Warfarin Pharmacogenomics: Designing Electrochemical DNA-Based Sensors to Detect CYP2C9*2 Gene Variation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Equipment and Electrodes
2.2. Chemicals, Samples, and Solutions
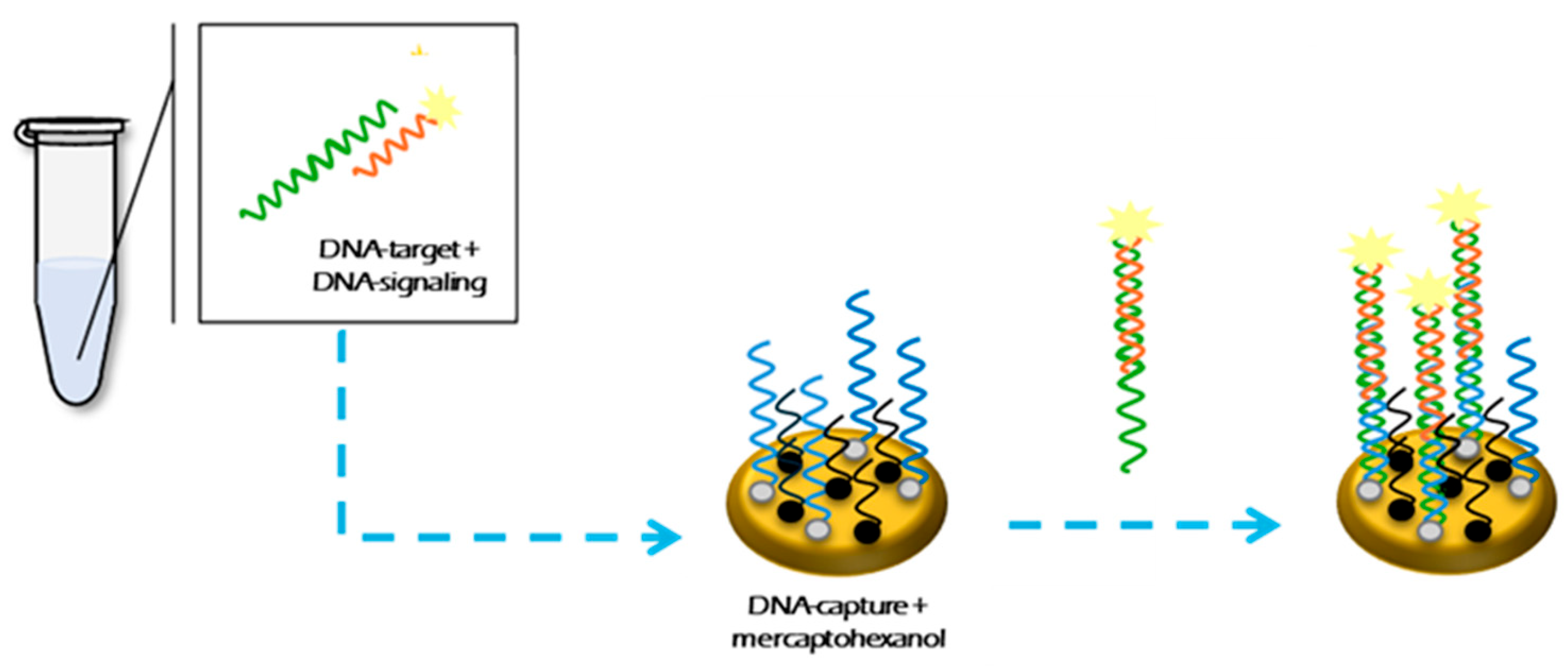
2.3. Electrochemical DNA-Based Sensor Design
3. Results
3.1. Bioinformatic Tools to Select DNA Probes
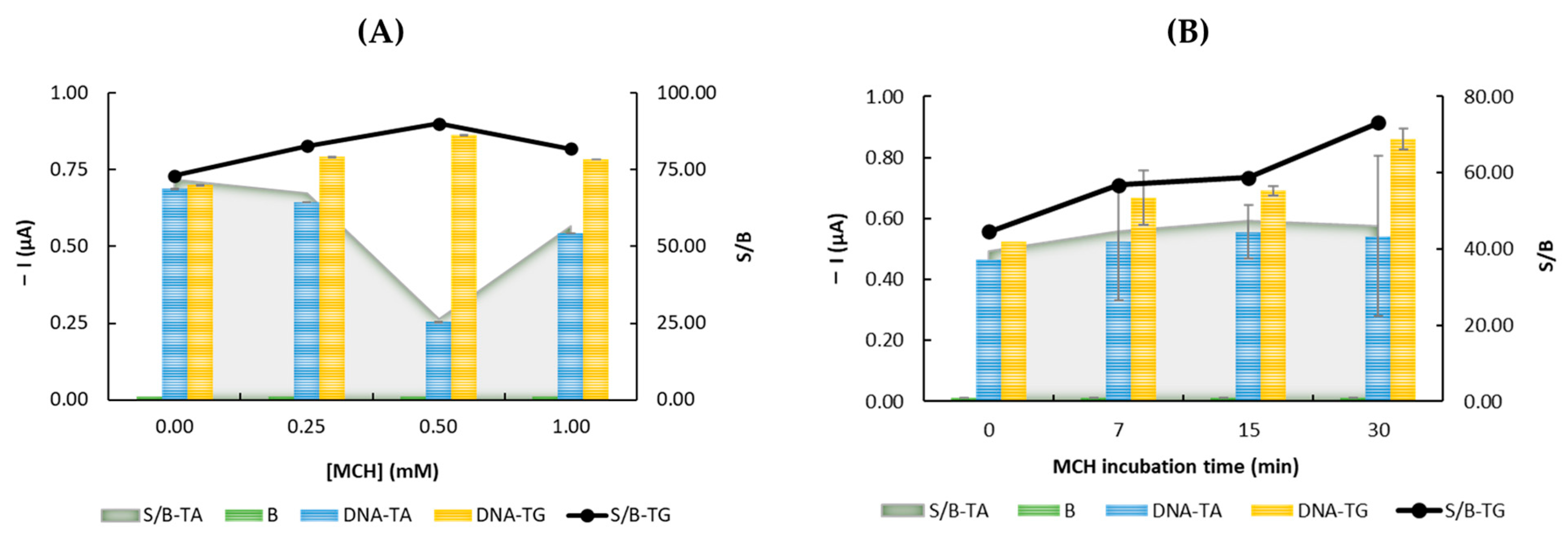
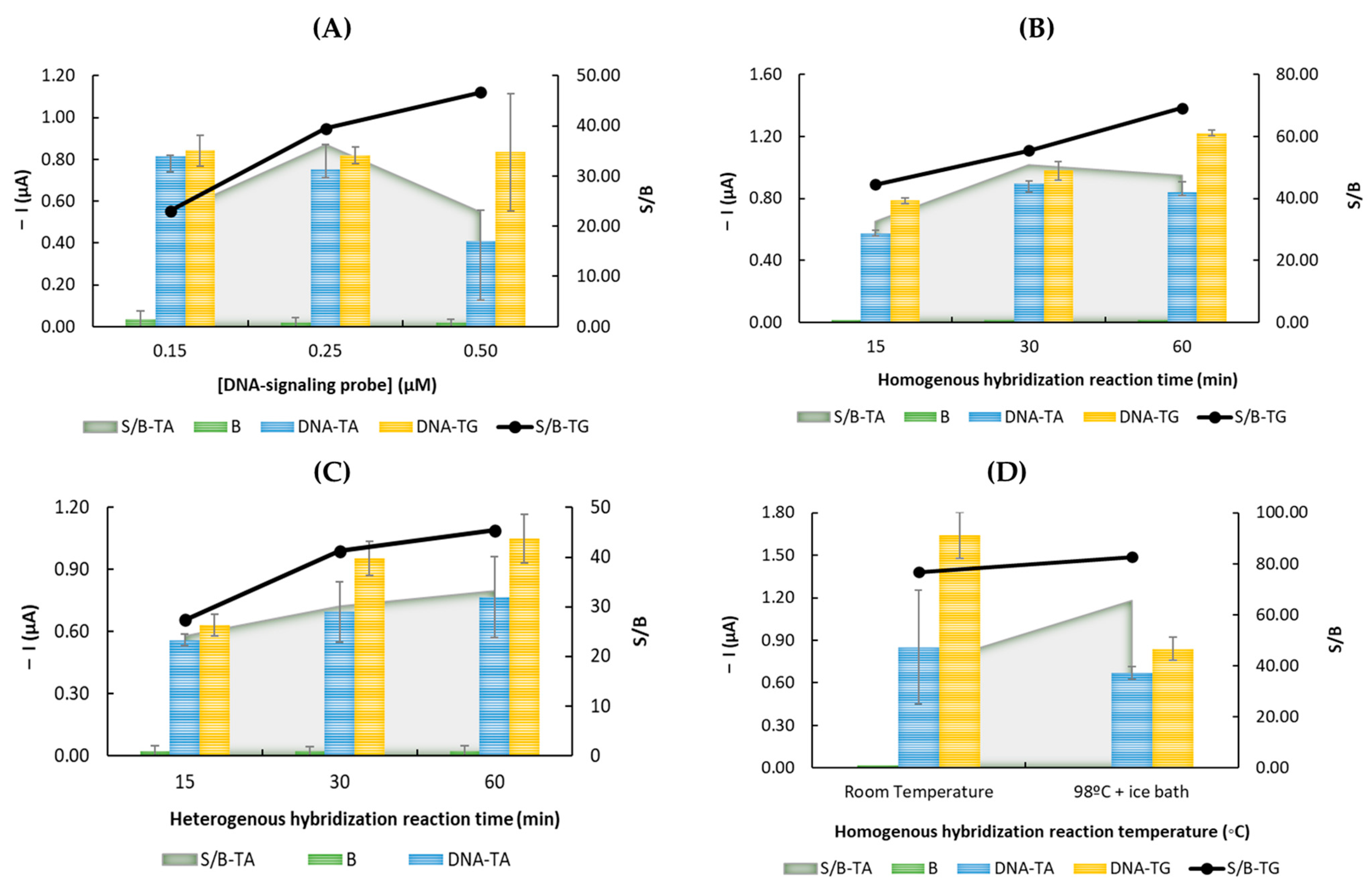
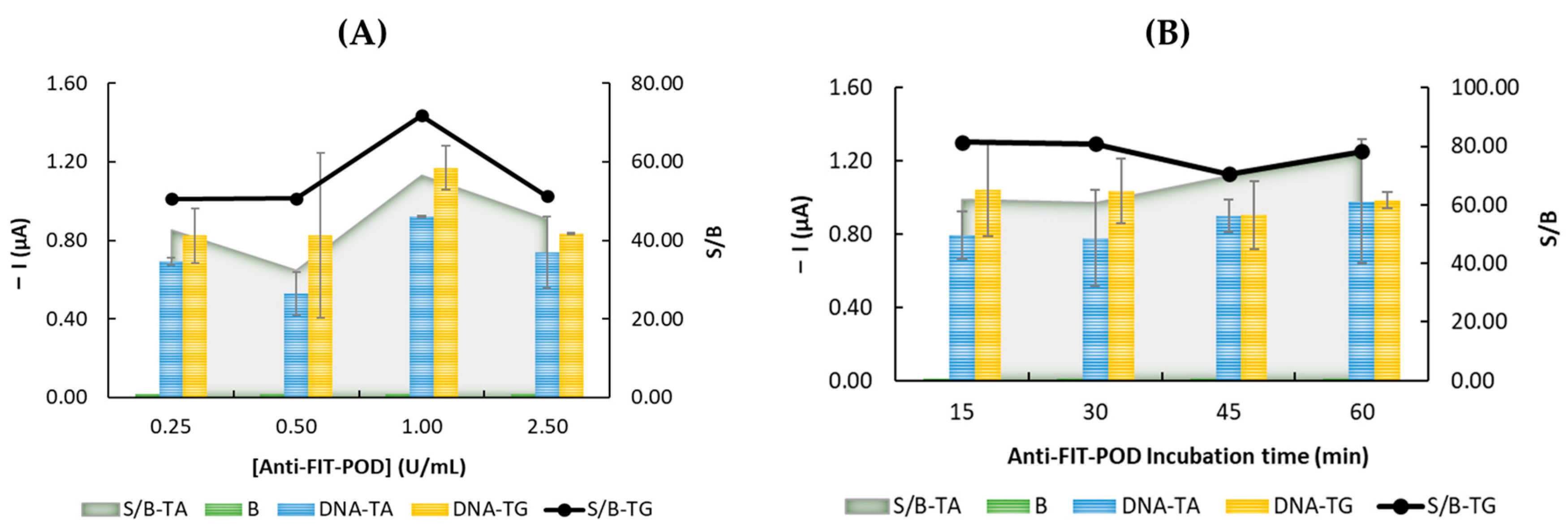
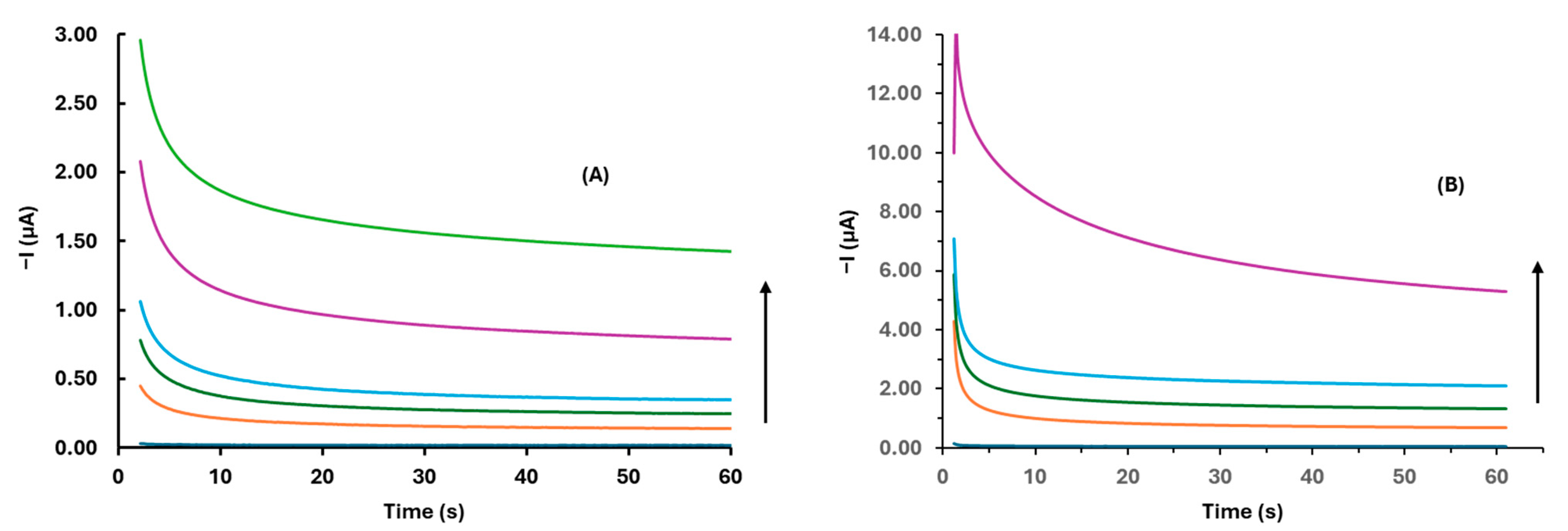
3.2. Optimization of the Experimental Parameters
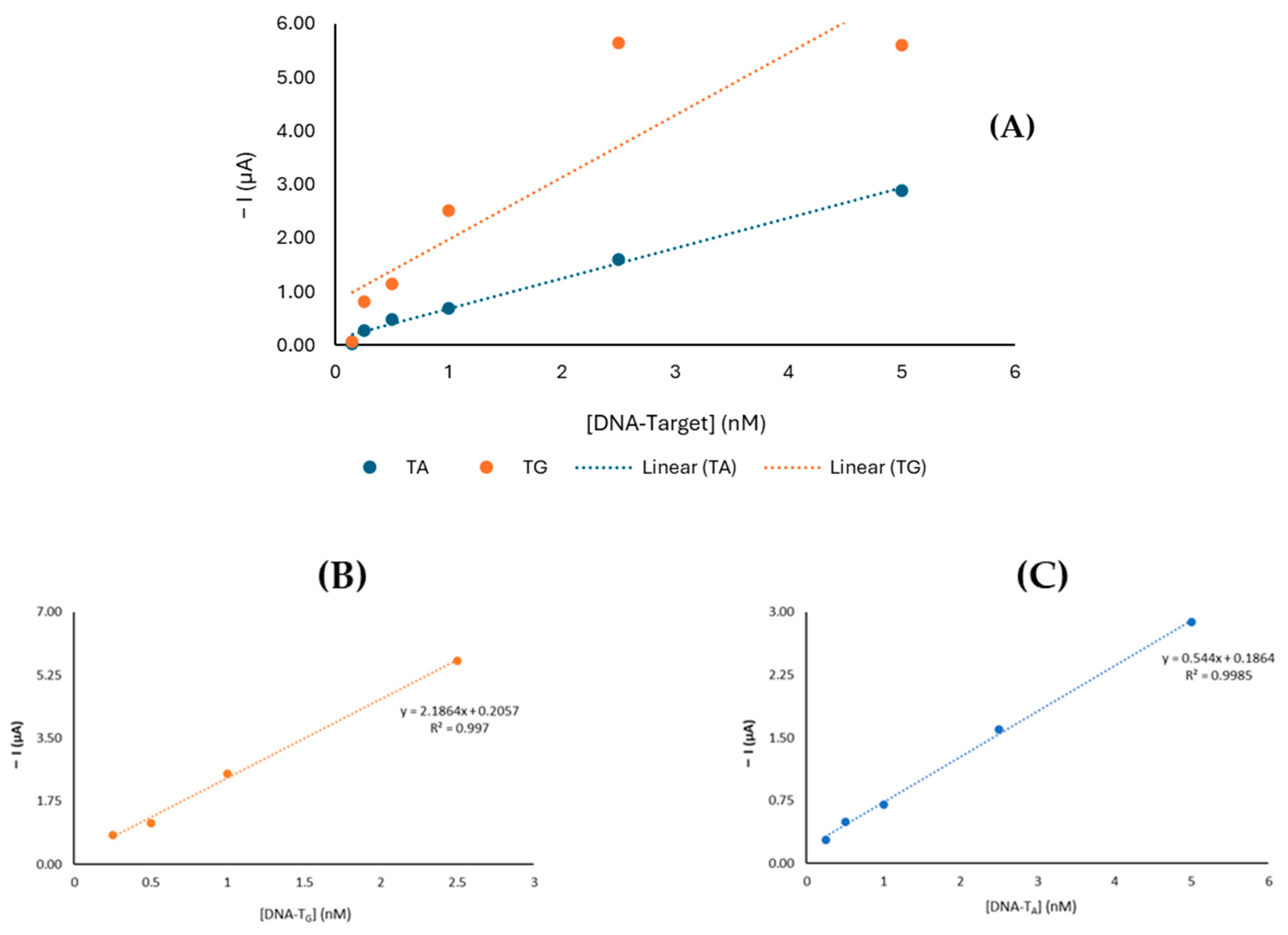
3.3. Analytical Performance
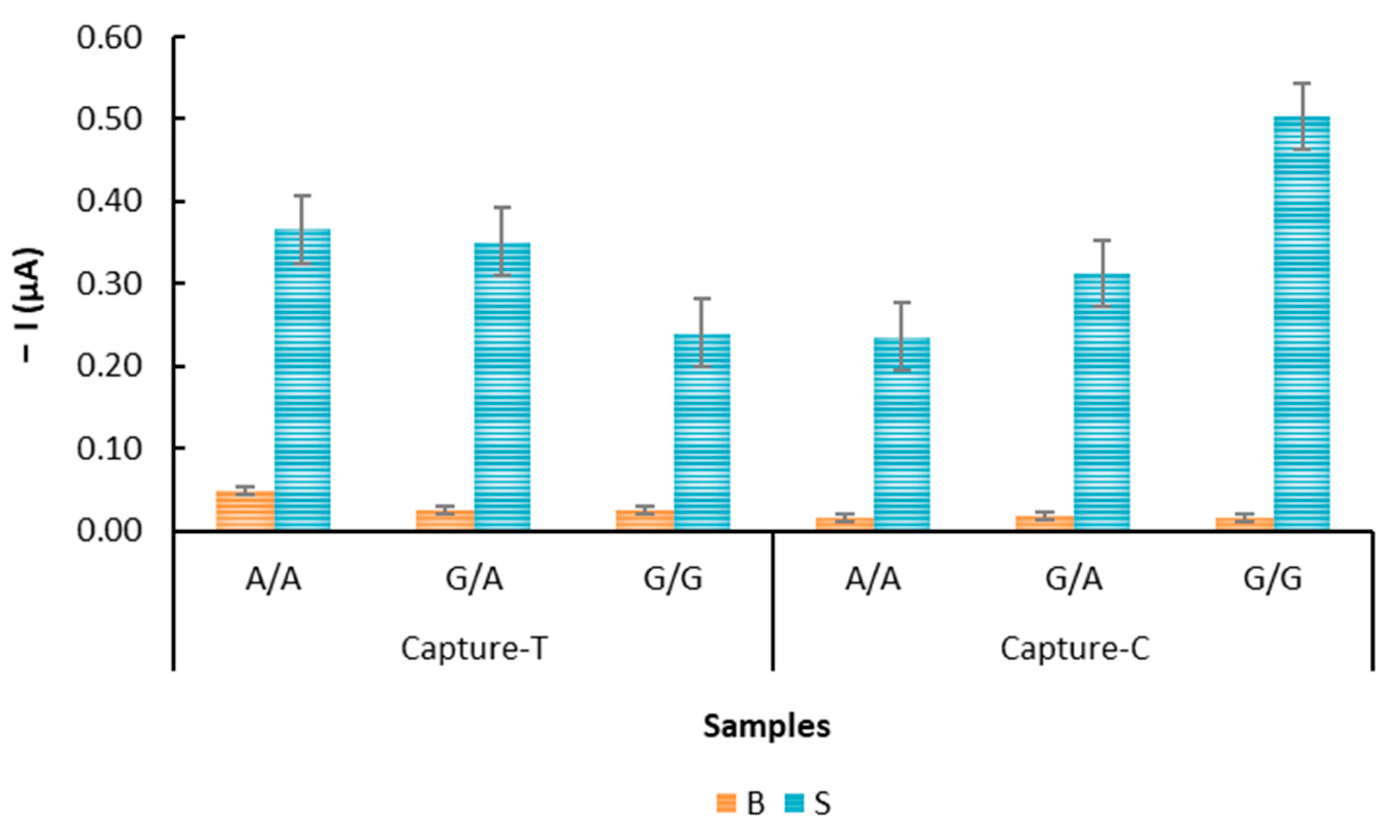
3.4. Biological DNA Samples: Evaluation by an Electrochemical DNA-Based Sensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elemento, O. The future of precision medicine: Towards a more predictive personalized medicine. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2020, 4, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, L.H.; Schork, N.J. Personalized medicine: Motivation, challenges and progress. Fertil. Steril. 2018, 109, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.B.; Wei, W.Q.; Weeraratne, D.; Frisse, M.E.; Misulis, K.; Rhee, K.; Zhao, J.; Snowdon, J.L. Precision Medicine, AI and the Future of Personalized Health Care. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2021, 14, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdes, R., Jr.; Yin, D.T. Fundamentals of Pharmacogenetics in Personalized, Precision Medicine. Clin. Lab. Med. 2016, 36, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dere, W.H.; Suto, T.S. The role of pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics in improving translational medicine. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2009, 6, 13–16. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2781217/ (accessed on 1 December 2024). [PubMed]
- Morais, S.L.; Magalhães, J.M.C.S.; Domingues, V.F.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Ramos-Jesus, J.; Ferreira-Fernandes, H.; Pinto, G.R.; Santos, M.; Barroso, M.F. Development of an electrochemical DNA-based biosensor for the detection of the cardiovascular pharmacogenetic-altering SNP CYP2C9*3. Talanta 2023, 264, 124692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Qi, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, F.; Zou, L.; Zhou, Q.; Geng, P.; Hong, Y.; Yang, H.; Luo, Q.; et al. Identification and in vitro functional assessment of 10 CYP2C9 variants found in Chinese Han subjects. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1139805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchenko, E.; Kropacheva, E.; Dobrovolsky, A.; Titaeva, E.; Zemlyanskaya, O.; Trofimov, D.; Galkina, I.; Lifshits, G.; Vereina, N.; Sinitsin, S.; et al. CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotyping for the quality of long-standing warfarin treatment in Russian patients. Pharmacogenomics J. 2020, 20, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, S.L.; Magalhães, J.; Domingues, V.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Ramos-Jesus, J.; Ferreira-Fernandes, H.; Pinto, G.R.; Barroso, M.F. Development of electrochemical genosensors applied to cardiovasular pharmacogenetics. In Proceedings of the 1st International Electronic Conference on Chemical Sensors and Analytical Chemistry, Virtual, 1–15 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, F.S.; Deignan, J.L.; Kuo, J.Z.; Bernstein, K.E.; Rotter, J.I.; Grody, W.W.; Das, K. Clinical utility of pharmacogenetic biomarkers in cardiovascular therapeutics: A challenge for clinical implementation. Pharmacogenomics 2012, 13, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, R.; Pandya, D.; Elston, R.C.; Ferlini, C. Defining “mutation” and “polymorphism” in the era of personal genomics. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, L. Warfarin Therapy and VKORC1 and CYP Genotype. In Medical Genetics Summaries; Pratt, V.M., Scott, S.A., Pirmohamed, M., Esquivel, B., Kattman, B.L., Malheiro, A.J., Eds.; National Center for Biotechnology Information (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK84174/ (accessed on 1 December 2024). [PubMed]
- Abad-Valle, P.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T.; Costa-García, A. DNA single-base mismatch study with an electrochemical enzymatic genosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinkhani, Z.; Sadeghalvad, M.; Norooznezhad, F.; Khodarahmi, R.; Fazilati, M.; Mahnam, A.; Fattahi, A.; Mansouri, K. The effect of CYP2C9*2, CYP2C9*3 and VKORC1-1639 G>A polymorphism in patients under warfarin therapy in city of Kermanshah. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.Y.; Hopping, G.C.; Vaidyanathan, U.; Ronquillo, Y.C.; Hoopes, P.C.; Moshirfar, M. Polymerase Chain Reaction and Its Application in the Diagnosis of Infectious Keratitis. Med. Hypothesis Discov. Innov. Ophthalmol. 2019, 8, 152–155. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31598517/ (accessed on 1 December 2024). [PubMed]
- Lázaro, A.; Yamanaka, E.S.; Maquieira, Á.; Tortajada-Genaro, L.A. Allele-specific ligation and recombinase polymerase amplification for the detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 298, 126877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-S.; Zhang, L.; He, Q.; Li, Y.-B.; Dai, Z.-L.; Zheng, J.-R.; Cheng, P.-Q.; He, Y-S. DNA sensors to assess the effect of VKORC1 and CYP2C9 gene polymorphisms on warfarin dose requirement in Chinese patients with atrial fibrillation. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2017, 40, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, T.R.; Santos, S.; Ribeiro-dos-Santos, Â.; Resque, R.L.; Pinto, G.R.; Yoshioka, F.K.N. Population Data of the 46 Insertion–Deletion (INDEL) Loci in Population in Piauí State, Northeastern Brazil. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2014, 9, e13–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Oligonucleotides | Sequence 5′ → 3′ | Bp |
|---|---|---|
| DNA capture | SHC6OH–GGA-A-GA-GGA-GCA-TTG-AGG-ACC-GTG-T | 25 |
| DNA signaling | TCA-AGA-GGA-AGC-CCG-CTG-CCT-TGT-GGA-GGA-GTT-GAG-AAA-AAC-CAA-G–FC | 46 |
| DNA target A | CTT-GGT-TTT-TCT-CAA-CTC-CTC-CAC-AAG-GCA-GCG-GGC-TTC-CTC-TTG-AAC-ACA-GTC-CTC-AAT-GCT-CCT-CTT-CC | 71 |
| DNA target G | CTT-GGT-TTT-TCT-CAA-CTC-CTC-CAC-AAG-GCA-GCG-GGC-TTC-CTC-TTG-AAC-ACG-GTC-CTC-AAT-GCT-CCT-CTT-CC | 71 |
| Variables | Tested Range | Selected Value |
|---|---|---|
| DNAcp concentration (μM) | 0.25–1.00 | 0.25 |
| MCH concentration (mM) | 0.25–1.00 | 0.50 |
| MCH incubation time (min) | 7.5–30 | 30 |
| Homogeneous hybridization incubation time (min) | 15–45 | 30 |
| DNA signaling concentration probe (μM) | 0.13–0.50 | 0.50 |
| Heterogeneous hybridization incubation time (min) | 30–120 | 60 |
| anti-FICT-POD enzyme concentration (U/mL) | 0.50–2.50 | 1.00 |
| anti-FICT-POD enzyme incubation time (min) | 15–60 | 60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbosa, T.; Morais, S.L.; Pereira, E.; Magalhães, J.M.C.S.; Domingues, V.F.; Ferreira-Fernandes, H.; Pinto, G.; Santos, M.; Barroso, M.F. Warfarin Pharmacogenomics: Designing Electrochemical DNA-Based Sensors to Detect CYP2C9*2 Gene Variation. Genes 2025, 16, 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040372
Barbosa T, Morais SL, Pereira E, Magalhães JMCS, Domingues VF, Ferreira-Fernandes H, Pinto G, Santos M, Barroso MF. Warfarin Pharmacogenomics: Designing Electrochemical DNA-Based Sensors to Detect CYP2C9*2 Gene Variation. Genes. 2025; 16(4):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040372
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbosa, Tiago, Stephanie L. Morais, Eduarda Pereira, Júlia M. C. S. Magalhães, Valentina F. Domingues, Hygor Ferreira-Fernandes, Giovanny Pinto, Marlene Santos, and Maria Fátima Barroso. 2025. "Warfarin Pharmacogenomics: Designing Electrochemical DNA-Based Sensors to Detect CYP2C9*2 Gene Variation" Genes 16, no. 4: 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040372
APA StyleBarbosa, T., Morais, S. L., Pereira, E., Magalhães, J. M. C. S., Domingues, V. F., Ferreira-Fernandes, H., Pinto, G., Santos, M., & Barroso, M. F. (2025). Warfarin Pharmacogenomics: Designing Electrochemical DNA-Based Sensors to Detect CYP2C9*2 Gene Variation. Genes, 16(4), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040372








