain protein; benzoate 1,2-dioxygenase alpha and beta subunits; 2-polyprenylphenol hydroxylase and related flavodoxin oxidoreductases; catechol 1,2-dioxygenase | No | Benzoate transport protein; benzoate MFS transporter BenK; Pca regulon regulatory protein PcaR; muconate cycloisomerase; muconolactone isomerase |
| 2 | AcrR family | 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase; alcohol dehydrogenase; acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, putative phosphotransferase; putative short-chain dehydrogenase | No | Transcriptional regulator, AcrR family; methylated-DNA–protein-cysteine methyltransferase; RNA polymerase sigma factor RpoE; methylated-DNA–protein-cysteine methyltransferase; DNA-3-methyladenine glycosylase II; DNA polymerase I |
| 3 | IclR family | Amino acid permease; flavin monoamine oxidase-related protein; RidA/YER057c/UK114 superfamily, group 3; putative hydrolase; TTP-dependent protein, related to E1 component of pyruvate/2-oxoglutarate/acetoin dehydrogenase; 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] synthase, KASIII; acyl-CoA dehydrogenase | No | Twin-arginine translocation protein TatA; two fluoride ion transporters CrcB; methyltransferase |
| 4 | LysR family | Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase; 3-oxosteroid 1-dehydrogenase; oxidoreductase, short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase family; enoyl-CoA hydratase; isochorismatase; oxidoreductase, short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase family | No | Conserved protein associated with acetyl-CoA C-acyltransferase |
| 5 | AcrR family | Succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase [NAD]; succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase [NADP+]; ferredoxin reductase; ferredoxin, 2Fe-2S; enoyl-CoA hydratase | Mobile element protein | Long-chain fatty acid–CoA ligase |
| 6 | Two-component transcriptional response regulator, LuxR family | Putative dioxygenase; oxidoreductase, short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase family; Gene No. 7 | No | Putative esterase; metallopeptidase; possible peptidase of M23/37 family; long-chain fatty acid–CoA ligase |
| 7 | AcrR family; MarR family | Gene No. 6; epoxide hydrolase | No | Two uncharacterized MFS-type transporters |
| 8 | XRE family | Hypothetical proteins | Mobile element protein | Putative transmembrane protein; putative peptidase |
| 9 | AcrR family | Enoyl-CoA hydratase; quinone oxidoreductase; oxidoreductase, short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase family; acyl-CoA dehydrogenase | Mobile element protein | DNA-binding response regulator PhoP; two-component system phosphate sensor kinase, PhoR; L-proline/glycine betaine transporter ProP; transcriptional regulator, IclR family |
| Gene No. | DNA Sequences | Amino Acid Sequences | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identity, % | Number of Strains | Identity, % | Number of Strains | |
| 1 | 81.91–100 | 21 | 65.10–100 | 25 |
| 2 | 80.30–100 | 20 | 66.75–100 | 51 |
| 3 | 79.99–100 | 23 | 63.31–100 | 51 |
| 4 | 100 | 6 | 100 | 6 |
| 5 | 79.50–100 | 9 | 66.37–100 | 7 |
| 6 | 95.43–100 | 18 | 61.56–100 | 33 |
| 7 | 95.36–100 | 18 | 97.67–100 | 23 |
| 8 | 82.74–100 | 10 | 56.36–100 | 26 |
| 9 | 75.77–100 | 22 | 59.76–100 | 36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plotnitskaya, N.A.; Maltseva, P.Y.; Ivshina, I.B. Genome Annotation and Catalytic Profile of Rhodococcus rhodochrous IEGM 107, Mono- and Diterpenoid Biotransformer. Genes 2025, 16, 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070739
Plotnitskaya NA, Maltseva PY, Ivshina IB. Genome Annotation and Catalytic Profile of Rhodococcus rhodochrous IEGM 107, Mono- and Diterpenoid Biotransformer. Genes. 2025; 16(7):739. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070739
Chicago/Turabian StylePlotnitskaya, Natalia A., Polina Yu. Maltseva, and Irina B. Ivshina. 2025. "Genome Annotation and Catalytic Profile of Rhodococcus rhodochrous IEGM 107, Mono- and Diterpenoid Biotransformer" Genes 16, no. 7: 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070739
APA StylePlotnitskaya, N. A., Maltseva, P. Y., & Ivshina, I. B. (2025). Genome Annotation and Catalytic Profile of Rhodococcus rhodochrous IEGM 107, Mono- and Diterpenoid Biotransformer. Genes, 16(7), 739. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070739







