Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the AS2/LOB Transcription Factor Family in Asparagus officinalis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification and Analysis of the Physicochemical Properties of AoAS Members
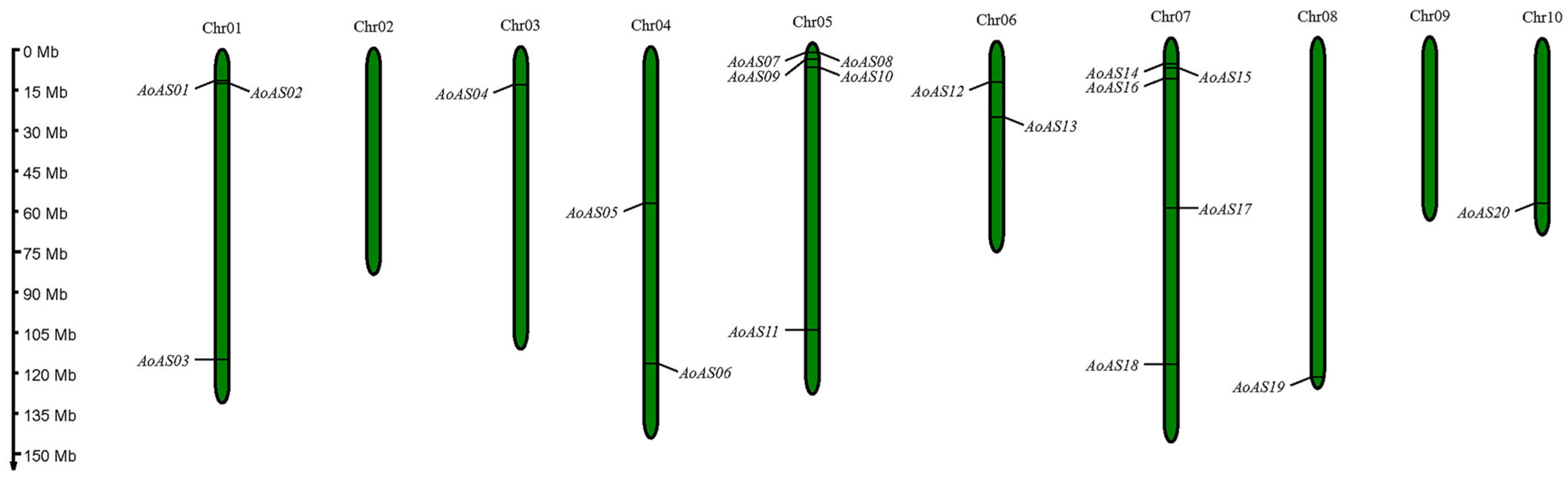
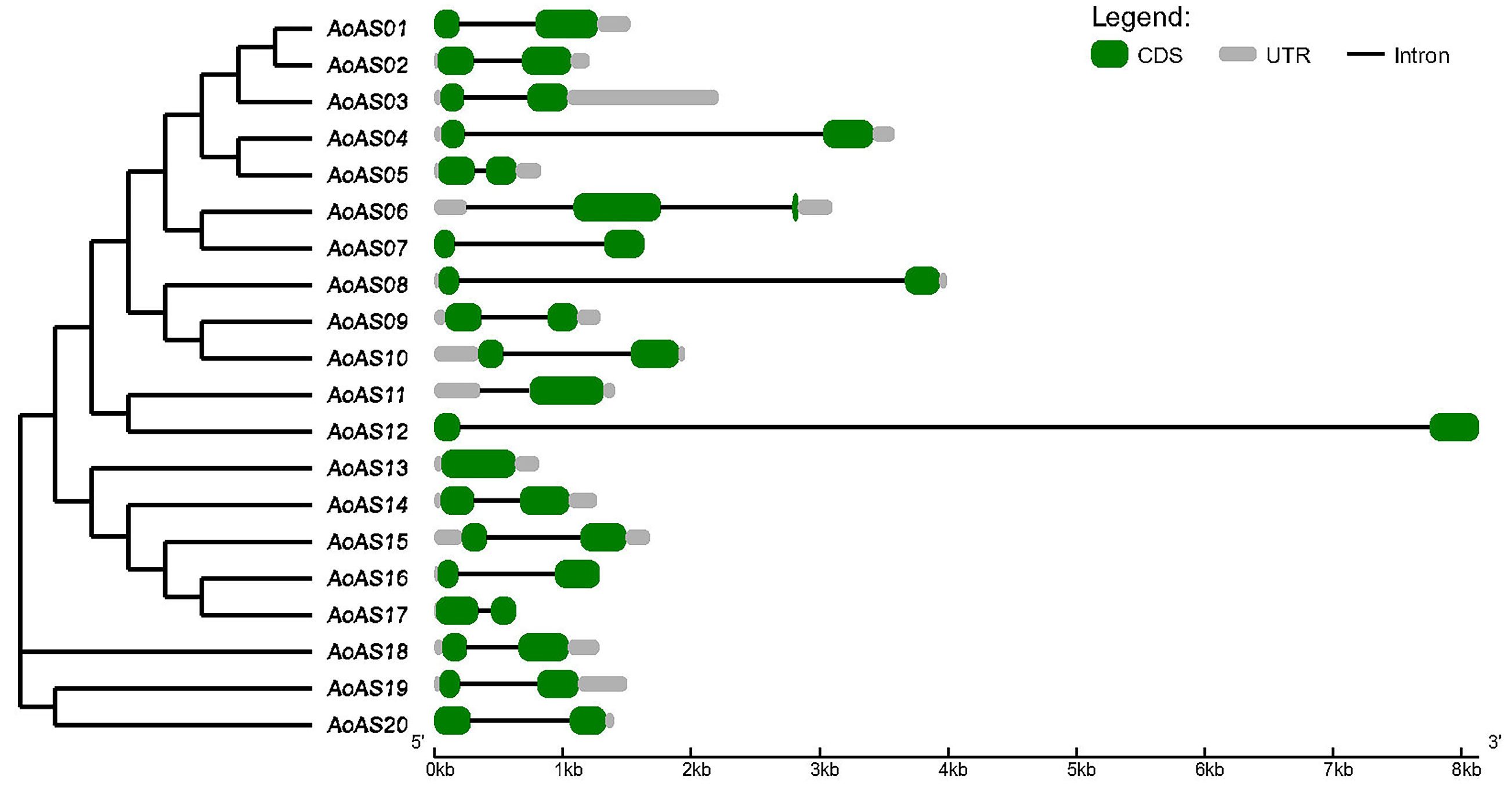
2.2. Structural Analysis and Chromosomal Localization of AoAS Genes
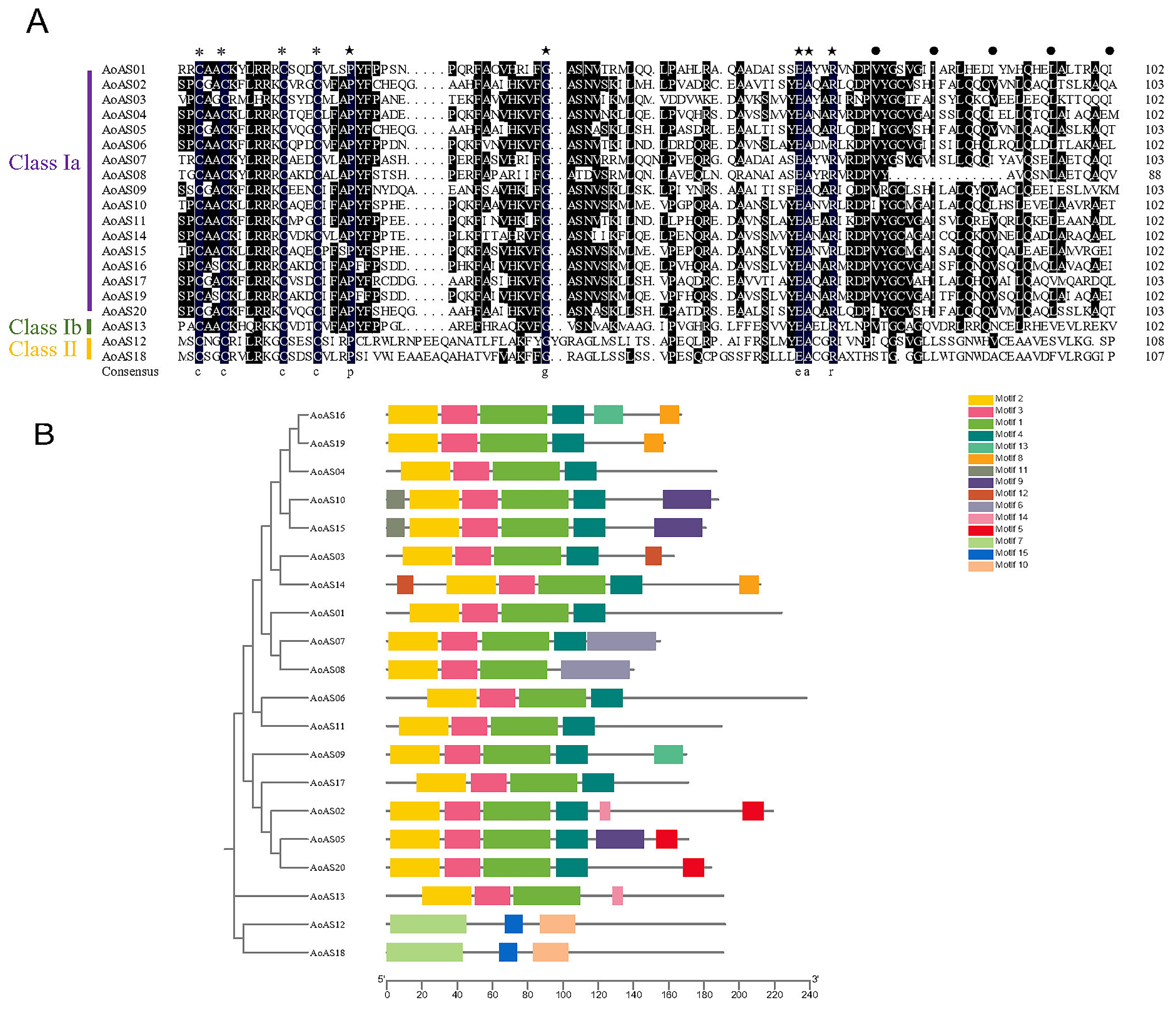
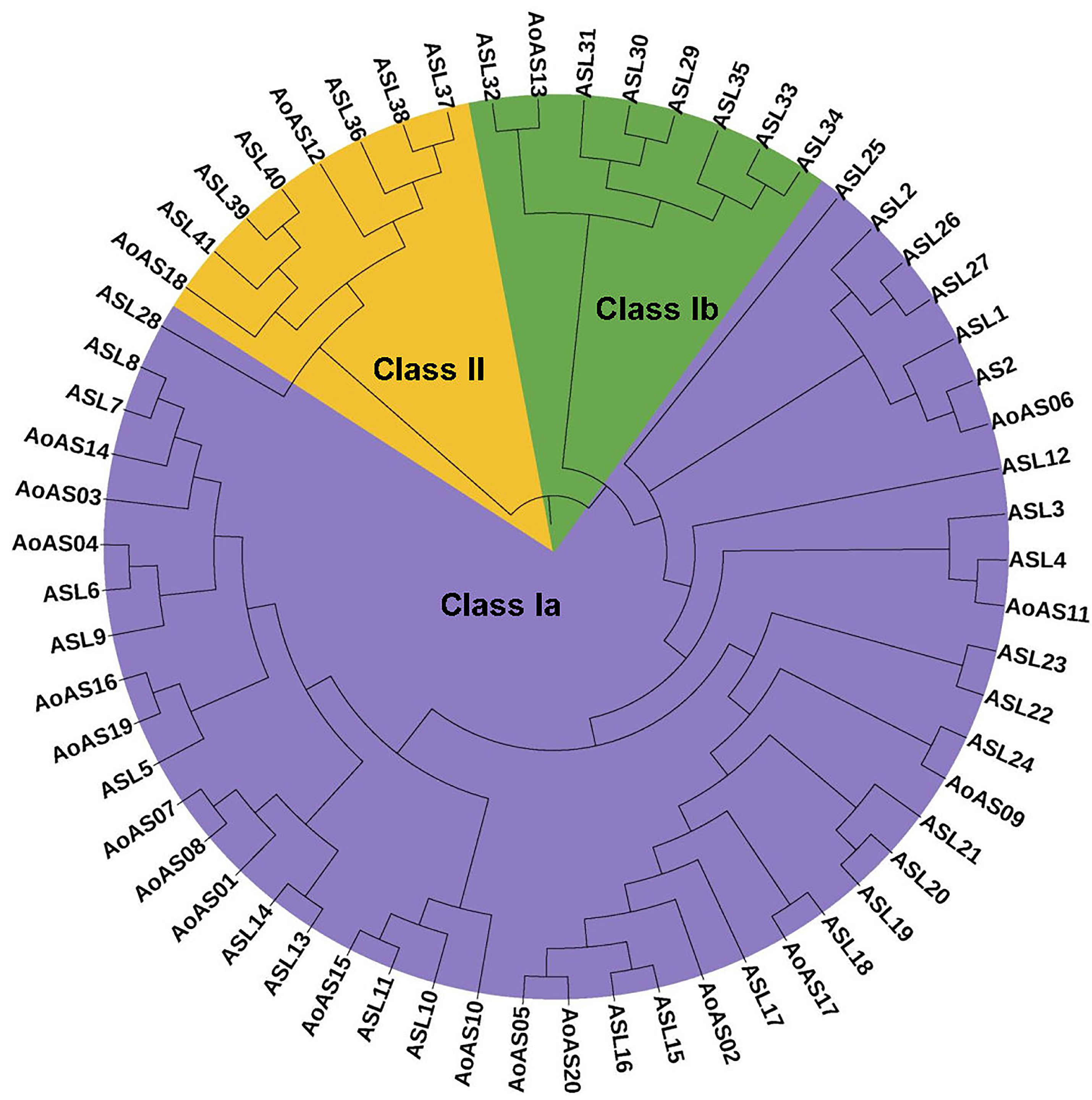
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis and Conserved Motif Characterization of AoAS Proteins
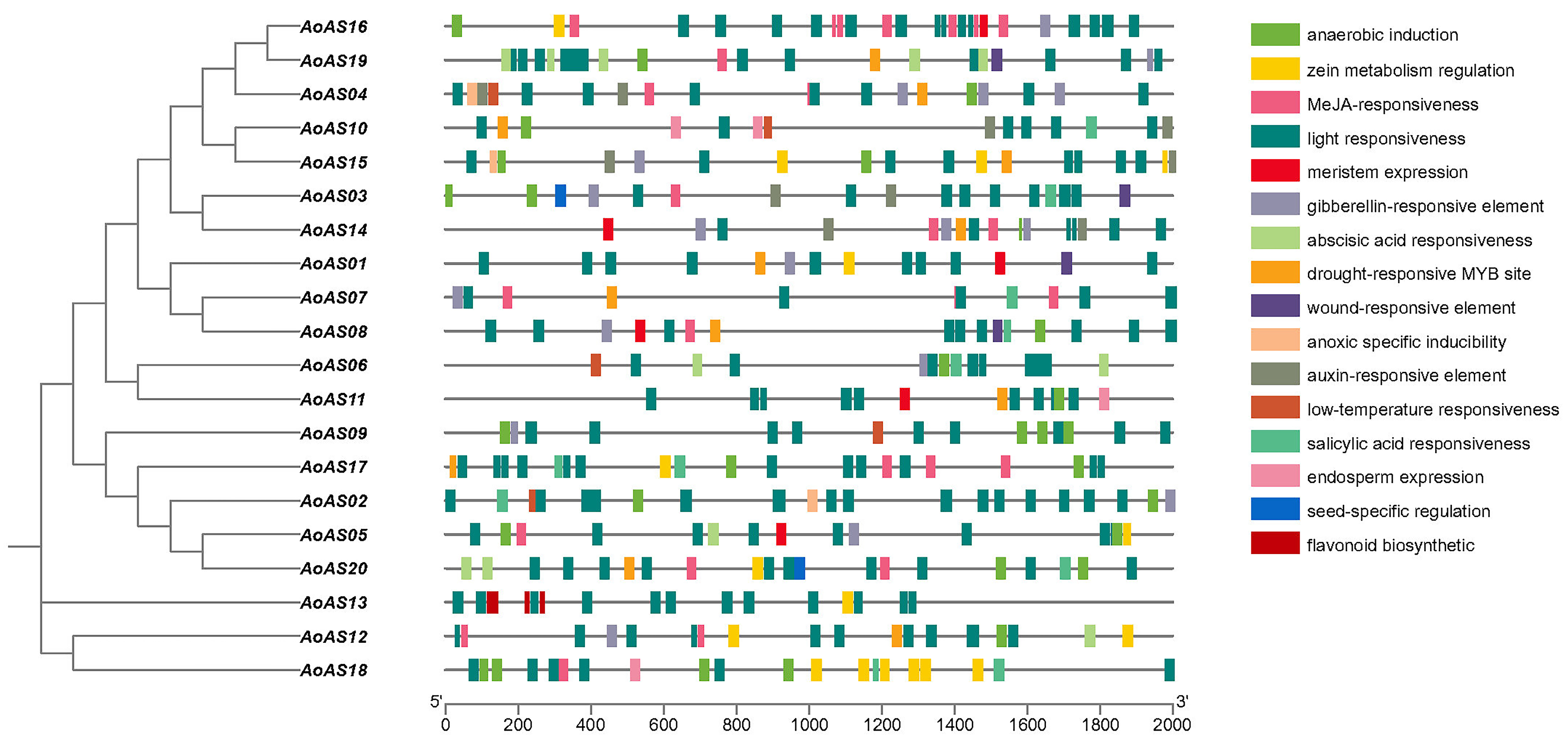
2.4. Cis-Acting Element Analysis of AoAS Gene Promoter Regions
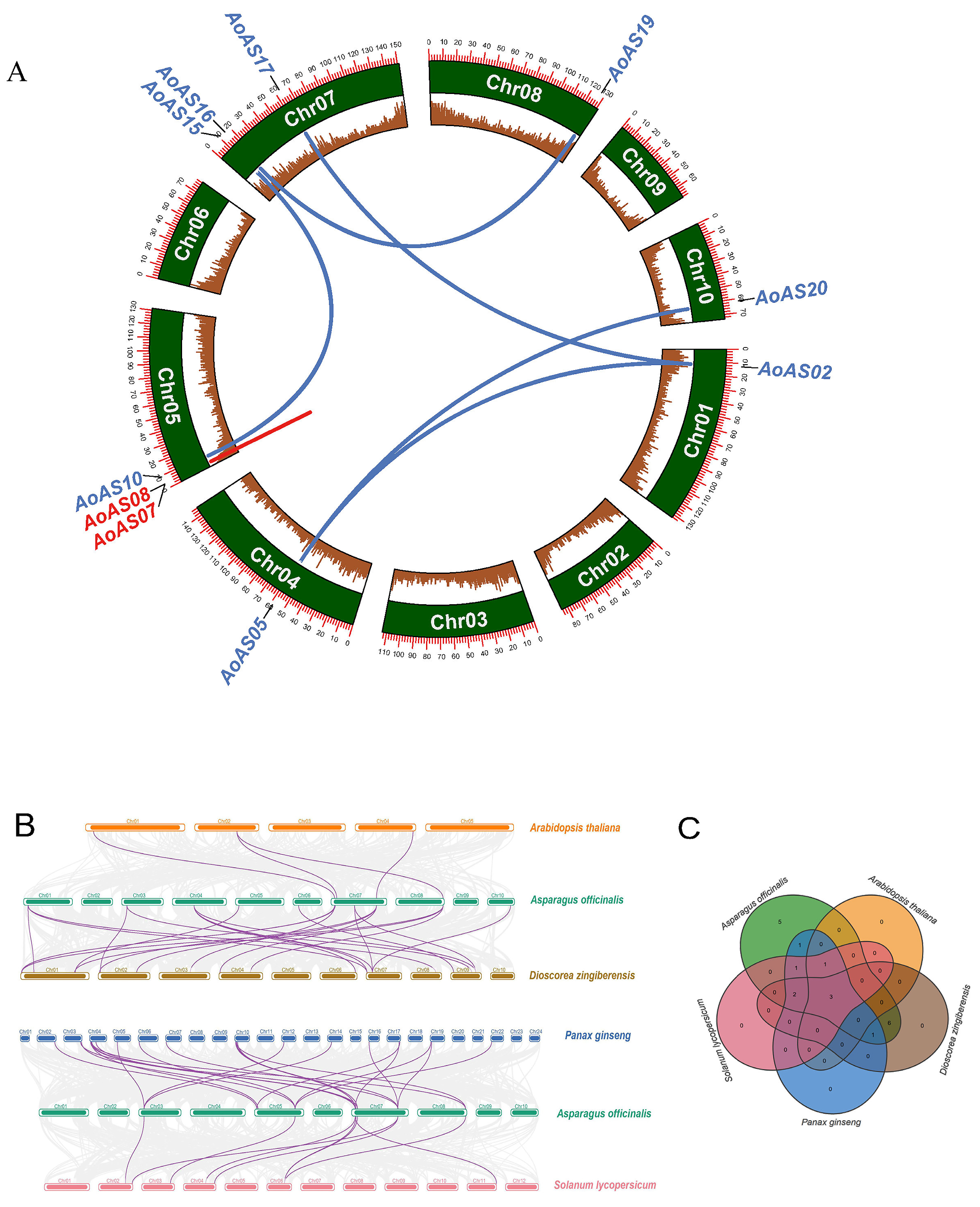
2.5. Analysis of Duplication Events and Synteny of AoAS Genes
2.6. Analysis of AoAS Protein Interaction Network
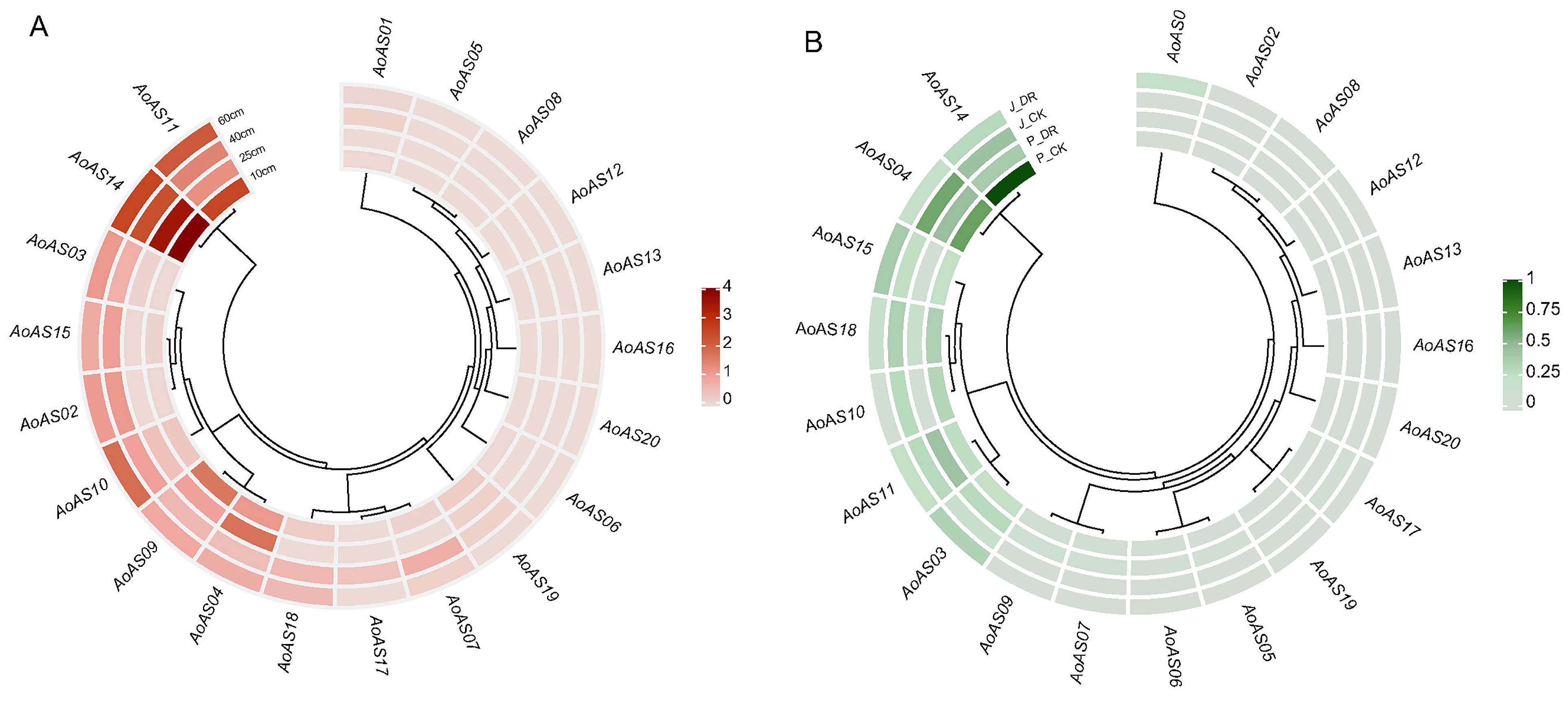
2.7. Expression Pattern Analysis of AoAS Genes
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Chromosome Localization of AS2/LOB Gene Family Members in Asparagus
3.2. Analysis of the Amino Acid Sequence of the Conserved Domain and Motifs in AoAS Proteins
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of AS2/LOB Proteins
3.4. Analysis of the Structure of AoAS Genes
3.5. Analysis of the Promoter Elements of AoAS Genes
3.6. Duplication Event and Synteny Analysis of AoAS Genes
3.7. Analysis of the Interaction of AoAS Proteins
3.8. Analysis of the Expression Pattern of AoAS Genes in the Stems of Asparagus at Different Growth Stages and Under Drought Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iwakawa, H.; Ueno, Y.; Semiarti, E.; Onouchi, H.; Kojima, S.; Tsukaya, H.; Hasebe, M.; Soma, T.; Ikezaki, M.; Machida, C. The ASYMMETRIC LEAVES2 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana, required for formation of a symmetric flat leaf lamina, encodes a member of a novel family of proteins characterized by cysteine repeats and a leucine zipper. Plant Cell Physiol. 2002, 43, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husbands, A.; Bell, E.M.; Shuai, B.; Smith, H.M.; Springer, P.S. LATERAL ORGAN BOUNDARIES defines a new family of DNA-binding transcription factors and can interact with specific bHLH proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 6663–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semiarti, E.; Ueno, Y.; Tsukaya, H.; Iwakawa, H.; Machida, C.; Machida, Y. The ASYMMETRIC LEAVES2 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana regulates formation of a symmetric lamina, establishment of venation and repression of meristem-related homeobox genes in leaves. Development 2001, 128, 1771–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimplet, J.; Pimentel, D.; Agudelo-Romero, P.; Martinez-Zapater, J.M.; Fortes, A.M. The LATERAL ORGAN BOUNDARIES Domain gene family in grapevine: Genome-wide characterization and expression analyses during developmental processes and stress responses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Luo, F.; Hochholdinger, F. LOB domain proteins: Beyond lateral organ boundaries. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuai, B.; Reynaga-Pena, C.G.; Springer, P.S. The lateral organ boundaries gene defines a novel, plant-specific gene family. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-J.; Kim, J. Identification of nuclear localization signal in asymmetric leaves2-like18/lateral organ boundaries domain16 (Asl18/lbd16) from Arabidopsis. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Bao, X. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the AS2/LOB gene family in physic nut. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1504093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Ji, Z.; Cao, Y.; Duan, Q.; Huang, J. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of AS2 genes in Brassica rapa reveal their potential roles in abiotic stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, C.; Liu, Y.-w.; Sun, L.; Wang, H.-j.; Dong, X.; Li, X.; Feng, R.-y. Identification and expression analysis of the AS2 gene family under abiotic stress in Solanum tuberosum L. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2020, 6, 1498–1507. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Machida, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Sasabe, M.; Iwakawa, H.; Kojima, S.; Machida, C. Arabidopsis ASYMMETRIC LEAVES2 (AS2): Roles in plant morphogenesis, cell division, and pathogenesis. J. Plant Res. 2022, 135, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.-J.; Wang, J.; Lin, S.; Tian, Z.; Zhou, K.; Luan, H.-y.; Lyu, C.; Zhang, X.-Z.; Xu, R.-G. A genome-wide analysis of the ASYMMETRIC LEAVES2/LATERAL ORGAN BOUNDARIES (AS2/LOB) gene family in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B 2016, 17, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Huang, Z.; Ma, R.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yrjälä, K. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of LBD transcription factor genes in Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Zeng, L.; Chen, X.; Rong, H.; Wu, J.; Batley, J.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y. Genome-wide analysis of the lateral organ boundaries domain gene family in Brassica napus. Genes 2020, 11, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, G.; Tohge, T.; Matsuda, F.; Saito, K.; Scheible, W.-R.d. Members of the LBD family of transcription factors repress anthocyanin synthesis and affect additional nitrogen responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 3567–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; He, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Xiang, Y. PheLBD29, an LBD transcription factor from Moso bamboo, causes leaf curvature and enhances tolerance to drought stress in transgenic Arabidopsis. J. Plant Physiol. 2023, 280, 153865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, K.; Lyu, Y. Functional study on the key gene LaLBD37 related to the lily bulblets formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, R.; Wu, Z.; Xu, S.; Hou, H.; Zhang, D.; Chen, F.; Teng, N. A novel lateral organ boundary-domain factor CmLBD2 positively regulates pollen development by activating CmACOS5 in Chrysanthemum morifolium. Plant Cell Physiol. 2021, 62, 1687–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, R.-M.; Yang, N.; Liu, C.-F.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Zhuang, J. CsLBD37, a LBD/ASL transcription factor, affects nitrate response and flowering of tea plant. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 306, 111457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; An, X.-H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Liu, R.; Li, C.; Tian, Y.; You, C.; Wang, X.-F. Cloning and functional identification of apple LATERAL ORGAN BOUNDARY DOMAIN 3 (LBD3) transcription factor in the regulation of drought and salt stress. Planta 2024, 259, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ji, X.; Luo, C.; Song, X.; Leng, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Fang, J.; Ren, Y. VvLBD39, a grape LBD transcription factor, regulates plant response to salt and drought stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2024, 226, 105918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, N.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Lu, L.; Wang, C. The bioactive compounds and biological functions of Asparagus officinalis L.—A review. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 65, 103727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegiou, E.; Mumm, R.; Acharya, P.; de Vos, R.C.H.; Hall, R.D. Green and White Asparagus (Asparagus officinalis): A Source of Developmental, Chemical and Urinary Intrigue. Metabolites 2019, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, A.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, X. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the NAC transcription factor gene family in garden asparagus (Asparagus officinalis). Genes 2022, 13, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Nasim, N.; Pudhuvai, B.; Koul, B.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Sethi, L.; Dey, N. Plant synthetic promoters: Advancement and prospective. Agriculture 2023, 13, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; Zhang, L.-M.; Xu, J.-J.; Zhu, J.-X.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.-J.; Xu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Li, C.-H.; Mu, Z.-S. Basic leucine zipper (bZIP) family in asparagus (Asparagus officinalis): Genome-wide identification, evolutionary, structure, collinearity, and expression analyses under abiotic stress at the seeding stage. J. Plant Interact. 2023, 18, 2268627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, T.J.; Eddy, S.R. nhmmer: DNA homology search with profile HMMs. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2487–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; Von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ødum, M.T.; Teufel, F.; Thumuluri, V.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Johansen, A.R.; Winther, O.; Nielsen, H. DeepLoc 2.1: Multi-label membrane protein type prediction using protein language models. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, gkae237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Aluko, O.O.; Wu, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G. MG2C: A user-friendly online tool for drawing genetic maps. Mol. Hortic. 2021, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Chen, P.; Li, M.; Lei, F.; Lu, W.; Jiang, C.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zheng, Y. Physiological and transcriptome analysis of changes in endogenous hormone and sugar content during the formation of tender asparagus stems. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Han, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Liang, Y.; Cao, Y. Integrated analysis of transcriptomics and metabolomics of garden asparagus (Asparagus officinalis L.) under drought stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 21 November 2025).
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.-C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchy, N.; Lehti-Shiu, M.; Shiu, S.-H. Evolution of gene duplication in plants. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 2294–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, N.A. Two genomes are better than one: Widespread paleopolyploidy in plants and evolutionary effects. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirakawa, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Fukuda, H. TDIF peptide signaling regulates vascular stem cell proliferation via the WOX4 homeobox gene in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2618–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galibina, N.A.; Moshchenskaya, Y.L.; Tarelkina, T.V.; Nikerova, K.M.; Korzhenevskii, M.A.; Serkova, A.A.; Afoshin, N.V.; Semenova, L.I.; Ivanova, D.S.; Guljaeva, E.N. Identification and expression Profile of CLE41/44-PXY-WOX genes in adult trees Pinus sylvestris L. trunk tissues during Cambial Activity. Plants 2023, 12, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, S.; Wang, J. Distinct transgenic effects of poplar TDIF genes on vascular development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2018, 37, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendelman, A.; Stav, R.; Zemach, H.; Arazi, T. The tomato NAC transcription factor SlNAM2 is involved in flower-boundary morphogenesis. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 5497–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepworth, S.R.; Pautot, V.A. Beyond the divide: Boundaries for patterning and stem cell regulation in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narise, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Baba, S.; Shimojima, M.; Masuda, S.; Fukaki, H.; Ohta, H. Involvement of auxin signaling mediated by IAA14 and ARF7/19 in membrane lipid remodeling during phosphate starvation. Plant Mol. Biol. 2010, 72, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Kim, J. EXPANSINA17 up-regulated by LBD18/ASL20 promotes lateral root formation during the auxin response. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, 1600–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Scheres, B. PLETHORA transcription factors orchestrate de novo organ patterning during Arabidopsis lateral root outgrowth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11709–11714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Lin, W.-c.; Huang, T.; Poethig, R.S.; Springer, P.S.; Kerstetter, R.A. KANADI1 regulates adaxial–abaxial polarity in Arabidopsis by directly repressing the transcription of ASYMMETRIC LEAVES2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16392–16397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertran Garcia de Olalla, E.; Cerise, M.; Rodríguez-Maroto, G.; Casanova-Ferrer, P.; Vayssières, A.; Severing, E.; López Sampere, Y.; Wang, K.; Schäfer, S.; Formosa-Jordan, P. Coordination of shoot apical meristem shape and identity by APETALA2 during floral transition in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.-L.; Shen, Y.; Xia, X.; Guo, H.; Li, Z. Transcription factor NAC075 delays leaf senescence by deterring reactive oxygen species accumulation in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 634040. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wan, Q.; Zhai, N.; Xie, D.; Liu, W.; Xu, L. WOX11: The founder of plant organ regeneration. Cell Regen. 2023, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhong, L.Y.; Chao, Z.F.; Gao, Y.Q.; Han, M.L.; Xu, L.; Chao, D.Y. Phytochrome B inhibits darkness--induced hypocotyl adventitious root formation by stabilizing IAA14 and suppressing ARF7 and ARF19. Plant J. 2021, 105, 1689–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanderbali, A.S.; He, F.; Soltis, P.S.; Soltis, D.E. Out of the water: Origin and diversification of the LBD gene family. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 1996–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkess, A.; Zhou, J.; Xu, C.; Bowers, J.E.; Van der Hulst, R.; Ayyampalayam, S.; Mercati, F.; Riccardi, P.; McKain, M.R.; Kakrana, A.; et al. The asparagus genome sheds light on the origin and evolution of a young Y chromosome. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkess, A.; Mercati, F.; Abbate, L.; McKain, M.; Pires, J.C.; Sala, T.; Sunseri, F.; Falavigna, A.; Leebens-Mack, J. Retrotransposon Proliferation Coincident with the Evolution of Dioecy in Asparagus. G3 2016, 6, 2679–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Lin, Z.; Jin, J.; Zhu, W.; Gao, J.; Li, J.; Xie, Q.; Lu, C.; Zhu, G.; Yang, F. Genome-wide identification and functional characterization of LBD gene family in four Cymbidium species (Orchidaceae) and potential regulatory role of CsiLBD27 in floral development of Cymbidium sinense. BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Deutsch, M. Intron—Exon structures of eukaryotic model organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V.; Csuros, M.; Rogozin, I.B. Whence genes in pieces: Reconstruction of the exon–intron gene structures of the last eukaryotic common ancestor and other ancestral eukaryotes. WIREs RNA 2013, 4, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JiaYan, W.; JingFa, X.; LingPing, W.; Jun, Z.; HongYan, Y.; ShuangXiu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jun, Y. Systematic analysis of intron size and abundance parameters in diverse lineages. Sci. China Life Sci. 2013, 56, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.-B.; Brendel, V. Genomewide comparative analysis of alternative splicing in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7175–7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marand, A.P.; Eveland, A.L.; Kaufmann, K.; Springer, N.M. cis-Regulatory elements in plant development, adaptation, and evolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2023, 74, 111–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.C.; Mähl, K.; Kappel, C.; Dakhiya, Y.; Sampathkumar, A.; Sicard, A.; Lenhard, M. Altered interactions between cis-regulatory elements partially resolve BLADE-ON-PETIOLE genetic redundancy in Capsella rubella. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 4637–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Luo, H.; Chen, Z.; Amin, B.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Wu, S.; Salmen, S.H.; Alharbi, S.A.; Fang, Z. Rice promoter editing: An efficient genetic improvement strategy. Rice 2024, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, E.; Wang, J.; Riaz, M.; Zhang, L.; Zuo, K. Designing artificial synthetic promoters for accurate, smart, and versatile gene expression in plants. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 100558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tian, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, J.; Fan, Y. Identification and characterization of promoters specifically and strongly expressed in maize embryos. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2014, 12, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-F.; Gao, W.-J.; Zhao, X.-P.; Dong, T.-Y.; Deng, C.-L.; Lu, L.-D. Analysis of transposable elements in the genome of Asparagus officinalis from high coverage sequence data. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feschotte, C.; Jiang, N.; Wessler, S.R. Plant transposable elements: Where genetics meets genomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnable, P.S.; Ware, D.; Fulton, R.S.; Stein, J.C.; Wei, F.; Pasternak, S.; Liang, C.; Zhang, J.; Fulton, L.; Graves, T.A. The B73 maize genome: Complexity, diversity, and dynamics. Science 2009, 326, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, T.V.; Uzunović, J.; Wright, S.I. Coevolution between transposable elements and recombination. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2017, 372, 20160458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, C.J.; Choi, K. Heterogeneous transposable elements as silencers, enhancers and targets of meiotic recombination. Chromosoma 2019, 128, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-F.; Su, T.; Cheng, G.-Q.; Wang, B.-X.; Li, X.; Deng, C.-L.; Gao, W.-J. Chromosome evolution in connection with repetitive sequences and epigenetics in plants. Genes 2017, 8, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Li, Q.; Yin, H.; Qi, K.; Li, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Paterson, A.H. Gene duplication and evolution in recurring polyploidization–diploidization cycles in plants. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Xu, P.; Jing, X.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Li, X. Decipher the ancestry of the plant-specific LBD gene family. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, Y.; Iwakawa, H.; Machida, Y.; Machida, C. Characterization of genes in the ASYMMETRIC LEAVES2/LATERAL ORGAN BOUNDARIES (AS2/LOB) family in Arabidopsis thaliana, and functional and molecular comparisons between AS2 and other family members. Plant J. 2009, 58, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, H.; Tan, X.; Ficklin, S.P.; Feltus, F.A.; Paterson, A.H. Modes of gene duplication contribute differently to genetic novelty and redundancy, but show parallels across divergent angiosperms. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rody, H.V.; Baute, G.J.; Rieseberg, L.H.; Oliveira, L.O. Both mechanism and age of duplications contribute to biased gene retention patterns in plants. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Schranz, M.E. Network approaches for plant phylogenomic synteny analysis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 36, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group, A.P.; Chase, M.W.; Christenhusz, M.J.; Fay, M.F.; Byng, J.; Judd, W.; Soltis, D.; Mabberley, D.; Sennikov, A.; Soltis, P. An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG IV. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2016, 181, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chileh-Chelh, T.; López-Ruiz, R.; García-Cervantes, A.M.; Rodríguez-García, I.; Rincón-Cervera, M.A.; Ezzaitouni, M.; Guil-Guerrero, J.L. Cytotoxicity and Chemotaxonomic Significance of Saponins from Wild and Cultured Asparagus Shoots. Molecules 2024, 29, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.x.; Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Ye, S.; Luan, Y. Identification of genetic variants controlling diosgenin content in Dioscorea zingiberensis tuber by genome-wide association study. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Wang, R.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Z. Ginsenosides in Panax genus and their biosynthesis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 1813–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Na, H.; Kwack, Y.; Chun, C. Secondary metabolite profiling in various parts of tomato plants. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, E.; Tohge, T.; Zuther, E.; Fernie, A.R.; Hincha, D.K. Flavonoids are determinants of freezing tolerance and cold acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.V.T.; Lee, S.; Cho, H.; Choi, K.; Hwang, I. The LBD11-ROS feedback regulatory loop modulates vascular cambium proliferation and secondary growth in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1131–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Han, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chen, S.; Ma, C. A systems approach to a spatio-temporal understanding of the drought stress response in maize. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wan, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Xiao, J.; Chen, K.; Han, X.; Chen, Y. Spatiotemporal transcriptomics reveals key gene regulation for grain yield and quality in wheat. Genome Biol. 2025, 26, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; An, H.; Tao, J. Unlocking the molecular secrets of Paeonia plants: Advances in key gene mining and molecular breeding technology. Hortic. Res. 2025, 12, uhaf090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, P.; Zong, H.; Han, Y.; Zhang, W.; Tian, Z.; Zhou, B.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, L. Two Melanthiaceae genomes with dramatic size difference provide insights into giant genome evolution and maintenance. Nat. Plants 2025, 11, 1500–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, X.; Li, Y.; Zhong, S.-F.; Huang, W.-N.; Zeng, J.; Zuo, Q.; Li, S.; Sun, P.; Tao, S.; Huang, L.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the AS2/LOB Transcription Factor Family in Asparagus officinalis. Genes 2025, 16, 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121411
Ye X, Li Y, Zhong S-F, Huang W-N, Zeng J, Zuo Q, Li S, Sun P, Tao S, Huang L, et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the AS2/LOB Transcription Factor Family in Asparagus officinalis. Genes. 2025; 16(12):1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121411
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Xiao, Yu Li, Sheng-Fu Zhong, Wei-Nian Huang, Jing Zeng, Qian Zuo, Shu Li, Pei Sun, Shan Tao, Ling Huang, and et al. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the AS2/LOB Transcription Factor Family in Asparagus officinalis" Genes 16, no. 12: 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121411
APA StyleYe, X., Li, Y., Zhong, S.-F., Huang, W.-N., Zeng, J., Zuo, Q., Li, S., Sun, P., Tao, S., Huang, L., Zhong, M.-Z., Zhao, W.-J., Shen, Y.-X., Tao, Y., & Deng, J.-Q. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the AS2/LOB Transcription Factor Family in Asparagus officinalis. Genes, 16(12), 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121411





