Cross-Kingdom Communication via Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Nucleic Acids in Genetically Engineered Nicotiana tabacum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Plant Extracellular Vesicles from Apoplastic Fluid
2.2. DNA Extraction and PCR
2.3. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription, and RT-qPCR
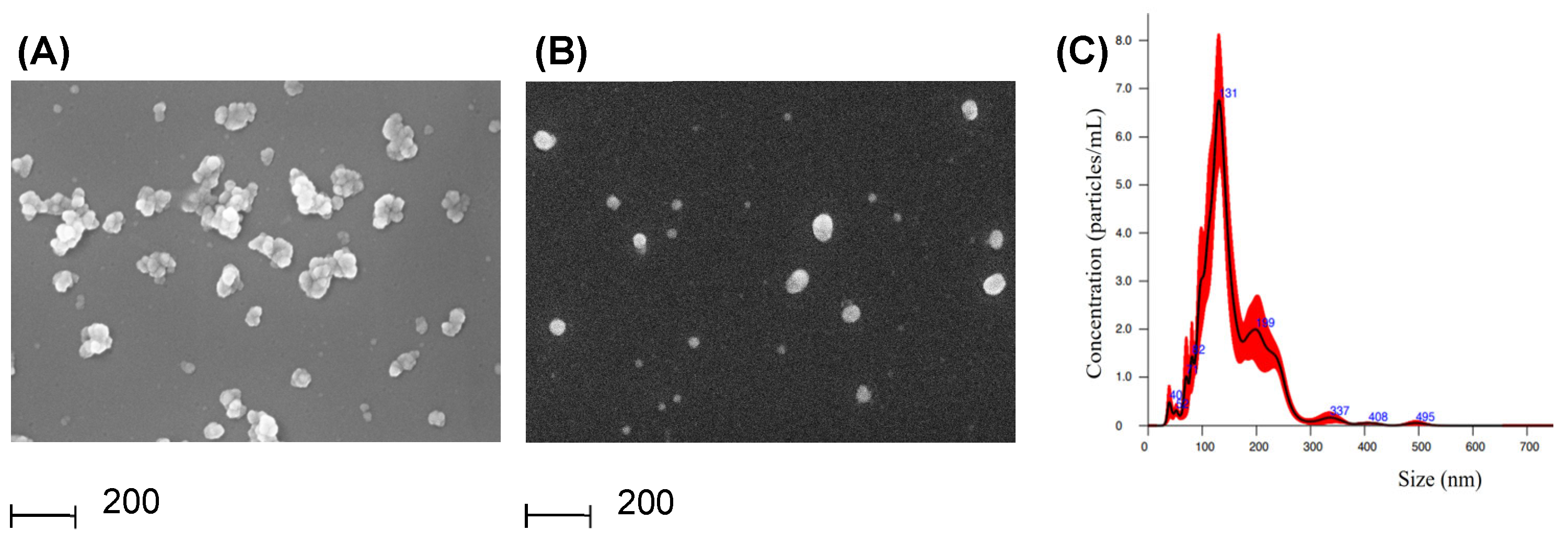
2.4. SEM Imaging (Scanning Electron Microscopy)
2.5. NTA (Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis)
2.6. Cell Stimulations and Treatments
3. Results
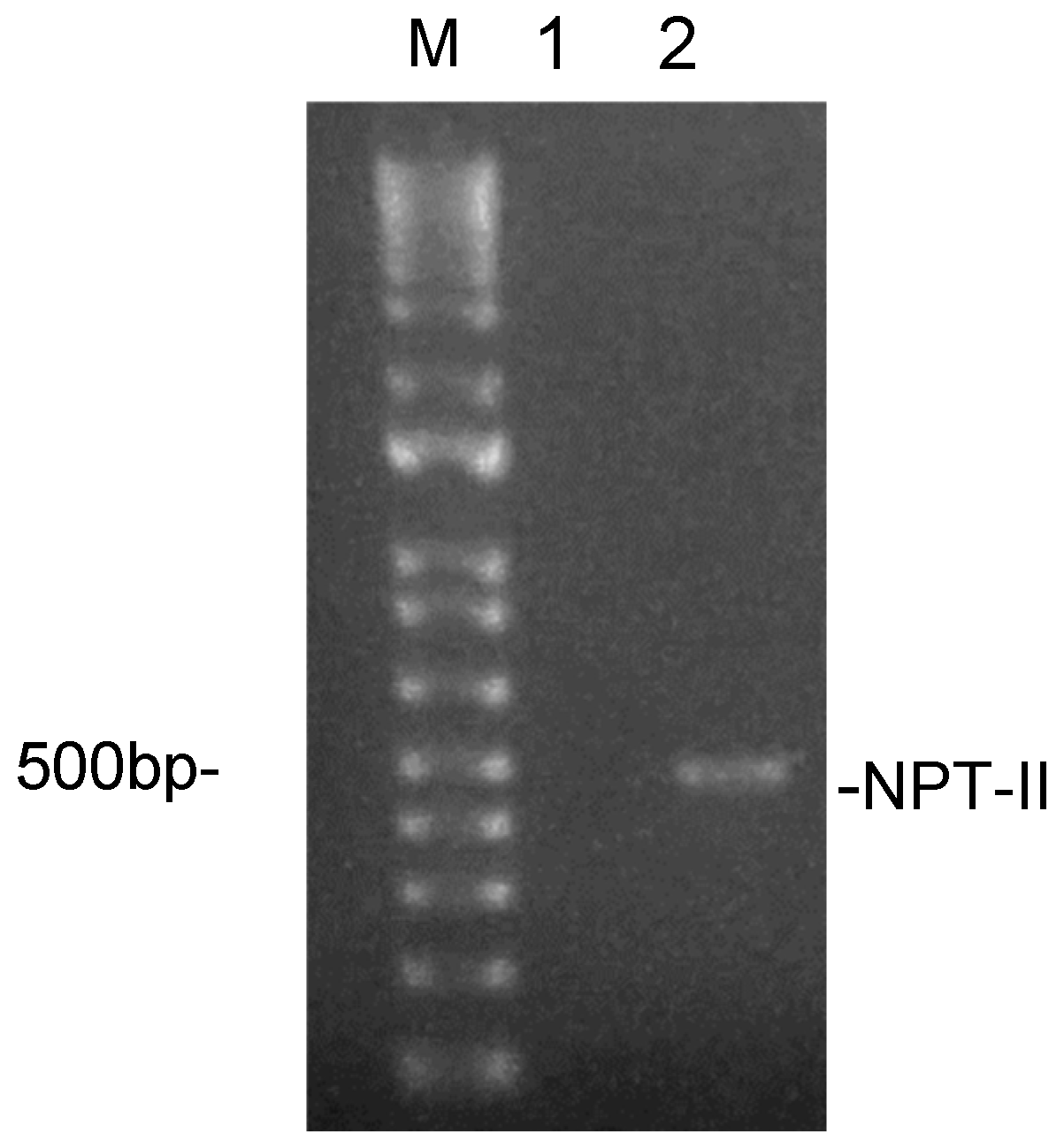
3.1. Experimental Model and PDEVs Isolation
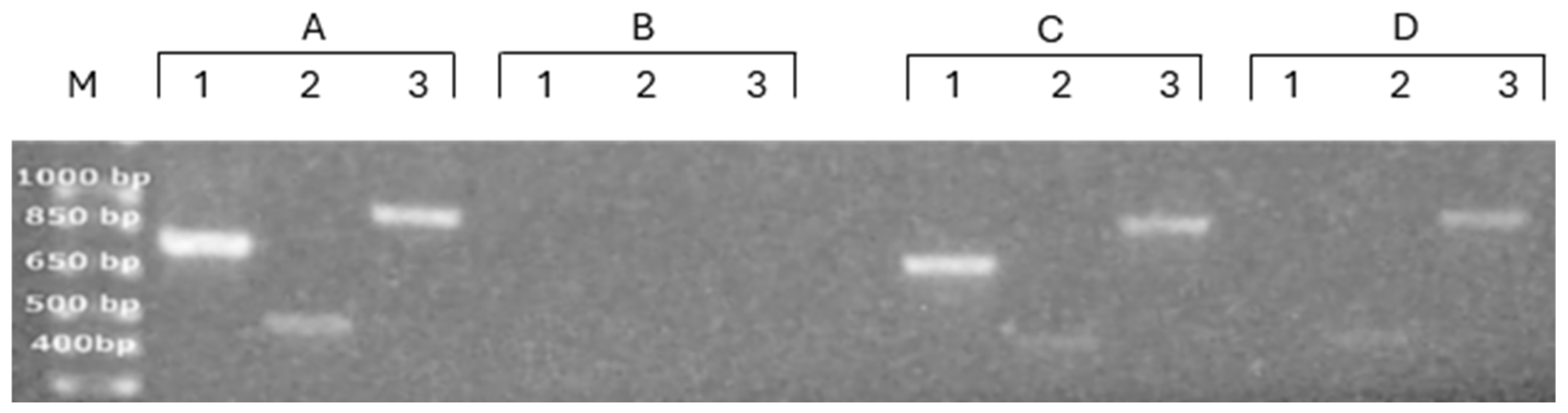
3.2. Characterization of Nucleic Acids’ Association with PDEVs
3.3. Gene Expression Kinetics of THP-1 Stimulated with LPS and EVs
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ambrosone, A.; Barbulova, A.; Cappetta, E.; Cillo, F.; De Palma, M.; Ruocco, M.; Pocsfalvi, G. Plant Extracellular Vesicles: Current Landscape and Future Directions. Plants 2023, 12, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calzoni, E.; Bertoldi, A.; Cusumano, G.; Buratta, S.; Urbanelli, L.; Emiliani, C. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Natural Nanocarriers for Biotechnological Drugs. Processes 2024, 12, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, B.D.; Innes, R.W. Extracellular vesicles as key mediators of plant-microbe interactions. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 44, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Ma, K.; Hu, H.; Xing, X.; Huang, X.; Gao, H. Extracellular vesicles: Their functions in plant-pathogen interactions. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 23, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Halilovic, L.; Shi, T.; Chen, A.; He, B.; Wu, H.; Jin, H. Extracellular vesicles: Cross-organismal RNA trafficking in plants, microbes, and mammalian cells. Extracell. Vesicles Circ. Nucl. Acids 2023, 4, 262–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lei, J.; Li, L.; Zhu, W.; Wu, D. Evidence of Cross-Kingdom Gene Regulation by Plant MicroRNAs and Possible Reasons for Inconsistencies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 4564–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.J.; Chen, J.Y.; Tang, C.H.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Zhang, J.M.; Qin, Y.C. Edible plant extracellular vesicles: An emerging tool for bioactives delivery. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1028418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanam, J.; Chetty, V.K.; Barthel, L.; Ghanam, J.; Chetty, V.K.; Barthel, L.; Reinhardt, D.; Hoyer, P.F.; Thakur, B.K. DNA in extracellular vesicles: From evolution to its current application in health and disease. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guescini, M.; Guidolin, D.; Vallorani, L.; Casadei, L.; Gioacchini, A.M.; Tibollo, P.; Battistelli, M.; Falcieri, E.; Battistin, L.; Agnati, L.F.; et al. C2C12 myoblasts release micro-vesicles containing mtDNA and proteins involved in signal transduction. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaj, L.; Lessard, R.; Dai, L.; Cho, Y.J.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Skog, J. Tumour microvesicles contain retrotransposon elements and amplified oncogene sequences. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiberg, A.; Wang, M.; Lin, F.M.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Kaloshian, I.; Huang, H.D.; Jin, H. Fungal small RNAs suppress plant immunity by hijacking host RNA interference pathways. Science 2013, 342, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhansi Rani, S.; Usha, R. Transgenic plants: Types, benefits, public concerns and future. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 6, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, M.F.; Tan, B.C. Genetic modification techniques in plant breeding: A comparative review of CRISPR/Cas and GM technologies. Hortic. Plant J. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andow, D.A.; Zwahlen, C. Assessing environmental risks of transgenic plants. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, P.B.; Gillespie, S.H. Antibiotic resistance markers in genetically modified plants: A risk to human health? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Aziz, M.; Brini, F.; Rouached, H.; Masmoudi, K. Genetically engineered crops for sustainably enhanced food production systems. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1027828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosellini, D.; Capomaccio, S.; Ferradini, N.; Savo Sardaro, M.L.; Nicolia, A.; Veronesi, F. Non-antibiotic, efficient selection for alfalfa genetic engineering. Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferradini, N.; Nicolia, A.; Capomaccio, S.; Veronesi, F.; Rosellini, D. A point mutation in the Medicago sativa GSA gene provides a novel, efficient, selectable marker for plant genetic engineering. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 156, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, B.D.; Innes, R.W. Extracellular Vesicles Isolated from the Leaf Apoplast Carry Stress-Response Proteins. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagini, K.; Buratta, S.; Delo, F.; Pellegrino, R.M.; Giovagnoli, S.; Urbanelli, L.; Emiliani, C. Drug-Induced Lysosomal Impairment Is Associated with the Release of Extracellular Vesicles Carrying Autophagy Markers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, M.Q.; Chng, W.H.; Liang, J.; Yeo, H.Q.; Lee, C.K.; Belaid, M.; Tollemeto, M.; Wacker, M.G.; Czarny, B.; Pastorin, G. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: Recent advancements and current challenges on their use for biomedical applications. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bent, R.; Moll, L.; Grabbe, S.; Bros, M. Interleukin-1 Beta—A Friend or Foe in Malignancies? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, M.; Vieira, P.; O’Garra, A. Biology and therapeutic potential of interleukin-10. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widdrington, J.D.; Gomez-Duran, A.; Pyle, A.; Ruchaud-Sparagano, M.H.; Scott, J.; Baudouin, S.V.; Rostron, A.J.; Lovat, P.E.; Chinnery, P.F.; Simpson, A.J. Exposure of Monocytic Cells to Lipopolysaccharide Induces Coordinated Endotoxin Tolerance, Mitochondrial Biogenesis, Mitophagy, and Antioxidant Defenses. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Hamby, R.; Jin, H. Plant extracellular vesicles: Trojan horses of cross-kingdom warfare. FASEB Bioadv. 2021, 3, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Kang, G.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Cai, Q. Extracellular Vesicles: Emerging Players in Plant Defense Against Pathogens. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 757925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urzì, O.; Gasparro, R.; Ganji, N.R.; Alessandro, R.; Raimondo, S. Plant-RNA in Extracellular Vesicles: The Secret of Cross-Kingdom Communication. Membranes 2022, 12, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldrich, P.; Rutter, B.D.; Karimi, H.Z.; Podicheti, R.; Meyers, B.C.; Innes, R.W. Plant Extracellular Vesicles Contain Diverse Small RNA Species and Are Enriched in 10- to 17-Nucleotide “Tiny” RNAs. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 315–324. [Google Scholar]
- Gruner, H.N.; McManus, M.T. Examining the evidence for extracellular RNA function in mammals. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Mustapic, M.; Kapogiannis, D.; Gorospe, M. RNA in extracellular vesicles. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2017, 8, e1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, A.; Oberkofler, L.; Robatzek, S.; Weiberg, A. Spotlight on plant RNA-containing extracellular vesicles. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2022, 69, 102272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Deindl, E. Characterization of RNA in Extracellular Vesicles. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo-Acebo, L.; López de Las Hazas, M.C.; Margollés, A.; Dávalos, A.; García-Ruiz, A. Eating microRNAs: Pharmacological opportunities for cross-kingdom regulation and implications in host gene and gut microbiota modulation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 2218–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Hou, D.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Bian, Z.; Liang, X.; Cai, X.; et al. Exogenous plant MIR168a specifically targets mammalian LDLRAP1: Evidence of crosskingdom regulation by microRNA. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintz-Buschart, A.; Yusuf, D.; Kaysen, A.; Etheridge, A.; Fritz, J.V.; May, P.; de Beaufort, C.; Upadhyaya, B.B.; Ghosal, A.; Galas, D.J.; et al. Small RNA profiling of low biomass samples: Identification and removal of contaminants. BMC Biol. 2018, 16, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosar, J.P.; Rovira, C.; Naya, H.; Cayota, A. Mining of public sequencing databases supports a non-dietary origin for putative foreign miRNAs: Underestimated effects of contamination in NGS. RNA 2014, 20, 754–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| RNA Source for cDNA Synthesis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Leaf | PDEVs | |
| RNA extraction method 1 | ||
| Ct | 30.08 ± 0.6 | 33.8 ± 0.3 |
| Tm (°C) | 89.1 ± 0.1 | 89.1 ± 0.1 |
| RNA extraction method 2 | ||
| Ct | 28.3 ± 0.2 | 33.7 ± 0.4 |
| Tm (°C) | 89.1 ± 0.1 | 89.1 ± 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urbanelli, L.; Delo, F.; Cerrotti, G.; Albertini, E.; Lucci, J.; Buratta, S.; Calzoni, E.; Giovagnoli, S.; Lugini, L.; Federici, C.; et al. Cross-Kingdom Communication via Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Nucleic Acids in Genetically Engineered Nicotiana tabacum. Genes 2025, 16, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030356
Urbanelli L, Delo F, Cerrotti G, Albertini E, Lucci J, Buratta S, Calzoni E, Giovagnoli S, Lugini L, Federici C, et al. Cross-Kingdom Communication via Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Nucleic Acids in Genetically Engineered Nicotiana tabacum. Genes. 2025; 16(3):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030356
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrbanelli, Lorena, Federica Delo, Giada Cerrotti, Emidio Albertini, Jacopo Lucci, Sandra Buratta, Eleonora Calzoni, Stefano Giovagnoli, Luana Lugini, Cristina Federici, and et al. 2025. "Cross-Kingdom Communication via Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Nucleic Acids in Genetically Engineered Nicotiana tabacum" Genes 16, no. 3: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030356
APA StyleUrbanelli, L., Delo, F., Cerrotti, G., Albertini, E., Lucci, J., Buratta, S., Calzoni, E., Giovagnoli, S., Lugini, L., Federici, C., Fratini, F., Mercati, V., & Emiliani, C. (2025). Cross-Kingdom Communication via Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Nucleic Acids in Genetically Engineered Nicotiana tabacum. Genes, 16(3), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030356











