Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of OTOGL-Associated Hearing Loss Identified in a Cohort of 7065 Japanese Patients with Hearing Loss
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Variant Analysis
2.3. Clinical Evaluations
3. Results
3.1. Identified OTOGL Variants
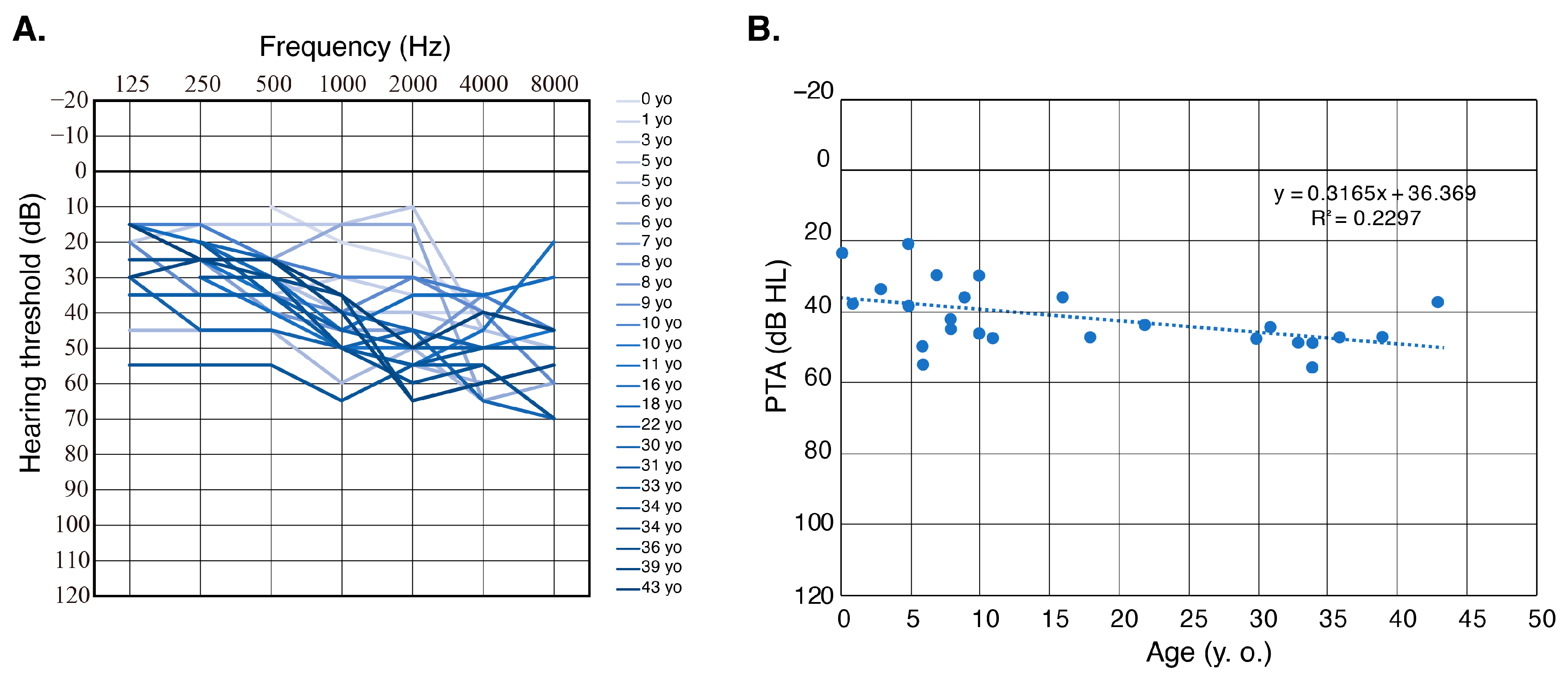
3.2. Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of OTOGL-Associated HL
4. Discussion
| Nucleotide Change | AA Change | Onset | Severity | Configuration | Progression | Vestibular Dysfunction | Population | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.[547C>T];[5238+5G>A] | p.[Arg183*];[IVS43 ds G-A +5] | Congenital | Moderate | - | No | No | Dutch | [5] |
| c.[547C>T];[5992+5G>A] | p.[Arg183*];[IVS48 ds G-A +5] | Congenital | Mild to moderate | - | - | No | US | [30] |
| c.[814_815delAT];[814_815delAT] | p.[Met272Valalfs*4];[Met272Valfs*4] | Congenital | Moderate to severe | - | No | - | French-Canadian | [31] |
| c.[814_815delAT];[5023G>A] | p.[Met272Valfs*4];[Gly1675Arg] | Congenital | Moderate | - | No | - | French-Canadian | [31] |
| c.[948delG];[948delG] | p.[Leu316Phefs*6];[Leu316Phefs*6] | Congenital | Moderate | - | - | - | Ashkenazi Jewish | [32] |
| c.[951_954delGTTT];[6328C>T] | p.[Gln317Hisfs*4];[Gln2110*] | Perilingual | Mild | - | No | No | Korea | [33] |
| c.[1430delT];[4132T>C] | p.[Val477Glufs*25];[Cys1378Arg] | Congenital | Moderate | - | No | Hypofunction | Dutch | [5] |
| c.[1558C>T];[2773C>T] | p.[Gln520*];[Arg925*] | 5 yo | Mild to moderate | Flat | No | No | France | [4] |
| c.[1558C>T];[4032_4054+30del53] | p.[Gln520*];[His1344Glnfs*13] | Congenital | Moderate | Mid frequency | No | No | Slovakia | [34] |
| c.[1666C>T];[5422C>T] | p.[Gln556*];[Arg1808*] | Congenital | Moderate | - | - | - | [35] | |
| c.[1849delA];[6601_6602delTG] | p.[Arg617Glyfs*10];[Trp2201Alafs*8] | Congenital | - | - | - | No | US | [30] |
| c.[1913G>A];[1913G>A] | p.[Trp638*][Trp638*] | Prelingual | Moderate | Low frequency | No | - | Brazil | [36] |
| c.[2533T>C];[4833G>A] | p.[Phe845Leu];[Lys1611*] | Congenital | Severe to profound | - | No | Left hypofunction | Netherlands | [37] |
| c.[2770C>T];[5038delG] | p.[Arg924*];[Asp1680Ilefs*6] | 4 yo | Mild | - | No | No | China | [18] |
| c.[2833C>T];[2911delG] | p.[Arg945*];[Asp971Ilefs*25] | Prelingual | Mild or moderate | - | - | - | China | [19] |
| c.[3166_3168dupAAA];[4564G>T] | p.[Lys1056dup];[Glu1522*] | Congenital | - | - | - | - | US | [30] |
| c.[3349C>A];[6095-8C>A] | p.[Gln1117Lys];[IVS49 as C-A -8] | Postnatal | Moderate | - | No | - | [38] | |
| c.[4252+1G>A];[6922T>C] | p.[IVS35 ds G-A +1];[Cys308Arg] | 5 yo | Mild | Down sloping | - | - | China | [39] |
| c.[5227T>C];[5227T>C] | p.[Cys1743Arg];[Cys1743Arg] | Prelingual | Mild to severe | - | - | - | US | [30] |
| c.[6467C>A];[6474dupA] | p.[Ser2156*];[Cys2159Metfs*2] | 7 yo and 9 yo | Moderate | HF_gentle | No | No | China | [20] |
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoshimura, H.; Okubo, T.; Shinagawa, J.; Nishio, S.Y.; Takumi, Y.; Usami, S.I. Epidemiology, aetiology and diagnosis of congenital hearing loss via hearing screening of 153 913 newborns. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2024, 53, dyae052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, A.M.; Smith, R.J.H. The Epidemiology of Deafness. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a033258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usami, S.I.; Nishio, S.Y. The genetic etiology of hearing loss in Japan revealed by the social health insurance-based genetic testing of 10K patients. Hum. Genet. 2022, 141, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, C.; Louha, M.; Loundon, N.; Michalski, N.; Verpy, E.; Smagghe, L.; Hardelin, J.P.; Rouillon, I.; Jonard, L.; Couderc, R.; et al. Biallelic nonsense mutations in the otogelin-like gene (OTOGL) in a child affected by mild to moderate hearing impairment. Gene 2013, 527, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yariz, K.O.; Duman, D.; Zazo Seco, C.; Dallman, J.; Huang, M.; Peters, T.A.; Sirmaci, A.; Lu, N.; Schraders, M.; Skromne, I.; et al. Mutations in OTOGL, encoding the inner ear protein otogelin-like, cause moderate sensorineural hearing loss. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 91, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Salmon, M.; El-Amraoui, A.; Leibovici, M.; Petit, C. Otogelin: A glycoprotein specific to the acellular membranes of the inner ear. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14450–14455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avan, P.; Le Gal, S.; Michel, V.; Dupont, T.; Hardelin, J.P.; Petit, C.; Verpy, E. Otogelin, otogelin-like, and stereocilin form links connecting outer hair cell stereocilia to each other and the tectorial membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2019, 116, 25948–25957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishio, S.Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Usami, S.I. Clinical application of a custom AmpliSeq library and ion torrent PGM sequencing to comprehensive mutation screening for deafness genes. Genet. Test Mol. Biomark. 2015, 19, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 1000 Genome Project. Available online: https://www.internationalgenome.org (accessed on 26 August 2015).
- Genome Aggregation Database. Available online: https://gnomad.broadinstitute.org (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- The Human Genetic Variation Database. Available online: https://www.hgvd.genome.med.kyoto-u.ac.jp (accessed on 15 November 2015).
- ToMMo 54KJPN-Integrative Japanese Genome Variation Database. Available online: https://jmorp.megabank.tohoku.ac.jp (accessed on 9 July 2023).
- Nishio, S.; Usami, S. The clinical next-generation sequencing database: A tool for the unified management of clinical information and genetic variants to accelerate variant pathogenicity classification. Hum. Mutat. 2017, 38, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, S.Y.; Moteki, H.; Usami, S.I. Simple and efficient germline copy number variant visualization method for the Ion AmpliSeq custom panel. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2018, 6, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. ACMG Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oza, A.M.; DiStefano, M.T.; Hemphill, S.E.; Cushman, B.J.; Grant, A.R.; Siegert, R.K.; Shen, J.; Chapin, A.; Boczek, N.J.; Schimmenti, L.A.; et al. ClinGen Hearing Loss Clinical Domain Working Group. Expert specification of the ACMG/AMP variant interpretation guidelines for genetic hearing loss. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 1593–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y. Novel heterozygous mutations in the otogelin-like (OTOGL) gene in a child with bilateral mild nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss. Gene 2022, 808, 146000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Hu, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Dong, X.; Xiao, T.; Xu, Z.; Wu, B.; Zhou, W. Association between expanded genomic sequencing combined with hearing screening and detection of hearing loss among newborns in a neonatal intensive care unit. JAMA Netw. Open. 2022, 5, e2220986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Sun, S.; Guo, L.; Lu, X.; Mei, H.; Lai, C.; Li, H. Novel biallelic OTOGL mutations in a Chinese family with moderate non-syndromic sensorineural hearing loss. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 79, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oonk, A.M.; Leijendeckers, J.M.; Huygen, P.L.; Schraders, M.; del Campo, M.; del Castillo, I.; Tekin, M.; Feenstra, I.; Beynon, A.J.; Kunst, H.P.; et al. Similar phenotypes caused by mutations in OTOG and OTOGL. Ear Hear. 2014, 35, e84–e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraders, M.; Ruiz-Palmero, L.; Kalay, E.; Oostrik, J.; del Castillo, F.J.; Sezgin, O.; Beynon, A.J.; Strom, T.M.; Pennings, R.J.; Zazo Seco, C.; et al. Mutations of the gene encoding otogelin are a cause of autosomal-recessive nonsyndromic moderate hearing impairment. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 91, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Choi, H.J.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; Rim, J.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Gee, H.Y.; Jung, J. A novel early truncation mutation in OTOG causes prelingual mild hearing loss without vestibular dysfunction. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2019, 62, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francey, L.J.; Conlin, L.K.; Kadesch, H.E.; Clark, D.; Berrodin, D.; Sun, Y.; Glessner, J.; Hakonarson, H.; Jalas, C.; Landau, C.; et al. Genome-wide SNP genotyping identifies the Stereocilin (STRC) gene as a major contributor to pediatric bilateral sensorineural hearing impairment. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2012, 158A, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plevova, P.; Paprskarova, M.; Tvrda, P.; Turska, P.; Slavkovsky, R.; Mrazkova, E. STRC Deletion is a Frequent Cause of Slight to Moderate Congenital Hearing Impairment in the Czech Republic. Otol. Neurotol. 2017, 38, e393–e400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čada, Z.; Šafka Brožková, D.; Balatková, Z.; Plevová, P.; Rašková, D.; Laštůvková, J.; Černý, R.; Bandúrová, V.; Koucký, V.; Hrubá, S.; et al. Moderate sensorineural hearing loss is typical for DFNB16 caused by various types of mutations affecting the STRC gene. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 3353–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloisio, N.; Morlé, L.; Bozon, M.; Godet, J.; Verhoeven, K.; Van Camp, G.; Plauchu, H.; Muller, P.; Collet, L.; Lina-Granade, G. Mutation in the zonadhesin-like domain of alpha-tectorin associated with autosomal dominant non-syndromic hearing loss. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 1999, 7, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hildebrand, M.S.; Morín, M.; Meyer, N.C.; Mayo, F.; Modamio-Hoybjor, S.; Mencía, A.; Olavarrieta, L.; Morales-Angulo, C.; Nishimura, C.J.; Workman, H.; et al. DFNA8/12 caused by TECTA mutations is the most identified subtype of nonsyndromic autosomal dominant hearing loss. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, K.; Moteki, H.; Kitajiri, S.I.; Kitano, T.; Nishio, S.Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Wakui, K.; Abe, S.; Ozaki, A.; Motegi, R.; et al. Mid-Frequency Hearing Loss Is Characteristic Clinical Feature of OTOA-Associated Hearing Loss. Genes 2019, 10, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan-Heggen, C.M.; Bierer, A.O.; Shearer, A.E.; Kolbe, D.L.; Nishimura, C.J.; Frees, K.L.; Ephraim, S.S.; Shibata, S.B.; Booth, K.T.; Campbell, C.A.; et al. Comprehensive genetic testing in the clinical evaluation of 1119 patients with hearing loss. Hum. Genet. 2016, 135, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, M.T.; Tardif, J.; Leblanc, J.; Lavoie, J.; Morin, P.; Harvey, M.; Thomas, M.J.; Pratte, A.; Braverman, N. First glance at the molecular etiology of hearing loss in French-Canadian families from Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean’s founder population. Hum. Genet. 2022, 141, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, K.T.; Hirsch, Y.; Vardaro, A.C.; Ekstein, J.; Yefet, D.; Quint, A.; Weiden, T.; Corey, D.P. Identification of novel and recurrent variants in MYO15A in Ashkenazi Jewish patients with autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 737782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.K.; Kim, A.R.; Park, K.T.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, M.Y.; Nam, J.Y.; Woo, S.J.; Oh, S.H.; Park, W.Y.; Choi, B.Y. Whole-exome sequencing reveals diverse modes of inheritance in sporadic mild to moderate sensorineural hearing loss in a pediatric population. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlenkova, Z.; Varga, L.; Borecka, S.; Karhanek, M.; Huckova, M.; Skopkova, M.; Profant, M.; Gasperikova, D. Comprehensive molecular-genetic analysis of mid-frequency sensorineural hearing loss. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.S.; Quental, S.; Fernandes, S.; Castedo, S.; Moura, C.P. Whole-Exome Sequencing Targeting a Gene Panel for Sensorineural Hearing Loss: The First Portuguese Cohort Study. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2022, 162, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaio, C.R.A.C.; Coelho, A.V.C.; Moura, L.M.S.; Guedes, R.L.M.; Chen, K.; Ceroni, J.R.M.; Minillo, R.M.; Caraciolo, M.P.; Reis, R.S.; de Azevedo, B.M.C.; et al. Genomic study of nonsyndromic hearing loss in unaffected individuals: Frequency of pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants in a Brazilian cohort of 2097 genomes. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 921324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazo Seco, C.; Wesdorp, M.; Feenstra, I.; Pfundt, R.; Hehir-Kwa, J.Y.; Lelieveld, S.H.; Castelein, S.; Gilissen, C.; de Wijs, I.J.; Admiraal, R.J.; et al. The diagnostic yield of whole-exome sequencing targeting a gene panel for hearing impairment in The Netherlands. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 25, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florentine, M.M.; Rouse, S.L.; Stephans, J.; Conrad, D.; Czechowicz, J.; Matthews, I.R.; Meyer, A.K.; Nadaraja, G.S.; Parikh, R.; Virbalas, J.; et al. Racial and ethnic disparities in diagnostic efficacy of comprehensive genetic testing for sensorineural hearing loss. Hum. Gene 2022, 141, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Li, J.; Chen, G.; Shi, T.; Lan, L.; Wu, X.; Zhao, C.; Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q. Family trio-based sequencing in 404 sporadic bilateral hearing loss patients discovers recessive and De novo genetic variants in multiple ways. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 64, 104311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmler, M.C.; Zwaenepoel, I.; Verpy, E.; Guillaud, L.; Elbaz, C.; Petit, C.; Panthier, J.J. Twister mutant mice are defective for otogelin, a component specific to inner ear acellular membranes. Mamm. Genome 2000, 11, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Nucleotide Change | AA Change | Exon | SIFT | PP2 | LRT | MutTaster | MutAssessor | REVEL | CADD | ToMMo 54KJPN | gnomAD All | Pathogenicity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.2770C>T | p.Arg924* | exon25 | . | . | . | A | . | . | 44 | . | 1.29 × 10−5 | Likely Pathogenic | [18] |
| c.2833C>T | p.Arg945* | exon25 | . | . | . | A | . | . | 38 | 0.000287 | 6.42 × 10−5 | Likely Pathogenic | [19] |
| c.2949C>A | p.Cys983* | exon26 | . | . | . | A | . | . | 37 | . | . | Likely Pathogenic | This study |
| c.3140G>A | p.Trp1047* | exon27 | . | . | . | A | . | . | 43 | . | . | Likely Pathogenic | This study |
| c.4172+1G>A | exon34 | . | . | . | D | . | . | 26.6 | . | . | Likely Pathogenic | This study | |
| c.4863_4864delinsAA | p.Pro1622Thr | exon42 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | VUS | This study |
| c.5380+3_+6del | exon49 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | 9.2 × 10−5 | 2.728 × 10−5 | VUS | This study | |
| c.6133_6134del | p.Ala2046Argfs*21 | exon50 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | 0.000184 | 1.613 × 10−5 | Likely Pathogenic | This study |
| c.6409G>T | p.Glu2137* | exon53 | . | . | N | A | . | . | 53 | 0.000166 | 1.413 × 10−5 | Likely Pathogenic | This study |
| c.6467C>A | p.Ser2156* | exon53 | . | . | D | A | . | . | 55 | 0.000267 | 0.0001 | VUS | [20] |
| c.6468delA | p.Lys2158Asnfs*40 | exon53 | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | 4.6 × 10−5 | 4.367 × 10−5 | Likely Pathogenic | This study |
| Family Number | ID | Base Change Allele 1 | AA Change Allele 1 | Base Change Allele 2 | AA Change Allele 2 | Hereditary | Onset | Age | Gender | Severity of HL | Type of HL | Progression | Vestibular Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | JHLB-0872 | c.2770C>T | p.Arg924* | c.4172+1G>A | Spl. | AR | 0 | 3 | F | Mild | Flat | N | N |
| JHLB-2210 | c.2770C>T | p. Arg 924* | c.4172+1G>A | Spl. | AR | 0 | 1 | M | Mild | Flat | Y | N | |
| 2 | JHLB-1937 | c.2833C>T | p. Arg 945* | c.6409G>T | p.Glu2137* | Sporadic | 0 | 10 | M | Moderate | HF_gentle | N | N |
| 3 | JHLB-7125 | c.2949C>A | p.Cys983* | c.3140G>A | p.Trp1047* | Sporadic | 6 | 10 | M | Moderate | HF_gentle | N | N |
| 4 | JHLB-3844 | c.4863_4864delinsAA | p.Pro1622Thr | c.4863_4864delinsAA | p.Pro1622Thr | Sporadic | 5 | 34 | F | Moderate | Flat | Y | Y |
| 5 | JHLB-7091 | c.5380+3_+6del | Spl. | c.6133_6134del | p.Ala2046Argfs*21 | Sporadic | 0 | 0 | F | Mild | HF_gentle | N | N |
| 6 | JHLB-6995 | c.6133_6134del | p.Ala2046Argfs*21 | c.6133_6134del | p.Ala2046Argfs*21 | AR | 6 | 43 | F | Mild | HF_gentle | Y | Y |
| JHLB-6996 | c.6133_6134del | p.Ala2046Argfs*21 | c.6133_6134del | p.Ala2046Argfs*21 | AR | 9 | 31 | F | Moderate | Flat | N | N | |
| 7 | JHLB-10297 | c.6133_6134del | p.Ala2046Argfs*21 | c.6467C>A | p.Ser2156* | Sporadic | 4 | 6 | M | Moderate | Flat | N | N |
| 8 | JHLB-0223 | c.6467C>A | p.Ser2156* | c.6468delA | p.Lys2158Asnfs*40 | AD | 10 | 30 | F | Moderate | Flat | Y | Y |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maekawa, K.; Nishio, S.-y.; Ishikawa, K.; Takahashi, M.; Kumakawa, K.; Okami, M.; Yoshimura, H.; Nakayama, J.; Teraoka, M.; Usami, S.-i. Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of OTOGL-Associated Hearing Loss Identified in a Cohort of 7065 Japanese Patients with Hearing Loss. Genes 2025, 16, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020123
Maekawa K, Nishio S-y, Ishikawa K, Takahashi M, Kumakawa K, Okami M, Yoshimura H, Nakayama J, Teraoka M, Usami S-i. Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of OTOGL-Associated Hearing Loss Identified in a Cohort of 7065 Japanese Patients with Hearing Loss. Genes. 2025; 16(2):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020123
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaekawa, Karuna, Shin-ya Nishio, Kotaro Ishikawa, Masahiro Takahashi, Kozo Kumakawa, Mayuri Okami, Hidekane Yoshimura, Jun Nakayama, Masato Teraoka, and Shin-ichi Usami. 2025. "Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of OTOGL-Associated Hearing Loss Identified in a Cohort of 7065 Japanese Patients with Hearing Loss" Genes 16, no. 2: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020123
APA StyleMaekawa, K., Nishio, S.-y., Ishikawa, K., Takahashi, M., Kumakawa, K., Okami, M., Yoshimura, H., Nakayama, J., Teraoka, M., & Usami, S.-i. (2025). Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of OTOGL-Associated Hearing Loss Identified in a Cohort of 7065 Japanese Patients with Hearing Loss. Genes, 16(2), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020123







