First Description of the Nuclear and Mitochondrial Genomes and Associated Host Preference of Trichopoda pennipes, a Parasitoid of Nezara viridula
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
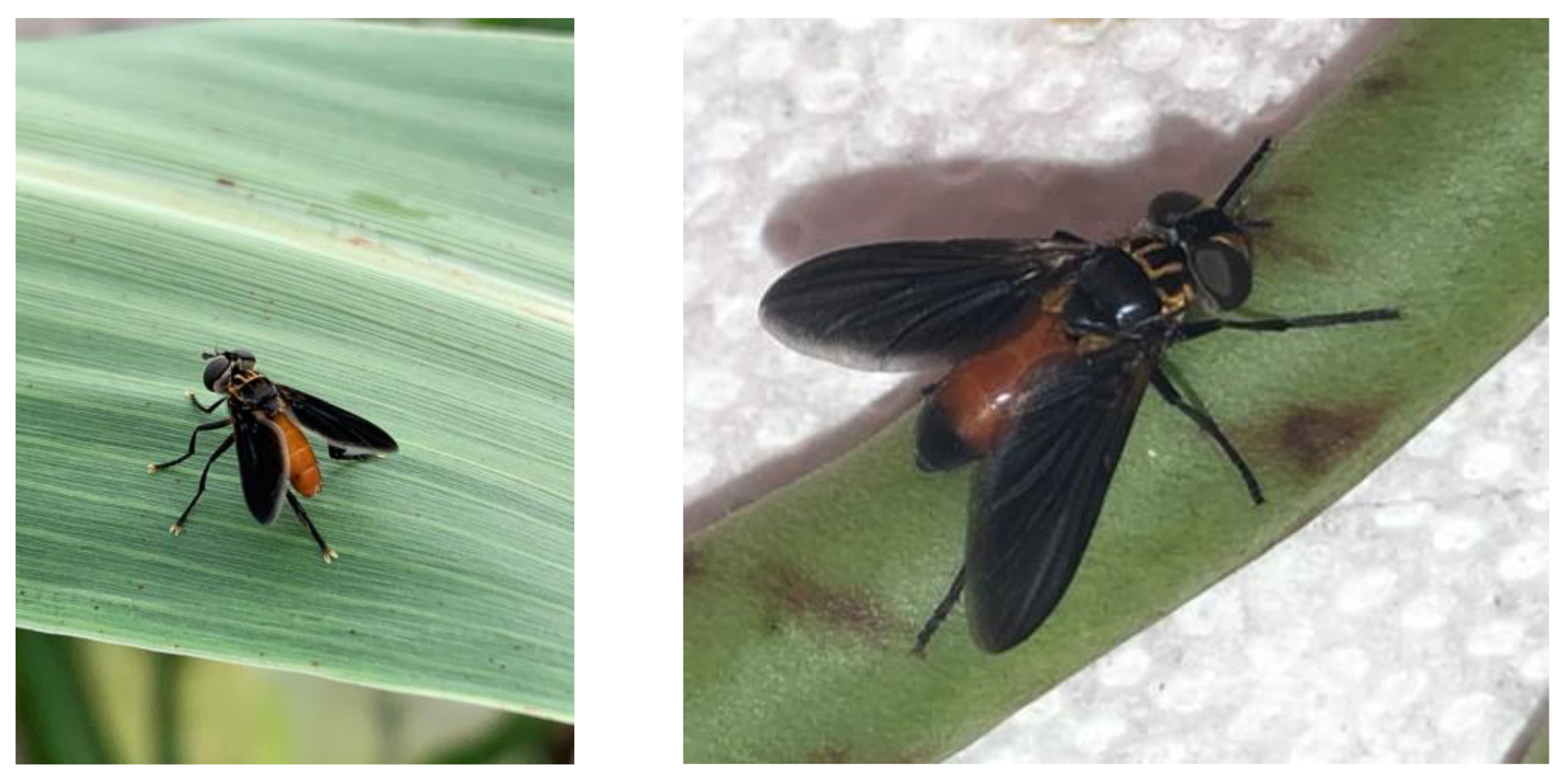
2.1. Sample Collection and Identification
2.2. PCR Amplification and Sequencing
2.3. Whole Genome Sequence Analysis
2.4. Mitogenome Annotation and Sequence Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nuclear Genome Sequence Analyses
3.2. Mitochondrial Genome Sequencing and Assembly
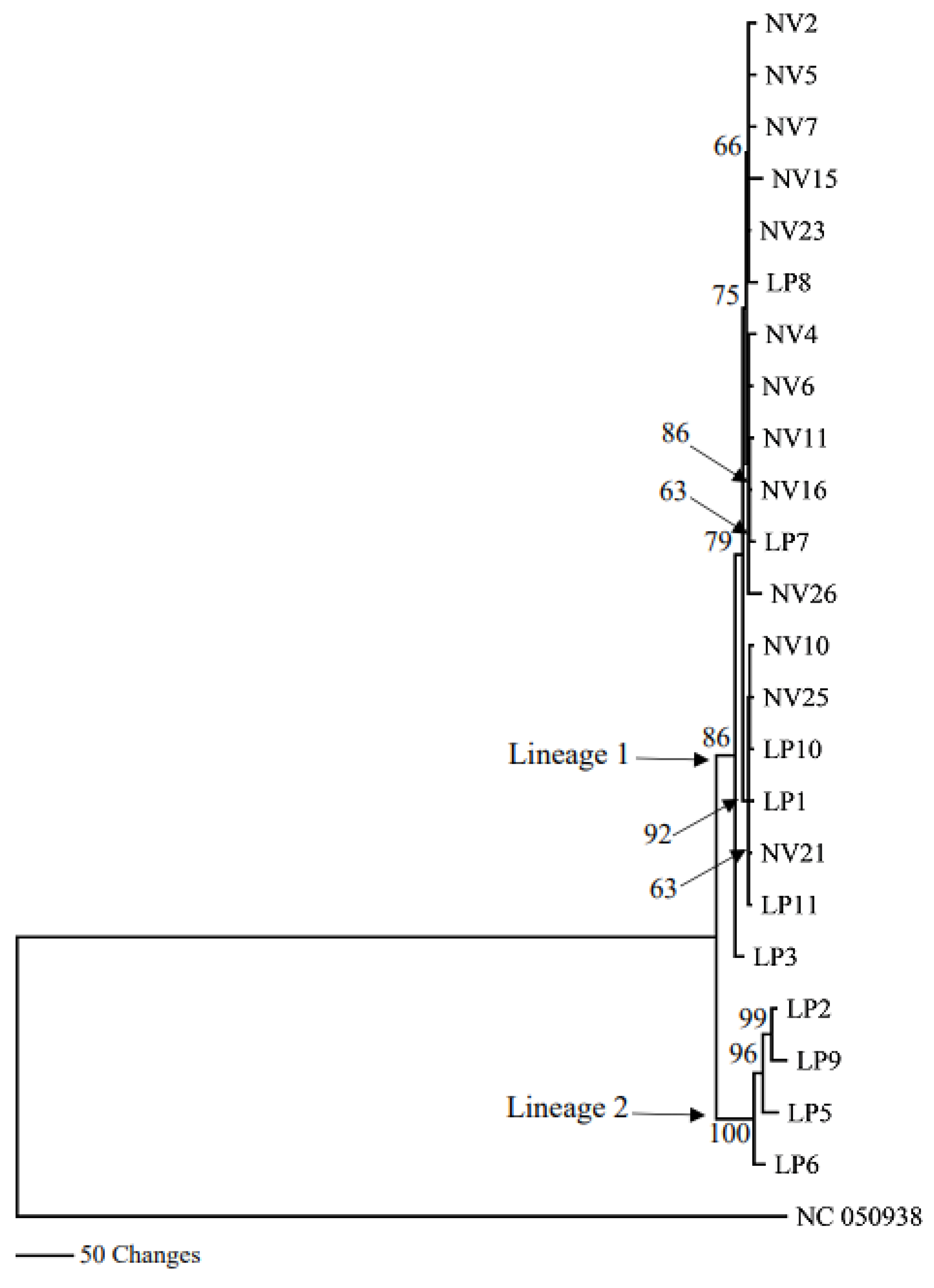
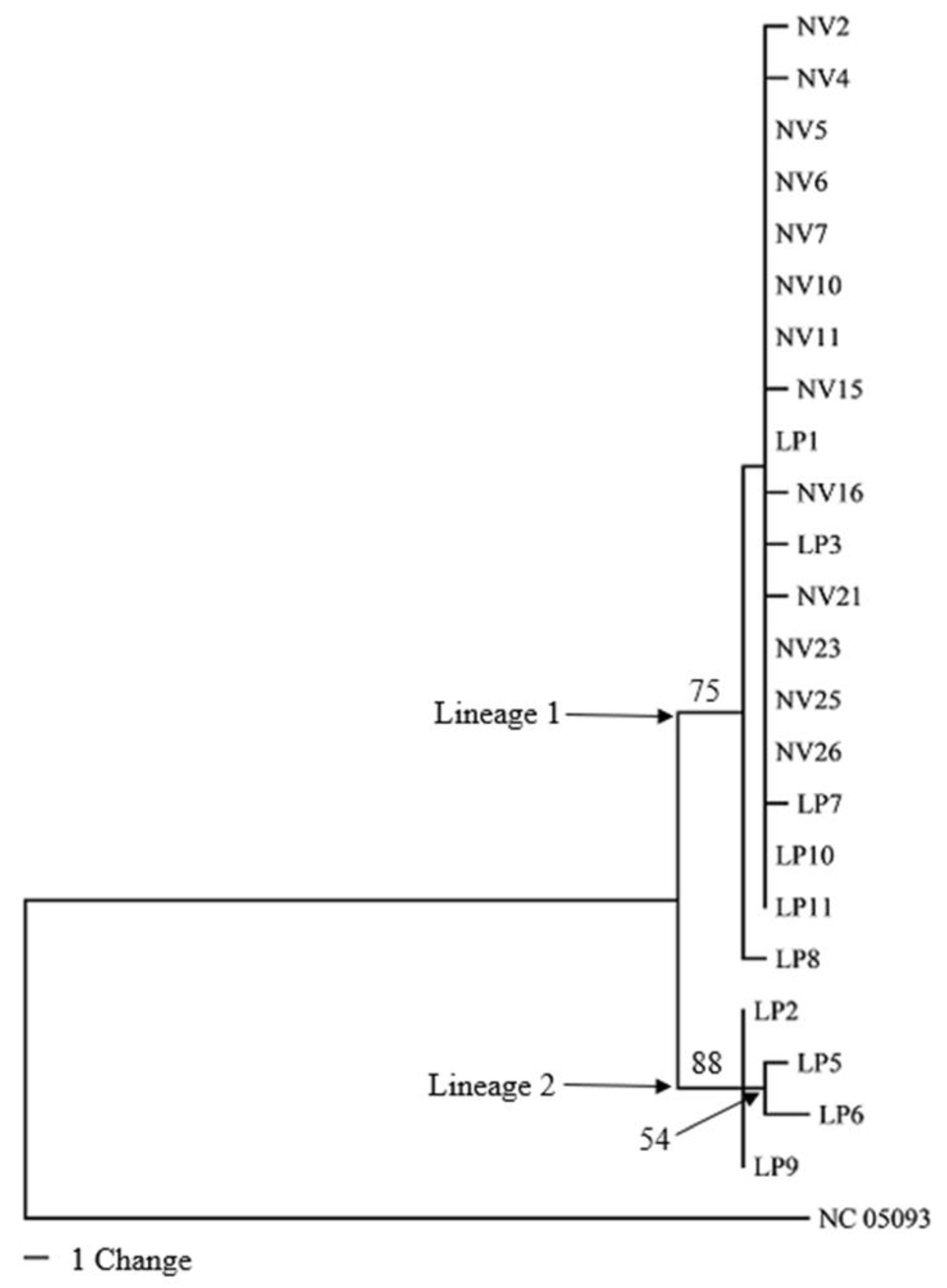
3.3. Phylogenetic Analyses of Mitogenomes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Esquivel, J.F.; Musolin, D.L.; Jones, W.A.; Rabitsch, W.; Greene, J.K.; Toews, M.D.; Schwertner, C.F.; Grazia, J.; McPherson, R.M. Nezara viridula (L.). In Invasive Stink Bugs and Related Species (Pentatomoidea); CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 351–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, W.A. World Review of the Parasitoids of the Southern Green Stink Bug, Nezara viridula (L.) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Ann. Èntomol. Soc. Am. 1988, 81, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, J.W. Ecology and Behavior of Nezara viridula. Annu. Rev. Èntomol. 2003, 34, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, J.H.; Davis, J.A.; Micinski, S.; Hardke, J.T.; Price, P.; Leonard, B.R. Species Composition and Seasonal Abundance of Stink Bugs (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in Louisiana Soybean. Environ. Èntomol. 2013, 42, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillman, P.G. Sorghum as a Trap Crop for Nezara viridula L. (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in Cotton in the Southern United States. Environ. Entomol. 2006, 35, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.A.; Pezzini, D.T.; Bueno, N.M.; Difonzo, C.D.; Finke, D.L.; Hunt, T.E.; Knodel, J.J.; Krupke, C.H.; McCornack, B.P.; Philips, C.R.; et al. Parasitism of Adult Pentatomidae by Tachinidae in Soybean in the North Central Region of the United States. J. Insect Sci. 2020, 3, 1–4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, K.B.; Bergh, C.J.; Bergmann, E.J.; Biddinger, D.J.; Dieckhoff, C.; Dively, G.; Fraser, H.; Gariepy, T.; Hamilton, G.; Haye, T.; et al. Biology, Ecology, and Management of Brown Marmorated Stink Bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2014, 5, A1–A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morehead, J.A.; Kuhar, T.P. Efficacy of Organically Approved Insecticides against Brown Marmorated Stink Bug, Halyomorpha halys and Other Stink Bugs. J. Pest Sci. 2017, 90, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokkanen, H. Polymorphism, Parasites, and the Native Area of Nezara viridula (Hemiptera, Pentatomidae). Ann. Zool. Fenn. 1986, 52, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ehler, L.E. An Evaluation of Some Natural Enemies of Nezara viridula in Northern California. BioControl 2002, 47, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, C.H.; Schoenig, S.E.; Hoffmann, M.P. Establishment of the Squash Bug Parasitoid, Trichopoda pennipes Fabr. (Diptera: Tachnidae), in Northern California. Pan-Pac. Entomol. 1996, 72, 220–226. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, N.K.; Leslie, T.W.; Biddinger, D.J. Parasitism of the Invasive Brown Marmorated Stink Bug, Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae), by the Native Parasitoid, Trichopoda pennipes (Diptera: Tachinidae). Biology 2019, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.J. The Introduction, Propagation, Liberation, and Establishment of Parasites to Control Nezara viridula variety smaragdula (Fabricius) in Hawaii (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Proc. Hawaii Entomol. Soc. 1964, 18, 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Caltagirone, L.E. Landmark Examples in Classical Biological Control. Anu. Rev. Entomol. 2003, 26, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, F.D. Potential for Biological Control of the Stink Bug Nezara viridula, A Pest of Macadamias. Acta Hortic. 1990, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, F.D. Biological Control of Insect Pests: Southeast Asian Prospects. In Monographs; Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research: Canberra, Australia, 1998; p. 114831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colazza, S.; Giangiuliani, G.; Bin, F. Fortuitous Introduction and Successful Establishment of Trichopoda pennipes F.: Adult Parasitoid of Nezara viridula (L.). Biol. Control 1996, 6, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrick, E.J.; Van Den Bosch, R. Insectary Propagation of the Squash Bug and Its Parasite Trichopoda pennipes Fabr. J. Econ. Entomol. 1957, 50, 627–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, N.J.; Kean, J.M. Behavioral Studies, Molecular Approaches, and Modeling: Methodological Contributions to Biological Control Success. Biol. Control 2010, 52, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabrosky, C.W. The Interrelations of Biological Control and Taxonomy. J. Econ. Entomol. 1955, 48, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschman, L.L.; Whitcomb, W.H. Parasites of Nezara viridula (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) and Other Hemiptera in Florida. Fla. Entomol. 1980, 63, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, P.H., Jr. A Host Parasite Catalog of North American Tachinidae (Diptera) [Control of Phytophagous Insecta]; Miscellaneous Publication—U.S. Dept. of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Buffington, M.L.; Talamas, E.J.; Hoelmer, K.A. Team Trissolcus: Integrating Taxonomy and Biological Control to Combat the Brown Marmorated Stink Bug. Am. Entomol. 2018, 64, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkay, G.L.; Reay-Jones, F.R.F.; Greene, J.K. Host Preference of the Parasitoid Trichopoda pennipes (Diptera: Tachinidae) with Euschistus servus and Nezara viridula (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J. Entomol. Sci. 2014, 49, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messenger, P.S.; van den Bosch, R. The Adaptability of Introduced Biological Control Agents. In Biological Control; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1971; pp. 68–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, C.; Buckley, T.R.; Frati, F.; Stewart, J.B.; Beckenbach, A.T. Incorporating Molecular Evolution into Phylogenetic Analysis, and a New Compilation of Conserved Polymerase Chain Reaction Primers for Animal Mitochondrial DNA. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2006, 37, 545–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babraham Bioinformatics—FastQC A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Cheng, H.; Concepcion, G.T.; Feng, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, H. Haplotype-Resolved de Novo Assembly Using Phased Assembly Graphs with Hifiasm. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laetsch, D.R.; Blaxter, M.L. BlobTools: Interrogation of Genome Assemblies. F1000Research 2017, 6, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality Assessment Tool for Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing Genome Assembly and Annotation Completeness with Single-Copy Orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allio, R.; Schomaker-Bastos, A.; Romiguier, J.; Prosdocimi, F.; Nabholz, B.; Delsuc, F. MitoFinder: Efficient Automated Large-Scale Extraction of Mitogenomic Data in Target Enrichment Phylogenomics. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 892–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Buso, N.; Gur, T.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Basutkar, P.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Potter, S.C.; Finn, R.D.; et al. The EMBL-EBI Search and Sequence Analysis Tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, w636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swofford, D.L.; PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (* and Other Methods). Version 4.0b10 Massachusetts: Sinauer Associates. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/0471650129.dob0522 (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecher, G.; Tamura, K.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) for MacOS. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1237–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillis, D. An Empirical Test of Bootstrapping as a Method for Assessing Confidence in Phylogenetic Analysis. Syst. Biol. 1993, 42, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, H.; Shi, A.; Štys, P.; Zhou, X.; Cai, W. The Complete Mitochondrial Genome and Novel Gene Arrangement of the Unique-Headed Bug Stenopirates sp. (Hemiptera: Enicocephalidae). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeWitt, J.R.; Armbrust, E.J. Polymorphic Size Variation of Adult Nezara viridula (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1973, 66, 555–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, J.R.; Lusby, W.R.; Marron, B.E.; Nicolaou, K.C.; Hoffmann, M.P.; Wilson, L.T. Pheromone Blends of Green Stink Bugs and Possible Parasitoid Selection. Naturwissenschaften 1989, 76, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.G.; Warren, W.C.; Beukeboom, L.W.; Bopp, D.; Clark, A.G.; Giers, S.D.; Hediger, M.; Jones, A.K.; Kasai, S.; Leichter, C.A.; et al. Genome of the House Fly, Musca domestica L., a Global Vector of Diseases with Adaptations to a Septic Environment. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, D.R. Animal Mitochondrial DNA: Structure and Evolution. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1992, 141, 173–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, R.L.; Boore, J.L. Molecular Mechanisms of Extensive Mitochondrial Gene Rearrangement in Plethodontid Salamanders. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 2104–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, G.L.; Butlin, R.K. Sympatric Speciation in Insects. In Adaptive Speciation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, M.W.; Kéry, M.; Hui, F.K.C.; Guillera-Arroita, G.; Knaus, P.; Sattler, T. Joint Species Distribution Models with Species Correlations and Imperfect Detection. Ecology 2019, 100, e02754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Assembly Statistics | |
|---|---|
| Size (MB) | 672 |
| Number of contigs Largest contigs (MB) | 561 28 |
| GC content (%) | 31.7 |
| N50 value (MB) | 11.9 |
| Number of predicted genes | 1367 |
| Complete BUSCOs | 1360 (99.4%) |
| Complete and single-copy BUSCOs | 1332 (97.4%) |
| Complete and duplicated BUSCOs | 28 (2.0%) |
| Fragmented BUSCOs | 3 (0.2%) |
| Missing BUSCOs | 4 (0.4%) |
| Sample ID | No. Reads | No. Bases | Quality | Unannotated Reads | Contig Size (bp) | AT% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NV1 | 12,671 | 13,160,480 | 64 | - | - | - |
| NV2 | 41,125 | 42,567,447 | 53 | 374 | 15,396 | 79.62 |
| NV3 | 17,292 | 17,961,830 | 54 | - | - | - |
| NV4 | 180,989 | 189,724,559 | 51 | 652 | 15,635 | 79.84 |
| NV5 | 22,630 | 24,017,062 | 54 | - | - | - |
| NV6 | 22,535 | 24,146,808 | 57 | - | - | - |
| NV7 | 110,361 | 115,066,499 | 51 | 689 | 15,671 | 79.91 |
| NV8 | 51,773 | 57,286,544 | 52 | - | - | - |
| NV9 | 24,866 | 23,880,487 | 54 | - | - | - |
| NV10 | 20,657 | 20,860,611 | 69 | - | - | - |
| NV11 | 16,898 | 16,575,717 | 55 | - | - | - |
| NV12 | 14,534 | 16,708,672 | 56 | - | - | - |
| NV13 | 63,726 | 62,656,733 | 50 | - | - | - |
| NV14 | 47,523 | 46,837,257 | 51 | - | - | - |
| NV15 | 11,798 | 12,414,661 | 58 | - | - | - |
| LP1 | 71,366 | 86,228,837 | 54 | 3426 | 18,399 | 78.52 |
| NV16 | 25,677 | 29,132,101 | 54 | - | - | - |
| LP2 | 67,150 | 74,432,675 | 52 | - | - | - |
| LP3 | 35,033 | 35,413,794 | 55 | 424 | 15,345 | 79.59 |
| NV17 | 26,902 | 26,680,575 | 59 | - | - | - |
| NV18 | 8626 | 8,261,140 | 63 | - | - | - |
| NV19 | 9404 | 9,392,892 | 57 | - | - | - |
| NV20 | 53,549 | 54,982,744 | 51 | - | - | - |
| LP4 | 4880 | 4,832,986 | 67 | - | - | - |
| NV21 | 57,424 | 67,139,567 | 53 | - | - | - |
| NV22 | 14,672 | 12,526,413 | 56 | - | - | - |
| NV23 | 39,343 | 36,938,437 | 51 | - | - | - |
| NV24 | 6290 | 4,868,262 | 49 | - | - | - |
| NV25 | 21,492 | 19,843,073 | 53 | 416 | 15,389 | 80.08 |
| NV26 | 51,002 | 57,801,828 | 53 | - | - | - |
| NV27 | 64,355 | 69,748,804 | 52 | - | - | - |
| LP5 | 91,453 | 11,3736,808 | 52 | - | - | - |
| LP6 | 43,750 | 52,865,748 | 55 | - | - | - |
| LP7 | 59,613 | 70,247,435 | 55 | 852 | 15,845 | 80.03 |
| LP8 | 96,846 | 120,505,089 | 55 | - | - | - |
| LP9 | 47,048 | 57,653,541 | 52 | - | - | - |
| LP10 | 91,610 | 106,733,059 | 52 | 1167 | 16,140 | 80.20 |
| LP11 | 69,224 | 72,032,812 | 54 | 1432 | 16,390 | 80.40 |
| Gene | No. Nucleotides | Strand | Direction | Start Codon | Stop Codon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| srRNA | 789 | J | R | 308 | 1096 |
| lrRNA | 1292 | J | R | 1226 | 2517 |
| ND1 | 948 | J | R | 2560 | 3507 |
| Cyt B | 1137 | J | F | 3589 | 4725 |
| ND6 | 525 | N | F | 4725 | 5249 |
| ND4L | 297 | N | R | 5386 | 5682 |
| ND4 | 1338 | J | R | 5676 | 7013 |
| ND5 | 1734 | J | R | 7080 | 8813 |
| ND3 | 354 | J | F | 9395 | 9748 |
| CoxIII | 789 | J | F | 9836 | 10,624 |
| ATP6 | 678 | N | F | 10,624 | 11,301 |
| ATP8 | 162 | J | F | 11,295 | 11,456 |
| CoxII | 687 | J | F | 11,599 | 12,285 |
| CoxI | 1536 | J | F | 12,349 | 13,884 |
| ND2 | 1017 | J | F | 14,087 | 15,103 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bogale, M.; Mishra, S.; Stacey, K.; Rooney, L.; Barreto, P.; Bishop, G.; Bossert, K.; Bremer, K.; Bustamante, D.; Chan, L.; et al. First Description of the Nuclear and Mitochondrial Genomes and Associated Host Preference of Trichopoda pennipes, a Parasitoid of Nezara viridula. Genes 2023, 14, 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061172
Bogale M, Mishra S, Stacey K, Rooney L, Barreto P, Bishop G, Bossert K, Bremer K, Bustamante D, Chan L, et al. First Description of the Nuclear and Mitochondrial Genomes and Associated Host Preference of Trichopoda pennipes, a Parasitoid of Nezara viridula. Genes. 2023; 14(6):1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061172
Chicago/Turabian StyleBogale, Mesfin, Shova Mishra, Kendall Stacey, Lillie Rooney, Paula Barreto, Gina Bishop, Katherine Bossert, Kalista Bremer, Daniel Bustamante, Lila Chan, and et al. 2023. "First Description of the Nuclear and Mitochondrial Genomes and Associated Host Preference of Trichopoda pennipes, a Parasitoid of Nezara viridula" Genes 14, no. 6: 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061172
APA StyleBogale, M., Mishra, S., Stacey, K., Rooney, L., Barreto, P., Bishop, G., Bossert, K., Bremer, K., Bustamante, D., Chan, L., Chau, Q., Cordo, J., Diaz, A., Hacker, J., Hadaegh, L., Hibshman, T., Lastra, K., Lee, F., Mattia, A., ... DiGennaro, P. (2023). First Description of the Nuclear and Mitochondrial Genomes and Associated Host Preference of Trichopoda pennipes, a Parasitoid of Nezara viridula. Genes, 14(6), 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061172