Molecular Characterization and Expression Patterns of Sox3 and Sox30 Genes and Response to Exogenous Hormones in the Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Experimental Materials
2.2. DNA Extraction and Embryonic Sex Identification
2.3. Total RNA Extraction and First-Strand cDNA Synthesis
2.4. Cloning of Sox3 and Sox30 Genes in P. sinensis
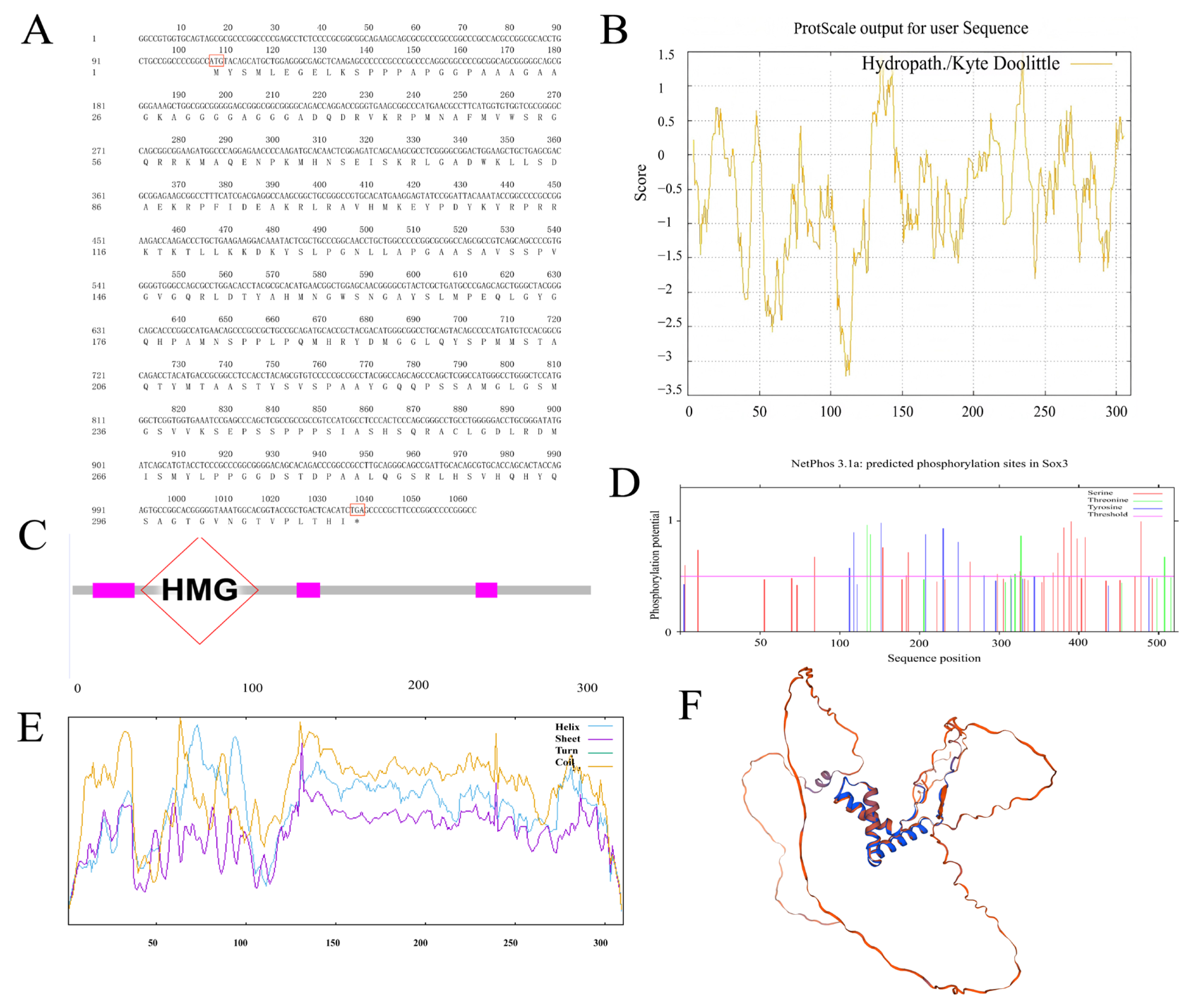
2.5. Bioinformatic Analysis of Sox3 and Sox30 Genes
2.6. Tissue Expression Analysis
2.7. Exogenous Hormone Treatment of P. sinensis Embryos
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cloning of Sox3 and Sox30 Genes in P. sinensis and Analysis of Their Deduced Amino Acid Sequences
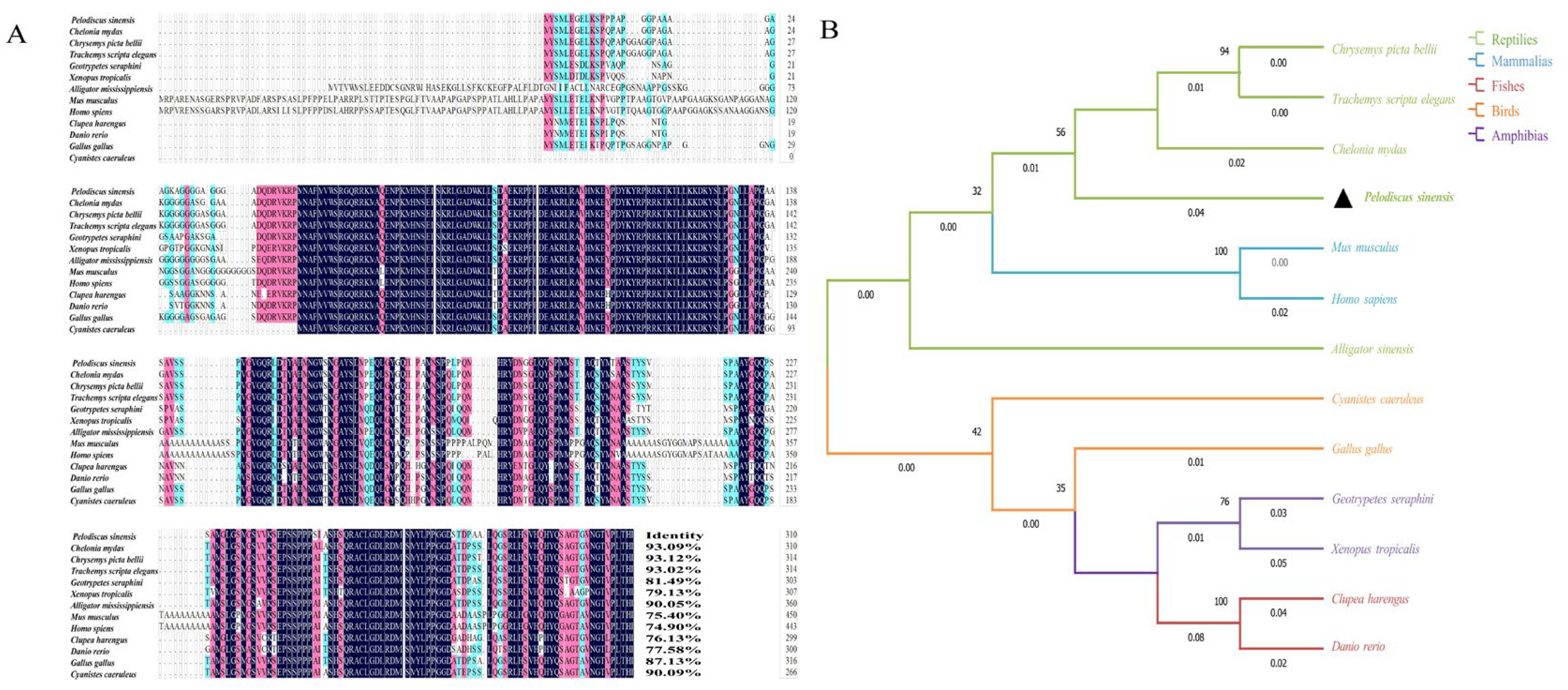
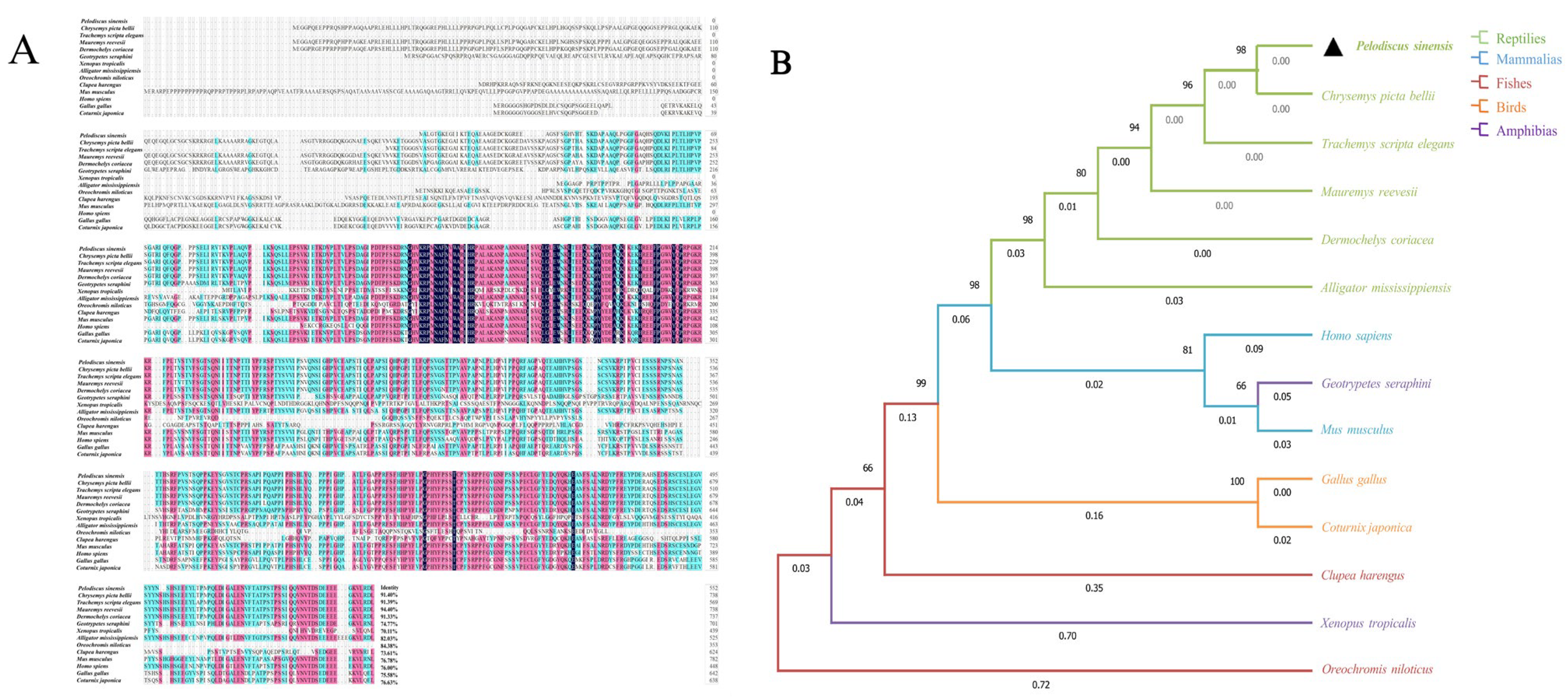
3.2. Homology Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Construction of the Sox3 and Sox30 Genes in P. sinensis
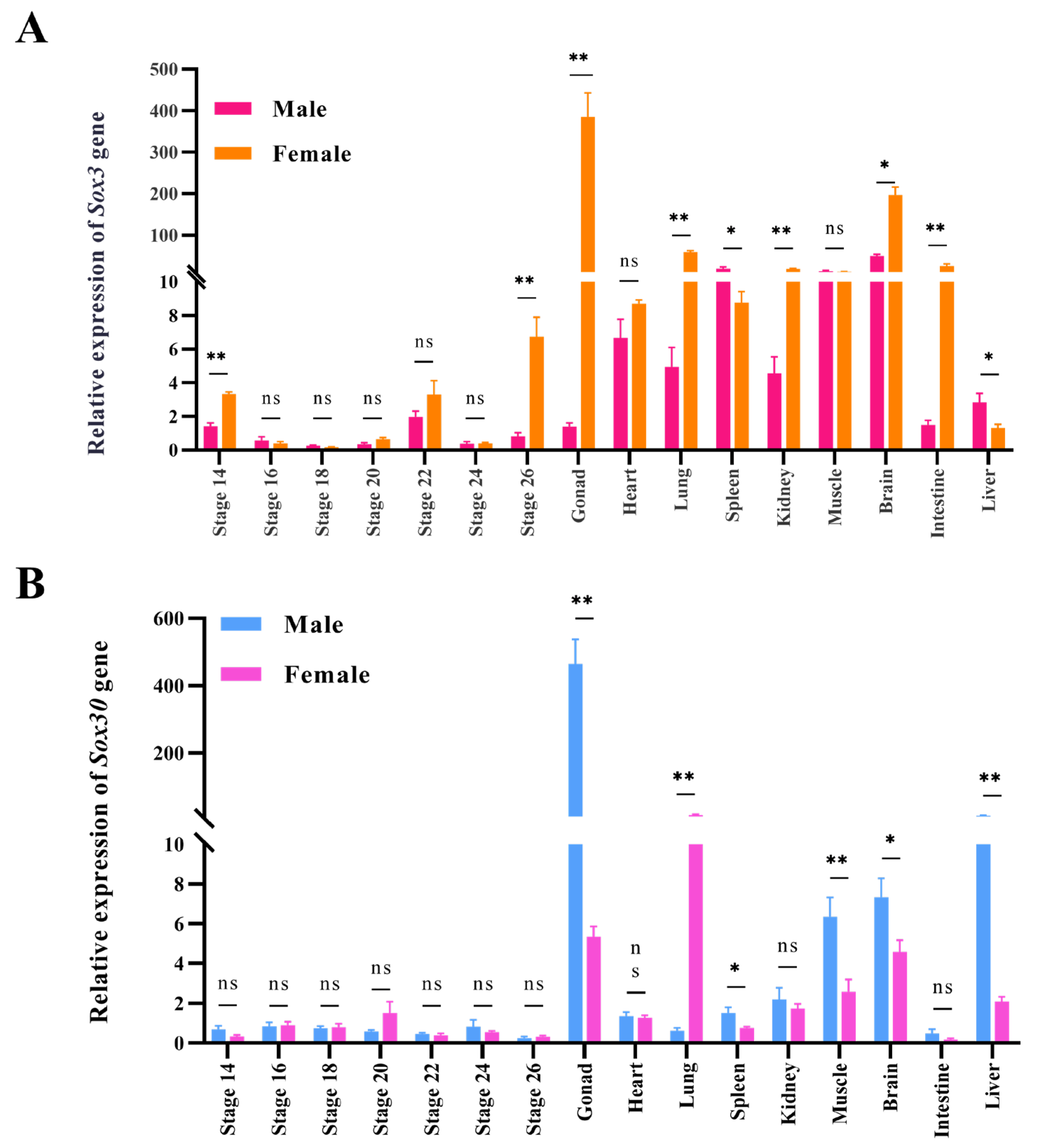
3.3. Expression of Sox3 and Sox30 Genes in Embryonic Gonads and Adult Tissues of P. sinensis
3.4. Effects of E2 and MT Treatments on the Expression of Sox3 and Sox30 Genes in Gonads of P. sinensis Embryonic Gonads at Different Developmental Stages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foster, J.W.; Dominguez-Steglich, M.A.; Guioli, S.; Kwok, C.; Weller, P.A.; Stevanović, M.; Weissenbach, J.; Mansour, S.; Young, I.D.; Goodfellow, P.N.; et al. Campomelic Dysplasia and Autosomal Sex Reversal Caused by Mutations in an SRY-Related Gene. Nature 1994, 372, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osaki, E. Identification of a Novel Sry-Related Gene and Its Germ Cell-Specific Expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 2503–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeng, S.R.; Wu, G.C.; Yueh, W.S.; Kuo, S.F.; Dufour, S.; Chang, C.F. Gonadal Development and Expression of Sex-Specific Genes during Sex Differentiation in the Japanese Eel. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018, 257, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q. Molecular Cloning, Promoter Analysis and Expression Profiles of the Sox3 Gene in Japanese Flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 27931–27944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Yang, C.; Tao, W.; Wang, D. Genome-Wide Identification and Transcriptome-Based Expression Profiling of the Sox Gene Family in the Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raverot, G.; Weiss, J.; Park, S.Y.; Hurley, L.; Jameson, J.L. Sox3 Expression in Undifferentiated Spermatogonia is Required for the Progression of Spermatogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2005, 283, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Li, C.; Ying, R.; Lin, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, R. Loss-of-Function of Sox3 Causes Follicle Development Retardation and Reduces Fecundity in Zebrafish. Protein Cell 2018, 10, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Fu, K.; Yin, H.; Cui, Y.; Yue, Q.; Li, W.; Cheng, L.; Tan, H.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; et al. Sox30 Initiates Transcription of Haploid Genes during Late Meiosis and Spermiogenesis in Mouse Testes. Development 2018, 145, dev164855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Tang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Deng, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, D. The Transcription Factor Sox30 is Involved in Nile Tilapia Spermatogenesis. J. Genet. Genom. 2022, 49, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, A.; Senthilkumaran, B. Role of Sox30 in Regulating Testicular Steroidogenesis of Common Carp. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 204, 105769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.F.; Li, Y.P. Roles of SOX Transcription Factors on Fate Decision of Germ Cells. Chin. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 41, 961–966. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, F.; Jiang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ouyang, W.; Liu, W.; Mao, C.; Chen, Q.; Huang, C.; et al. Epigenetic Inactivation of SOX30 is Associated with Male Infertility and Offers a Therapy Target for Non-Obstructive Azoospermia. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Chen, C.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Geng, L.; Su, J.; Li, W.; Zhu, X. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Key Genes and Pathways Related to Sex Differentiation in the Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. D 2022, 42, 100986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Lei, L.; Chen, C.; Ji, L.; Li, J.; Wu, C.; Yu, W.; Luo, L.; Chen, W.; et al. Comparative Genomic Survey and Functional Analysis of DKKL1 during Spermatogenesis in the Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Luo, H.; Hou, M.; Chen, J.; Tao, B.; Zhu, Z.; Song, Y.; Hu, W. Aromatase Inhibitor Induces Sex Reversal in the Protogynous Hermaphroditic Rice Field Eel (Monopterus albus). Aquaculture 2022, 551, 737960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Qiao, L.; Yang, Q.; Rong, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, W.; Song, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Effects of 17α-Methyltestosterone on the Transcriptome and Sex Hormones in the Brain of Gobiocypris rarus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieau, C.; Girondot, M.; Richard-Mercier, N.; Desvages, G.; Dorizzi, M.; Zaborski, P. Temperature Sensitivity of Sexual Differentiation of Gonads in the European Pond Turtle: Hormonal Involvement. J. Exp. Zool. 1994, 270, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Greisy, Z.A.; El-Gamal, A.E. Monosex Production of Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus Using Different Doses of 17α-Methyltestosterone with Respect to the Degree of Sex Stability After One Year of Treatment. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2012, 38, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Hur, S.W.; Na, O.S.; Baek, H.J.; Noh, C.H.; Han, S.H.; Lee, Y.D. Induction of Primary Male in Juvenile Red Spotted Grouper Epinephelus akaara by Immersion of 17α-Methyltestosterone. Dev. Reprod. 2014, 18, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokita, M.; Kuratani, S. Normal Embryonic Stages of the Chinese Softshelled Turtle Pelodiscus sinensis (Trionychidae). Zool. Sci. 2001, 18, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lei, L.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, Y.; Hong, X.; Liu, X.; Yu, L.; et al. Development and Evaluation of a Medium-Free Incubation Method for Hatching Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) Eggs. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 31, 101643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Ji, L.; Hong, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Wei, C.; Zhu, X.; Li, W. Identification of Sex-Specific Markers and Candidate Genes Using WGS Sequencing Reveals a ZW-Type Sex-Determination System in the Chinese Soft-Shell Turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artimo, P.; Jonnalagedda, M.; Arnold, K.; Baratin, D.; Csardi, G.; De Castro, E.; Duvaud, S.; Flegel, V.; Fortier, A.; Gasteiger, E.; et al. ExPASy: SIB Bioinformatics Resource Portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W597–W603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.; Tognolli, M.; Bairoch, A. The Swiss-Prot Protein Knowledgebase and ExPASy: Providing the Plant Community with High Quality Proteomic Data and Tools. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2004, 42, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, N.; Sicheritz-Pontén, T.; Gupta, R.; Gammeltoft, S.; Brunak, S. Prediction of Post-translational Glycosylation and Phosphorylation of Proteins from the Amino Acid Sequence. Proteomics 2004, 4, 1633–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geourjon, C.; Deléage, G. SOPMA: Significant Improvements in Protein Secondary Structure Prediction by Consensus Prediction from Multiple Alignments. Bioinformatics 1995, 11, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology Modelling of Protein Structures and Complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, H.; Shao, F.; Yu, J.; Gilbert, E.; Gu, Z. Molecular Cloning, Tissue Expression and Polymorphism Analysis of the Caveolin-3 Gene in Ducks. Br. Poult. Sci. 2020, 62, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Lei, L.; Hong, X.; Yu, L.; Xu, H.; Li, W.; Zhu, X. Cloning and expression analysis of histone H2A variant in oocytes of Chinese soft-shelledturtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Acta Hydrobiol. Sin 2021, 45, 1207–1213. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.L. Molecularcloning, Expression of Foxl2 and the Influence of Temperature and Exogenoushormone on Expression of Foxl2 in the Pelodiscus sinensis. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 26 May 2016. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Sun, W.; Bao, H.; Liang, X.; Li, P.; Shi, S.; Wang, Z.; Qian, G.; Ge, C. The Forkhead Factor Foxl2 Participates in the Ovarian Differentiation of Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle Pelodiscus sinensis. Dev. Biol. 2022, 492, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thépot, D. Sex Chromosomes and Master Sex-Determining Genes in Turtles and Other Reptiles. Genes 2021, 12, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ao, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Characterization of the Transcription Factor Sox3 Regulating the Gonadal Development of Pearlscale Angelfish (Centropyge vrolikii). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 48, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAninch, D.; Mäkelä, J.-A.; La, H.M.; Hughes, J.N.; Lovell-Badge, R.; Hobbs, R.M.; Thomas, P.Q. SOX3 Promotes Generation of Committed Spermatogonia in Postnatal Mouse Testes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q. Molecular Mechanismof Oocyte Development Regulated by Sox3 in Zebrafish. Master’s Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 10 April 2018. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Gui, L.; Xiong, X.X.; Chen, X.R.; Liu, Y.Y.; Tan, G.H. Transcriptional regulatory role of the Sox gene family in adult neurogenesis. Prog. Physiol. Sci. 2020, 51, 289–293. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, B.; Jerry, D.R.; Shen, X.; Koh, J.; Terence, C.; Nayfa, M.G.; Nguyen, V.; Loo, G.; Vij, S.; Domingos, J.A. Transcriptomic Analysis of Gonads in Malabar Red Snapper (Lutjanus malabaricus) Reveals Genes Associated with Gonad Development. Aquaculture 2024, 592, 741258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Xia, W.; Gui, J. Differential Expression and Dynamic Changes of SOX3 during Gametogenesis and Sex Reversal in Protogynous Hermaphroditic Fish. J. Exp. Zool. Part A Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 2007, 307, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, P.; Liu, T.; Qiao, D.; Hu, Q.; Su, S. Identification and Functional Analysis of SOX Transcription Factors in the Genome of the Chinese Soft-Shell Turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Comp. Biochem. Phys. B 2020, 242, 110407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Yin, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, N.; Yang, J.; Ouyang, W.; Hao, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, Y.; et al. Identification of SRY-Box 30 (Sox30) as an Age-Related Essential Gatekeeper for Male Germ-Cell Meiosis and Differentiation. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, S.P.; Errington, F.; Ashworth, A.; Jowett, T.; Austin, C.A. Sox30: A Novel Zebrafish Sox Gene Expressed in a Restricted Manner at the Midbrain-Hindbrain Boundary during Neurogenesis. Dev. Genes Evol. 1999, 209, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.-W.A.; Spiller, C.; Merriner, D.J.; O’Bryan, M.K.; Bowles, J.; Koopman, P. SOX30 is Required for Male Fertility in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.H. Study on the Functionand Regulatory Mechanism of Transcription Factor Sox30 in Spermatogenesis of Nile tilapia. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 24 April 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Shioda, K.; Odajima, J.; Kobayashi, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Cordazzo, B.; Isselbacher, K.J.; Shioda, T. Transcriptomic and Epigenetic Preservation of Genetic Sex Identity in Estrogen-Feminized Male Chicken Embryonic Gonads. Mol. Endocrinol. 2020, 162, bqaa208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Crews, D. Molecular Mechanisms of Temperature-Dependent Sex Determination in the Context of Ecological Developmental Biology. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 354, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhu, C.; Sun, J.; Wang, W.; Wu, T.; Chen, H.; Shi, S.; Li, G. Foxl2 of the Hong Kong Catfish (Clarias fuscus): cDNA Cloning, Tissue Distribution and Changes in Gene Expression Towards Methyltestosterone, Estradiol and Letrozole Exposure of the Fries During Gonadal Differentiation. Genes Genom. 2015, 37, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, G.; Xin, Q.; Tian, X.; Wu, L.; Shi, X.; Ma, W.; Liu, H.; Jiang, H.; et al. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of Sirt1 and Its Role in the Follicle of Juvenile Chinese Soft-shelled Turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Gene 2023, 860, 147211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Recalde, O.; Goikoetxea, A.; Hore, T.A.; Todd, E.V.; Gemmell, N.J. The Genetics and Epigenetics of Sex Change in Fish. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2020, 8, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Xiao, H.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Wei, L. Transcription of the Sox30 Gene is Positively Regulated by Dmrt1 in Nile Tilapia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenugu, S.; Pranoty, A.; Mamta, S.K.; Senthilkumaran, B. Development and Organisation of Gonadal Steroidogenesis in Bony Fishes—A Review. Aquac. Fish. 2021, 6, 223–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Bengochea, A.; Doretto, L.; Rosa, I.F.; Oliveira, M.A.; Silva, C.; Silva, D.M.Z.A.; Santos, G.R.; Santos, J.S.F.; Avelar, M.M.; Silva, L.V.; et al. Effects of 17β-Estradiol on Early Gonadal Development and Expression of Genes Implicated in Sexual Differentiation of a South American Teleost, Astyanax altiparanae. Comp. Biochem. Phys. B 2020, 248–249, 110467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Sequences (5′–3′) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| PB1-F | GGATCTCATTTGTGAGCCTACATGT | Sex identification |
| PB1-R | CCCACAGCTTGCTTTCCWTGTTTAG | |
| Sox3-F | TTGGCCGTGGTGCAGTAGC | cDNA cloning |
| Sox3-R | ATGAGTGTAGAGGTGGAATGGAAA | |
| Sox30-F | GAGGAGAGCCAGAAAGAGGAGC | cDNA cloning |
| Sox30-R | TATTAGTGGGAGTGGGGGTGACAGAA | |
| Sox3-qF | GCAGTACAGCCCCATGATGT | Real-time fluorescence quantification |
| Sox3-qR | GATCATATCCCGCAGGTCC | |
| Sox30-qF | CGAATGCCTGGGCTTTTA | Real-time fluorescence quantification |
| Sox30-qR | GATGGGGTTGCCGTGAAA | |
| Ef1αF | ACTCGTCCAACTGACAAGCCTC | Reference genes |
| Ef1αR | CACGGCGAACATCTTTCACAG |
| Gene | Species | Accession |
|---|---|---|
| Sox3 | Chelonia mydas | XP_037764741.1 |
| Sox3 | Chrysemys picta bellii | XP_005294674.2 |
| Sox3 | Trachemys scripta elegans | XP_034636385.1 |
| Sox3 | Geotrypetes seraphini | XP_033802893.1 |
| Sox3 | Xenopus tropicalis | NP_001007502.1 |
| Sox3 | Alligator mississippiensis | XP_006031121.1 |
| Sox3 | M. musculus | NP_033263.2 |
| Sox3 | H. sapiens | NP_005625.2 |
| Sox3 | Clupea harengus | XP_012695760.1 |
| Sox3 | D. rerio | NP_001001811.2 |
| Sox3 | Gallus gallus | NP_989526.1 |
| Sox3 | Cyanistes caeruleus | XP_023782651.1 |
| Sox30 | C. picta bellii | XP_005300115.3 |
| Sox30 | T. scripta elegans | XP_034635714.1 |
| Sox30 | Mauremys reevesii | XP_039340705.1 |
| Sox30 | Dermochelys coriacea | XP_038267805.1 |
| Sox30 | G. seraphini | XP_033783385.1 |
| Sox30 | X. tropicalis | XP_031753986.1 |
| Sox30 | A. mississippiensis | XP_019331538.2 |
| Sox30 | O. niloticus | XP_003447014.1 |
| Sox30 | Clupea harengus | XP_042564328.1 |
| Sox30 | M. musculus | NP_775560.1 |
| Sox30 | G. gallus | XP_414564.1 |
| Sox30 | Coturnix japonica | XP_015731686.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, K.; Li, Y.; Ren, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Chen, C.; Ji, L.; Liu, X.; Hong, X.; Wei, C.; et al. Molecular Characterization and Expression Patterns of Sox3 and Sox30 Genes and Response to Exogenous Hormones in the Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Genes 2025, 16, 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111249
Xiao K, Li Y, Ren T, Wang Z, Zhu J, Chen C, Ji L, Liu X, Hong X, Wei C, et al. Molecular Characterization and Expression Patterns of Sox3 and Sox30 Genes and Response to Exogenous Hormones in the Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Genes. 2025; 16(11):1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111249
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Kailin, Yue Li, Tong Ren, Ziman Wang, Junxian Zhu, Chen Chen, Liqin Ji, Xiaoli Liu, Xiaoyou Hong, Chengqing Wei, and et al. 2025. "Molecular Characterization and Expression Patterns of Sox3 and Sox30 Genes and Response to Exogenous Hormones in the Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis)" Genes 16, no. 11: 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111249
APA StyleXiao, K., Li, Y., Ren, T., Wang, Z., Zhu, J., Chen, C., Ji, L., Liu, X., Hong, X., Wei, C., Chen, H., Zhu, X., Lai, X., & Li, W. (2025). Molecular Characterization and Expression Patterns of Sox3 and Sox30 Genes and Response to Exogenous Hormones in the Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Genes, 16(11), 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111249






