Expression of Connexins 37, 40 and 45, Pannexin 1 and Vimentin in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Study Protocol
2.2. Immunofluorescence
2.3. Quantification and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
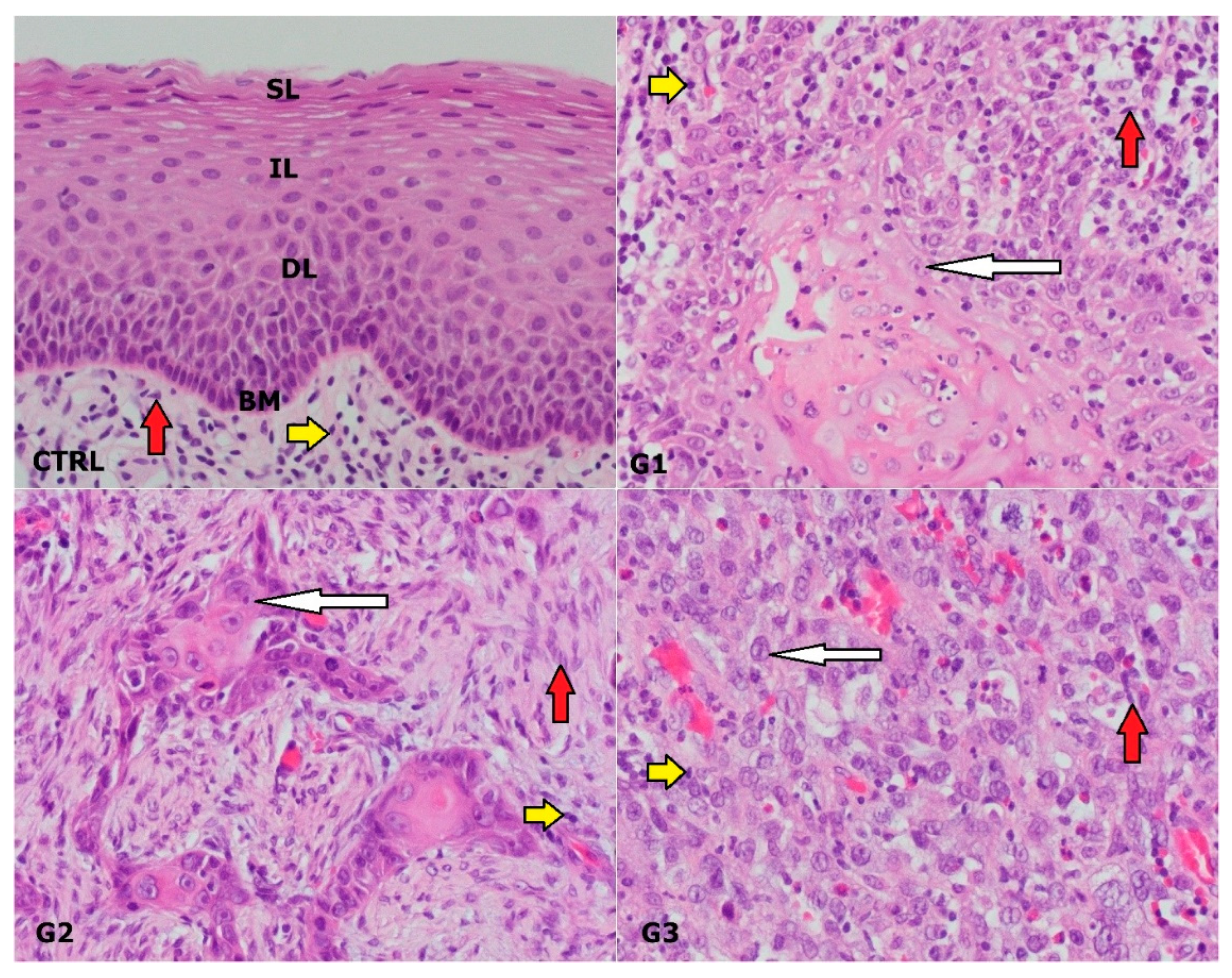
3.1. Clinical and Pathological Characteristics of the Study Sample
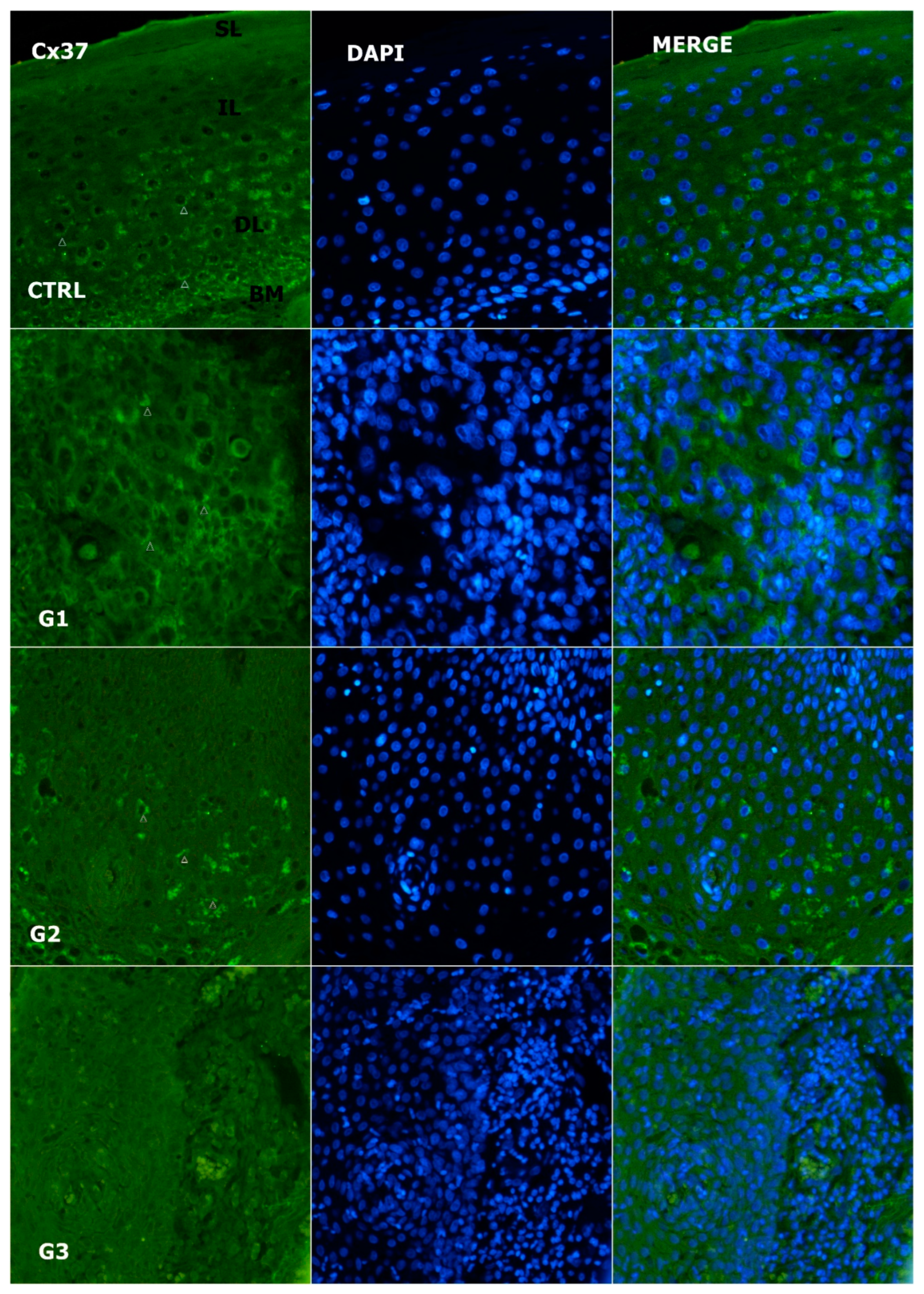
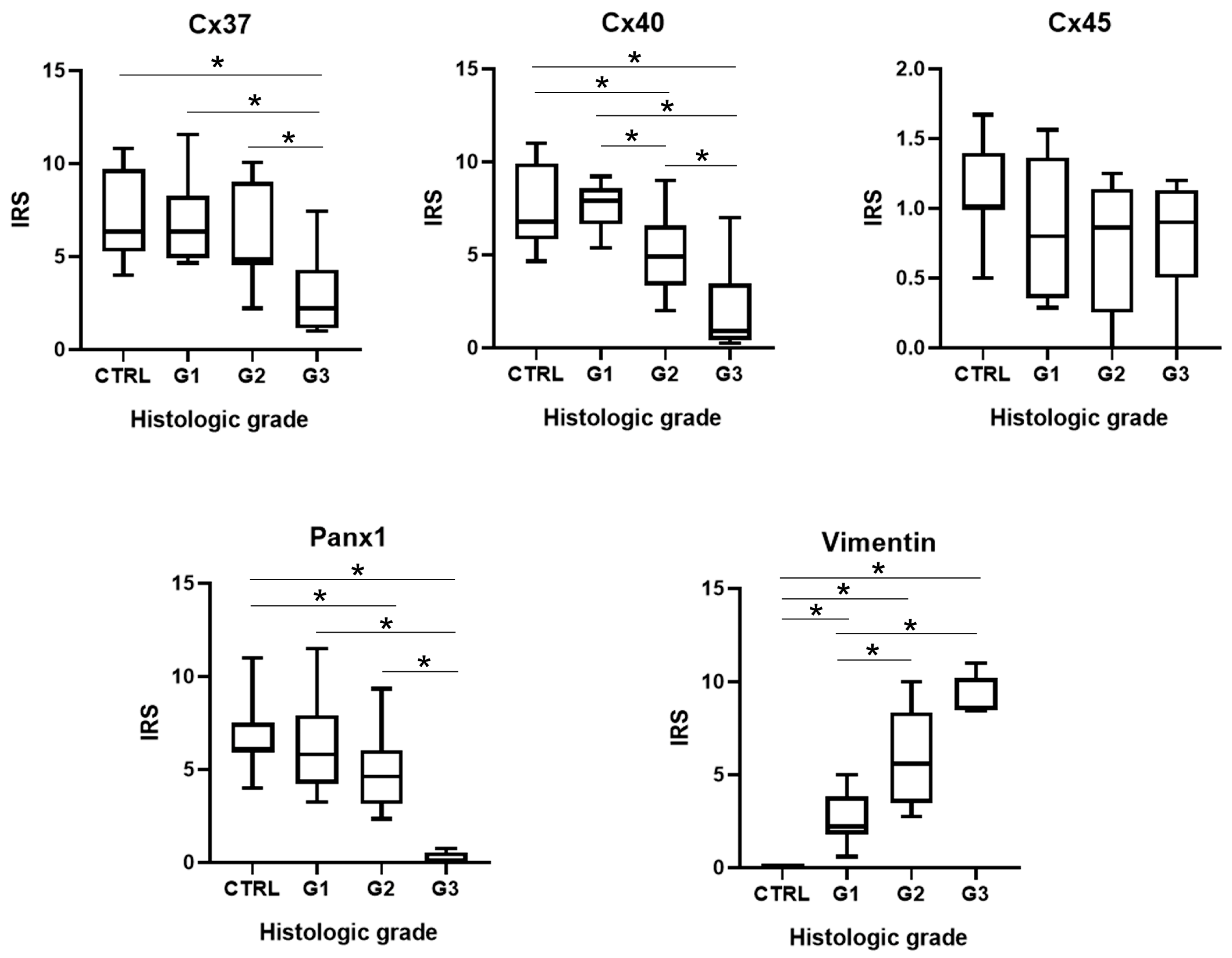
3.2. Expression of Cx37
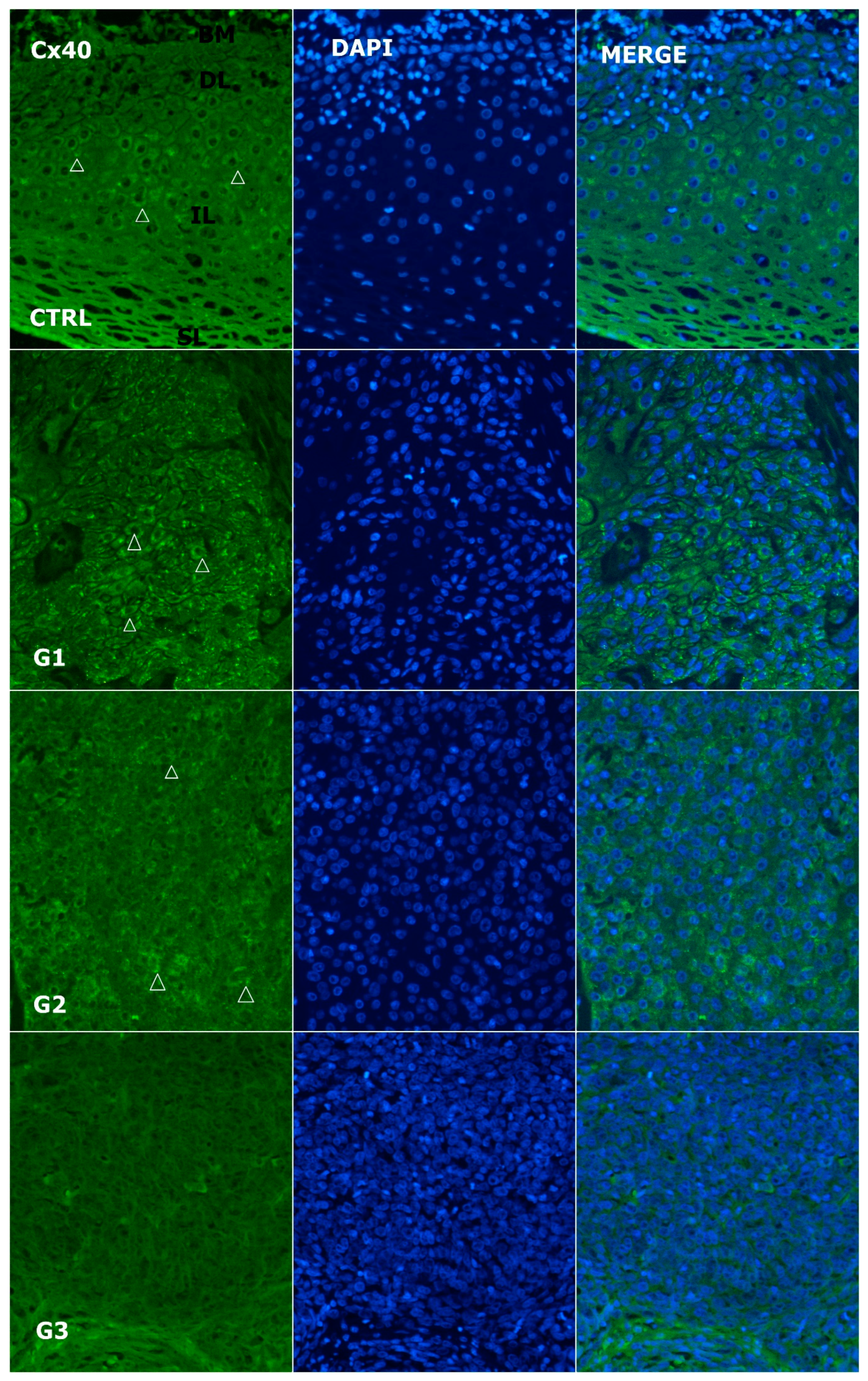
3.3. Alteration of Expression of Cx40
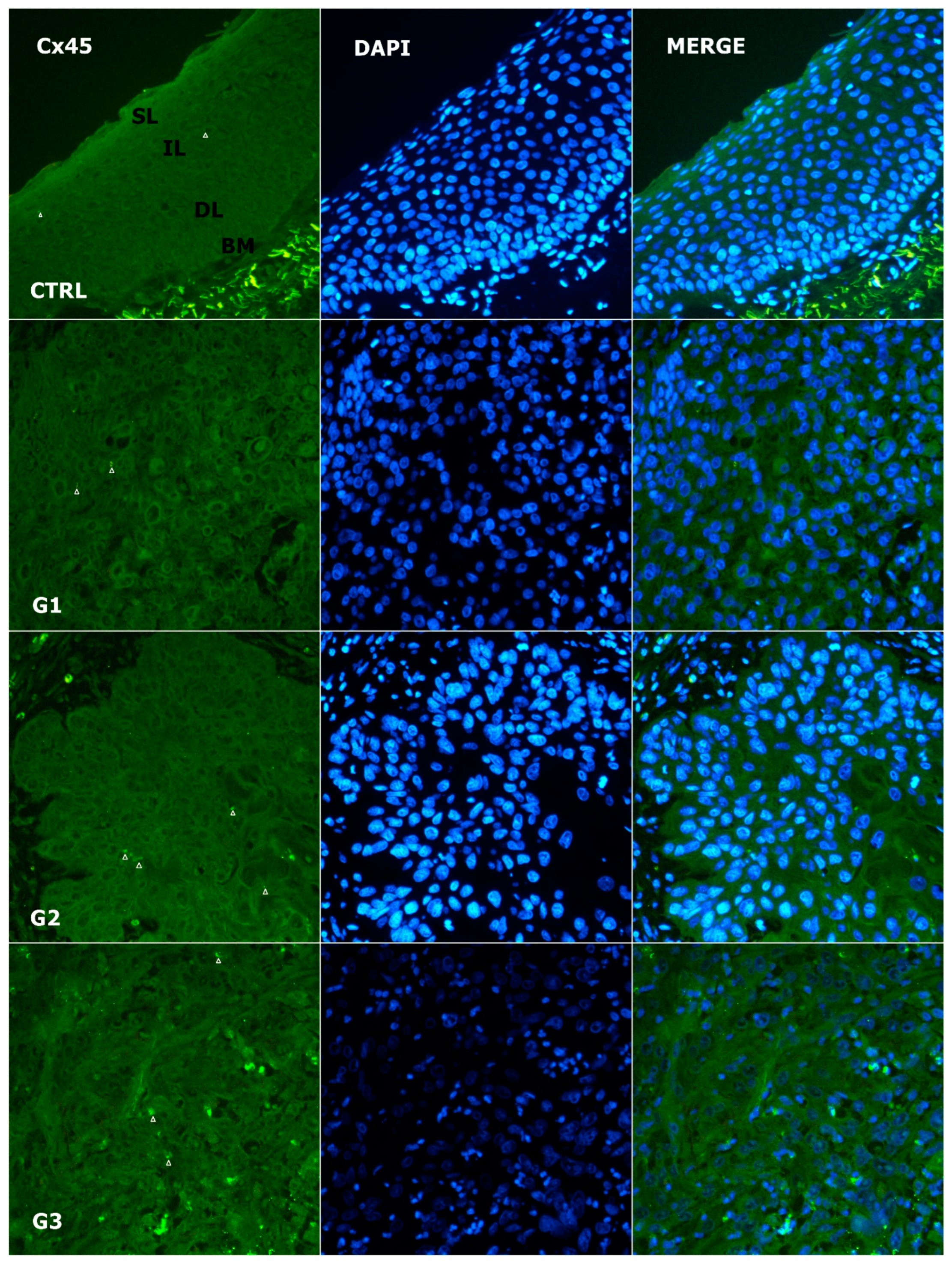
3.4. Alteration of Expression of Cx45
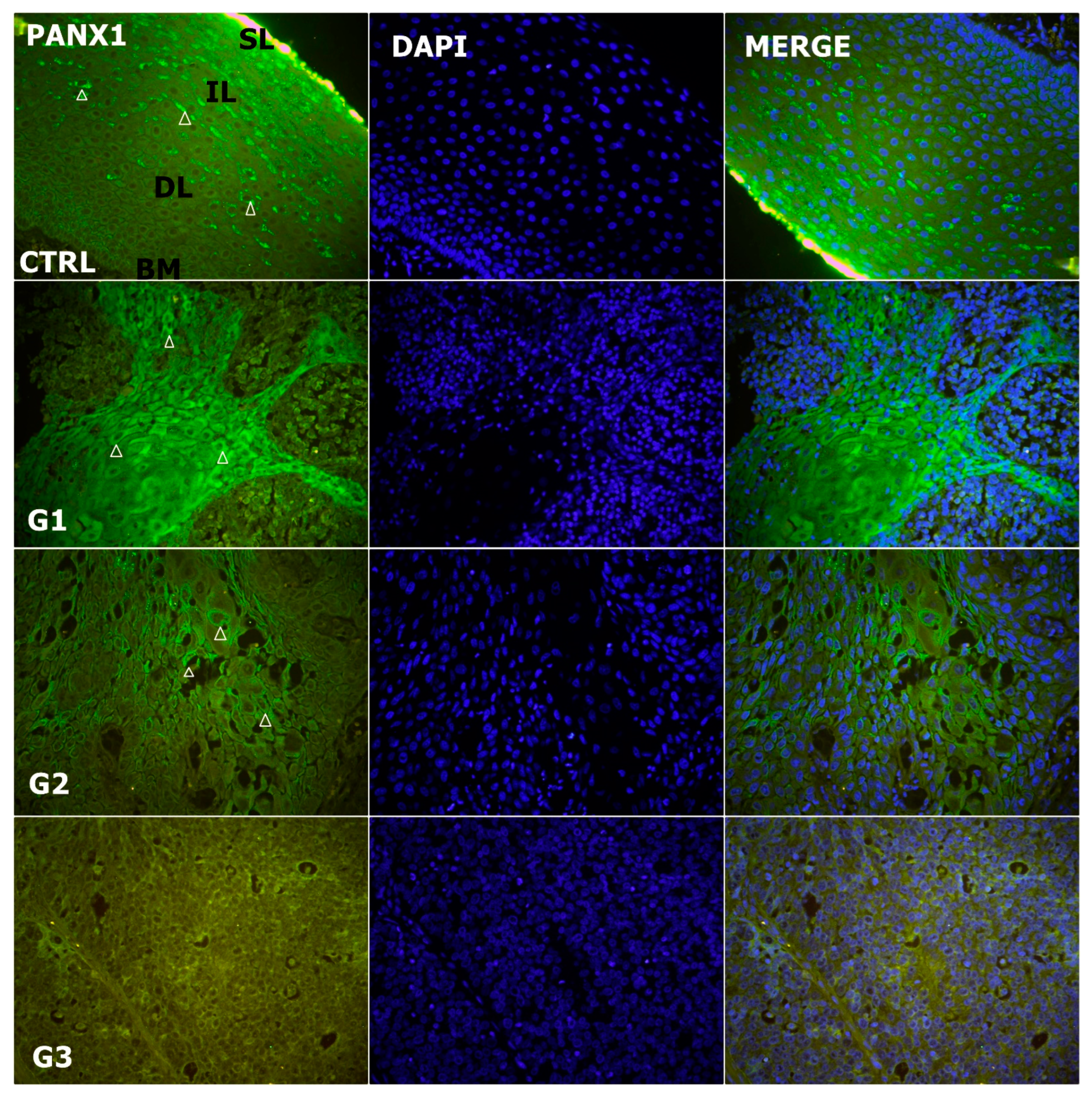
3.5. Alteration of Expression of Panx1
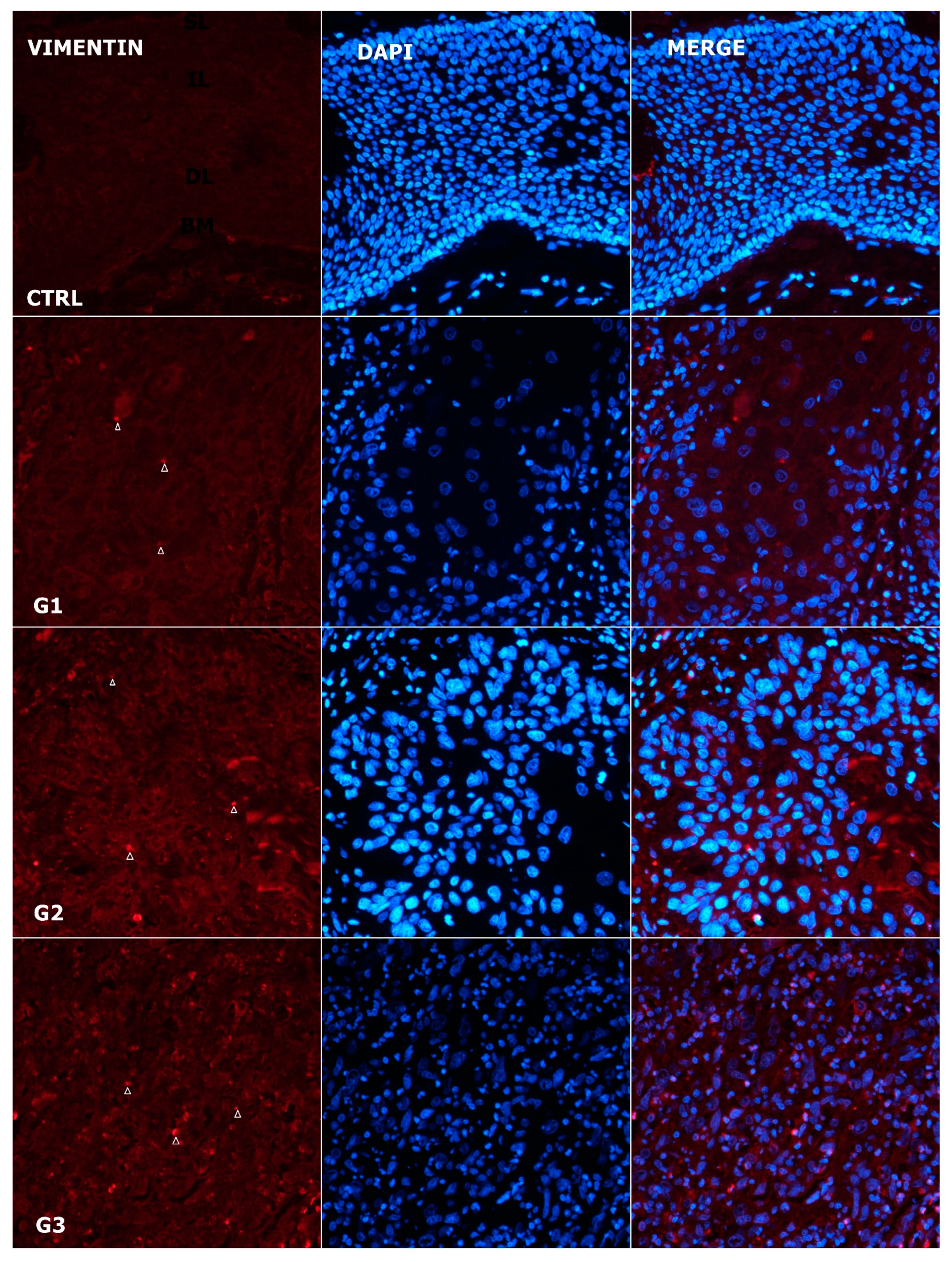
3.6. Expression Pattern of Vimentin
3.7. Alteration in Expression Pattern of Cx37, Cx40, C45, Panx1 and Vimentin in Comparison to Pathological Characteristics
3.8. Diagnostic and Prognostic Role of Cx37, Cx40, Cx45, Panx1 and Vimentin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiodoni, C.; Di Martino, M.T.; Zazzeroni, F.; Caraglia, M.; Donadelli, M.; Meschini, S.; Leonetti, C.; Scotlandi, K. Cell communication and signaling: How to turn bad language into positive one. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willebrords, J.; Crespo Yanguas, S.; Maes, M.; Decrock, E.; Wang, N.; Leybaert, L.; Kwak, B.R.; Green, C.R.; Cogliati, B.; Vinken, M. Connexins and their channels in inflammation. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 51, 413–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinken, M.; Papeleu, P.; Snykers, S.; De Rop, E.; Henkens, T.; Chipman, J.K.; Rogiers, V.; Vanhaecke, T. Involvement of cell junctions in hepatocyte culture functionality. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2006, 36, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinken, M.; Decrock, E.; De Vuyst, E.; Ponsaerts, R.; D’hondt, C.; Bultynck, G.; Ceelen, L.; Vanhaecke, T.; Leybaert, L.; Rogiers, V. Connexins: Sensors and regulators of cell cycling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1815, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinken, M. Gap junctions and non-neoplastic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurić, M.; Zeitler, J.; Vukojević, K.; Bočina, I.; Grobe, M.; Kretzschmar, G.; Saraga-Babić, M.; Filipović, N. Expression of Connexins 37, 43 and 45 in Developing Human Spinal Cord and Ganglia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.V.; Jiang, J.X.; Mesnil, M. Connexins and Pannexins: Important Players in Tumorigenesis, Metastasis and Potential Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decrock, E.; De Bock, M.; Wang, N.; Bultynck, G.; Giaume, C.; Naus, C.C.; Green, C.R.; Leybaert, L. Connexin and pannexin signaling pathways, an architectural blueprint for CNS physiology and pathology? Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 2823–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.X.; Penuela, S. Connexin and pannexin channels in cancer. BMC Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasen, T.; Leithe, E.; Graham, S.V.; Kameritsch, P.; Mayán, M.D.; Mesnil, M.; Pogoda, K.; Tabernero, A. Connexins in cancer: Bridging the gap to the clinic. Oncogene 2019, 38, 4429–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirnes, S.; Lind, G.E.; Bruun, J.; Fykerud, T.A.; Mesnil, M.; Lothe, R.A.; Rivedal, E.; Kolberg, M.; Leithe, E. Connexins in colorectal cancer pathogenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.W.; Demarco, B.; Heilig, R.; Shkarina, K.; Boettcher, A.; Farady, C.J.; Pelczar, P.; Broz, P. Extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis activate pannexin-1 to drive NLRP3 inflammasome assembly. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e101638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Locovei, S.; Dahl, G. Pannexin membrane channels are mechanosensitive conduits for ATP. FEBS Lett. 2004, 572, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, L.; Wu, D.; Chen, L.; Jiang, Z. Pannexin-1 channels and their emerging functions in cardiovascular diseases. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2015, 47, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penuela, S.; Harland, L.; Simek, J.; Laird, D.W. Pannexin channels and their links to human disease. Biochem. J. 2014, 461, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, J.; Sun, X.; Li, B.; Yan, Z.; Xue, S.; Ai, A.; Lyu, Q.; Li, W.; et al. A pannexin 1 channelopathy causes human oocyte death. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaav8731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, S.R.; Naus, C.C. The pannexins: Past and present. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Charles, E.J.; Zhao, Y.; Narahari, A.K.; Baderdinni, P.K.; Good, M.E.; Lorenz, U.M.; Kron, I.L.; Bayliss, D.A.; Ravichandran, K.S.; et al. Pannexin-1 channels on endothelial cells mediate vascular inflammation during lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2018, 315, L301–L312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douanne, T.; André-Grégoire, G.; Trillet, K.; Thys, A.; Papin, A.; Feyeux, M.; Hulin, P.; Chiron, D.; Gavard, J.; Bidère, N. Pannexin-1 limits the production of proinflammatory cytokines during necroptosis. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e47840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanden Abeele, F.; Bidaux, G.; Gordienko, D.; Beck, B.; Panchin, Y.V.; Baranova, A.V.; Ivanov, D.V.; Skryma, R.; Prevarskaya, N. Functional implications of calcium permeability of the channel formed by pannexin 1. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 174, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.H.; Jin, X.; Medina, C.B.; Leonhardt, S.A.; Kiessling, V.; Bennett, B.C.; Shu, S.; Tamm, L.K.; Yeager, M.; Ravichandran, K.S.; et al. A quantized mechanism for activation of pannexin channels. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groome, P.A.; O’Sullivan, B.; Irish, J.C.; Rothwell, D.M.; Schulze, K.; Warde, P.R.; Schneider, K.M.; Mackenzie, R.G.; Hodson, D.I.; Hammond, J.A.; et al. Management and outcome differences in supraglottic cancer between Ontario, Canada, and the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results areas of the United States. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spector, J.G.; Sessions, D.G.; Haughey, B.H.; Chao, K.S.; Simpson, J.; El Mofty, S.; Perez, C.A. Delayed regional metastases, distant metastases, and second primary malignancies in squamous cell carcinomas of the larynx and hypopharynx. Laryngoscope 2001, 111, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naipal, K.A.T.; Raams, A.; Bruens, S.T.; Brandsma, I.; Verkaik, N.S.; Jaspers, N.G.J.; Hoeijmakers, J.H.J.; van Leenders, G.J.L.H.; Pothof, J.; Kanaar, R.; et al. Attenuated XPC Expression Is Not Associated with Impaired DNA Repair in Bladder Cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, R.M.; Razzaq, F.; Akbar, A.; Farooqui, A.A.; Iftikhar, A.; Latif, A.; Hassan, H.; Zhao, J.; Carew, J.S.; Nawrocki, S.T.; et al. Role and mechanism of autophagy-regulating factors in tumorigenesis and drug resistance. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 17, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Xu, Y.; Ding, T.; Zu, Y.; Yang, C.; Yu, L. Pairing of integrins with ECM proteins determines migrasome formation. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1397–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamagkiolas, S.; Giotakis, I.; Kyrodimos, E.; Giotakis, E.I.; Kataki, A.; Karagianni, F.; Lazaris, A.M. Expression of vimentin (VIM) and metastasis-associated 1 (MTA1) protein in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma are associated with prognostic outcome of patients. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2019, 40, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzzo, L.; Caltabiano, R.; Parenti, R.; Trapasso, S.; Allegra, E. Connexin 43 (Cx43) Expression in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas: Preliminary Data on Its Possible Prognostic Role. Head Neck Pathol. 2016, 10, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, B.; Teschner, M.; Sudermann, T.; Pikula, B.; Lautermann, J. Expression of gap junction proteins (connexin 26, 30, 32, 43) in normal mucosa, hyperkeratosis and carcinoma of the human larynx. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2002, 64, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Xie, D.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, X.; Xia, K.; Liu, F.; Huang, B. The expressions and clinical significance of tumor suppressor gene CX26 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2008, 22, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Mulkearns-Hubert, E.E.; Reizes, O.; Lathia, J.D. Connexins in Cancer: Jekyll or Hyde? Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.P.; Bechberger, J.F.; Thompson, R.J.; MacVicar, B.A.; Bruzzone, R.; Naus, C.C. Tumor-suppressive effects of pannexin 1 in C6 glioma cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalper, K.A.; Carvajal-Hausdorf, D.; Oyarzo, M.P. Possible role of hemichannels in cancer. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, K.N.; Langlois, S.; Penuela, S.; Cowan, B.J.; Laird, D.W. Pannexin1 and Pannexin3 exhibit distinct localization patterns in human skin appendages and are regulated during keratinocyte differentiation and carcinogenesis. Cell Commun. Adhes. 2012, 19, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, C.R.; Ferlito, A.; Devaney, K.O.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Rinaldo, A. Prognostic factors in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2020, 5, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, M.; Gioacchini, F.M.; Scarpa, A.; Cassandro, C.; Tulli, M.; Cassandro, E. The prognostic significance of E-cadherin expression in laryngeal squamous-cell carcinoma: A systematic review. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2018, 38, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioacchini, F.M.; Alicandri-Ciufelli, M.; Magliulo, G.; Rubini, C.; Presutti, L.; Re, M. The clinical relevance of Ki-67 expression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 272, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioacchini, F.M.; Alicandri-Ciufelli, M.; Rubini, C.; Magliulo, G.; Re, M. Prognostic value of Bcl-2 expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx: A systematic review. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2015, 30, e155-60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machiels, J.P.; René Leemans, C.; Golusinski, W.; Grau, C.; Licitra, L.; Gregoire, V. Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity, larynx, oropharynx and hypopharynx: EHNS-ESMO-ESTRO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1462–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antibodies | Host | Dilution | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Anti-Cx 37/GJA4 ab 181701 | Rabbit | 1:100 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) |
| Anti-Cx40/ GJA5 ab213688 | Rabbit | 1:100 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | |
| Anti-Cx 45/GJA7 ab135474 | Rabbit | 1:100 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | |
| Anti-pannexin 1/PANX1 | Rabbit | 1:300 | Temecula California 92590 ABN 242 | |
| Anti-vimentin ab11256 | Goat | 1:300 | R & D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA | |
| Secondary | Anti-Rabbit IgG Alexa Fluor 488 711-545-152 | Donkey | 1:400 | Molecular Probes Life Technologies, Eugene, OR, USA |
| Anti-Sheep IgG Rhodamine Red 713-295-003 | Donkey | 1:400 | Jackson Immuno Research Laboratories, Inc. (Baltimore, PA, USA) | |
| Parameter | Grade 1 N = 10 | Grade 2 N = 12 | Grade 3 N = 10 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 67.5 (51–84) | 67 (47–82) | 68 (43–80) | 0.996 * | |
| Sex | Male | 9 | 11 | 9 | 0.177 ** |
| Female | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Localization of cancer | Glottic | 8 | 3 | 1 | 0.012 ** |
| Supraglottic | 1 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Transglottic | 1 | 7 | 7 | ||
| Tumor volume Median (min–max) | cm3 | 3.455 (0.280–36) | 6 (0.245–10.500) | 5 (2–48) | 0.540 * |
| Lymphovascular invasion | yes | 0 | 4 | 8 | 0.049 ** |
| no | 10 | 8 | 2 | ||
| TNM | T1 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0.003 ** |
| T2 | 3 | 2 | 0 | ||
| T3 | 2 | 9 | 5 | ||
| T4 | 1 | 0 | 5 | ||
| N pos. | 9 | 8 | 5 | 0.047 ** | |
| N neg. | 1 | 4 | 5 | ||
| M neg. | 10 | 12 | 10 | 0.031 ** | |
| M pos. | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Stage | Early (I + II) | 7 | 3 | 0 | 0.001 ** |
| Advanced (III + IV) | 3 | 9 | 10 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mizdrak, I.; Mizdrak, M.; Racetin, A.; Bošković, B.; Benzon, B.; Durdov, M.G.; Vukojević, K.; Filipović, N. Expression of Connexins 37, 40 and 45, Pannexin 1 and Vimentin in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Genes 2023, 14, 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020446
Mizdrak I, Mizdrak M, Racetin A, Bošković B, Benzon B, Durdov MG, Vukojević K, Filipović N. Expression of Connexins 37, 40 and 45, Pannexin 1 and Vimentin in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Genes. 2023; 14(2):446. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020446
Chicago/Turabian StyleMizdrak, Ivan, Maja Mizdrak, Anita Racetin, Braco Bošković, Benjamin Benzon, Merica Glavina Durdov, Katarina Vukojević, and Natalija Filipović. 2023. "Expression of Connexins 37, 40 and 45, Pannexin 1 and Vimentin in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas" Genes 14, no. 2: 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020446
APA StyleMizdrak, I., Mizdrak, M., Racetin, A., Bošković, B., Benzon, B., Durdov, M. G., Vukojević, K., & Filipović, N. (2023). Expression of Connexins 37, 40 and 45, Pannexin 1 and Vimentin in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Genes, 14(2), 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020446






