Two oncomiRs, miR-182-5p and miR-103a-3p, Involved in Intravenous Leiomyomatosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
- Localization: intra the uterus or beyond the uterus;
- Localization: intravenous or beyond the vein.
2.2. Total RNA Isolation and RT-qPCR
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
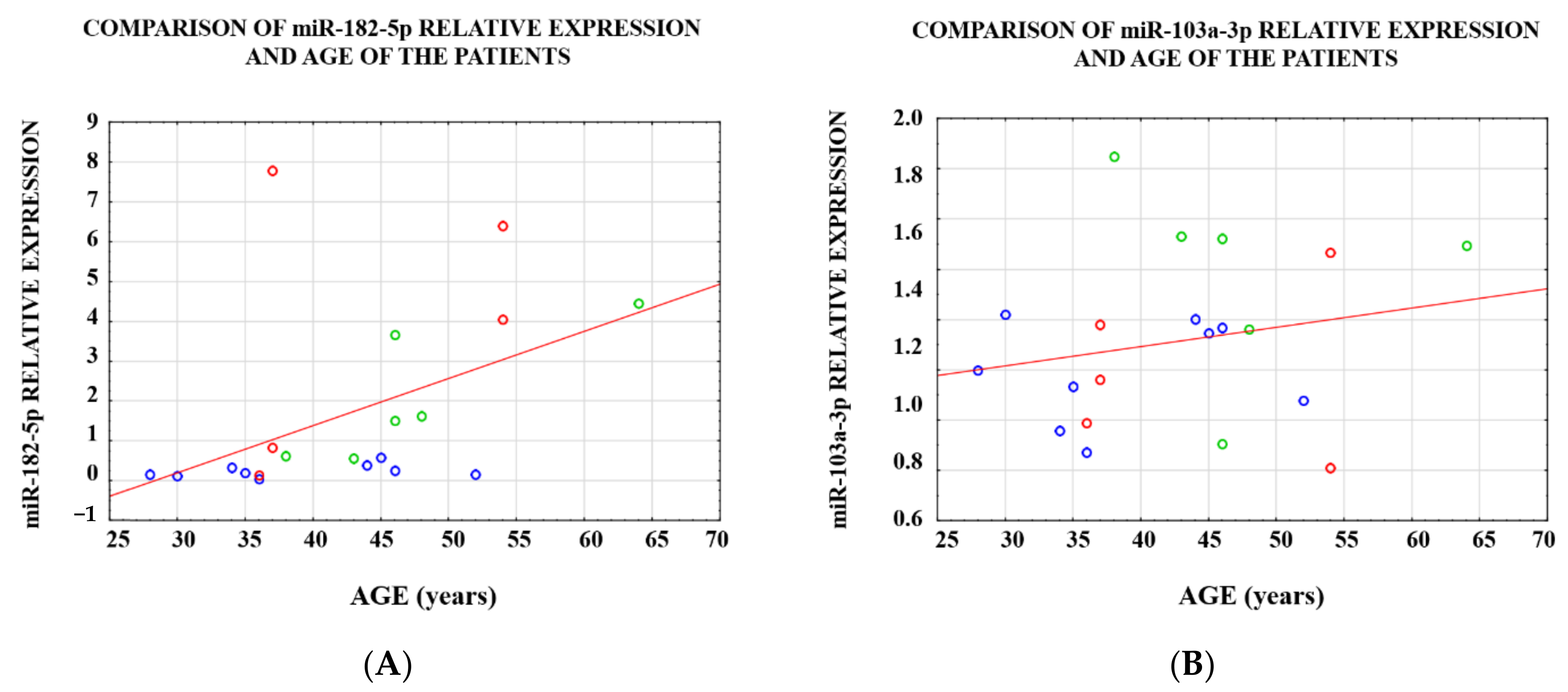
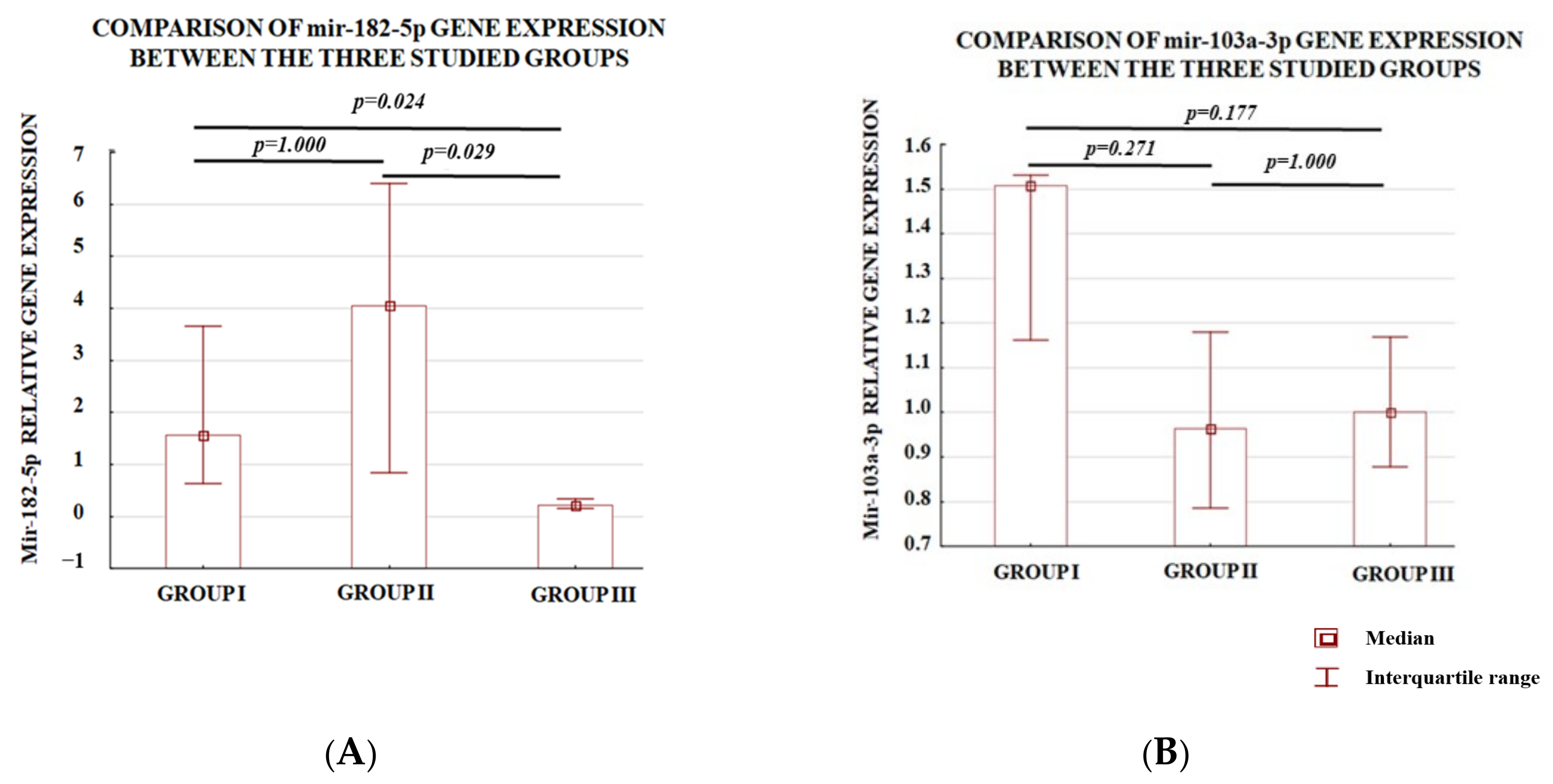
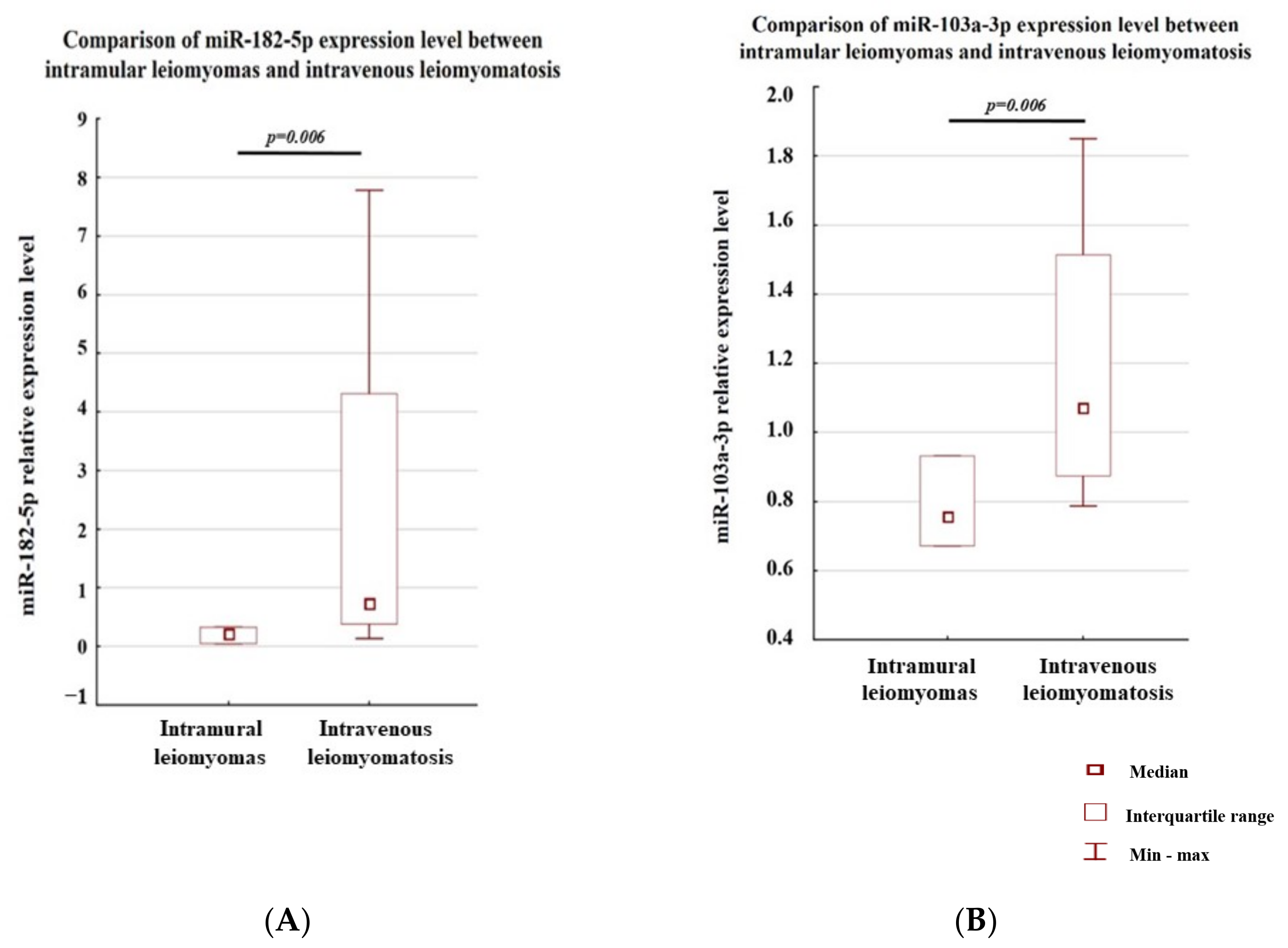
3.1. Analysis of the Level of Expression between the Study Groups
3.2. Analysis of the Level of Expression within a Single Case
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fasih, N.; Prasad Shanbhogue, A.K.; Macdonald, D.B.; Fraser-Hill, M.A.; Papadatos, D.; Kielar, A.Z.; Doherty, G.P.; Walsh, C.; McInnes, M.; Atri, M. Leiomyomas beyond the Uterus: Unusual Locations, Rare Manifestations. RadioGraphics 2008, 28, 1931–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnaś, E.; Raś, R.; Skręt-Magierło, J.; Wesecki, M.; Filipowska, J.; Książek, M.; Skręt, A.; Widenka, K. Natural history of leiomyomas beyond the uterus. Medicine 2019, 98, e15877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordulu, Z.; Cin, P.D.; Chong, W.W.S.; Choy, K.W.; Lee, C.; Muto, M.G.; Quade, B.J.; Morton, C.C. Disseminated peritoneal leiomyomatosis after laparoscopic supracervical hysterectomy with characteristic molecular cytogenetic findings of uterine leiomyoma. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2010, 49, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Miao, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Shao, J.; Cheng, N.; Du, S.; Hu, Z.; et al. Different surgical strategies of patients with intravenous leiomyomatosis. Medicine 2016, 95, e4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Segura, M.F.; Shao, C.; Lee, P.; Gong, Y.; Hernando, E.; Wei, J.-J. MiR-182 overexpression in tumourigenesis of high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2012, 228, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Shi, W.; Dong, F.; Xin, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, C. Breast cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicles transfer miR-182-5p and promote breast carcinogenesis via the CMTM7/EGFR/AKT axis. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.-Q.; You, A.B.; Zhu, X.-D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, S.-Z.; Zhang, K.-W.; Cai, H.; Shi, W.-K.; Li, X.-L.; et al. miR-182-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by repressing FOXO3a. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafford, M.Y.C.; McKenna, D.J. MiR-182 Is Upregulated in Prostate Cancer and Contributes to Tumor Progression by Targeting MITF. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, M.F.; Hanniford, D.; Menendez, S.; Reavie, L.; Zou, X.; Alvarez-Diaz, S.; Zakrzewski, J.; Blochin, E.; Rose, A.; Bogunovic, D.; et al. Aberrant miR-182 expression promotes melanoma metastasis by repressing FOXO3 and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1814–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, M.; Mito, J.K.; Lee, C.-L.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Dodd, R.D.; Cason, D.; Luo, L.; Ma, Y.; Van Mater, D.; et al. MicroRNA-182 drives metastasis of primary sarcomas by targeting multiple genes. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Jia, Y.; Chen, H. MicroRNA-103 regulates the progression in endometrial carcinoma through ZO-1. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2019, 33, 2058738419872621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Yang, J.; Meng, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. The promotional effect of microRNA-103a-3p in cervical cancer cells by regulating the ubiquitin ligase FBXW7 function. Hum. Cell 2022, 35, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, B.; Tang, N.; Hu, J.; Liang, S.; Pang, Y.; Xu, H.; Ao, J.; Yang, J.; et al. MiR-103a promotes tumour growth and influences glucose metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Shao, W.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, F.; Qin, J. MicroRNA-103 regulates tumorigenesis in colorectal cancer by targeting ZO-1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasihi, A.; Soltani, B.M.; Atashi, A.; Nasiri, S. Introduction of hsa-miR-103a and hsa-miR-1827 and hsa-miR-137 as new regulators of Wnt signaling pathway and their relation to colorectal carcinoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 5104–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.-L.; Sha, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.-Y.; Guo, Z.-Y.; Sun, S.-A.; He, J.-D. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0007142 Is Upregulated and Targets miR-103a-2-5p in Colorectal Cancer. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 9836819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberinia, A.; Alinezhad, A.; Jafari, F.; Soltany, S.; Akhavan Sigari, R. Oncogenic miRNAs and target therapies in colorectal cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 508, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, S. miR-103 Promotes Proliferation and Metastasis by Targeting KLF4 in Gastric Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinge, C. Estrogen Regulation of MicroRNA Expression. Curr. Genom. 2009, 10, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, F.; Ahtiainen, M.; Lazzarini, R.; Pöllänen, E.; Capri, M.; Lorenzi, M.; Fulgenzi, G.; Albertini, M.C.; Salvioli, S.; Alen, M.J.; et al. Hormone replacement therapy enhances IGF-1 signaling in skeletal muscle by diminishing miR-182 and miR-223 expressions: A study on postmenopausal monozygotic twin pairs. Aging Cell 2014, 13, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Song, Y.; Cao, B.; An, X. miR-182 aids in receptive endometrium development in dairy goats by down-regulating PTN expression. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lu, Z.; Qiang, W.; Vidimar, V.; Kong, B.; Kim, J.J.; Wei, J.-J. Inactivation of AKT Induces Cellular Senescence in Uterine Leiomyoma. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Feng, Z.; Sai, Z.; Tao, S. PER3, a novel target of miR-103, plays a suppressive role in colorectal cancer in vitro. BMB Rep. 2014, 47, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouyssou, J.M.C.; Manier, S.; Huynh, D.; Issa, S.; Roccaro, A.M.; Ghobrial, I.M. Regulation of microRNAs in cancer metastasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2014, 1845, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nothnick, W.B. The role of micro-RNAs in the female reproductive tract. Reproduction 2012, 143, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.S.; Zhong, B.; Zhang, M.S.; Gao, Y. Upregulation of serum miR-103 predicts unfavorable prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 4518–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.-W.; Mendell, J.T. MicroRNAs in cell proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogribny, I.P. MicroRNAs as biomarkers for clinical studies. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, C.M. miRNAs in the spotlight: Understanding cancer gene dependency. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 935–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankasha, S.J.; Shafiee, M.N.; Wahab, N.A.; Ali, R.A.R.; Mokhtar, N.M. Post-transcriptional regulation of microRNAs in cancer: From prediction to validation. Oncol. Rev. 2018, 12, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciebiera, M.; Włodarczyk, M.; Zgliczyński, S.; Łoziński, T.; Walczak, K.; Czekierdowski, A. The Role of miRNA and Related Pathways in Pathophysiology of Uterine Fibroids—From Bench to Bedside. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgieva, B.; Milev, I.; Minkov, I.; Dimitrova, I.; Bradford, A.P.; Baev, V. Characterization of the uterine leiomyoma microRNAome by deep sequencing. Genomics 2012, 99, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.; Shin, J.; Kim, H.; Ku, S.-Y.; Suh, C. Variation in MicroRNA Expression Profile of Uterine Leiomyoma with Endometrial Cavity Distortion and Endometrial Cavity Non-Distortion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuovo, G.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Benign Metastasizing Leiomyoma of the Lung. Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 2008, 17, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodner-Adler, B.; Bodner, K.; Kimberger, O.; Czerwenka, K.; Leodolter, S.; Mayerhofer, K. Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Patients With Uterine Smooth Muscle Tumors: An Immunohistochemical Analysis of MMP-1 and MMP-2 Protein Expression in Leiomyoma, Uterine Smooth Muscle Tumor of Uncertain Malignant Potential, and Leiomyosarcoma. J. Soc. Gynecol. Investig. 2004, 11, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, S.G.; Valenti, G.; Cianci, A. Crosstalk between transforming growth factor-β3 and microRNA-29c in leiomyoma: Are we stepping forward? Fertil. Steril. 2019, 112, 1055–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarelli, L.; Geißler, C.; Csaba, G.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, M.; di Francesco, A.; Hartmann, P.; Zimmer, R.; Schober, A. miR-103 promotes endothelial maladaptation by targeting lncWDR59. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.S.; Davidson, L.A.; Chapkin, R.S. Mechanistic insights into the role of microRNAs in cancer: Influence of nutrient crosstalk. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.-Y.; Gong, H.-T.; Li, B.-F.; Lv, C.-L.; Wang, H.-T.; Zhou, H.-H.; Li, X.-X.; Xie, S.-Y.; Jiang, B.-F. Higher expression of circulating miR-182 as a novel biomarker for breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 6, 1681–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, G.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. MicroRNA-182 promotes proliferation and metastasis by targeting FOXF2 in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 4805–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttilla, I.K.; White, B.A. Coordinate Regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in Breast Cancer Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 23204–23216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, K.; Steptoe, A.L.; Martin, H.C.; Wani, S.; Nones, K.; Waddell, N.; Mariasegaram, M.; Simpson, P.T.; Lakhani, S.R.; Gabrielli, B.; et al. MicroRNA-182-5p targets a network of genes involved in DNA repair. RNA 2013, 19, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, H.; Xu, H.; Zhao, H.; Xiong, N. Hypoxic Cancer-Secreted Exosomal miR-182-5p Promotes Glioblastoma Angiogenesis by Targeting Kruppel-like Factor 2 and 4. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 1218–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wu, D.; Xu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; He, F.; Xu, J.; Su, L.; et al. miR-182-5p affects human bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion through regulating Cofilin 1. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Fang, R.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Li, F.; Ye, X.; Chen, H. Hsa-mir-182 suppresses lung tumorigenesis through down regulation of RGS17 expression in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 396, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.-Q.; Bai, R.; Liu, T.; Cai, C.-L.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. MicroRNA-182 targets cAMP-responsive element-binding protein 1 and suppresses cell growth in human gastric adenocarcinoma. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, C.E.; Dart, D.A.; Bevan, C.L. Interplay between steroid signalling and microRNAs: Implications for hormone-dependent cancers. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2014, 21, R409–R429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.P.H.; Cabrera, R.M.; Segall, J.E. Tumor cell intravasation. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2016, 311, C1–C14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Lei, R.; Zhuang, X.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Lev, S.; Segura, M.F.; Zhang, X.; Hu, G. MicroRNA-182 targets SMAD7 to potentiate TGFβ-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciebiera, M.; Włodarczyk, M.; Wrzosek, M.; Męczekalski, B.; Nowicka, G.; Łukaszuk, K.; Ciebiera, M.; Słabuszewska-Jóźwiak, A.; Jakiel, G. Role of Transforming Growth Factor β in Uterine Fibroid Biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T.; Shi, H.; Xu, Q.; Song, Q.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y. Effects of TGF-β on uterine fibroids of women of childbearing age and uterine artery embolization. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2017, 26, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, D.; Zhou, C.; Lu, H.; Xu, R.; Xu, X.; He, X. LncRNA GAS5 inhibits proliferation and progression of prostate cancer by targeting miR-103 through AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 16187–16197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, B.S.; Jørgensen, S.; Fog, J.U.; Søkilde, R.; Christensen, I.J.; Hansen, U.; Brünner, N.; Baker, A.; Møller, S.; Nielsen, H.J. High levels of microRNA-21 in the stroma of colorectal cancers predict short disease-free survival in stage II colon cancer patients. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2011, 28, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.-L.; Yin, X.-R.; Zhang, S.-Q. miR-103 promotes the metastasis and EMT of hepatocellular carcinoma by directly inhibiting LATS2. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 2433–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-P.; Zhang, N.-N.; Ren, X.-Q.; He, J.; Li, Y. miR-103/miR-195/miR-15b Regulate SALL4 and Inhibit Proliferation and Migration in Glioma. Molecules 2018, 23, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kfir-Erenfeld, S.; Haggiag, N.; Biton, M.; Stepensky, P.; Assayag-Asherie, N.; Yefenof, E. miR-103 inhibits proliferation and sensitizes hemopoietic tumor cells for glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 472–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 with a peduncle
with a peduncle  . Objective 10×, H&E. The scale bar showed 200 μm in distance. Immunohistochemical features of intravenous leiomyomatosis beyond the uterus. (B) Strong positivity for smooth muscle actin. (C) Estrogen receptors. (D) Progesterone receptors. (E) Desmin. (F) H-caldesmon. Objective 10×.
. Objective 10×, H&E. The scale bar showed 200 μm in distance. Immunohistochemical features of intravenous leiomyomatosis beyond the uterus. (B) Strong positivity for smooth muscle actin. (C) Estrogen receptors. (D) Progesterone receptors. (E) Desmin. (F) H-caldesmon. Objective 10×.
 with a peduncle
with a peduncle  . Objective 10×, H&E. The scale bar showed 200 μm in distance. Immunohistochemical features of intravenous leiomyomatosis beyond the uterus. (B) Strong positivity for smooth muscle actin. (C) Estrogen receptors. (D) Progesterone receptors. (E) Desmin. (F) H-caldesmon. Objective 10×.
. Objective 10×, H&E. The scale bar showed 200 μm in distance. Immunohistochemical features of intravenous leiomyomatosis beyond the uterus. (B) Strong positivity for smooth muscle actin. (C) Estrogen receptors. (D) Progesterone receptors. (E) Desmin. (F) H-caldesmon. Objective 10×.
| Localization | Number of Cases | Mean Age (Years) ± Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| intravenous leiomyomatosis located in myometrium—group I | 6 | 47.5 ± 9 |
| intravenous leiomyomatosis beyond the uterus—group II | 5 | 43.6 ± 9 |
| intramural leiomyomas—group III | 9 | 38.9 ± 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barnaś, E.; Skręt-Magierło, J.E.; Paszek, S.; Kaznowska, E.; Potocka, N.; Skręt, A.; Sakowicz, A.; Zawlik, I. Two oncomiRs, miR-182-5p and miR-103a-3p, Involved in Intravenous Leiomyomatosis. Genes 2023, 14, 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030712
Barnaś E, Skręt-Magierło JE, Paszek S, Kaznowska E, Potocka N, Skręt A, Sakowicz A, Zawlik I. Two oncomiRs, miR-182-5p and miR-103a-3p, Involved in Intravenous Leiomyomatosis. Genes. 2023; 14(3):712. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030712
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarnaś, Edyta, Joanna Ewa Skręt-Magierło, Sylwia Paszek, Ewa Kaznowska, Natalia Potocka, Andrzej Skręt, Agata Sakowicz, and Izabela Zawlik. 2023. "Two oncomiRs, miR-182-5p and miR-103a-3p, Involved in Intravenous Leiomyomatosis" Genes 14, no. 3: 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030712
APA StyleBarnaś, E., Skręt-Magierło, J. E., Paszek, S., Kaznowska, E., Potocka, N., Skręt, A., Sakowicz, A., & Zawlik, I. (2023). Two oncomiRs, miR-182-5p and miR-103a-3p, Involved in Intravenous Leiomyomatosis. Genes, 14(3), 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030712







