Whole-Exome Sequencing for Molecular Diagnosis of Paediatric Nephrotic Syndrome in Africa: A Call for Implementation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
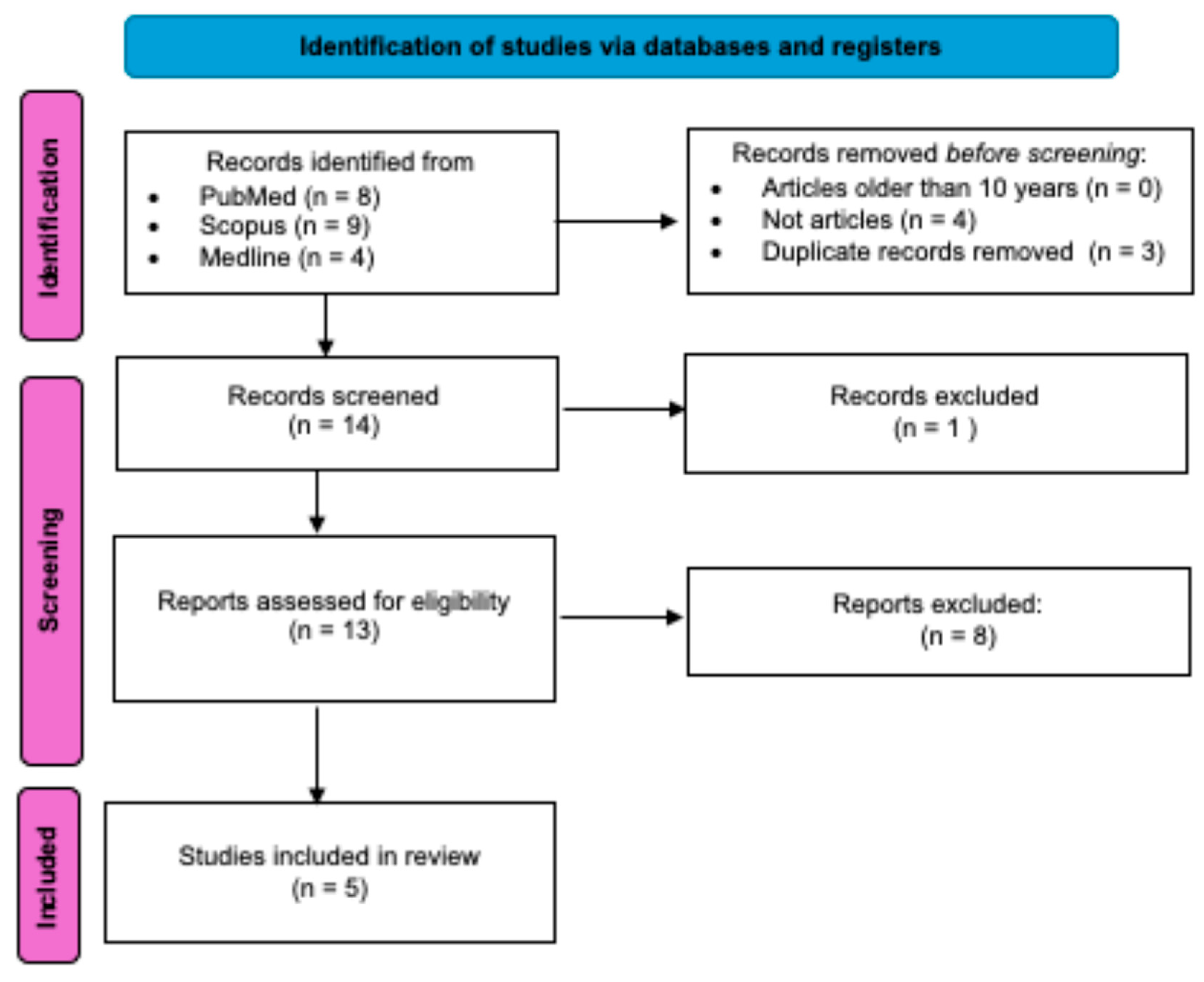
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
2.2. Screening and Selection of Studies
3. Results
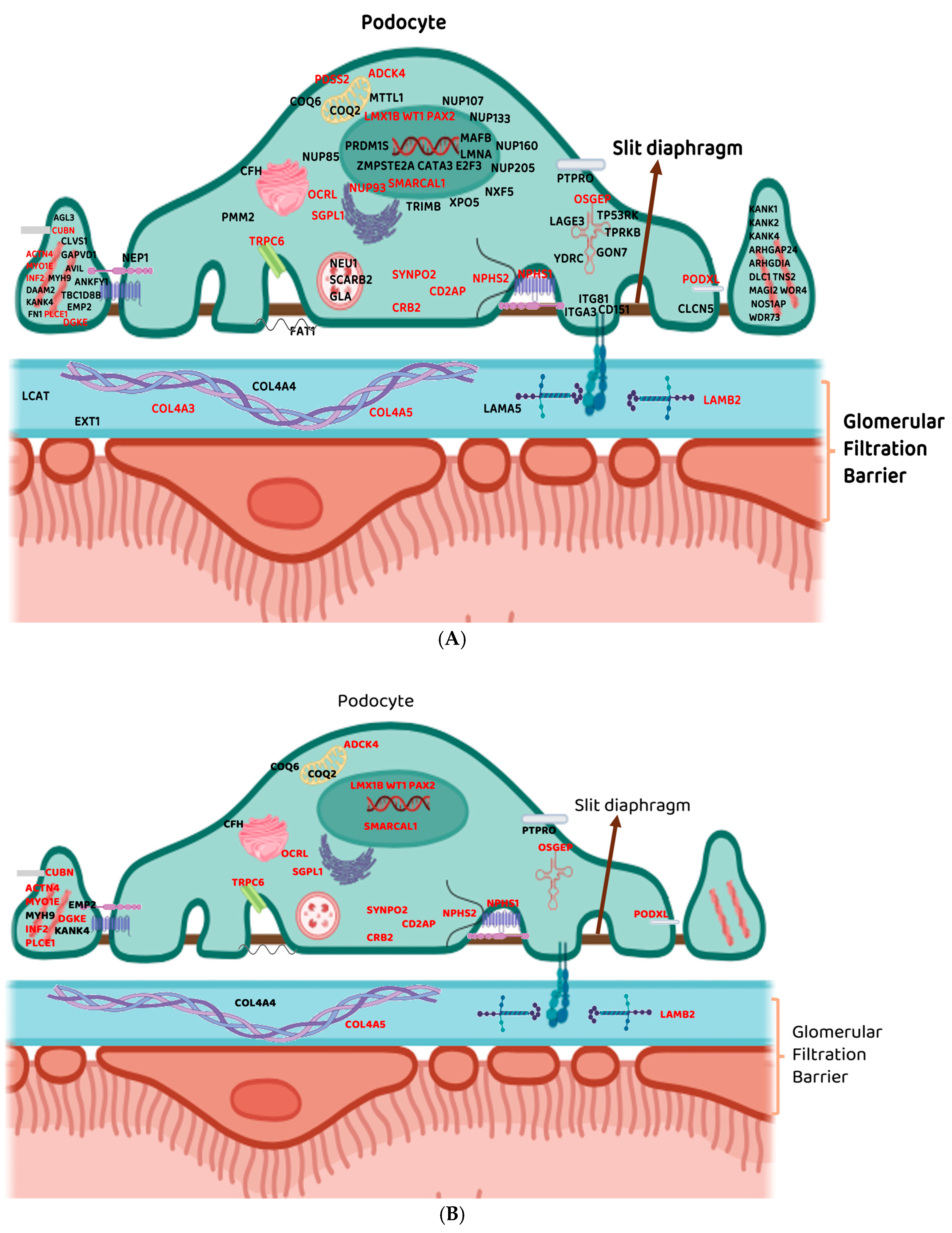
3.1. Commonly Reported Genes Across All the Retrieved Studies Utilising Next-Generation Sequencing Techniques
3.1.1. NPHS1 and NPHS2
3.1.2. PLCE1 and WT1
3.2. Other Commonly Reported Gene Across All the Retrieved Studies Utilising Next-Generation Sequencing Techniques
3.2.1. COL4A3 and COL4A5
3.2.2. TRPC6
3.2.3. LAMB2
3.3. Genes Specific to Each Retrieved Study Identified Using Next-Generation Sequencing Techniques
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Presenting a Strong Call for Utilisation of WES and Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bagga, A.; Mantan, M. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children. Indian J. Med. Res. 2005, 122, 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Tapia, C.; Bashir, K. Nephrotic Syndrome; Updated 2023 May 29. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470444/ (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Floege, J.; Gibson, K.L.; Vivarelli, M.; Liew, A.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Rovin, B.H. KDIGO 2025 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Nephrotic Syndrome in Children. Kidney Int. 2025, 107, S241–S289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Eckardt, K.U.; Dorman, N.M.; Christiansen, S.L.; Cheung, M.; Jadoul, M.; Winkelmayer, W.C. Nomenclature for Kidney Function and Disease: Executive Summary and Glossary from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Consensus Conference. Kidney Dis. 2020, 6, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanchlani, R.; Parekh, R.S. Ethnic Differences in Childhood Nephrotic Syndrome. Front. Pediatr. 2016, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCloskey, O.; Maxwell, A.P. Diagnosis and Management of Nephrotic Syndrome. Practitioner 2017, 261, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olowu, W.A.; Ademola, A.; Ajite, A.B.; Saad, Y.M. Childhood Nephrotic Syndrome in Tropical Africa: Then and Now. Paediatr. Int. Child. Health 2017, 37, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wine, R.; Vasilevska-Ristovska, J.; Banh, T.; Knott, J.; Noone, D.; Gbadegesin, R.; Ilori, T.O.; Okafor, H.U.; Furia, F.; Ulasi, I.; et al. Trends in the Epidemiology of Childhood Nephrotic Syndrome in Africa: A Systematic Review. Glob. Epidemiol. 2021, 3, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Hao, J.; Fu, T.; Du, Y. Evaluating the Quality of Life of 231 Children With Primary Nephrotic Syndrome and Assessing Parental Awareness of the Disease. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 745444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Greenbaum, L.A. Nephrotic Syndrome. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 66, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkes, B.G.; Mucha, B.; Vlangos, C.N.; Gbadegesin, R.; Liu, J.; Hasselbacher, K.; Hangan, D.; Ozaltin, F.; Zenker, M.; Hildebrandt, F. Nephrotic Syndrome in the First Year of Life: Two Thirds of Cases Are Caused by Mutations in 4 Genes (NPHS1, NPHS2, WT1, and LAMB2). Pediatrics 2007, 119, e907–e909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérody, S.; Heidet, L.; Gribouval, O.; Harambat, J.; Niaudet, P.; Baudouin, V.; Bacchetta, J.; Boudaillez, B.; Dehennault, M.; De Parscau, L.; et al. Treatment and Outcome of Congenital Nephrotic Syndrome. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asharam, K.; Bhimma, R.; David, V.A.; Coovadia, H.M.; Qulu, W.P.; Naicker, T.; Gillies, C.E.; Vega-Warner, V.; Johnson, R.C.; Limou, S.; et al. NPHS2 V260E Is a Frequent Cause of Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome in Black South African Children. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feehally, J.; Burden, A.C.; Mayberry, J.F.; Probert, C.S.; Roshan, M.; Samanta, A.K.; Woods, K.L. Disease Variations in Asians in Leicester. QJM Int. J. Med. 1993, 86, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- McKinney, P.A.; Feltbower, R.G.; Brocklebank, J.T.; Fitzpatrick, M.M. Time Trends and Ethnic Patterns of Childhood Nephrotic Syndrome in Yorkshire, UK. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2001, 16, 1040–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, T.; Simon, S.D.; Alon, U.S. High Incidence of Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis in Nephrotic Syndrome of Childhood. Pediatr. Nephrol. 1999, 13, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandlal, L.; Winkler, C.A.; Bhimma, R.; Cho, S.; Nelson, G.W.; Haripershad, S.; Naicker, T. Causal and Putative Pathogenic Mutations Identified in 39% of Children with Primary Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome in South Africa. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 3595–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierzynska, A.; McCarthy, H.J.; Soderquest, K.; Sen, E.S.; Colby, E.; Ding, W.Y.; Nabhan, M.M.; Kerecuk, L.; Hegde, S.; Hughes, D.; et al. Genomic and Clinical Profiling of a National Nephrotic Syndrome Cohort Advocates a Precision Medicine Approach to Disease Management. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trautmann, A.; Lipska-Ziętkiewicz, B.S.; Schaefer, F. Exploring the Clinical and Genetic Spectrum of Steroid Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome: The PodoNet Registry. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.E.; Esezobor, C.I.; Lane, B.M.; Gbadegesin, R.A. Hiding in Plain Sight: Genetics of Childhood Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome in Sub-Saharan Africa. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2023, 38, 2003–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafey, S.A.; Thabet, M.A.E.H.; Abo Elwafa, R.A.H.; Schneider, R.; Shril, S.; Buerger, F.; Hildebrandt, F.; Fathy, H.M. Genetic Stratification Reveals COL4A Variants and Spontaneous Remission in Egyptian Children with Proteinuria in the First 2 Years of Life. Acta Paediatr. Int. J. Paediatr. 2023, 112, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribouval, O.; Boyer, O.; Knebelmann, B.; Karras, A.; Dantal, J.; Fourrage, C.; Alibeu, O.; Hogan, J.; Dossier, C.; Tête, M.J.; et al. APOL1 Risk Genotype in European Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome and/or Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis Patients of Different African Ancestries. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 1885–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.A.; Elmonem, M.A.; El-Sayed, A.F.; Ramadan, E.; Badr, A.M.; Atia, F.M.; Helmy, R.; Amer, M.O.; El-Raouf, A.A.; El-Garhy, F.M.; et al. Whole Genome Sequencing Identifies Monogenic Disease in 56.1% of Families with Early-Onset Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome. Hum. Genet. 2025, 144, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopanos, C.; Tsiolkas, V.; Kouris, A.; Chapple, C.E.; Albarca Aguilera, M.; Meyer, R.; Massouras, A. VarSome: The Human Genomic Variant Search Engine. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1978–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Riley, G.R.; Jang, W.; Rubinstein, W.S.; Church, D.M.; Maglott, D.R. ClinVar: Public Archive of Relationships among Sequence Variation and Human Phenotype. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D980–D985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierzynska, A.; Soderquest, K.; Dean, P.; Colby, E.; Rollason, R.; Jones, C.; Inward, C.D.; McCarthy, H.J.; Simpson, M.A.; Lord, G.M.; et al. MAGI2 Mutations Cause Congenital Nephrotic Syndrome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen, N.P. Congenital Nephrotic Syndrome of Finnish Type Study of 75 Patients. Arch. Dis. Child. 1976, 51, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.H. The Familial Nephrotic Syndrome. I. A European Survey. Clin. Nephrol. 1973, 1, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Churg, J.; Habib, R.; White, R.H.R. Pathology of the Nephrotic Syndrome in Children: A Report for the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. Lancet 1970, 295, 1299–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukaguchi, H.; Sudhakar, A.; Le, T.C.; Nguyen, T.; Yao, J.; Schwimmer, J.A.; Schachter, A.D.; Poch, E.; Abreu, P.F.; Appel, G.B.; et al. NPHS2 Mutations in Late-Onset Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis: R229Q Is a Common Disease-Associated Allele. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kestilä, M.; Lenkkeri, U.; Männikkö, M.; Lamerdin, J.; McCready, P.; Putaala, H.; Ruotsalainen, V.; Morita, T.; Nissinen, M.; Herva, R.; et al. Positionally Cloned Gene for a Novel Glomerular Protein—Nephrin—Is Mutated in Congenital Nephrotic Syndrome. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boute, N.; Gribouval, O.; Roselli, S.; Benessy, F.; Lee, H.; Fuchshuber, A.; Dahan, K.; Gubler, M.; Niaudet, P.; Antignac, C. Correction to “NPHS2, Encoding the Glomerular Protein Podocin, Is Mutated in Autosomal Recessive Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome”. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadowski, C.E.; Lovric, S.; Ashraf, S.; Pabst, W.L.; Gee, H.Y.; Kohl, S.; Engelmann, S.; Vega-Warner, V.; Fang, H.; Halbritter, J.; et al. A Single-Gene Cause in 29.5% of Cases of Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeb, D.S.; Chernin, G.; Heeringa, S.F.; Matejas, V.; Held, S.; Vega-Warner, V.; Bockenhauer, D.; Vlangos, C.N.; Moorani, K.N.; Neuhaus, T.J.; et al. Nineteen Novel NPHS1 Mutations in a Worldwide Cohort of Patients with Congenital Nephrotic Syndrome (CNS). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 2970–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.; Ray Chaudhury, A.; Sarkar, S.; Banerjee, S.; Pulai, S.; Dasgupta, S.; Muorah, M.; Datta, D. High Incidence of COL4A Genetic Variants Among a Cohort of Children With Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome From Eastern India. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, 913–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbarek, I.B.; Abroug, S.; Omezzine, A.; Pawtowski, A.; Gubler, M.C.; Bouslama, A.; Harbi, A.; Antignac, C. Novel Mutations in Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome Diagnosed in Tunisian Children. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2011, 26, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.M.; Ahmed, H.M.; El-Dessouky, S.H.; Ramadan, A.; Botrous, O.E.; Abdel-Hamid, M.S. Spectrum of NPHS1 and NPHS2 Variants in Egyptian Children with Focal Segmental Glomerular Sclerosis: Identification of Six Novel Variants and Founder Effect. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2022, 297, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, M.A.; Fabian, J.; Gottlich, E.; Levy, C.; Moonsamy, G.; Maher, H.; Winkler, C.A.; Ramsay, M. The Podocin V260E Mutation Predicts Steroid Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome in Black South African Children with Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemo, A.; Esezobor, C.; Solarin, A.; Abeyagunawardena, A.; Kari, J.A.; El Desoky, S.; Greenbaum, L.A.; Kamel, M.; Kallash, M.; Silva, C.; et al. HLA-DQA1 and APOL1 as Risk Loci for Childhood-Onset Steroid-Sensitive and Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 71, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruchi, R.; Genovese, G.; Lee, J.; Charoonratana, V.T.; Bernhardy, A.J.; Alper, S.L.; Kopp, J.B.; Thadhani, R.; Friedman, D.J.; Pollak, M.R. Copy Number Variation at the APOL1 Locus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, G.; Friedman, D.J.; Ross, M.D.; Lecordier, L.; Uzureau, P.; Freedman, B.I.; Bowden, D.W.; Langefeld, C.D.; Oleksyk, T.K.; Uscinski Knob, A.L.; et al. Association of Trypanolytic ApoL1 Variants with Kidney Disease in African Americans. Science (1979) 2010, 329, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, M.R. Familial FSGS. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2014, 21, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.; Gribouval, O.; Esquivel, E.L.; Morinière, V.; Tête, M.-J.; Legendre, C.; Niaudet, P.; Antignac, C. NPHS2 Mutation Analysis Shows Genetic Heterogeneity of Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome and Low Post-Transplant Recurrence. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrakka, J.; Kestilä, M.; Wartiovaara, J.; Ruotsalainen, V.; Tissari, P.; Lenkkeri, U.; Männikkö, M.; Visapää, I.; Holmberg, C.; Rapola, J.; et al. Congenital Nephrotic Syndrome (NPHS1): Features Resulting from Different Mutations in Finnish Patients. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guaragna, M.S.; de Brito Lutaif, A.C.G.; de Souza, M.L.; Maciel-Guerra, A.T.; Belangero, V.M.S.; Guerra-Júnior, G.; de Mello, M.P. Promises and Pitfalls of Whole-Exome Sequencing Exemplified by a Nephrotic Syndrome Family. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2020, 295, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulati, A.; Somlo, S. Whole Exome Sequencing: A State-of-the-Art Approach for Defining (and Exploring!) Genetic Landscapes in Pediatric Nephrology. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 745–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, N.; Braun, D.A.; Amann, K.; Tan, W.; Shril, S.; Connaughton, D.M.; Nakayama, M.; Schneider, R.; Kitzler, T.M.; Van Der Ven, A.T.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing Enables a Precision Medicine Approach for Kidney Transplant Recipients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, G.; Gbadegesin, R.A. Translating Genetic Findings in Hereditary Nephrotic Syndrome: The Missing Loops. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2015, 309, F24–F28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aymé, S.; Bockenhauer, D.; Day, S.; Devuyst, O.; Guay-Woodford, L.M.; Ingelfinger, J.R.; Klein, J.B.; Knoers, N.V.A.M.; Perrone, R.D.; Roberts, J.; et al. Common Elements in Rare Kidney Diseases: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renkema, K.Y.; Stokman, M.F.; Giles, R.H.; Knoers, N.V.A.M. Next-Generation Sequencing for Research and Diagnostics in Kidney Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, S.; Ndungwani, R.; Burgert, M.; Sibandze, D.; Matse, S.; Hettema, A. The Costs of Creatinine Testing in the Context of a HIV Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis Demonstration Project in Eswatini. AIDS Behav. 2022, 26, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetterstrand, K.A. DNA Sequencing Costs: Data from the NHGRI Genome Sequencing Program (GSP); National Human Genome Research Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- McGuire, A.L.; Gabriel, S.; Tishkoff, S.A.; Wonkam, A.; Chakravarti, A.; Furlong, E.E.M.; Treutlein, B.; Meissner, A.; Chang, H.Y.; López-Bigas, N.; et al. The Road Ahead in Genetics and Genomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, J.; Munung, S.N.; Matimba, A.; McCurdy, S.; Ouwe Missi Oukem-Boyer, O.; Staunton, C.; Yakubu, A.; Tindana, P. Regulation of Genomic and Biobanking Research in Africa: A Content Analysis of Ethics Guidelines, Policies and Procedures from 22 African Countries. BMC Med. Ethics 2017, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonkam, A.; Munung, N.S.; Dandara, C.; Esoh, K.K.; Hanchard, N.A.; Landoure, G. Five Priorities of African Genomics Research: The Next Frontier. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2022, 23, 499–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorval, G.; Gribouval, O.; Martinez-Barquero, V.; Machuca, E.; Tête, M.-J.; Baudouin, V.; Benoit, S.; Chabchoub, I.; Champion, G.; Chauveau, D.; et al. Clinical and Genetic Heterogeneity in Familial Steroid-Sensitive Nephrotic Syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majmundar, A.J.; Buerger, F.; Forbes, T.A.; Klämbt, V.; Schneider, R.; Deutsch, K.; Kitzler, T.M.; Howden, S.E.; Scurr, M.; Tan, K.S.; et al. Recessive NOS1AP Variants Impair Actin Remodeling and Cause Glomerulopathy in Humans and Mice. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovric, S.; Fang, H.; Vega-Warner, V.; Sadowski, C.E.; Gee, H.Y.; Halbritter, J.; Ashraf, S.; Saisawat, P.; Soliman, N.A.; Kari, J.A.; et al. Rapid Detection of Monogenic Causes of Childhood-Onset Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anigilaje, E.A.; Olutola, A. Prospects of Genetic Testing for Steroid-Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome in Nigerian Children: A Narrative Review of Challenges and Opportunities. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2019, 12, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, M.; Nowicki, M. Detailed Pathophysiology of Minimal Change Disease: Insights into Podocyte Dysfunction, Immune Dysregulation, and Genetic Susceptibility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetsch, A.L.; Kimelman, D.; Woodruff, T.K. Fertility Preservation and Restoration for Patients with Complex Medical Conditions; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-52315-6. [Google Scholar]
- Colvin, R.B.; Chang, A.; Farris, A.B.; Kambham, N.; Cornell, L.D.; Meehan, S.M.; Liapis, H.; Gaut, J.P.; Bonsib, S.M.; Seshan, S.V.; et al. Diagnostic Pathology: Kidney Diseases: A Volume in Diagnostic Pathology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Ye, Y.; Fu, H.; Gu, W.; Zhao, M.; Sun, J.; Cao, Z.; Huang, G.; Xie, Y.; Liu, F.; et al. Effects of a Novel ANLN E841K Mutation Associated with SRNS on Podocytes and Its Mechanism. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopazo, J.; Amadoz, A.; Bleda, M.; Garcia-Alonso, L.; Alemán, A.; García-García, F.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Daub, J.T.; Muntané, G.; Rueda, A.; et al. 267 Spanish Exomes Reveal Population-Specific Differences in Disease-Related Genetic Variation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esezobor, C.I.; Solarin, A.U.; Gbadegesin, R. Changing Epidemiology of Nephrotic Syndrome in Nigerian Children: A Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| NS Type | Presentation of NS Type |
|---|---|
| Response to Treatment: | |
| SSNS | Respond well to conventional corticosteroid therapy with a favourable long-term prognosis |
| SRNS | Experience partial, late, or complete resistance to corticosteroid treatment, thus experiencing frequent relapses and require alternative immunosuppressants. |
| Age of Disease Manifestation: | |
| CNS | From birth to 3 months |
| INS | From 3 months to 12 months |
| Childhood NS | From 12 months and beyond |
| Histopathological Feature: | |
| FSGS | Identified by podocyte depletion; a reduction of 20–40% in podocyte count results in segmental scarring of the glomeruli, leading to enlargement of the glomerulus and subsequent additional podocyte loss |
| MCD/MCNS | Distinguished by reversible alterations in podocyte architecture without significant podocyte loss |
| GN | Inflammation of the glomeruli |
| MN | Characterised as an autoimmune disorder that facilitates the accumulation of immune proteins within the glomerular basement membrane of the kidneys. |
| MDS | Characterised by sclerosis of the mesangial matrix resulting in minimal or no cell proliferation. |
| Population or Country | Sample Size | Age Range | NS Phenotypes | NGS Platform Used | Coverage Metrics | Genes with High Frequency of Mutations/Commonly Mutated Genes in NS Reported | Pathogenicity Tools Used | Diagnostic Yield (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| South African | 56 | 60–100 months | SRNS-FSGS | WES LC Sciences (Houston, TX, USA): Illumina HiSeq4000 | Paired-end sequencing: average sequencing depth of >80× | NPHS2, INF2, CD2AP and TRPC6 | PolyPhen-2 and SIFT | 17 | [17] |
| Egyptian | 58 | <2 years | NS, asymptomatic proteinuria | WES N/A | N/A | NPHS1, NPHS2 and PLCE1 | Mutation Taster, SIFT and PolyPhen | 64.4 | [22] |
| United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland | 187 | <19 years | INS, primary or secondary SRNS | WES Illumina HiSeq | 100 paired-end sequencing: average sequencing depth ~100× | NPHS1, WT1 and NPHS2 | MutPred, SIFT, Mutation Taster and Alamut splicing predictions. | 26.2 | [18] |
| France | 152 | 0–64 years | SRNS and/or FSGS | NGS gene panel Multiplicom | N/A | APOL1, NPHS1 and NPHS2 | Mutation Taster, SIFT and PolyPhen2 | 11.2 | [23] |
| Egyptian | 47 | 7 months–22 years | SRNS | WGS IlluminaNovaSeq 6000 | 30× | NPHS2, NPHS2 and WT1 | Revel, CADD, SpliceAI | 57.4 | [24] |
| Gene | Variant | Predicted Effects | Genome Assembly | Type of NS | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRPC6 | NM_004621.6:c.485G>T p.(Gly162Val) | Pathogenic Moderate | Hg19 | SR-FSGS | [17] * |
| INF2 | ENST00000252527.8:c.1226A>C p.(Lys409Thr) | ||||
| PLCE1 | NM_016341.4:c.3194C>A p.(Ala1065Glu) | Benign Supporting | |||
| ACTN4 | ENST00000390009.3:c.174C>T p.(Ala58=) | Benign Strong | |||
| PLCE1 | NM_001288989.2:c.689_690del p.(Tyr230CysfsTer6) | Pathogenic | - | NS | [22] ** |
| NM_016341.4:c.5364C>G p.(Tyr1788Ter) | Likely Pathogenic | SRNS, Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome | |||
| COL4A3 | NM_000091.5:c.820_821delGGinsC p.(Gly274HisfsTer49) | Likely Pathogenic | Isolated SRNS | ||
| OSGEP | NM_017807.4:c.775A>T p.(Ile259Phe) | Likely Pathogenic | Pierson and Galloway Mowart syndromes and adrenalin insufficiency | ||
| LAMB2 | NM_002292.4:c.5368C>T p.(Gln1790Ter) | Likely Pathogenic | |||
| SGPL1 | NM_003901.4:c.1013A>G p.(Asp338Gly) | Likely Pathogenic | |||
| PAX2 | NM_003989.5:c.869del p.(Pro290LeufsTer16) | Pathogenic | Multicystic dysplastic kidney | ||
| NPHS1 | Deletion of exon 8 | - | Hg19 | N/A | [18] *** |
| NM_004646.4:c.2387G>A p.(Gly796Glu) | Likely Pathogenic | Diffuse mesangial sclerosis (DMS) | |||
| NM_004646.4:c.136G>T p.(Gly46Trp) | Uncertain Significance | N/A | |||
| NM_004646.4:c.925G>A p.(Glu309Lys) | Uncertain Significance | ||||
| NM_004646.4:c.1584C>T p.(Cys528=) | Benign Moderate | CNS | |||
| NM_004646.4:c.1910_1912del p.(Phe637del) | - | N/A | |||
| NPHS2 | NM_014625.4:c.156del p.(Thr53ProfsTer46) | Pathogenic/Likely Pathogenic | N/A | ||
| NM_014625.4:c.378+2_378+3del p.? | Likely Pathogenic | SRNS | |||
| ACTN4 | NM_001322033.2:c.779_787del p.(Tyr260_Ser262del) | - | FSGS | ||
| TRPC6 | NM_004621.6:c.523C>T p.(Arg175Trp) | Pathogenic/Likely Pathogenic | FSGS | ||
| MYO1E | NM_004998.4:c.2094T>A p.(Tyr698Ter) | - | N/A | ||
| DGKE | ENST00000284061.3:c.1303C>T p.(Arg435Ter) | - | N/A | ||
| LMX1B | NM_002316.4:c.676C>T p.(Leu226Phe) | Pathogenic Strong/Uncertain Significance | N/A | ||
| COL4A5 | NM_033380.3:c.3097G>C p.(Gly1033Arg) | Pathogenic Moderate | N/A | ||
| ADCK4/ COQ8B | NM_024876.4:c.101G>A p.(Trp34Ter) | Benign Moderate | SRNS | ||
| NM_024876.4:c.954_956dup p.(Thr319dup) | - | ||||
| CRB2 | NM_173689.7:c.3089_3104dup p.(Gly1036AlafsTer43) | Pathogenic/Likely Pathogenic | SRNS | ||
| PODXL | NM_005397.4:c.1427A>T p.(His476Leu) | Pathogenic Moderate | N/A | ||
| OCRL | NM_001587.4:c.1467-2A>G p.? | Pathogenic Strong | N/A | ||
| COL4A3 | NM_000091.5:c.2126-1G>A | Likely Pathogenic | Hg38 | SRNS | [24] ** |
| MYO1E | NM_004998.4:c.1616+1G>C | Likely Pathogenic | |||
| NPHS1 | NM_004646.4: c.2758T>C p.(Cys920Arg) | Likely Pathogenic | |||
| NPHS2 | NM_014625.4:c.596dup p.(Asn199LysfsTer14) | Likely Pathogenic | |||
| NUP93 | NM_014669.5:c.554 A>G p.(Tyr185Cys) | Variant of Uncertain Significance | |||
| PLCE1 | NM_016341.4:c.2779G>T p(.Gly927Ter) | Likely Pathogenic | |||
| PODXL | NM_001018111.3:c.1101+2T>C | Likely Pathogenic | |||
| SMARCAL1 | NM_014140.4:c.1096+4A>G | Variant of Uncertain Significance | |||
| WT1 | NM_024426.6:c.700G>C p.(Gly234 Arg) | Variant of Uncertain Significance |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gcobo, T.; Katsukunya, J.N.; Lamola, L.; Awany, D.; Ndadza, A.; Dandara, C.; Mnika, K. Whole-Exome Sequencing for Molecular Diagnosis of Paediatric Nephrotic Syndrome in Africa: A Call for Implementation. Genes 2025, 16, 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111295
Gcobo T, Katsukunya JN, Lamola L, Awany D, Ndadza A, Dandara C, Mnika K. Whole-Exome Sequencing for Molecular Diagnosis of Paediatric Nephrotic Syndrome in Africa: A Call for Implementation. Genes. 2025; 16(11):1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111295
Chicago/Turabian StyleGcobo, Thina, Jonathan N. Katsukunya, Lindie Lamola, Denis Awany, Arinao Ndadza, Collet Dandara, and Khuthala Mnika. 2025. "Whole-Exome Sequencing for Molecular Diagnosis of Paediatric Nephrotic Syndrome in Africa: A Call for Implementation" Genes 16, no. 11: 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111295
APA StyleGcobo, T., Katsukunya, J. N., Lamola, L., Awany, D., Ndadza, A., Dandara, C., & Mnika, K. (2025). Whole-Exome Sequencing for Molecular Diagnosis of Paediatric Nephrotic Syndrome in Africa: A Call for Implementation. Genes, 16(11), 1295. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111295







