Whole-Genome DNA Methylation Analysis in Age-Related Hearing Loss
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Audioprofiles
2.3. DNA Isolation and Bisulfite Conversion
2.4. Candidate Genes Approach
2.5. Array-Based Methylation Assay
2.6. Data Analysis
2.7. Methylation-Specific Polymerase Chain Reaction Validation
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Description
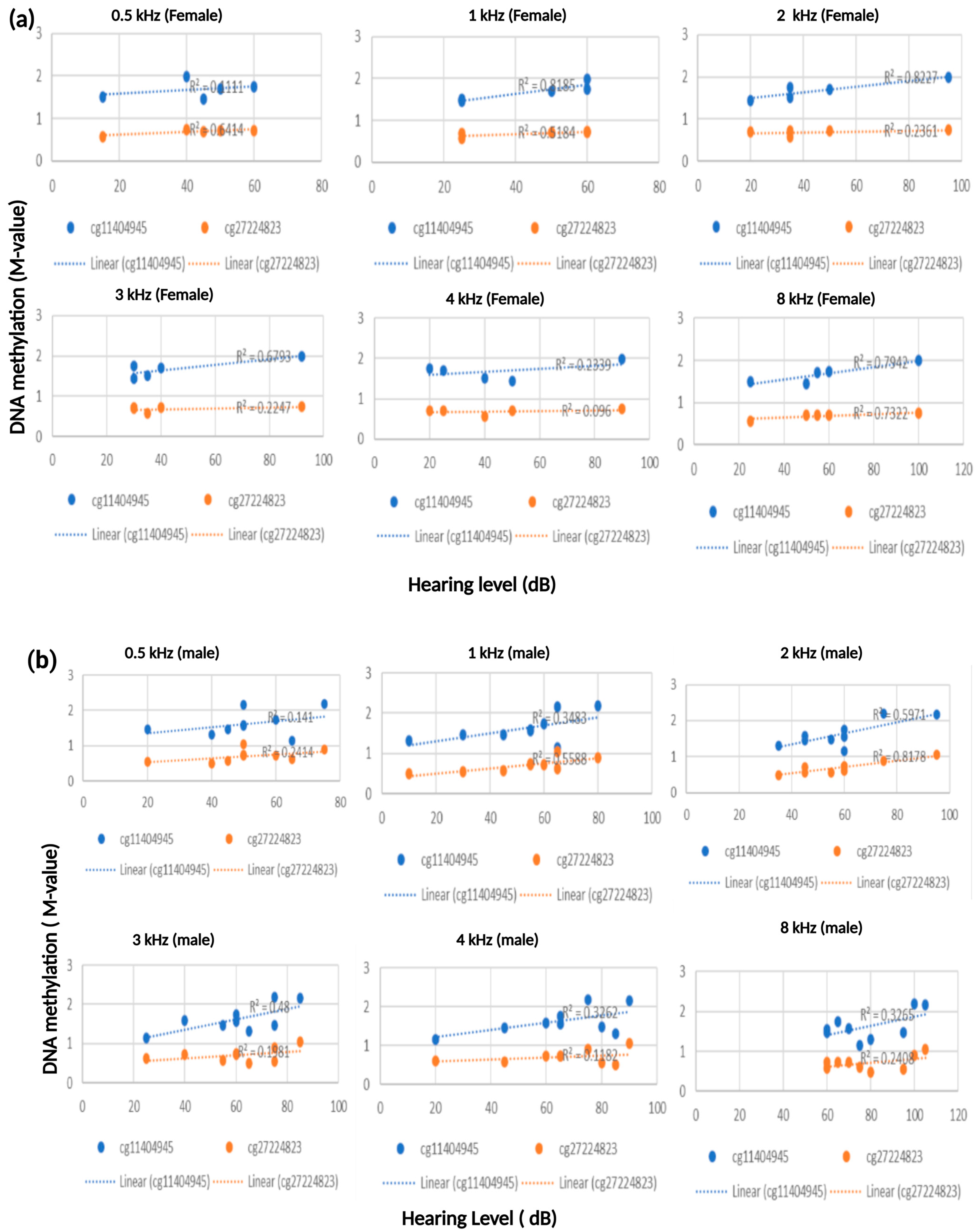
3.2. Robust Association Between ESPN and TNFRSF25 CpG Sites with Patients’ Hearing Thresholds
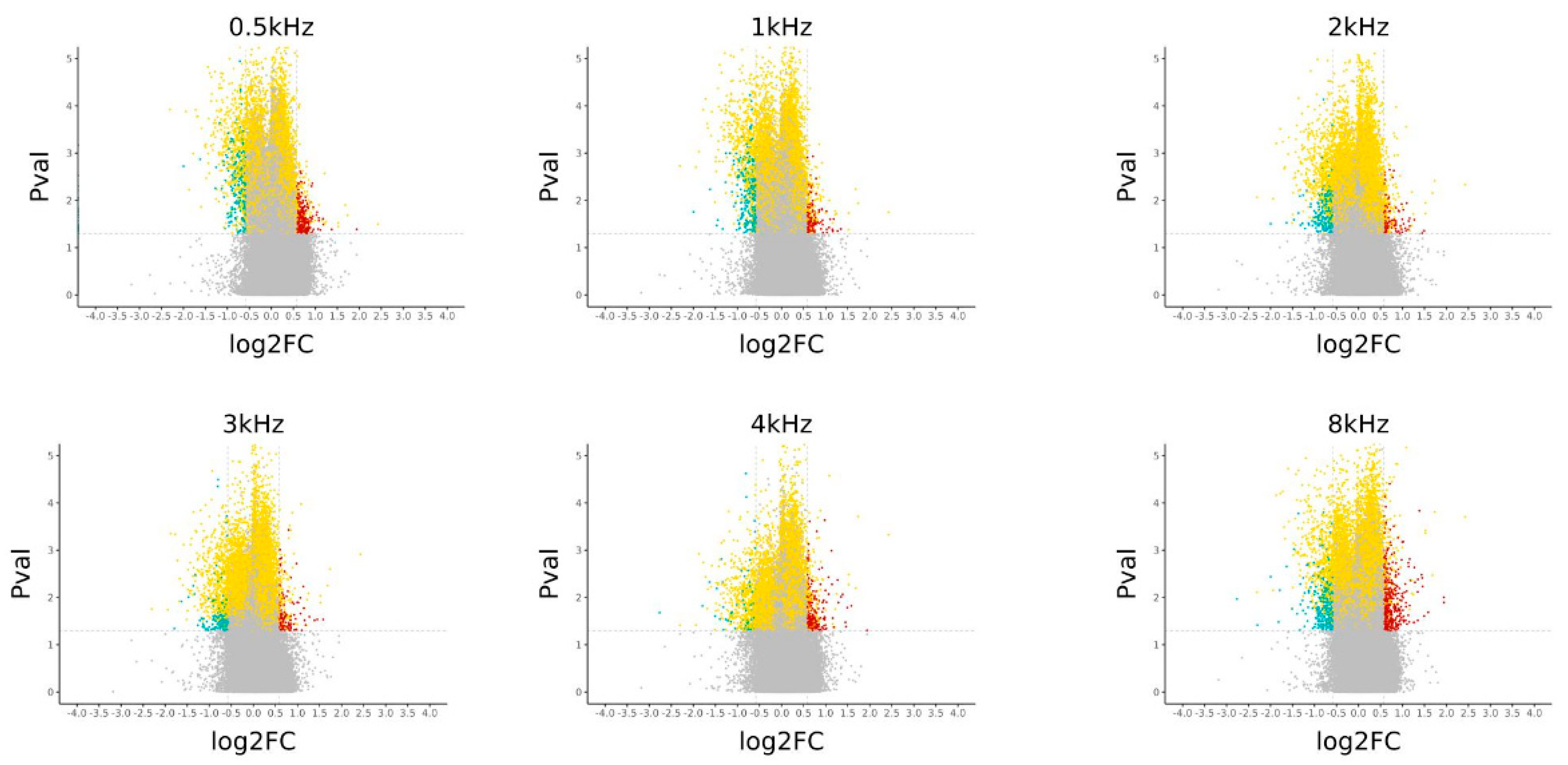
3.3. Correlation Between Patients’ DNA Methylation Level and Hearing Score at 8 kHZ
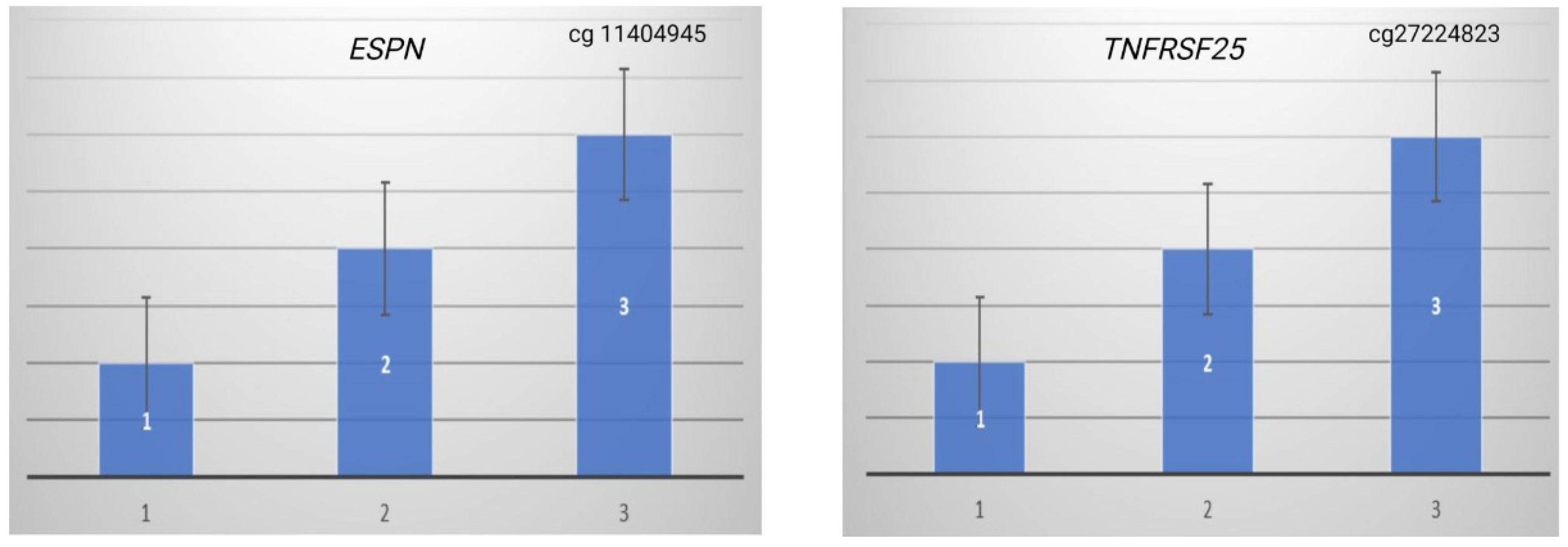
3.4. Methylation-Specific PCR Validation
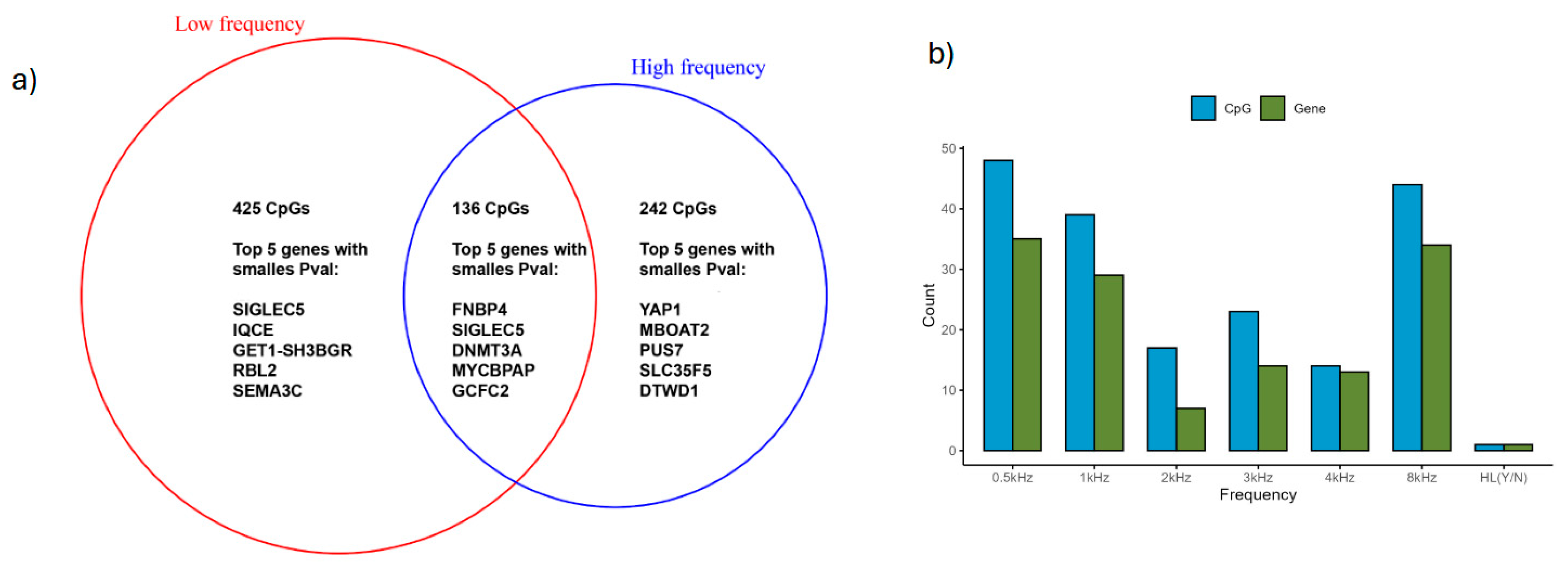
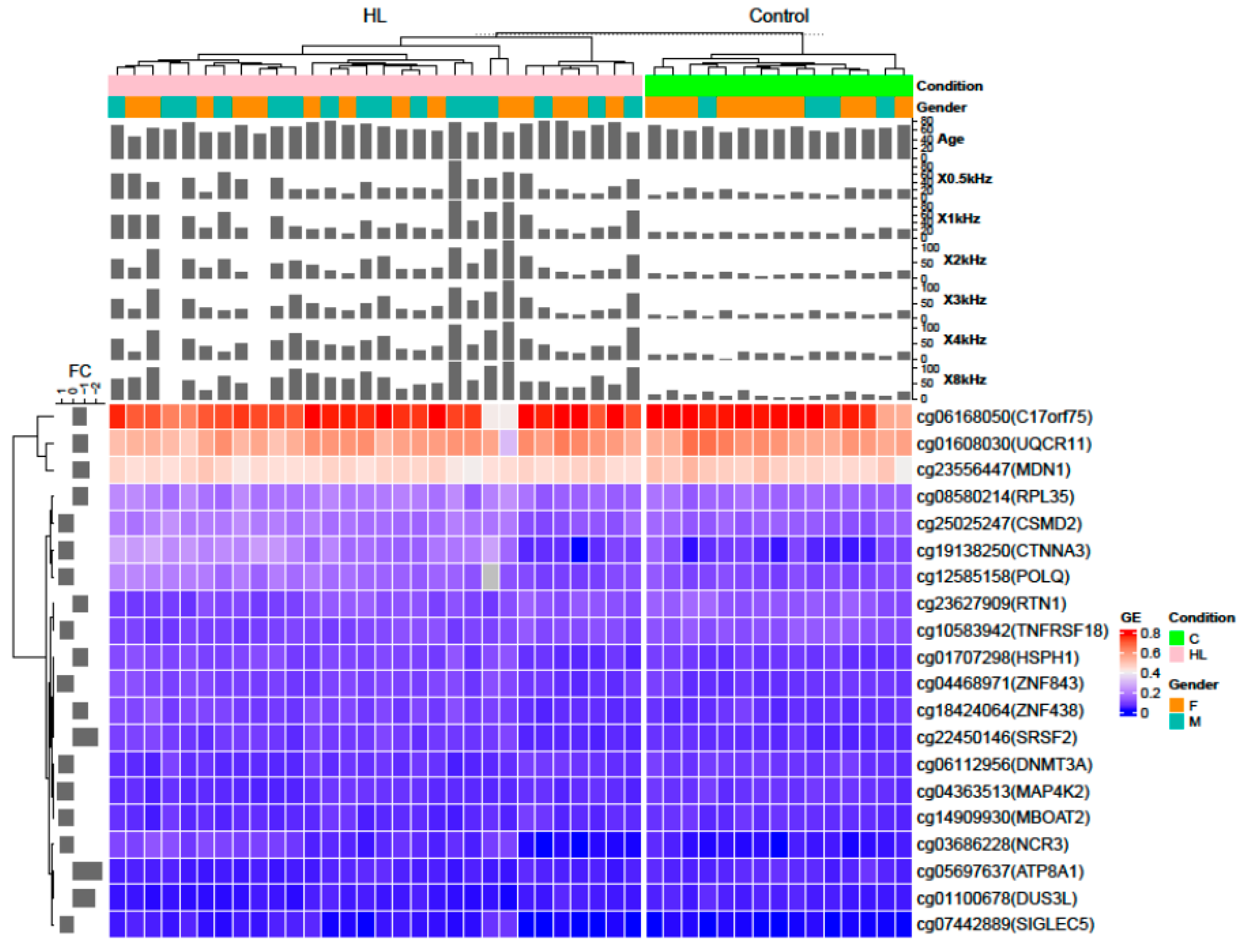
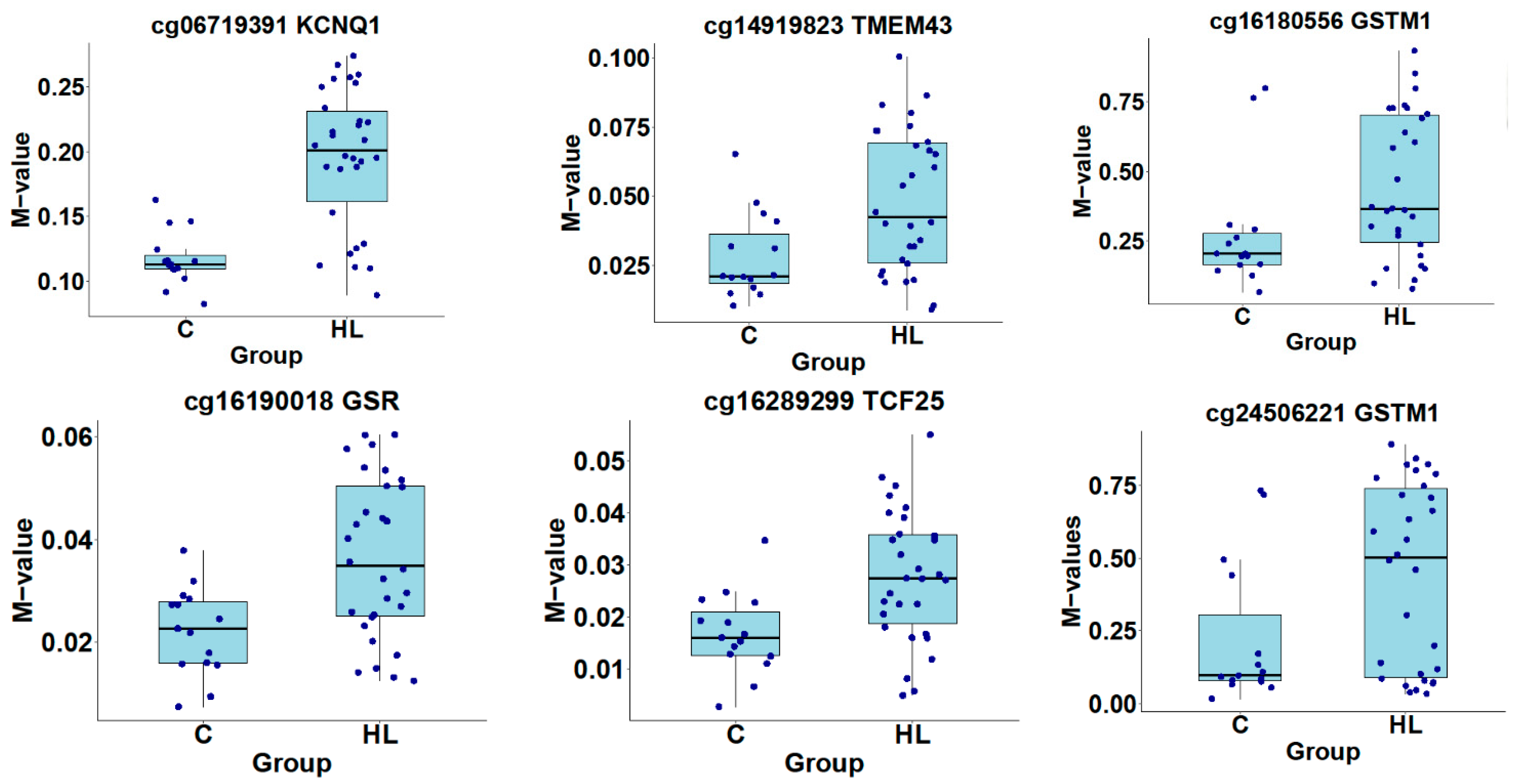
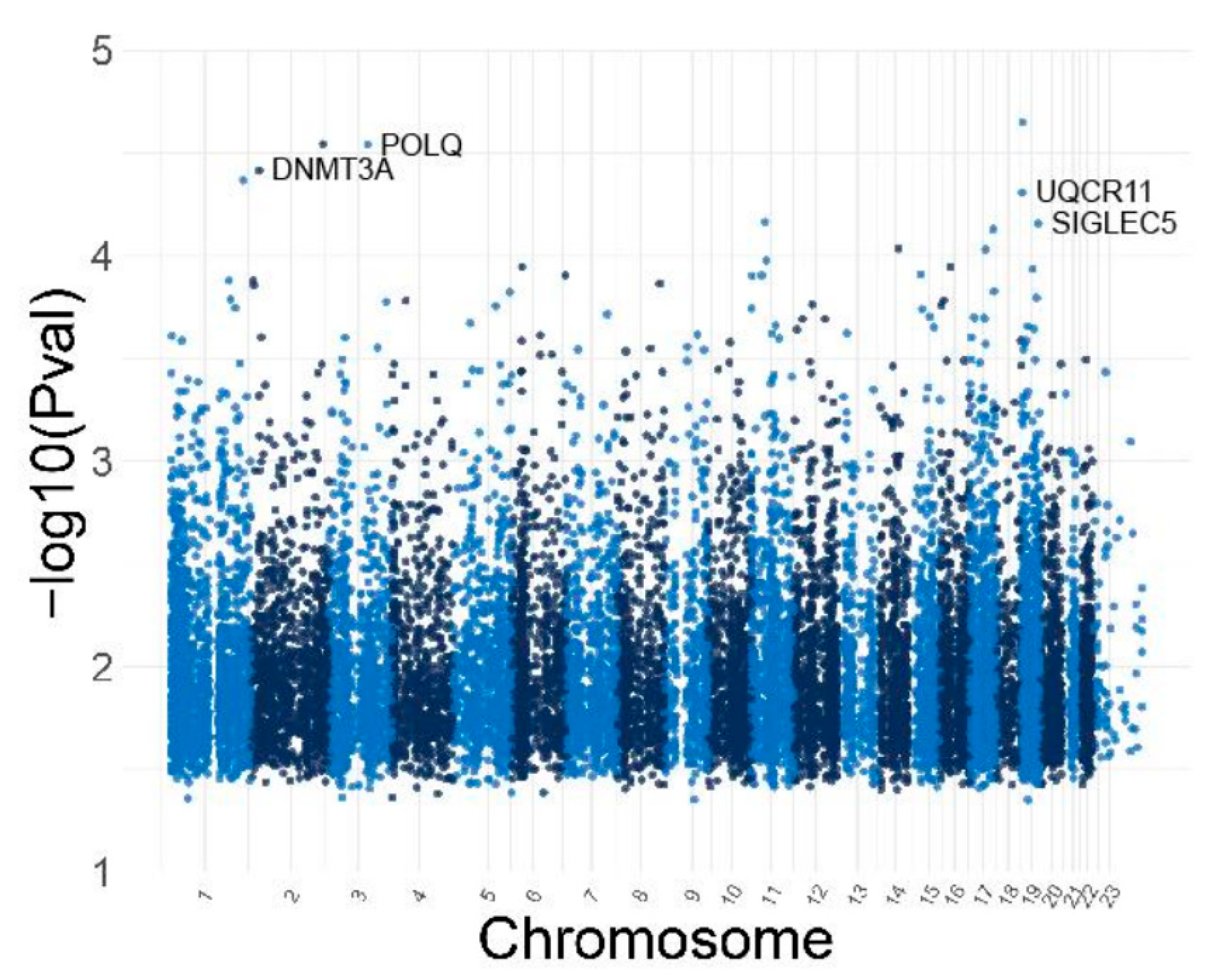
3.5. Identification of Differentially Methylated CpG and Genes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tu, N.C.; Friedman, R.A. Age-related hearing loss: Unraveling the pieces. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2018, 3, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Puel, J.L. Presbycusis: An Update on Cochlear Mechanisms and Therapies. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, G.A.; Mills, J.H. Presbycusis. Lancet 2005, 366, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheslock, M.; De Jesus, O. Presbycusis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nadol, J.B., Jr. Schuknecht: “Presbycusis.” (Laryngoscope. 1955;65:402–419). Laryngoscope 1996, 106, 1327–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlemiller, K.K. Age-related hearing loss: The status of Schuknecht’s typology. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2004, 12, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowl, M.R.; Dawson, S.J. Age-Related Hearing Loss. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a033217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.H.; Schrepfer, T.; Schacht, J. Age-related hearing impairment and the triad of acquired hearing loss. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasoba, T.; Lin, F.R.; Someya, S.; Kashio, A.; Sakamoto, T.; Kondo, K. Current concepts in age-related hearing loss: Epidemiology and mechanistic pathways. Hear. Res. 2013, 303, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.G.; Park, J.S.; Ko, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-S. Regulation of gene expression by altered promoter methylation using a CRISPR/Cas9-mediated epigenetic editing system. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layman, W.S.; Zuo, J. Epigenetic regulation in the inner ear and its potential roles in development, protection, and regeneration. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, M.J.; Domann, F.E. A role for epigenetics in hearing: Establishment and maintenance of auditory specific gene expression patterns. Hear. Res. 2007, 233, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, R.; Bencie, N.; Liu, G.; Eshraghi, N.; Nisenbaum, E.; Blanton, S.H.; Yan, D.; Mittal, J.; Dinh, C.T.; Young, J.I.; et al. Recent advancements in understanding the role of epigenetics in the auditory system. Gene 2020, 761, 144996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Shen, L.; Huang, X.; Lin, X.; Kong, W. Reduced expression of Connexin26 and its DNA promoter hypermethylation in the inner ear of mimetic aging rats induced by d-galactose. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 452, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouzid, A.; Smeti, I.; Chakroun, A.; Loukil, S.; Gibriel, A.A.; Grati, M.; Ghorbel, A.; Masmoudi, S. CDH23 Methylation Status and Presbycusis Risk in Elderly Women. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, S.I.; Bared, A.; Ouyang, X.; Du, L.L.; Yan, D.; Liu, X.Z. Audioprofiles and antioxidant enzyme genotypes in presbycusis. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 2539–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bared, A.; Ouyang, X.; Angeli, S.; Du, L.L.; Hoang, K.; Yan, D.; Liu, X.Z. Antioxidant enzymes, presbycusis, and ethnic variability. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 143, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeester, K.; van Wieringen, A.; Hendrickx, J.-J.; Topsakal, V.; Fransen, E.; van Laer, L.; Van Camp, G.; Van de Heyning, P. Audiometric shape and presbycusis. Int. J. Audiol. 2009, 48, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, L. Nonsyndromic hearing loss: An analysis of audiograms. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1994, 103, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.A.; Zwinderman, A.H. On the Benjamini–Hochberg method. Ann. Stat. 2006, 34, 1827–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jaehnig, E.J.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, B. WebGestalt 2019: Gene set analysis toolkit with revamped UIs and APIs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W199–W205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Guo, Y.; Sheng, Q.; Shyr, Y. Advanced heat map and clustering analysis using heatmap3. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 986048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaudy, F.; Zheng, L.; Ficarella, R.; Ballana, E.; Carella, M.; Melchionda, S.; Estivill, X.; Bartles, J.R.; Gasparini, P. Espin gene (ESPN) mutations associated with autosomal dominant hearing loss cause defects in microvillar elongation or organisation. J. Med Genet. 2006, 43, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.M.; Jaworek, T.J.; Sarangdhar, G.N.; Zheng, L.; Gul, K.; Khan, S.N.; Friedman, T.B.; Sisk, R.A.; Bartles, J.R.; Riazuddin, S.; et al. Inframe deletion of human ESPN is associated with deafness, vestibulopathy and vision impairment. J. Med Genet. 2018, 55, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, T.H.; Wolf, D.; Podack, E.R. The role of TNFRSF25:TNFSF15 in disease… and health? Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 691, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takashima, S.; Takehashi, M.; Lee, J.; Chuma, S.; Okano, M.; Hata, K.; Suetake, I.; Nakatsuji, N.; Miyoshi, H.; Tajima, S.; et al. Abnormal DNA methyltransferase expression in mouse germline stem cells results in spermatogenic defects. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 81, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Zhao, L.; Nie, G.; Li, H. Inhibiting DNA methylation alleviates cisplatin-induced hearing loss by decreasing oxidative stress-induced mitochondria-dependent apoptosis via the LRP1-PI3K/AKT pathway. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 1305–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.A.; Groves, A.K. Transcription Factor Reprogramming in the Inner Ear: Turning on Cell Fate Switches to Regenerate Sensory Hair Cells. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 660748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Cheng, X.; Qin, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; et al. Uqcr11 alleviates oxidative stress and apoptosis after traumatic brain injury. Exp. Neurol. 2023, 370, 114582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyme, S.B.; Schier, A.F. Polq-Mediated End Joining Is Essential for Surviving DNA Double-Strand Breaks during Early Zebrafish Development. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochner, B.S.; Zimmermann, N. Role of siglecs and related glycan-binding proteins in immune responses and immunoregulation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujioka, M.; Okano, H.; Ogawa, K. Inflammatory and immune responses in the cochlea:potential therapeutic targets for sensorineural hearing loss. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Primer Set | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Size, bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| ESPNM cg11404945 | TATGTTTTGATTTATCGGATTTG C | GAAAATATAAACGCAACAACGAA | 146 |
| ESPNU cg11404945 | GTTTTGATTTATTGGATTTAGTG G | ACAAAAATATAAACACAACAACA | 145 |
| TNFRSF25 M cg27224823 | GTCGTTTTCGAGATTAGTAGTAC G | AAAACGCCTAAATAACAAATAAAC | 179 |
| TNFRSF25 U cg27224823 | GGTTGTTTTTGAGATTAGTAGTA TG | CCAAAACACCTAAATAACAAATAAA CAC | 182 |
| ARHL (n = 31) | Control (n = 15) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| Mean (SD) | 65.42 (10.03) | 60.67 (4.06) |
| Median [Q1, Q3] | 66 (57, 74) | 61 (58.5, 62) |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 45% | 67% |
| Male | 55% | 33% |
| Audiometric | ||
| 0.5 kHz Mean (SD) | 39.03 (20.85) | 15 (6.58) |
| 1 kHz Mean (SD) | 42.26 (23.55) | 15 (4.83) |
| 2 kHz Mean (SD) | 50.16 (26.81) | 15.33 (5.62) |
| 3 kHz Mean (SD) | 50.71 (26.33) | 15.33 (6.94) |
| 4 kHz Mean (SD) | 55.97 (27.46) | 13.33 (6.24) |
| 8 kHz Mean (SD) | 69.19 (24.79) | 14.67 (6.18) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roche, M.V.; Yan, D.; Guo, Y.; Hamad, N.; Young, J.I.; Blanton, S.H.; Gong, F.; Liu, X.Z. Whole-Genome DNA Methylation Analysis in Age-Related Hearing Loss. Genes 2025, 16, 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050526
Roche MV, Yan D, Guo Y, Hamad N, Young JI, Blanton SH, Gong F, Liu XZ. Whole-Genome DNA Methylation Analysis in Age-Related Hearing Loss. Genes. 2025; 16(5):526. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050526
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoche, Marie Valerie, Denise Yan, Yan Guo, Naser Hamad, Juan I. Young, Susan H. Blanton, Feng Gong, and Xue Zhong Liu. 2025. "Whole-Genome DNA Methylation Analysis in Age-Related Hearing Loss" Genes 16, no. 5: 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050526
APA StyleRoche, M. V., Yan, D., Guo, Y., Hamad, N., Young, J. I., Blanton, S. H., Gong, F., & Liu, X. Z. (2025). Whole-Genome DNA Methylation Analysis in Age-Related Hearing Loss. Genes, 16(5), 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16050526






