Genetic Variants in the ABCB1 and ABCG2 Gene Drug Transporters Involved in Gefitinib-Associated Adverse Reaction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Characteristics of Studies, Adverse Drug Reactions, Genes/Genetic Variants, and Participants
3.3. Adverse Drug Reactions versus ABCB1 and ABCG2 Genes
3.4. Quality Assessment
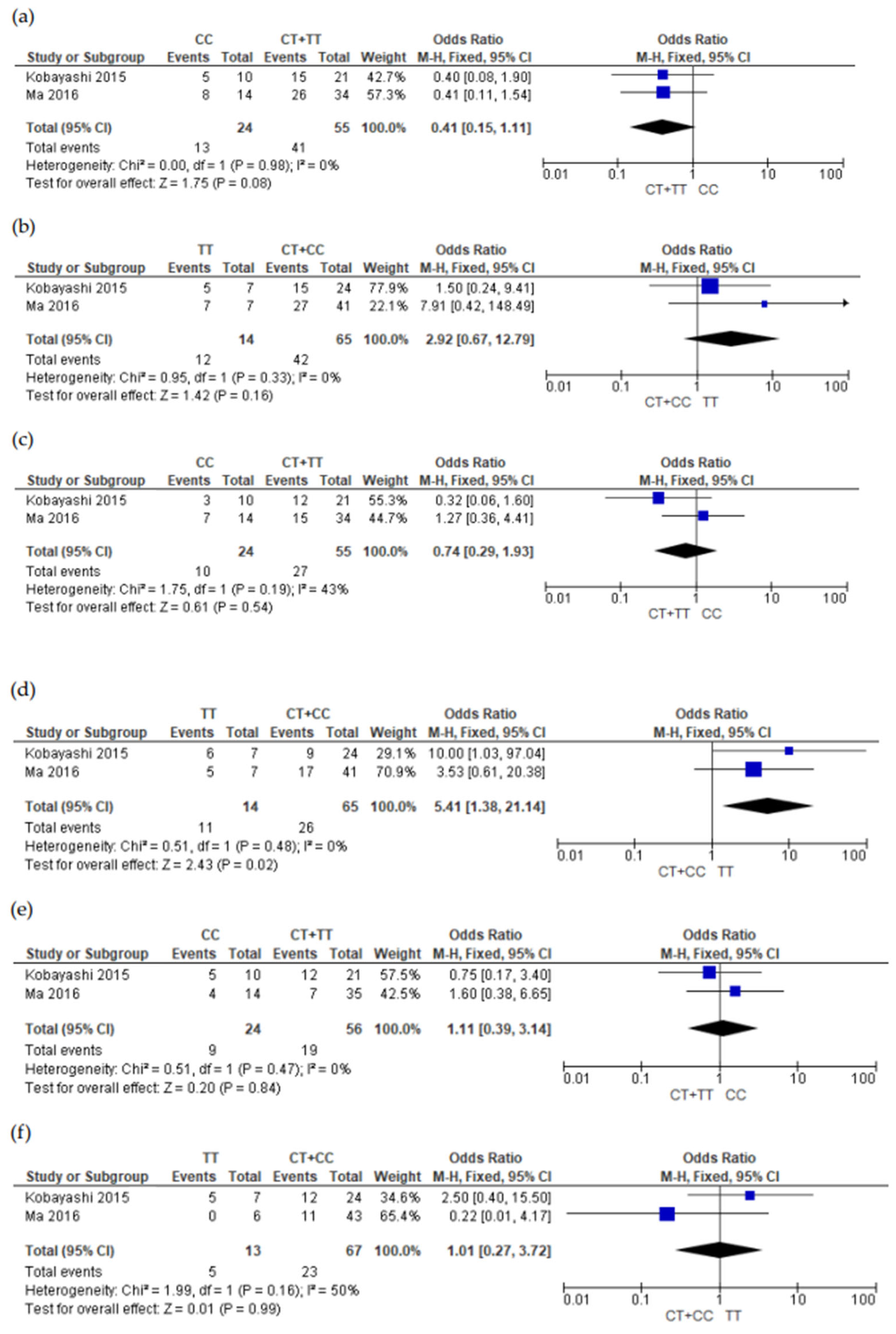
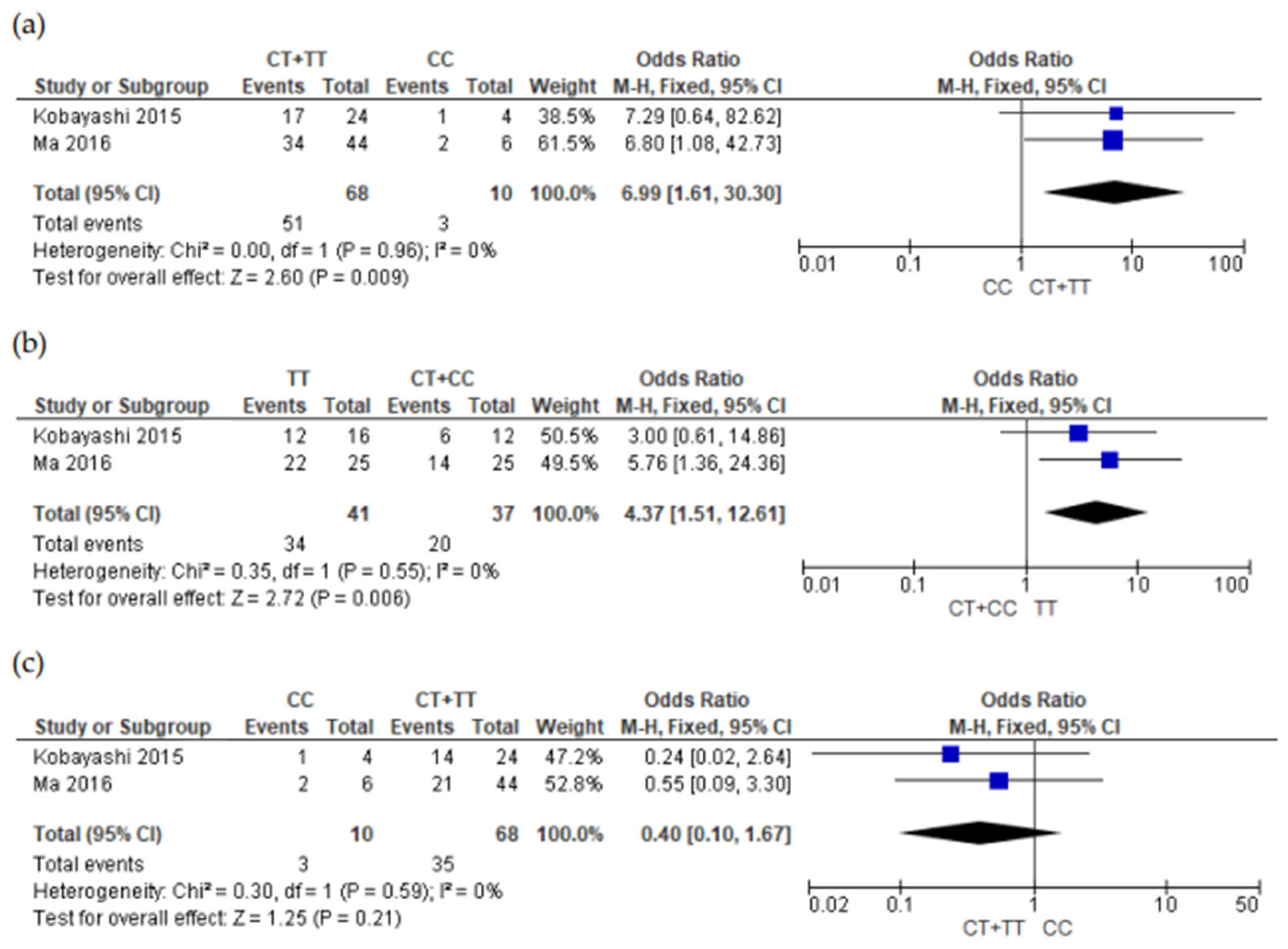
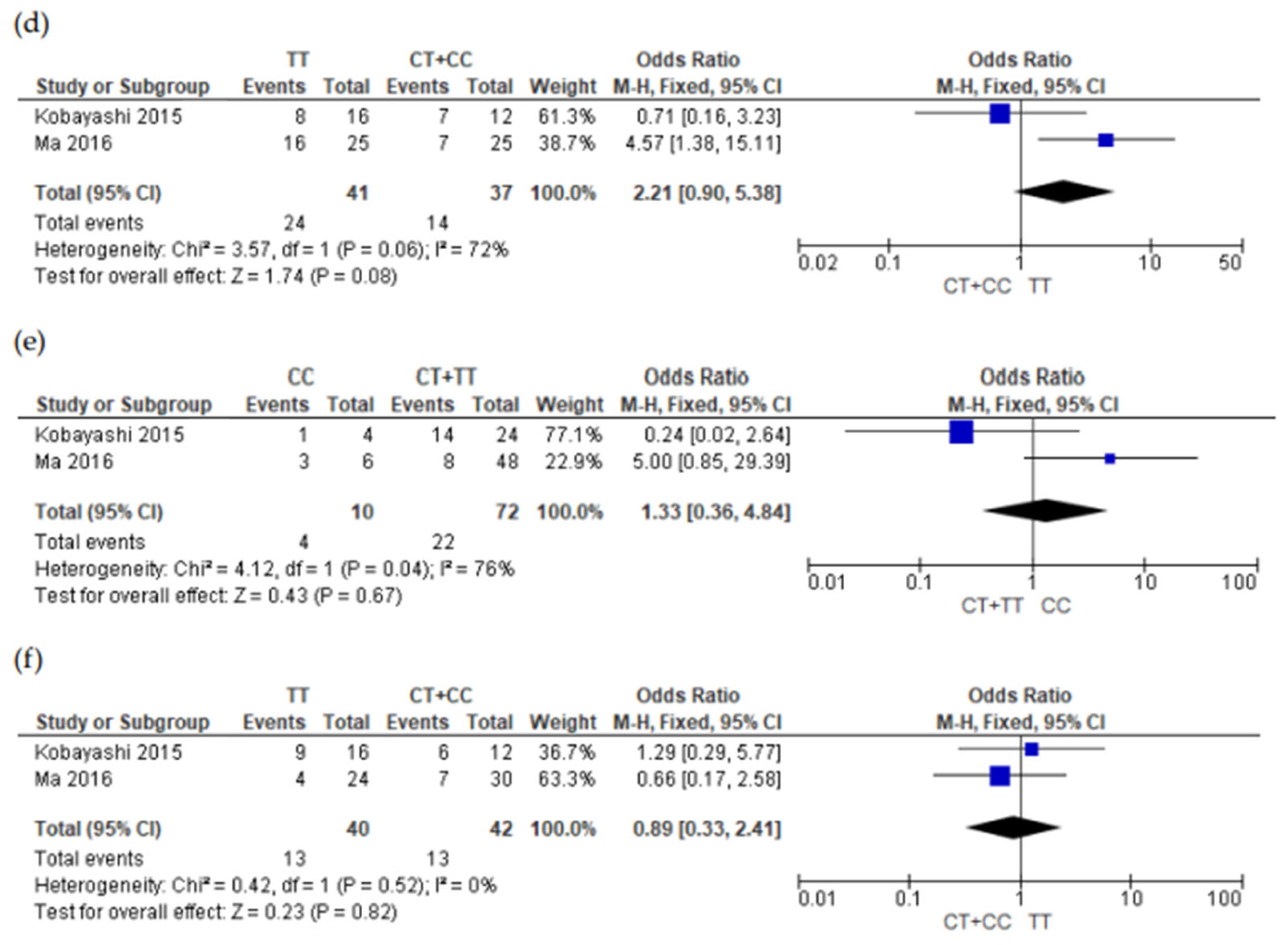
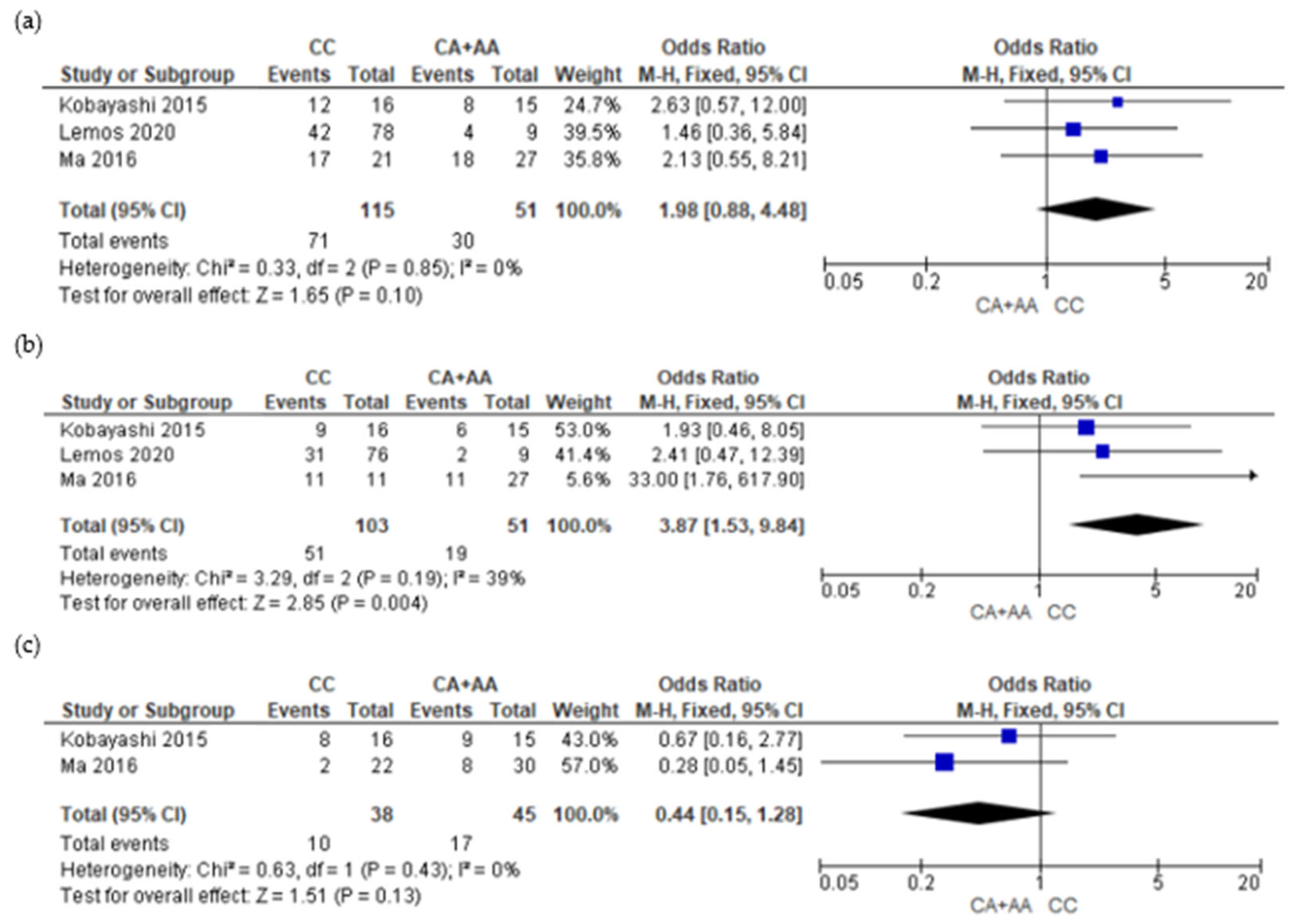
3.5. Meta-Analysis Results
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Birnbaum, A.; Ready, N. Gefitinib therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2005, 6, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cataldo, V.D.; Gibbons, D.L.; Pérez-Soler, R.; Quintás-Cardama, A. Treatment of Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Erlotinib or Gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Murakami, H.; Yang, P.-C.; He, J.; Nakagawa, K.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Wang, X.; Enatsu, S.; Puri, T.; et al. Randomized phase II trial of gefitinib with and without pemetrexed as first-line therapy in patients with advanced nonsquamous non–small-cell lung cancer with activating epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3258–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelsohn, J.; Baselga, J. The EGF receptor family as targets for cancer therapy. Oncogene 2000, 19, 6550–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilenbaum, R.A.; Horn, L.A. Management of EGFR Mutation–Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2016, 14, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culy, C.R.; Faulds, D. Gefitinib. Drugs 2002, 62, 2237–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, J.T.; Haap, M.; Kopp, H.-G.; Lipp, H.-P. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors—A Review on Pharmacology, Metabolism and Side Effects. Curr. Drug Metab. 2009, 10, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofheinz, R.-D.; Deplanque, G.; Komatsu, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ocvirk, J.; Racca, P.; Guenther, S.; Zhang, J.; Lacouture, M.E.; Jatoi, A. Recommendations for the Prophylactic Management of Skin Reactions Induced by Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors in Patients with Solid Tumors. Oncologist 2016, 21, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; National Institute of Health; National Cancer Institute (NCI). U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE). Version 5.0; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute: 2018. Available online: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm#ctc_50 (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Takeda, M.; Okamoto, I.; Nakagawa, K. Pooled safety analysis of EGFR-TKI treatment for EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2015, 88, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kong, J. Effect of aerobic exercise on acquired gefitinib resistance in lung adenocarcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirmohamed, M.; Breckenridge, A.M.; Kitteringham, N.R.; Park, K. Adverse drug reactions. BMJ 1998, 316, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, B.; Tulsyan, S.; Kumar, S.; Mittal, R.D.; Agarwal, G. Cytochrome P450 in Cancer Susceptibility and Treatment. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2015, 71, 77–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takimoto, T.; Kijima, T.; Otani, Y.; Nonen, S.; Namba, Y.; Mori, M.; Yokota, S.; Minami, S.; Komuta, K.; Uchida, J.; et al. Polymorphisms of CYP2D6 Gene and Gefitinib-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Clin. Lung Cancer 2013, 14, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, E.; Umemura, S.; Nomura, S.; Kirita, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Yoh, K.; Niho, S.; Ohmatsu, H.; Tsuboi, M.; Ohe, Y.; et al. Impact of single nucleotide polymorphisms on severe hepatotoxicity induced by EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzumura, T.; Kimura, T.; Kudoh, S.; Umekawa, K.; Nagata, M.; Matsuura, K.; Tanaka, H.; Mitsuoka, S.; Yoshimura, N.; Kira, Y.; et al. Reduced CYP2D6 function is associated with gefitinib-induced rash in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glavinas, H.; Krajcsi, P.; Cserepes, J.; Sarkadi, B. The role of ABC transporters in drug resistance, metabolism and toxicity. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2004, 1, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umamaheswaran, G.; Kumar, D.K.; Adithan, C. Distribution of genetic polymorphisms of genes encoding drug metabolizing enzymes & drug transporters—A review with Indian perspective. Indian J. Med. Res. 2014, 139, 27–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Lim, H.; Yoo, Y.; Shin, E.S.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, H.T.; Lee, J.S. Associations of ABCB1, ABCC2, and ABCG2 polymorphisms with irinotecan-pharmacokinetics and clinical outcome in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer 2007, 110, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özvegy-Laczka, C.; Hegedűs, T.; Várady, G.; Ujhelly, O.; Schuetz, J.D.; Váradi, A.; Kéri, G.; Őrfi, L.; Német, K.; Sarkadi, B. High-Affinity Interaction of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors with the ABCG2 Multidrug Transporter. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 1485–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, C.; Giovannetti, E.; A Zucali, P.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Scheffer, G.L.; van der Straaten, T.; D’Incecco, A.; Falcone, A.; Guchelaar, H.-J.; Danesi, R.; et al. Impact of ABCG2 polymorphisms on the clinical outcome and toxicity of gefitinib in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Pharmacogenomics 2020, 12, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Sato, K.; Niioka, T.; Miura, H.; Ito, H.; Miura, M. Relationship among gefitinib exposure, polymorphisms of Its metabolizing enzymes and transporters, and side effects in Japanese patients with non–small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2015, 16, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Xin, S.; Huang, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Determinants of Gefitinib toxicity in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A pharmacogenomic study of metabolic enzymes and transporters. Pharmacogenom. J. 2017, 17, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Non-Randomized Studies in Meta-Analysis|Request PDF. 2012. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261773681_The_Newcastle-Ottawa_Scale_NOS_for_Assessing_the_Quality_of_Non-Randomized_Studies_in_Meta-Analysis (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Little, J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Moher, D.; Gagnon, F.; von Elm, E.; Khoury, M.J.; Cohen, B.; Davey-Smith, G.; Grimshaw, J.; et al. STrengthening the REporting of Genetic Association Studies (STREGA)—An extension of the STROBE statement. Genet. Epidemiol. 2009, 33, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersey, P.J.; Allen, J.E.; Christensen, M.; Davis, P.; Falin, L.J.; Grabmueller, C.; Hughes, D.S.T.; Humphrey, J.; Kerhornou, A.; Khobova, J.; et al. Ensembl Genomes 2013: Scaling up access to genome-wide data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D546–D552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, S.; Chen, X.; Xin, S.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Fang, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhuang, W.; et al. Establishment and application of a predictive model for gefitinib-induced severe rash based on pharmacometabolomic profiling and polymorphisms of transporters in non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 100951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, M.; Kondo, M.; Horio, M.; Ando, M.; Saito, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Horio, Y.; Hasegawa, Y. Genetic polymorphisms of the adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporters (abcg2, abcb1) and gefitinib toxicity. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Esteban-Villarrubia, J.; Soto-Castillo, J.J.; Pozas, J.; Román-Gil, M.S.; Orejana-Martín, I.; Torres-Jiménez, J.; Carrato, A.; Alonso-Gordoa, T.; Molina-Cerrillo, J. Tyrosine Kinase Receptors in Oncology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, K.; Kumar, G. Cancer multidrug-resistance reversal by ABCB1 inhibition: A recent update. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 239, 114542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, K.; Tiriveedhi, V. Perplexing Role of P-Glycoprotein in Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 515011. [Google Scholar]
- Jeleń, A.M.; Sałagacka, A.; Żebrowska, M.K.; Mirowski, M.; Talarowska, M.; Gałecki, P.; Balcerczak, E.I. The Influence of C3435T Polymorphism of the ABCB1 Gene on Genetic Susceptibility to Depression and Treatment Response in Polish Population—Preliminary Report. Int. J. Med Sci. 2015, 12, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, E.M.; Deeley, R.G.; Cole, S.P. Multidrug resistance proteins: Role of P-glycoprotein, MRP1, MRP2, and BCRP (ABCG2) in tissue defense. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 204, 216–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhani, S.; Jamil, K.; Nirni, S.S. Association of MDR1 Gene (C3435T) Polymorphism and Gene Expression Profiling in Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Platinum-Based Chemotherapy. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2015, 19, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawadzka, I.; Jeleń, A.; Pietrzak, J.; Żebrowska-Nawrocka, M.; Michalska, K.; Szmajda-Krygier, D.; Mirowski, M.; Łochowski, M.; Kozak, J.; Balcerczak, E. The impact of ABCB1 gene polymorphism and its expression on non-small-cell lung cancer development, progression and therapy—Preliminary report. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmeyer, S.; Burk, O.; von Richter, O.; Arnold, H.P.; Brockmöller, J.; Johne, A.; Cascorbi, I.; Gerloff, T.; Roots, I.; Eichelbaum, M.; et al. Functional polymorphisms of the human multidrug-resistance gene: Multiple sequence variations and correlation of one allele with P-glycoprotein expression and activity in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3473–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukal, S.; Guin, D.; Rawat, C.; Bora, S.; Mishra, M.K.; Sharma, P.; Paul, P.R.; Kanojia, N.; Grewal, G.K.; Kukreti, S.; et al. Multidrug efflux transporter ABCG2: Expression and regulation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 6887–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safar, Z.; Kis, E.; Erdo, F.; Zolnerciks, J.K.; Krajcsi, P. ABCG2/BCRP: Variants, transporter interaction profile of substrates and inhibitors. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2019, 15, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suominen, L.; Sjostedt, N.; Vellonen, K.-S.; Gynther, M.; Auriola, S.; Kidron, H. In vitro identification of decreased function phenotype ABCG2 variants. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 188, 106527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamber, C.P.; Lamba, J.K.; Yasuda, K.; Farnum, J.; Thummel, K.; Schuetz, J.D.; Schuetz, E.G. Natural allelic variants of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) and their relationship to BCRP expression in human intestine. Pharmacogenetics 2003, 13, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-H.; See, L.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chung, W.-H.; Chang, L.-C.; Yang, S.-F.; Su, S.-C. Impact of ABCG2 Gene Polymorphism on the Predisposition to Psoriasis. Genes 2021, 12, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, C.; He, H.; Pan, Z.; Fan, D.; He, Y.; You, H.; Li, Y. Associations between ABCG2 gene polymorphisms and gefitinib toxicity in non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusatis, G.; Gregorc, V.; Li, J.; Spreafico, A.; Ingersoll, R.G.; Verweij, J.; Ludovini, V.; Villa, E.; Hidalgo, M.; Sparreboom, A.; et al. Pharmacogenetics of ABCG2 and Adverse Reactions to Gefitinib. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 1739–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.A.; Jose, W.M.; Pavithran, K.; Triavadi, G.S. The Role of Gefitinib in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in India. Indian J. Palliat. Care 2013, 19, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, F.A.; Gil Ferreira, C.; Dienstmann, R.; Ferrari, B.L.; E Silva, M.C.; Junior, P.N.A.; Salles, P.G.d.O.; Diniz, P.H.C. Barriers in precision medicine implementation among Advanced Nonsquamous Cell Lung Cancer-patients: A Real-World Evidence Scenario. J. Mark. Access Health Policy 2022, 10, 2077905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Z.; Guo, L.; Li, P.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, B.; Ren, L.; Yan, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L. Determinants of Gefitinib Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Chinese Male Subjects: A Pharmacogenomic Study of Cytochrome P450 Enzymes and Transporters. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2020, 45, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiseo, M.; Rossi, G.; Capelletti, M.; Sartori, G.; Spiritelli, E.; Marchioni, A.; Bozzetti, C.; De Palma, G.; Lagrasta, C.; Campanini, N.; et al. Predictors of Gefitinib Outcomes in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): Study of a Comprehensive Panel of Molecular Markers. Lung Cancer 2010, 67, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Sato, K.; Niioka, T.; Takeda, M.; Okuda, Y.; Asano, M.; Ito, H.; Miura, M. Effects of Polymorphisms in CYP2D6 and ABC Transporters and Side Effects Induced by Gefitinib on the Pharmacokinetics of the Gefitinib Metabolite, O-Desmethyl Gefitinib. Med. Oncol. 2016, 33, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.C.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Sriuranpong, V.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; Okamoto, I.; Zhou, C.; et al. Osimertinib versus Standard of Care EGFR TKI as First-Line Treatment in Patients with EGFRm Advanced NSCLC: FLAURA Asian Subset. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, K.; Gu, W.; Gu, C.; Zhang, J.; Qwang, W.; Ren, G.; Tian, J. Relationship between MiR-7 Expression and Treatment Outcomes with Gefitinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 4613–4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ruan, Y.; Jiang, J.; Guo, L.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Shen, L.; Luan, M.; Li, M.; Du, H.; Ma, C.; et al. Genetic Association of Curative and Adverse Reactions to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chinese Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akasaka, K.; Kaburagi, T.; Yasuda, S.; Ohmori, K.; Abe, K.; Sagara, H.; Ueda, Y.; Nagao, K.; Imura, J.; Imai, Y. Impact of Functional ABCG2 Polymorphisms on the Adverse Effects of Gefitinib in Japanese Patients with Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 66, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Ren, S.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, J.; Su, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, W.; Gao, G.; et al. Comparing EGFR-TKI with EGFR-TKI plus Chemotherapy as 1st Line Treatment in Advanced NSCLC Patients with Both Mutated EGFR and Bim Polymorphism. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, S1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, E.K.; Shin, J.-Y.; Cho, E.K.; Kang, J.-H. The Association between SNP of EGFR and Response to EGFRTKIs According to EGFR Mutation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncilogy 2010, 5 (Suppl. 5), S371. [Google Scholar]
- Suzumura, T.; Kimura, T.; Kudoh, S.; Umekawa, K.; Nagata, M.; Kira, Y.; Nakai, T.; Matsuura, K.; Yoshimura, N.; Hirata, K. Reduced CYP2D6 Function Potentiates the Gefitinib-Induced Rash in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, ix79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, M. Correlation of Polymorphisms of JAK and STAT with Gefitinib-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, e19102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannetti, E.; Zucali, P.A.; Peters, G.J.; Cortesi, F.; D’Incecco, A.; Smit, E.F.; Falcone, A.; Burgers, J.A.; Santoro, A.; Danesi, R.; et al. Association of Polymorphisms in AKT1 and EGFR with Clinical Outcome and Toxicity in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Gefitinib. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregorc, V.; Hidalgo, M.; Spreafico, A.; Cusatis, G.; Ludovini, V.; Ingersoll, R.G.; Marsh, S.; Steinberg, S.M.; Viganò, M.G.; Ghio, D.; et al. Germline Polymorphisms in EGFR and Survival in Patients with Lung Cancer Receiving Gefitinib. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.L.; Yang, C.H.; Yeh, K.H.; Hu, F.C.; Chen, K.Y.; Shih, J.Y.; Lin, Z.Z.; Yu, C.J.; Cheng, A.L.; Yang, P.C. EGFR Intron 1 Dinucleotide Repeat Polymorphism Is Associated with the Occurrence of Skin Rash with Gefitinib Treatment. Lung Cancer 2009, 64, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannetti, E.; Erdem, L.; Olcay, E.; Leon, L.G.; Peters, G.J. Influence of Polymorphisms on EGFR Targeted Therapy in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Biosci. 2011, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xin, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhuang, W.; Ma, Y.; Huang, M.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Polymorphisms of NF-ΚB Pathway Genes Influence Adverse Drug Reactions of Gefitinib in NSCLC Patients. Pharmacogenom. J. 2020, 20, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Gurubhagavatula, S.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Yeap, B.Y.; Asomaning, K.; Su, L.; Heist, R.; Lynch, T.J.; Christiani, D.C. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Polymorphisms and Clinical Outcomes in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Gefitinib. Pharmacogenom. J. 2008, 8, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

| Author, Year | Country | Study Design | Sample Size (Male, %) | Age, Mean ± SD or Median (Range) | Population | Gefitinib Treatment | Adverse Reaction Assessment | Adverse Reaction Severity Frequency (Grade) | Funding Sources/Sponsors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guan et al., 2021 [30] | China | Prospective (C) | 184 (40.2) | NR | NSCLC patients | 250 mg/ day | Skin rash | 98 (0–2) 22 (3–4) B | NA |
| Kobayashi et al., 2015 [22] | Japan | Prospective (C) | 31 (41.9) | 68 ± 8.6 (51–81) | NSCLC patients | 250 mg/ day | Skin rash Diarrhea Liver dysfunction | 9/11 (1/2) 10/4/1 (1/2/3) 12/1/3/1 (1/2/3/4) B | NA |
| Lemos et al., 2020 [21] | Netherlands | Retrospective (C) | 94 (56.4) | 63.5 | NSCLC patients | 250 mg/ day | Skin rash Diarrhea | 65/2 (0–1/2–3) 79/6 (0–1/2–3) A | NA |
| Ma et al., 2017 [23] | China | Retrospective (CC) | 59 (49.0) | 56.0 (31–77) | NSCLC patients | 250 mg/ day | Skin rash Diarrhea Liver dysfunction | 18/13/1/4 (1/2/3/4) 19/4 (1/2) 6/2/2/1 (1/2/3/4) B | NA |
| Tamura et al., 2012 [31] | Japan | Retrospective (C) | 83 (42.0) | 65.0 (36–86) | NSCLC patients | 250 mg/ day | Skin rash Diarrhea Liver dysfunction ILD | 23 (2–4) 4 (2–4) 15 (2–4) 5 (2–4) B | NR |
| Gene | Author, Year | Sample | Genotype Method | dbID/rs (Genetic Variants/ Polymorphism) | Frequency Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABCB1 | Guan et al., 2021 [30] | Blood | Agena MassARRAY system | rs1128503 (1236C>T) rs2032582 (2677G>T/A) | NR |
| Kobayashi et al., 2015 [22] | Blood | PCR-RFLP | rs1128503 (1236C>T) rs2032582 (2677G>T/A) rs1045642 (3435C>T) | C/C (n = 4) C/T (n = 8) T/T (n = 16) G/G (n = 3) G/T (n = 13) T/T (n = 6) T/A (n = 4) A/A (n = 1) C/C (n = 10) C/T (n = 14) T/T (n = 7) | |
| Ma et al., 2017 [23] | Blood | Sequenom MassARRAY system | rs1128503 (1236C>T) rs2032582 (2677G>T/A) rs1045642 (3435C>T) rs10256836 (C>G) | Wt/Wt (n = 25) Wt/m (n = 26) m/m (n = 8) Wt/Wt (n = 9) Wt/m (n = 23) m/m (n = 6) Wt/Wt (n = 19) Wt/m (n = 29) m/m (n = 7) Wt/Wt (n = 39) Wt/m (n = 18) m/m (n = 1) | |
| Tamura et al., 2012 [31] | Blood | Real-time PCR | rs1045642 (3435C>T) | CC (n = 23) CT (n = 44) TT (n = 16) | |
| ABCG2 | Kobayashi et al., 2015 [22] | Blood | PCR-RFLP | rs2231142 (421C>A) | C/C (n = 16) C/A + A/A (n = 15) |
| Ma et al., 2017 [23] | Blood | Sequenom MassARRAY system | rs2231142 (421C>A) rs2231137 (34G>A) | Wt/Wt (n = 26) Wt/m (n = 25) m/m (n = 5) Wt/Wt (n = 25) Wt/m (n = 28) m/m (n = 4) | |
| Tamura et al., 2012 [31] | Blood | Real-time PCR | rs2231142 (421C>A) rs2231137 34G>A | CC (n = 45) CA (n = 31) AA (n = 7) GG (n = 51) GA (n = 28) AA (n = 4) | |
| Lemos et al., 2020 [21] | Blood or paraffin-embedded tumor sample | Real-time PCR | rs2231142 (421C>A) rs2622604 (1143C>T) 15622C/T | CC (n = 83) CA (n = 10) AA (n = 1) CC (n = 54) CT (n = 34) TT (n = 3) CC (n = 47) CT (n = 35) TT (n = 7) |
| Gene | dbID/rs (Genetic Variants/ Polymorphism) | ADRs (Number of Patients) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skin Rash | Diarrhea | Liver Dysfunction | Author, Year | |||||
| Grades 1–4 or 2+ | Association Significative? | Grades 1–4 or 2+ | Association Significative? | Grades 1–4 or 2+ | Association Significative? | |||
| ABCB1 | rs1045642 (3435C>T) | 7 (CC) 16 (CT + TT) b | No | 1 (CC) 3 (CT + TT) b | No | 3 (CC) 12 (CT + TT) b | No | Tamura et al., 2012 [31] |
| 8 (CC) 19 (CT) 7 (TT) a | Yes ** | 6 (CC) 8 (CT) 4 (TT) a | No | 7 (CC) 10 (CT) 5 (TT) a | No | Ma et al., 2017 [23] | ||
| 5 (CC) 10 (CT) 5 (TT) a | No | 3 (CC) 6 (CT) 6 (TT) a | No | 5 (CC) 7 (CT) 5 (TT) a | No | Kobayashi et al., 2015 [22] | ||
| rs1128503 (1236C>T) | 2 (CC) 12 (CT) 22 (TT) a | Yes * | 2 (CC) 5 (CT) 16 (TT) a | Yes * | 3 (CC) 4 (CT) 4 (TT) a | No | Ma et al., 2017 [23] | |
| 1 (CC) 5 (CT) 12 (TT) a | No | 1 (CC) 6 (CT) 8 (TT) a | No | 1 (CC) 5 (CT) 9 (TT) a | No | Kobayashi et al., 2015 [22] | ||
| rs2032582 (2677G>T/A) | 4 (GG) 14 (GT) 8 (TT) a | No | 4 (GG) 11 (GT) 1 (TT) a | No | 0 (GG) 7 (GT) 2 (TT) a | Yes ** | Ma et al., 2017 [23] | |
| 1 (GG) 6 (GT) 8 (TT + TA + AA) a | No | 0 (GG) 9 (GT) 9 (TT + TA + AA) a | No | 1 (GG) 8 (GT) 6 (TT + TA + AA) a | No | Kobayashi et al., 2015 [22] | ||
| rs10256836 (C>G) | 0 (CC) 7 (CG) 28 (GG) a | No | 0 (CC) 2 (CG) 20 (GG) a | Yes * | 0 (CC) 4 (CG) 7 (GG) a | No | Ma et al., 2017 [23] | |
| rs1045642 rs1128503 rs2032582 | 16 (TTT) 10 non (TTT) a | No | 7 (TTT) 9 non (TTT) a | a No | 5 (TTT) 4 non (TTT) a | No | ||
| ABCG2 | rs2231142 (421C>A) | 14 (CC) 9 (CA + AA) b | No | 3 (CC) 1 (CA + AA) b | No | 8 (CC) 7 (CA + AA) b | No | Tamura et al., 2012 [31] |
| 17 (CC) 14 (CA) 4 (AA) a | No | 11 (CC) 8 (CA) 3 (AA) a | No | 2 (CC) 8 (CA) 0 (AA) a | Yes * | Ma et al., 2017 [23] | ||
| 12 (CC) 8 (CA + AA) a | No | 9 (CC) 6 (CA + AA) a | No | 8(CC) 9(CA + AA) a | No | Kobayashi et al., 2015 [22] | ||
| 63 (CC) 5 (CA + AA) a | No | 37 (CC) 2 (CA + AA) a | No | N.A. | N.A. | Lemos et al., 2020 [21] | ||
| rs2231137 (34G>A) | 10 (GG) 13 (GA + AA)b | Yes * | 2 (GG) 2 (GA + AA) b | No | 10 (GG) 15 (GA + AA) b | No | Tamura et al., 2012 [31] | |
| 13 (GG) 18 (GA) 4 (AA) a | No | 9 (GG) 11 (GA) 2 (AA) a | No | 3 (GG) 8 (GA) 0 (AA) a | Yes ** | Ma et al., 2017 [23] | ||
| rs2622604 (1143C>T) | 68 (CC + CT) 0 (TT) a | No | 39 (CC + CT) 0 (TT) a | No | N.A. | N.A. | Lemos et al., 2020 [21] | |
| 15622C/T | 59 (CC + CT) 6 (TT) a | No | 30 (CC + CT) 6 (TT) a | Yes * | N.A. | N.A. | ||
| haplotype 1143C/T and 15622 C/T | 6 (TT-TT + TT-other) 59 (other–other) a | No | 6 (TT-TT + TT–other) 30 (other–other) a | Yes * | N.A. | N.A. | ||
| Author, Year | Selection | Comparability | Outcome/Exposure | Total Score | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item 1 | Item 2 | Item 3 | Item 4 | Item 1 | Item 1 | Item 2 | Item 3 | ||
| Guan et al., 2021 [30] | ** | * | * | * | * | 6 | |||
| Kobayashi et al., 2015 [22] | ** | * | * | * | ** | * | 8 | ||
| Lemos et al., 2020 [21] | ** | * | * | * | ** | * | 8 | ||
| Ma et al., 2017 [23] | ** | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | ||
| Tamura et al., 2012 [31] | ** | * | * | * | ** | * | 8 | ||
| Author, Year | Description of Genotyping Methods and Errors | Description of Modeling Population Stratification? | Description of Modeling Haplotype Variation? | Hardy–Weinberg Equilibrium Was Considered? | Statement of Whether the Study Is the First Report of a Genetic Association, a Replication Effort, or Both? | Score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotyping Methods and Platforms? | Error Rates and Call Rates? | Genotyping in Batches? | Laboratory/Center Where the Genotyping Was Performed? | The Numbers of Individuals Were Successful Genotyped? | ||||||
| Kobayashi et al., 2015 [22] | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | 5 |
| Lemos et al., 2020 [21] | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 7 |
| Ma et al., 2017 [23] | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 5 |
| Tamura et al., 2012 [31] | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morau, M.V.; Seguin, C.S.; Visacri, M.B.; Pincinato, E.d.C.; Moriel, P. Genetic Variants in the ABCB1 and ABCG2 Gene Drug Transporters Involved in Gefitinib-Associated Adverse Reaction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Genes 2024, 15, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15050591
Morau MV, Seguin CS, Visacri MB, Pincinato EdC, Moriel P. Genetic Variants in the ABCB1 and ABCG2 Gene Drug Transporters Involved in Gefitinib-Associated Adverse Reaction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Genes. 2024; 15(5):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15050591
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorau, Mariana Vieira, Cecília Souto Seguin, Marília Berlofa Visacri, Eder de Carvalho Pincinato, and Patricia Moriel. 2024. "Genetic Variants in the ABCB1 and ABCG2 Gene Drug Transporters Involved in Gefitinib-Associated Adverse Reaction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Genes 15, no. 5: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15050591
APA StyleMorau, M. V., Seguin, C. S., Visacri, M. B., Pincinato, E. d. C., & Moriel, P. (2024). Genetic Variants in the ABCB1 and ABCG2 Gene Drug Transporters Involved in Gefitinib-Associated Adverse Reaction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Genes, 15(5), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15050591





