Delineating the Spectrum of Genetic Variants Associated with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome in Consanguineous Pakistani Pedigrees
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Enrollment of Participants
2.2. Blood Sampling and Clinical History
2.3. Whole Exome Sequencing Data Analysis
2.4. Sanger Sequencing Method
2.5. Computational Analysis for Protein Predictions
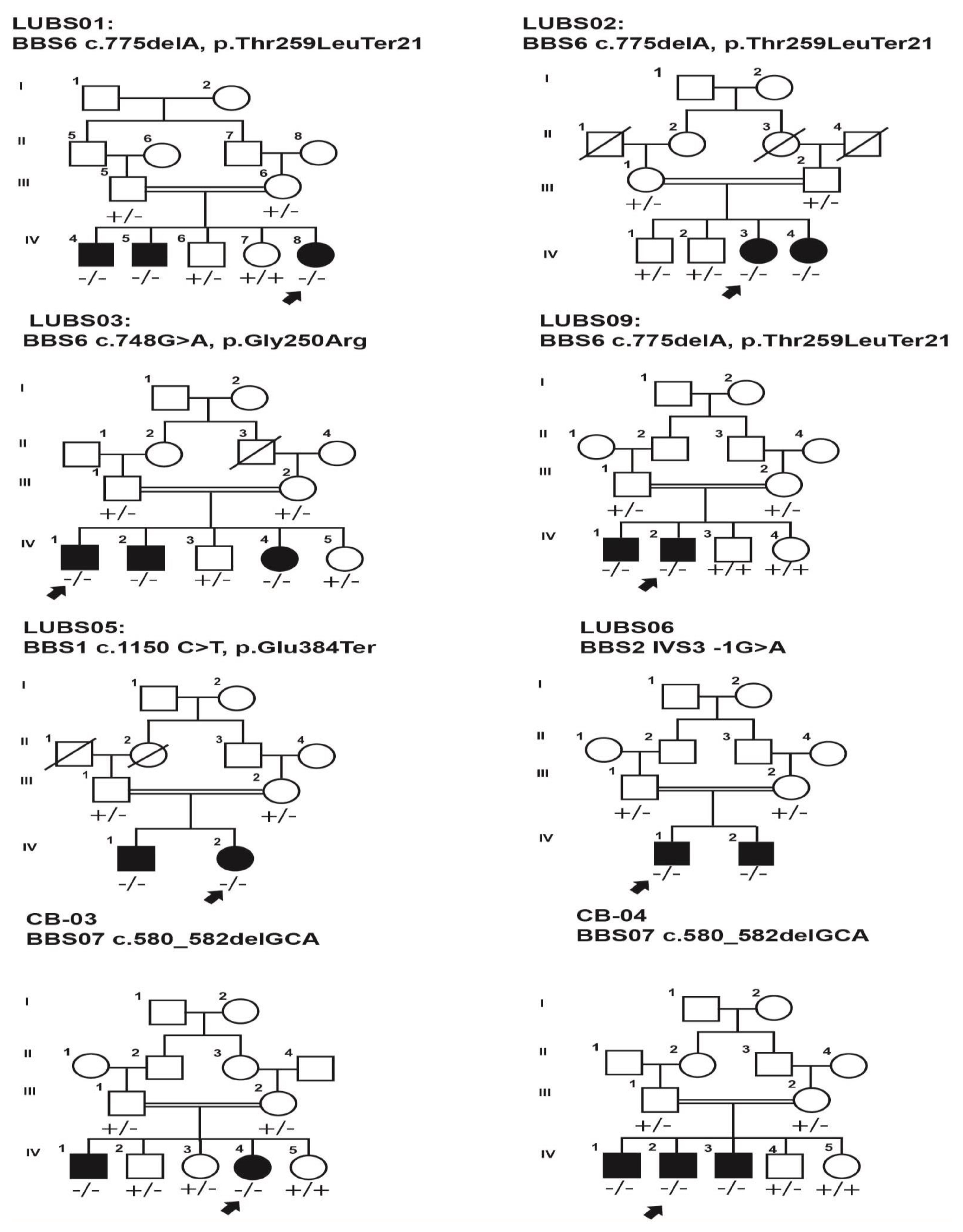
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forsyth, R.; Gunay-Aygun, M. Bardet-Biedl syndrome overview. In GeneReviews; National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Beales, P.L.; Elcioglu, N.; Woolf, A.S.; Parker, D.; Flinter, F. New criteria for improved diagnosis of Bardet-Biedl syndrome: Results of a population survey. J. Med. Genet. 1999, 36, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Hamdi, O.; Ouertani, I.; Chaabouni-Bouhamed, H. Update on the genetics of bardet-biedl syndrome. Mol. Syndromol. 2014, 5, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsythe, E.; Beales, P.L. Bardet–Biedl syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 21, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbari, N.F.; Lewis, J.S.; Bishop, G.A.; Askwith, C.C.; Mykytyn, K. Bardet-Biedl syndrome proteins are required for the localization of G protein-coupled receptors to primary cilia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4242–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederlova, V.; Modrak, M.; Tsyklauri, O.; Huranova, M.; Stepanek, O. Meta-analysis of genotype-phenotype associations in Bardet-Biedl syndrome uncovers differences among causative genes. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 40, 2068–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjortshøj, T.D.; Grønskov, K.; Brøndum-Nielsen, K.; Rosenberg, T. A novel founder BBS1 mutation explains a unique high prevalence of Bardet–Biedl syndrome in the Faroe Islands. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 93, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.J.; Green, J.S.; Fan, Y.; Bhogal, A.K.; Dicks, E.; Fernandez, B.A.; Stefanelli, M.; Murphy, C.; Cramer, B.C.; Dean, J.C.S.; et al. Clinical and genetic epidemiology of Bardet-Biedl syndrome in Newfoundland: A 22-year prospective, population-based, cohort study. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2005, 132A, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teebi, A.S. Autosomal recessive disorders among Arabs: An overview from Kuwait. J. Med. Genet. 1994, 31, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beales, P.L.; Warner, A.M.; Hitman, G.A.; Thakker, R.; Flinter, F.A. Bardet-Biedl syndrome: A molecular and phenotypic study of 18 families. J. Med. Genet. 1997, 34, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D.; Ammann, F. The syndrome of Laurence-Moon-Bardet-Biedl and allied diseases in Switzerland. Clinical, genetic and epidemiological studies. J. Neurol. Sci. 1969, 9, 479–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Lin, M.; Lin, N.; Xu, L.; Huang, H. Novel homozygous nonsense mutation associated with Bardet-Biedl syndrome in fetuses with congenital renal malformation. Medicine 2022, 101, e30003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Zakar, R.; Fischer, F.; Zakar, M.Z. Consanguineous marriages and their association with women’s reproductive health and fertility behavior in Pakistan: Secondary data analysis from Demographic and Health Surveys, 1990–2018. BMC Women’s Health 2022, 22, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamy, H. Consanguineous marriages: Preconception consultation in primary health care settings. J. Community Genet. 2012, 3, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, M.; Chung, H.; Waryah, Y.M.; Makrythanasis, P.; Falconnet, E.; Rao, A.R.; Guipponi, M.; Narsani, A.K.; Fingerhut, R.; Santoni, F.A.; et al. Visual impairment and progressive phthisis bulbi caused by recessive pathogenic variant in MARK3. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 2703–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, M.; Riazuddin, S.; Sarwar, M.T.; Makrythanasis, P.; Paracha, S.A.; Iqbal, Z.; Khan, J.; Assir, M.Z.; Hussain, M.; Razzaq, A.; et al. Biallelic variants in LINGO1 are associated with autosomal recessive intellectual disability, microcephaly, speech and motor delay. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePristo, M.A.; Banks, E.; Poplin, R.; Garimella, K.V.; Maguire, J.R.; Hartl, C.; Philippakis, A.A.; del Angel, G.; Rivas, M.A.; Hanna, M.; et al. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, F.; Darvish, H.; Paracha, S.A.; Tafakhori, A.; Firouzabadi, S.G.; Chapi, M.; Baig, H.M.A.; Reymond, A.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Ansar, M. Biallelic truncation variants in ATP9A are associated with a novel autosomal recessive neurodevelopmental disorder. NPJ Genom. Med. 2021, 6, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, S.; Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alföldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.L.; Laricchia, K.M.; Ganna, A.; et al. Addendum: The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 2021, 597, E3–E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Henikoff, S.; Ng, P.C. Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adzhubei, I.A.; Schmidt, S.; Peshkin, L.; Ramensky, V.E.; Gerasimova, A.; Bork, P.; Kondrashov, A.S.; Sunyaev, S.R. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Cooper, D.N.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster2: Mutation prediction for the deep-sequencing age. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, G.M.; Stone, E.A.; Asimenos, G.; Green, E.D.; Batzoglou, S.; Sidow, A. Distribution and intensity of constraint in mammalian genomic sequence. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, H.; Waryah, A.M.; Narsani, A.K.; Iqbal, M.; Shahzad, M.; Waryah, Y.M.; Shaikh, A.; Mahmood, A. Genetic testing of non-familial deaf patients for CIB2 and GJB2 mutations: Phenotype and genetic counselling. Biochem. Genet. 2017, 55, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waryah, Y.M.; Iqbal, M.; Sheikh, S.A.; Baig, M.A.; Narsani, A.K.; Atif, M.; Bhinder, M.A.; Rahman, A.U.; Memon, A.I.; Pirzado, M.S.; et al. Two novel variants in CYP1B1 gene: A major contributor of autosomal recessive primary congenital glaucoma with allelic heterogeneity in Pakistani patients. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Venselaar, H.; Te Beek, T.A.; Kuipers, R.K.; Hekkelman, M.L.; Vriend, G. Protein structure analysis of mutations causing inheritable diseases. An e-Science approach with life scientist friendly interfaces. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Sims, G.E.; Murphy, S.; Miller, J.R.; Chan, A.P. Predicting the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. PLoS ONE 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, R.; Szymanska, K.; Basu, B.; Patel, N.; Ewida, N.; Faqeih, E.; Al Hashem, A.; Derar, N.; Alsharif, H.; Aldahmesh, M.A.; et al. Characterizing the morbid genome of ciliopathies. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jespersgaard, C.; Fang, M.; Bertelsen, M.; Dang, X.; Jensen, H.; Chen, Y.; Bech, N.; Dai, L.; Rosenberg, T.; Zhang, J.; et al. Molecular genetic analysis using targeted NGS analysis of 677 individuals with retinal dystrophy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Smaoui, N.; Hammer, M.B.H.; Jiao, X.; Riazuddin, S.A.; Harper, S.; Katsanis, N.; Riazuddin, S.; Chaabouni, H.; Berson, E.L.; et al. Molecular analysis of Bardet-Biedl syndrome families: Report of 21 novel mutations in 10 genes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 5317–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenson, P.D.; Ball, E.V.; Mort, M.; Phillips, A.D.; Shaw, K.; Cooper, D.N. The Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD) and its exploitation in the fields of personalized genomics and molecular evolution. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2012, 39, 1.13.1–1.13.20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ece Solmaz, A.; Onay, H.; Atik, T.; Aykut, A.; Gunes, M.C.; Yuregir, O.O.; Bas, V.N.; Hazan, F.; Kirbiyik, O.; Ozkinay, F. Targeted multi-gene panel testing for the diagnosis of Bardet Biedl syndrome: Identification of nine novel mutations across BBS1, BBS2, BBS4, BBS7, BBS9, BBS10 genes. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 58, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajmal, M.; Khan, M.I.; Neveling, K.; Tayyab, A.; Jaffar, S.; Sadeque, A.; Ayub, H.; Abbasi, N.M.; Riaz, M.; Micheal, S.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies a novel and a recurrent BBS1 mutation in Pakistani families with Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Mol. Vis. 2013, 19, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Tuan, H.F.; Nguyen, D.H.; Sun, V.; Keser, V.; Bowne, S.J.; Sullivan, L.S.; Luo, H.; Zhao, L.; et al. Next generation sequencing-based molecular diagnosis of retinitis pigmentosa: Identification of a novel genotype-phenotype correlation and clinical refinements. Hum. Genet. 2014, 133, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, M.; Lamers, I.J.; Schmidts, M.; Ajmal, M.; Jaffar, S.; Ullah, E.; Mustafa, B.; Ahmad, S.; Nazmutdinova, K.; Hoskins, B.; et al. Genetic and clinical characterization of Pakistani families with Bardet-Biedl syndrome extends the genetic and phenotypic spectrum. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Umair, M.; Yousaf, M.; Khan, S.A.; Shah, K.; Ahmad, F.; Azeem, Z.; Ali, G.; Alhaddad, B.; Rafique, A.; et al. Sequence variants in four genes underlying Bardet-Biedl syndrome in consanguineous families. Mol. Vis. 2017, 23, 482–494. [Google Scholar]
- Pereiro, I.; Valverde, D.; Piñeiro-Gallego, T.; Baiget, M.; Borrego, S.; Ayuso, C.; Searby, C.; Nishimura, D. New mutations in BBS genes in small consanguineous families with Bardet-Biedl syndrome: Detection of candidate regions by homozygosity mapping. Mol. Vis. 2010, 16, 137. [Google Scholar]
- Muzammal, M.; Zubair, M.; Bierbaumer, S.; Blatterer, J.; Graf, R.; Gul, A.; Abbas, S.; Badar, M.; Abbasi, A.A.; Khan, M.A.; et al. Exome sequence analysis in consanguineous Pakistani families inheriting Bardet-Biedle syndrome determined founder effect of mutation c. 299delC (p. Ser100Leufs* 24) in BBS9 gene. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e834. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Ullah, I.; Touseef, M.; Basit, S.; Khan, M.N.; Ahmad, W. Novel homozygous mutations in the genes ARL6 and BBS10 underlying Bardet–Biedl syndrome. Gene 2013, 515, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safieh, L.A.; Aldahmesh, M.A.; Shamseldin, H.; Hashem, M.; Shaheen, R.; Alkuraya, H.; Al Hazzaa, S.A.F.; Al-Rajhi, A.; Alkuraya, F.S. Clinical and molecular characterisation of Bardet–Biedl syndrome in consanguineous populations: The power of homozygosity mapping. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 47, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hichri, H.; Stoetzel, C.; Laurier, V.; Caron, S.; Sigaudy, S.; Sarda, P.; Hamel, C.; Martin-Coignard, D.; Gilles, M.; Leheup, B.; et al. Testing for triallelism: Analysis of six BBS genes in a Bardet–Biedl syndrome family cohort. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 13, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, A.B.; Sandberg, M.A.; Chen, J.; Weigel-DiFranco, C.; Hejtmancik, J.F.; Berson, E.L. Genotype-phenotype correlations in Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2012, 130, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Family Identity | Gene | Variants | Sex | Age (Years) | Retinitis Pigmentosa | Polydactyly | Intellectual Disability | Hypogonadism | Renal Failure | Obesity | Nystagmus | Deafness | Bone Deformity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LUBS-01 | BBS6/MKKS | c.775delA, p.Thr259LeuTer21 | |||||||||||
| IV:4 | M | 12 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | ||
| IV:5 | M | 08 | Yes | Yes | No | NA | No | Yes | No | No | No | ||
| IV:8 | F | 6 | Yes | Yes | No | NA | No | Yes | No | No | No | ||
| LUBS-02 | BBS6/MKKS | c.775-delA, p.Thr259LeuTer21 | |||||||||||
| IV:03 | F | 15 | Yes | No | No | NA | No | Yes | No | No | No | ||
| IV:04 | F | 11 | Yes | No | No | NA | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| LUBS-03 | MKKS | c.748G>A, p.gly250Arg | |||||||||||
| IV:01 | M | 12 | Yes | Yes | No | NA | NA | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| IV:04 | F | 5 | Yes | Yes | No | NA | NA | Yes | No | No | No | ||
| LUBS-04 | BBS9 | c.223C>T, p.Arg75Ter | |||||||||||
| IV:03 | M | 21 | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | ||
| IV:04 | M | 17 | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | ||
| V:02 | M | 14 | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| V:05 | F | 07 | Yes | Yes | No | NA | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| LUBS-05 | BBS1 | c.1150 C>T,Glu384Ter | |||||||||||
| IV:01 | M | 06 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | ||
| IV:02 | F | 03 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | ||
| LUBS-06 | BBS2 | c.471 +1G>A | No | ||||||||||
| IV:01 | M | 30 | Yes | Yes | NA | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| IV:02 | M | 18 | Yes | Yes | NA | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| LUBS-09 | MKKS | c.775delA, p.Thr259LeuTer21 | |||||||||||
| IV:01 | M | 10 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| IV:02 | F | 14 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| IV:03 | F | 17 | Yes | Yes | Yes | NA | NA | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| LUBS-10 | BBS9 | c.252delA, p.Lys85SerTer39 | |||||||||||
| IV:02 | M | 16 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| IV:03 | M | 18 | Yes | Yes | yes | Yes | No | Yes | yes | No | No | ||
| CB-03 | BBS7 | c.580_582delGCA, p.Ala194del | |||||||||||
| IV:01 | M | 30 | Yes | Yes | No | NA | NA | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| IV:04 | F | 34 | Yes | Yes | No | NA | NA | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| CB-44 | BBS7 | c.580_582delGCA,p.Ala194del | |||||||||||
| IV:01 | M | 11 | Yes | Yes | No | NA | NA | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| IV:02 | M | 22 | Yes | Yes | Yes | NA | NA | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| IV:03 | M | 21 | Yes | Yes | Yes | NA | NA | Yes | Yes | No | No | ||
| VI-65 | ARL6 | c.387_394delAAATAAAA | |||||||||||
| IV:01 | M | 19 | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | ||
| IV:04 | F | 10 | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | ||
| IV:06 | M | 12 | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | ||
| RP-04 | MKKS | 1226G>A,p.Gly409Glu | |||||||||||
| IV:01 | M | 20 | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | ||
| IV:02 | M | 25 | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Gene | Variants | No. of Families | No. of Alleles | Frequency (gnomAD Database) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBS1 | c.1150G>T,p.Glu Ter384 | 1 | 2 | 0 | [34] |
| c.47 +1G>T | 1 | 2 | 0.00000399 | [35] [35] | |
| c.442 G>A,p.Asp148Asn | 1 | 2 | 0.00029 | ||
| BBS2 | c.471 +1G>A | 1 | 2 | 0 | [36] |
| BBS3/ ARL6 | c.534A>G.p.Gln178Gln | 1 | 2 | 0.00000796 | [37] |
| c.387_394delAAATAAAA | 1 | 2 | 0 | In this study | |
| BBS5 | c.734_744del,p.Glu245Gly Ter18 | 2 | 4 | 0 | [37] |
| BBS6/MKKS | c.775delA, p.Thr259LeuTer21 | 4 | 8 | 0.0000438 | [38] |
| c.1226G>A,pGly409Glu | 1 | 2 | 0 | In this study | |
| c.287 C>T,p.Ala96Val | 1 | 2 | 0 | [39] | |
| c.748 G>A,p.gly250Arg | 1 | 2 | 0.0000159 | ||
| c.822 C>G,p.Ser40 * | 1 | 2 | 0 | [38] | |
| BBS7 | c.580_582delGCA | 3 | 6 | 0 | [38] |
| c.1592_1592delTCCAG | 1 | 2 | 0 | ||
| BBS8 | c.1347G>C,p.Gln449His | 1 | 2 | 0 | [38] |
| BBS9 | c.223C>T, p.Arg Ter75 | 1 | 2 | 0.0000199 | In this study |
| c.252delA, p.Lys85S Ter39 | 1 | 2 | 0 | ||
| c.299delC (p.Ser100Leu Ter24) | 3 | 06 | 0 | [40] | |
| c.1789 C>T,p.Gln Ter597 | 1 | 2 | 0 | [37] | |
| BBS10 | c.271_272insT | 1 | 2 | 0.000579 | [38] |
| BBS12 | c.2014G>A,p.Ala672Thr | 1 | 2 | 0.001102 | [37] |
| Total | 29 | 58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, A.R.; Nazir, A.; Imtiaz, S.; Paracha, S.A.; Waryah, Y.M.; Ujjan, I.D.; Anwar, I.; Iqbal, A.; Santoni, F.A.; Shah, I.; et al. Delineating the Spectrum of Genetic Variants Associated with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome in Consanguineous Pakistani Pedigrees. Genes 2023, 14, 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020404
Rao AR, Nazir A, Imtiaz S, Paracha SA, Waryah YM, Ujjan ID, Anwar I, Iqbal A, Santoni FA, Shah I, et al. Delineating the Spectrum of Genetic Variants Associated with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome in Consanguineous Pakistani Pedigrees. Genes. 2023; 14(2):404. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020404
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, Ali Raza, Aamir Nazir, Samina Imtiaz, Sohail Aziz Paracha, Yar Muhammad Waryah, Ikram Din Ujjan, Ijaz Anwar, Afia Iqbal, Federico A. Santoni, Inayat Shah, and et al. 2023. "Delineating the Spectrum of Genetic Variants Associated with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome in Consanguineous Pakistani Pedigrees" Genes 14, no. 2: 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020404
APA StyleRao, A. R., Nazir, A., Imtiaz, S., Paracha, S. A., Waryah, Y. M., Ujjan, I. D., Anwar, I., Iqbal, A., Santoni, F. A., Shah, I., Gul, K., Baig, H. M. A., Waryah, A. M., Antonarakis, S. E., & Ansar, M. (2023). Delineating the Spectrum of Genetic Variants Associated with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome in Consanguineous Pakistani Pedigrees. Genes, 14(2), 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020404






