A Comparative Analysis of the Chloroplast Genomes of Three Lonicera Medicinal Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cp Genome Organizations
2.2. Repeat and Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) Analyses
2.3. IR Expansion and Contraction
2.4. Sequence Divergence Analysis
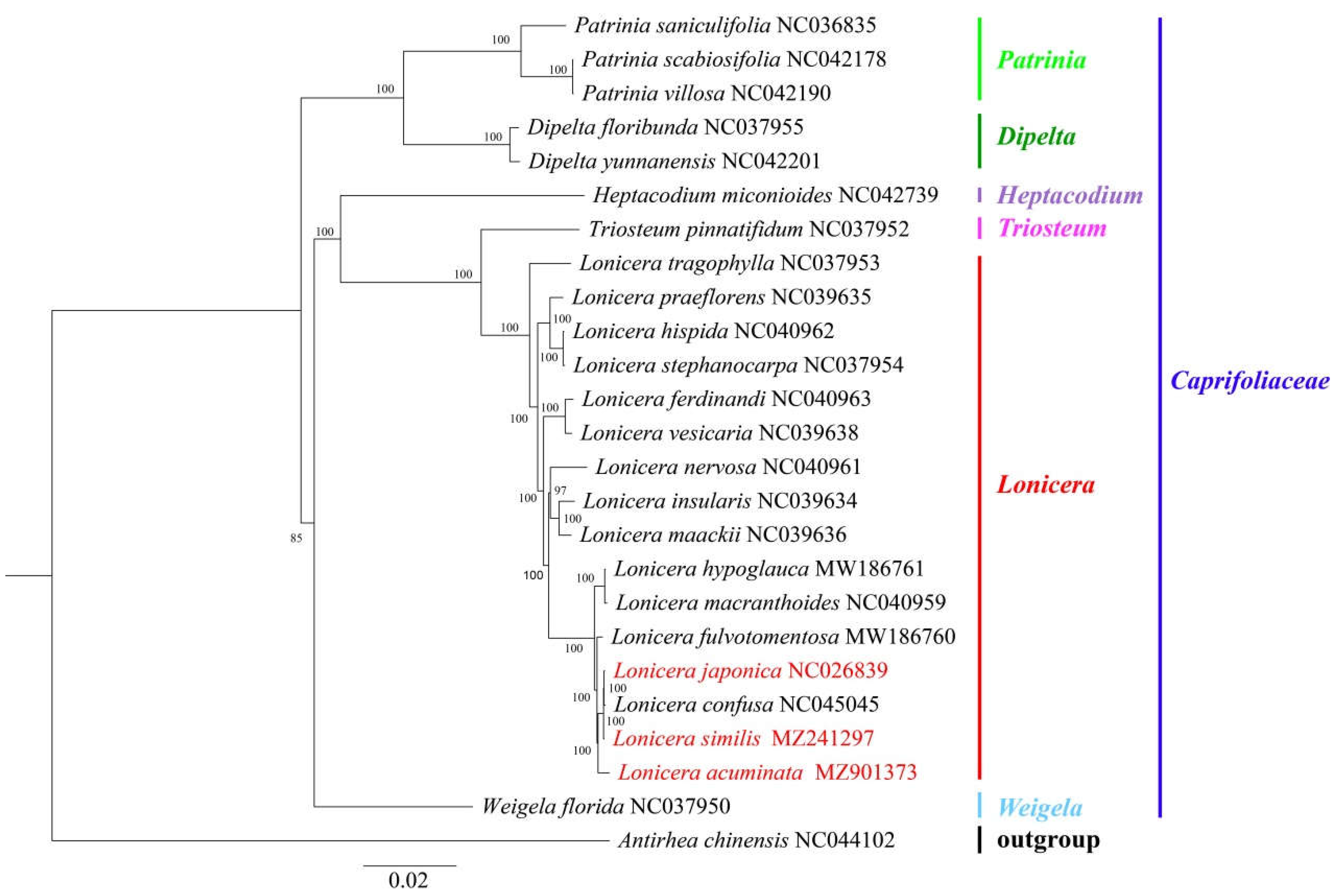
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.6. Plant Morphology
2.7. HPLC Fingerprints and the Content of Main Q-Marker
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Material and DNA Extraction
3.2. Assembly and Annotation
3.3. Characterization of Repeat Sequences and SSRs
3.4. Comparative Genome Analysis and Sequence Variation
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.6. HPLC Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Lu, C. Lonicera japonica Thunb (Jinyinhua, Honey Suckle); Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Cai, W.; Weng, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, X.; et al. Lonicerae Japonicae Flos and Lonicerae Flos: A Systematic Pharmacology Review. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 905063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Fu, C.; Song, Y.; Fu, Q. Lonicerae japonicae flos and Lonicerae flos: A systematic review of ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology. Phytochem. Rev. 2020, 19, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.-R.; Zeng, T.; Yuan, H.-W.; Li, B.; Peng, C.-Y.; Wang, S.-C.; Jian, Y.-Q.; Qin, Y.; Choudhary, M.I.; Wang, W. Lonicerae Flos: A review of chemical constituents and biological activities. Digit. Chin. Med. 2018, 1, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Pharmacopoeia Committee. The Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China: One; The 2020 Edition; China Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 230–232. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, O.-H.; Choi, Y.-A.; Park, H.-J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, D.-K.; Choi, S.-C.; Kim, T.-H.; Nah, Y.-H.; Yun, K.-J.; Kim, Y.-H.; et al. Inhibition of trypsin-induced mast cell activation by water fraction of Lonicera japonica. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2004, 27, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Jiang, J.-G. Origin and concept of medicine food homology and its application in modern functional foods. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 1727–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.-T.; Liu, C.-J.; Yeh, C.-C. Protective and immunomodulatory effect of flos Lonicerae japonicae by augmenting IL-10 expression in a murine model of acute lung inflammation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 168, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, C.; Wu, M.; Su, H.; Ma, X.; Zang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, X. Spectrum-Effect Relationships Between Chemical Fingerprints and Antibacterial Effects of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos and Lonicerae Flos Base on UPLC and Microcalorimetry. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-C.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Zhou, W.-C.; Chen, J.; Jin, H.-Q.; Fang, H.-M.; Chen, Q.; Jin, Y.-C.; Qu, J.; Kan, L.-D. Lianhua Qingwen prescription for Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment: Advances and prospects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Rong, G.; Meng, Q.; Yu, M.; Xie, Q.; Fang, J. Outlining the keyword co-occurrence trends in Shuanghuanglian injection research: A bibliometric study using CiteSpace III. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Sci. 2020, 7, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Alcalde, J.; Yan, Y.; Witt, C.M.; Barth, J. Current State of Research About Chinese Herbal Medicines (CHM) for the Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Scoping Review. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2020, 26, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Peng, B.; Li, A.; Li, Z.; Song, P.; Li, J.; Xu, R.; Li, N. Broad Anti-Viral Capacities of Lian-Hua-Qing-Wen Capsule and Jin-Hua-Qing-Gan Granule and Rational use Against COVID-19 Based on Literature Mining. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 640782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Huang, F.; Zhang, M.; Huang, B.; Wang, Y. Current status of traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of COVID-19 in China. Chin. Med. 2021, 16, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Youn, J.Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Cai, H. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) in the treatment of COVID-19 and other viral infections: Efficacies and mechanisms. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 225, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, H.F.; Chan, L.W.C.; Cho, W.C.S.; Yu, A.C.S.; Yim, A.K.Y.; Chan, A.K.C.; Ng, L.P.W.; Wong, Y.K.E.; Pei, X.M.; Li, M.J.W.; et al. An update on COVID-19 pandemic: The epidemiology, pathogenesis, prevention and treatment strategies. Expert Rev. Anti-infective 2021, 19, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.J.; Suo, C.X.; Pan, L.Y.; Li, G.W.; Hu, Q.P.; Sun, D.M. The quality evaluation of Lonicerae japonicae Flos, Lonicerae Flos and Lonicerae similis Flos based on multivariate statistical analysis. J. Guangdong Pharm. Univ. 2020, 36, 620–626. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.W.; Ma, Y.Y.; Deng, W.; Mi, X.Q.; Zheng, G.Y. Observation of pollen grains of Chuanyinhua with scanning electron microscope. Pharm. Clin. Chin. Materia Medica 2010, 1, 10–76. [Google Scholar]
- Si Chuan Food and Drug Administration. Sichuansheng Zhongyaocai Biaozhun (2010 Edition); Sichuan Science and Technology Press: Chengdu, China, 2011; pp. 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Suo, C.X.; Cheng, X.R.; Pan, L.Y.; Qiu, Y.J.; Wu, W.P.; Li, G.W. Comparative Study of Lonicera L.-derived Medicinal Materials: Lonicerae Similis Flos, Lonicerae Japonicae Flos, and Lonicerae Flos. Mod. Chin. Med. 2021, 23, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, W.W.; Huang, H.Y. Comparative analyses of the main active ingredients of Lonicerae japonicae flos and Lonicerae flos. Int. J. Trad. Chin. Med. 2016, 38, 926–931. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.X.; Li, L. Advance in Germplasm Identification Technology of Lonicera Speices. Hortic. Seed 2013, 2013, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.H.; Yuan, Q.Z.; Cai, G.X.; Feng, X.Y.; Shao, Y. Fingerprint of different polarity extracts from superfine powder of Lonicera japonica and its correlation of antibacterial activity. Chin. Tradit. Herb Drugs 2011, 42, 2226–2230. [Google Scholar]
- Pferschy-Wenzig, E.-M.; Ortmann, S.; Atanasov, A.G.; Hellauer, K.; Hartler, J.; Kunert, O.; Gold-Binder, M.; Ladurner, A.; Heiß, E.H.; Latkolik, S.; et al. Characterization of Constituents with Potential Anti-Inflammatory Activity in Chinese Lonicera Species by UHPLC-HRMS Based Metabolite Profiling. Metabolites 2022, 12, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicke, S.; Schneeweiss, G.M.; Depamphilis, C.W.; Müller, K.F.; Quandt, D. The evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: Gene content, gene order, gene function. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 76, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cui, L.; Feng, K.; Deng, P.; Du, X.; Wan, F.; Weining, S.; Nie, X. Comparative Analysis of Asteraceae Chloroplast Genomes: Structural Organization, RNA Editing and Evolution. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1526–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Wang, L.; Lei, J.; Duan, B.; Ma, W.; Xiao, S.; Qi, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shen, X.; et al. A Comparative Analysis of the Chloroplast Genomes of Four Salvia Medicinal Plants. Engineering 2019, 5, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.-J.; Cheng, C.-L.; Chang, C.-C.; Wu, C.-L.; Su, T.-M.; Chaw, S.-M. Dynamics and evolution of the inverted repeat-large single copy junctions in the chloroplast genomes of monocots. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raubeson, L.A.; Peery, R.; Chumley, T.W.; Dziubek, C.; Fourcade, H.M.; Boore, J.L.; Jansen, R.K. Comparative chloroplast genomics: Analyses including new sequences from the angiosperms Nuphar advena and Ranunculus macranthus. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.-S.; Li, P.; Qiu, Y.-X. The Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Three Cardiocrinum (Liliaceae) Species: Comparative Genomic and Phylogenetic Analyses. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Duan, D.; Yang, J.; Feng, L.; Zhao, G. Comparative Analysis of the Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Five Quercus Species. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xu, W.; Wan, M.; Sun, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, C.; Sun, K.; Shu, Y. Comparative analysis of chloroplast genomes of three medicinal Carpesium species: Genome structures and phylogenetic relationships. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Hou, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, Q.; Ding, W.; Weng, Q. Characterization of the chloroplast genome of Lonicera ruprechtiana Regel and comparison with other selected species of Caprifoliaceae. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Guo, W.; Gupta, S.; Fan, W.; Mower, J.P. Evolutionary dynamics of the plastid inverted repeat: The effects of expansion, contraction, and loss on substitution rates. New Phytol. 2016, 209, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Chen, S.; Liang, Y.-Z.; Wang, X.; Tian, R.; Upton, R. Chromatographic fingerprint analysis—A rational approach for quality assessment of traditional Chinese herbal medicine. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1112, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.; Bauer, R.; Melchart, D.; Xiao, P.G.; Staudinger, A. Chromatographic Fingerprint Analysis of Herbal Medicines; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yaradua, S.S.; Alzahrani, D.A.; Albokhary, E.J.; Abba, A.; Bello, A. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Justicia flava: Genome comparative analysis and phylogenetic relationships among Acanthaceae. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, C.; Zhao, X.; Chen, S.; Qu, G.-Z. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Betula platyphylla: Gene organization, RNA editing, and comparative and phylogenetic analyses. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Gao, Y.; Sari, I.; Jiao, R.-F.; Saqib, S.; Gao, X.-F. Macro-Morphological and Ecological Variation in Rosa sericea Complex. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-J.; Yu, W.-B.; Yang, J.-B.; Song, Y.; Depamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.-S.; Li, D.-Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq—Versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, T.; Michalek, W.; Varshney, R.; Graner, A. Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32 (Suppl. 2), W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Ma, P.-F.; Li, D.-Z. High-Throughput Sequencing of Six Bamboo Chloroplast Genomes: Phylogenetic Implications for Temperate Woody Bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvönen, J.; Poczai, P. IRscope: An online program to visualize the junction sites of chloroplast genomes. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3030–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Liu, B.; Liang, Y.; Ye, J.; Saqib, S.; Meng, Z.; Lu, L.; Chen, Z. An updated Chinese vascular plant tree of life: Phylogenetic diversity hotspots revisited. J. Syst. Evol. 2020, 58, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Jiang, C.; Feng, X.; Yang, C.; Yu, Z. The complete chloroplast genome of Lonicera similis Hemsl. and its phylogenetic analysis. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2021, 6, 3151–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wu, S.; Feng, X.; Yang, C.; Yu, Z. The complete chloroplast genome of Lonicera pampaninii Levl. and its phylogenetic analysis. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2021, 6, 3025–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Moral, R. On the variability of chlorogenic acid concentration. Oecologia 1972, 9, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhu, S.; Ma, C.; Wang, Z. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Action of Chlorogenic Acid. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, M398–M403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Hejazi, V.; Abbas, M.; Kamboh, A.A.; Khan, G.J.; Shumzaid, M.; Ahmad, F.; Babazadeh, D.; FangFang, X.; Modarresi-Ghazani, F.; et al. Chlorogenic acid (CGA): A pharmacological review and call for further research. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Itagaki, S.; Kurokawa, T.; Ogura, J.; Kobayashi, M.; Hirano, T.; Sugawara, M.; Iseki, K. In vitro and in vivo antioxidant properties of chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 403, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Ballevre, O.; Luo, H.; Zhang, W. Antihypertensive effects and mechanisms of chlorogenic acids. Hypertens. Res. 2012, 35, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.Q. Mechanism of Tanreqing Capsule on treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 based on network pharmacology. Chin. Tradit. Herb Drugs 2020, 51, 2967–2976. [Google Scholar]
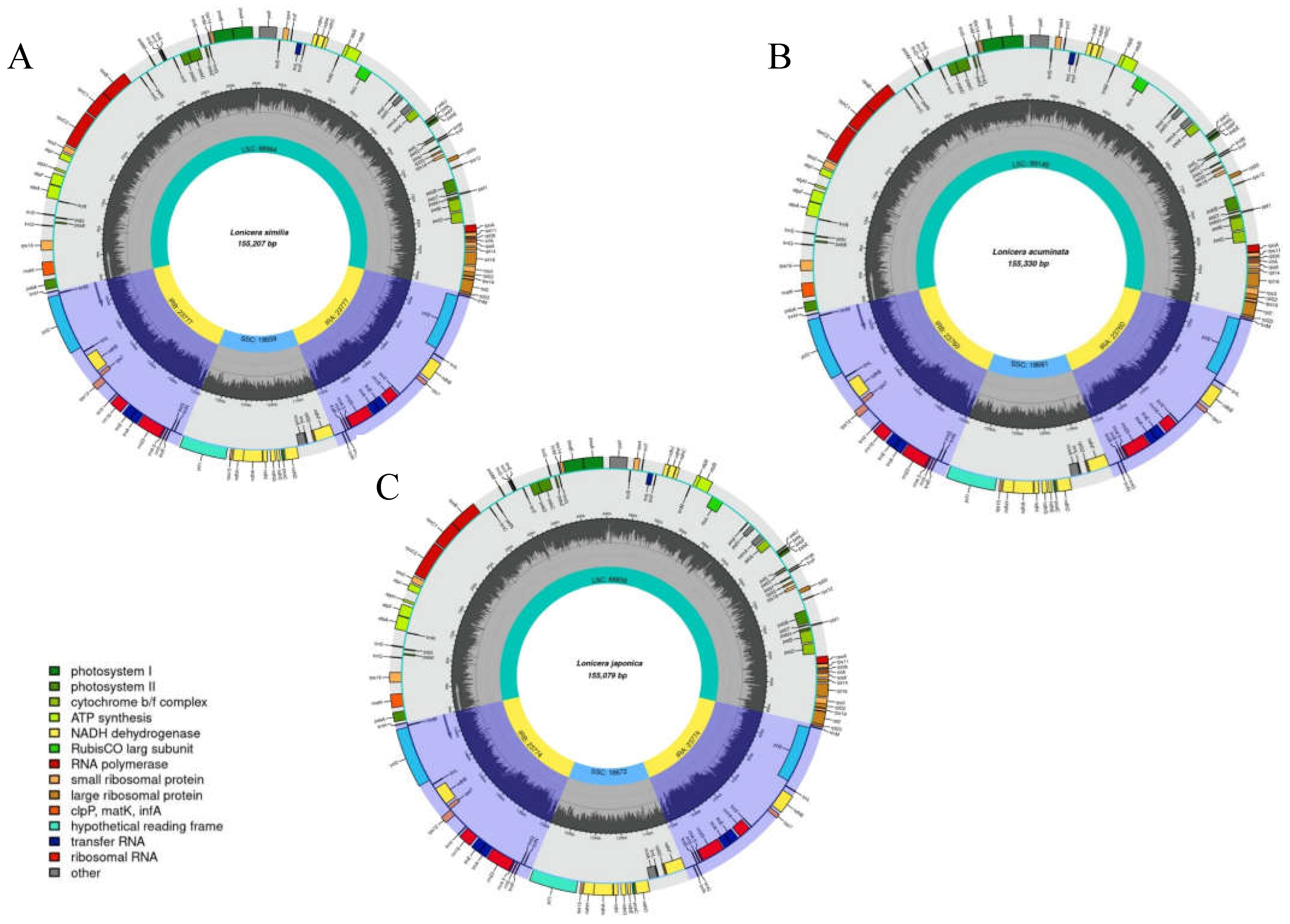

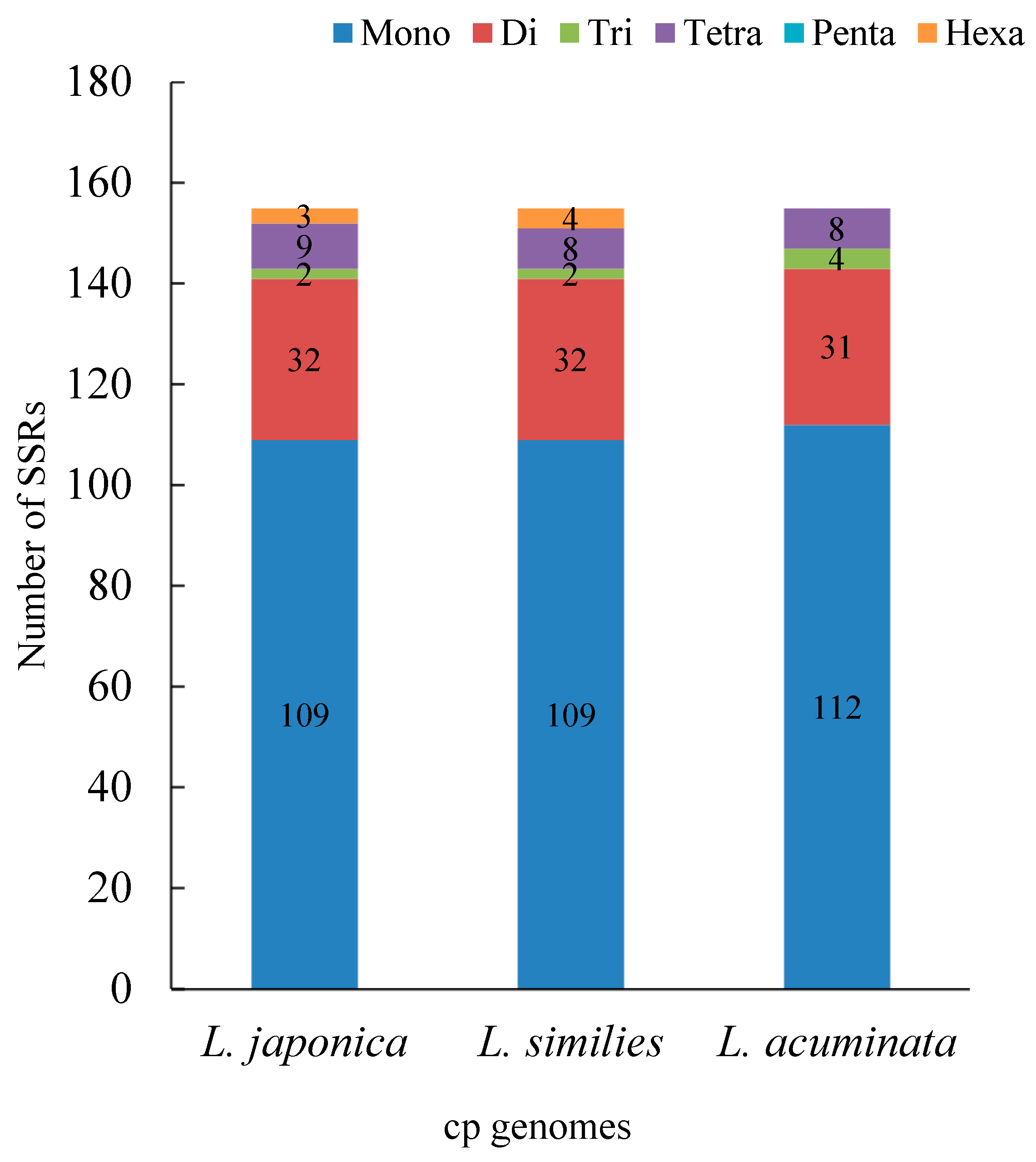
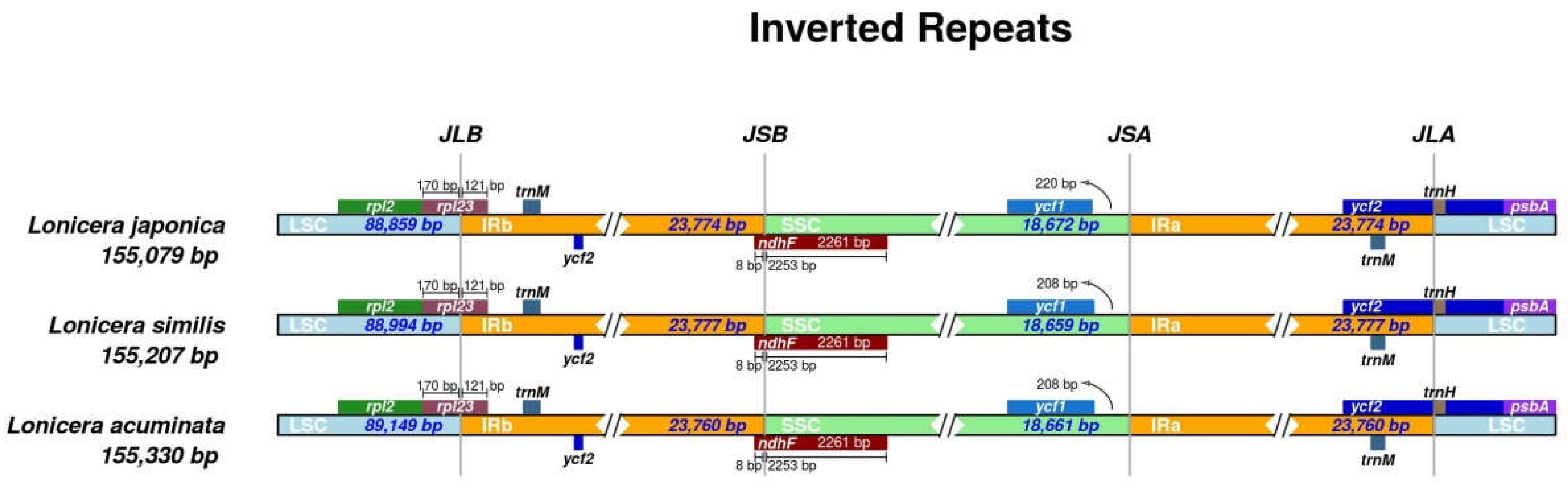
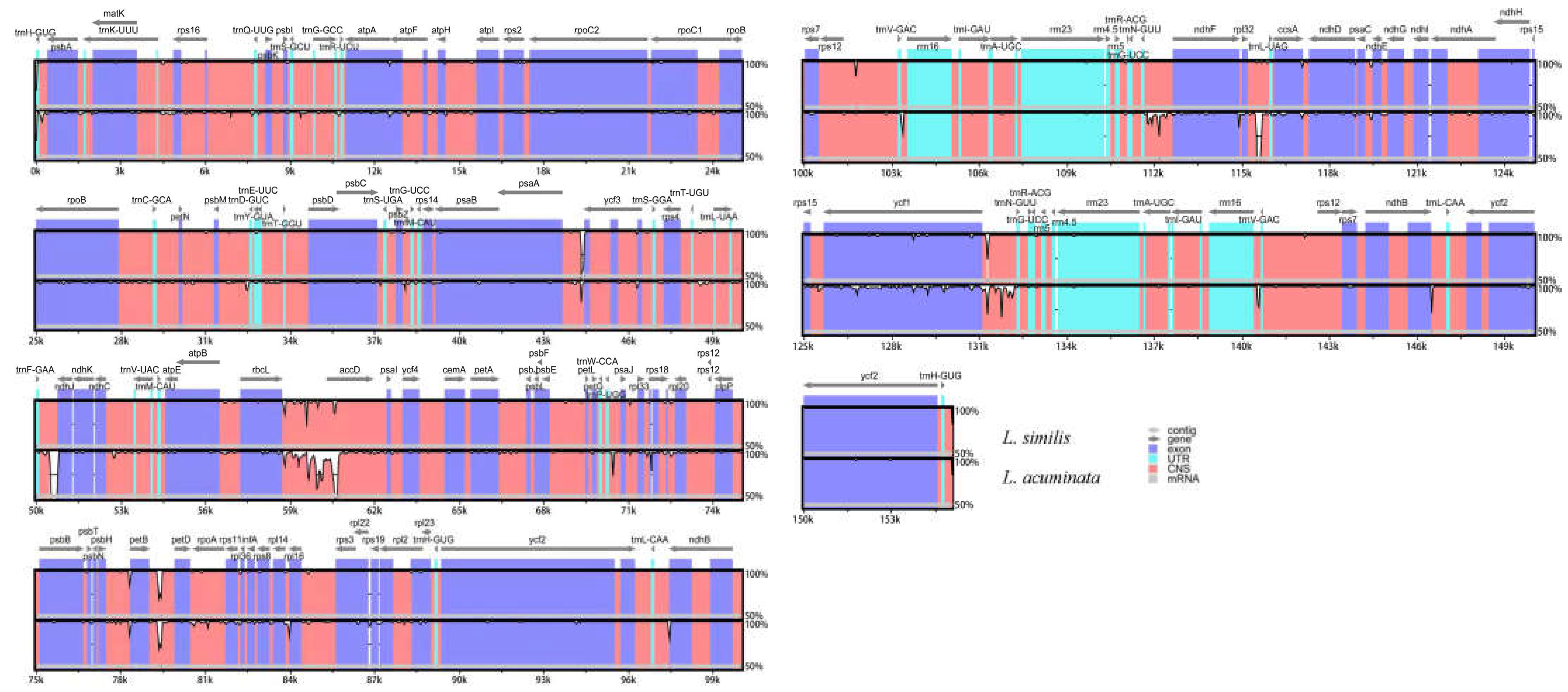
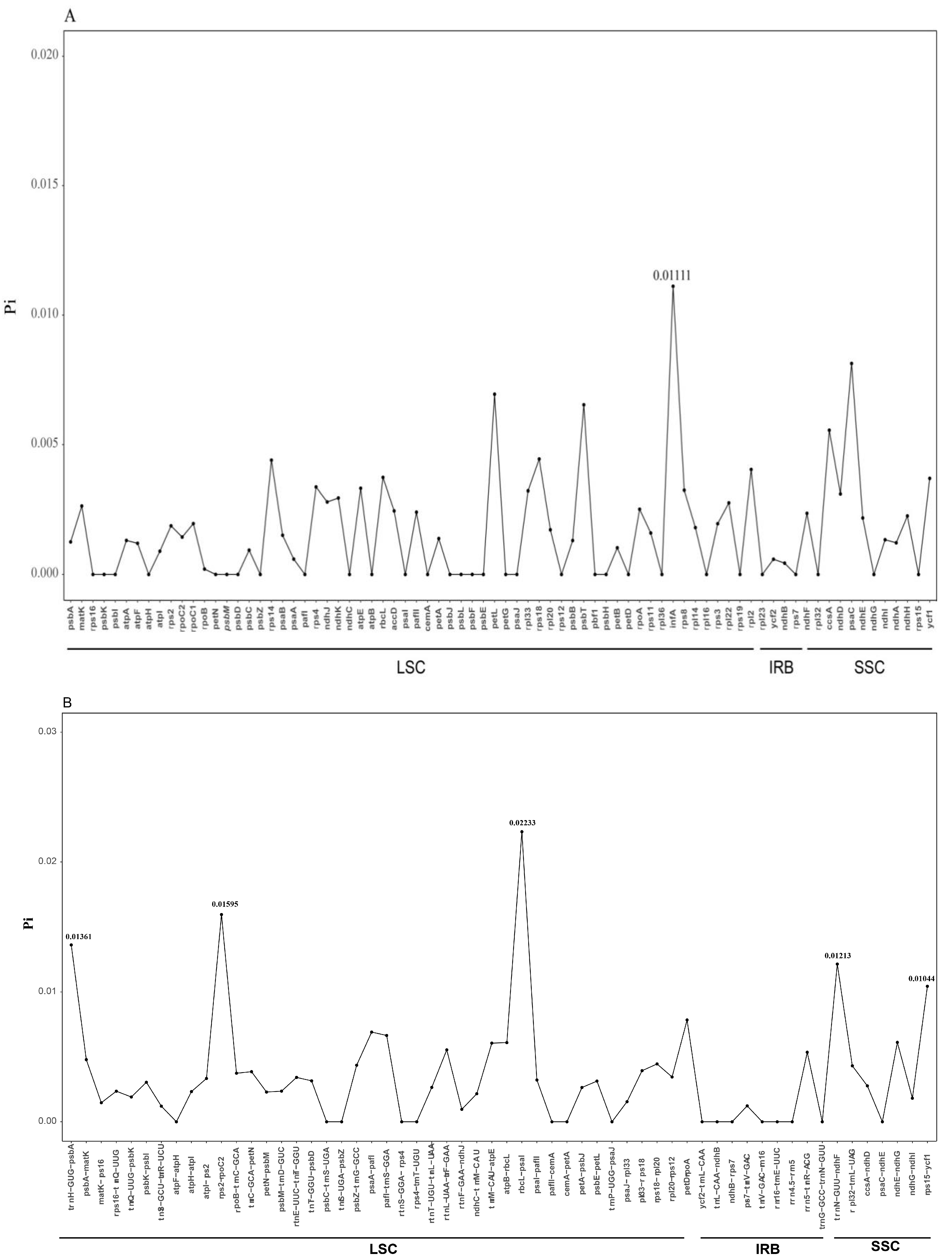

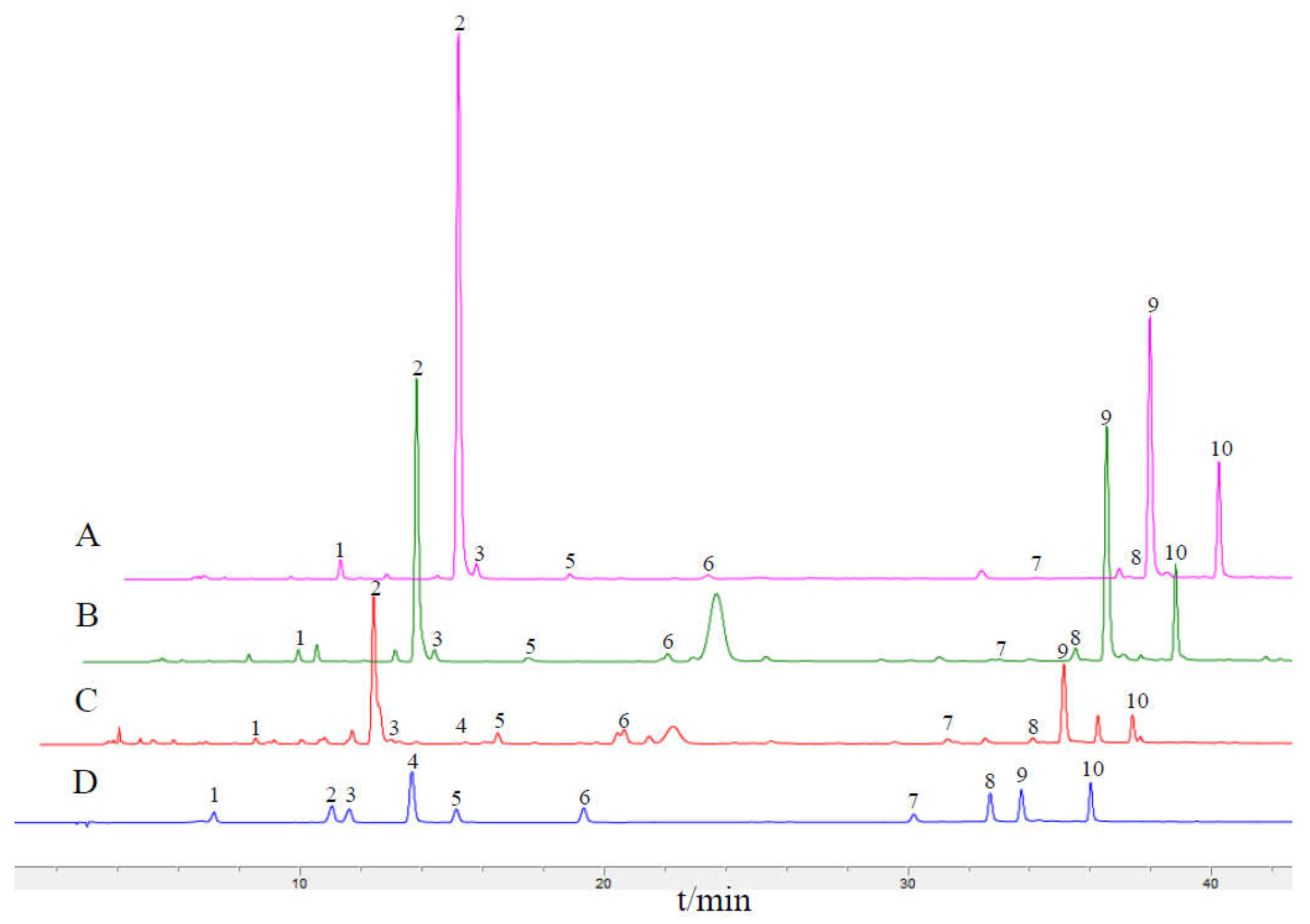
| Species | Genome Size(bp) | LSC Region (bp) | IR Region (bp) | SSC Region (bp) | Number of Genes | PCGs | tRNAs | rRNAs | GC Content (%) | Accession Number in Genbank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. japonica | 155,079 | 88,859 | 23,774 | 18,672 | 126 | 82 | 36 | 8 | 38.58 | NC_026839 |
| L. similis | 155,207 | 88,994 | 23,777 | 18,659 | 126 | 82 | 36 | 8 | 38.59 | MZ241297 |
| L. acuminata | 155,330 | 89,149 | 23,760 | 18,661 | 126 | 82 | 36 | 8 | 38.55 | MZ901373 |
| Botanical Traits | L. japonica | L. similis | L. acuminata |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color and glandular hairs | Surface yellow-white or green-white, densely pubescent | Surface yellow-green, green-brown or yellow-brown, covered with long, short coarse or glandular hairs, some glabrous | Surface yellow-green, brown-yellow, pale-purple to purplish-brown, glabrous or sparse |
| Shape | Rod-shaped, slightly curved, 2–3 cm long, upper diameter about 3 mm, lower 1.5 mm | Slender rod-shaped, slightly curved, 3–6 cm long, slightly inflated above, upper diameter 1.8–2 mm, lower 1.2–1.5 mm | Short rod-shaped, 1–2 cm long, distally expanded, upper diameter 1.5–3.5 mm, lower 0.6–1.5 mm |
| Smell and taste | Fresh scent, light and slightly bitter taste | Fresh scent, light and slightly bitter taste | Fresh scent, light and slightly bitter taste |
| Flower buds and flowers |  |  |  |
| Reference | National Pharmacopoeia Committee, 2020 | Si Chuan Food and Drug Administration, 2011 | Si Chuan Food and Drug Administration, 2011 |
| Species | NA | CA | 4-DA | SW | LS | IA-B | IA-A | IA-C | TPC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. japonica | 0.0773 ± 0.007 | 3.9729 ± 0.0928 | 0.0584 ± 0.0041 | 0.1835 ± 0.0086 | 0.0549 ± 0.0001 | 0.0227 ± 0.0004 | 1.7260 ± 0.0161 | 0.3975 ± 0.0461 | 6.0964 ± 0.1228 |
| L. similis | 0.3098 ± 0.0013 | 14.8953 ± 0.0728 | 0.2749 ± 0.0515 | 0.0729 ± 0.0062 | 0.0291 ± 0.0044 | 0.0603 ± 0.0014 | 5.4567 ± 0.0278 | 1.6262 ± 0.0882 | 21.9782 ± 0.1331 |
| L. acuminata | 0.2462 ± 0.0400 | 7.4631 ± 0.4461 | 0.1519 ± 0.0507 | 0.0852 ± 0.0011 | 0.2248 ± 0.0256 | 0.0613 ± 0.0024 | 5.4267 ± 0.3922 | 1.2156 ± 0.2027 | 14.1055 ± 0.2566 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.; Zhang, N.; Wu, S.; Jiang, C.; Xie, L.; Yang, F.; Yu, Z. A Comparative Analysis of the Chloroplast Genomes of Three Lonicera Medicinal Plants. Genes 2023, 14, 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030548
Yang C, Zhang N, Wu S, Jiang C, Xie L, Yang F, Yu Z. A Comparative Analysis of the Chloroplast Genomes of Three Lonicera Medicinal Plants. Genes. 2023; 14(3):548. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030548
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Chenju, Ni Zhang, Shaoxiong Wu, Chunyan Jiang, Lian Xie, Feng Yang, and Zhengwen Yu. 2023. "A Comparative Analysis of the Chloroplast Genomes of Three Lonicera Medicinal Plants" Genes 14, no. 3: 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030548
APA StyleYang, C., Zhang, N., Wu, S., Jiang, C., Xie, L., Yang, F., & Yu, Z. (2023). A Comparative Analysis of the Chloroplast Genomes of Three Lonicera Medicinal Plants. Genes, 14(3), 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030548







