When Protein Structure Embedding Meets Large Language Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a contact map-based method to encode the 3D protein structure into a fixed-dimensional numerical representation, which can be used for efficient protein function prediction.
- We incorporate extra features within our contact map-based embeddings using the features extracted from large language models for protein sequences, which enhance the overall predictive performance of the proposed model.
- We also incorporate the features designed from protein sequences within our 3D structure-based embeddings to further improve the classification accuracy for protein function prediction.
- The in-depth analysis of the proposed embedding model on two benchmark datasets shows superior predictive performance for the proposed method compared to recent baselines.
2. Related Work
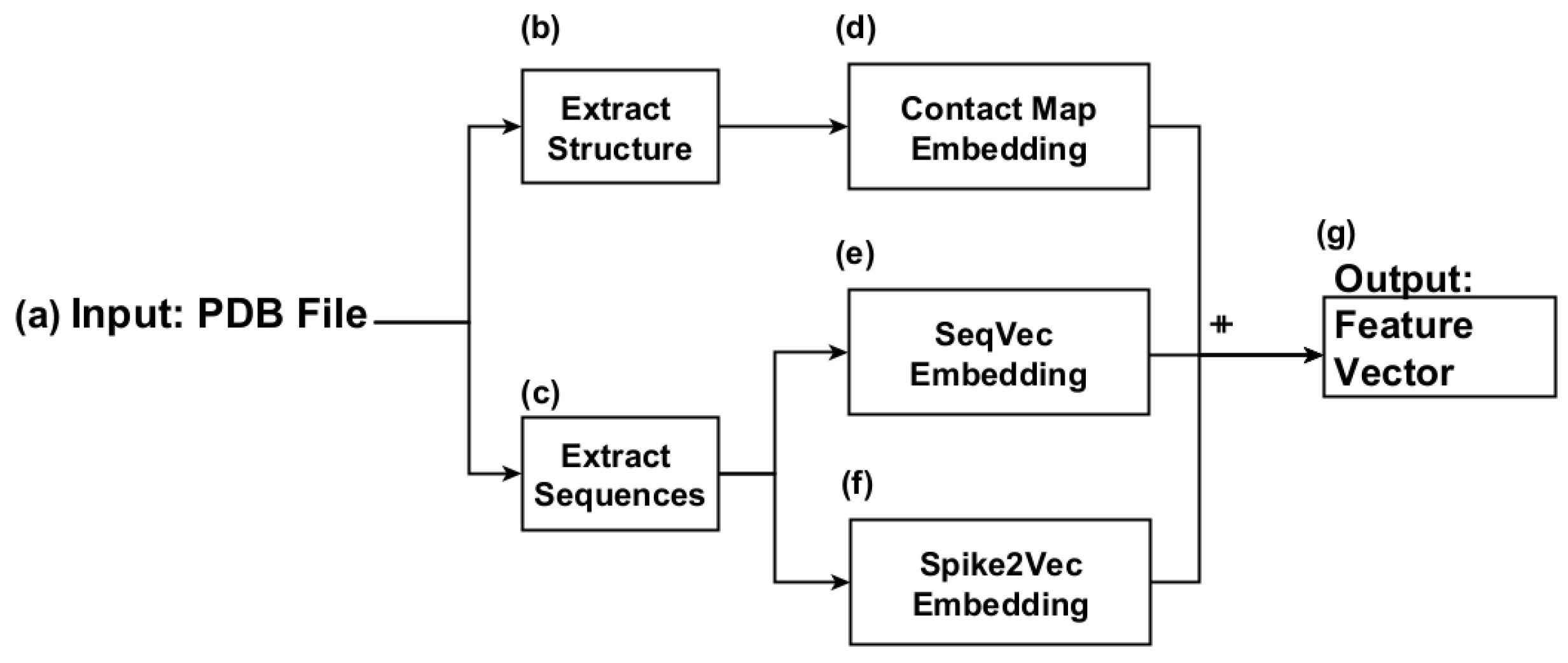
3. Proposed Approach
3.1. Sequence Extraction
3.2. Contact Map-Based Embedding Generation
| Algorithm 1 Generating Contact Map-Based Embedding |
|
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. STCRDAB
4.2. PDB Bind
4.3. Baseline Models
4.3.1. Spike2Vec [47]
4.3.2. SeqVec [37]
4.3.3. Unsupervised Protein Embeddings (UPE) [56]
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AlQuraishi, M. Machine learning in protein structure prediction. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2021, 65, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubinyi, H. Structure-based design of enzyme inhibitors and receptor ligands. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 1998, 1, 4–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, L.; Chen, L.; Lu, Y. Top-k subgraph matching query in a large graph. In Proceedings of the ACM First Ph.D. Workshop in CIKM, Lisbon, Portugal, 9 November 2007; pp. 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Licheri, N.; Amparone, E.; Bonnici, V.; Giugno, R.; Beccuti, M. An Entropy Heuristic to Optimize Decision Diagrams for Index-driven Search in Biological Graph Databases. In Proceedings of the CIKM Workshops, Virtual. 1–5 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Batool, M.; Ahmad, B.; Choi, S. A structure-based drug discovery paradigm. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burley, S.K.; Berman, H.M.; Kleywegt, G.J.; Markley, J.L.; Nakamura, H.; Velankar, S. Protein Data Bank (PDB): The single global macromolecular structure archive. In Protein Crystallography: Methods and Protocols; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 627–641. [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik, S.; Gront, D.; Kolinski, M.; Wieteska, L.; Dawid, A.E.; Kolinski, A. Coarse-grained protein models and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7898–7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.; Bergner, A.; Schwede, T. Modelling three-dimensional protein structures for applications in drug design. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lounnas, V.; Ritschel, T.; Kelder, J.; McGuire, R.; Bywater, R.P.; Foloppe, N. Current progress in structure-based rational drug design marks a new mindset in drug discovery. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 5, e201302011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lucrezia, D.; Slanzi, D.; Poli, I.; Polticelli, F.; Minervini, G. Do natural proteins differ from random sequences polypeptides? Natural vs. random proteins classification using an evolutionary neural network. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, W.T.; Radivojac, P. Analysis of protein function and its prediction from amino acid sequence. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2011, 79, 2086–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radivojac, P.; Clark, W.T.; Oron, T.R.; Schnoes, A.M.; Wittkop, T.; Sokolov, A.; Graim, K.; Funk, C.; Verspoor, K.; Ben-Hur, A.; et al. A large-scale evaluation of computational protein function prediction. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Williams, N.; Misleh, C.; Li, W.W. MEME: Discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W369–W373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rives, A.; Meier, J.; Sercu, T.; Goyal, S.; Lin, Z.; Liu, J.; Guo, D.; Ott, M.; Zitnick, C.L.; Ma, J.; et al. Biological structure and function emerge from scaling unsupervised learning to 250 million protein sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2016239118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavasotto, C.N.; Phatak, S.S. Homology modeling in drug discovery: Current trends and applications. Drug Discov. Today 2009, 14, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Homer, N. A survey of sequence alignment algorithms for next-generation sequencing. Brief. Bioinform. 2010, 11, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amitai, G.; Shemesh, A.; Sitbon, E.; Shklar, M.; Netanely, D.; Venger, I.; Pietrokovski, S. Network analysis of protein structures identifies functional residues. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 344, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, B.; Eismann, S.; Suriana, P.; Townshend, R.J.; Dror, R. Learning from protein structure with geometric vector perceptrons. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.01411. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, J.; Roth, S.; Arnold, K.; Kiefer, F.; Schmidt, T.; Bordoli, L.; Schwede, T. The Protein Model Portal—a comprehensive resource for protein structure and model information. Database 2013, 2013, bat031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.C.; Yue, Z.X.; Xu, H.Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Hong, Y.F.; Chen, G.X.; Tao, L.; Xie, T. A systematic review of state-of-the-art strategies for machine learning-based protein function prediction. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 154, 106446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonetta, R.; Valentino, G. Machine learning techniques for protein function prediction. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2020, 88, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Deep recurrent neural network for protein function prediction from sequence. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.08318. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlman, B.; Bradley, P. Advances in protein structure prediction and design. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, A.; Krause, B.; Greene, E.R.; Subramanian, S.; Mohr, B.P.; Holton, J.M.; Olmos Jr, J.L.; Xiong, C.; Sun, Z.Z.; Socher, R.; et al. Large language models generate functional protein sequences across diverse families. Nature Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, F.; Treangen, T.; Kavraki, L. Leveraging Large Language Models for Predicting Microbial Virulence from Protein Structure and Sequence. In Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology, and Health Informatics, Houston, TX, USA, 3–6 September 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Akin, H.; Rao, R.; Hie, B.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, W.; Smetanin, N.; Verkuil, R.; Kabeli, O.; Shmueli, Y.; et al. Evolutionary-scale prediction of atomic-level protein structure with a language model. Science 2023, 379, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofer, D.; Brandes, N.; Linial, M. The language of proteins: NLP, machine learning & protein sequences. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Akin, H.; Rao, R.; Hie, B.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, W.; dos Santos Costa, A.; Fazel-Zarandi, M.; Sercu, T.; Candido, S.; et al. Language models of protein sequences at the scale of evolution enable accurate structure prediction. bioRxiv 2022, 2022, 500902. [Google Scholar]
- Forslund, K.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting protein function from domain content. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Shen, H.B. RNA-protein binding motifs mining with a new hybrid deep learning based cross-domain knowledge integration approach. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, P.; Delisi, C. Prediction of protein structural class from the amino acid sequence. Biopolym. Orig. Res. Biomol. 1986, 25, 1659–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinga, S.; Gouveia-Oliveira, R.; Almeida, J.S. Comparative evaluation of word composition distances for the recognition of SCOP relationships. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ie, E.; Weston, J.; Noble, W.S.; Leslie, C. Multi-class protein fold recognition using adaptive codes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Bonn, Germany, 7–11 August 2005; pp. 329–336. [Google Scholar]
- Shamim, M.T.A.; Anwaruddin, M.; Nagarajaram, H.A. Support vector machine-based classification of protein folds using the structural properties of amino acid residues and amino acid residue pairs. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 3320–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, K.; Adeniyi, A.E.; DaSouza, A.K., Jr.; Lim, D.; Nguyen, H.; Molina, N.R.; Xiong, L.; Weber, I.T.; Harrison, R.W. Machine learning methods accurately predict host specificity of coronaviruses based on spike sequences alone. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 533, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Sahoo, B.; Ullah, N.; Zelikovskiy, A.; Patterson, M.; Khan, I. A k-mer based approach for SARS-CoV-2 variant identification. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Bioinformatics Research and Applications, Shenzhen, China, 26–28 November 2021; pp. 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Heinzinger, M.; Elnaggar, A.; Wang, Y.; Dallago, C.; Nechaev, D.; Matthes, F.; Rost, B. Modeling aspects of the language of life through transfer-learning protein sequences. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandes, N.; Ofer, D.; Peleg, Y.; Rappoport, N.; Linial, M. ProteinBERT: A universal deep-learning model of protein sequence and function. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, M.A.; Wani, M.A. Improving Prediction of Protein Secondary Structures using Attention-enhanced Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 9th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development, New Delhi, India, 23–25 March 2022; pp. 664–668. [Google Scholar]
- Buchan, D.W.; Jones, D.T. The PSIPRED protein analysis workbench: 20 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W402–W407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozemberczki, B.; Gogleva, A.; Nilsson, S.; Edwards, G.; Nikolov, A.; Papa, E. MOOMIN: Deep Molecular Omics Network for Anti-Cancer Drug Combination Therapy. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management (CIKM), Atlanta, GA, USA, 17–21 October 2022; pp. 3472–3483. [Google Scholar]
- Apeltsin, L.; Morris, J.H.; Babbitt, P.C.; Ferrin, T.E. Improving the quality of protein similarity network clustering algorithms using the network edge weight distribution. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Wootton, J.C.; Gertz, E.M.; Agarwala, R.; Morgulis, A.; Schäffer, A.A.; Yu, Y.K. Protein database searches using compositionally adjusted substitution matrices. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 5101–5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Bello, B.; Chourasia, P.; Punathil, R.T.; Zhou, Y.; Patterson, M. PWM2Vec: An Efficient Embedding Approach for Viral Host Specification from Coronavirus Spike Sequences. Biology 2022, 11, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Patterson, M. Spike2vec: An efficient and scalable embedding approach for COVID-19 spike sequences. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Orlando, FL, USA, 15–18 December 2021; pp. 1533–1540. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, D.; Salzberg, S. Kraken: Ultrafast metagenomic sequence classification using exact alignments. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girotto, S.; Pizzi, C.; Comin, M. MetaProb: Accurate metagenomic reads binning based on probabilistic sequence signatures. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, i567–i575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, S.; Deane, C. Co-evolution techniques are reshaping the way we do structural bioinformatics. F1000Research 2017, 6, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuksa, P.; Khan, I.; Pavlovic, V. Generalized Similarity Kernels for Efficient Sequence Classification. In Proceedings of the SIAM International Conference on Data Mining (SDM), Anaheim, CA, USA, 26–28 April 2012; pp. 873–882. [Google Scholar]
- Kané, H.; Coulibali, M.K.; Ajanoh, P.; Abdallah, A. Augmenting protein network embeddings with sequence information. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leem, J.; de Oliveira, S.H.P.; Krawczyk, K.; Deane, C.M. STCRDab: The structural T-cell receptor database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D406–D412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Han, L.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Nie, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R. PDB-wide collection of binding data: Current status of the PDBbind database. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzynska-Wawer, J.; Wawer, A.; Pawlak, A.; Szymanowska, J.; Stefaniak, I.; Jarkiewicz, M.; Okruszek, L. Detecting formal thought disorder by deep contextualized word representations. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 304, 114135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Morcillo, A.; Makrodimitris, S.; van Ham, R.C.; Gomez, A.M.; Sanchez, V.; Reinders, M.J. Unsupervised protein embeddings outperform hand-crafted sequence and structure features at predicting molecular function. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Count |
|---|---|
| Human | 325 |
| Mouse | 155 |
| Total | 480 |
| Target Name | Count | Target Name | Count |
|---|---|---|---|
| SERINE/THREONINE—PROTEIN | 404 | PROTEIN | 138 |
| TYROSINE—PROTEIN | 381 | E3 | 138 |
| MITOGEN—ACTIVATED | 325 | CYCLIN-DEPENDENT | 128 |
| BETA—SECRETASE | 299 | GLUTAMATE | 112 |
| BETA—LACTAMASE | 220 | DUAL | 111 |
| BROMODOMAIN—CONTAINING | 174 | HEAT | 110 |
| HIV-1 | 164 | PROTEASOME | 110 |
| CARBONIC | 159 | TANKYRASE-2 | 108 |
| CELL | 157 | LYSINE-SPECIFIC | 105 |
| GLYCOGEN | 144 | DNA | 104 |
| PHOSPHATIDYLINOSITOL-45-BISPHOSPHATE | 100 | COAGULATION | 101 |
| Total | 3792 |
| Category | Embedding | Algo. | Acc. ↑ | Prec. ↑ | Recall ↑ | F1 (Weig.) ↑ | F1 (Macro) ↑ | ROC-AUC ↑ | Train Time (s) ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence Only (Baselines) | Spike2Vec [47] | SVM | 0.976 | 0.977 | 0.976 | 0.976 | 0.972 | 0.967 | 1.824 |
| NB | 0.978 | 0.978 | 0.978 | 0.978 | 0.974 | 0.967 | 0.189 | ||
| MLP | 0.983 | 0.984 | 0.983 | 0.983 | 0.981 | 0.982 | 5.145 | ||
| KNN | 0.963 | 0.963 | 0.963 | 0.962 | 0.956 | 0.948 | 0.087 | ||
| RF | 0.975 | 0.975 | 0.975 | 0.975 | 0.971 | 0.967 | 0.462 | ||
| LR | 0.988 | 0.988 | 0.988 | 0.987 | 0.985 | 0.986 | 0.119 | ||
| DT | 0.957 | 0.957 | 0.957 | 0.957 | 0.950 | 0.948 | 0.204 | ||
| SeqVec [37] | SVM | 0.794 | 0.795 | 0.794 | 0.783 | 0.750 | 0.737 | 0.025 | |
| NB | 0.743 | 0.741 | 0.743 | 0.739 | 0.708 | 0.702 | 0.004 | ||
| MLP | 0.726 | 0.734 | 0.726 | 0.727 | 0.700 | 0.705 | 3.297 | ||
| KNN | 0.829 | 0.830 | 0.829 | 0.820 | 0.793 | 0.778 | 0.047 | ||
| RF | 0.812 | 0.854 | 0.812 | 0.788 | 0.747 | 0.726 | 0.590 | ||
| LR | 0.886 | 0.886 | 0.886 | 0.884 | 0.871 | 0.864 | 0.030 | ||
| DT | 0.790 | 0.787 | 0.790 | 0.786 | 0.757 | 0.749 | 0.114 | ||
| SeqVec + Spike2Vec | SVM | 0.882 | 0.886 | 0.882 | 0.876 | 0.857 | 0.840 | 0.051 | |
| NB | 0.829 | 0.828 | 0.829 | 0.827 | 0.803 | 0.795 | 0.002 | ||
| MLP | 0.767 | 0.769 | 0.767 | 0.768 | 0.739 | 0.741 | 0.651 | ||
| KNN | 0.926 | 0.933 | 0.926 | 0.924 | 0.912 | 0.893 | 0.033 | ||
| RF | 0.913 | 0.917 | 0.913 | 0.910 | 0.895 | 0.877 | 0.331 | ||
| LR | 0.982 | 0.982 | 0.982 | 0.982 | 0.980 | 0.980 | 0.019 | ||
| DT | 0.897 | 0.897 | 0.897 | 0.897 | 0.884 | 0.881 | 0.053 | ||
| Sequence + Structure (Baseline) | UPE [56] | SVM | 0.916 | 0.989 | 0.916 | 0.988 | 0.909 | 0.907 | 0.961 |
| NB | 0.897 | 0.908 | 0.897 | 0.895 | 0.896 | 0.911 | 0.975 | ||
| MLP | 0.915 | 0.929 | 0.915 | 0.928 | 0.983 | 0.971 | 1.097 | ||
| KNN | 0.921 | 0.928 | 0.921 | 0.929 | 0.981 | 0.979 | 0.452 | ||
| RF | 0.894 | 0.885 | 0.894 | 0.892 | 0.881 | 0.893 | 0.813 | ||
| LR | 0.957 | 0.942 | 0.957 | 0.954 | 0.975 | 0.963 | 0.128 | ||
| DT | 0.901 | 0.899 | 0.901 | 0.900 | 0.921 | 0.943 | 0.042 | ||
| Structure Only (ours) | Contact Map | SVM | 0.569 | 0.556 | 0.569 | 0.560 | 0.514 | 0.517 | 0.040 |
| NB | 0.639 | 0.644 | 0.639 | 0.624 | 0.584 | 0.591 | 0.007 | ||
| MLP | 0.563 | 0.563 | 0.563 | 0.544 | 0.498 | 0.515 | 4.255 | ||
| KNN | 0.621 | 0.554 | 0.621 | 0.537 | 0.453 | 0.509 | 0.048 | ||
| RF | 0.646 | 0.554 | 0.646 | 0.511 | 0.403 | 0.506 | 0.747 | ||
| LR | 0.664 | 0.653 | 0.664 | 0.648 | 0.605 | 0.603 | 0.037 | ||
| DT | 0.579 | 0.572 | 0.579 | 0.573 | 0.531 | 0.532 | 0.207 | ||
| Sequence + Structure (ours) | Contact Map + Spike2Vec | SVM | 0.789 | 0.805 | 0.789 | 0.769 | 0.729 | 0.713 | 0.152 |
| NB | 0.847 | 0.853 | 0.847 | 0.843 | 0.821 | 0.810 | 0.008 | ||
| MLP | 0.614 | 0.619 | 0.614 | 0.603 | 0.552 | 0.559 | 18.721 | ||
| KNN | 0.939 | 0.945 | 0.939 | 0.937 | 0.928 | 0.913 | 0.283 | ||
| RF | 0.924 | 0.932 | 0.924 | 0.921 | 0.910 | 0.891 | 2.191 | ||
| LR | 0.981 | 0.981 | 0.981 | 0.981 | 0.978 | 0.978 | 0.243 | ||
| DT | 0.913 | 0.915 | 0.913 | 0.913 | 0.902 | 0.905 | 0.330 | ||
| Sequence + Structure (ours) | Contact Map + SeqVec | SVM | 0.840 | 0.869 | 0.840 | 0.819 | 0.768 | 0.737 | 0.061 |
| NB | 0.800 | 0.798 | 0.800 | 0.784 | 0.730 | 0.710 | 0.007 | ||
| MLP | 0.690 | 0.697 | 0.690 | 0.688 | 0.632 | 0.639 | 3.287 | ||
| KNN | 0.844 | 0.844 | 0.844 | 0.843 | 0.813 | 0.810 | 0.043 | ||
| RF | 0.824 | 0.850 | 0.824 | 0.800 | 0.743 | 0.714 | 0.779 | ||
| LR | 0.879 | 0.881 | 0.879 | 0.880 | 0.858 | 0.861 | 0.077 | ||
| DT | 0.799 | 0.801 | 0.799 | 0.799 | 0.764 | 0.766 | 0.286 | ||
| Sequence + Structure (ours) | Contact Map + SeqVec + Spike2Vec | SVM | 0.991 | 0.990 | 0.991 | 0.990 | 0.988 | 0.985 | 81.170 |
| NB | 0.988 | 0.988 | 0.988 | 0.987 | 0.985 | 0.982 | 0.320 | ||
| MLP | 0.988 | 0.988 | 0.988 | 0.988 | 0.985 | 0.988 | 11.968 | ||
| KNN | 0.940 | 0.942 | 0.940 | 0.939 | 0.924 | 0.909 | 0.330 | ||
| RF | 0.979 | 0.980 | 0.979 | 0.979 | 0.974 | 0.970 | 0.745 | ||
| LR | 0.986 | 0.986 | 0.986 | 0.986 | 0.983 | 0.980 | 0.889 | ||
| DT | 0.956 | 0.957 | 0.956 | 0.956 | 0.948 | 0.951 | 0.410 |
| Category | Embedding | Algo. | Acc. ↑ | Prec. ↑ | Recall ↑ | F1 (Weig.) ↑ | F1 (Macro) ↑ | ROC-AUC ↑ | Train Time (s) ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence Only (Baselines) | Spike2Vec [47] | SVM | 0.960 | 0.965 | 0.960 | 0.961 | 0.954 | 0.975 | 263.112 |
| NB | 0.943 | 0.956 | 0.943 | 0.944 | 0.931 | 0.964 | 8.230 | ||
| MLP | 0.934 | 0.939 | 0.934 | 0.934 | 0.919 | 0.958 | 85.427 | ||
| KNN | 0.896 | 0.954 | 0.896 | 0.910 | 0.897 | 0.941 | 1.961 | ||
| RF | 0.960 | 0.966 | 0.960 | 0.961 | 0.954 | 0.975 | 6.888 | ||
| LR | 0.966 | 0.967 | 0.966 | 0.966 | 0.959 | 0.978 | 8.471 | ||
| DT | 0.939 | 0.942 | 0.939 | 0.939 | 0.929 | 0.962 | 4.682 | ||
| SeqVec [37] | SVM | 0.845 | 0.881 | 0.845 | 0.846 | 0.857 | 0.909 | 4.124 | |
| NB | 0.301 | 0.550 | 0.301 | 0.299 | 0.300 | 0.632 | 0.209 | ||
| MLP | 0.745 | 0.756 | 0.745 | 0.741 | 0.735 | 0.865 | 32.370 | ||
| KNN | 0.828 | 0.849 | 0.828 | 0.830 | 0.817 | 0.901 | 0.311 | ||
| RF | 0.822 | 0.876 | 0.822 | 0.829 | 0.844 | 0.898 | 7.645 | ||
| LR | 0.874 | 0.880 | 0.874 | 0.874 | 0.870 | 0.927 | 19.388 | ||
| DT | 0.783 | 0.782 | 0.783 | 0.781 | 0.782 | 0.887 | 7.134 | ||
| SeqVec + Spike2Vec | SVM | 0.883 | 0.905 | 0.883 | 0.882 | 0.884 | 0.925 | 12.571 | |
| NB | 0.688 | 0.765 | 0.688 | 0.703 | 0.692 | 0.841 | 0.136 | ||
| MLP | 0.757 | 0.768 | 0.757 | 0.754 | 0.747 | 0.873 | 9.640 | ||
| KNN | 0.919 | 0.942 | 0.919 | 0.924 | 0.912 | 0.954 | 2.412 | ||
| RF | 0.935 | 0.943 | 0.935 | 0.937 | 0.929 | 0.961 | 6.024 | ||
| LR | 0.958 | 0.962 | 0.958 | 0.959 | 0.951 | 0.974 | 22.074 | ||
| DT | 0.878 | 0.881 | 0.878 | 0.878 | 0.865 | 0.930 | 2.765 | ||
| Sequence + Structure (Baseline) | UPE [56] | SVM | 0.891 | 0.912 | 0.891 | 0.942 | 0.929 | 0.899 | 6.581 |
| NB | 0.922 | 0.941 | 0.922 | 0.918 | 0.919 | 0.896 | 1.675 | ||
| MLP | 0.963 | 0.922 | 0.963 | 0.921 | 0.905 | 0.896 | 4.254 | ||
| KNN | 0.959 | 0.923 | 0.959 | 0.949 | 0.938 | 0.893 | 0.234 | ||
| RF | 0.921 | 0.944 | 0.921 | 0.932 | 0.928 | 0.948 | 4.563 | ||
| LR | 0.954 | 0.925 | 0.954 | 0.930 | 0.929 | 0.965 | 9.753 | ||
| DT | 0.939 | 0.928 | 0.939 | 0.935 | 0.912 | 0.945 | 0.973 | ||
| Structure Only (ours) | Contact Map | SVM | 0.585 | 0.823 | 0.585 | 0.627 | 0.665 | 0.779 | 25.248 |
| NB | 0.352 | 0.440 | 0.352 | 0.345 | 0.325 | 0.657 | 0.947 | ||
| MLP | 0.502 | 0.570 | 0.502 | 0.505 | 0.510 | 0.748 | 80.370 | ||
| KNN | 0.571 | 0.706 | 0.571 | 0.599 | 0.574 | 0.760 | 0.482 | ||
| RF | 0.690 | 0.759 | 0.690 | 0.694 | 0.702 | 0.821 | 19.493 | ||
| LR | 0.712 | 0.726 | 0.712 | 0.713 | 0.699 | 0.840 | 151.352 | ||
| DT | 0.578 | 0.586 | 0.578 | 0.579 | 0.571 | 0.777 | 17.549 | ||
| Sequence + Structure (ours) | Contact Map + Spike2Vec | SVM | 0.678 | 0.827 | 0.678 | 0.706 | 0.731 | 0.821 | 17.635 |
| NB | 0.426 | 0.501 | 0.426 | 0.431 | 0.409 | 0.690 | 0.575 | ||
| MLP | 0.535 | 0.588 | 0.535 | 0.535 | 0.536 | 0.767 | 105.944 | ||
| KNN | 0.593 | 0.769 | 0.593 | 0.637 | 0.634 | 0.784 | 0.475 | ||
| RF | 0.841 | 0.866 | 0.841 | 0.841 | 0.844 | 0.904 | 14.192 | ||
| LR | 0.918 | 0.923 | 0.918 | 0.919 | 0.908 | 0.952 | 138.618 | ||
| DT | 0.775 | 0.779 | 0.775 | 0.774 | 0.766 | 0.880 | 12.891 | ||
| Sequence + Structure (ours) | Contact Map + SeqVec | SVM | 0.802 | 0.870 | 0.802 | 0.807 | 0.810 | 0.877 | 34.657 |
| NB | 0.459 | 0.533 | 0.459 | 0.451 | 0.443 | 0.715 | 1.630 | ||
| MLP | 0.553 | 0.598 | 0.553 | 0.554 | 0.558 | 0.777 | 64.202 | ||
| KNN | 0.552 | 0.717 | 0.552 | 0.589 | 0.573 | 0.754 | 0.465 | ||
| RF | 0.798 | 0.853 | 0.798 | 0.806 | 0.820 | 0.885 | 19.770 | ||
| LR | 0.804 | 0.809 | 0.804 | 0.803 | 0.802 | 0.894 | 196.321 | ||
| DT | 0.714 | 0.717 | 0.714 | 0.713 | 0.710 | 0.850 | 25.274 | ||
| Sequence + Structure (ours) | Contact Map + SeqVec + Spike2Vec | SVM | 0.677 | 0.816 | 0.677 | 0.701 | 0.728 | 0.818 | 17.343 |
| NB | 0.430 | 0.528 | 0.430 | 0.441 | 0.425 | 0.697 | 0.498 | ||
| MLP | 0.524 | 0.568 | 0.524 | 0.524 | 0.530 | 0.761 | 120.589 | ||
| KNN | 0.671 | 0.726 | 0.671 | 0.682 | 0.686 | 0.828 | 0.429 | ||
| RF | 0.839 | 0.860 | 0.839 | 0.839 | 0.844 | 0.904 | 14.844 | ||
| LR | 0.968 | 0.972 | 0.968 | 0.969 | 0.966 | 0.980 | 134.948 | ||
| DT | 0.764 | 0.772 | 0.764 | 0.766 | 0.762 | 0.875 | 12.175 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, S.; Chourasia, P.; Patterson, M. When Protein Structure Embedding Meets Large Language Models. Genes 2024, 15, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010025
Ali S, Chourasia P, Patterson M. When Protein Structure Embedding Meets Large Language Models. Genes. 2024; 15(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Sarwan, Prakash Chourasia, and Murray Patterson. 2024. "When Protein Structure Embedding Meets Large Language Models" Genes 15, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010025
APA StyleAli, S., Chourasia, P., & Patterson, M. (2024). When Protein Structure Embedding Meets Large Language Models. Genes, 15(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010025





