Transcriptomic Characterization of miRNAs in Apis cerana Larvae Responding to Ascosphaera apis Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Honey Bee Larvae and Fungi
2.2. Preparation of Larval Gut Samples
2.3. Small RNA Sequencing (sRNA-seq) and Quality Control
2.4. Quality Control of Raw Data
2.5. Identification of miRNAs
2.6. Screening of DEmiRNAs
2.7. Stem-Loop RT-PCR Verification of miRNAs
2.8. Target Prediction of DEmiRNAs
2.9. Stem-Loop RT-qPCR Detection of DEmiRNAs
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of miRNAs in the A. c. cerana Larval Guts
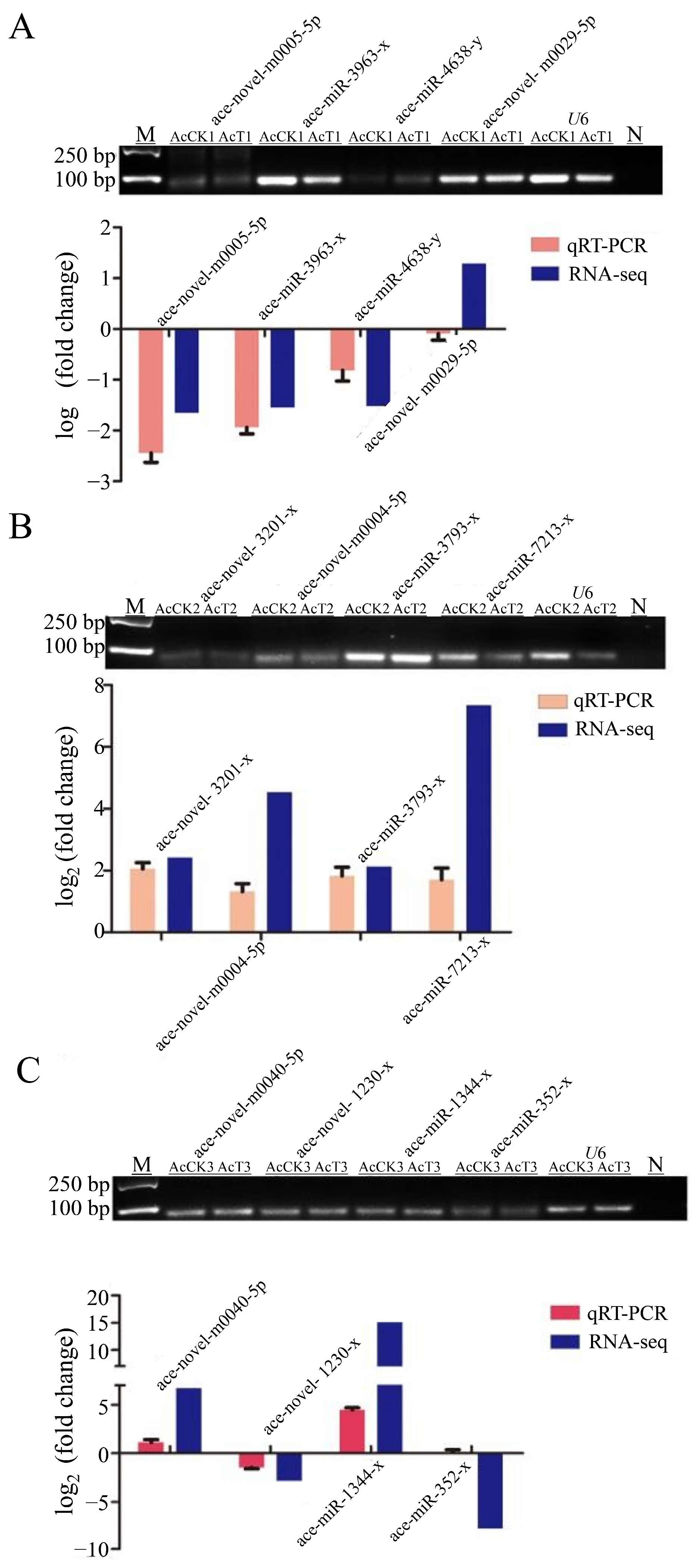
3.2. Stem-Loop RT-PCR Identification of DEmiRNA
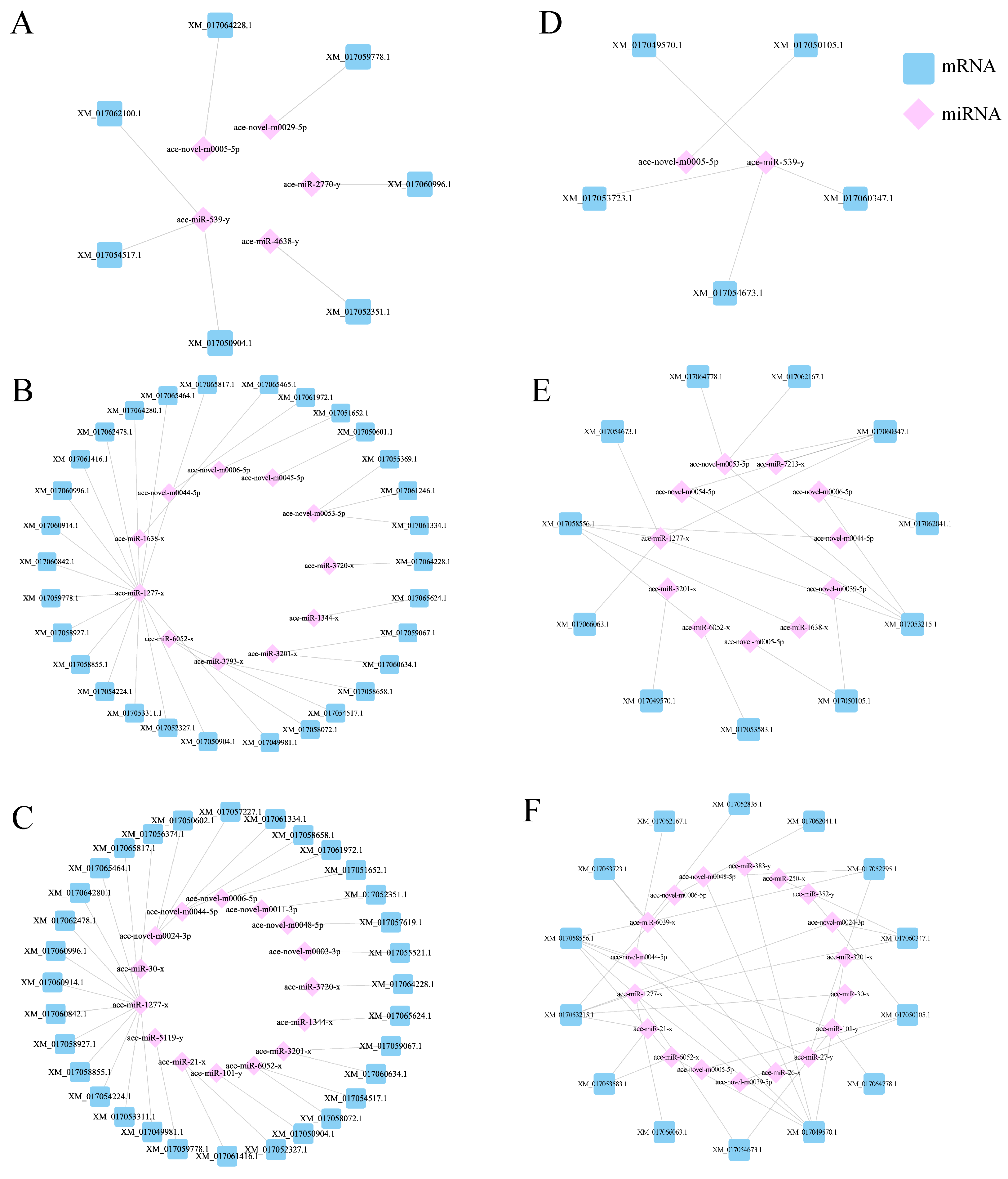
3.3. Target Gene Prediction and Functional Annotation of DEmiRNAs in the Gut of A. cerana Larvae
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, Z.J. Apiculture; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Aronstein, K.A.; Murray, K.D. Chalkbrood disease in honey bees. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 103 (Suppl. 1), S20–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabian, M.R.; Sonenberg, N.; Filipowicz, W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 351–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, T.C.; Blomberg, K.E.M.; Smith, C.I.E.; Andaloussi, S.E.; Wood, M.J. MRNA and microRNA transcriptomics analyses in a murine model of dystrophin loss and therapeutic restoration. Genom. Data 2016, 7, 88–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vidal, E.A.; Moyano, T.C.; Krouk, G.; Katari, M.S.; Tanurdzic, M.; McCombie, W.R.; Coruzzi, G.M.; Gutiérrez, R.A. Integrated RNA-seq and sRNA-seq analysis identifies novel nitrate-responsive genes in Arabidopsis thaliana roots. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Sheng, J.; Jiang, T.; Stevens, J.; Feng, X.; Wei, N. Transcriptional profiling reveals molecular basis and novel genetic targets for improved resistance to multiple fermentation inhibitors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, K.J.; Zhao, B.; Liu, S.; Raikhel, A.S. Regulation of physiological processes by microRNAs in insects. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Jagadeeswaran, G.; Ren, R.; Sunkar, R.; Jiang, H. Identification of conserved and novel microRNAs in Manduca sexta and their possible roles in the expression regulation of immunity-related genes. Insect Biochem. Mol. 2014, 47, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamipour, N.; Fathipour, Y.; Talebi, A.A.; Asgari, S.; Mehrabadi, M. The microRNA pathway is involved in Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf9) cells antiviral immune defense against Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus infection. Insect Biochem. Mol. 2019, 112, 103202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Su, S.; Geir, S.; Li, W.F.; Li, Z.G.; Zhang, S.W.; Chen, S.L.; Chen, R.S. Differential expression of miRNAs related to caste differentiation in the honey bee, Apis mellifera. Apidologie 2016, 47, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michely, J.; Kraft, S.; Müller, U. MiR-12 and miR-124 contribute to defined early phases of long-lasting and transient memory. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.F.; Du, Y.; Chen, H.Z.; Fan, Y.C.; Fan, X.X.; Zhu, Z.W.; Wang, J.; Xiong, C.L.; Zheng, Y.Z.; Hou, C.S.; et al. Comparative identification of microRNAs in Apis cerana cerana workers’ midguts in response to Nosema ceranae invasion. Insects 2019, 10, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.; Jing, X.; Liu, Z.; Feng, P.; Liu, X.; et al. Ame-miR-34 modulates the larval body weight and immune response of Apis mellifera workers to Ascosphara apis invasion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diggins, N.L.; Hancock, M.H. Viral miRNA regulation of host gene expression. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 146, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Ruiz-Manriquez, L.M.; Serrano-Cano, F.I.; Estrada-Meza, C.; Solorio-Diaz, K.A.; Srivastava, A. Human microRNAs in host-parasite interaction: A review. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, T.S.; Silva, J.A.; Lago, E.L.; Carvalho, E.M.; Zanette, D.L.; Castellucci, L.C. The miRNA 361-3p, a Regulator of GZMB and TNF Is Associated with Therapeutic Failure and Longer Time Healing of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Caused by L. (viannia) braziliensis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.D.; Huang, Q. Interactions among host–parasite microRNAs during Nosema ceranae proliferation in Apis mellifera. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 350112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.X.; Zhang, W.D.; Zhang, K.Y.; Zhang, J.X.; Long, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, K.H.; Zhu, L.R.; Chen, D.F.; Guo, R. In-depth investigation of microRNA-mediated cross-kingdom regulation between Asian honey bee and microsporidian. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1003294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Wang, S.; Guo, S.; Fan, X.; Zang, H.; Gao, X.; Jing, X.; Liu, Z.; Na, Z.; Zou, P.; et al. Regulatory roles of long non-coding RNAs relevant to antioxidant enzymes and immune responses of Apis cerana larvae following Ascosphaera apis invasion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Fan, X.; Long, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Cai, Z.; Sun, M.; Gu, X.; Zou, P.; Chen, D.; et al. Comprehensive investigation and regulatory function of lncRNAs engaged in western honey bee larval immune response to Ascosphaera apis invasion. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1082522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.B.; Aronstein, K.; José, M.F.; Vojvodic, S.; Palacio, M.A.; Spivak, M. Standard methods for fungal brood disease research. J. Apicult. Res. 2013, 52, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betel, D.; Wilson, M.; Gabow, A.; Marks, D.S.; Sander, C. The microRNA. org resource: Targets and expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D149–D153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehmsmeier, M.; Steffen, P.; Höchsmann, M.; Giegerich, R. Fast and effective prediction of microRNA/target duplexes. RNA 2004, 10, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, E.; Xie, Z.; Gustafson, A.M.; Carrington, J.C. MicroRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell 2005, 121, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoot, M.E.; Ono, K.; Ruscheinski, J.; Wang, P.L.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, A.A. Trials and tribulations of MicroRNA therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Chakraborti, S.; Devi, D.; Sahu, R.; Mandal, S.; Mandal, L. A conserved nutrient responsive axis mediates autophagic degradation of miRNA–mRNA hybrids in blood cell progenitors. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2024, 52, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegler, J.L.; Oultram, J.M.J.; Grof, C.P.L.; Eamens, A.L. DRB1, DRB2 and DRB4 Are Required for an Appropriate miRNA-Mediated Molecular Response to Osmotic Stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Kim, C.J.; Shin, B.H.; Lim, D.H. The biological roles of microRNAs in Drosophila development. Insects 2024, 15, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Meeus, I.; De Coninck, D.I.; Deforce, D.; Etebari, K.; Asgari, S.; Smagghe, G. Infections of virulent and avirulent viruses differentially influenced the expression of dicer-1, ago-1, and microRNAs in Bombus terrestris. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagadorn, M.A.; Hunter, F.K.; DeLory, T.; Johnson, M.M.; Pitts-Singer, T.L.; Kapheim, K.M. Maternal body condition and season influence RNA deposition in the oocytes of alfalfa leafcutting bees (Megachile rotundata). Front Genet. 2023, 13, 1064332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.F.; Chi, X.P.; Song, H.Y.; Wang, H.F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.G.; Xu, B.H. Ame-miR-980-3p participates in autophagy-mediated midgut remodelling in Apis mellifera via targeting Atg2B. Insect Mol. Biol. 2023, 32, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Li, K.; Zang, H.; Song, Y.; Kang, J.; Chen, Y.; Du, L.; Wang, N.; Chen, D.; Luo, Q.; et al. ame-miR-5119-Eth axis modulates larval-pupal transition of western honeybee worker. Front Physiol. 2024, 15, 1475306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.C.; Lee, S.W.; Ryu, D.Y.; Cui, F.J.; Bhak, J.; Kim, Y. Identification and characterization of microRNAs in normal equine tissues by next generation sequencing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Zhong, Y.; Qin, M.; Lin, B.M.; Chen, F.Y.; Yan, H.C.; Li, W.C.; Lin, J.R. Differentially expressed microRNAs in diapausing versus HCl-treated Bombyx embryos. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, W.J.; Luo, Q.H.; Sun, G.H.; Feng, Y.W.; Ma, J.J.; Yang, J.M. Bioinformatics analysis of regulatory non-coding RNA in gonad of Crassostrea gigas. J. Fish. China 2020, 44, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Huang, A.; Li, H.; Feng, L.Z.; Zhang, F.P.; Guo, W.S. Identification and comparative analysis of microRNAs in Pinus massoniana, infected by Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Plant Growth Regul. 2016, 83, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.X.; Du, Y.; Zhang, W.D.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.B.; Fan, Y.C.; Feng, R.R.; Wan, J.Q.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Xiong, C.L.; et al. Omics analysis of Nosema ceranae miRNAs involved in gene expression regulation in the midgut of Apis mellifera ligustica workers and their regulatory networks. Acta Entom. Sin. 2021, 64, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsanto-Hearne, V.; Johnson, K.N. Micro-RNA Modulation of Insect Virus Replication. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2019, 34, 61–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.K.; Hyun, S. Conserved microRNA miR-8 in fat body regulates innate immune homeostasis in Drosophila. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2012, 37, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, M.L. Regulating metabolism to shape immune function: Lessons from Drosophila. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 138, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.N.; Meng, J.Y.; Wang, Z.; Lin, S.Y.; Shen, J.; Yan, S. Research progress of aphid immunity system: Potential effective target for green pest management. Insect Sci. 2024, 31, 1662–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, P.; Villalobos, E.; Szawarski, N.; Damiani, N.; Gende, L.; Garrido, M.; Maggi, M.; Quintana, S.; Lamattina, L.; Eguaras, M. Towards Precision Nutrition: A Novel Concept Linking Phytochemicals, Immune Response and Honey Bee Health. Insects 2019, 10, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMenamin, A.J.; Daughenbaugh, K.F.; Parekh, F.; Pizzorno, M.C.; Flenniken, M.L. Honey bee and bumble bee antiviral defense. Viruses 2018, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.J.; Wang, W.W.; Liu, Y.; Chai, L.Q.; Wang, G.X.; Liu, X.S.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, J.L. Steroid hormone 20-hydroxyecdysone promotes CTL1-mediated cellular immunity in Helicoverpa armigera. Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 1399–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, A.P.; Guidugli-Lazzarini, K.R.; Freitas, F.C.; Bitondi, M.M.; Simões, Z.L. Bacterial infection activates the immune system response and dysregulates microRNA expression in honey bees. Insect Biochem. Mol. 2013, 43, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbouzova, N.I.; Zeidler, M.P. JAK/STAT signalling in Drosophila: Insights into conserved regulatory and cellular functions. Development 2006, 133, 2605–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Ma, R.; Tan, W.; Zhang, L.I. MiR-152 suppresses the proliferation and invasion of NSCLC cells by inhibiting FGF2. Exp. Mol. Med. 2014, 46, e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Tong, X.Y.; Zhou, D.D.; Chen, D.F.; Xiong, C.L.; Zheng, Y.Z.; Xu, G.J.; Wang, H.P.; Chen, H.Z.; Guo, Y.L.; et al. MicroRNA response analysis of intestinal response to A. apis stress in Apis cerana cerana larvae. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2019, 59, 1747–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Fan, Y.; Yang, A.; Liang, L.; Cao, J. MicroRNA-539 functions as a tumour suppressor in prostate cancer via the TGF-β/Smad4 signalling pathway by down-regulating DLX1. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 5934–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
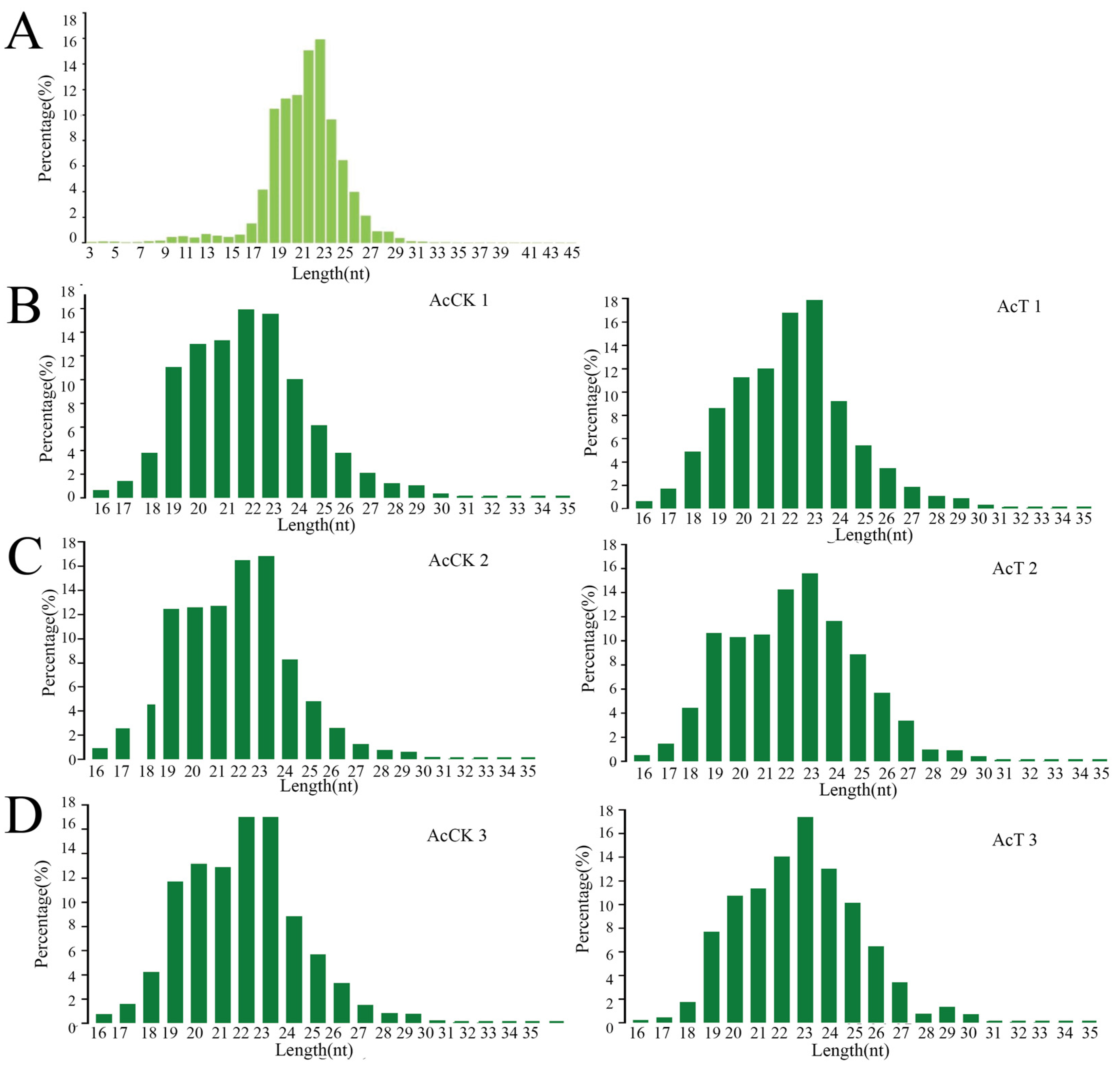
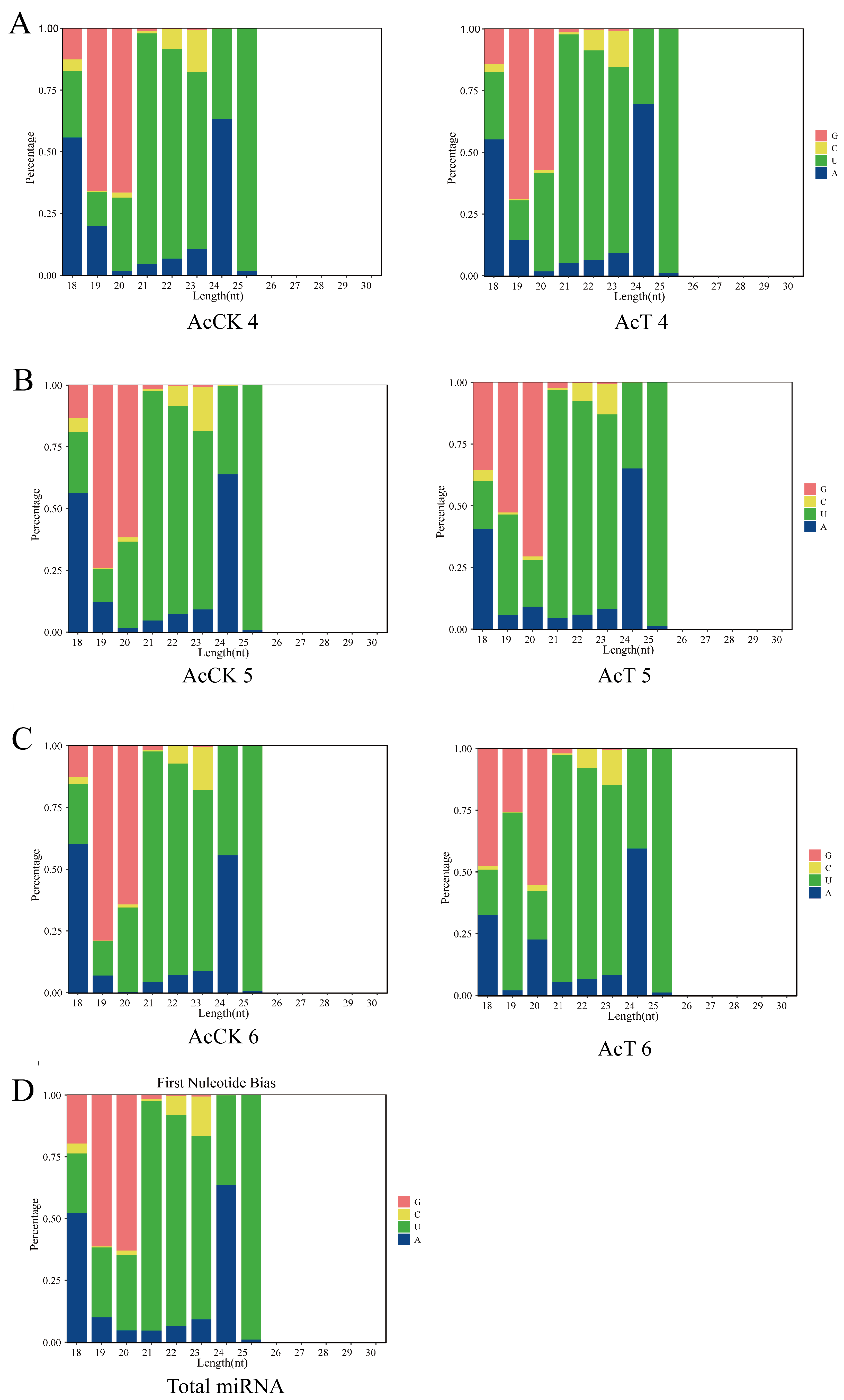
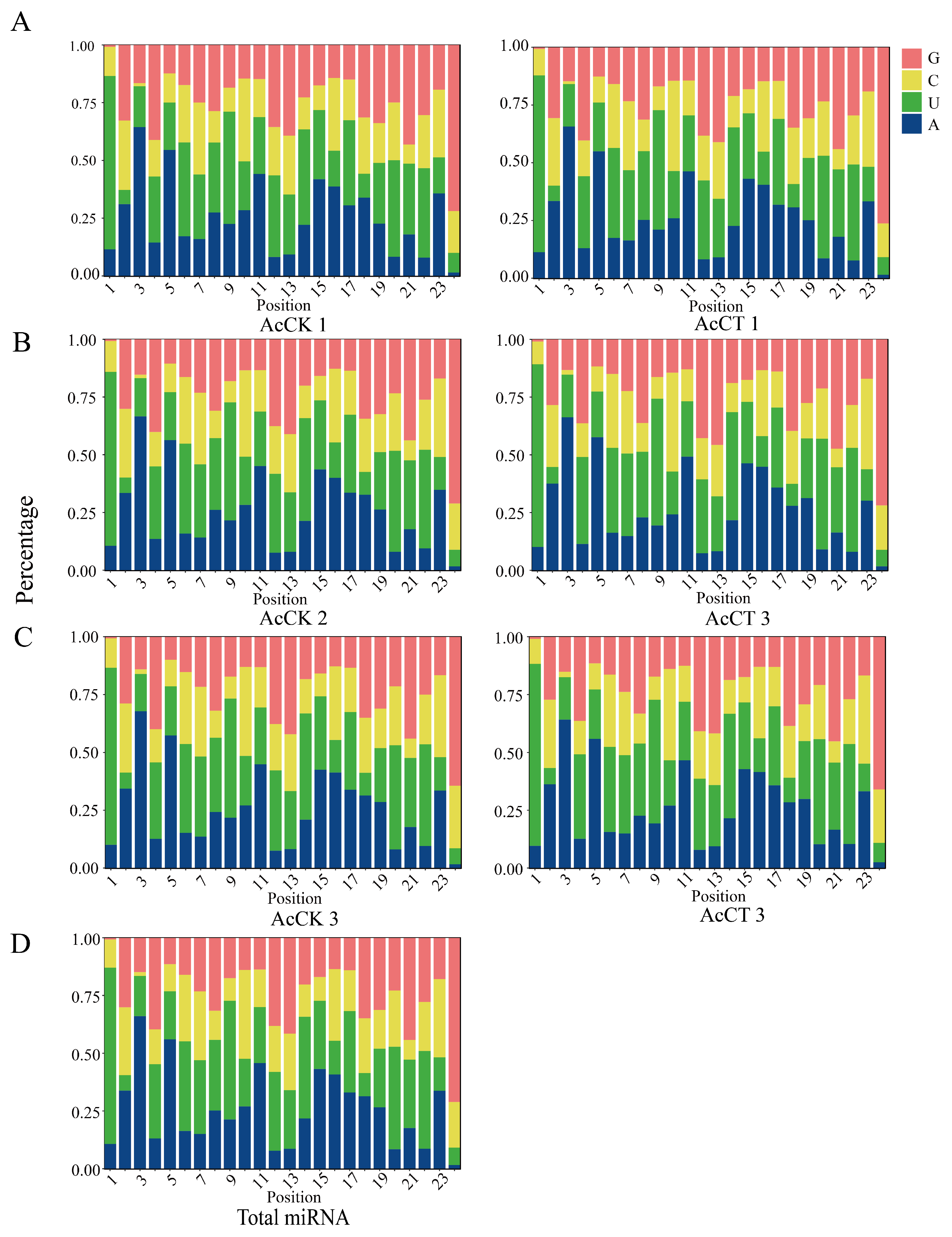

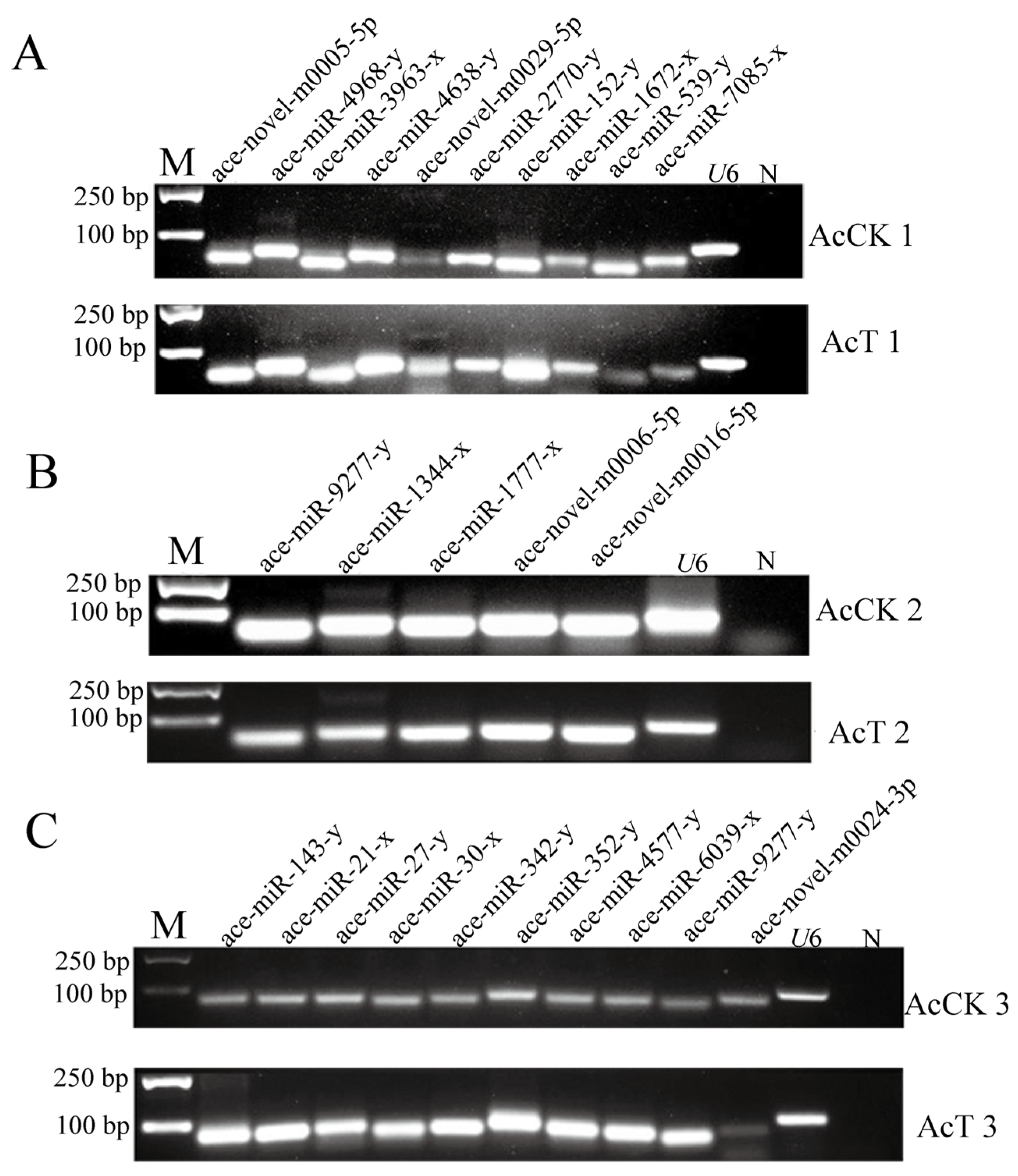

| Age of Workers | 4-Day-Old | 5-Day-Old | 6-Day-Old |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | AcCK1-1 AcCK1-2 AcCK1-3 | AcCK2-1 AcCK2-2 AcCK2-3 | AcCK3-1 AcCK3-2 AcCK3-3 |
| A. apis-infected | AcT1-1 AcT1-2 AcT1-3 | AcT2-1 AcT2-2 AcT2-3 | AcT3-1 AcT3-2 AcT3-3 |
| Primers | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| ace-novel-m0005-5p | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGACACCACG F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGCGCGTGCAAGTT |
| ace-miR-4968-y | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGTGCTGCTG F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGCAGCAGCAGCAG |
| ace-miR-3963-x | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGCGGTGTCA F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGTATCCCACTCC |
| ace-miR-4638-y | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGCGGCTGAG F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGCCTGGAAACGG |
| ace-novel-m0029-5p | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGCACCGACT F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGTTGTTGCTATTATT |
| ace-miR-2770-y | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGACCACTAC F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGGTTATCCCCGT |
| ace-miR-152-y | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGCCAAGTTC F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGGTTATCCCCGT |
| ace-miR-1672-x | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGTCCCTTCC F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGCGGTCAGGCCC |
| ace-miR-539-y | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGAAAAAAGA F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGAAGTATAATT |
| ace-miR-7085-x | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGTGCTGGCC F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGGGTGGGGGCC |
| ace-miR-9277-y | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGAGTCGGTA F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGAGGTTCGAGTCC |
| ace-miR-1344-x | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGCCGAGCAC F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGTGGGAAATGT |
| ace-miR-1777-x | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGCGCCCCCG F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGCGCCCCCGAC |
| ace-novel-m0006-5p | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGGCATGGTA F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGGCATGGTATATCTCA |
| ace-novel-m0016-5p | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGTATACCCT F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGTATACCCTAGAA |
| ace-miR-143-y | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGAGAGCTAC F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGAGAGCTACAGTG |
| ace-miR-21-x | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGTCAACATC F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGTCAACATCAGTCTG |
| ace-miR-27-y | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGGCAGAACT F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGGCAGAACTTAGCC |
| ace-miR-30-x | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGAGCTTCCA F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGAGCTTCCAGTCGGGGA |
| ace-miR-342-y | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGGGTGCGAA F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGGGTGCGAATTCT |
| ace-miR-352-y | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGACTATACA F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGACTATACAACCT |
| ace-miR-4577-y | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGCGTTCGCT F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGCGTTCGCTAT |
| ace-miR-6039-x | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGACGTAAAC F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGACGTAAACTCACGC |
| ace-miR-9277-y | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGAGTCGGTA F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGAGTCGGTAGGAC |
| ace-novel-m0024-3p | Loop:CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGACACCACGAGGTAATA F:ACACTCCAGCTGGGAGGTAATAACTTGA |
| Primer-R | CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGA |
| Top3 miRNA | Number of mRNA | |
|---|---|---|
| AcCK1 vs. AcT1 group | ace-miR-539-y | 1464 |
| ace-miR-152-y | 426 | |
| ace-novel-m0029-5p | 320 | |
| AcCK2 vs. AcT2 group | ace-miR-1277-x | 6018 |
| ace-novel-m0053-5p | 3037 | |
| ace-novel-m0054-5p- | 3037 | |
| AcCK3 vs. AcT3 group | ace-miR-1277-x | 6018 |
| ace-novel-m0024-3p | 1837 | |
| ace-miR-6052-x | 1474 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Qiu, J.; Kang, J.; Chen, Y.; Cao, R.; Wang, W.; Dai, M.; Chen, D.; Fu, Z.; Guo, R. Transcriptomic Characterization of miRNAs in Apis cerana Larvae Responding to Ascosphaera apis Infection. Genes 2025, 16, 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020156
Song Y, Qiu J, Kang J, Chen Y, Cao R, Wang W, Dai M, Chen D, Fu Z, Guo R. Transcriptomic Characterization of miRNAs in Apis cerana Larvae Responding to Ascosphaera apis Infection. Genes. 2025; 16(2):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020156
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yuxuan, Jianfeng Qiu, Jing Kang, Ying Chen, Ruihua Cao, Wei Wang, Mengyuan Dai, Dafu Chen, Zhongmin Fu, and Rui Guo. 2025. "Transcriptomic Characterization of miRNAs in Apis cerana Larvae Responding to Ascosphaera apis Infection" Genes 16, no. 2: 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020156
APA StyleSong, Y., Qiu, J., Kang, J., Chen, Y., Cao, R., Wang, W., Dai, M., Chen, D., Fu, Z., & Guo, R. (2025). Transcriptomic Characterization of miRNAs in Apis cerana Larvae Responding to Ascosphaera apis Infection. Genes, 16(2), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020156







