Specific Patterns in Correlations of Super-Short Tandem Repeats (SSTRs) with G+C Content, Genic and Intergenic Regions, and Retrotransposons on All Human Chromosomes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
STRs/SSTRs and k-mer Analysis
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. NCBI and RefSeq
2.1.2. Super-Short Tandem Repeats
2.1.3. Gene Categories
2.1.4. Retrotransposons
2.2. Methods
2.3. Nucleotide Models and Significance of Correlations
3. Results
3.1. G+C Content and Repeat Motif Groupings
3.1.1. SSTRs and Genes
3.1.2. SSTRs and Retrotransposons
4. Discussion
4.1. Chromosomal Properties
4.2. Repeat Motif Groups
4.3. Genic Categories
4.4. Retrotransposons
4.5. SINE Alu
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hare, M.P. High Intron Sequence Conservation across Three Mammalian Orders Suggests Functional Constraints. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Olman, V.; Xu, Y. Barcodes for Genomes and Applications. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chor, B.; Horn, D.; Goldman, N.; Levy, Y.; Massingham, T. Genomic DNA K-Mer Spectra: Models and Modalities. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, W.R.; Wörheide, G. Similar Ratios of Introns to Intergenic Sequence across Animal Genomes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 1582–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deininger, P. Alu elements: Know the SINEs. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, S.R.; Doucet, A.J.; Kopera, H.C.; Moldovan, J.B.; Garcia-Perez, J.L.; Moran, J.V. The Influence of LINE-1 and SINE Retrotransposons on Mammalian Genomes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, 1165–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Yu, J. New Understanding of the Relevant Role of LINE-1 Retrotransposition in Human Disease and Immune Modulation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. The Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1983; ISBN 9780511623486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, E.V.; Goode, D.L.; Sirota, M.; Cooper, G.M.; Sidow, A.; Batzoglou, S. Identifying a high fraction of the human genome to be under selective constraint using GERP++. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6, e1001025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, A.; Bosiek, K.; Bisch, M.; Dreessen, C.; Riedel, J.; Froß, P.; Hausmann, M.; Hildenbrand, G. K-mer Content, Correlation, and Position Analysis of Genome DNA Sequences for the Identification of Function and Evolu-tionary Features. Genes 2017, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, A.; Sauer, L.; Hausmann, M.; Hildenbrand, G. Eukaryotic Genomes Show Strong Evolutionary Con-servation of k-mer Composition and Correlation Contributions between Introns and Intergenic Regions. Genes 2021, 12, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, A.; Wenz, F.; Hausmann, M.; Hildenbrand, G. Conservation of k-mer Composition and Correlation Contribution between Introns and Intergenic Regions of Animalia Genomes. Genes 2018, 9, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raveh-Sadka, T.; Levo, M.; Shabi, U.; Shany, B.; Keren, L.; Lotan-Pompan, M.; Zeevi, D.; Sharon, E.; Weinberger, A.; Segal, E. Manipulating nucleosome disfavoring sequences allows fine-tune regulation of gene expression in yeast. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.; Chen, Y.J.; Phillips, R. Poly(dA:dT)-Rich DNAs Are Highly Flexible in the Context of DNA Looping. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharerin, H.; Bhat, P.J.; Padinhateeri, R. Role of nucleosome positioning in 3D chromatin organization and loop for-mation. J. Biosci. 2020, 45, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-C.; Korol, A.B.; Fahima, T.; Beiles, A.; Nevo, E. Microsatellites: Genomic distribution, putative functions and mutational mechanisms: A review. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 2453–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, C.A.; Alexandari, A.M.; Hayes, M.G.B.; Marklund, E.; Schaepe, J.M.; Aditham, A.K.; Shah, N.; Suzuki, P.H.; Shrikumar, A.; Afek, A.; et al. Short tandem repeats bind transcription factors to tune eukaryotic gene expression. Science 2023, 381, eadd1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K. Note on regression and inheritance in the case of two parents Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1895, 58, 240–242. [Google Scholar]
- Wuitschick, J.D.; Karrer, K.M. Analysis of genomic G + C content, codon usage, initiator codon context and translation termination sites in Tetrahymena thermophila. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1999, 46, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, R.E.; Van Sickle, C. Autolysis of high-GC isolates of Pseudomonas putrefaciens. Antonie Van Leeu-Wenhoek 1976, 42, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovchuk, P.; Protozanova, E.; Frank-Kamenetskii, M.D. Base-stacking and base-pairing contributions into thermal stability of the DNA double helix. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, L.D.; Merchant, A.R. High guanine-cytosine content is not an adaptation to high temperature: A comparative analysis amongst prokaryotes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2001, 268, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birdsell, J.A. Integrating genomics, bioinformatics, and classical genetics to study the effects of recombination on genome evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 1181–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbarbary, R.A.; Lucas, B.A.; Maquat, L.E. Retrotransposons as regulators of gene expression. Science 2016, 351, aac7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayers, E.W.; Beck, J.; Bolton, E.E.; Brister, J.R.; Chan, J.; Comeau, D.C.; Connor, R.; DiCuccio, M.; Farrell, C.M.; Feldgarden, M.; et al. Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D20–D26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, A.F.A.; Hubley, R.; Green, P. RepeatMasker Open-4.0. 2013–2015. Available online: http://www.repeatmasker.org (accessed on 11 January 2021).
- Nurk, S.; Koren, S.; Rhie, A.; Rautiainen, M.; Bzikadze, A.V.; Mikheenko, A.; Vollger, M.R.; Altemose, N.; Uralsky, L.; Gershman, A.; et al. The complete sequence of a human genome. Science 2022, 376, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosandić, M.; Vlahović, I.; Pilaš, I.; Glunčić, M.; Paar, V. An Explanation of Exceptions from Chargaff’s Second Parity Rule/Strand Symmetry of DNA Molecules. Genes 2022, 13, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, A.; Sauer, L.; Bisch, M.; Sprengel, J.; Hausmann, M.; Hildenbrand, G. Moderation of Structural DNA Properties by Coupled Dinucleotide Contents in Eukaryotes. Genes 2023, 14, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudner, R.; Karkas, J.D.; Chargaff, E. Separation of B. subtilis DNA into complementary strands. 3. Direct analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1968, 60, 921–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shporer, S.; Chor, B.; Rosset, S.; Horn, D. Inversion symmetry of DNA k-mer counts: Validity and deviations. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
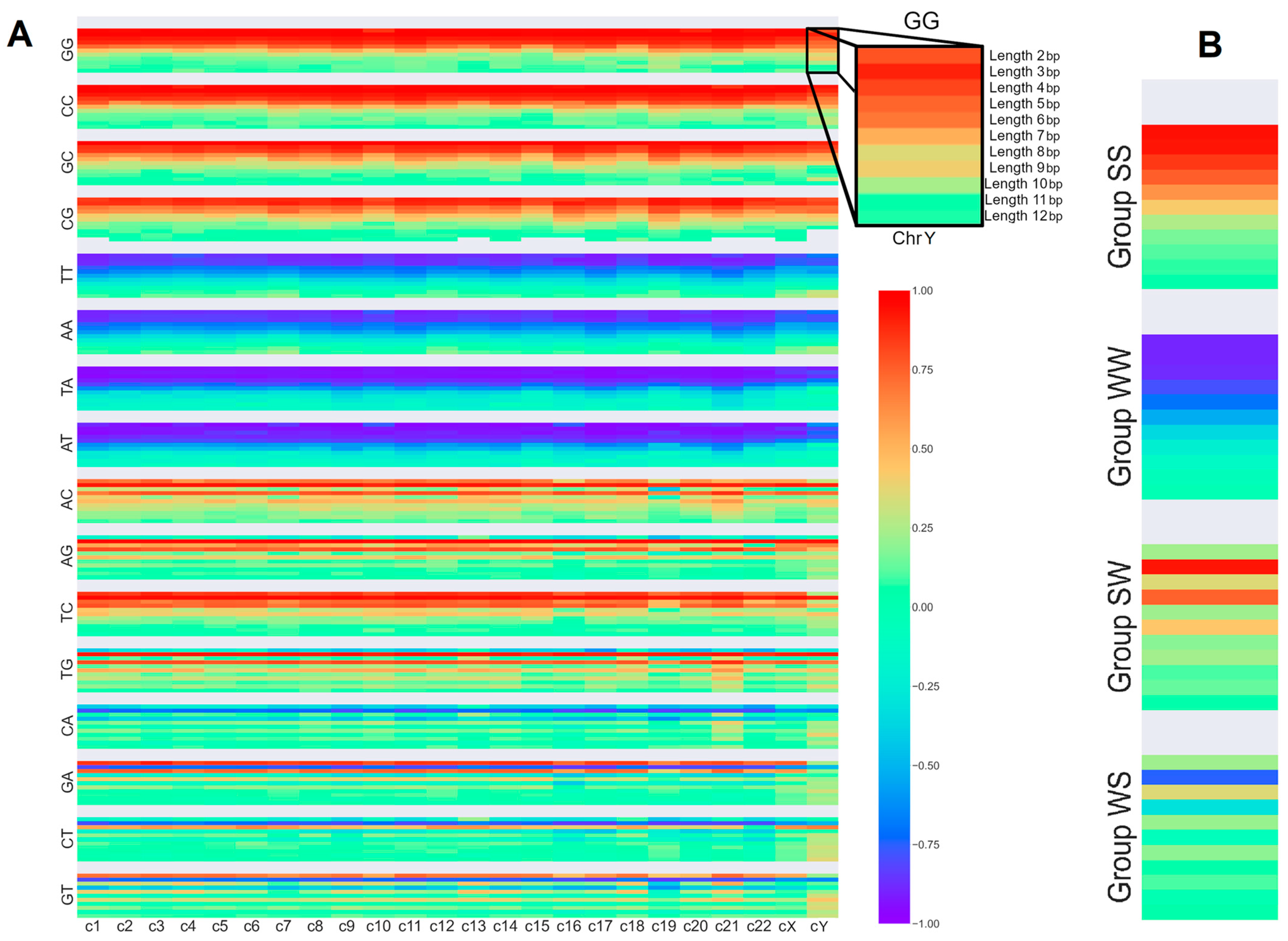
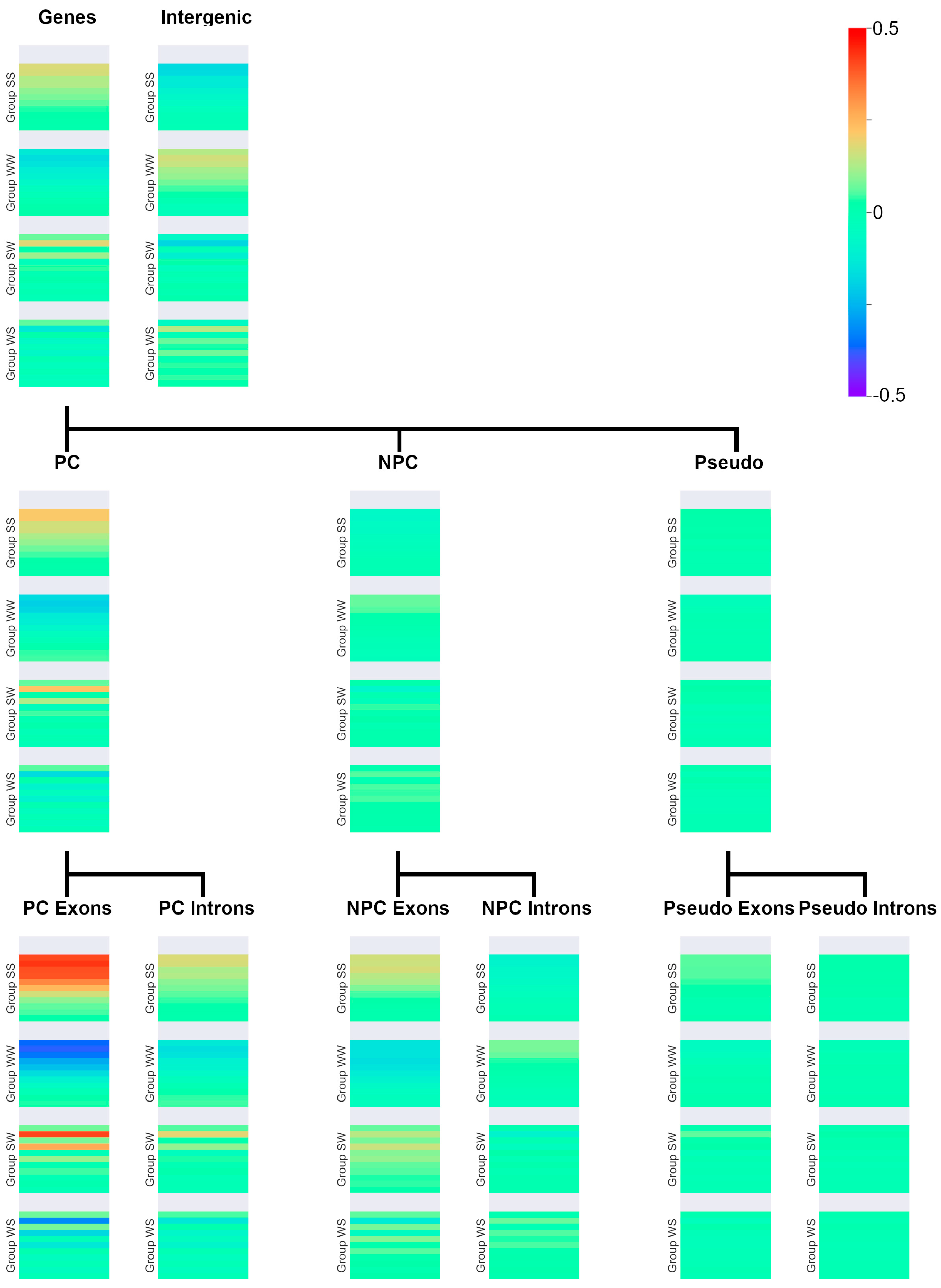

| (SS)n | (WW)n | (SW)n | (WS)n |
|---|---|---|---|
| (CC)n | (AA)n | (GA)n | (AG)n |
| (GG)n | (TT)n | (CA)n | (AC)n |
| (GC)n | (AT)n | (GT)n | (TG)n |
| (CG)n | (TA)n | (CT)n | (TC)n |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Henn, L.; Sievers, A.; Hausmann, M.; Hildenbrand, G. Specific Patterns in Correlations of Super-Short Tandem Repeats (SSTRs) with G+C Content, Genic and Intergenic Regions, and Retrotransposons on All Human Chromosomes. Genes 2024, 15, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010033
Henn L, Sievers A, Hausmann M, Hildenbrand G. Specific Patterns in Correlations of Super-Short Tandem Repeats (SSTRs) with G+C Content, Genic and Intergenic Regions, and Retrotransposons on All Human Chromosomes. Genes. 2024; 15(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleHenn, Lukas, Aaron Sievers, Michael Hausmann, and Georg Hildenbrand. 2024. "Specific Patterns in Correlations of Super-Short Tandem Repeats (SSTRs) with G+C Content, Genic and Intergenic Regions, and Retrotransposons on All Human Chromosomes" Genes 15, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010033
APA StyleHenn, L., Sievers, A., Hausmann, M., & Hildenbrand, G. (2024). Specific Patterns in Correlations of Super-Short Tandem Repeats (SSTRs) with G+C Content, Genic and Intergenic Regions, and Retrotransposons on All Human Chromosomes. Genes, 15(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010033







