Cloning, Characterization, and Expression Analysis of the DEAD-Box Family Genes, Vasa and PL10, in Pacific Abalone (Haliotis discus hannai)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Tissue Collection
2.2. Embryos and Larvae Collection
2.3. RNA Isolation and Reverse Transcription
2.4. Cloning and Orthology Assignment of Vasa and PL10
2.5. Selection of Suitable Reference Genes for RT-qPCR
2.6. RT-qPCR
2.7. WMISH
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Cloning and Characterization of H. discus hannai Vasa and PL10
3.2. Evaluation of Expression Stability of the Reference Genes for the Various Tissues and Different Embryonic Stages of H. discus hannai
3.2.1. Selection of Reference Genes for Different Tissues
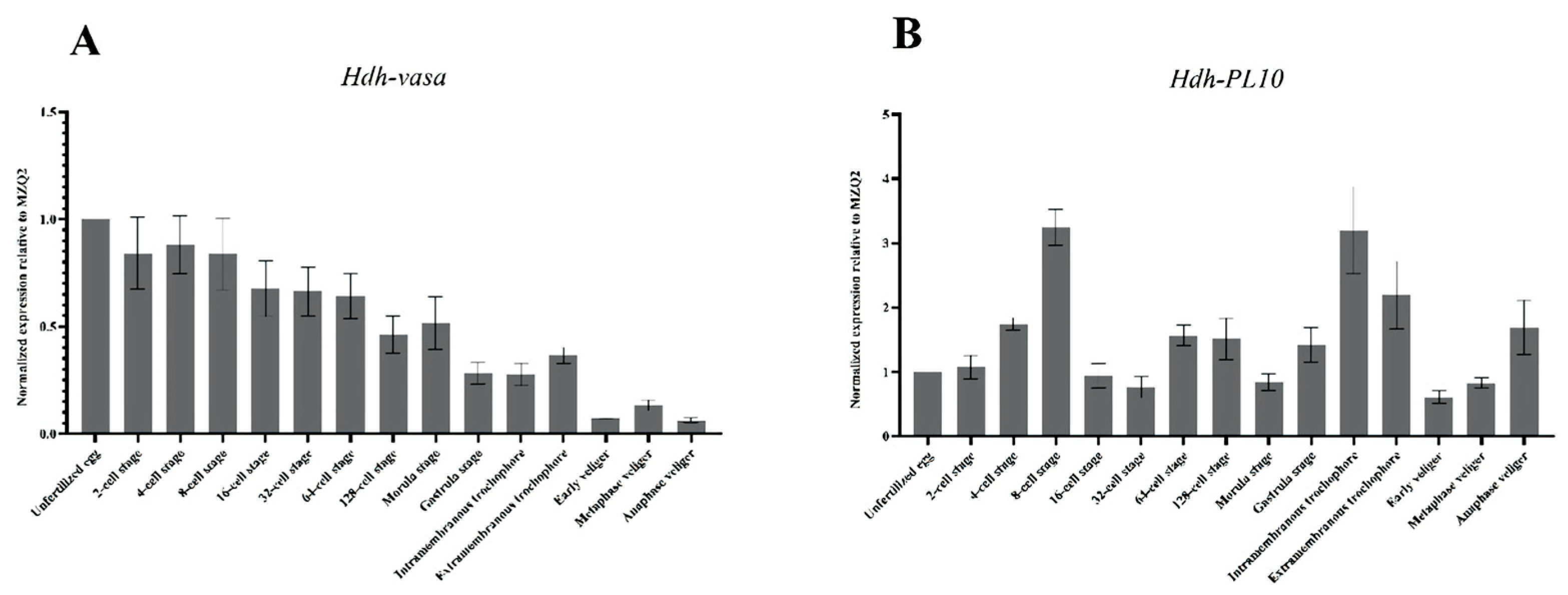
3.2.2. Selection of Candidate Reference Genes for Different Embryonic Developmental Stages
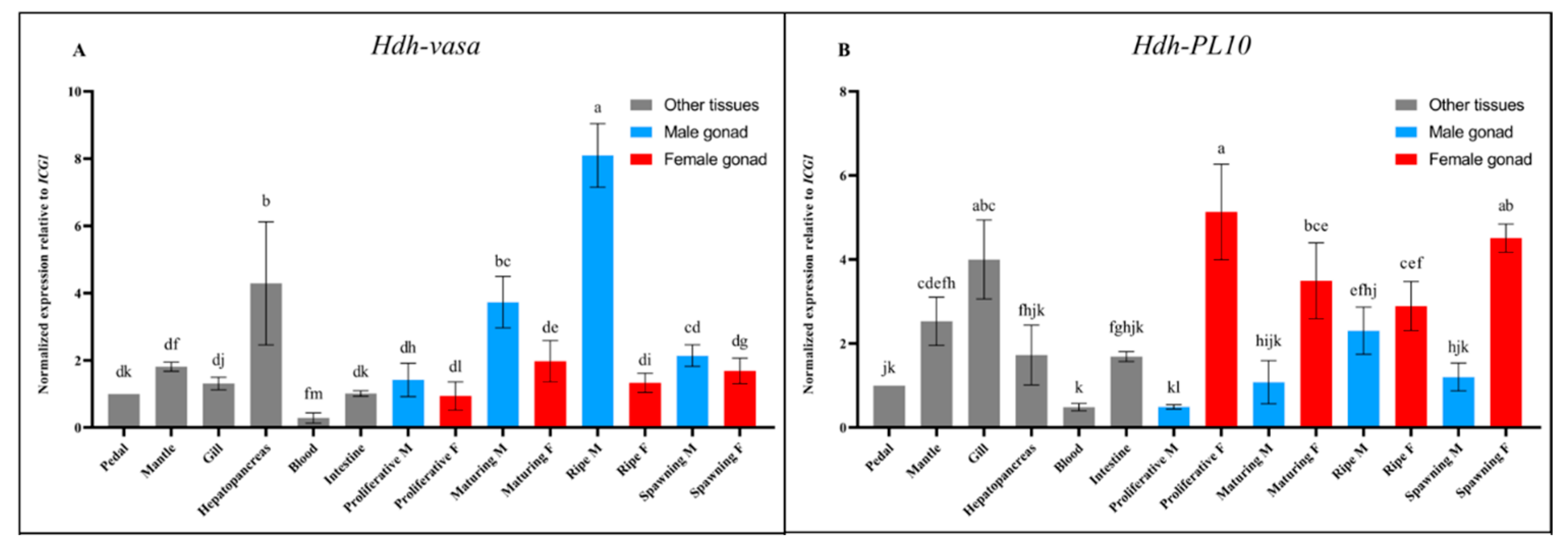
3.3. Tissue-Specific Expression of Hdh-Vasa and Hdh-PL10
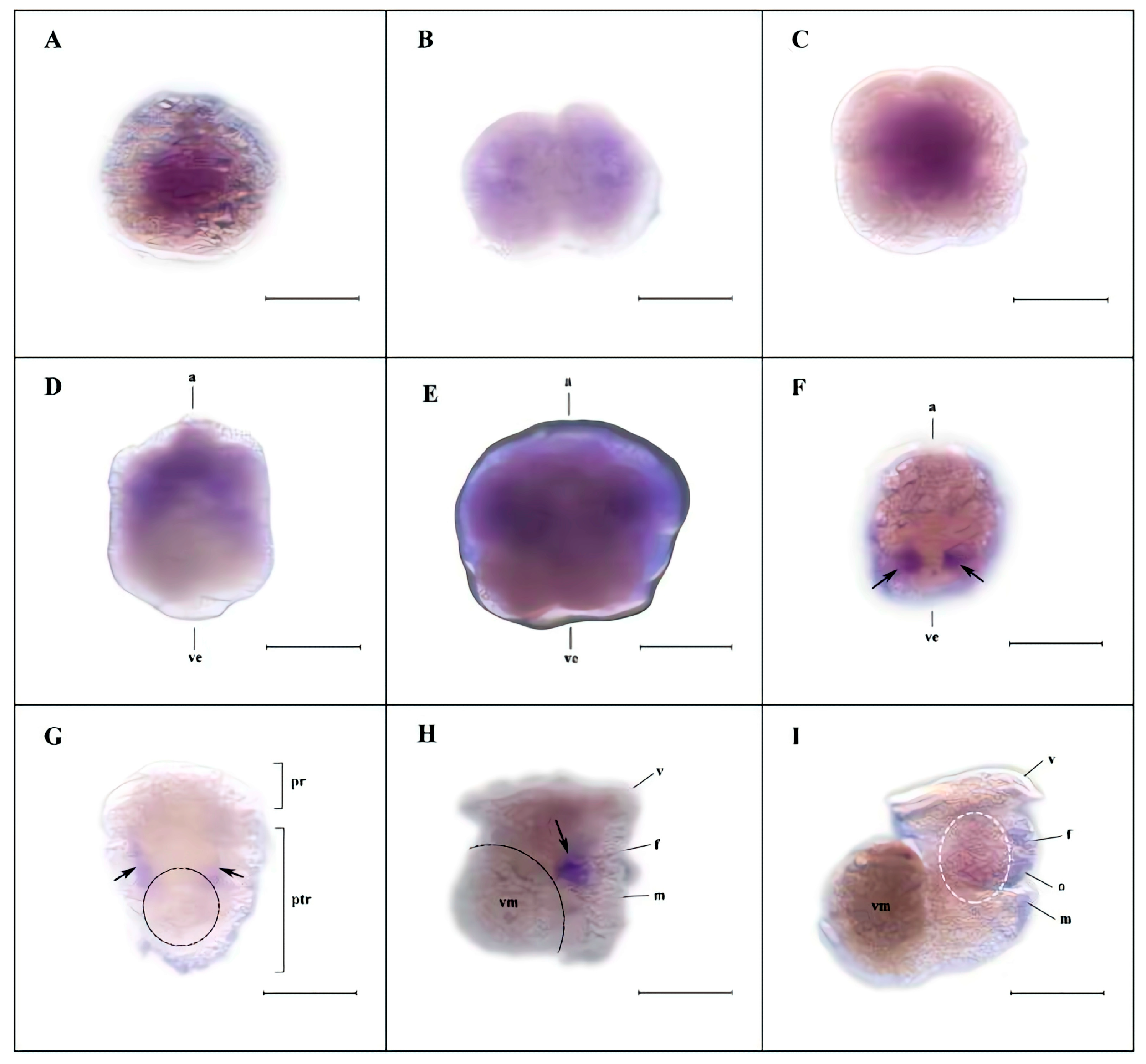
3.4. Spatiotemporal Expression of Hdh-Vasa and Hdh-PL10 Throughout Embryonic and Larval Development
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raz, E. The function and regulation of vasa-like genes in germ-cell development. Genome Biol. 2000, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclère, L.; Jager, M.; Barreau, C.; Chang, P.; Le Guyader, H.; Manuel, M.; Houliston, E. Maternally localized germ plasm mRNAs and germ cell/stem cell formation in the cnidarian Clytia. Dev. Biol. 2012, 364, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozin, V.V.; Kostyuchenko, R.P. Vasa, PL10, and Piwi gene expression during caudal regeneration of the polychaete annelid Alitta virens. Dev. Genes Evol. 2015, 225, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebert, S.; Goetz, F.; Church, S.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Zapata, F.; Haddock, S.; Dunn, C. Stem cells in Nanomia bijuga (Siphonophora), a colonial animal with localized growth zones. EvoDevo 2015, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro-Constaín, L.; Schenkelaars, Q.; Gazave, E.; Haguenauer, A.; Rocher, C.; Ereskovsky, A.; Borchiellini, C.; Renard, E. The Conservation of the Germline Multipotency Program, from Sponges to Vertebrates: A Stepping Stone to Understanding the Somatic and Germline Origins. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Fang, D.A.; Sun, J.L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.H. Characterization of the vasa gene in the Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis: A germ line molecular marker. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, P.; Lasko, P.F.; Ashburner, M.; Leroy, P.; Nielsen, P.J.; Nishi, K.; Schnier, J.; Slonimski, P.P. Birth of the D-E-A-D box. Nature 1989, 337, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, S.R.; Linder, P. D-E-A-D protein family of putative RNA helicases. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Komiya, T.; Kawabata, H.; Sato, M.; Fujimoto, H.; Furusawa, M.; Noce, T. Isolation of a DEAD-family protein gene that encodes a murine homolog of Drosophila vasa and its specific expression in germ cell lineage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 91, 12258–12262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komiya, T.; Itoh, K.; Ikenishi, K.; Furusawa, M. Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Gene of the DEAD Box Protein Family Which Is Specifically Expressed in Germ Cells of Xenopus laevis. Dev. Biol. 1994, 162, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabioux, C.; Pouvreau, S.; Le Roux, F.; Huvet, A. The oyster vasa-like gene: A specific marker of the germline in Crassostrea gigas. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 315, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.R.; Shao, M.Y.; Qin, Z.K.; Kang, Q.H.; Zhang, Z.F. Cloning, characterization, and expression analysis of the DEAD-box family genes, Fc-vasa and Fc-PL10a, in Chinese shrimp (Fenneropenaeus chinensis). Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2010, 28, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüking, A.; Stahl, U.; Schmidt, U. The protein family of RNA helicases. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 33, 259–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schüpbach, T.; Wieschaus, E. Maternal-effect mutations altering the anterior-posterior pattern of the Drosophila embryo. Rouxs Arch. Dev. Biol. Off. Organ Edbo 1986, 195, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasko, F.P.; Ashburner, M. The product of the Drosophila gene vasa is very similar to eukaryotic initiation factor-4A. Nature 1988, 335, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adashev, V.E.; Kotov, A.A.; Olenina, L.V. RNA Helicase Vasa as a Multifunctional Conservative Regulator of Gametogenesis in Eukaryotes. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 5677–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wang, F.Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.Z.; Zhang, H.H.; Liu, Z.Z.; Zhou, Z.C.; Zhao, D.Q.; Zhang, M.; et al. Characteristics of the Vasa Gene in Silurus asotus and Its Expression Response to Letrozole Treatment. Genes 2024, 15, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, P. Yeast RNA helicases of the DEAD-box family involved in translation initiation. Biol. Cell 2003, 95, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, K.; Nishimiya-Fujisawa, C.; Fujisawa, T. Universal occurrence of the vasa-related genes among metazoans and their germline expression in Hydra. Dev. Genes Evol. 2001, 211, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solana, J.; Romero, R. SpolvlgA is a DDX3/PL10-related DEAD-box RNA helicase expressed in blastomeres and embryonic cells in planarian embryonic development. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 5, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotov, A.A.; Olenkina, O.M.; Kibanov, M.V.; Olenina, L.V. RNA helicase Belle (DDX3) is essential for male germline stem cell maintenance and division in Drosophila. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863 Pt A, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhaleem, M. RNA helicases: Regulators of differentiation. Clin. Biochem. 2005, 38, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, M.; Wessel, G.M. Essential elements for translation: The germline factor Vasa functions broadly in somatic cells. Development 2015, 142, 1960–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, N.; Umesono, Y.; Orii, H.; Sakurai, T.; Watanabe, K.; Agata, K. Expression of vasa(vas)-Related Genes in Germline Cells and Totipotent Somatic Stem Cells of Planarians. Dev. Biol. 1999, 206, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebscher, N.; Zelada-González, F.; Banisch, T.U.; Raible, F.; Arendt, D. Vasa unveils a common origin of germ cells and of somatic stem cells from the posterior growth zone in the polychaete Platynereis dumerilii. Dev. Biol. 2007, 306, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solana, J. Closing the circle of germline and stem cells: The Primordial Stem Cell hypothesis. EvoDevo 2013, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.D.; Huang, M.; Lü, W.G.; Chen, X.; Shen, M.H.; Li, X.M.; Wang, R.X.; Ke, C.H. Involvement of Antizyme Characterized from the Small Abalone Haliotis diversicolor in Gonadal Development. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabioux, C.; Corporeau, C.; Quillien, V.; Favrel, P.; Huvet, A. In vivo RNA interference in oyster—vasa silencing inhibits germ cell development. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 2566–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saffman, E.E.; Lasko, P. Germline development in vertebrates and invertebrates. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1999, 55, 1141–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabioux, C.; Huvet, A.; Lelong, C.; Robert, R.; Pouvreau, S.; Daniel, J.Y.; Minguant, C.; Le Pennec, M. Oyster vasa-like gene as a marker of the germline cell development in Crassostrea gigas. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 320, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartz, S.Z.; Chan, X.Y.; Lambert, J.D. Localization of Vasa mRNA during early cleavage of the snail Ilyanassa. Dev. Genes Evol. 2008, 218, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obata, M.; Sano, N.; Kimata, S.; Nagasawa, K.; Yoshizaki, G.; Komaru, A. The proliferation and migration of immature germ cells in the mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis: Observation of the expression pattern in the M. galloprovincialis vasa-like gene (Myvlg) by in situ hybridization. Dev. Genes Evol. 2010, 220, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, W.W.; Guo, Q.; Fan, F.L.; Ren, P.; Luo, X.; Ke, C.H. Experimental hybridization and genetic identification of Pacific abalone Haliotis discus hannai and green abalone H. Fulgens. Aquaculture 2015, 448, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J. Embryonic development of abalone (Haliotis Diversicolor Reeve). Acta Zool. Sin. 2001, 47, 317–323. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Tamura, K.; Jakobsen, I.B.; Nei, M. MEGA2: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kõressaar, T.; Lepamets, M.; Kaplinski, L.; Raime, K.; Andreson, R.; Remm, M. Primer3_masker: Integrating masking of template sequence with primer design software. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1937–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, 00341–003411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, C.L.; Jensen, J.L.; Ørntoft, T.F. Normalization of Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR Data: A Model-Based Variance Estimation Approach to Identify Genes Suited for Normalization, Applied to Bladder and Colon Cancer Data Sets. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5245–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Nam, Y.K. Transcriptional responses of metallothionein gene to different stress factors in Pacific abalone (Haliotis discus hannai). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 58, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.A.; Degnan, B.M.; Gunter, H.; Jackson, D.J.; Woodcroft, B.J.; Degnan, S.M. Widespread transcriptional changes pre-empt the critical pelagic-benthic transition in the vetigastropod Haliotis asinina. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 1006–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauptmann, G.; Gerster, T. Two-color whole-mount in situ hybridization to vertebrate and Drosophila embryos. Trends Genet. 1994, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cordin, O.; Banroques, J.; Tanner, N.K.; Linder, P. The DEAD-box protein family of RNA helicases. Gene 2006, 367, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svitkin, Y.V.; Pause, A.; Haghighat, A.; Pyronnet, S.; Witherell, G.; Belsham, G.J.; Sonenberg, N. The requirement for eukaryotic initiation factor 4A (elF4A) in translation is in direct proportion to the degree of mRNA 5′ secondary structure. RNA 2001, 7, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.E.; Saraste, M.; Runswick, M.J.; Gay, N.J. Distantly related sequences in the α- and β-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982, 1, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, B.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N. A protein component of Drosophila polar granules is encoded by vasa and has extensive sequence similarity to ATP-dependent helicases. Cell 1988, 55, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Diehl-Jones, W.; Lasko, P. Localization of vasa protein to the Drosophila pole plasm is independent of its RNA-binding and helicase activities. Development 1994, 120, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Dearden, P.; Akam, M. Germ line development in the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria: Vasa as a marker. Dev. Biol. 2002, 252, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakoi, S.; Kin, K.; Miyazaki, K.; Wada, H. Early Development of the Japanese Spiny Oyster (Saccostrea kegaki): Characterization of Some Genetic Markers. Zool. Sci. 2008, 25, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kranz, A.M.; Tollenaere, A.; Norris, B.J.; Degnan, B.M.; Degnan, S.M. Identifying the germline in an equally cleaving mollusc: Vasa and Nanos expression during embryonic and larval development of the vetigastropod Haliotis asinina. J. Exp. Zool. Part B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2010, 314, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, P.; Alzari, P.; Sassoon, D.; Wolgemuth, D.; Fellous, M. The protein encoded by a murine male germ cell-specific transcript is a putative ATP-dependent RNA helicase. Cell 1989, 57, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlo, F.; Alberto, F.; Enrico, M. Deletion and expression analysis of AZFa genes on the human Y chromosome revealed a major role for DBY in male infertility. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone, O.; Deuring, R.; Bock, R.; Linder, P.; Fuller, M.T.; Lasko, P. Belle is a Drosophila DEAD-box protein required for viability and in the germ line. Dev. Biol. 2005, 277, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, L.; Cinelli, F.; Iannello, M.; Lazzari, M.; Franceschini, V.; Maurizii, M.G. Immunolocalization of Vasa, PIWI, and TDRKH proteins in male germ cells during spermatogenesis of the teleost fish Poecilia reticulata. Acta Histochem. 2022, 124, 151870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alié, A.; Leclère, L.; Jager, M.; Dayraud, C.; Chang, P.; Le Guyader, H.; Quéinnec, E.; Manuel, M. Somatic stem cells express Piwi and Vasa genes in an adult ctenophore: Ancient association of “germline genes” with stemness. Dev. Biol. 2010, 350, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, T.C.G. Hydra and the evolution of stem cells. Bioessays 2010, 31, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, T.C.; Anton-Erxleben, F.; Hemmrich, G.; Khalturin, K. The Hydra polyp: Nothing but an active stem cell community. Dev. Growth Differ. 2010, 52, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowerman, B. 3 Maternal Control of Pattern Formation in Early Caenorhabditis elegans Embryos. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 1998, 39, 73–117. [Google Scholar]
- Luschnig, S.; Moussian, B.; Krauss, J.; Desjeux, I.; Perkovic, J.; Nüsslein-Volhard, C. An F1 Genetic Screen for Maternal-Effect Mutations Affecting Embryonic Pattern Formation in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 2004, 167, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droin, A. The developmental mutants of Xenopus. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1993, 36, 455–464. [Google Scholar]
- Dosch, R. Next generation mothers: Maternal control of germline development in zebrafish. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 50, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condic, M.L. The Role of Maternal-Effect Genes in Mammalian Development: Are Mammalian Embryos Really an Exception? Stem. Cell Rev. 2016, 12, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andéol, Y. Early transcription in different animal species: Implication for transition from maternal to zygotic control in development. Roux’s Arch. Dev. Biol. 1994, 204, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaut, H.; Pelegri, F.; Bohmann, K.; Schwarz, H.; Nüsslein-Volhard, C. Zebrafish vasa RNA but Not Its Protein Is a Component of the Germ Plasm and Segregates Asymmetrically before Germline Specification. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 149, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, E. Primordial Germ-Cell Development: The Zebrafish Perspective. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2003, 4, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Extavour, C.; Akam, M. Mechanisms of Germ Cell Specification Across the Metazoans: Epigenesis and Preformation. Development 2003, 130, 5869–5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, C.; Kawakami, K.; Hopkins, N. Zebrafish vasa homologue RNA is localized to the cleavage planes of 2- and 4-cell-stage embryos and is expressed in the primordial germ cells. Development 1997, 124, 3157–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimura, M.; Takamura, K. Characterization of an ascidian DEAD-box gene, Ci-DEAD1: Specific expression in the germ cells and its mRNA localization in the posterior-most blastomeres in early embryos. Dev. Genes Evol. 2000, 210, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, K.; Sano, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Nishimiya-Fujisawa, C.; Fujisawa, T. Expression and evolutionary conservation of nanos-related genes in Hydra. Dev. Genes Evol. 2000, 210, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

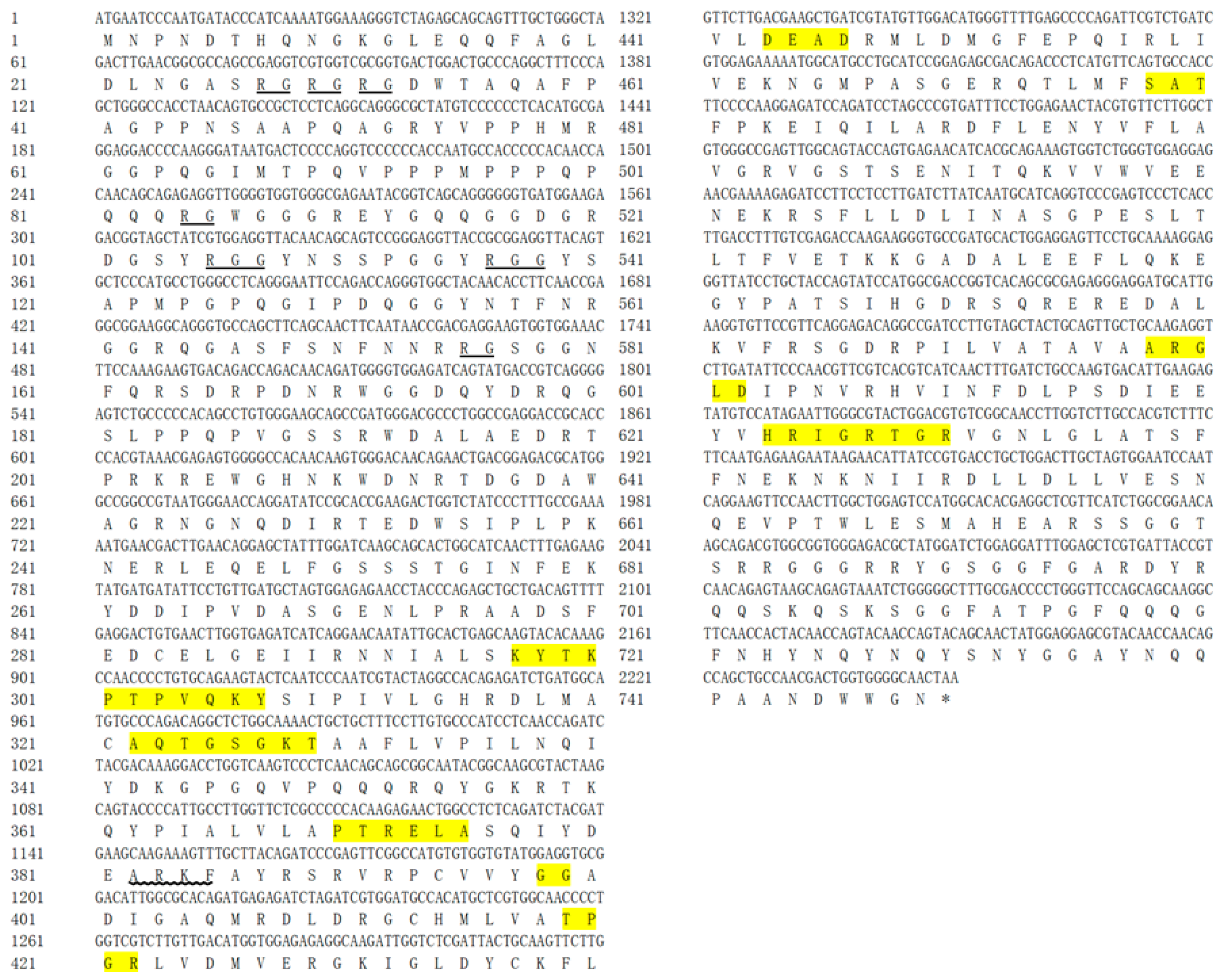



| Genes | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) | Amplicon Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| vasa | ATGAAAATGTGCCCTGTAAAGGCGCTGACCAATCAG | ACAAATTTCCCCTAACATTGATACCCAGGGGAACAGTG | 2559 |
| PL10 | ATGAATCCCAATGATACCCATCAAAATGG | TTAGTTGCCCCACCAGTCGTTG | 2247 |
| Genes | GenBank Code | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICG1 | PV224500 | CGACATCACAACAGAAGGCAAAA | TTTTCTTTCCTGATGTGCTCACC |
| ICG2 | PV224501 | CCAACAAGACCGTGATGAGAGA | GAGATCATACAGCTCTGCCCTC |
| ICG3 | PV231213 | AGGTAAGACTGGTGGGAAGGT | GCCATTTCTCACCAGCTTGTC |
| ICG4 | PV224502 | ACTCCAGCCCTTATCCTAGCA | CGCAACATTTGTCCGAGGATC |
| ICG5 | PV224503 | AGTATCAGACCAAGCTTGCAGAA | CGCCATCATTGTTCTCTTCTTCC |
| ICG6 | PV224504 | ATTGGTCCCCTCGGTTTGTC | GCCTGCCGATTCTGGATGAT |
| ICG7 | PV224505 | GCCAACACATTTGCAATCACC | TCCCTCTCCAGCAGCATTTG |
| ICG8 | PV224506 | TCCAGAGGACAAAGGAAGTGC | GACCTCCGACAAGACCTCTCT |
| GAPDH | PV224499 | TGACAGTGGTGCCGAATATGT- | AACGTTCAGATCGGGTGTGTA |
| β-actin | AY380809 | AACTTAGTCAGCGGCCG | AACCCGGCCTTACACAT |
| Genes | GenBank Code | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MZQ1 | PV231213 | TACTTTCTCTTCCTTGCCGACC | CCACCCTTTCTCCATTCTTCCA |
| MZQ2 | PV224495 | TTACCTGCCCTTGTCATGCA | AGCGGTTTCTTGTCACAGGT |
| MZQ3 | PV224496 | AGAAGTTGAAACAGTCGAAGCAGA | TGGTGAATTGTTCCAGATAAGCAG |
| MZQ4 | PV224497 | AAGCTTCGACGAAATGGTTGG | ATTCTTTCGCCATGTCAGGGT |
| MZQ5 | PV224498 | CGCCCATGAGAAGTGTGTTTT | TGCTCACTTTAGGCCTTCTGT |
| UBE2 | KP698948 | CCAAGCTCTTCTTAGTGCAC | CTCCCCACTTCCATCACTTT |
| RPL8 | KP698947 | TGGAAACTACGCCACAGTCA | GTCCTGCCTTCAACATTGGT |
| GAPDH | PV224499 | TGACAGTGGTGCCGAATATGT- | AACGTTCAGATCGGGTGTGTA |
| β-actin | AY380809 | AACTTAGTCAGCGGCCG | AACCCGGCCTTACACAT |
| 18S | AY319437 | CCGAGGGTCTCACTAAACCATTC′ | ACTACAATGAAGACGAAGCCCA |
| Genes | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) | Amplicon Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| vasa | CATTCTGGATGAGGCTGACAGGATG | GGCGGCAACTGATGTGGCAATA | 472 |
| PL10 | AGGACTACTTTGGGTTGTGTCAGGA | CCGATGGCTTGGCAGATTGGAC | 529 |
| Gene | GeNorm | NormFinder | BestKeeper | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (M Value) | (Stability Value) | (r) | (SD) | (CV) | |
| ICG1 | 1.157 | 0.452 | 0.740 | 0.98 | 3.71 |
| ICG2 | 1.189 | 0.504 | 0.796 | 1.11 | 4.19 |
| ICG3 | 1.403 | 0.538 | 0.616 | 1.52 | 6.56 |
| ICG4 | 1.340 | 0.549 | 0.755 | 1.28 | 4.52 |
| ICG5 | 1.236 | 0.575 | 0.619 | 1.08 | 4.41 |
| ICG6 | 1.203 | 0.656 | 0.681 | 1.02 | 4.86 |
| ICG7 | 1.193 | 0.690 | 0.707 | 1.07 | 4.97 |
| ICG8 | 1.306 | 0.714 | 0.555 | 1.06 | 4.21 |
| β-actin | 1.577 | 0.778 | 0.234 | 1.12 | 5.36 |
| GAPDH | 1.358 | 0.917 | 0.612 | 1.20 | 5.38 |
| Gene | GeNorm | NormFinder | BestKeeper | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (M Value) | (Stability Value) | (r) | (SD) | (CV) | |
| MZQ1 | 0.964 | 0.185 | 0.959 | 0.72 | 3.66 |
| MZQ2 | 1.037 | 0.202 | 0.873 | 0.70 | 2.52 |
| MZQ3 | 1.247 | 0.258 | 0.794 | 0.95 | 3.50 |
| MZQ4 | 1.023 | 0.443 | 0.903 | 0.76 | 2.90 |
| MZQ5 | 1.505 | 0.562 | 0.537 | 1.24 | 4.63 |
| RPL8 | 1.227 | 0.583 | 0.672 | 0.84 | 3.79 |
| UBE2 | 1.131 | 0.697 | 0.618 | 0.41 | 1.80 |
| 18s rRNA | 1.881 | 0.881 | 0.592 | 1.43 | 7.42 |
| β-actin | 1.703 | 1.024 | 0.726 | 1.50 | 6.81 |
| GAPDH | 1.313 | 1.208 | 0.505 | 0.86 | 3.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, F.; Wu, W.; Li, M.; Su, Y.; Huang, M.; Luo, X.; You, W.; Ke, C. Cloning, Characterization, and Expression Analysis of the DEAD-Box Family Genes, Vasa and PL10, in Pacific Abalone (Haliotis discus hannai). Genes 2025, 16, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030329
Chen F, Wu W, Li M, Su Y, Huang M, Luo X, You W, Ke C. Cloning, Characterization, and Expression Analysis of the DEAD-Box Family Genes, Vasa and PL10, in Pacific Abalone (Haliotis discus hannai). Genes. 2025; 16(3):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030329
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Fei, Wenwei Wu, Min Li, Ying Su, Miaoqing Huang, Xuan Luo, Weiwei You, and Caihuan Ke. 2025. "Cloning, Characterization, and Expression Analysis of the DEAD-Box Family Genes, Vasa and PL10, in Pacific Abalone (Haliotis discus hannai)" Genes 16, no. 3: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030329
APA StyleChen, F., Wu, W., Li, M., Su, Y., Huang, M., Luo, X., You, W., & Ke, C. (2025). Cloning, Characterization, and Expression Analysis of the DEAD-Box Family Genes, Vasa and PL10, in Pacific Abalone (Haliotis discus hannai). Genes, 16(3), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030329




