A Missense Mutation in the Collagen Triple Helix of EDA Is Associated with X-Linked Recessive Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia in Fleckvieh Cattle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animals
2.3. Histopathological Examination
2.4. Cytogenetics
2.5. RNA and DNA Extraction
2.6. EDA, EDA2R and WNT10A Sequencing
2.7. Whole Genome Sequencing
2.8. Validation
2.9. RNA Expression, and Production of Recombinant EDA1
2.10. Cell-Based EDA1 Activity Assay
3. Results
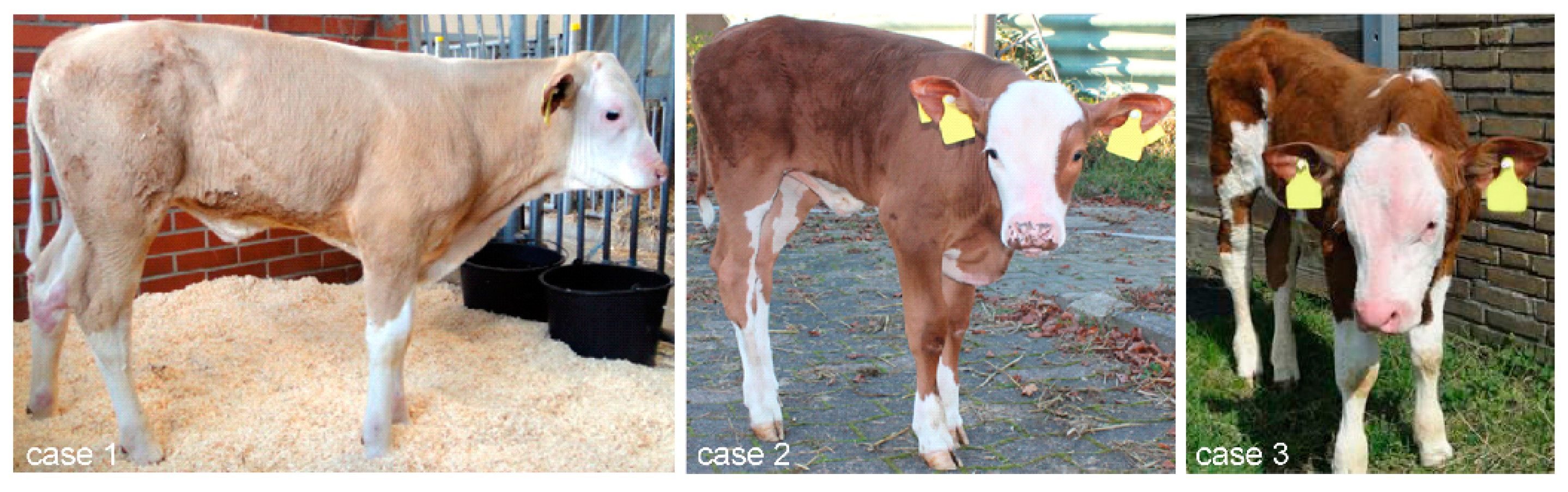
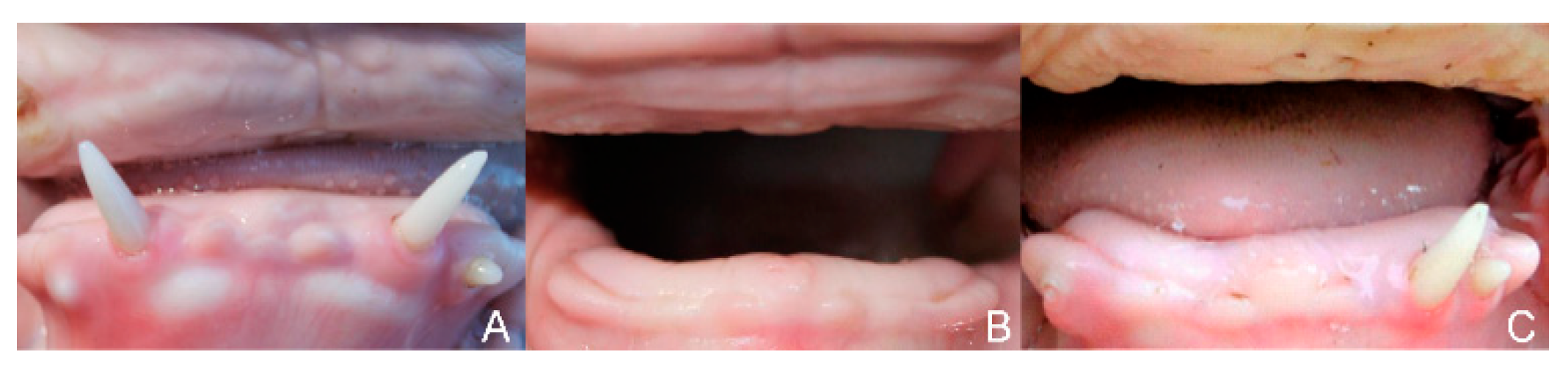
3.1. Phenotype
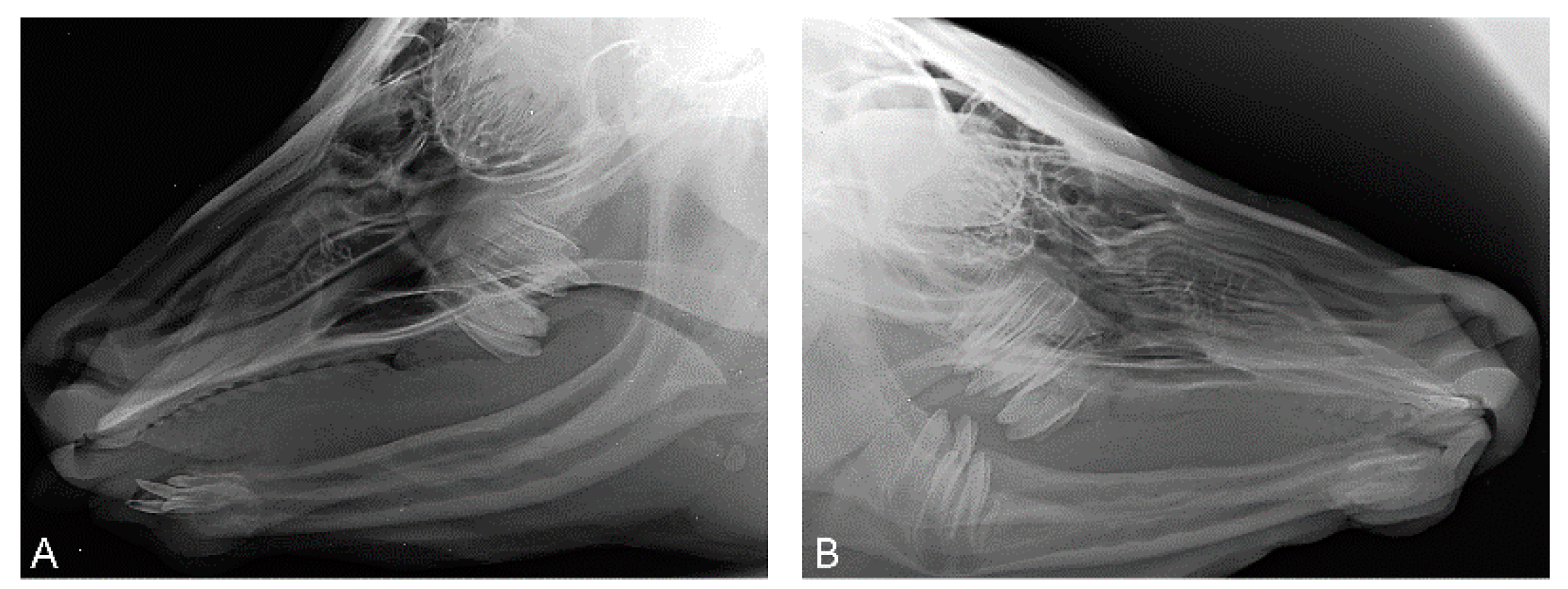
3.2. Histopathological Findings
3.3. Pedigree Analysis and Cytogenetics
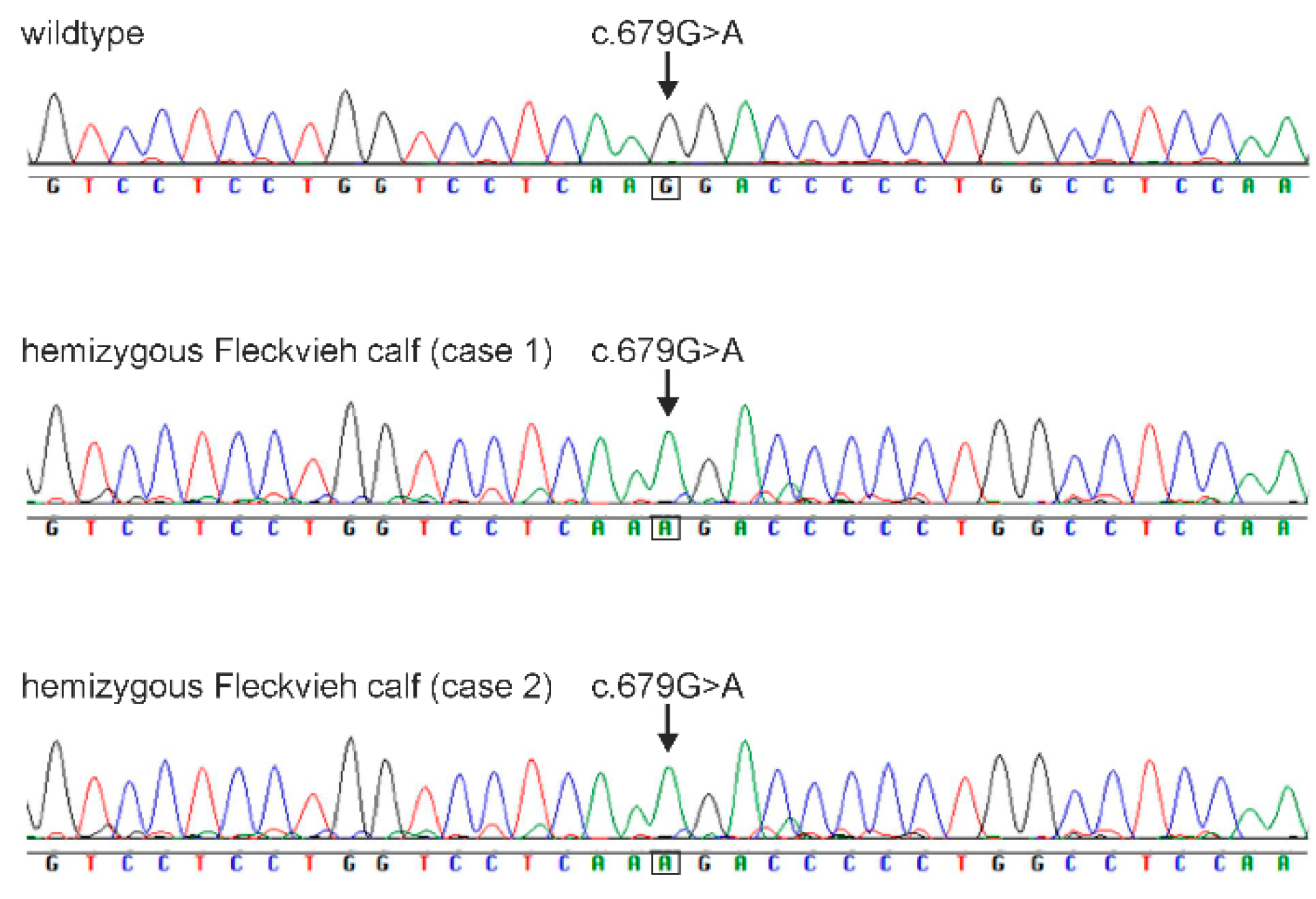
3.4. Whole Genome Sequence and Mutation Analysis
3.5. Validation
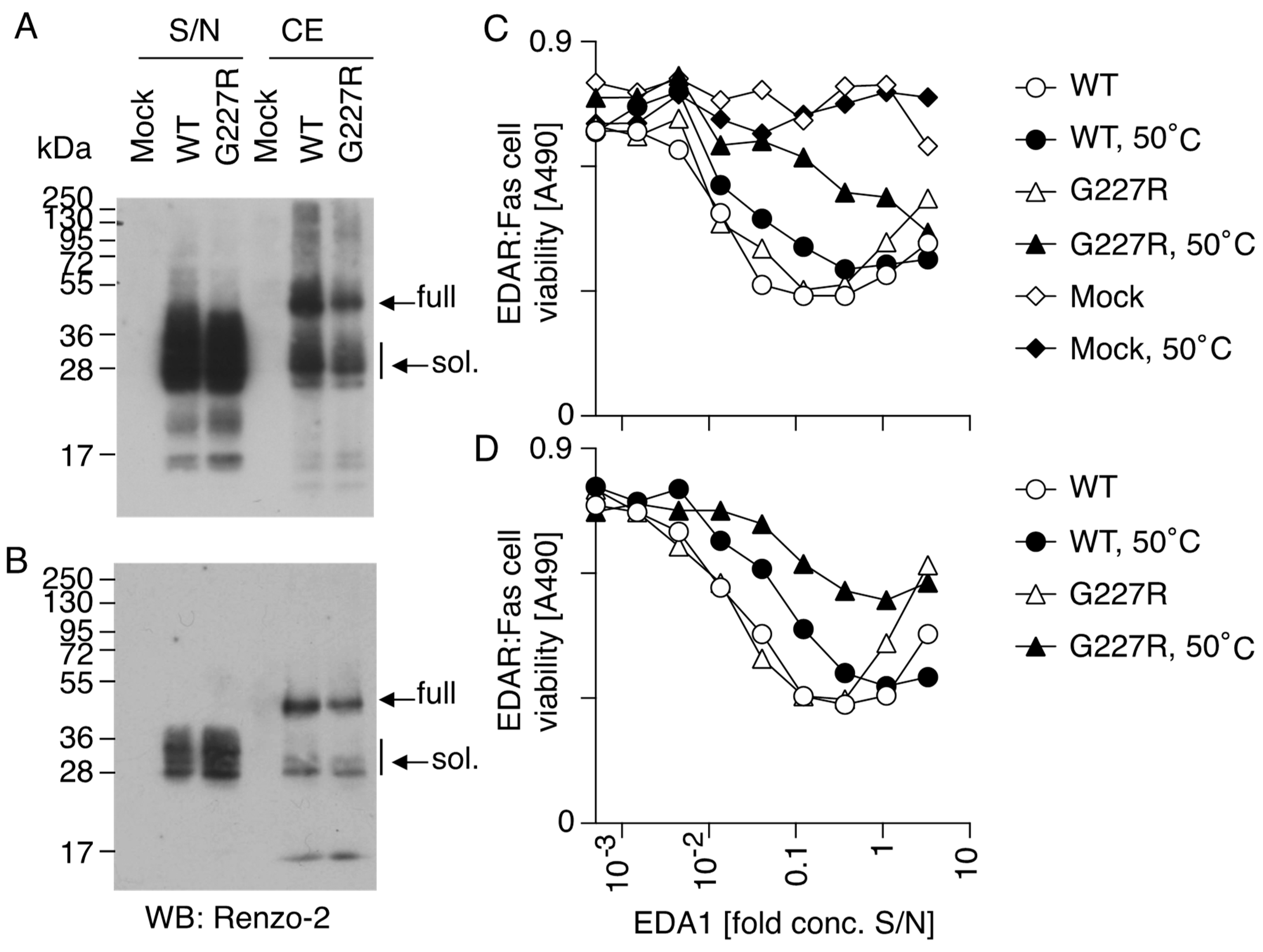
3.6. RNA and Protein Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kupietzky, A.; Houpt, M. Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia: Characteristics and treatment. Quintessence Int. 1995, 26, 285–291. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, B.M.; Brockdorff, N.; Formstone, E.; Ngyuen, T.; Kronmiller, J.E.; Zonana, J. Cloning of Tabby, the murine homolog of the human EDA gene: Evidence for a membrane-associated protein with a short collagenous domain. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997, 6, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieck, G.W. [Hypotrichia-hypodontia syndrome in cattle (brief report)]. Dtsch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 1985, 92, 328–329. [Google Scholar]
- Wijeratne, W.V.; O’Toole, D.; Wood, L.; Harkness, J.W. A genetic, pathological and virological study of congenital hypotrichosis and incisor anodontia in cattle. Vet. Rec. 1988, 122, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, U.; Ansari, H.; Hediger, R.; Suss, U.; Ehrensperger, F. Hypotrichose und Oligodontie, verbunden mit einer Xq-Deletion, bei einem Kalb der schweizerischen Fleckviehrasse. Tierarztl. Prax. 1988, 16, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Drögemüller, C.; Distl, O.; Leeb, T. Partial deletion of the bovine ED1 gene causes anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in cattle. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Drögemüller, C.; Kuiper, H.; Peters, M.; Guionaud, S.; Distl, O.; Leeb, T. Congenital hypotrichosis with anodontia in cattle: A genetic, clinical and histological analysis. Vet. Dermat. 2002, 13, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drögemüller, C.; Peters, M.; Pohlenz, J.; Distl, O.; Leeb, T. A single point mutation within the ED1 gene disrupts correct splicing at two different splice sites and leads to anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in cattle. J. Mol. Med. 2002, 80, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drögemüller, C.; Kuiper, H.; Leeb, T.; Peters, M.; Pohlenz, J.; Distl, O. Kongenitale Hypotrichose und Oligodontie beim Rind. Tierarztl. Prax. 2003, 31, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Seeliger, F.; Drogemuller, C.; Tegtmeier, P.; Baumgartner, W.; Distl, O.; Leeb, T. Ectodysplasin-1 deficiency in a German Holstein bull associated with loss of respiratory mucous glands and chronic rhinotracheitis. J. Comp. Pathol. 2005, 132, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drögemüller, C.; Barlund, C.S.; Palmer, C.W.; Leeb, T. A novel mutation in the bovine EDA gene causing anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (Brief report). Arch. Tierz. Dummerstorf. 2006, 49, 615–616. [Google Scholar]
- Barlund, C.S.; Clark, E.G.; Leeb, T.; Drögemüller, C.; Palmer, C.W. Congenital hypotrichosis and partial anodontia in a crossbred beef calf. Can. Vet. J. 2007, 48, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karlskov-Mortensen, P.; Cirera, S.; Nielsen, O.L.; Arnbjerg, J.; Reibel, J.; Fredholm, M.; Agerholm, J.S. Exonization of a LINE1 fragment implicated in X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in cattle. Anim. Genet. 2011, 42, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, A.; Kohama, N.; Ishikawa, S.; Tomita, K.; Nonaka, S.; Shimizu, K.; Tanabe, Y.; Okawa, H.; Morita, M. A novel mutation of the bovine EDA gene associated with anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in Holstein cattle. Hereditas 2011, 148, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogino, A.; Shimizu, K.; Tanabe, Y.; Morita, M. De novo mutation of the bovine EDA gene associated with anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in Japanese Black cattle. Anim. Genet. 2012, 43, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargani, M.; Valentini, A.; Pariset, L. A novel point mutation within the EDA gene causes an exon dropping in mature RNA in Holstein Friesian cattle breed affected by X-linked anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. BMC Vet. Res. 2011, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.; Reiter, A.; Mauldin, E.; Casal, M. Dental abnormalities associated with X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in dogs. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2010, 13, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Wang, L.C.; Hymowitz, S.G.; Schilbach, S.; Lee, J.; Goddard, A.; de Vos, A.M.; Gao, W.Q.; Dixit, V.M. Two-amino acid molecular switch in an epithelial morphogen that regulates binding to two distinct receptors. Science 2000, 290, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourneuf, E.; Otz, P.; Pausch, H.; Jagannathan, V.; Michot, P.; Grohs, C.; Piton, G.; Ammermüller, S.; Deloche, M.-C.; Fritz, S. Rapid discovery of de novo deleterious mutations in cattle enhances the value of livestock as model species. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thesleff, I. The genetic basis of tooth development and dental defects. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2006, 140, 2530–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastardis, H.; Karimbux, N.; Guthua, S.W.; Seidman, J.G.; Seidman, C.E. A human MSX1 homeodomain missense mutation causes selective tooth agenesis. Nat. Genet. 1996, 13, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockton, D.W.; Das, P.; Goldenberg, M.; D’Souza, R.N.; Patel, P.I. Mutation of PAX9 is associated with oligodontia. Nat. Genet. 2000, 24, 18–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammi, L.; Arte, S.; Somer, M.; Jarvinen, H.; Lahermo, P.; Thesleff, I.; Pirinen, S.; Nieminen, P. Mutations in AXIN2 cause familial tooth agenesis and predispose to colorectal cancer. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 74, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, A.S.; Headon, D.J.; Courtney, J.M.; Overbeek, P.; Sharpe, P.T. The activation level of the TNF family receptor, Edar, determines cusp number and tooth number during tooth development. Dev. Biol. 2004, 268, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtney, J.M.; Blackburn, J.; Sharpe, P.T. The Ectodysplasin and NFkappaB signalling pathways in odontogenesis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2005, 50, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurikkala, J.; Mikkola, M.; Mustonen, T.; Aberg, T.; Koppinen, P.; Pispa, J.; Nieminen, P.; Galceran, J.; Grosschedl, R.; Thesleff, I. TNF signaling via the ligand-receptor pair ectodysplasin and edar controls the function of epithelial signaling centers and is regulated by Wnt and activin during tooth organogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2001, 229, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tomann, P.; Andl, T.; Gallant, N.M.; Huelsken, J.; Jerchow, B.; Birchmeier, W.; Paus, R.; Piccolo, S.; Mikkola, M.L.; et al. Reciprocal requirements for EDA/EDAR/NF-kappaB and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways in hair follicle induction. Dev. Cell. 2009, 17, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arte, S.; Parmanen, S.; Pirinen, S.; Alaluusua, S.; Nieminen, P. Candidate gene analysis of tooth agenesis identifies novel mutations in six genes and suggests significant role for WNT and EDA signaling and allele combinations. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.L.; Smith, D.W. Diminished sweat pores in hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia: A new method for assessment. J. Pediatr. 1968, 72, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burck, U.; Held, K.R. Athelia in a female infant—Heterozygous for anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Clin. Genet. 1981, 19, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escouflaire, C.; Rebours, E.; Charles, M.; Orellana, S.; Cano, M.; Rivière, J.; Grohs, C.; Hayes, H.; Capitan, A. A de novo 3.8-Mb inversion affecting the EDA and XIST genes in a heterozygous female calf with generalized hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punj, V.; Matta, H.; Chaudhary, P.M. X-linked ectodermal dysplasia receptor is downregulated in breast cancer via promoter methylation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, A.; Phillips, D.I.; Brown, R.; Harper, P.S. Clinical aspects of X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Arch. Dis. Child. 1987, 62, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustonen, T.; Pispa, J.; Mikkola, M.L.; Pummila, M.; Kangas, A.T.; Pakkasjärvi, L.; Jaatinen, R.; Thesleff, I. Stimulation of ectodermal organ development by Ectodysplasin-A1. Dev. Biol. 2003, 259, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, M.; Fu, W.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, D.; Ding, X.; Liu, J. A Multiple-SNP Approach for Genome-Wide Association Study of Milk Production Traits in Chinese Holstein Cattle. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wöckl, F.; Mayr, B.; Schleger, W. Möglichkeiten der Diagnose von Erbfehlern mit Hilfe der Chromosomenanalyse bei Rind, Pferd und Schwein-eine Ubersicht. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 1980, 93, 81–83. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.A.; Dykes, D.D.; Polesky, H.F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tom, R.; Bisson, L.; Durocher, Y. Transfection of HEK293-EBNA1 Cells in Suspension with Linear PEI for Production of Recombinant Proteins. CSH Protoc. 2008, 2008, pdb.prot4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mues, G.; Tardivel, A.; Willen, L.; Kapadia, H.; Seaman, R.; Frazier-Bowers, S.; Schneider, P.; D’Souza, R.N. Functional analysis of Ectodysplasin-A mutations causing selective tooth agenesis. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 18, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becher, V., Ettle, T., Obermaier, A., Spiekers, H., Ridehutscord, M., Eds.; Effect of a different energy supply on feed intake and growth of simmental and brown swiss dairy heifers. In Proceedings of the 21th International Scientific Symposium on Nutrition of Farm Animals ‘Zadravec-Erjavec Days’, Radenci, Slovenia, 8–9 November 2012; Kmetijsko Gozdarska Zbornica Slovenije: Murska Sobota, Slovenia; Kmetijsko Gozdarski Zavod: Murska Sobota, Slovenia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ramensky, V.; Bork, P.; Sunyaev, S. Human non-synonymous SNPs: Server and survey. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3894–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podzus, J.; Kowalczyk-Quintas, C.; Schuepbach-Mallepell, S.; Willen, L.; Staehlin, G.; Vigolo, M.; Tardivel, A.; Headon, D.; Kirby, N.; Mikkola, M.L.; et al. Ectodysplasin A in biological fluids and diagnosis of ectodermal dysplasia. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 96, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Street, S.L.; Gaide, O.; Hertig, S.; Tardivel, A.; Tschopp, J.; Runkel, L.; Alevizopoulos, K.; Ferguson, B.M.; Zonana, J. Mutations leading to X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia affect three major functional domains in the tumor necrosis factor family member ectodysplasin-A. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18819–18827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drieux, H.; Priouzeau, M.; Thiéry, G.; Priouzeau, M.L. Hypotrichose congénitale avec anodontie, acérie et macroglossie chez le Veau. Recl. Méd. Vét. 1950, 126, 385–399. [Google Scholar]
- Schleger, A.V.; Thompson, B.J.; Hewetson, R.W. Histopathology of hypotrichosis in calves. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 1967, 20, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, B.; Théret, M.; Blin, P.; Bernard, C.; Lauvergne, J. Hypotrichose congénitale en race bovine normande. I.—Étude descriptive. Ann. Genet. Sel. Anim. 1975, 7, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Han, D.; Gong, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Yan, M.; Wang, X.; Qu, H.; Feng, H.; Song, S. Novel EDA mutation resulting in X-linked non-syndromic hypodontia and the pattern of EDA-associated isolated tooth agenesis. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2008, 51, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pispa, J.; Jung, H.S.; Jernvall, J.; Kettunen, P.; Mustonen, T.; Tabata, M.J.; Kere, J.; Thesleff, I. Cusp patterning defect in Tabby mouse teeth and its partial rescue by FGF. Dev. Biol. 1999, 216, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustonen, T.; Ilmonen, M.; Pummila, M.; Kangas, A.T.; Laurikkala, J.; Jaatinen, R.; Pispa, J.; Gaide, O.; Schneider, P.; Thesleff, I.; et al. Ectodysplasin A1 promotes placodal cell fate during early morphogenesis of ectodermal appendages. Development 2004, 131, 4907–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Simmer, J.P.; Lin, B.P.; Hu, J.C. Novel MSX1 frameshift causes autosomal-dominant oligodontia. J. Dent. Res. 2006, 85, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieminen, P. Genetic basis of tooth agenesis. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2009, 312b, 320–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dassule, H.R.; McMahon, A.P. Analysis of epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in the initial morphogenesis of the mammalian tooth. Dev. Biol. 1998, 202, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casal, M.L.; Lewis, J.R.; Mauldin, E.A.; Tardivel, A.; Ingold, K.; Favre, M.; Paradies, F.; Demotz, S.; Gaide, O.; Schneider, P. Significant correction of disease after postnatal administration of recombinant ectodysplasin A in canine X-linked ectodermal dysplasia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lexner, M.O.; Bardow, A.; Hertz, J.M.; Nielsen, L.A.; Kreiborg, S. Anomalies of tooth formation in hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2007, 17, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visinoni, A.F.; de Souza, R.L.; Freire-Maia, N.; Gollop, T.R.; Chautard-Freire-Maia, E.A. X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia mutations in Brazilian families. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2003, 122a, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikopensius, T.; Annilo, T.; Jagomägi, T.; Gilissen, C.; Kals, M.; Krjutškov, K.; Mägi, R.; Eelmets, M.; Gerst-Talas, U.; Remm, M. Non-syndromic tooth agenesis associated with a nonsense mutation in ectodysplasin-A (EDA). J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putz, M.; Wiedenmann, F. Deutsches Fleckvieh nach 2000. Tierzuechter Z. Veredl. 1993, 45, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Pichler, W.A.; Frickh, J.J. Untersuchungen zum Einfluß von Rationsgestaltung, Mastdauer und Herkunft auf die Mastleistung und den Schlachtwert von Jungmaststieren der Rasse Fleckvieh. Die Bodenkult. J. Land Manag. Food Environ. 2000, 51, 187–205. [Google Scholar]
- Bayés, M.; Hartung, A.J.; Ezer, S.; Pispa, J.; Thesleff, I.; Srivastava, A.K.; Kere, J. The anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia gene (EDA) undergoes alternative splicing and encodes ectodysplasin-A with deletion mutations in collagenous repeats. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1998, 7, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monreal, A.W.; Zonana, J.; Ferguson, B. Identification of a new splice form of the EDA1 gene permits detection of nearly all X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia mutations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1998, 63, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.; Veitinger, S.; Peek, I.; Busse, D.; Eckardt, J.; Vladimirova, D.; Jovancevic, N.; Wojcik, S.; Gisselmann, G.; Altmüller, J.; et al. Two olfactory receptors–OR2A4/7 and OR51B5–differentially affect epidermal proliferation and differentiation. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busse, D.; Kudella, P.; Grüning, N.M.; Gisselmann, G.; Ständer, S.; Luger, T.; Jacobsen, F.; Steinsträßer, L.; Paus, R.; Gkogkolou, P.; et al. A synthetic sandalwood odorant induces wound-healing processes in human keratinocytes via the olfactory receptor OR2AT4. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2823–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Episkopou, V.; Arkell, R.; Timmons, P.M.; Walsh, J.J.; Andrew, R.L.; Swan, D. Induction of the mammalian node requires Arkadia function in the extraembryonic lineages. Nature. 2001, 410, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, T.; Lei, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Tong, X.; Yang, W.T.; Zhao, J.; Gu, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. RNF111/Arkadia is regulated by DNA methylation and affects TGF–β/Smad signaling associated invasion in NSCLC cells. Lung Cancer. 2015, 90, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reinartz, S.; Weiß, C.; Heppelmann, M.; Hewicker-Trautwein, M.; Hellige, M.; Willen, L.; Feige, K.; Schneider, P.; Distl, O. A Missense Mutation in the Collagen Triple Helix of EDA Is Associated with X-Linked Recessive Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia in Fleckvieh Cattle. Genes 2024, 15, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010008
Reinartz S, Weiß C, Heppelmann M, Hewicker-Trautwein M, Hellige M, Willen L, Feige K, Schneider P, Distl O. A Missense Mutation in the Collagen Triple Helix of EDA Is Associated with X-Linked Recessive Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia in Fleckvieh Cattle. Genes. 2024; 15(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleReinartz, Sina, Christine Weiß, Maike Heppelmann, Marion Hewicker-Trautwein, Maren Hellige, Laure Willen, Karsten Feige, Pascal Schneider, and Ottmar Distl. 2024. "A Missense Mutation in the Collagen Triple Helix of EDA Is Associated with X-Linked Recessive Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia in Fleckvieh Cattle" Genes 15, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010008
APA StyleReinartz, S., Weiß, C., Heppelmann, M., Hewicker-Trautwein, M., Hellige, M., Willen, L., Feige, K., Schneider, P., & Distl, O. (2024). A Missense Mutation in the Collagen Triple Helix of EDA Is Associated with X-Linked Recessive Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia in Fleckvieh Cattle. Genes, 15(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010008




