GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Solid Tumour Therapy: Exploring Their Anticancer Potential and Underlying Molecular Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
3. Materials and Methods
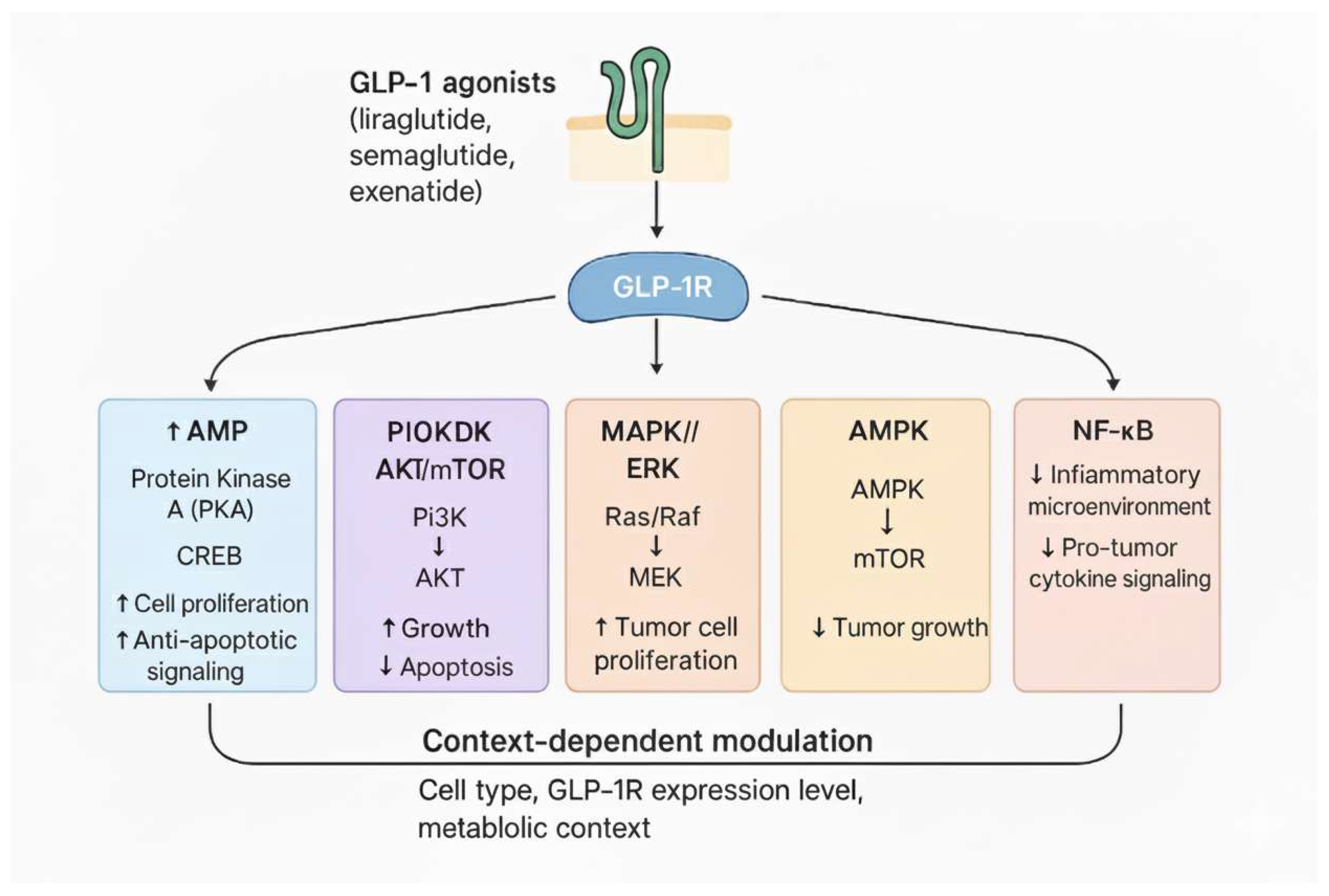
4. Molecular Mechanisms of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Cancer
4.1. Influences on Cellular Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Angiogenesis
4.2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
5. Role of GLP-1 Agonists in Cancer: Preclinical Evidence
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, C.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Z. GLP-1 receptor agonists and risk of cancer in type 2 diabetes: An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Endocrine 2019, 66, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Li, Y.; Lee, Y.A.; Lu, Y.; George, T.J.; Donahoo, W.T.; Lee, K.P.; Nakshatri, H.; Allen, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Cancer Risk in Adults With Obesity. JAMA Oncol. 2025, 11, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Saha, S.; Mahapatra, S.; Khanra, S.; Mishra, B.; Swain, B.; Malhotra, D.; Saha, S.; Panda, V.K.; Kumari, K.; Jena, S.; et al. Decoding breast cancer treatment resistance through genetic, epigenetic, and immune-regulatory mechanisms: From molecular insights to translational perspectives. Cancer Drug Resist. 2025, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Makena, M.R.; Ranjan, A.; Thirumala, V.; Reddy, A.P. Cancer stem cells: Road to therapeutic resistance and strategies to overcome resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomiyama, T.; Yanase, T. GLP-1 receptor agonist as treatment for cancer as well as diabetes: Beyond blood glucose control. Expert. Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 11, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.; Hyde, A.; Davidson, T.L. Reframing appetitive reinforcement learning and reward valuation as effects mediated by hippocampal-dependent behavioral inhibition. Nutr. Res. 2020, 79, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, M.; Wen, Z.; Lu, Z.; Cui, L.; Fu, C.; Xue, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Beyond Their Pancreatic Effects. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 721135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Parkes, D.G.; Mace, K.F.; Trautmann, M.E. Discovery and development of exenatide: The first antidiabetic agent to leverage the multiple benefits of the incretin hormone, GLP-1. Expert. Opin. Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 219–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; Quast, D.R.; Wefers, J.; Meier, J.J. GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes-state-of-the-art. Mol. Metab. 2021, 46, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Drab, S.R. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for Type 2 Diabetes: A Clinical Update of Safety and Efficacy. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2016, 12, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ruggiero, R.; Mascolo, A.; Spezzaferri, A.; Carpentieri, C.; Torella, D.; Sportiello, L.; Rossi, F.; Paolisso, G.; Capuano, A. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Suicidal Ideation: Analysis of Real-Word Data Collected in the European Pharmacovigilance Database. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, X.N.; Bu, H.M.; Ma, X.H.; Lu, S.; Zhao, S.; Cui, Y.L.; Sun, J. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Analogues Inhibit Proliferation and Increase Apoptosis of Human Prostate Cancer Cells in vitro. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2017, 125, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.D.; Finan, B.; Bloom, S.R.; D’Alessio, D.; Drucker, D.J.; Flatt, P.R.; Fritsche, A.; Gribble, F.; Grill, H.J.; Habener, J.F.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Mol. Metab. 2019, 30, 72–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ji, L.; He, X.; Min, X.; Yang, H.; Wu, W.; Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Mei, A. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in neoplastic diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1465881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bjerre Knudsen, L.; Madsen, L.W.; Andersen, S.; Almholt, K.; de Boer, A.S.; Drucker, D.J.; Gotfredsen, C.; Egerod, F.L.; Hegelund, A.C.; Jacobsen, H.; et al. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonists activate rodent thyroid C-cells causing calcitonin release and C-cell proliferation. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1473–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.J.; Jiang, X.; Hu, L.J.; Yang, L.; Deng, L.D.; Wang, Y.P.; Ren, Z.P. Activation of GLP-1 receptor enhances the chemosensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2020, 64, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, B.; Bin Zafar, M.D.; Changez, M.I.K.; Abdullah, M.; Safwan, M.; Qamar, B.; Shinwari, A.; Rai, S. Exploring the potential impact of GLP-1 receptor agonists in cancer therapy. Minerva Endocrinol. 2023, 50, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.; Ding, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, A.; Liu, Z.; Wong, H.Z.H.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Luo, P. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists and cancer risk: Advancing precision medicine through mechanistic understanding and clinical evidence. Biomark. Res. 2025, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hardie, D.G.; Scott, J.W.; Pan, D.A.; Hudson, E.R. Management of cellular energy by the AMP-activated protein kinase system. FEBS Lett. 2003, 546, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowlands, J.; Heng, J.; Newsholme, P.; Carlessi, R. Pleiotropic Effects of GLP-1 and Analogs on Cell Signaling, Metabolism, and Function. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Buteau, J.; Spatz, M.L.; Accili, D. Transcription factor FoxO1 mediates glucagon-like peptide-1 effects on pancreatic beta-cell mass. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buteau, J.; Roduit, R.; Susini, S.; Prentki, M. Glucagon-like peptide-1 promotes DNA synthesis, activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and increases transcription factor pancreatic and duodenal homeobox gene 1 (PDX-1) DNA binding activity in beta (INS-1)-cells. Diabetologia 1999, 42, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastien-Dionne, P.O.; Valenti, L.; Kon, N.; Gu, W.; Buteau, J. Glucagon-like peptide 1 inhibits the sirtuin deacetylase SirT1 to stimulate pancreatic β-cell mass expansion. Diabetes 2011, 60, 3217–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Shao, S. Exenatide regulates Th17/Treg balance via PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 pathway in db/db mice. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, D.; Ma, M.; Liu, Y. Protective Effects of Incretin Against Age-Related Diseases. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosowska, A.; Gallego-Colon, E.; Garczorz, W.; Kych-Ratuszny, A.; Aghdam, M.R.F.; Woz Niak, M.; Witek, A.; Wróblewska-Czech, A.; Cygal, A.; Wojnar, J.; et al. Exenatide modulates tumor-endothelial cell interactions in human ovarian cancer cells. Endocr. Connect. 2017, 6, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chang, T.J.; Tseng, H.C.; Liu, M.W.; Chang, Y.C.; Hsieh, M.L.; Chuang, L.M. Glucagon-like peptide-1 prevents methylglyoxal-induced apoptosis of beta cells through improving mitochondrial function and suppressing prolonged AMPK activation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23403, Erratum in Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuamnaichati, N.; Parichatikanond, W.; Mangmool, S. Cardioprotective Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (9-36) Against Oxidative Injury in H9c2 Cardiomyoblasts: Potential Role of the PI3K/Akt/NOS Pathway. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 79, e50–e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdogdu, O.; Nathanson, D.; Sjöholm, A.; Nyström, T.; Zhang, Q. Exendin-4 stimulates proliferation of human coronary artery endothelial cells through eNOS-, PKA- and PI3K/Akt-dependent pathways and requires GLP-1 receptor. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2010, 325, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monami, M.; Nreu, B.; Scatena, A.; Cresci, B.; Andreozzi, F.; Sesti, G.; Mannucci, E. Safety issues with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer and cholelithiasis): Data from randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Huang, T.; Chen, A.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Shen, F.; Gu, X. Glucagon-like peptide 1 improves insulin resistance in vitro through anti-inflammation of macrophages. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2016, 49, e5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, X.; Huang, Q.; Feng, J.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L. GLP-1 alleviates NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent inflammation in perivascular adipose tissue by inhibiting the NF-κB signalling pathway. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 300060521992981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bray, J.J.H.; Foster-Davies, H.; Salem, A.; Hoole, A.L.; Obaid, D.R.; Halcox, J.P.J.; Stephens, J.W. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists improve biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 1806–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcidiacono, B.; Iiritano, S.; Nocera, A.; Possidente, K.; Nevolo, M.T.; Ventura, V.; Foti, D.; Chiefari, E.; Brunetti, A. Insulin resistance and cancer risk: An overview of the pathogenetic mechanisms. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 789174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Kaelber, D.C.; Xu, R.; Berger, N.A. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Colorectal Cancer Risk in Drug-Naive Patients With Type 2 Diabetes, With and Without Overweight/Obesity. JAMA Oncol. 2024, 10, 256–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dankner, R.; Murad, H.; Agay, N.; Olmer, L.; Freedman, L.S. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Pancreatic Cancer Risk in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2350408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, Y.S.; Jun, H.S. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of GLP-1-Based Therapies beyond Glucose Control. Mediators Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 3094642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Atasoy, O.; Anadol, E.; Yar Saglam, A.S.; Akdemir, E.Y.; Coskun, Y.S.; Atak, E.; Dincer, S.; Usta, D.D.; Emniyet Sert, A.; Kaplanoglu, G.T.; et al. Synergistic Potential of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer Treatment: A New Therapeutic Avenue (TROD-GROG 006). Curr. Radiopharm. 2025, 18, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Wei, R.; Xiu, D.; Tao, M.; Ke, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Hong, T. Activation of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor inhibits tumourigenicity and metastasis of human pancreatic cancer cells via PI3K/Akt pathway. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, G.; Peng, T.; Chen, Y.; Sha, L.; Dai, H.; Xiang, Y.; Zou, Z.; He, H.; Wang, S. Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists on Biological Behavior of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 901559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Espinosa De Ycaza, A.E.; Brito, J.P.; McCoy, R.G.; Shao, H.; Singh Ospina, N. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Thyroid Cancer: A Narrative Review. Thyroid 2024, 34, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Trakoonsenathong, R.; Kunprom, W.; Aphivatanasiri, C.; Yueangchantuek, P.; Pimkeeree, P.; Sorin, S.; Khawkhiaw, K.; Chiu, C.F.; Okada, S.; Wongkham, S.; et al. Liraglutide exhibits potential anti-tumor effects on the progression of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, Q.; Yin, D. Semaglutide Reprograms Macrophages via the GLP-1R/PPARG/ACSL1 Pathway to Suppress Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Growth. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 110, 2777–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Machida, A.; Suzuki, K.; Nakayama, T.; Miyagi, S.; Maekawa, Y.; Murakami, R.; Uematsu, M.; Kitaoka, T.; Oishi, A. Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist Stimulation Inhibits Laser-Induced Choroidal Neovascularization by Suppressing Intraocular Inflammation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2025, 66, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lu, C.; Xie, T.; Guo, X.; Wu, D.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist exendin-4 mitigates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 77, 105969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobo-Tovar, E.; Medel-Sánchez, A.; Durán-Castillo, C.; Guardado-Mendoza, R. Insulin resistance in cancer risk and prognosis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2025, 114, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cencioni, C.; Malatesta, S.; Vigiano Benedetti, V.; Licursi, V.; Perfetto, L.; Conte, F.; Ranieri, D.; Bartolazzi, A.; Kunkl, M.; Tuosto, L.; et al. The GLP-1R agonist semaglutide reshapes pancreatic cancer associated fibroblasts reducing collagen proline hydroxylation and favoring T lymphocyte infiltration. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2025, 44, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Eftekhari, S.; Montazeri, H.; Tarighi, P. Synergistic anti-tumor effects of Liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, along with Docetaxel on LNCaP prostate cancer cell line. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 878, 173102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroldi, F.; Lord, S.R. Window of opportunity clinical trial designs to study cancer metabolism. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, M.; Kim, S.C.; Kim, J.; Kim, B.H. Use of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Does Not Increase the Risk of Cancer in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. J. 2025, 49, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xu, D.; Nair, A.; Sigston, C.; Ho, C.; Li, J.; Yang, D.; Liao, X.; Chen, W.; Kuang, M.; Li, Y.; et al. Potential Roles of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1 RAs) in Nondiabetic Populations. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2022, 2022, 6820377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dian, Y.; Zeng, F.; Deng, G.; Lei, S. Association of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists with risk of cancers-evidence from a drug target Mendelian randomization and clinical trials. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 4688–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Drug Name | Brand Name | Year of Approval |
|---|---|---|
| Exenatide | Beyetta | 2009 |
| Liraglutide | Victoza | 2009 |
| Lixisenatide | Lyxumia | 2013 |
| Dulaglutide | Trulicity | 2014 |
| Semaglutide | Ozempic | 2018 |
| Tirzepatide | Mounjaro | 2024 |
| Category | GLP-1 RA Mechanism/Effect | Key Pathways and Details | Associated Cancer Types/Preclinical Models |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antitumor Activity | Inhibition of Cell Proliferation | Modulates oncogenic (MAPK/ERK) and tumour-suppressive (AMPK, p53) signals. | Breast, Prostate, Ovarian, Pancreatic, Colorectal, etc. |
| Inhibition of Growth & Metastasis | Reduces tumorigenicity and metastatic spread by inhibiting pathways like EMT. | Pancreatic Carcinoma (Liraglutide); iCCA (Liraglutide). | |
| Induction of Apoptosis | Modulates apoptotic cascades, including Caspase-3 activity. | Indicated as a modulated process. | |
| Synergy with Chemotherapy | Enhances efficacy when combined with standard agents (e.g., gemcitabine). | Pancreatic Carcinoma (Exendin-4 + Gemcitabine). | |
| Molecular Signalling | PI3K/Akt Modulation | Inhibition of this crucial survival pathway in cancer cells. | Proposed mechanism for effect in Pancreatic Carcinoma. |
| PKA and AMPK Modulation | Involved in regulating cell survival and metabolic stress response. | General mechanism of action. | |
| Anti-Inflammatory Effects | Suppression of Cytokine Release | Reduces pro-inflammatory mediators (TNF-β, IL-6, IL-1\beta). | Cancers linked to inflammation (e.g., Colorectal, Pancreatic). |
| Inhibition of Macrophage Infiltration | Reduces immune cells that promote the pro-tumour microenvironment. | General anti-inflammatory effect. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lucente, D.; Bellino, S.; La Salvia, A. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Solid Tumour Therapy: Exploring Their Anticancer Potential and Underlying Molecular Pathways. Genes 2025, 16, 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111352
Lucente D, Bellino S, La Salvia A. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Solid Tumour Therapy: Exploring Their Anticancer Potential and Underlying Molecular Pathways. Genes. 2025; 16(11):1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111352
Chicago/Turabian StyleLucente, Daniela, Stefania Bellino, and Anna La Salvia. 2025. "GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Solid Tumour Therapy: Exploring Their Anticancer Potential and Underlying Molecular Pathways" Genes 16, no. 11: 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111352
APA StyleLucente, D., Bellino, S., & La Salvia, A. (2025). GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Solid Tumour Therapy: Exploring Their Anticancer Potential and Underlying Molecular Pathways. Genes, 16(11), 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111352





