Xenopus Sox11 Partner Proteins and Functional Domains in Neurogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmids
2.2. Identifying Cells Using Xenopus Time Series Database
2.3. Xenopus Animal Usage and Embryo Manipulation
2.4. Whole-Mount In Situ Hybridization
2.5. Frog Microinjection
2.6. In Vitro Translation (IVT) and Co-Immunoprecipitation (co-IP)
2.7. Western Blotting
3. Results and Discussion
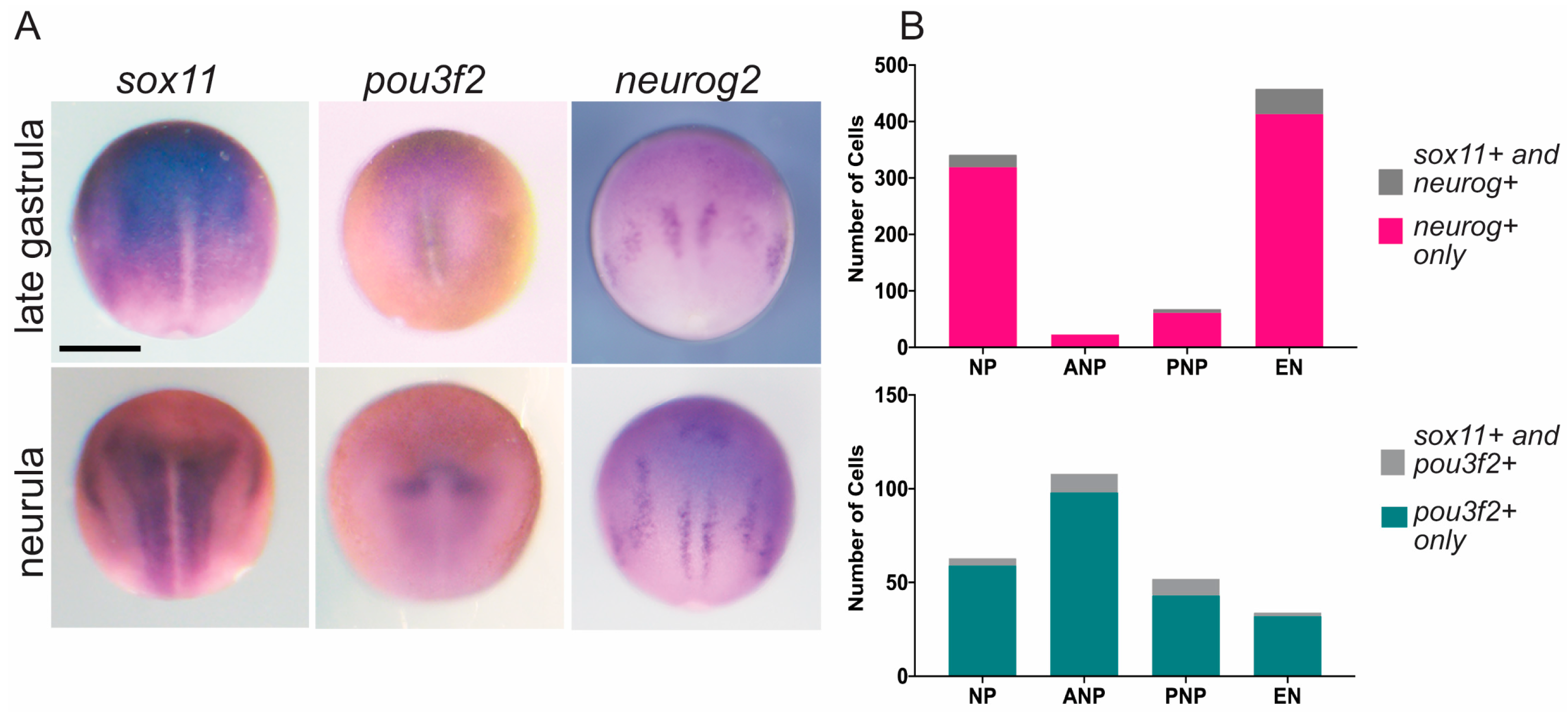
3.1. Sox11, Neurog, and Pou3f2 Are Co-Expressed in Distinct Cell Types of the Neural Plate
3.2. Sox11 Partners with Neurog2 and Pou3f2 but Not Neurog1
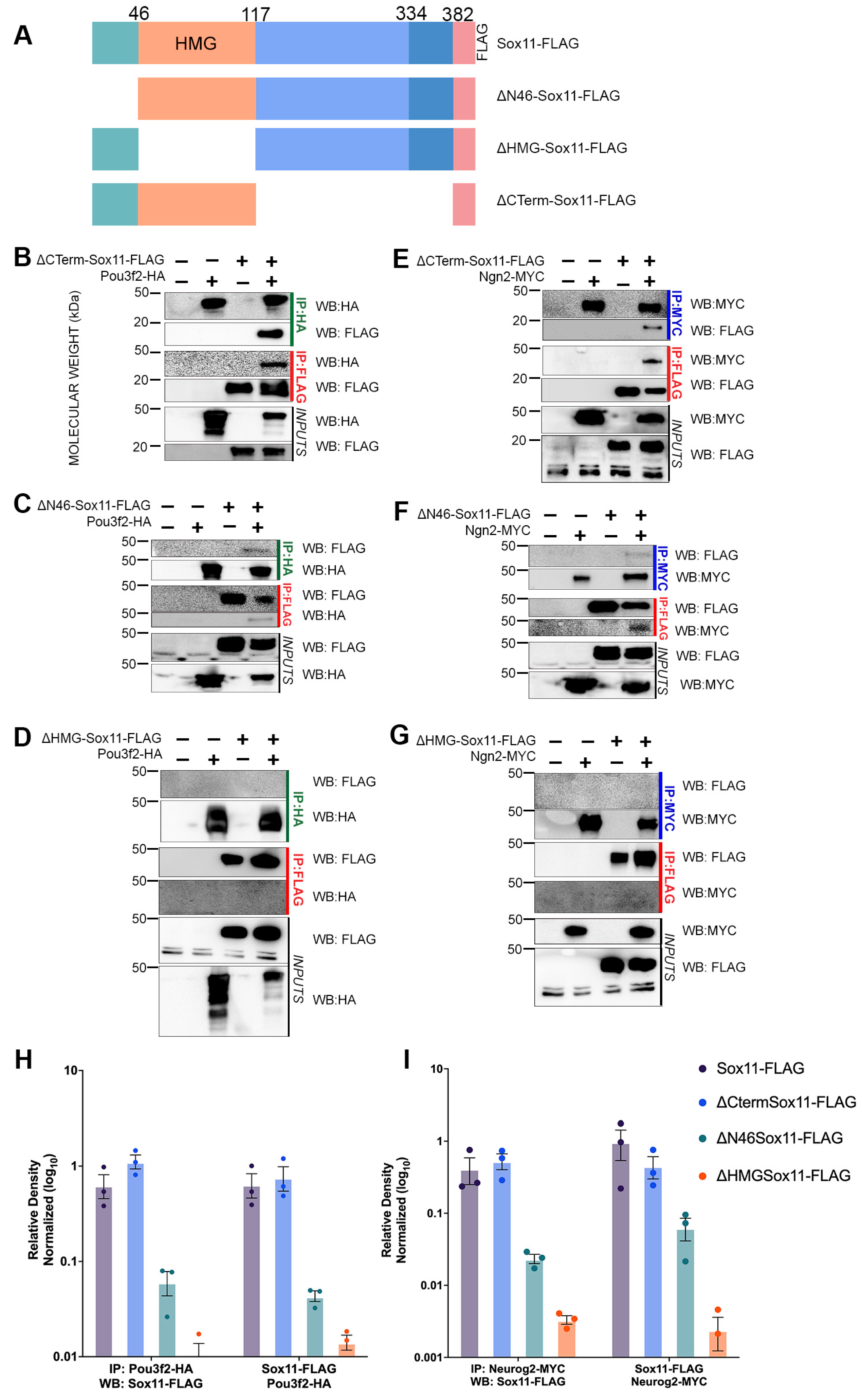
3.3. Sox11 N-Terminus and HMG Domain Are Necessary for Protein–Protein Interactions
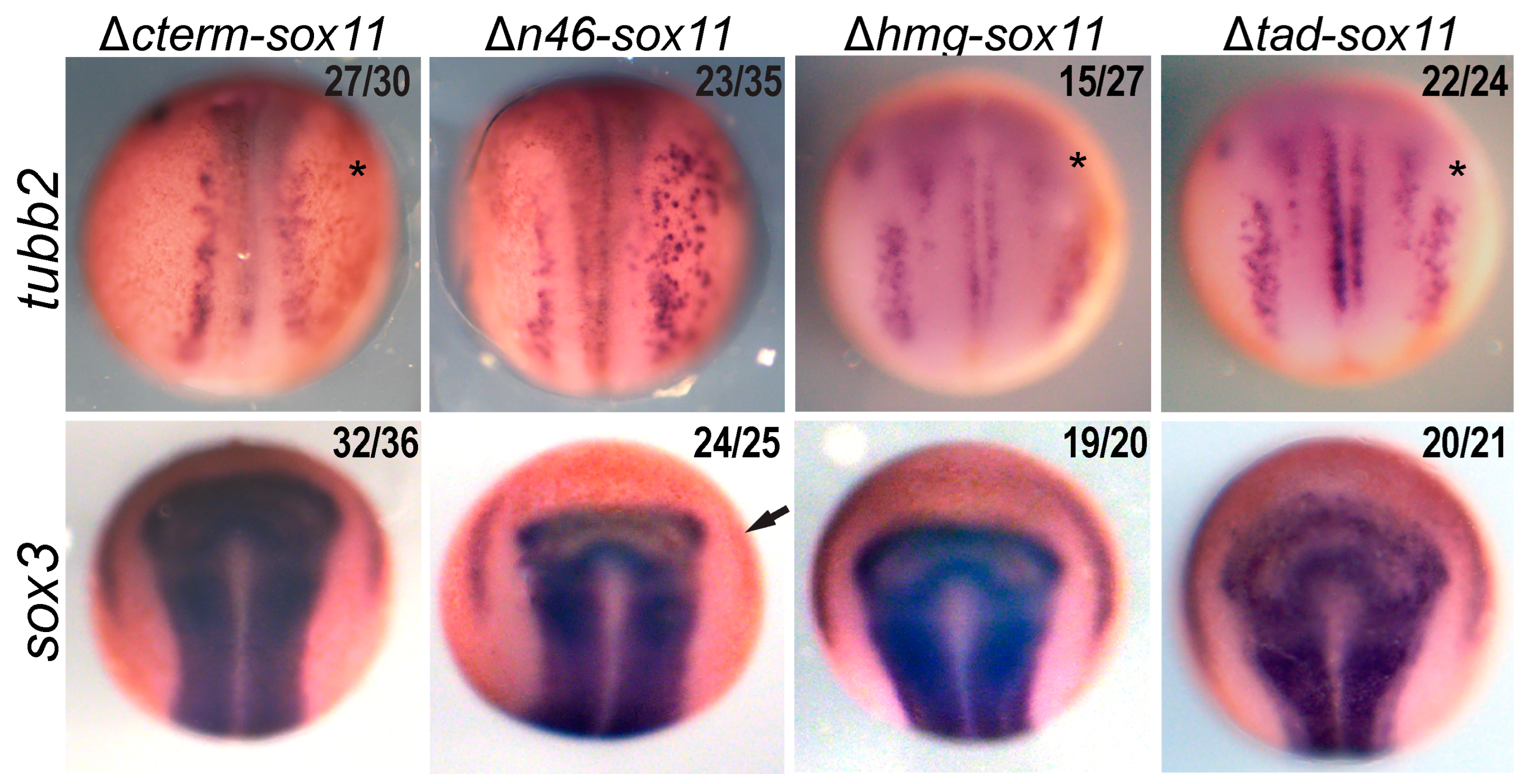
3.4. Sox11 C-Terminus Is Required for Neuron Formation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarkar, A.; Hochedlinger, K. The Sox family of transcription factors: Versatile regulators of stem and progenitor cell fate. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phochanukul, N.; Russell, S. No backbone but lots of Sox: Invertebrate Sox genes. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondoh, H.; Kamachi, Y. SOX-partner code for cell specification: Regulatory target selection and underlying molecular mechanisms. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, J.C. Back to basics: Sox genes. Dev. Dyn. 2007, 236, 2356–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsland, M.; Ramsköld, D.; Zaouter, C.; Klum, S.; Sandberg, R.; Muhr, J.; Ramskold, D.; Zaouter, C.; Klum, S.; Sandberg, R.; et al. Sequentially acting Sox transcription factors in neural lineage development. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 2453–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiprich, S.; Wegner, M. From CNS stem cells to neurons and glia: Sox for everyone. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 359, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyodo-Miura, J.; Urushiyama, S.; Nagai, S.; Nishita, M.; Ueno, N.; Shibuya, H. Involvement of NLK and Sox11 in neural induction in Xenopus development. Genes Cells 2002, 7, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, N.; Cunningham, D.; Le, T.K.; De Maria, D.; Silva, E.M. Sox21 regulates the progression of neuronal differentiation in a dose-dependent manner. Dev. Biol. 2015, 397, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, J.L.; Ormsbee, B.D.; Desler, M.; Rizzino, A. Small Increases in the Level of Sox2 Trigger the Differentiation of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taranova, O.V.; Magness, S.T.; Fagan, B.M.; Wu, Y.; Surzenko, N.; Hutton, S.R.; Pevny, L.H. SOX2 is a dose-dependent regulator of retinal neural progenitor competence. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1187–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, A.L.; Cavallaro, M.; Braida, D.; Di Cristofano, A.; Canta, A.; Vezzani, A.; Ottolenghi, S.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Sala, M.; DeBiasi, S.; et al. Sox2 deficiency causes neurodegeneration and impaired neurogenesis in the adult mouse brain. Development 2004, 131, 3805–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, M. From head to toes: The multiple facets of Sox proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1409–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlbrodt, K.; Herbarth, B.; Sock, E.; Enderich, J.; Hermans-Borgmeyer, I.; Wegner, M. Cooperative function of POU proteins and SOX proteins in glial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 16050–16057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamachi, Y.; Uchikawa, M.; Kondoh, H. Pairing SOX off: With partners in the regulation of embryonic development. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.; Koopman, P. Matching SOX: Partner proteins and co-factors of the SOX family of transcriptional regulators. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2002, 12, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, J.-L.; Loh, Y.-H.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Tam, W.-L.; Yeap, L.-S.; Li, P.; Ang, Y.-S.; Lim, B.; Robson, P.; et al. Reciprocal Transcriptional Regulation of Pou5f1 and Sox2 via the Oct4/Sox2 Complex in Embryonic Stem Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 6031–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallanna, S.K.; Ormsbee, B.D.; Iacovino, M.; Gilmore, J.M.; Cox, J.L.; Kyba, M.; Washburn, M.P.; Rizzino, A. Proteomic analysis of Sox2-associated proteins during early stages of mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation identifies Sox21 as a novel regulator of stem cell fate. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, M.; Stolt, C.C. From stem cells to neurons and glia: A Soxist’s view of neural development. Trends Neurosci. 2005, 28, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, L.J.; Gallo, V. The Yin and Yang of Sox proteins: Activation and repression in development and disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 3277–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Corbi, N.; Basilico, C.; Dailey, L. Developmental-specific activity of the FGF-4 enhancer requires the synergistic action of Sox2 and Oct-3. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 2635–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Kamachi, Y.; Tanouchi, A.; Hamada, H.; Jing, N.; Kondoh, H. Interplay of SOX and POU factors in regulation of the Nestin gene in neural primordial cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 8834–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Zhu, T.; Lu, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, L. Neurogenin 2 enhances the generation of patient-specific induced neuronal cells. Brain Res. 2015, 1615, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wissmüller, S.; Kosian, T.; Wolf, M.; Finzsch, M.; Wegner, M.; Wißmü, S.; Kosian, T.; Wolf, M.; Finzsch, M.; Wegner, M. The high-mobility-group domain of Sox proteins interacts with DNA-binding domains of many transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Lu, M.L.; Li, T.; Balk, S.P. SRY Interacts with and Negatively Regulates Androgen Receptor Transcriptional Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 46647–46654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santa Barbara, P.; Bonneaud, N.; Boizet, B.; Desclozeaux, M.; Moniot, B.; Sudbeck, P.; Scherer, G.; Poulat, F.; Berta, P. Direct Interaction of SRY-Related Protein SOX9 and Steroidogenic Factor 1 Regulates Transcription of the Human Anti-Müllerian Hormone Gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 6653–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botquin, V.; Hess, H.; Fuhrmann, G.; Anastassiadis, C.; Gross, M.K.; Vriend, G.; Schöler, H.R. New POU dimer configuration mediates antagonistic control of an osteopontin preimplantation enhancer by Oct-4 and Sox-2. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 2073–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.L.; Mallanna, S.K.; Luo, X.; Rizzino, A. Sox2 uses multiple domains to associate with proteins present in Sox2-protein complexes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, J.; Schepers, G.; Koopman, P. Phylogeny of the SOX family of developmental transcription factors based on sequence and structural indicators. Dev. Biol. 2000, 227, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uy, B.R.; Simoes-Costa, M.; Koo, D.E.S.; Sauka-Spengler, T.; Bronner, M.E. Evolutionarily conserved role for SoxC genes in neural crest specification and neuronal differentiation. Dev. Biol. 2015, 397, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lee, G.A.; Pourmorady, A.; Sock, E.; Donoghue, M.J. Orchestration of Neuronal Differentiation and Progenitor Pool Expansion in the Developing Cortex by SoxC Genes. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 10629–10642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsland, M.; Werme, M.; Malewicz, M.; Perlmann, T.; Muhr, J. The establishment of neuronal properties is controlled by Sox4 and Sox11. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 3475–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowski, M.P.; Cornuet, P.K.; McIlwrath, S.; Koerber, H.R.; Albers, K.M. SRY-box containing gene 11 (Sox11) transcription factor is required for neuron survival and neurite growth. Neuroscience 2006, 143, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Jin, J.; Lee, G.A.; Silva, E.; Donoghue, M. Cross-species functional analyses reveal shared and separate roles for Sox11 in frog primary neurogenesis and mouse cortical neuronal differentiation. Biol. Open 2016, 5, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carl, S.H.; Russell, S. Common binding by redundant group B Sox proteins is evolutionarily conserved in Drosophila. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sive, H.L.; Grainger, R.M.; Harland, R.M. Baskets for In Situ Hybridization and Immunohistochemistry. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2007, 2007, pdb.prot4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sive, H.L.; Grainger, R.M.; Harland, R.M. Early Development of Xenopus laevis: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Long Island, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 9780879695040. [Google Scholar]
- Harland, R.M. In situ hybridization: An improved whole-mount method for Xenopus embryos. Methods Cell Biol. 1991, 36, 685–695. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmati-Brivanlou, A.; Frank, D.; Bolce, M.E.; Brown, B.D.; Sive, H.L.; Harland, R.M. Localization of specific mRNAs in Xenopus embryos by whole-mount in situ hybridization. Development 1990, 110, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassmann, M.; Grenacher, B.; Rohde, B.; Vogel, J. Quantifying Western blots: Pitfalls of densitometry. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 1845–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.Y.; Ng, T.W. Accurate step wedge calibration for densitometry of electrophoresis gels. Opt. Commun. 2008, 281, 3013–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowes, J.B.; Snyder, K.A.; Segerdell, E.; Jarabek, C.J.; Azam, K.; Zorn, A.M.; Vize, P.D. Xenbase: Gene expression and improved integration. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, D607–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosse-Etchepare, C.; Gervi, I.; Buisson, I.; Formery, L.; Schubert, M.; Riou, J.F.; Umbhauer, M.; Le Bouffant, R. Pou3f transcription factor expression during embryonic development highlights distinct pou3f3 and pou3f4 localization in the Xenopus laevis kidney. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2018, 62, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, J.A.; Weinreb, C.; Wagner, D.E.; Megason, S.; Peshkin, L.; Kirschner, M.W.; Klein, A.M. The dynamics of gene expression in vertebrate embryogenesis at single-cell resolution. Science 2018, 360, eaar5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balta, E.A.; Wittmann, M.T.; Jung, M.; Sock, E.; Haeberle, B.M.; Heim, B.; von Zweydorf, F.; Heppt, J.; von Wittgenstein, J.; Gloeckner, C.J.; et al. Phosphorylation modulates the subcellular localization of SOX11. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.-C.C.; Hertz, J.; Zhang, X.; Jin, X.-L.L.; Shaw, P.; Derosa, B.A.; Li, J.Y.; Venugopalan, P.; Valenzuela, D.A.; Patel, R.D.; et al. Novel Regulatory Mechanisms for the SoxC Transcriptional Network Required for Visual Pathway Development. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 4967–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Nadal-Vicens, M.; Misono, S.; Lin, M.Z.; Zubiaga, A.; Hua, X.; Fan, G.; Greenberg, M.E. Neurogenin promotes neurogenesis and inhibits glial differentiation by independent mechanisms. Cell 2001, 104, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, O.J.; Harley, V.R. Identification of an interaction between SOX9 and HSP70. FEBS Lett. 2001, 496, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosking, B.M.; Wang, S.C.M.; Chen, S.L.; Penning, S.; Koopman, P.; Muscat, G.E.O. SOX18 directly interacts with MEF2C in endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 287, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, P.; Harley, V.R. Acquisition of SOX transcription factor specificity through protein-protein interaction, modulation of Wnt signalling and post-translational modification. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.A. Floppy SOX: Mutual induced fit in hmg (high-mobility group) box-DNA recognition. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001, 15, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dy, P.; Penzo-Méndez, A.; Wang, H.; Pedraza, C.E.; Macklin, W.B.; Lefebvre, V.; Penzo-Mendez, A.; Wang, H.; Pedraza, C.E.; Macklin, W.B.; et al. The three SoxC proteins–Sox4, Sox11 and Sox12–exhibit overlapping expression patterns and molecular properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3101–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebe, M.S.; Nowling, T.K.; Rizzino, A. Identification of novel domains within Sox-2 and Sox-11 involved in autoinhibition of DNA binding and partnership specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 17901–17911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moody, S.A.; Lamantia, A.-S. Transcriptional regulation of cranial sensory placode development HHS Public Access. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2015, 111, 301–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saint-Jeannet, J.P.; Moody, S.A. Establishing the pre-placodal region and breaking it into placodes with distinct identities. Dev. Biol. 2014, 389, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singleton, K.S.; Silva-Rodriguez, P.; Cunningham, D.D.; Silva, E.M. Xenopus Sox11 Partner Proteins and Functional Domains in Neurogenesis. Genes 2024, 15, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15020243
Singleton KS, Silva-Rodriguez P, Cunningham DD, Silva EM. Xenopus Sox11 Partner Proteins and Functional Domains in Neurogenesis. Genes. 2024; 15(2):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15020243
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingleton, Kaela S., Pablo Silva-Rodriguez, Doreen D. Cunningham, and Elena M. Silva. 2024. "Xenopus Sox11 Partner Proteins and Functional Domains in Neurogenesis" Genes 15, no. 2: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15020243
APA StyleSingleton, K. S., Silva-Rodriguez, P., Cunningham, D. D., & Silva, E. M. (2024). Xenopus Sox11 Partner Proteins and Functional Domains in Neurogenesis. Genes, 15(2), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15020243





