Phenotypic and Genetic Heterogeneity of a Pakistani Cohort of 15 Consanguineous Families Segregating Variants in Leber Congenital Amaurosis-Associated Genes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval and Enrollment of Families
2.2. Targeted Exome Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.3. Sanger’s Sequencing and Segregation Test
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Phenotype
3.2. Genetic Screening
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, C.-H.; Yang, C.-M.; Yang, C.-H.; Hou, Y.-C.; Chen, T.-C. Leber’s Congenital Amaurosis: Current Concepts of Genotype-Phenotype Correlations. Genes 2021, 12, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, K.; Nishina, S.; Yokoi, T.; Katagiri, S.; Saitsu, H.; Kurata, K.; Miyamichi, D.; Hikoya, A.; Mizobuchi, K.; Nakano, T.; et al. Molecular Diagnosis of 34 Japanese Families with Leber Congenital Amaurosis Using Targeted Next Generation Sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, M.D.; de Guimaraes, T.A.C.; Georgiou, M.; Michaelides, M. Leber congenital amaurosis/early-onset severe retinal dystrophy: Current management and clinical trials. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 106, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaran, N.; Moore, A.T.; Weleber, R.G.; Michaelides, M. Leber congenital amaurosis/early-onset severe retinal dystrophy: Clinical features, molecular genetics and therapeutic interventions. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 101, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Hollander, A.I.; Roepman, R.; Koenekoop, R.K.; Cremers, F.P. Leber congenital amaurosis: Genes, proteins and disease mechanisms. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2008, 27, 391–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sather, R., III; Ihinger, J.; Simmons, M.; Lobo, G.P.; Montezuma, S.R. The Clinical Findings, Pathogenic Variants, and Gene Therapy Qualifications Found in a Leber Congenital Amaurosis Phenotypic Spectrum Patient Cohort. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehreem, R.; Chen, I.; Shah, M.R.; Li, Y.; Khan, M.A.; Afshan, K.; Chen, R.; Firasat, S. Exome sequencing identified molecular determinants of retinal dystrophies in nine consanguineous Pakistani families. Genes 2022, 13, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Tuan, H.-F.; Nguyen, D.H.; Sun, V.; Keser, V.; Bowne, S.J.; Sullivan, L.S.; Luo, H.; Zhao, L. Next generation sequencing-based molecular diagnosis of retinitis pigmentosa: Identification of a novel genotype-phenotype correlation and clinical refinements. Hum. Genet. 2014, 133, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.H.; Pellissier, L.P.; Wijnholds, J. The CRB1 and adherens junction complex proteins in retinal development and maintenance. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2014, 40, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talib, M.; van Schooneveld, M.J.; Wijnholds, J.; van Genderen, M.M.; Schalij-Delfos, N.E.; Klaver, C.C.; Talsma, H.E.; Fiocco, M.; Florijn, R.J.; Ten Brink, J.B. CRB1-associated retinal dystrophies: A prospective natural history study in anticipation of future clinical trials. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 234, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Varela, M.D.; Georgiou, M.; Alswaiti, Y.; Kabbani, J.; Fujinami, K.; Fujinami-Yokokawa, Y.; Khoda, S.; Mahroo, O.A.; Robson, A.G.; Webster, A.R. CRB1-associated retinal dystrophies: Genetics, clinical characteristics, and natural history. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 246, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corton, M.; Avila-Fernandez, A.; Vallespín, E.; López-Molina, M.I.; Almoguera, B.; Martín-Garrido, E.; Tatu, S.D.; Khan, M.I.; Blanco-Kelly, F.; Riveiro-Alvarez, R. Involvement of LCA5 in Leber congenital amaurosis and retinitis pigmentosa in the Spanish population. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelstowska, S.; Widjaja-Adhi, M.A.K.; Silvaroli, J.A.; Golczak, M. Molecular basis for vitamin A uptake and storage in vertebrates. Nutrients 2016, 8, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikelle, L.; Makia, M.; Lewis, T.; Crane, R.; Kakakhel, M.; Conley, S.M.; Birtley, J.R.; Arshavsky, V.Y.; Al-Ubaidi, M.R.; Naash, M.I. Comparative study of PRPH2 D2 loop mutants reveals divergent disease mechanism in rods and cones. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2023, 80, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezquerra-Inchausti, M.; Anasagasti, A.; Barandika, O.; Garay-Aramburu, G.; Galdós, M.; López de Munain, A.; Irigoyen, C.; Ruiz-Ederra, J. A new approach based on targeted pooled DNA sequencing identifies novel mutations in patients with Inherited Retinal Dystrophies. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodenbender, J.-P.; Marino, V.; Bethge, L.; Stingl, K.; Haack, T.B.; Biskup, S.; Kohl, S.; Kühlewein, L.; Dell’Orco, D.; Weisschuh, N. Biallelic variants in TULP1 are associated with heterogeneous phenotypes of retinal dystrophy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberger, T.; Neuhaus, C.; Khan, A.O.; Decker, C.; Preising, M.N.; Friedburg, C.; Bieg, A.; Gliem, M.; Issa, P.C.; Holz, F.G.; et al. Increasing the Yield in Targeted next-Generation Sequencing by Implicating CNV Analysis, Non-Coding Exons and the Overall Variant Load: The Example of Retinal Dystrophies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, N.; Mehmood Baig, S.; Sheikh, M.A.; Jamil, A. Autosomal Recessive Retinitis Pigmentosa is Associated with Missense Mutation in CRB1 in a Consanguineous Pakistani Family. Pak. J. Life Soc. Sci. 2013, 11, 171. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, A.U.; Peter, V.G.; Quinodoz, M.; Rashid, A.; Khan, S.A.; Superti-Furga, A.; Rivolta, C. Exploring the genetic landscape of inherited retinal diseases in North-Western Pakistan reveals a high degree of autozygosity and prevalent founder mutations. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 2385. [Google Scholar]
- Hull, S.; Owen, N.; Islam, F.; Tracey-White, D.; Plagnol, V.; Holder, G.E.; Michaelides, M.; Carss, K.; Raymond, F.L.; Rozet, J.-M. Nonsyndromic retinal dystrophy due to bi-allelic mutations in the ciliary transport gene IFT140. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hollander, A.I.; Koenekoop, R.K.; Yzer, S.; Lopez, I.; Arends, M.L.; Voesenek, K.E.; Zonneveld, M.N.; Strom, T.M.; Meitinger, T.; Brunner, H.G. Mutations in the CEP290 (NPHP6) gene are a frequent cause of Leber congenital amaurosis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 79, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-Cuzcano, A.; Koenekoop, R.K.; Senechal, A.; De Baere, E.B.; de Ravel, T.; Banfi, S.; Kohl, S.; Ayuso, C.; Sharon, D.; Hoyng, C.B.; et al. BBS1 mutations in a wide spectrum of phenotypes ranging from nonsyndromic retinitis pigmentosa to Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2012, 130, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Caballero, L.; Martín-Merida, I.; Blanco-Kelly, F.; Avila-Fernandez, A.; Carreño, E.; Fernandez-San Jose, P.; Irigoyen, C.; Jimenez-Rolando, B.; Lopez-Grondona, F.; Mahillo, I. PRPH2-related retinal dystrophies: Mutational spectrum in 103 families from a Spanish cohort. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Ouyang, J.; Yi, Z.; Li, S.; Jia, X.; Xiao, X.; Sun, W. New Insight into the Genotype-Phenotype Correlation of PRPH2-Related Diseases Based on a Large Chinese Cohort and Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, V.; Tuan, H.-F.; Keser, V.; Wang, K.; Ren, H.; Lopez, I.; Zaneveld, J.E.; Siddiqui, S. Comprehensive molecular diagnosis of 179 Leber congenital amaurosis and juvenile retinitis pigmentosa patients by targeted next generation sequencing. J. Med. Genet. 2013, 50, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, S.M.; Naash, M.I. Gene therapy for PRPH2-associated ocular disease: Challenges and prospects. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a017376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kalyanasundaram, T.; Black, G.; O’Sullivan, J.; Bishop, P. A novel peripherin/RDS mutation resulting in a retinal dystrophy with phenotypic variation. Eye 2009, 23, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sohocki, M.M.; Daiger, S.P.; Bowne, S.J.; Rodriquez, J.A.; Northrup, H.; Heckenlively, J.R.; Birch, D.G.; Mintz-Hittner, H.; Ruiz, R.S.; Lewis, R.A. Prevalence of mutations causing retinitis pigmentosa and other inherited retinopathies. Hum. Mutat. 2001, 17, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, M.; Bueno, J.; Osorio, A.; Sanz, R.; Garcia-Sandoval, B.; Ramos, C.; Ayuso, C. Three novel RDS-peripherin mutations (689delT, 857del17, G208D) in Spanish familes affected with autosomal dominant retinal degenerations. Hum. Mutat. 1998, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, M.H.A.; Khan, M.; Rooijakkers, A.A.B.; Mulders, T.; Haer-Wigman, L.; Boon, C.J.; Klaver, C.C.; van den Born, L.I.; Hoyng, C.B.; Cremers, F.P. PRPH2 mutation update: In silico assessment of 245 reported and 7 novel variants in patients with retinal disease. Hum. Mutat. 2021, 42, 1521–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Sun, W.; Li, S.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Q. Spectrum, frequency, and genotype–phenotype of mutations in SPATA7. Mol. Vis. 2019, 25, 821. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kannabiran, C. The spermatogenesis-associated protein-7 (SPATA7) gene–an overview. Ophthalmic Genet. 2020, 41, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, D.S.; Ocaka, L.A.; Borman, A.D.; Sergouniotis, P.I.; Henderson, R.H.; Moradi, P.; Robson, A.G.; Thompson, D.A.; Webster, A.R.; Moore, A.T. Screening of SPATA7 in patients with Leber congenital amaurosis and severe childhood-onset retinal dystrophy reveals disease-causing mutations. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 3032–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; den Hollander, A.I.; Moayedi, Y.; Abulimiti, A.; Li, Y.; Collin, R.W.; Hoyng, C.B.; Lopez, I.; Bray, M.; Lewis, R.A. Mutations in SPATA7 cause Leber congenital amaurosis and juvenile retinitis pigmentosa. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Xiong, K.; Qian, X.; Choi, J.; Shim, Y.-K.; Burnett, J.; Mardon, G.; Chen, R. Spata7 is required for maintenance of the retinal connecting cilium. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
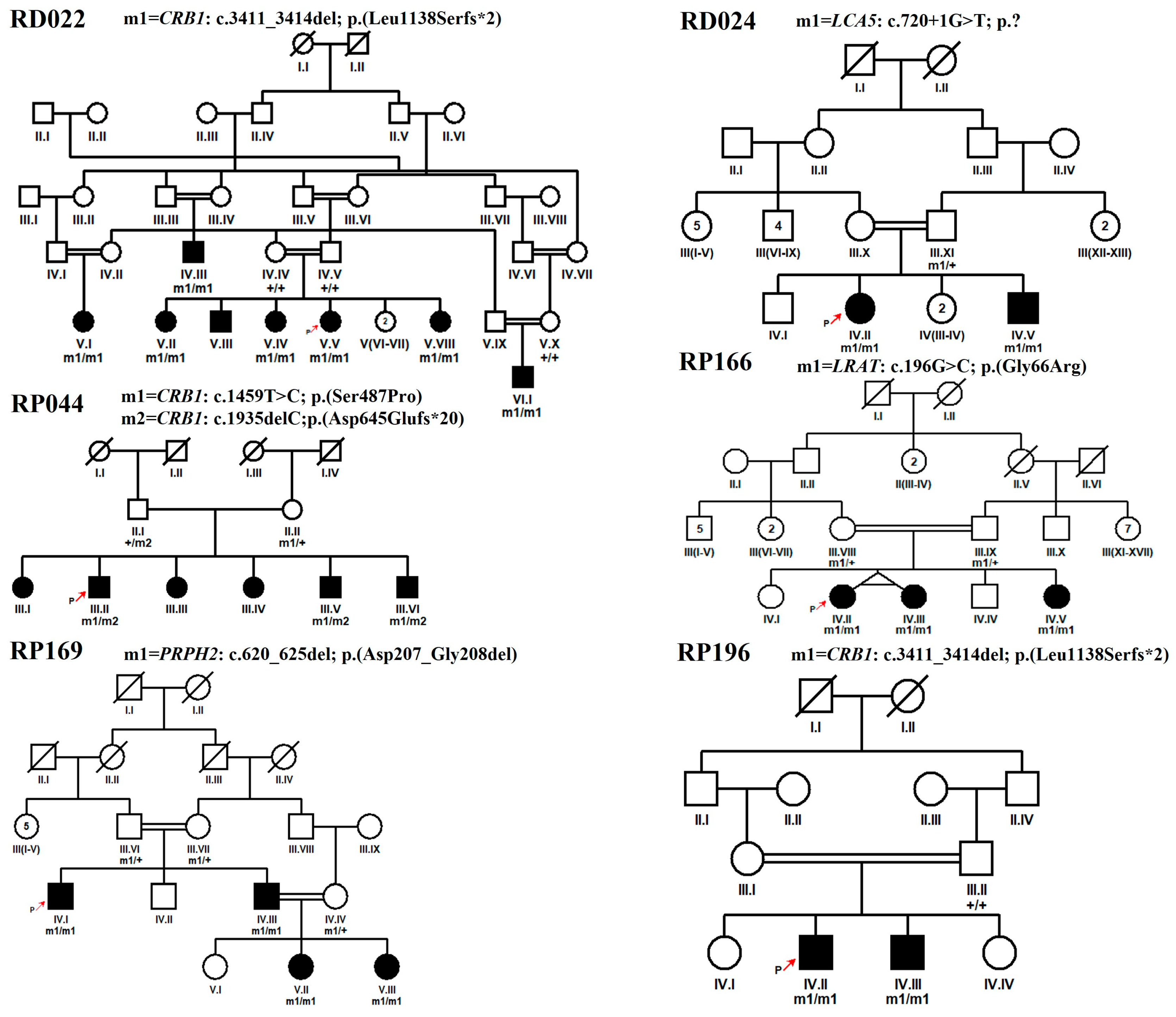
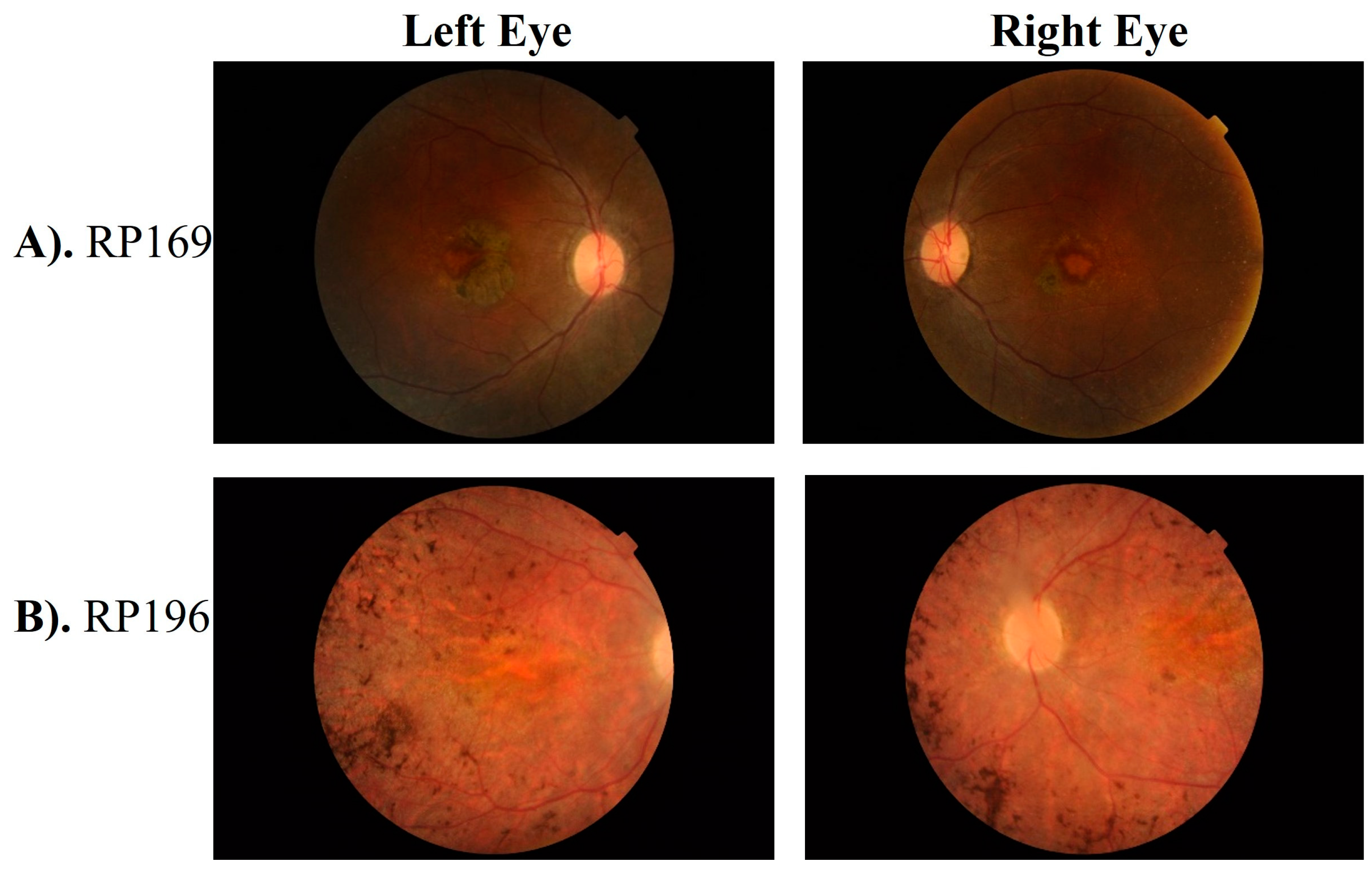
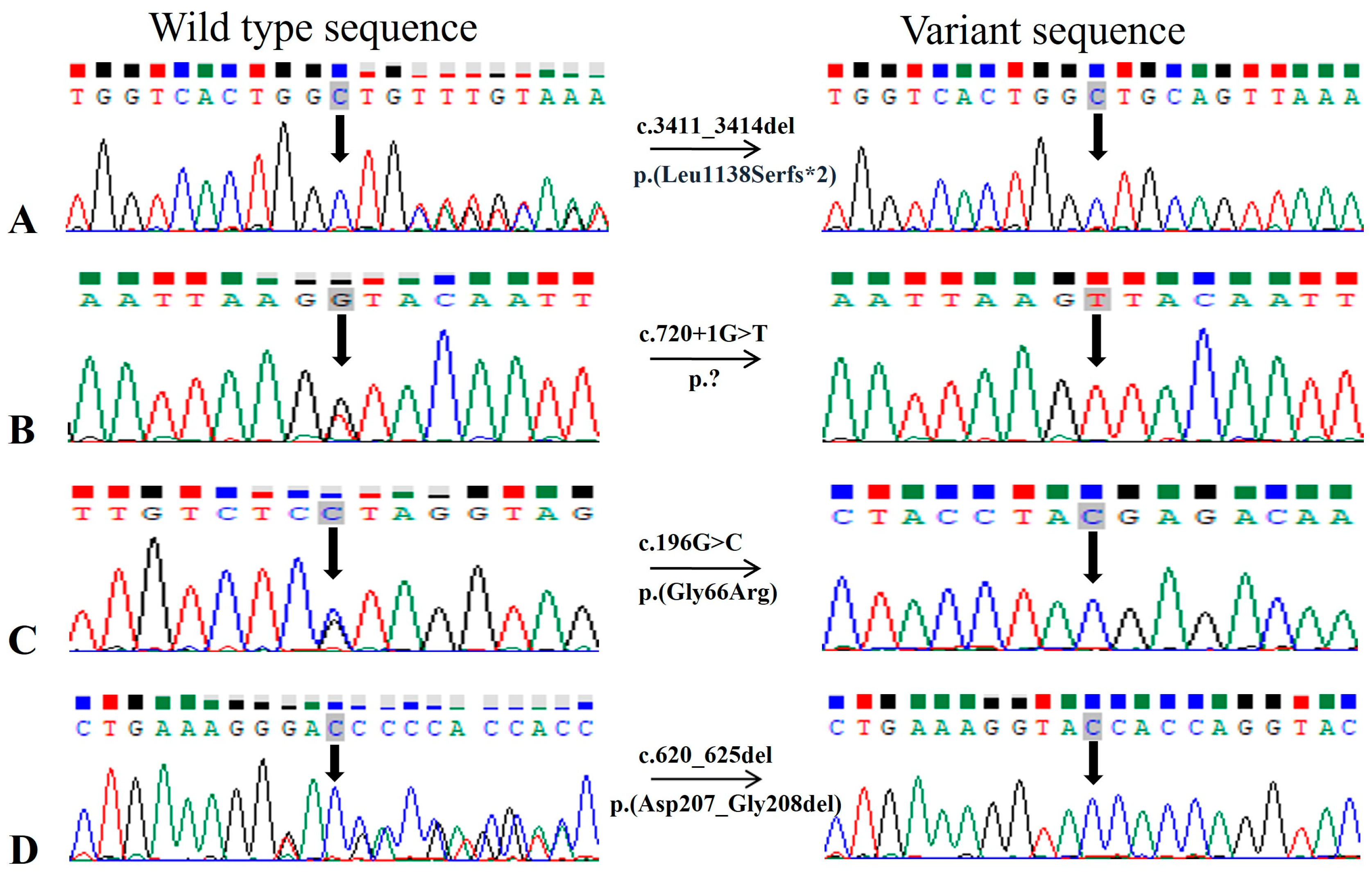
| Sr. No. | Family ID | Proband ID | Age in Years at | Ethnicity | No. of Affected Cases in Family | Visual Acuity | Symptoms | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enrollment | Onset | OD | OS | Nyctalopia | Photophobia | Color Vision Problems | Hyperopia | Other/s | |||||
| 1 | RD022 | V.V | 11 | By birth | Punjabi | 8 | H.M | H.M | + | + | + | + | Oculo-digital sign |
| 2 | RD023 | IV.III | 12 | One year | Pashtun | 2 | 6/192 * | 1/60 * | + | + | + | + | Nystagmus, HL, hypertension |
| 3 | RD024 | IV.II | 12 | By birth | Saraiki | 2 | PL | PL | + | − | + | − | Nystagmus, Strabismus |
| 4 | RD027 | III.II | 20 | By birth | Pothohari | 4 | 6/60 * | 6/60 * | + | − | − | − | Nystagmus, Myopia, Squint, BD |
| 5 | RD036 | V.I | 12 | By birth | Pashtun | 3 | PL | PL | + | + | − | − | Nystagmus, Astigmatism |
| 6 | RP002 | IV.VIII | 48 | By birth | Punjabi | 8 | NA | NA | + | − | − | − | - |
| 7 | RP028 | IV.III | 8 | By birth | Punjabi | 2 | 6/24 * | 6/19 * | + | + | − | − | - |
| 8 | RP044 | III.II | 25 | By birth | Pashtun | 6 | H.M | H.M | + | − | − | − | - |
| 9 | RP159 | IV.IV | 18 | By birth | Pashtun | 5 | H.M | C.F | + | + | − | − | Nystagmus |
| 10 | RP166 | IV.II | 17 | By birth | Pashtun | 3 | 6/60 * | 6/60 * | + | − | − | − | Oculo-digital sign, Myopia |
| 11 | RP169 | IV.I | 32 | By birth | Punjabi | 4 | 6/19 * | 6/19 * | + | + | + | − | - |
| 12 | RP184 | IV.VI | 9 | By birth | Punjabi | 3 | 6/120 ** | 6/120 ** | + | − | + | + | Nystagmus, teeth and BD, ID/MR |
| 13 | RP187 | IV.I | 15 | By birth | Pashtun | 5 | PL | PL | + | − | − | − | - |
| 14 | RP194 | IV.VIII | 44 | By birth | Punjabi | 6 | 6/48 * | 6/76 * | + | + | − | − | K and H problems |
| 15 | RP196 | IV.II | 18 | By birth | Punjabi | 2 | C.F | C.F | + | + | − | − | Nystagmus, Myopia |
| Sr. No. | Family ID | Accession Number | Gene | Variant | Nucleotide Change | Protein Change | GnomAD | db SNP ID | Clin Var ID/Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RD022 | NM_201253 | CRB1 | Chr1:197404401CTGTT>C | c.3411_3414del | p.(Leu1138Serfs*2) | NA | NA | NA |
| 2 | RD023 | NM_201253 | CRB1 | Chr1:197390417T>C | c.1459T>C | p.(Ser487Pro) | NA | NA | 2572562/likely pathogenic |
| 3 | RD024 | NM_181714 | LCA5 | Chr6:80222928C>A | c.720+1G>T | p.? | NA | NA | NA |
| 4 | RD027 | NM_018418.5 | SPATA7 | Chr14:88895738T>TA | c.864dup | p.(Thr289Aspfs*3) | 0.000007081 | rs386834241 | 1396/pathogenic |
| 5 | RD036 | NM_003322 | TULP1 | Chr6:35467757C>T | c.1495+1G>A | p.? | 0.00001195 | rs281865168 | 99665/pathogenic |
| 6 | RP002 | NM_152443 | RDH12 | Chr14:68191944C>T | c.316C>T | p.(Arg106*) | 0.00001591 | rs752242512 | 835782/pathogenic |
| 7 | RP028 | NM_152443 | RDH12 | Chr14:68193755G>A | c.506G>A | p.(Arg169Gln) | 0.00001193 | rs971610277 | 623219/pathogenic |
| 8 | RP044 | NM_201253 | CRB1 | Chr1:197390417T>C | c.1459T>C | p.(Ser487Pro) | NA | NA | 2572562/likely pathogenic |
| Chr1:197390892AC>A | c.1935delC | p.(Asp645Glufs*20) | NA | NA | NA | ||||
| 9 | RP159 | NM_201253 | CRB1 | Chr1:197390417T>C | c.1459T>C | p.(Ser487Pro) | NA | NA | 2572562/likely pathogenic |
| 10 | RP166 | NM_004744 | LRAT | Chr4:155665674G>C | c.196G>C | p.(Gly66Arg) | NA | NA | NA |
| 11 | RP169 | NM_000322 | PRPH2 | Chr6:42672305ACGCCGT>A | c.620_625del | p.(Asp207_Gly208del) | NA | NA | NA |
| 12 | RP184 | NM_181714 | LCA5 | Chr6:80201334TGTTTTCG>T | c.1062_1068del | p.(Tyr354*) | NA | rs1769845495 | 810630/pathogenic |
| 13 | RP187 | NM_018418 | SPATA7 | Chr14:88895791C>T | c.1012C>T | p.(Gln338*) | 0.000003986 | rs1188647815 | NA |
| 14 | RP194 | NM_014714 | IFT140 | Chr16:1637210C>T | c.998G>A | p.(Cys333Tyr) | 0.00001990 | rs773372123 | 438181/pathogenic |
| 15 | RP196 | NM_201253 | CRB1 | Chr1:197404401CTGTT>C | c.3411_3414del | p.(Leu1138Serfs*2) | NA | NA | NA |
| Sr. No. | Gene | Nucleotide Change | Clin Var ID/Classification | Variant Interpretation (Codes Met) | Curated Variant Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CRB1 | c.3411_3414del | NA | PM2_supporting, PVS1, PP4, PP1, PP3 | pathogenic |
| 2 | CRB1 | c.1459T>C | 2572562/likely pathogenic | PM2_supporting, PP3, PP4, PP1 | pathogenic |
| 3 | CRB1 | c.1935delC | NA | PM2_supporting, PVS1, PP4, PP1, PP3 | pathogenic |
| 4 | LCA5 | c.720+1G>T | NA | PM2_supporting, PVS1, PP4, PP1, PP3 | pathogenic |
| 5 | LRAT | c.196G>C | NA | PM2_supporting, PP3, PP4, PP1, PP2 | pathogenic |
| 6 | PRPH2 | c.620_625del | NA | PM2_supporting, PP4, PP1, PM4 | pathogenic |
| 7 | SPATA7 | c.1012C>T | NA | PM2_supporting, PVS1, PP4, PP1, PP3 | pathogenic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akhtar, Z.; Altaf, S.; Li, Y.; Bibi, S.; Shah, J.; Afshan, K.; Wang, M.; Hussain, H.M.J.; Qureshi, N.; Chen, R.; et al. Phenotypic and Genetic Heterogeneity of a Pakistani Cohort of 15 Consanguineous Families Segregating Variants in Leber Congenital Amaurosis-Associated Genes. Genes 2024, 15, 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121646
Akhtar Z, Altaf S, Li Y, Bibi S, Shah J, Afshan K, Wang M, Hussain HMJ, Qureshi N, Chen R, et al. Phenotypic and Genetic Heterogeneity of a Pakistani Cohort of 15 Consanguineous Families Segregating Variants in Leber Congenital Amaurosis-Associated Genes. Genes. 2024; 15(12):1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121646
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkhtar, Zainab, Sumaira Altaf, Yumei Li, Sana Bibi, Jamal Shah, Kiran Afshan, Meng Wang, Hafiz Muhammad Jafar Hussain, Nadeem Qureshi, Rui Chen, and et al. 2024. "Phenotypic and Genetic Heterogeneity of a Pakistani Cohort of 15 Consanguineous Families Segregating Variants in Leber Congenital Amaurosis-Associated Genes" Genes 15, no. 12: 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121646
APA StyleAkhtar, Z., Altaf, S., Li, Y., Bibi, S., Shah, J., Afshan, K., Wang, M., Hussain, H. M. J., Qureshi, N., Chen, R., & Firasat, S. (2024). Phenotypic and Genetic Heterogeneity of a Pakistani Cohort of 15 Consanguineous Families Segregating Variants in Leber Congenital Amaurosis-Associated Genes. Genes, 15(12), 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15121646







