Molecular Diagnosis and Identification of Novel Pathogenic Variants in a Large Cohort of Italian Patients Affected by Polycystic Kidney Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Recruitment, Clinic and Biochemical Evaluation
2.2. NGS Custom Panel Design and Panel Content
2.3. DNA Isolation and NGS Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.4. NGS Data Analysis
2.5. Sanger Sequencing
2.6. Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA)
2.7. Variant’s Pathogenicity Predictions
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fujimaru, T.; Mori, T.; Sekine, A.; Mandai, S.; Chiga, M.; Kikuchi, H.; Ando, F.; Mori, Y.; Nomura, N.; Iimori, S.; et al. Kidney enlargement and multiple liver cyst formation implicate mutations in PKD1/2 in adult sporadic polycystic kidney disease. Clin. Genet. 2018, 94, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliuta, I.-A.; Kalatharan, V.; Wang, K.; Gall, E.C.-L.; Conklin, J.; Pourafkari, M.; Ting, R.; Chen, C.; Borgo, A.C.; He, N.; et al. Polycystic Kidney Disease without an Apparent Family History. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2768–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwabe, T.; Shukoor, S.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Killian, J.M.; King, B.F.; Edwards, M.; Senum, S.R.; Madsen, C.D.; Chebib, F.T.; Hogan, M.C.; et al. Epidemiology of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease in Olmsted County. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornec-Le Gall, E.; Alam, A.; Perrone, R.D. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet 2019, 393, 919–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, C.; Guay-Woodford, L.M.; Harris, P.C.; Horie, S.; Peters, D.J.M.; Torres, V.E. Polycystic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, I.; Buonanno, P.; Riccio, E.; Rizzo, M.; Pisani, A. Tolvaptan vs. somatostatin in the treatment of ADPKD: A review of the literature. Clin. Nephrol. 2022, 97, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orisio, S.; Noris, M.; Rigoldi, M.; Bresin, E.; Perico, N.; Trillini, M.; Donadelli, R.; Perna, A.; Benigni, A.; Remuzzi, G. Mutation Analysis of PKD1 and PKD2 Genes in a Large Italian Cohort Reveals Novel Pathogenic Variants Including A Novel Complex Rearrangement. Nephron, 2023; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönauer, R.; Baatz, S.; Nemitz-Kliemchen, M.; Frank, V.; Petzold, F.; Sewerin, S.; Popp, B.; Münch, J.; Neuber, S.; Bergmann, C.; et al. Matching clinical and genetic diagnoses in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease reveals novel phenocopies and potential candidate genes. Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 1374–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanova, N.; Markoff, A.; Gerke, V.; McCluskey, M.; Horst, J.; Dworniczak, B. Homologues to the first gene for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease are pseudogenes. Genomics 2001, 74, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornec-Le Gall, E.; Audrézet, M.P.; Renaudineau, E.; Hourmant, M.; Charasse, C.; Michez, E.; Frouget, T.; Vigneau, C.; Dantal, J.; Siohan, P.; et al. PKD2-Related Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Prevalence, Clinical Presentation, Mutation Spectrum, and Prognosis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 70, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Roy, S.; Li, L.; Ma, M. Polycystic kidney disease: Novel insights into polycystin function. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, C. Genetics of Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease and Its Differential Diagnoses. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 5, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losekoot, M.; Haarloo, C.; Ruivenkamp, C.; White, S.J.; Breuning, M.H.; Peters, D.J. Analysis of missense variants in the PKHD1-gene in patients with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). Hum. Genet. 2005, 118, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, A.; Hidaka, S.; Moriyama, T.; Shikida, Y.; Shimazu, K.; Ishikawa, E.; Uchiyama, K.; Kataoka, H.; Kawano, H.; Kurashige, M.; et al. Cystic Kidney Diseases That Require a Differential Diagnosis from Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD). J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoek, R.; van Jaarsveld, R.H.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Peters, E.D.J.; Elferink, M.G.; Ernst, R.F.; Rookmaaker, M.B.; Lilien, M.R.; Spierings, E.; Goldschmeding, R.; et al. Genetics-first approach improves diagnostics of ESKD patients younger than 50 years. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, V.; Bin, S.; Graziano, C.; Capelli, I.; Minardi, R.; Aiello, V.; Ambrosini, E.; Cristalli, C.P.; Mattiaccio, A.; Pariali, M.; et al. Gene Panel Analysis in a Large Cohort of Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Allows the Identification of 80 Potentially Causative Novel Variants and the Characterization of a Complex Genetic Architecture in a Subset of Families. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleyer, A.J.; Westemeyer, M.; Xie, J.; Bloom, M.S.; Brossart, K.; Eckel, J.J.; Jones, F.; Molnar, M.Z.; Kotzker, W.; Anand, P.; et al. Genetic Etiologies for Chronic Kidney Disease Revealed through Next-Generation Renal Gene Panel. Am. J. Nephrol. 2022, 53, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, T.; Teraoka, A.; Akagawa, H.; Makabe, S.; Akihisa, T.; Sato, M.; Kataoka, H.; Mitobe, M.; Furukawa, T.; Tsuchiya, K.; et al. Mutation analyses by next-generation sequencing and multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification in Japanese autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease patients. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2019, 23, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renkema, K.Y.; Stokman, M.F.; Giles, R.H.; Knoers, N.V. Next-generation sequencing for research and diagnostics in kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, H.-H.; Chang, C.L.; Song, S.H.; Kim, N. Novel PKD1 Mutations in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Lab. Med. 2021, 52, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Anesth. Analg. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thong, M.K.; Fietz, M.; Nicholls, C.; Lee, M.H.; Asma, O. Congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ia in a Malaysian family: Clinical outcome and description of a novel PMM2 mutation. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2009, 32, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stekrova, J.; Reiterova, J.; Svobodova, S.; Kebrdlova, V.; Lnenicka, P.; Merta, M.; Viklicky, O.; Kohoutova, M. New mutations in the PKD1 gene in Czech population with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. BMC Med. Genet. 2009, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Liu, X.; Jia, X.; Miao, H.; Ji, W.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Su, H.; et al. Disease causing property analyzation of variants in 12 Chinese families with polycystic kidney disease. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.C.; Blumenfeld, J.D.; Anghel, R.; Donahue, S.; Belenkaya, R.; Balina, M.; Parker, T.; Levine, D.; Leonard, D.G.; Rennert, H. Novel method for genomic analysis of PKD1 and PKD2 mutations in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, H.P.; Jilg, C.; Bacher, J.; Nabulsi, Z.; Malinoc, A.; Hummel, B.; Hoffmann, M.M.; Ortiz-Bruechle, N.; Glasker, S.; Pisarski, P.; et al. Epidemiology of autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease: An in-depth clinical study for south-western Germany. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 1472–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacchia, M.; Blanco, F.D.V.; Trepiccione, F.; Blasio, G.; Torella, A.; Melluso, A.; Capolongo, G.; Pollastro, R.M.; Piluso, G.; Di Iorio, V.; et al. Nephroplex: A kidney-focused NGS panel highlights the challenges of PKD1 sequencing and identifies a founder BBS4 mutation. J. Nephrol. 2021, 34, 1855–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ma, Y.; Gu, X.; Bian, R.; Lu, Y.; Xing, X.; Mei, C. Novel Mutations in the PKD1 and PKD2 Genes of Chinese Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2018, 43, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.Y.; Alipanahi, B.; Lee, L.J.; Bretschneider, H.; Merico, D.; Yuen, R.K.; Hua, Y.; Gueroussov, S.; Najafabadi, H.S.; Hughes, T.R.; et al. RNA splicing. The human splicing code reveals new insights into the genetic determinants of disease. Science 2015, 347, 1254806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Gallego, A.; Pybus, M.; Bullich, G.; Furlano, M.; Ejarque-Vila, L.; Lorente-Grandoso, L.; Ruiz, P.; Fraga, G.; González, M.L.; Piñero-Fernández, J.A.; et al. Clinical utility of genetic testing in early-onset kidney disease: Seven genes are the main players. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.; Hiemstra, T.F.; Spencer, D.; Waller, S.; Daboo, L.; Karet Frankl, F.E.; Sandford, R.N. Clinical utility of PKD2 mutation testing in a polycystic kidney disease cohort attending a specialist nephrology out-patient clinic. BMC Nephrol. 2012, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viribay, M.; Hayashi, T.; Tellería, D.; Mochizuki, T.; Reynolds, D.M.; Alonso, R.; Lens, X.M.; Moreno, F.; Harris, P.C.; Somlo, S.; et al. Novel stop and frameshifting mutations in the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease 2 (PKD2) gene. Hum. Genet. 1997, 101, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillano, D.; Bullich, G.; Ossowski, S.; Ballarín, J.; Torra, R.; Estivill, X.; Ars, E. Diagnosis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease using efficient PKD1 and PKD2 targeted next-generation sequencing. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2014, 2, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenglet, M.; Robriquet, F.; Schwarz, K.; Camps, C.; Couturier, A.; Hoogewijs, D.; Buffet, A.; Knight, S.J.L.; Gad, S.; Couvé, S.; et al. Identification of a new VHL exon and complex splicing alterations in familial erythrocytosis or von Hippel-Lindau disease. Blood 2018, 132, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuster, S.; Keunen, J.; Shannon, P.; Watkins, N.; Chong, K.; Chitayat, D. Prenatal detection of isolated bilateral hyperechogenic kidneys: Etiologies and outcomes. Prenat. Diagn. 2019, 39, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossetti, S.; Strmecki, L.; Gamble, V.; Burton, S.; Sneddon, V.; Peral, B.; Roy, S.; Bakkaloglu, A.; Komel, R.; Winearls, C.G.; et al. Mutation analysis of the entire PKD1 gene: Genetic and diagnostic implications. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 68, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lata, S.; Marasa, M.; Li, Y.; Fasel, D.A.; Groopman, E.; Jobanputra, V.; Rasouly, H.; Mitrotti, A.; Westland, R.; Verbitsky, M.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing in adults with chronic kidney disease: A pilot study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 168, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallawaarachchi, A.C.; Ben Lundie, B.; Hort, Y.; Schonrock, N.; Senum, S.R.; Gayevskiy, V.; Minoche, A.E.; Hollway, G.; Ohnesorg, T.; Hinchcliffe, M.; et al. Genomic diagnostics in polycystic kidney disease: An assessment of real-world use of whole-genome sequencing. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 29, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, P.; Calzavara, S.; Magistroni, R.; Dunnen, J.T.D.; Rigo, F.; Stenirri, S.; Testa, F.; Messa, P.; Cerutti, R.; Scolari, F.; et al. Deciphering Variability of PKD1 and PKD2 in an Italian Cohort of 643 Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.C.; Torres, V.E. Genetic mechanisms and signaling pathways in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2315–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johar, L.; Lee, G.; Martin-Rios, A.; Hall, K.; Cheng, C.; Lombardo, D.; Pahl, M.; Kimonis, V. Polycystic kidney disease complicates renal pathology in a family with Fabry disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2022, 33, 100934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, A.; Daniele, A.; Di Domenico, C.; Nigro, E.; Salvatore, F.; Riccio, E. Late diagnosis of Fabry disease caused by a de novo mutation in a patient with end stage renal disease. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Hu, F.; Ge, X.; Lei, J.; Yu, S.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Q.; Mei, C.; Shi, Y. Structure of the human PKD1-PKD2 complex. Science 2018, 361, eaat9819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cnossen, W.R.; Morsche, R.H.M.T.; Hoischen, A.; Gilissen, C.; Chrispijn, M.; Venselaar, H.; Mehdi, S.; Bergmann, C.; Veltman, J.A.; Drenth, J.P.H. Whole-exome sequencing reveals LRP5 mutations and canonical Wnt signaling associated with hepatic cystogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5343–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cnossen, W.R.; Drenth, J.P.H. Polycystic liver disease: An overview of pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and management. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cnossen, W.R.; te Morsche, R.H.; Hoischen, A.; Gilissen, C.; Venselaar, H.; Mehdi, S.; Bergmann, C.; Losekoot, M.; Breuning, M.H.; Peters, D.J.; et al. LRP5 variants may contribute to ADPKD. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 24, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Laarschot, L.F.M.; Morsche, R.H.M.T.; Hoischen, A.; Venselaar, H.; Roelofs, H.M.; Cnossen, W.R.; Banales, J.M.; Roepman, R.; Drenth, J.P.H. Novel GANAB variants associated with polycystic liver disease. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.-H.; Conklin, J.; Chan, W.; Roslin, N.M.; Liu, J.; He, N.; Wang, K.; Sundsbak, J.L.; Heyer, C.M.; Haider, M.; et al. Refining Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, E.C.-L.; Audrézet, M.-P.; Chen, J.-M.; Hourmant, M.; Morin, M.-P.; Perrichot, R.; Charasse, C.; Whebe, B.; Renaudineau, E.; Jousset, P.; et al. Type of PKD1 mutation influences renal outcome in ADPKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Hussain, N.; Naim, M.; Zayed, M.; Al-Mulla, F.; Kehinde, E.O.; Seaburg, L.M.; Sundsbak, J.L.; Harris, P.C. A novel PKD1 variant demonstrates a disease-modifying role in trans with a truncating PKD1 mutation in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanktree, M.B.; Haghighi, A.; di Bari, I.; Song, X.; Pei, Y. Insights into autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease from genetic studies. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masyuk, A.I.; LaRusso, N.F. Therapeutic Targets in Polycystic Liver Disease. Curr. Drug Targets 2017, 18, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanktree, M.B.; Haghighi, A.; Guiard, E.; Iliuta, I.-A.; Song, X.; Harris, P.C.; Paterson, A.D.; Pei, Y. Prevalence Estimates of Polycystic Kidney and Liver Disease by Population Sequencing. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 2593–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, I.; Buonanno, P.; Riccio, E.; Amicone, M.; Pisani, A. Therapeutic advances in ADPKD: The future awaits. J. Nephrol. 2022, 35, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, M.; Pezone, I.; Amicone, M.; Capuano, I.; Buonanno, P.; Riccio, E.; Pisani, A. Familial polycystic kidneys with no genetic confirmation: Are we sure it is ADPKD? Clin. Nephrol. 2022, 99, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasinghe, K.; Dm, Z.S.; Kerr, P.G.; Gaff, C.; Martyn, M.; Whitlam, J.; Creighton, B.; Bn, E.D.; Hunter, M.; Jarmolowicz, A.; et al. Clinical impact of genomic testing in patients with suspected monogenic kidney disease. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.X.; Torres, V.E. Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Therapies on the Horizon. Adv. Kidney Dis. Health 2023, 30, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, W.; Liang, C.; Li, C.; Wei, T.; Feng, Z.; Guo, Q.; Yang, K.; Liu, Z. Comprehensive strategy improves the genetic diagnosis of different polycystic kidney diseases. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 6318–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.P.; Daloul, R.; Lentine, K.L.; Gohh, R.; Anand, P.M.; Rasouly, H.M.; Sharfuddin, A.A.; Schlondorff, J.; Rodig, N.; Freese, M.E.; et al. Genetic evaluation of living kidney donor candidates: A review and recommendations for best practices. Am. J. Transplant. 2023, 23, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


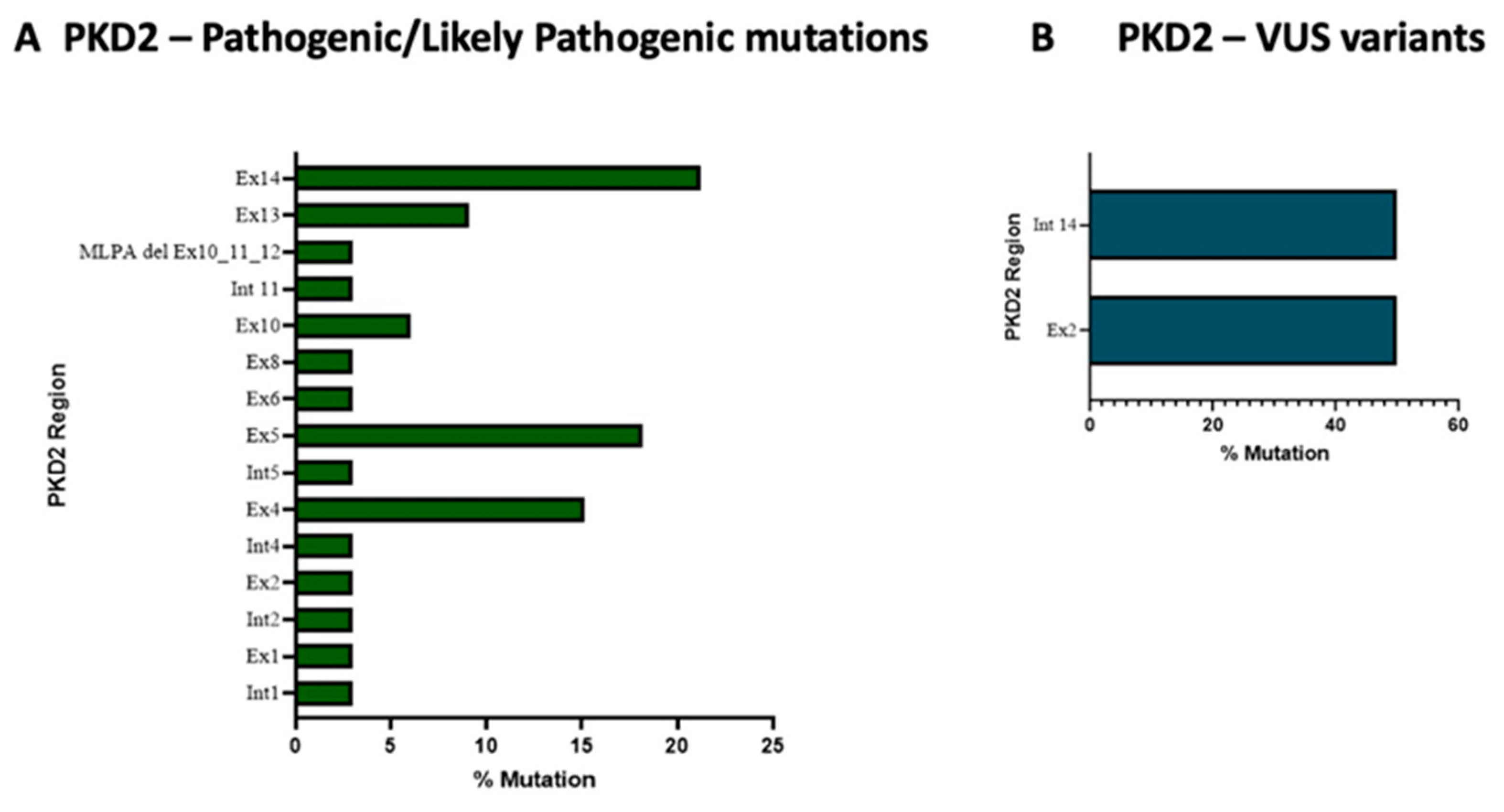
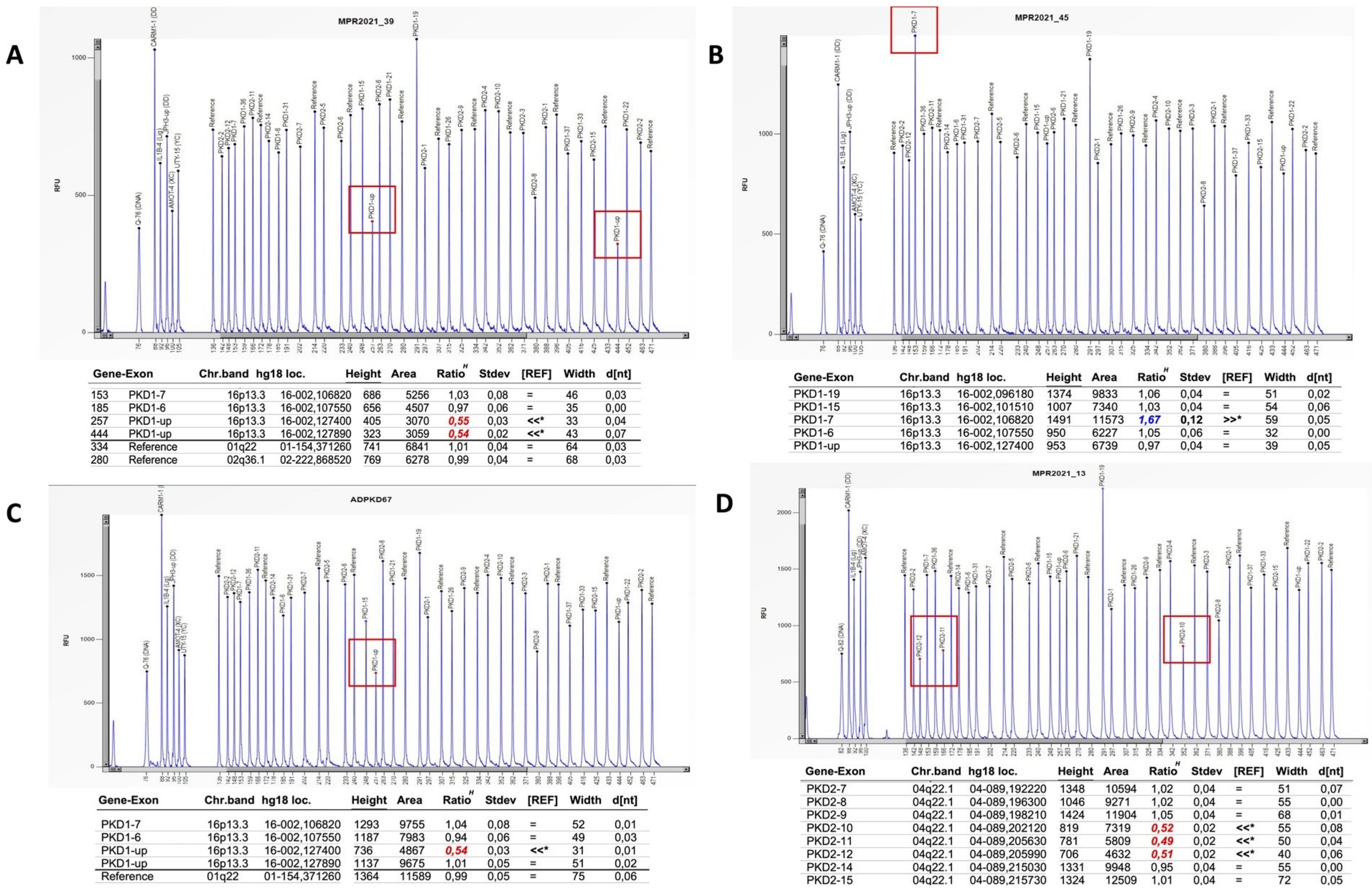
| ADPKD Patients (n) | Age at Clinical Diagnosis (Mean ± SD) | Sex (%) | Family History (%) | eGFR (Mean ± SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PKD1 | 124 | 26.57 ± 12.97 | M (43.9) | 73.17 | 73.54 ± 33.54 | |
| PKD2 | 31 | 39.6 ± 11.68 | 64.5 | 54.1 ± 33.29 | ||
| GANAB | 4 | 20.12 ± 6.2 | M (25) | 100 | 79.25 ± 13.48 | |
| HNF1B | 1 | 0 | F | No | 83 | |
| VHL | 2 | 26 ± 12.72 | M (50) | 100 | 100 | |
| UMOD | 2 | 38 ± 9.89 | F (100) | 100 | 39.5 ± 27.57 | |
| TSC2 | 1 | 11 | F | No | 90 | |
| LRP5 | 2 | 17.5 ± 17.6 | F | 100 | 46.3 ± 13.91 | |
| Genes bearing LP/P variants | ARPKD Patients (n) | Age at clinical diagnosis (mean ± SD) | Sex (%) | Family history (%) | eGFR (mean ± SD) | |
| PKHD1 | 2 | 25 ± 4.94 | F (100) | 0 | 75 ± 11.31 | |
| MAPKBP1 | 1 | 20 | M | No | 9 | |
| Trans-heterozygous patients | Age at clinical diagnosis | Sex | Family history | eGFR (mean± SD) | ||
| CRB2 | 1 | 58 | F | Yes | 100 | |
| PMM2 | ||||||
| CC2D2A | 1 | 45 | F | Yes | 48 | |
| PMM2 | ||||||
| Patients with singleton status (n) | Age at clinical diagnosis (mean ± SD) | Sex (%) | Family history (%) | eGFR (mean ± SD) | ||
| PMM2 | 2 | 60 ± 21.21 | M (50) | 100 | 35.5 ± 17.6 | |
| CEP164 | 1 | 26 | M | No | 71 | |
| ATP6V1B1 | 1 | 58 | M | No | 60 | |
| Genes bearing VUS variants | ADPKD Patients (n) | Age at clinical diagnosis (mean ± SD) | Sex (%) | Family history (%) | eGFR (mean ± SD) | |
| PKD1 | 18 | 33.09 ± 20,39 | M (61.5) | Yes (77.7) | 74.21 ± 35.47 | |
| PKD2 | 2 | 45 ±4.24 | M (50) | Yes (100) | 57.5 ± 20.50 | |
| LRP5 | 2 | 61 ± 8.48 | F (100) | Yes (50) | 64.5 ± 37.47 | |
| HNF1B | 1 | 66 | M | Yes | 37 | |
| ACTN4 | 1 | 49 | M | Yes | 81 | |
| ARPKD Patients (n) | Age at clinical diagnosis (mean ± SD) | Sex (%) | Family history (%) | eGFR (mean ± SD) | ||
| PKHD1 | 2 | 35.5 ± 45.96 | M (100) | Yes (100) | 74 ± 8.48 | |
| Trans-heterozygous patients | Age at clinical diagnosis (mean ± SD) | Sex | Family history | eGFR (mean ± SD) | ||
| FOXI1 TTC21B | 1 | birth | F | Yes | 78 | |
| COL4A4 INVS | 1 | 46 | F | Yes | 43 | |
| PKHD1 CD2AP | 1 | 55 | F | Yes | 72 | |
| NPHS2 ANKS6 | 1 | 75 | F | No | 43 | |
| FOXI1 TTC21b | 1 | 63 | M | No | 80 | |
| BBS4 NPHS1 | 1 | 68 | M | No | 39 | |
| Patients with singleton status (n) | Age at clinical diagnosis (mean ± SD) | Sex (%) | Family history (%) | eGFR (mean ± SD) | ||
| PKHD1 | 3 | 57 ± 13.85 | M (66.6) | Yes (66.6) | 67.33 ± 2.08 | |
| NPHS1 | 2 | 55 ± 15.91 | M (100) | Yes (100) | 73 ± 20.2 | |
| NPHS2 | 1 | 69 | M | Yes | 78 | |
| NPHS3 | 1 | 74 | M | No | 67 | |
| CEP290 | 1 | 4 | M | No | 20 | |
| MAPKBP1 | 1 | 47 | M | Yes | 22 | |
| CD2AP | 1 | 50 | M | Yes | 80 | |
| MYO1E | 1 | 27 | F | Yes | 33 | |
| ZNF423 | 1 | 48 | F | Yes | 93 | |
| CC2D2A | 1 | 61 | M | Yes | 60 | |
| NEK8 | 2 | 61.5 ± 10.8 | M (100) | Yes (100) | 68.89 ± 20.12 | |
| No mutation | 32 | 52.6 ± 19.74 | M (56) | Yes (56.7) | 58.68 ± 37.02 | |
| Total patients | 255 |
| Gene | c.DNA Change | Region | Protein Variant | ACMG Classification and Sub-Criteria | gnomAD Allele Frequency | Coding Impact | Age at Diagnosis | Liver Cysts | e-GFR | CKD-Stage | Literature and/or ClinVar Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PKHD1 | c.1690C>T | Exon 18 | p.Arg564Ter | VUS | 0.0000239 | Missense | 32 | Yes | 67 | G2 | VCV000594333.13—ClinVar—NCBI (nih.gov) |
| c.9107T>G | Exon 58 | p.Val3036Gly | Missense | ||||||||
| c.431C>T | Exon 6 | p.Pro144Leu | Pathogenic (PP3-PM2-PP5-BP1) | 0.0000239 | Missense | 22 | No | 83 | G2 | VCV000594333.13—ClinVar—NCBI (nih.gov) | |
| c.9107T>G | Exon 58 | p.Val3036Gly | Missense | ||||||||
| c.10036T>C | Exon 60 | p.Cys3346Arg | VUS | Not found | Missense | 68 | Yes | 68 | G2 | - | |
| c.5585C>T | Exon 34 | p.Ser1862Leu | Pathogenic (PP3-PM2-PP5-BP1) | Missense | |||||||
| c.5665G>A | Exon 35 | p.Glu1889Lys | VUS | Not found | Missense | 1 | No | 82 | G2 | - | |
| c.7911+19T>C | Int49 | - | VUS | Intronic | |||||||
| MAPKBP1 | c.2271delA | Exon 19 | p.Gly758AspfsTer74 | VUS | Not found | Nonsense | 46 | No | 9 | G5 | - |
| VUS | (age at ESKD: 46) |
| Gene | c.DNA Change | Region | Protein Variant | ACMG Classification and Sub-Criteria | gnomAD Allele Frequency | Coding Impact | Age at Diagnosis | Liver Cysts | e-GFR | CKD-Stage | Literature and/or ClinVar Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRB2 | c.357T>G | Exon 2 | p.His119Gln | VUS | Not found | Missense | 58 | No | 100 | Normal | VCV000198714.31—ClinVar—NCBI (nih.gov) |
| PMM2 | c.713G>A | Exon 8 | p.Arg238His | Likely Pathogenic (PM1-PM5-PM2-PP5-BP4) | Missense | ||||||
| FOXI1 | c.908G>A | Exon 2 | p.Gly303Glu | VUS | Not found | Missense | At birth | No | 78 | G2 | - |
| TTC21b | c.667C>G | Exon 6 | p.Leu223Val | VUS | Missense | ||||||
| COL4A4 | c.1460G>A | Exon 22 | p.Gly487Glu | VUS | Not found | Missense | 46 | Yes | 43 | G3b | - |
| INVS | c.2296C>A | Exon 15 | p.Leu766Met | VUS | Missense | ||||||
| NPHS2 | c.686G>A | Exon 5 | p.Arg229Gln | VUS | Not found | Missense | 75 | No | 43 | G3b | - |
| ANKS6 | c.1400G>A | Exon 7 | p.Arg467Gln | VUS | Missense | ||||||
| FOXI1 | c.908G>A | Exon 2 | p.Gly303Glu | VUS | Not found | Missense | 63 | No | 70 | Normal | - |
| TTC21b | c.667C>G | Exon 6 | p.Leu223Val | VUS | Missense | ||||||
| BBS4 | c.1027C>A | Exon 12 | p.Leu343Ile | VUS | Not found | Missense | 62 | No | 75 | Normal | - |
| NPHS1 | c.2819G>T | Exon 21 | p.Arg940Leu | VUS | Missense | ||||||
| CC2D2A | c.823a>g | Exon 10 | p.Ile275Val | VUS | Not found | Missense | 46 | No | 48 | G3b | [22] |
| PMM2 | c.422g>a | Exon 5 | p.Arg141His | Pathogenic (PS3-PP5-PM1-PM5-PM2-BP4) | Missense | ||||||
| PKHD1 | c.11338C>T | Exon 63 | p.Pro3780Ser | VUS | Not found | Missense | 52 | Yes | 40 | G3b | - |
| CD2AP | c.491A>T | Exon 5 | p.Glu164Val | VUS | Missense |
| cDNA Change | Region | Protein Variant | ACMG Classification and Sub-Criteria | gnomAD Allele Frequency | Literature and/or ClinVar Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PKD1 | c.12008dup | Exon 44 | p.Gln4005AlafsTer152 | Likely Pathogenic PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - |
| c.12058C>T | Exon 44 | p.Arg4021Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | [23] | |
| c.11705_11708del | Exon 42 | p.Thr3902ArgfsTer41 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.8698C>T | Exon 23 | p.Gln2900Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | VCV000562271.2— ClinVar—NCBI (nih.gov) | |
| c.7984C>T | Exon 21 | p.Gln2662Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | 0.000004405 | VCV000636940.5— ClinVar—NCBI (nih.gov) | |
| c.12908A>T | Exon 46 | p.4303LeuextTer35 | Likely Pathogenic (PM4-PM2-BP4) | Not found | - | |
| c.3745delG | Exon 15 | p.Asp1249ThrfsTer24 | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | VCV000972837.1— ClinVar—NCBI (nih.gov) | |
| c.11438_11439del | Exon 41 | p.Tyr3813Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.11881C>T | Exon 43 | p.Gln3961Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2 | Not found | VCV000997175.4— ClinVar—NCBI (nih.gov) | |
| c.5869_5870dup | Exon 15 | p.Ser1957ArgfsTer16 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.3398_3399delTG | Exon 15 | p.Val1133GlufsTer2 | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | [16] | |
| c.8238del | Exon 23 | p.Met2747TrpfsTer9 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.4951C>T | Exon 15 | p.Gln1651Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2 | Not found | PMID: 23431742 | |
| c.1198C>T | Exon 5 | p.Arg400Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | 0.00001398 | [24] | |
| c.11568C>G | Exon 42 | p.Tyr3856Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.3706C>T | Exon 15 | p.Gln1236Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | [16] | |
| c.11571C>G | Exon 42 | p.Tyr3857Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PP3-PM1-PM2-BP1) | Not found | - | |
| c.10591C>T | Exon 35 | p.Gln3531Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.10459C>T | Exon 34 | p.Gln3487Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | 0 | [23] | |
| c.4888C>T | Exon 15 | p.Gln1630Ter | Pathogenic ((PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | [25] | |
| c.5154_5163dup | Exon 15 | p.Met1722GlyfsTer52 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.7597_7598del | Exon 19 | p.Ser2533GlnfsTer61 | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | [26] | |
| c.11967_11974dup | Exon 43 | p.Ser3992TrpfsTer49 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.8371_8372dup | Exon 23 | p.Ser2792GlyfsTer84 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.2215dup | Exon 11 | p.Gln739ProfsTer59 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.5014_5015delAG | Exon 15 | p.Arg1672GlyfsTer98 | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | [27] | |
| c.10722G>A | Exon 7 | p.Trp3574Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2…) | Not found | VCV000997310.4— ClinVar—NCBI (nih.gov) | |
| c.11646_11659del | Exon 42 | p.Ser3883CysfsTer72 | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | VCV000811475.8— ClinVar—NCBI (nih.gov) | |
| c.11560_11561del | Exon 42 | p.Thr3854AlafsTer105 | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | VCV000522397.6— ClinVar—NCBI (nih.gov) | |
| c.7416_7417ins | Exon 18 | p.Gly2473ArgfsTer28 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.5607dupC | Exon 15 | p.Asn1870GlnfsTer120 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.2085delC | Exon 10 | p.Ala696ArgfsTer89 | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | VCV000811793.10— ClinVar—NCBI (nih.gov) | |
| c.1105_1106delAG | Exon 5 | p.Ser369Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.10420C>T | Exon 34 | p.Gln3474Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.3520_3527del | Exon 15 | p.Gln1174Cysfs34Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.3802C>T | Exon 15 | p.Gln1268Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.6199C>T | Exon 15 | p.Gln2067Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.9425_9426ins | Exon 27 | p.Tyr3143ValfsTer36 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.1987C>T | Exon 10 | p.Gln663Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | [28] | |
| c.3349C>T | Exon 15 | p.Gln1117Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | [29] | |
| c.11267-1G>T | Int39 | - | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.9771_9774delCTTT | Exon 29 | p.Phe3257LeufsTer58 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.2711_2712delAG | Exon 11 | p.Glu904GlyfsTer196 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.3067C>T | Exon 13 | p.Gln1023Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | [30] | |
| c.427C>T | Exon 4 | p.Gln143Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.11357_11361dup | Exon 40 | p.His3788ValfsTer39 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.10549G>T | Exon 35 | p.Glu3517Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.6560G>A | Exon 15 | p.Trp2187Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | 0 | VCV000997397.1— ClinVar—NCBI (nih.gov) | |
| c.11763G>A | Exon 43 | p.Trp3922Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | VCV000997191.2— ClinVar—NCBI (nih.gov) | |
| c.3202C>T | Exon 14 | p.Gln1068Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | VCV000972875.4— ClinVar—NCBI (nih.gov) | |
| c.271_272delTC | Exon 2 | p.Ser91GlyfsTer22 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.2028dupC | Exon 10 | p.Gly677ArgfsTer37 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.12010C>T | Exon 44 | p.Gln4004Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | 0.000004091 | - | |
| c.5905G>T | Exon 15 | p.Glu1969Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.6504C>G | Exon 15 | p.Tyr2168Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.10894_10895del | Exon 37 | p.Ser3632ProfsTer88 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.5884C>T | Exon 15 | p.Gln1962Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | VCV000916425.13— ClinVar—NCBI (nih.gov) | |
| c.3514C>T | Exon 14 | p.Gln1172Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.1837C>T | Exon 8 | p.Gln613Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | [31] | |
| c.2117delA | Exon 10 | p.Lys706ArgfsTer10 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.261G>A | Exon 1 | p.Trp87Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | VCV000805202.1— ClinVar—NCBI (nih.gov) | |
| c.1249C>T | Exon 5 | p.Arg417Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | [27] | |
| c.2419C>T | Exon 13 | p.Arg807Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | [32] | |
| c.958C>T | Exon 4 | p.Arg320Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | [10] | |
| c.1395T>A | Exon 6 | p.Tyr465Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | 0.000003982 | - | |
| c.2358del | Exon 10 | p.Glu787ArgfsTer14 | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | - | |
| c.916C>T | Exon 4 | p.Arg306Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | 0.000003981 | [24] | |
| c.637C>T | Exon 2 | p.Arg213Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | 0.00003188 | [33] | |
| c.2614C>T | Exon 14 | p.Arg872Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | 0.000003983 | - | |
| VHL | c.217C>T | Exon 1 | p.Gln73Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Not found | [34] |
| PKHD1 | c.1690C>T | Exon 18 | p.Arg564Ter | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | 0.00000398 | [35] |
| MAPKBP1 | c.2271delA | Exon 19 | p.Gly758AspfsTer74 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Not found | - |
| Gene | cDNA Change | Region | Protein Variant | ACMG Classification and Criteria | Variant Type | Molecular Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PKD1 | c.12008dup | Exon 44 | p.Gln4005AlafsTer152 | Likely Pathogenic PVS1-PM2) | Duplication | Frameshift |
| c.11705_11708del | Exon 42 | p.Thr3902ArgfsTer41 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Deletion | Frameshift | |
| c.5869_5870dup | Exon 15 | p.Ser1957ArgfsTer16 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Duplication | Frameshift | |
| c.8238del | Exon 23 | p.Met2747TrpfsTer9 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Deletion | Frameshift | |
| c.5154_5163dup | Exon 15 | p.Met1722GlyfsTer52 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Duplication | Frameshift | |
| c.7597_7598del | Exon 19 | p.Ser2533GlnfsTer61 | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Deletion | Frameshift | |
| c.11967_11974dup | Exon 43 | p.Ser3992TrpfsTer49 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Duplication | Frameshift | |
| c.8371_8372dup | Exon 23 | p.Ser2792GlyfsTer84 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Duplication | Frameshift | |
| c.2215dup | Exon 11 | p.Gln739ProfsTer59 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Duplication | Frameshift | |
| c.7416_7417ins | Exon 18 | p.Gly2473ArgfsTer28 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Insertion | Frameshift | |
| c.5607dup | Exon 15 | p.Asn1870GlnfsTer120 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Duplication | Frameshift | |
| c.3520_3527del | Exon 15 | p.Gln1174Cysfs34Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Deletion | Frameshift | |
| c.9425_9426ins | Exon 27 | p.Tyr3143ValfsTer36 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Insertion | Frameshift | |
| c.11357_11361dup | Exon 40 | p.His3788ValfsTer39 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Duplication | Frameshift | |
| c.7864_7899del | Exon 21 | p.Tyr2622_Lys2633del | Likely Pathogenic (PS2-PM4-PM2) | Deletion | In frame | |
| c.10973_10987del | Exon 37 | p.Glu3658_Lys3662del | Likely Pathogenic (PM1-PM4-PM2) | Deletion | In frame | |
| c.10807G>C | Exon 36 | p.Glu3603Gln | Likely Pathogenic (PM1-PM5-PM2-PP3) | SNV | Missense | |
| c.5609A>G | Exon 15 | p.Asn1870Ser | Pathogenic(PM5-PP3-PM1-PM2) | SNV | Missense | |
| c.11534G>T | Exon 41 | p.Arg3845Met | Likely Pathogenic (PP3-PM2-PM1-BP1) | SNV | Missense | |
| c.11438_11439del | Exon 41 | p.Tyr3813Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Deletion | Frameshift | |
| c.11568C>G | Exon 42 | p.Tyr3856Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | SNV | Nonsense | |
| c.10591C>T | Exon 35 | p.Gln3531Ter | Likely Pathogenic(PVS1-PM2) | SNV | Nonsense | |
| c.3802C>T | Exon 15 | p.Gln1268Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | SNV | Nonsense | |
| c.427C>T | Exon 4 | p.Gln143Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | SNV | Nonsense | |
| c.3295+2T>C | Int14 | - | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | SNV | Nonsense | |
| c.359+2T>G | Int3 | - | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | SNV | Splicing | |
| c.10217+2T>G | Int32 | - | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | SNV | Splicing | |
| c.11267-1G>T | Int39 | - | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | SNV | Splicing | |
| c.12908A>T | Exon 46 | p.4303LeuextTer35 | Likely Pathogenic (PM4-PM2-BP4) | SNV | Stoploss | |
| c.2028dupC | Exon 10 | p.Gly677ArgfsTer37 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | Duplication | Frameshift | |
| c.10549G>T | Exon 46 | p.Glu3517Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | SNV | Nonsense | |
| PKD2 | c.1244T>G | Exon 5 | p.Leu415Arg | Likely Pathogenic (PP3-PM1-PM2) | SNV | Missense |
| c.1142G>T | Exon 5 | p.Gly381Val | Likely Pathogenic (PM1-PP3-PM2-BP1) | SNV | Missense | |
| c.1395T>A | Exon 6 | p.Tyr465Ter | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | SNV | Nonsense | |
| c.2358delG | Exon 10 | p.Glu787ArgfsTer14 | Pathogenic (PVS1-PP5-PM2) | Deletion | Splicing | |
| MAPKBP1 | c.2271delA | Exon 19 | p.Gly758AspfsTer74 | Likely Pathogenic (PVS1-PM2) | SNV | Frameshift |
| UMOD | c.767G>A | Exon 3 | p.Cys256Tyr | Likely Pathogenic (PP3-PM1-PM2) | SNV | Missense |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nigro, E.; Amicone, M.; D’Arco, D.; Sellitti, G.; De Marco, O.; Guarino, M.; Riccio, E.; Pisani, A.; Daniele, A. Molecular Diagnosis and Identification of Novel Pathogenic Variants in a Large Cohort of Italian Patients Affected by Polycystic Kidney Diseases. Genes 2023, 14, 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061236
Nigro E, Amicone M, D’Arco D, Sellitti G, De Marco O, Guarino M, Riccio E, Pisani A, Daniele A. Molecular Diagnosis and Identification of Novel Pathogenic Variants in a Large Cohort of Italian Patients Affected by Polycystic Kidney Diseases. Genes. 2023; 14(6):1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061236
Chicago/Turabian StyleNigro, Ersilia, Maria Amicone, Daniela D’Arco, Gina Sellitti, Oriana De Marco, Maria Guarino, Eleonora Riccio, Antonio Pisani, and Aurora Daniele. 2023. "Molecular Diagnosis and Identification of Novel Pathogenic Variants in a Large Cohort of Italian Patients Affected by Polycystic Kidney Diseases" Genes 14, no. 6: 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061236
APA StyleNigro, E., Amicone, M., D’Arco, D., Sellitti, G., De Marco, O., Guarino, M., Riccio, E., Pisani, A., & Daniele, A. (2023). Molecular Diagnosis and Identification of Novel Pathogenic Variants in a Large Cohort of Italian Patients Affected by Polycystic Kidney Diseases. Genes, 14(6), 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061236







