GH1 Gene Polymorphisms Reveal Population-Level Allele Variation in North African (Clarias gariepinus) and Bighead Catfish (Clarias macrocephalus)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethic Statement
2.2. Specimen Collection and DNA Extraction
2.3. PCR Amplification and IlluminaTM Short-Read Sequencing
2.4. Sequence Quality Control and Read Processing
2.5. Genetic Diversity and Data Analysis
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.7. Selection Analysis
2.8. Multiple Sequence Alignment of GH1 Amino Acid Residues
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Catfish Based on GH1 Gene
3.2. Selection and Selective-Sweep Analyses of Catfish Species
3.3. Multiple Sequence Alignment of GH1 Amino Acid Residues and Prediction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Department of Fisheries. Fisheries Statistic of Thailand 2023; Department of Fisheries: Bangkok, Thailand, 2024; Available online: https://www4.fisheries.go.th/local/file_document/20240819161939_1_file.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Wachirachaikarn, A.; Rungsin, W.; Srisapoome, P.; Na-Nakorn, U. Crossing of African catfish, Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822), strains based on strain selection using genetic diversity data. Aquaculture 2009, 290, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaivichoo, P.; Koonawootrittriron, S.; Chatchaiphan, S.; Srimai, W.; Na-Nakorn, U. Genetic components of growth traits of the hybrid between ♂ North African catfish (Clarias gariepinus Burchell, 1822) and ♀ bighead catfish (C. macrocephalus Günther, 1864). Aquaculture 2020, 521, 735082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisachov, A.; Nguyen, D.H.M.; Panthum, T.; Ahmad, S.F.; Singchat, W.; Ponjarat, J.; Jaisamut, K.; Srisapoome, P.; Duengkae, P.; Hatachote, S.; et al. Emerging importance of bighead catfish (Clarias macrocephalus) and North African catfish (C. gariepinus) as a bioresource and their genomic perspective. Aquaculture 2023, 573, 739585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na-Nakorn, U.; Brummett, R.E. Use and exchange of aquatic genetic resources for food and aquaculture: Clarias catfish. Rev. Aquac. 2009, 1, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nukwan, S.; Tangtrongpiros, M.; Lawanyawut, K.; Veerasidth, P. Cross breeding between Clarias macrocephalus and Clarias gariepinus. In Proceedings of the 28th Kasetsart University Conference, Bangkok, Thailand, 30 January–2 February 1990; Ministry of Science, Technology and Energy: Bangkok, Thailand; pp. 553–567. [Google Scholar]
- Nukwan, S.; Lawanyawut, K.; Tangtrongpiros, M.; Veerasidth, P. Backcrossing experiment of hybrid between Clarias macrocephalus and Clarias gariepinus. In Proceedings of the 28th Kasetsart University Conference, Bangkok, Thailand, 30 January–2 February 1990; pp. 529–544. [Google Scholar]
- Na-Nakorn, U.; Kamonrat, W.; Ngamsiri, T. Genetic diversity of walking catfish, Clarias macrocephalus, in Thailand and evidence of genetic introgression from introduced farmed C. gariepinus. Aquaculture 2004, 240, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patta, C.; Panthum, T.; Thatukan, C.; Wongloet, W.; Chalermwong, P.; Wattanadilokchatkun, P.; Thong, T.; Srikampa, P.; Singchat, W.; Ahmad, S.F.; et al. Questioning inbreeding: Could outbreeding affect productivity in the North African catfish in Thailand? PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0302584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponjarat, J.; Singchat, W.; Monkheang, P.; Suntronpong, A.; Tawichasri, P.; Sillapaprayoon, S.; Ogawa, S.; Muangmai, N.; Baicharoen, S.; Peyachoknagul, S.; et al. Evidence of dramatic sterility in F1 male hybrid catfish [male Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822) × female C. macrocephalus (Günther, 1864)] resulting from the failure of homologous chromosome pairing in meiosis I. Aquaculture 2019, 505, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedukh, D.; Lisachov, A.; Panthum, T.; Singchat, W.; Matsuda, Y.; Imai, Y.; Janko, K.; Srikulnath, K. Meiotic deviations and endoreplication lead to diploid oocytes in female hybrids between bighead catfish (Clarias macrocephalus) and North African catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1465335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office of Agricultural Economics. The Ministry of Agriculture Approved the Forecast of Agricultural Production in the Year 2023/24; Office of Agricultural Economics: Bangkok, Thailand, 2024; Available online: https://www.oae.go.th/ (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Na-Nakorn, U. A perspective on breeding and genetics of walking catfish in Thailand. Sustain. Aquac. 2004, 9, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Senanan, W.; Kapuscinski, A.R.; Na-Nakorn, U.; Miller, L.M. Genetic impacts of hybrid catfish farming (Clarias macrocephalus × C. gariepinus) on native catfish populations in central Thailand. Aquaculture 2004, 235, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalermwong, P.; Panthum, T.; Singchat, W.; Budi, T.; Tanglertpaibul, N.; Muangmai, N.; Chaiyes, A.; Duengkae, P.; Srikulnath, K. Is it correct that “Hybrid catfish” only produced by hybridization between bighead and North African catfish. Sarawit Sar. 2024, 133, 55–60. Available online: https://waa.inter.nstda.or.th/stks/pub/ebook/sarawit-pdf/Sarawit-Issue133.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- Rey, J.; Singchat, W.; Jaito, W.; Punthum, T.; Lisachov, A.; Pongsanarm, T.; Thatukan, C.; Wongloet, W.; Budi, T.; Chalermwong, P.; et al. Near-stop in spermatogonia progression and reduced sperm motility in two testis forms of captive North African catfish in Kalasin, Thailand. Aquaculture 2024, 595, 741646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Clarias gariepinus Burchell, 1822. In Fisheries and Aquaculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2024; Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/en/aqspecies/2982/en (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Aboukila, R.S.; Hemeda, S.A.E.; El Nahas, A.F.; Abd El Naby, W.S.H. Molecular characterization of GHR1 gene and expression analysis of some growth-related genes in Oreochromis niloticus. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2021, 9, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebo, C.; Portella, M.C.; Carani, F.R.; de Almeida, F.L.A.; Padovani, C.R.; Carvalho, R.F.; Dal-Pai-Silva, M. Short periods of fasting followed by refeeding change the expression of muscle growth-related genes in juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 2013, 164, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.N.; Valdés, J.A.; Molina, A.; Björnsson, B.T. Regulation of skeletal muscle growth in fish by the growth hormone–insulin-like growth factor system. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 192, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.A.D.; Reis Neto, R.V.; Bueno Filho, J.S.d.S.; Jaser, S.K.K.; de Lago, A.; Hilsdorf, A.W.S. Growth hormone gene polymorphism associated with grow-out performance of Oreochromis niloticus strains. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, T.; Zhao, X.; Li, C.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Pan, C.; Liu, E.; Ling, Q. Cloning and expression of IGF-I, IGF-II, and GHR genes and the role of their single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the growth of pikeperch (Sander lucioperca). Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 1547–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez, E.J.; Nasri, A.; Unniappan, S. Nesfatin-1 and nesfatin-1-like peptide suppress basal and TRH-induced expression of prolactin and prolactin regulatory element-binding protein mRNAs in rat GH3 somatolactotrophs. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2021, 529, 111269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez, E.J.; Unniappan, S. A comparative update on the neuroendocrine regulation of growth hormone in vertebrates. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 11, 614981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.K.K.; Wong, M.W.; Chan, A.P.Y. Cloning and sequencing of the grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) growth hormone gene. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1090, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almuly, R.; Cavari, B.; Ferstman, H.; Kolodny, O.; Funkenstein, B. Genomic structure and sequence of the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) growth hormone-encoding gene: Identification of minisatellite polymorphism in intron I. Genome 2000, 43, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, J.S.; Wolff, J.L.C.; Araújo, R.C.; Hilsdorf, A.W.S. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of growth hormone cDNA of Neotropical freshwater fish pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus). Genet. Mol. Biol. 2008, 31, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, S.J.; Trautner, J.; Smith, M.J.; Koop, B.F.; Devlin, R.H. Evolution of duplicated growth hormone genes in autotetraploid salmonid fishes. Genome 2004, 47, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, J.; Martin, R.S.; Flores, C.; Grothusen, H.; Kausel, G. Seasonal modulation of growth hormone mRNA and protein levels in carp pituitary: Evidence for two expressed genes. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2005, 175, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocour, M.; Kohlmann, K. Growth hormone gene polymorphisms in tench, Tinca tinca L. Aquaculture 2011, 310, 298–304. Aquaculture 2011, 310, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.A.R.S.; Attee, R.S.; Radhi, A.G. Association between the growth hormone gene GH-1 and growth indicators of common carp Cyprinus carpio L. in three different ecosystems. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1225, 012033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanck, D.V.; Gasparino, E.; Ribeiro, R.P.; Marques, D.S. Polymorphism in the GH1-PstI gene associated to corporal characteristics in Nile tilapia strains. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2009, 44, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggatt, R.A.; Biagi, C.A.; Smith, J.L.; Devlin, R.H. Growth of growth hormone transgenic coho salmon Oncorhynchus kisutch is influenced by construct promoter type and family line. Aquaculture 2012, 356, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasaruddin, K.; Majumdar, K.C. Clarias gariepinus Growth Hormone Gene (Genomic) Complete CDS. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/AF416488 (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- Poen, S.; Pornbanlualap, S. Growth hormone from striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus): Genomic organization, recombinant expression and biological activity. Gene 2013, 518, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.Y.; Scribner, K.T. Regional variation in genetic diversity between wild and cultured populations of bighead catfish (Clarias macrocephalus) in the Mekong Delta. Fish. Res. 2018, 207, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachirachaikarn, A.; Na-Nakorn, U. Genetic diversity of the North African catfish, Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822) hatchery stocks in Thailand. Sci. Asia 2019, 45, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazia, A.K.; Tam, B.M.; Jamaluddin, J.A.F.; Mohd Nor, S.A. High genetic structure between natural populations of bighead catfish Clarias macrocephalus (Günther, 1864) from the Mekong Delta and Peninsular Malaysia. Fish. Res. 2021, 241, 105993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.H.M.; Ponjarat, J.; Laopichienpong, N.; Panthum, T.; Singchat, W.; Ahmad, S.F.; Kraichak, E.; Muangmai, N.; Duengkae, P.; Peyachoknagul, S.; et al. Genome-wide SNP analysis of hybrid clariid fish reflects the existence of polygenic sex determination in the lineage. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 789573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patta, C.; Sriphairoj, K.; Budi, T.; Quanoo, D.K.; Nguyen, T.H.D.; Jaito, W.; Chalermwong, P.; Pongsanarm, T.; Thatukan, C.; Wongloet, W.; et al. Genetic structural changes while maintaining effective population size of bighead catfish in Nong Han Lake: Implications of metapopulation dynamics or release activities. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2024, 31, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supikamolseni, A.; Ngaoburanawit, N.; Sumontha, M.; Chanhome, L.; Suntrarachun, S.; Peyachoknagul, S.; Srikulnath, K. Molecular barcoding of venomous snakes and species-specific multiplex PCR assay to identify snake groups for which antivenom is available in Thailand. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 13981–13997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wringe, B.F.; Devlin, R.H.; Ferguson, M.M.; Moghadam, H.K.; Sakhrani, D.; Danzmann, R.G. Growth-related quantitative trait loci in domestic and wild rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). BMC Genet. 2010, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data; 2010. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Sebastian, A.; Herdegen, M.; Migalska, M.; Radwan, J. Amplisas: A web server for multilocus genotyping using next--generation amplicon sequencing data. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lighten, J.; van Oosterhout, C.; Bentzen, P. Critical review of NGS analyses for de novo genotyping multigene families. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 3957–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—An update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normala, J.; Okomoda, V.T.; Mohd, A.A.; Nur, A.A.; Abol-Munafi, A.B.; Md Sheriff, S. Genetic Variation between Triploid and Diploid Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822) Using RAPD Markers. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudet, J. FSTAT (version 1.2): A computer program to calculate F-statistics. J. Hered. 1995, 86, 485–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budi, T.; Kumnan, N.; Singchat, W.; Chalermwong, P.; Thong, T.; Wongloet, W.; Faniriharisoa Maxime Toky, R.; Pathomvanich, P.; Panthum, T.; Wattanadilokchatkun, P.; et al. Weak purifying selection in allelic diversity of the ADSL gene in indigenous and local chicken breeds and red junglefowl in Thailand. Gene 2024, 923, 148587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budi, T.; Singchat, W.; Tanglertpaibul, N.; Wongloet, W.; Chaiyes, A.; Ariyaraphong, N.; Thienpreecha, W.; Wannakan, W.; Mungmee, A.; Thong, T.; et al. Thai local chicken breeds, Chee Fah and Fah Luang, originated from Chinese black-boned chicken with introgression of red junglefowl and domestic chicken breeds. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Liu, J.X. StructureSelector: A web-based software to select and visualize the optimal number of clusters using multiple methods. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jombart, T.; Devillard, S.; Dufour, A.B.; Pontier, D. Revealing cryptic spatial patterns in genetic variability by a new multivariate method. Heredity 2008, 101, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M.; Gojobori, T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1986, 3, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, U.K.; Abburi, L.; Abburi, V.L.; Saminathan, T.; Cantrell, R.; Vajja, V.G.; Reddy, R.; Tomason, Y.R.; Levi, A.; Wehner, T.C.; et al. A genome-wide scan of selective sweeps and association mapping of fruit traits using microsatellite markers in watermelon. J. Hered. 2015, 106, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, W.R. BLAST and FASTA similarity searching for multiple sequence alignment. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 75–101. [Google Scholar]
- Meiklejohn, K.A.; Damaso, N.; Robertson, J.M. Assessment of BOLD and GenBank—Their accuracy and reliability for the identification of biological materials. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulisija, D.; Kim, Y. Emergence of long-term balanced polymorphism under cyclic selection of spatially variable magnitude: Balanced polymorphism under cyclic selection. Evolution 2015, 69, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeaman, S. Evolution of polygenic traits under global vs local adaptation. Genetics 2022, 220, iyab134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, W. Selective sweeps. Genetics 2019, 211, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qu, W.; Obrycki, J.J.; Meng, L.; Zhou, X.; Chu, D.; Li, B. Optimizing sample size for population genomic study in a global invasive lady beetle, Harmonia axyridis. Insects 2020, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, J.F.; Winker, K. An empirical examination of sample size effects on population demographic estimates in birds using single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) data. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.D.; Zemlak, T.S.; Innes, B.H.; Last, P.R.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigand, H.; Leese, F. Detecting signatures of positive selection in non-model species using genomic data. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2018, 184, 528–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.P.; Lundberg, J.G.; Hardman, M. A phylogenetic analysis of the major groups of catfishes (Teleostei: Siluriformes) using rag1 and rag2 nuclear gene sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 41, 636–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappas, I.; Vittas, S.; Pantzartzi, C.N.; Drosopoulou, E.; Scouras, Z.G. A time-calibrated mitogenome phylogeny of catfish (Teleostei: Siluriformes). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohling, J.H.; Adams, J.R.; Waits, L.P. Evaluating the ability of Bayesian clustering methods to detect hybridization and introgression using an empirical red wolf data set. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millar, D.S.; Lewis, M.D.; Horan, M.; Newsway, V.; Rees, D.A.; Easter, T.E.; Pepe, G.; Rickards, O.; Norin, M.; Scanlon, M.F.; et al. Growth hormone (GH1) gene variation and the growth hormone receptor (GHR) exon 3 deletion polymorphism in a West-African population. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2008, 296, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaser, S.K.K.; Dias, M.A.D.; Lago, A.A.; Reis Neto, R.V.; Hilsdorf, A.W.S. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the growth hormone gene of Oreochromis niloticus and their association with growth performance. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 5835–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.A.; Hassan, T.G.M.; El-Hedainy, D.K.A.; El-Barbary, A.S.A.; Sharaby, M.A.; Hafez, E.E.; Rashad, A.M.A. IGF-I and GH genes polymorphism and their association with milk yields, composition and reproductive performance in Holstein-Friesian dairy cattle. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryther, R.C.C.; Flynt, A.S.; Harris, B.D.; Phillips, J.A.; Patton, J.G. GH1 splicing is regulated by multiple enhancers whose mutation produces a dominant-negative GH isoform that can be degraded by allele-specific small interfering RNA (siRNA). Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2988–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Qin, Z.S.; Liu, J.S.; Chen, T.; Waterman, M.S.; Sun, F. Haplotype block partitioning and tag SNP selection using genotype data and their applications to association studies. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, R.T.H.; Liu, X.; Poh, W.T.; Sim, X.; Chia, K.S.; Teo, Y.Y. A method for identifying haplotypes carrying the causative allele in positive natural selection and genome-wide association studies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, X.; Rong, Y.; Han, M.; Wang, X.; Xia, Q.; Shang, F.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Su, R.; et al. Combined genome-wide association study and haplotype analysis identifies candidate genes affecting growth traits of Inner Mongolian cashmere goats. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, L.; Wang, Y.; Tan, L.; Wen, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y. Haplotype analysis incorporating ancestral origins identified novel genetic loci associated with chicken body weight using an advanced intercross line. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2024, 56, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanamati, F.; da Silva, S.C.C.; Rodriguez, M.D.P.R.; Schuroff, G.P.; Nascimento, C.S.D.; Del Vesco, A.P.; Gasparino, E. GHR and IGF-I gene expression and production characteristics associated with GH gene polymorphism in Nile tilapia. Aquaculture 2015, 435, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, C.; Luan, P.; Ge, Y.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, L. A novel diplotype in the GH gene associated with body weight traits around the first overwintering period in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) cultured in Northeast China. Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Pan, Z.; Chang, G.; Wang, H.; Ding, H.; Wu, N.; Qiang, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J. Polymorphisms of the growth hormone gene and their association with growth traits and sex in Sarcocheilichthys sinensis. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2020, 295, 1477–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Joshi, R.; Gjøen, H.M.; Lv, Z.; Kent, M. Construction of genetic linkage maps from a hybrid family of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 792666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, K.; Storici, F. A mechanism of gene amplification driven by small DNA fragments. PLoS Genet. 2019, 13, e1003119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

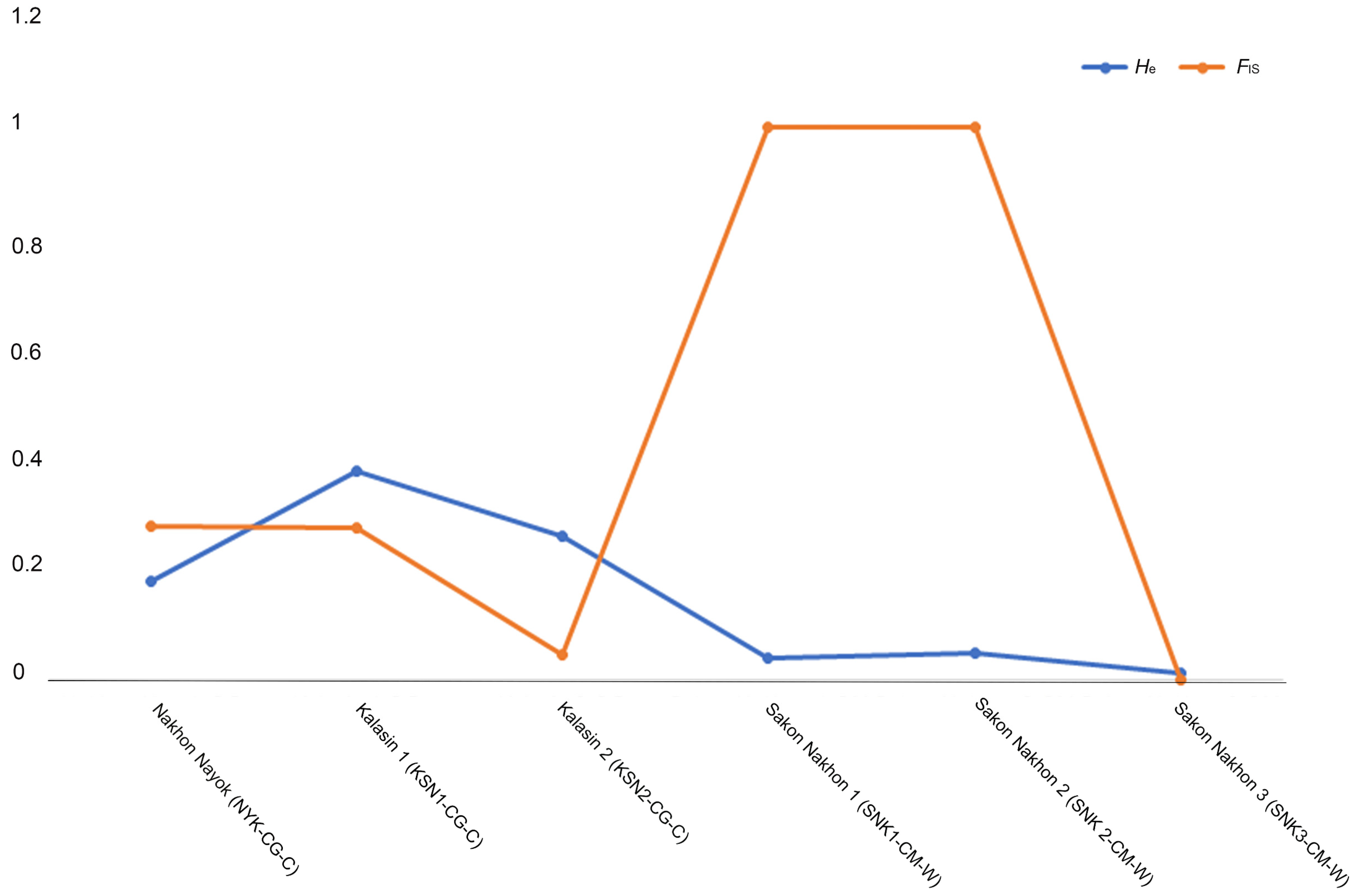
| Species | Population | Code | N | Na | Ne | AR | Ho | He | F | FIS | π | HWE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. gariepinus | Nakhon Nayok | NYK-CG-C | 31 | 3.000 | 1.218 | 3.000 | 0.129 | 0.179 | 0.279 | 0.279 | 0.0027 ± 0.0008 | 0.79 ns |
| Kalasin 1 | KSN1-CG-C | 88 | 4.000 | 1.607 | 4.000 | 0.273 | 0.378 | 0.278 | 0.277 | 0.0053 ± 0.0015 | 0.003 ** | |
| Kalasin 2 | KSN2-CG-C | 137 | 2.000 | 1.351 | 2.000 | 0.248 | 0.260 | 0.044 | 0.046 | 0.0031 ± 0.0003 | 0.607 ns | |
| C. macrocephalus | Sing Buri | SBR-CM-C | 19 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | - | 0 | - |
| Sakon Nakhon 1 | SNK1-CM-W | 49 | 2.000 | 1.042 | 2.000 | 0.000 | 0.040 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.0022 ± 0.0021 | 0.000 *** | |
| Sakon Nakhon 2 | SNK2-CM-W | 78 | 2.000 | 1.053 | 2.000 | 0.000 | 0.050 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.0026 ± 0.0017 | 0.000 *** | |
| Sakon Nakhon 3 | SNK3-CM-W | 82 | 2.000 | 1.012 | 2.000 | 0.012 | 0.012 | −0.006 | 0.000 | 0.0001 ± 0.0001 | 0.956 ns | |
| Sakon Nakhon 4 | SNK4-CM-C | 25 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | - | 0 | - | |
| Suphan Buri 1 | SPB1-CM-W | 5 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | - | 0 | - | |
| Suphan Buri 2 | SPB2-CM-W | 3 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | - | - | - | |
| Nakhon Pathom 1 | NPT1-CM-W | 2 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | - | - | - | |
| Nakhon Pathom 2 | NPT2-CM-W | 2 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | - | - | - | |
| Nakhon Si Thammarat 1 | NST1-CM-W | 3 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | - | - | - | |
| Nakhon Si Thammarat 2 | NST2-CM-C | 10 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | - | 0 | - | |
| Surat Thani | STN-CM-C | 25 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | - | 0 | - | |
| Laos | LAO-CM-C | 30 | 2.000 | 1.034 | 2.000 | 0.033 | 0.033 | −0.017 | - | 0.0005 ± 0.0005 | 0.926 ns | |
| Overall | - | 589 | 1.625 | 1.082 | 1.625 | 0.043 | 0.059 | 0.368 | 0.271 | 0.04402 | - | |
| SD | - | - | ±0.221 | ±0.043 | ±0.221 | ±0.023 | ±0.028 | ±0.112 | ±0.178 | - | - |
| Species | Population | Code | Tajima’s D | Fu and Li’s D | Fu and Li’s F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. gariepinus | Nakhon Nayok | NYK-CG-C | −0.382 ns | 0.927 ns | 0.631 ns |
| Kalasin 1 | KSN1-CG-C | −1.95 * | −5.751 ** | −5.17 ** | |
| Kalasin 2 | KSN2-CG-C | 1.392 ns | 0.647 ns | 1.038 ns | |
| C. macrocephalus | Sing Buri | SBR-CM-C | - | - | - |
| Sakon Nakhon 1 | SNK1-CM-W | −2.427 ** | −4.974 ** | −4.875 ** | |
| Sakon Nakhon 2 | SNK2-CM-W | −2.074 * | −1.473 ns | 0.275 ns | |
| Sakon Nakhon 3 | SNK3-CM-W | −1.044 ns | −1.991 ns | −1.988 ns | |
| Sakon Nakhon 4 | SNK4-CM-C | - | - | - | |
| Suphan Buri 1 | SPB1-CM-W | −1.093 ns | −1.093 ns | −1.113 ns | |
| Suphan Buri 2 | SPB2-CM-W | - | - | - | |
| Nakhon Pathom 1 | NPT1-CM-W | - | - | - | |
| Nakhon Pathom 2 | NPT2-CM-W | - | - | - | |
| Nakhon Si Thammarat 1 | NST1-CM-W | - | - | - | |
| Nakhon Si Thammarat 2 | NST2-CM-C | - | - | - | |
| Surat Thani | STN-CM-C | - | - | - | |
| Laos | LAO-CM-C | −1.503 ns | −2.319 ns | −2.408 ns | |
| C. gariepinus | - | −1.827 * | −7.310 ** | −6.174 ** | |
| C. macrocephalus | - | −0.312 ns | 0.972 ns | 0.523 ns | |
| Overall mean value | - | −2.093 * | −8.383 ** | −6.267 ** |
| Species | Population | Code | N | dS (±SE) | dN (±SE) | ω (dN/dS) | Z-Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | Z-Value | |||||||
| C. gariepinus | Nakhon Nayok | NYK-CG-C | 31 | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 0.013 ± 0.008 | - | 0.075 | 1.794 |
| Kalasin 1 | KSN1-CG-C | 88 | 0.337 ± 0.103 | 0.401 ± 0.078 | 1.189 | 0.061 | 1.891 | |
| Kalasin 2 | KSN2-CG-C | 137 | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 0.014 ± 0.010 | - | 0.159 | 1.417 | |
| C. macrocephalus | Sing Buri | SBR-CM-C | 19 | - | - | - | - | |
| Sakon Nakhon 1 | SNK1-CM-W | 49 | 0.376 ± 0.118 | 0.263 ± 0.666 | 0.699 | 0.991 | 0.011 | |
| Sakon Nakhon 2 | SNK2-CM-W | 78 | 0.376 ± 0.118 | 0.263 ± 0.062 | 0.699 | 0.991 | 0.011 | |
| Sakon Nakhon 3 | SNK3-CM-W | 82 | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 0.0070 ± 0.006 | - | 0.322 | 0.994 | |
| Sakon Nakhon 4 | SNK4-CM-C | 25 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Suphan Buri 1 | SPB1-CM-W | 5 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Suphan Buri 2 | SPB2-CM-W | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Nakhon Pathom 1 | NPT1-CM-W | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Nakhon Pathom 2 | NPT2-CM-W | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Nakhon Si Thammarat 1 | NST1-CM-W | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Nakhon Si Thammarat 2 | NST2-CM-C | 10 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Surat Thani | STN-CM-C | 25 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Laos | LAO-CM-C | 30 | 0.020 ± 0.021 | 0.006 ± 0.006 | 0.3 | 0.583 | −0.550 | |
| Overall mean | - | 589 | 0.485 ± 0.120 | 0.497 ± 0.093 | 1.024 | 0.071 | 1.822 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thammachak, P.; Chalermwong, P.; Patta, C.; Jaito, W.; Singchat, W.; Panthum, T.; Budi, T.; Sriphairoj, K.; Hatachote, S.; Srisapoome, P.; et al. GH1 Gene Polymorphisms Reveal Population-Level Allele Variation in North African (Clarias gariepinus) and Bighead Catfish (Clarias macrocephalus). Genes 2025, 16, 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111266
Thammachak P, Chalermwong P, Patta C, Jaito W, Singchat W, Panthum T, Budi T, Sriphairoj K, Hatachote S, Srisapoome P, et al. GH1 Gene Polymorphisms Reveal Population-Level Allele Variation in North African (Clarias gariepinus) and Bighead Catfish (Clarias macrocephalus). Genes. 2025; 16(11):1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111266
Chicago/Turabian StyleThammachak, Phonemany, Piangjai Chalermwong, Chananya Patta, Wattanawan Jaito, Worapong Singchat, Thitipong Panthum, Trifan Budi, Kednapat Sriphairoj, Sittichai Hatachote, Prapansak Srisapoome, and et al. 2025. "GH1 Gene Polymorphisms Reveal Population-Level Allele Variation in North African (Clarias gariepinus) and Bighead Catfish (Clarias macrocephalus)" Genes 16, no. 11: 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111266
APA StyleThammachak, P., Chalermwong, P., Patta, C., Jaito, W., Singchat, W., Panthum, T., Budi, T., Sriphairoj, K., Hatachote, S., Srisapoome, P., Muangmai, N., Sawatdichaikul, O., Griffin, D. K., Antunes, A., Duengkae, P., Na-Nakorn, U., Matsuda, Y., & Srikulnath, K. (2025). GH1 Gene Polymorphisms Reveal Population-Level Allele Variation in North African (Clarias gariepinus) and Bighead Catfish (Clarias macrocephalus). Genes, 16(11), 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111266











