Genome Identification of the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) ASMT Gene Family and Its Expression Analysis under Abiotic Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Treatment
2.2. Genome-Wide Identification of ASMT Proteins in C. sinensis
2.3. Phylogenetic and Structural Analyses of C. sinensis ASMT Genes
2.4. Analysis of C. sinensis ASMT Motifs and Promoter Cis-Acting Elements
2.5. Chromosome Localization and Collinearity Analysis
2.6. Expression Profiling of ASMT Family Genes in C. sinensis
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time Fluorescence Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genome-Wide Identification of ASMT Genes in C. sinensis
3.2. Systematic Analysis and Conserved Motifs of C. sinensis ASMT Genes
3.3. Chromosome Distribution and Collinearity Analysis
3.4. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements of the C. sinensis ASMT Promoter
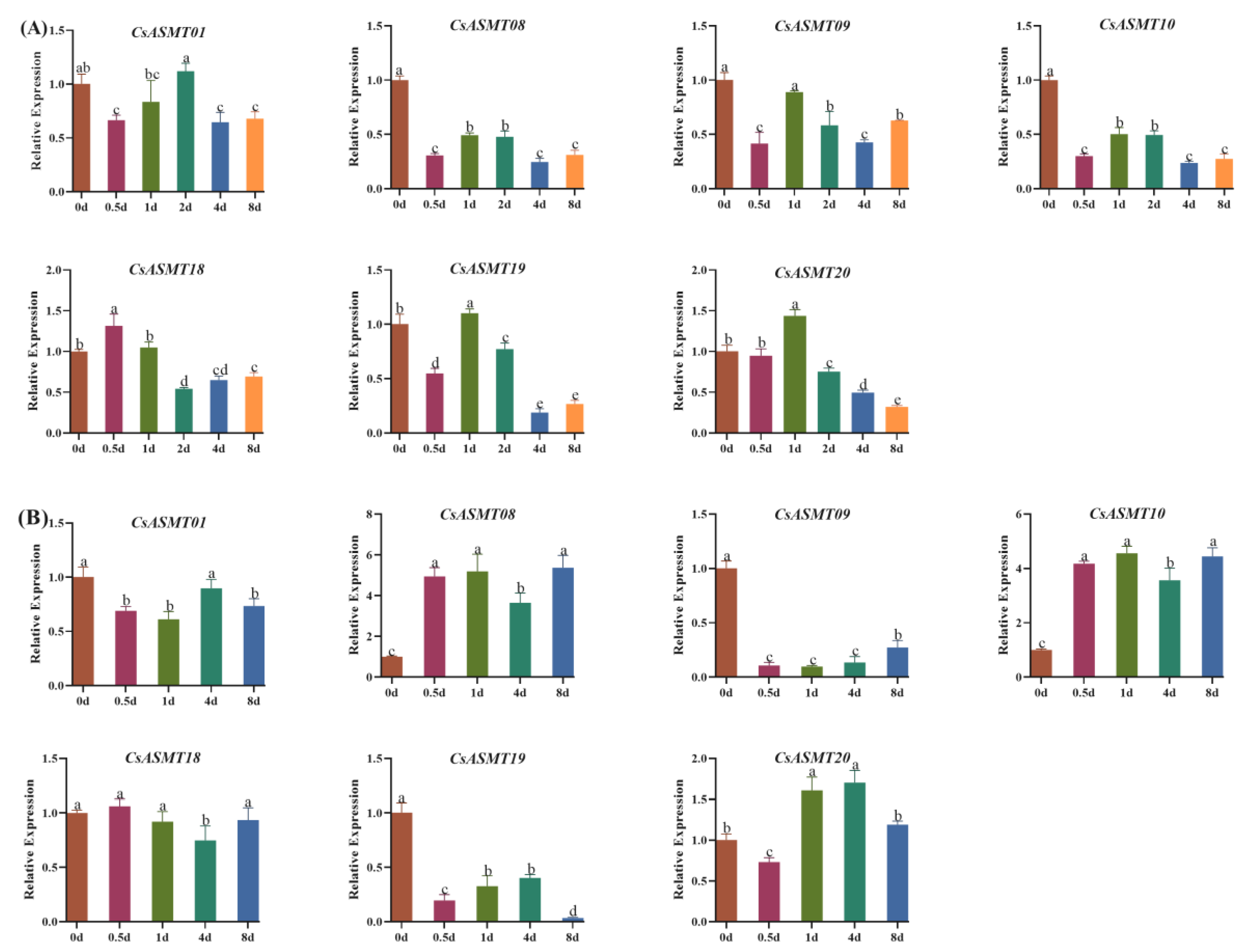
3.5. Expression Profiles of CsASMT Genes under Different Types of Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kobylińska, A.; Borek, S.; Posmyk, M.M. Melatonin redirects carbohydrates metabolism during sugar starvation in plant cells. J. Pineal Res. 2018, 64, e12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Brestic, M.; Tan, D.X.; Zivcak, M.; Zhu, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, F. Melatonin alleviates low PS I-limited carbon assimilation under elevated CO2 and enhances the cold tolerance of offspring in chlorophyll b-deficient mutant wheat. J. Pineal Res. 2018, 64, e12453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano, A.; Alcaraz, O.; Arnao, M.B. Free radical-scavenging activity of indolic compounds in aqueous and ethanolic media. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 376, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.-X.; Manchester, L.C.; Helton, P.; Reiter, R.J. Phytoremediative Capacity of Plants Enriched with Melatonin. Plant Signal. Behav. 2007, 2, 514–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.-X.; Manchester, L.C.; Reiter, R.J.; Qi, W.-B.; Karbownik, M.; Calvo, J.R. Significance of Melatonin in Antioxidative Defense System: Reactions and Products. Neurosignals 2000, 9, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tassel, D.L.; O’Neill, S.D. Putative regulatory molecules in plants: Evaluating melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 2001, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Byeon, Y.; Back, K. Melatonin as a signal molecule triggering defense responses against pathogen attack in Arabidopsis and tobacco. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Tan, D.-X.; Reiter, R.J.; Ye, T.; Yang, F.; Chan, Z. Melatonin induces class A1 heat-shock factors (HSFA1s) and their possible involvement of thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 58, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-J.; Zhang, N.; Yang, R.-C.; Wang, L.; Sun, Q.-Q.; Li, D.-B.; Cao, Y.-Y.; Weeda, S.; Zhao, B.; Ren, S.; et al. Melatonin promotes seed germination under high salinity by regulating antioxidant systems, ABA and GA4 interaction in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, L.; Su, T.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, L.; Ma, F. Melatonin regulates carbohydrate metabolism and defenses against Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC 3000 infection in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 59, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Choi, G.H.; Back, K. Cadmium-induced melatonin synthesis in rice requires light, hydrogen peroxide, and nitric oxide: Key regulatory roles for tryptophan decarboxylase and caffeic acid O-methyltransferase. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 63, e12441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Feng, C.; Zheng, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, F.; Shan, D.; Liu, X.; Kong, J. Plant mitochondria synthesize melatonin and enhance the tolerance of plants to drought stress. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 63, e12429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.-H.; Huang, B.; Ding, C.-B.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Chen, Y.-E.; Hu, C.; Zhou, L.-J.; Huang, Y.; Liao, J.-Q.; Yuan, S.; et al. Effects of Melatonin on Anti-oxidative Systems and Photosystem II in Cold-Stressed Rice Seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnao, M.B.; Hernández-Ruiz, J. Melatonin: Plant growth regulator and/or biostimulator during stress? Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L. Melatonin: A Multifunctional Factor in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Lee, H.Y.; Back, K. Rice histone deacetylase 10 and Arabidopsis histone deacetylase 14 genes encode N-acetylserotonin deacetylase, which catalyzes conversion of N-acetylserotonin into serotonin, a reverse reaction for melatonin biosynthesis in plants. J. Pineal Res. 2018, 64, e12460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, C.; Chen, C.; Peng, X.; Cheng, Y.; Wan, H. Genomic analysis of the ASMT gene family in Solanum lycopersicum. Molecules 2017, 22, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-K. Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zheng, J.; Liu, J.; Guo, J.; Liu, F.; Liu, L.; Wan, H. Analysis of the ASMT gene family in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.): Identification, phylogeny, and expression profiles. Int. J. Genom. 2019, 2019, 7241096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Song, C.; Fang, S.; Wang, Z.; Song, S.; Jiao, J.; Wang, M.; Zheng, X.; Bai, T. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the ASMT gene family reveals their role in abiotic stress tolerance in apple. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 293, 110683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Xu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Han, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Li, N. Walnut N-Acetylserotonin Methyltransferase Gene Family Genome-Wide Identification and Diverse Functions Characterization during Flower Bud Development. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, C.; Fan, W.; Xiang, Z.; Zhao, A. Genome-wide identification and characterization of genes involved in melatonin biosynthesis in Morus notabilis (wild mulberry). Phytochemistry 2021, 189, 112819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.; Kong, K.; Park, S.; Natsagdorj, U.; Kim, Y.S.; Back, K. Molecular cloning of a plant N-acetylserotonin methyltransferase and its expression characteristics in rice. J. Pineal Res. 2011, 50, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Byeon, Y.; Back, K. Functional analyses of three ASMT gene family members in rice plants. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 55, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, B.; Zheng, X.; He, P.; Wang, L.; Lei, Q.; Feng, C.; Zhou, J.; Li, Q.; Han, Z.; Kong, J. Overexpression of MzASMT improves melatonin production and enhances drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plants. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, H.R.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lim, Y.J.; Duan, S.; Eom, S.H.; Jung, K.-H. Key Genes in the Melatonin Biosynthesis Pathway with Circadian Rhythm Are Associated with Various Abiotic Stresses. Plants 2021, 10, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, Y.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.Y.; Back, K. Back Cloning and functional characterization of the Arabidopsis N-acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase responsible for melatonin synthesis. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 60, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.Q.; Wang, J.; Wong, G.K.S.; Yu, J. KaKs_Calculator: Calculating Ka and Ks through model selection and model averaging. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2006, 4, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, G.; Wolfe, K.H. Widespread paleopolyploidy in model plant species inferred from age distributions of duplicate genes. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, S.K.; Howlader, P. Melatonin plays multifunctional role in horticultural crops against environmental stresses: A review. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 176, 104063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, G.; Bradnam, K.; Rose, A.B.; Korf, I. Comparative and functional analysis of intron-mediated enhancement signals reveals conserved features among plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 5328–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sémon, M.; Wolfe, K.H. Consequences of genome duplication. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2007, 17, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J. Evolution by gene duplication: An update. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.C.; Purugganan, M.D. The early stages of duplicate gene evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15682–15687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ni, Y.; Qiao, T.; Ji, X.; Xu, J.; Li, B.; Sun, Q. Overexpression of VvASMT1 from grapevine enhanced salt and osmotic stress tolerance in Nicotiana benthamiana. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.R. Drought inducible OsDhn1 promoter is activated by OsDREB1A and OsDREB1D. J. Plant Biol. 2013, 56, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Jan, A.; Todaka, D.; Maruyama, K.; Goto, S.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Comparative functional analysis of six drought-responsive promoters in transgenic rice. Planta 2014, 239, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, L.; An, H.; Wu, C.; Guo, X. GhMPK16, a novel stress-responsive group D MAPK gene from cotton, is involved in disease resistance and drought sensitivity. BMC Mol. Biol. 2011, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


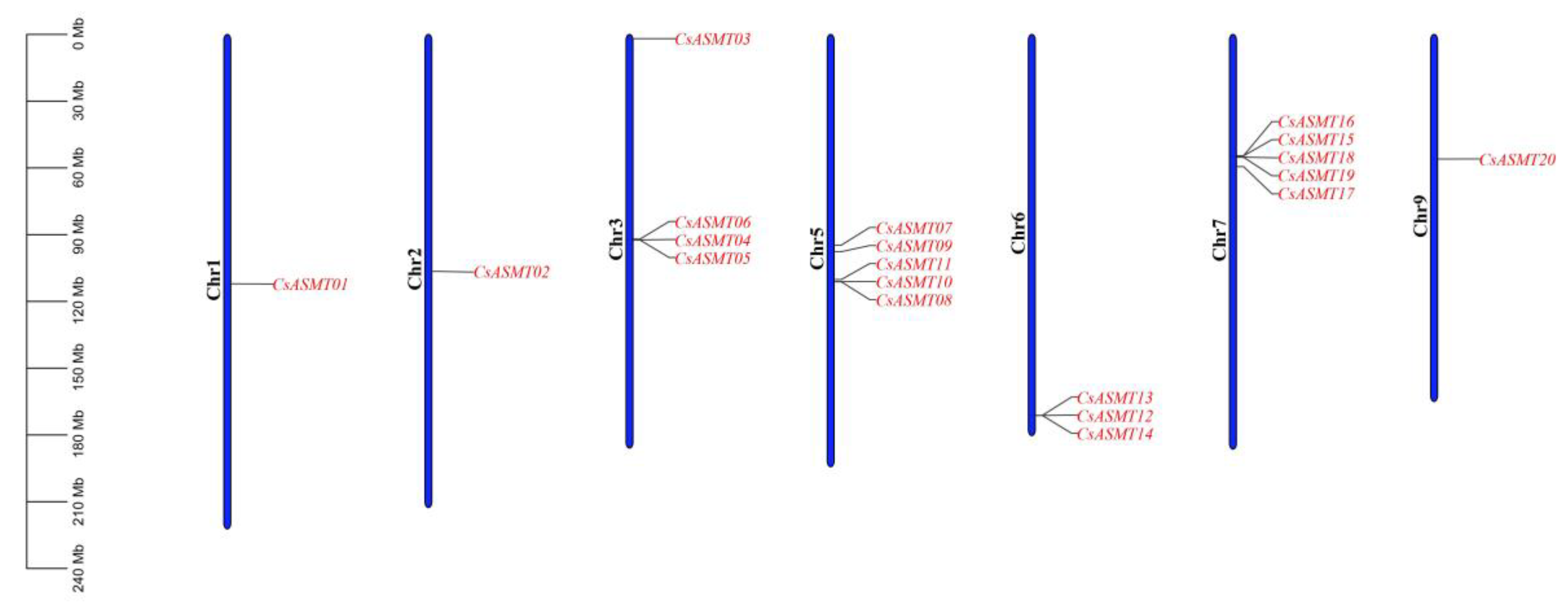
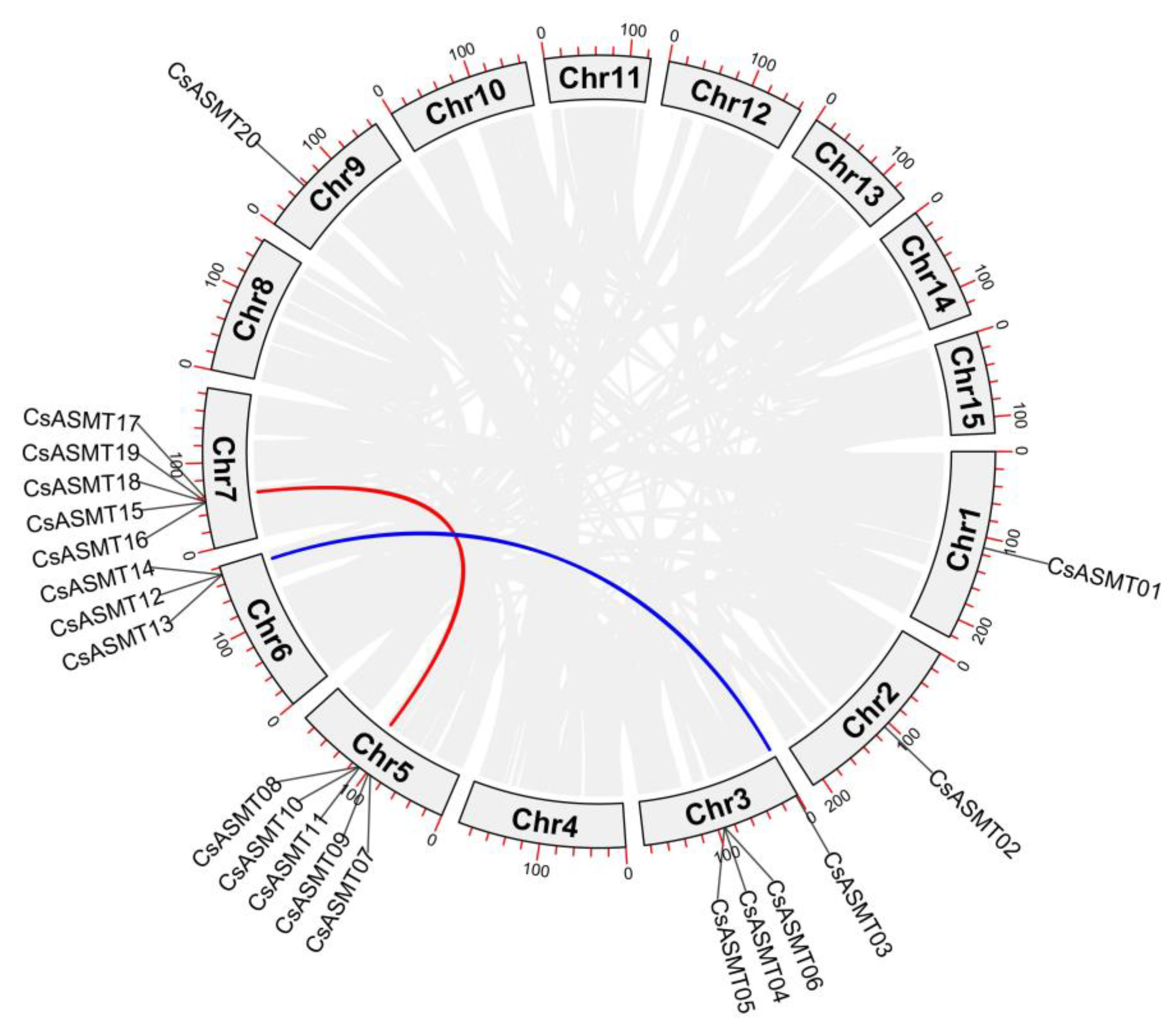


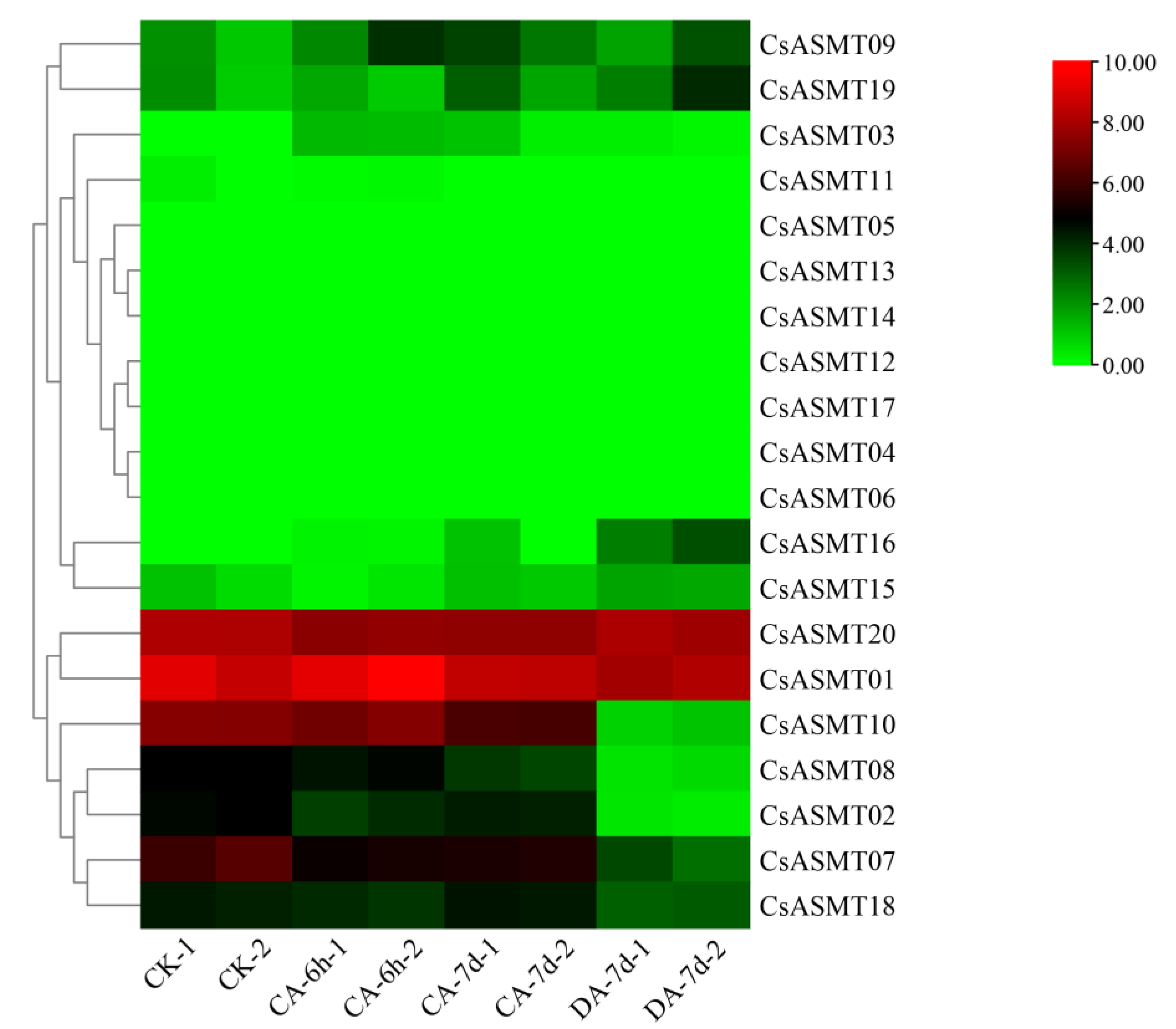
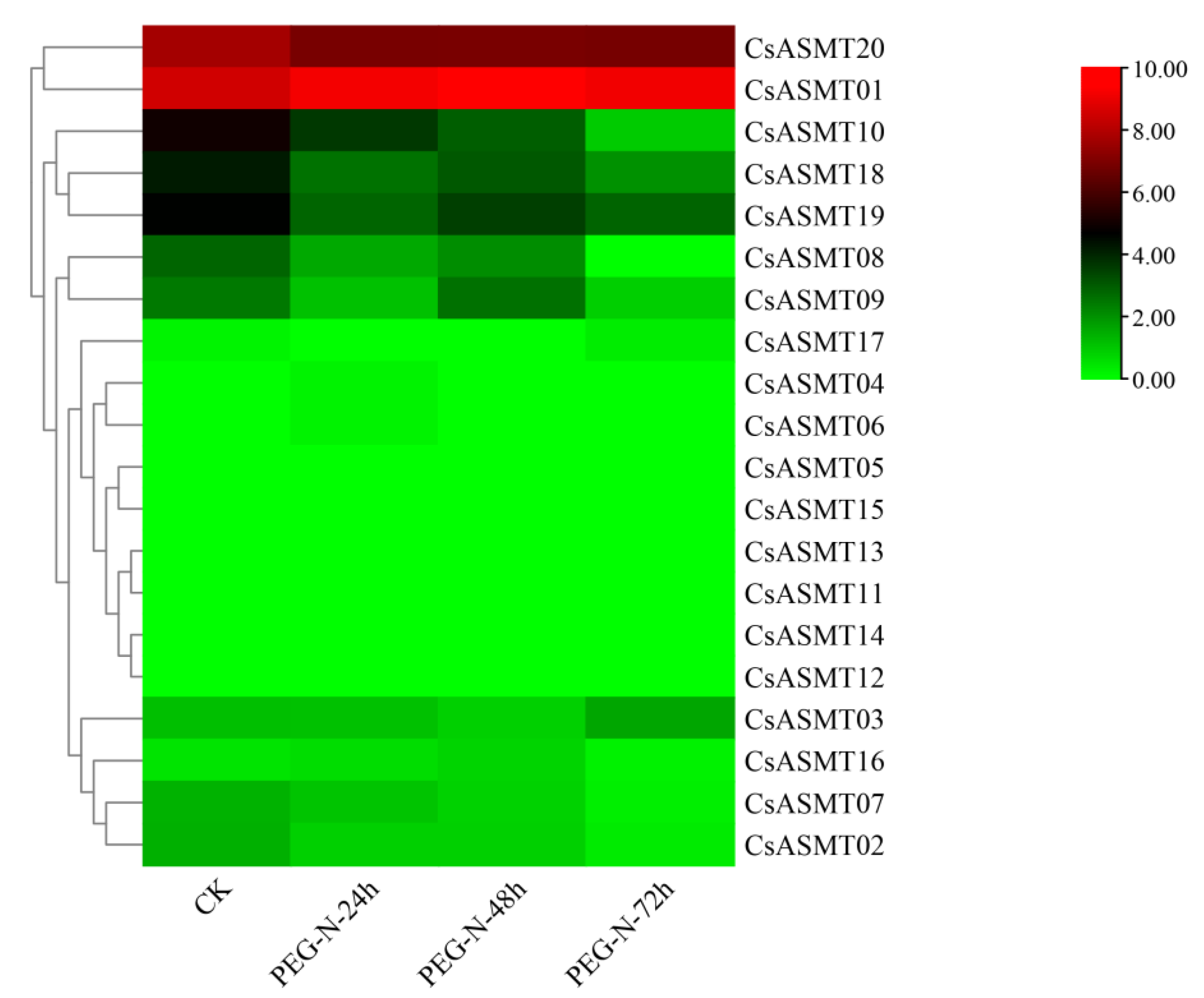
| Gene Name | Gene ID | Group | Chr | Location | AA | MW | pI | ORF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CsASMT01 | CSS0048493 | III | Chr1 | 112085937-112091308 | 351 | 38.32 | 5.94 | 1056 |
| CsASMT02 | CSS0025746 | I | Chr2 | 106494711-106504385 | 319 | 34.95 | 5.64 | 960 |
| CsASMT03 | CSS0006416 | III | Chr3 | 1899577-1901052 | 350 | 38.66 | 5.49 | 1107 |
| CsASMT04 | CSS0037320 | III | Chr3 | 92351303-92356400 | 368 | 39.85 | 5.14 | 1107 |
| CsASMT05 | CSS0039718 | III | Chr3 | 92432006-92437542 | 371 | 40.17 | 4.94 | 1116 |
| CsASMT06 | CSS0037946 | III | Chr3 | 91956040-91961165 | 368 | 39.87 | 5.14 | 1053 |
| CsASMT07 | CSS0007434 | I | Chr5 | 94698511-94711799 | 354 | 39.10 | 5.45 | 1065 |
| CsASMT08 | CSS0003573 | II | Chr5 | 111181605-111186182 | 346 | 38.95 | 5.87 | 1068 |
| CsASMT09 | CSS0006936 | I | Chr5 | 97659841-97664938 | 355 | 39.16 | 5.6 | 888 |
| CsASMT10 | CSS0044619 | II | Chr5 | 111082799-111087666 | 340 | 38.50 | 5.88 | 1023 |
| CsASMT11 | CSS0003281 | II | Chr5 | 110166060-110167265 | 295 | 32.28 | 5.24 | 1041 |
| CsASMT12 | CSS0033599 | III | Chr6 | 171235170-171238679 | 347 | 38.85 | 5.47 | 1044 |
| CsASMT13 | CSS0000080 | III | Chr6 | 171195877-171200372 | 347 | 38.88 | 5.47 | 1044 |
| CsASMT14 | CSS0015347 | III | Chr6 | 171279383-171282903 | 347 | 38.85 | 5.47 | 1044 |
| CsASMT15 | CSS0042551 | I | Chr7 | 54550266-54552772 | 357 | 39.62 | 5.57 | 975 |
| CsASMT16 | CSS0023656 | I | Chr7 | 54505207-54507188 | 324 | 36.28 | 6 | 1074 |
| CsASMT17 | CSS0035451 | II | Chr7 | 59409307-59412279 | 358 | 40.53 | 5.55 | 1074 |
| CsASMT18 | CSS0029228 | I | Chr7 | 55144050-55147115 | 357 | 39.59 | 5.57 | 1182 |
| CsASMT19 | CSS0036567 | I | Chr7 | 55209520-55211648 | 393 | 43.80 | 6.06 | 1077 |
| CsASMT20 | CSS0036494 | III | Chr9 | 56007566-56012718 | 366 | 40.16 | 5.95 | 1101 |
| Gene Name | Gene Name | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks | Date (Million Years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CsASMT03 | CsASMT13 | 0.13 | 0.59 | 0.23 | 17.89 |
| CsASMT10 | CsASMT17 | 0.22 | 1.04 | 0.21 | 34.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, F.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Alam, P.; Zheng, W.; Faizan, M. Genome Identification of the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) ASMT Gene Family and Its Expression Analysis under Abiotic Stress. Genes 2023, 14, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020409
Xu F, Liu W, Wang H, Alam P, Zheng W, Faizan M. Genome Identification of the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) ASMT Gene Family and Its Expression Analysis under Abiotic Stress. Genes. 2023; 14(2):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020409
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Fangfang, Wenxiang Liu, Hui Wang, Pravej Alam, Wei Zheng, and Mohammad Faizan. 2023. "Genome Identification of the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) ASMT Gene Family and Its Expression Analysis under Abiotic Stress" Genes 14, no. 2: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020409
APA StyleXu, F., Liu, W., Wang, H., Alam, P., Zheng, W., & Faizan, M. (2023). Genome Identification of the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) ASMT Gene Family and Its Expression Analysis under Abiotic Stress. Genes, 14(2), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020409








