Identification of a Homozygous Variant in the CYP21A2 Gene by Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis of Circulating Cell-Free Fetal DNA
Abstract
1. Introduction
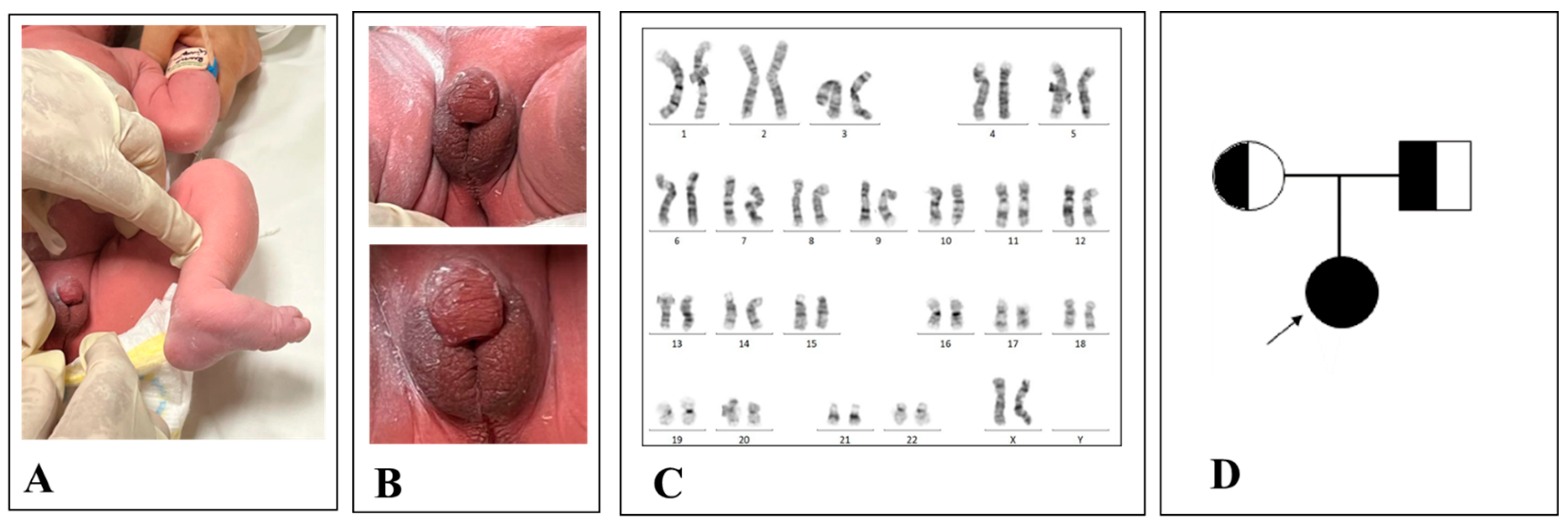
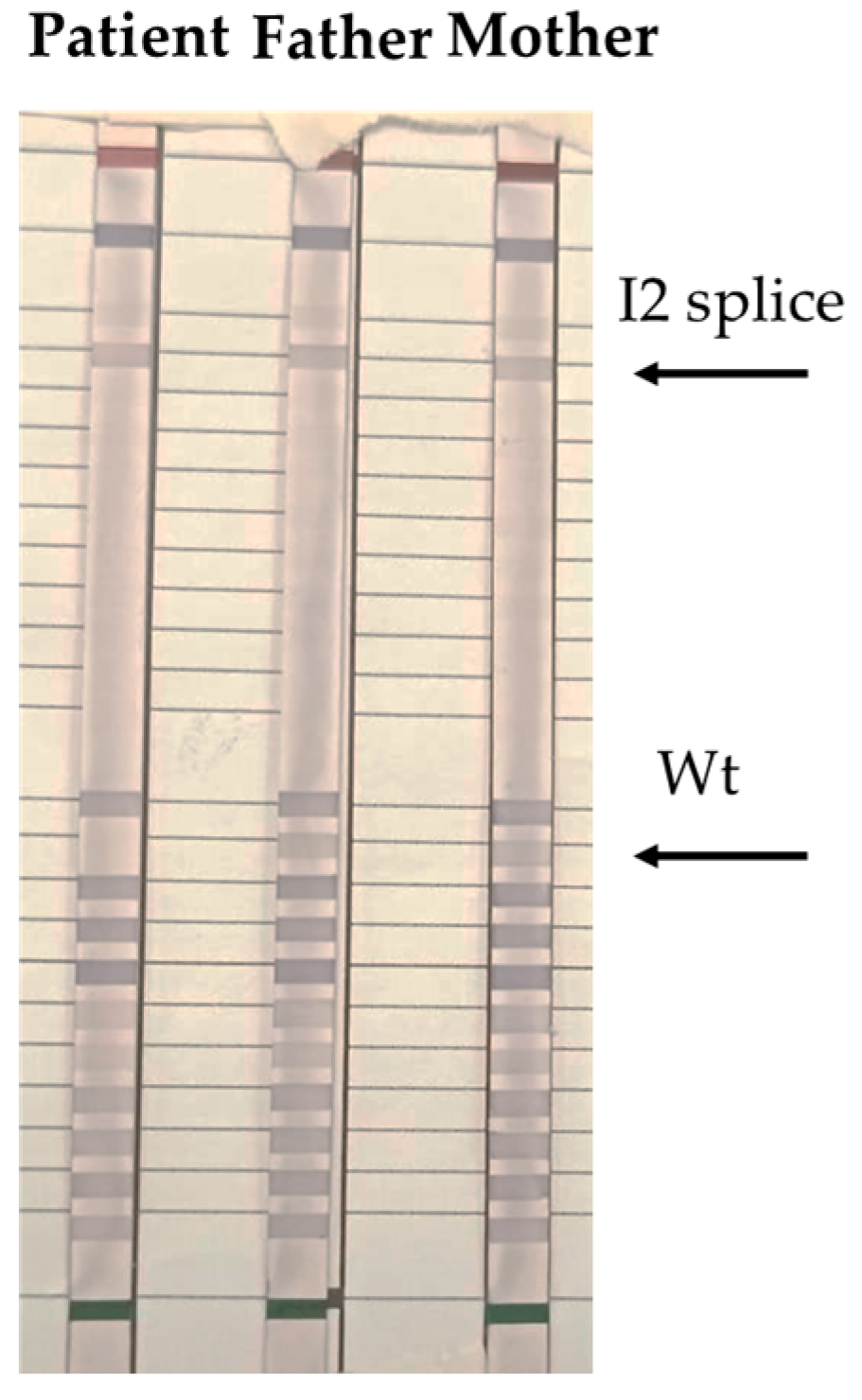
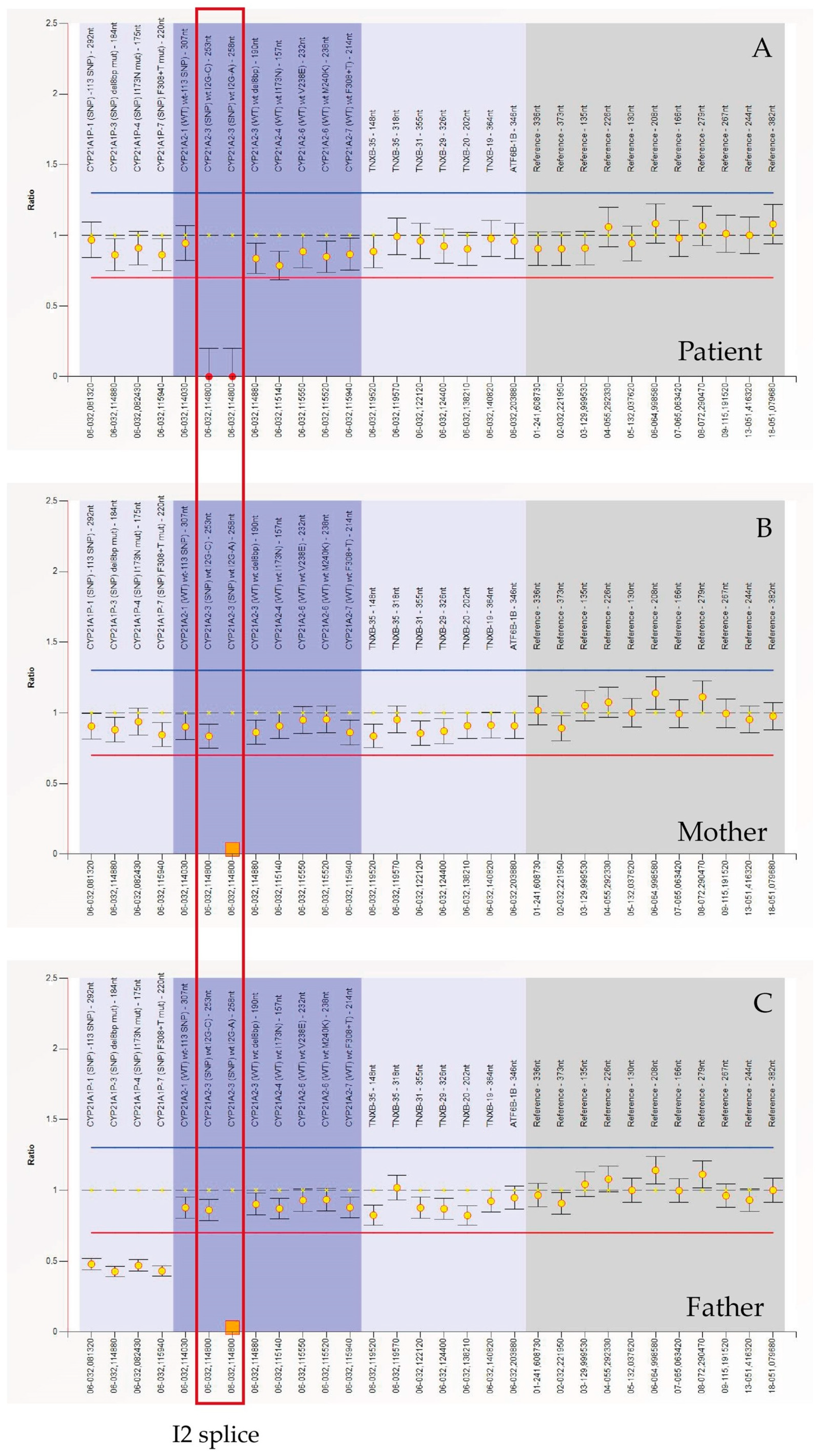
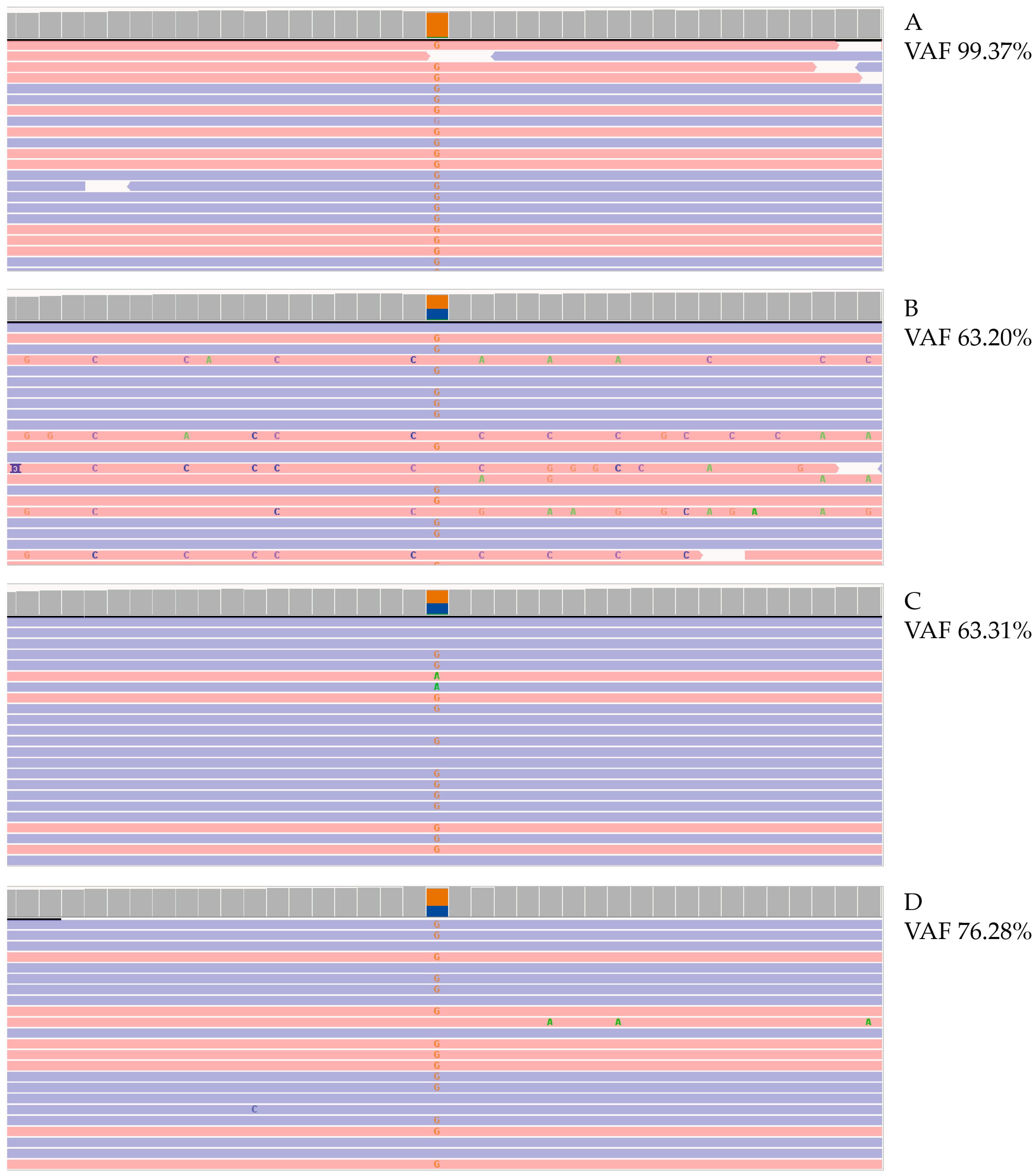
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Auer, M.K.; Nordenstrom, A.; Lajic, S.; Reisch, N. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Lancet 2023, 401, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa Reyes, T.M.; Collazo Mesa, T.; Lantigua Cruz, P.A.; Agramonte Machado, A.; Dominguez Alonso, E.; Falhammar, H. Molecular diagnosis of patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2020, 20, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimhan, M.L.; Khattab, A. Genetics of congenital adrenal hyperplasia and genotype-phenotype correlation. Fertil. Steril. 2019, 111, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podgorski, R.; Aebisher, D.; Stompor, M.; Podgorska, D.; Mazur, A. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia: Clinical symptoms and diagnostic methods. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2018, 65, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamed, M.H.; Al-Ghamdi, W.M.; Al-Agha, A.E. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Among Female Adolescents with Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. Cureus 2021, 13, e20698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Kashimada, K.; Amano, N.; Takasawa, K.; Nakamura-Utsunomiya, A.; Yatsuga, S.; Mukai, T.; Ida, S.; Isobe, M.; Fukushi, M.; et al. Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of 21-hydroxylase deficiency (2021 revision). Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2022, 31, 116–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotchman, E.; Shaw, J.; Paternoster, B.; Chandler, N.; Chitty, L.S. Non-invasive prenatal diagnosis and screening for monogenic disorders. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 253, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorr, H.G.; Wollmann, H.A.; Hauffa, B.P.; Woelfle, J.; on behalf of the German Society of Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology. Mortality in children with classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia and 21-hydroxylase deficiency (CAH) in Germany. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2018, 18, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedalthagafi, M.; Bawazeer, S.; Fawaz, R.I.; Heritage, A.M.; Alajaji, N.M.; Faqeih, E. Non-invasive prenatal testing: A revolutionary journey in prenatal testing. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1265090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkielstain, G.P.; Vieites, A.; Bergada, I.; Rey, R.A. Disorders of Sex Development of Adrenal Origin. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 770782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudzinska, B.; Leubner, J.; Ventz, M.; Quinkler, M. Sexual well-being in adult male patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 469289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignatelli, D.; Carvalho, B.L.; Palmeiro, A.; Barros, A.; Guerreiro, S.G.; Macut, D. The Complexities in Genotyping of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibaut, D.; Walter, M.R.; McGonegal, C.; Daniel, R.; Goodman, J. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia and Human Leukocyte Antigen B: A Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2023, 15, e35900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Kim, G.H.; Yoo, H.W. Recent advances in biochemical and molecular analysis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ozdemir, C.M.; Nielsen, M.M.; Liimatta, J.; Voegel, C.D.; Elzenaty, R.N.; Wasehuus, V.S.; Lind-Holst, M.; Ornstrup, M.J.; Gram, S.B.; Ousager, L.B.; et al. Late diagnosis of partial 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 deficiency-characterization of a new genetic variant. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2024, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, Y.; Tanae, A.; Inoue, H.; Hiromasa, T.; Fujii-Kuriyama, Y. Aberrant splicing and missense mutations cause steroid 21-hydroxylase [P-450(C21)] deficiency in humans: Possible gene conversion products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 7486–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, A.T.; Daiger, S.P.; Weleber, R.G. Nonsyndromic Retinitis Pigmentosa Overview. In GeneReviews(R); Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Amemiya, A., Eds.; NIH NLM: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Boucher, I.; Yu, W.; Beaudry, S.; Negoro, H.; Tran, M.; Pollak, M.R.; Henderson, J.M.; Denker, B.M. Galpha12 activation in podocytes leads to cumulative changes in glomerular collagen expression, proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis. Lab. Investig. 2012, 92, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, A.; Yuen, T.; Sun, L.; Yau, M.; Barhan, A.; Zaidi, M.; Lo, Y.M.; New, M.I. Noninvasive Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. Endocr. Dev. 2016, 30, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Yuan, Y.; Luo, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Guo, F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, J.; et al. Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of 21-Hydroxylase deficiency using target capture sequencing of maternal plasma DNA. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, M.I.; Tong, Y.K.; Yuen, T.; Jiang, P.; Pina, C.; Chan, K.C.; Khattab, A.; Liao, G.J.; Yau, M.; Kim, S.M.; et al. Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia using cell-free fetal DNA in maternal plasma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1022–E1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior-de Castro, C.; Gomez-Gonzalez, C.; Rodriguez-Lopez, R.; Macher, H.C.; Prenatal Diagnosis, C.; Prenatal Diagnosis Commission and the Genetics Commission of the Spanish Society of Laboratory Medicine. Prenatal genetic diagnosis of monogenic diseases. Adv. Lab. Med. 2023, 4, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary-Goldman, J.; D’Alton, M.E.; Berkowitz, R.L. Prenatal diagnosis and multiple pregnancy. Semin. Perinatol. 2005, 29, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, E.K.L.; Hui, W.W.I.; Chiu, R.W.K. cfDNA screening and diagnosis of monogenic disorders-where are we heading? Prenat. Diagn. 2018, 38, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Militaru, M.S.; Babliuc, I.M.; Bloaje-Florica, V.L.; Danci, V.A.; Filip-Deac, I.; Kutasi, E.; Simon, V.; Militaru, M.; Catana, A. The Impact of Chromosomal Mosaicisms on Prenatal Diagnosis and Genetic Counseling—A Narrative Review. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, D.; Lin, Y.; Luo, C.; Li, H.; Hu, P.; Xu, Z. Noninvasive prenatal screening in a pregnant woman with a history of stem cell transplant from a male donor: A case report and literature review. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2024, 12, e2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabieva, E.; Sharma, S.M.; Kapushev, Y.; Garushyants, S.K.; Fedotova, A.V.; Moskalenko, V.N.; Serebrenikova, T.E.; Glazyrina, E.; Kanivets, I.V.; Pyankov, D.V.; et al. Accurate fetal variant calling in the presence of maternal cell contamination. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 28, 1615–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, A.; Akbar, F.; Kirmani, S.; Jaffarali, A.; Zainab, G.; Malik, A.; Ansar, Z.; Afroze, B. Experience in prenatal genetic testing and reproductive decision-making for monogenic disorders from a single tertiary care genetics clinic in a low-middle income country. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2023, 23, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosme Cruz, R.M.; Clark, C.M.; Shin, L. A 10-year-old boy with ADHD symptoms. Pediatr. Ann. 2012, 41, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, E.; Gill, T.M.; Mayerl, H.; Freidl, W. Short-Term Disability Fluctuations in Late Life. J. Gerontol. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2019, 74, e135–e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, J.C.W.; Chan, Y.M.; Tsang, S.Y.; Yau, C.I.; Yeung, S.Y.; Au, K.K.; Chow, C.K. Noninvasive prenatal paternity testing by means of SNP-based targeted sequencing. Prenat. Diagn. 2020, 40, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Fu, Y.P.; Chang, W.X.; Yi, C.R.; Liu, L.H.; Xing, H.Y. Functional Variant of C-689T in the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-gamma2 Promoter is Associated with Coronary Heart Disease in Chinese Nondiabetic Han People. Chin. Med. Sci. J. 2017, 32, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochrein, A.; Zinser, W.; Spahn, G.; Angele, P.; Loer, I.; Albrecht, D.; Niemeyer, P. What parameters affect knee function in patients with untreated cartilage defects: Baseline data from the German Cartilage Registry. Int. Orthop. 2019, 43, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolnik, D.L.; Yong, Y.; Lee, T.J.; Tse, C.; McLennan, A.C.; da Silva Costa, F. Influence of Body Mass Index on Fetal Fraction Increase with Gestation and Cell-Free DNA Test Failure. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 132, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manokhina, I.; Singh, T.K.; Robinson, W.P. Cell-Free Placental DNA in Maternal Plasma in Relation to Placental Health and Function. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2017, 41, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shree, R.; Kolarova, T.R.; MacKinnon, H.J.; Hedge, J.M.; Vinopal, E.; Ma, K.K.; Lockwood, C.M.; Chandrasekaran, S. Low fetal fraction in obese women at first trimester cell-free DNA based prenatal screening is not accompanied by differences in total cell-free DNA. Prenat. Diagn. 2021, 41, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Batey, A.; Struble, C.; Musci, T.; Song, K.; Oliphant, A. Gestational age and maternal weight effects on fetal cell-free DNA in maternal plasma. Prenat. Diagn. 2013, 33, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krone, N.; Arlt, W. Genetics of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 23, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, J.Y.; Gomez-Lobo, V.; Merke, D.P. The management of congenital adrenal hyperplasia during preconception, pregnancy, and postpartum. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Soliman, A.T.; Ramadan, M.A.; Elawwa, A.; Abugabal, A.M.S.; Emam, M.H.A.; De Sanctis, V. Long-term prednisone versus hydrocortisone treatment in children with classic Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) and a brief review of the literature. Acta Biomed. 2019, 90, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livadas, S.; Bothou, C. Management of the Female with Non-classical Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (NCCAH): A Patient-Oriented Approach. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hormone Profile | 1st Month | 2nd Month | 3rd Month | 4th Month | 5th Month | Normal Range Values |
| 17-OHP (ng/mL) | >20 | 208 | 4.17 | 0.2 | 0.43 | 0.2–2, 9 |
| ACTH (pg/mL) | 724 | 549 | 22.5 | 133.1 | 9.6 | 7.0–65 |
| Testosterone (ng/dL) | 389.9 | 275.9 | 7.8 | 0.5 | 0.05 | Male < 10 years:0.30 Female < 10: 0.01–0.12 |
| DHEA-S (mcg/dL) | 2986 | 1600 | 144 | 798 | 261 | <2500 |
| Androstenedione (ng/mL) | >10 | 86.4 | 1.75 | 30 | 72 | 20–290 |
| Cortisol (mcg/dL) | 12.72 | 13.63 | <0.5 | 2.9 | 22.7 | Morning: 3.2–12.0 Evening: 0.1–8.0 |
| Renin (pUI/mL) | 88.23 | 608.30 | 149.2 | 55 | 26.2 | 3.11–41.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrillo, N.; Marcella, S.; Sirica, R.; Ianniello, M.; Ruggiero, R.; Mori, A.; Castiello, R.; Ramiro, C.; D’Angelo, R.; Pennacchio, G.; et al. Identification of a Homozygous Variant in the CYP21A2 Gene by Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis of Circulating Cell-Free Fetal DNA. Genes 2025, 16, 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030311
Petrillo N, Marcella S, Sirica R, Ianniello M, Ruggiero R, Mori A, Castiello R, Ramiro C, D’Angelo R, Pennacchio G, et al. Identification of a Homozygous Variant in the CYP21A2 Gene by Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis of Circulating Cell-Free Fetal DNA. Genes. 2025; 16(3):311. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030311
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrillo, Nadia, Simone Marcella, Roberto Sirica, Monica Ianniello, Raffaella Ruggiero, Alessio Mori, Rosa Castiello, Cristina Ramiro, Rossana D’Angelo, Giuliano Pennacchio, and et al. 2025. "Identification of a Homozygous Variant in the CYP21A2 Gene by Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis of Circulating Cell-Free Fetal DNA" Genes 16, no. 3: 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030311
APA StylePetrillo, N., Marcella, S., Sirica, R., Ianniello, M., Ruggiero, R., Mori, A., Castiello, R., Ramiro, C., D’Angelo, R., Pennacchio, G., Barletta, E., Passaro, R., Fico, A., & Savarese, G. (2025). Identification of a Homozygous Variant in the CYP21A2 Gene by Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis of Circulating Cell-Free Fetal DNA. Genes, 16(3), 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16030311






