Neuroimaging in Adolescents: Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Risk for Substance Use Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Adolescence
2.1. Development of the Adolescent Limbic System
2.2. Adolescent Memory
3. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
3.1. Risk Factors
3.2. Effects on the Limbic System
3.3. Brain Network Connectivity
4. Substance Use Disorder
4.1. PTSD as a Risk Factor of SUD
4.2. SUD: Effects on the Limbic System and Links to Its Development
4.3. Brain Network Connectivity
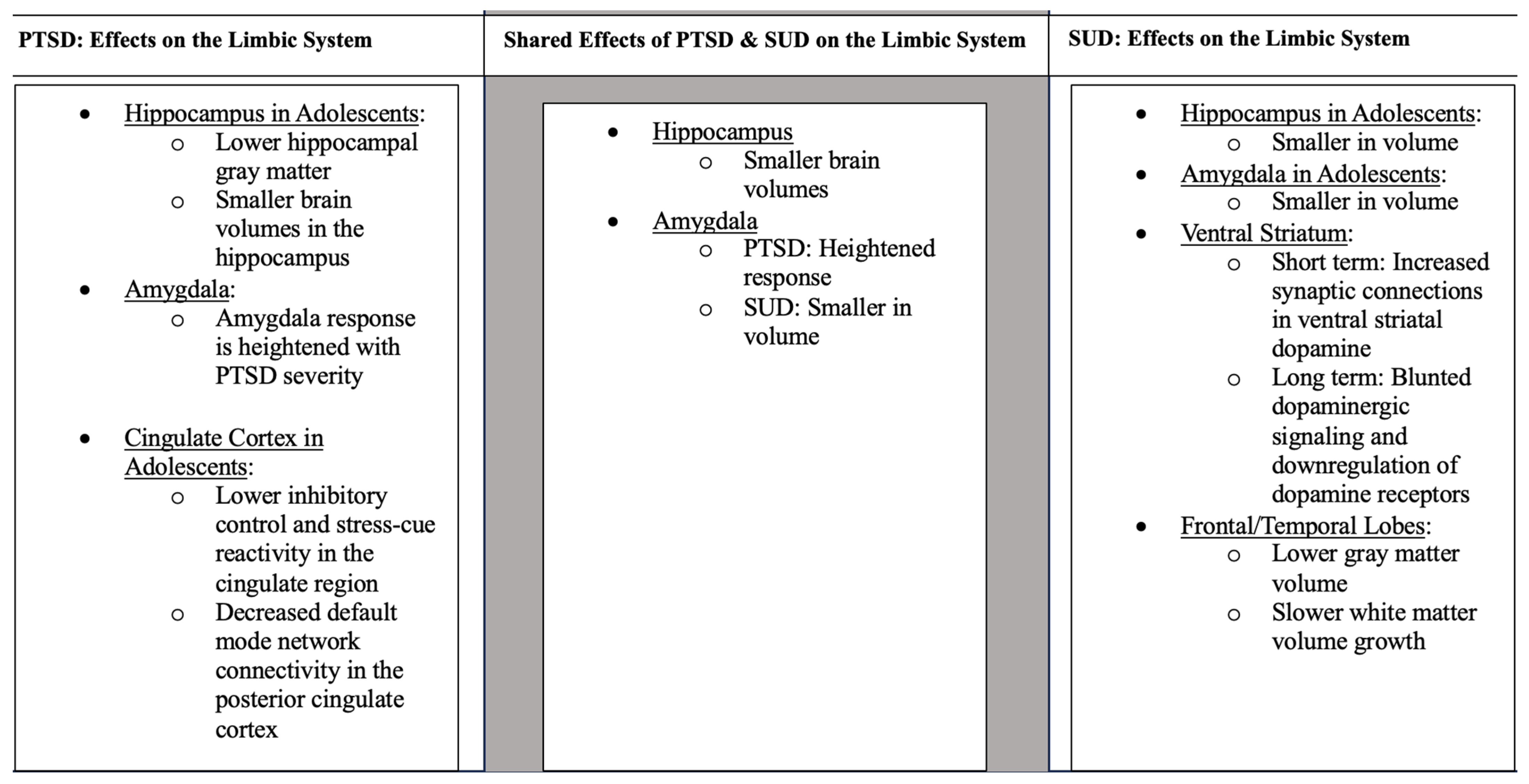
5. Brain Regions Linked to Both PTSD and SUD
6. Epigenetics
How Stress and Drug Use Lead to Epigenetic Changes
7. Research Gaps
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arain, M.; Haque, M.; Johal, L.; Mathur, P.; Nel, W.; Rais, A.; Sandhu, R.; Sharma, S. Maturation of the adolescent brain. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2013, 9, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol, J.; Vendrell, P.; Junqué, C.; Martí-Vilalta, J.L.; Capdevila, A. When does human brain development end? Evidence of corpus callosum growth up to adulthood. Ann. Neurol. 1993, 34, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogtay, N.; Giedd, J.N.; Lusk, L.; Hayashi, K.M.; Greenstein, D.; Vaituzis, A.C.; Nugent, T.F.; Herman, D.H.; Clasen, L.S.; Toga, A.W.; et al. Dynamic mapping of human cortical development during childhood through early adulthood. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8174–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, S.; Suárez, L. Substance Abuse and Trauma. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 25, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basedow, L.A.; Kuitunen-Paul, S.; Roessner, V.; Golub, Y. Traumatic Events and Substance Use Disorders in Adolescents. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakemore, S.-J.; Mills, K.L. Is Adolescence a Sensitive Period for Sociocultural Processing? Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2014, 65, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, R.C.; Berglund, P.; Demler, O.; Jin, R.; Merikangas, K.R.; Walters, E.E. Lifetime Prevalence and Age-of-Onset Distributions of DSM-IV Disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2005, 62, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, S.M.; Azzopardi, P.S.; Wickremarathne, D.; Patton, G.C. The age of adolescence. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2018, 2, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, K.A.; Greif Green, J.; Gruber, M.J.; Sampson, N.A.; Zaslavsky, A.M.; Kessler, R.C. Childhood Adversities and First Onset of Psychiatric Disorders in a National Sample of US Adolescents. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2012, 69, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworska, N.; MacQueen, G. Adolescence as a unique developmental period. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2015, 40, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogtay, N.; Thompson, P.M. Mapping gray matter development: Implications for typical development and vulnerability to psychopathology. Brain Cogn. 2010, 72, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greven, C.U.; Bralten, J.; Mennes, M.; O’Dwyer, L.; van Hulzen KJ, E.; Rommelse, N.; Schweren LJ, S.; Hoekstra, P.J.; Hartman, C.A.; Heslenfeld, D.; et al. Developmentally stable whole-brain volume reductions and developmentally sensitive caudate and putamen volume alterations in those with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and their unaffected siblings. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, P.; Eckstrand, K.; Sharp, W.; Blumenthal, J.; Lerch, J.P.; Greenstein, D.; Clasen, L.; Evans, A.; Giedd, J.; Rapoport, J.L. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder is characterized by a delay in cortical maturation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19649–19654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenroot, R.K.; Giedd, J.N. Brain development in children and adolescents: Insights from anatomical magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2006, 30, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, J.; Cheng, W.; Yang, Z. Altered gray matter volume and structural co-variance in adolescents with social anxiety disorder: Evidence for a delayed and unsynchronized development of the fronto-limbic system. Psychol. Med. 2021, 51, 1742–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttenlocher, P.R.; Dabholkar, A.S. Regional differences in synaptogenesis in human cerebral cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 1997, 387, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paus, T.; Keshavan, M.; Giedd, J.N. Why do many psychiatric disorders emerge during adolescence? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferbaum, A.; Mathalon, D.H.; Sullivan, E.V.; Rawles, J.M.; Zipursky, R.B.; Lim, K.O. A Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study of Changes in Brain Morphology From Infancy to Late Adulthood. Arch. Neurol. 1994, 51, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovlev, P.I.; Lecours, A.-R. The Myelogenetic Cycles of Regional Maturation of the Brain. Regional Development of the Brain in Early Life–ScienceOpen. 1967. Available online: https://www.scienceopen.com/document?vid=1c16c21a-8793-4f48-bfcc-87c6f65e1bf9 (accessed on 20 November 2023).
- Andre, Q.R.; Geeraert, B.L.; Lebel, C. Brain structure and internalizing and externalizing behavior in typically developing children and adolescents. Brain Struct. Funct. 2020, 225, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barch, D.M.; Harms, M.P.; Tillman, R.; Hawkey, E.; Luby, J.L. Early Childhood Depression, Emotion Regulation, Episodic Memory and Hippocampal Development. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2019, 128, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechie, I.R.; Plaisted-Grant, K.; Cheke, L.G. How does episodic memory develop in adolescence? Learn. Mem. 2021, 28, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggins, T. Longitudinal investigation of source memory reveals different developmental trajectories for item memory and binding. Dev. Psychol. 2014, 50, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard, L.; Cousin, S.; Guillery-Girard, B.; Eustache, F.; Piolino, P. How do the different components of episodic memory develop? Role of executive functions and short-term feature-binding abilities. Child Dev. 2012, 83, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frangou, S.; Chitins, X.; Williams SC, R. Mapping IQ and gray matter density in healthy young people. NeuroImage 2004, 23, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddings, A.-L.; Mills, K.L.; Clasen, L.S.; Giedd, J.N.; Viner, R.M.; Blakemore, S.-J. The influence of puberty on subcortical brain development. NeuroImage 2014, 88, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenroot, R.K.; Schmitt, J.E.; Ordaz, S.J.; Wallace, G.L.; Neale, M.C.; Lerch, J.P.; Kendler, K.S.; Evans, A.C.; Giedd, J.N. Differences in genetic and environmental influences on the human cerebral cortex associated with development during childhood and adolescence. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhu, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Cheng, S.; Qin, X.; Wu, H.; Liu, D.; Pan, F. Effects of traumatic stress in adolescence on PTSD-like behaviors, dendrite development, and H3K9me2/BDNF expression in the amygdala of male rats. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 296, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bosch, G.E.; El Marroun, H.; Schmidt, M.N.; Tibboel, D.; Manoach, D.S.; Calhoun, V.D.; White, T.J.H. Brain connectivity during verbal working memory in children and adolescents. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 35, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannest, J.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Gutierrez-Colina, A.M.; Wade, S.L.; Maloney, T.; Combs, A.; Turnier, L.; Merder, S.; Altaye, M.; Kraus, T.H.; et al. Altered functional network connectivity and working memory dysfunction in adolescents with epilepsy. Brain Imaging Behav. 2021, 15, 2513–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, M.; Tian, T.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, J.; Hao, L.; Xu, J.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y.; et al. Development of brain state dynamics involved in working memory. Cereb. Cortex 2023, 33, 7076–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.A.; Emory, E. Executive function and the frontal lobes: A meta-analytic review. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2006, 16, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Steinberg, J.L.; Hasan, K.M.; Narayana, P.A.; Kramer, L.A.; Moeller, F.G. Working memory load modulation of parieto-frontal connections: Evidence from dynamic causal modeling. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2012, 33, 1850–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, A.M.; McMillan, K.M.; Laird, A.R.; Bullmore, E. N-back working memory paradigm: A meta-analysis of normative functional neuroimaging studies. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2005, 25, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewin, C.R. What is it that a neurobiological model of PTSD must explain? In Progress in Brain Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 167, pp. 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.D.; Randall, P.; Vermetten, E.; Staib, L.; Bronen, R.A.; Mazure, C.; Capelli, S.; McCarthy, G.; Innis, R.B.; Charney, D.S. Magnetic resonance imaging-based measurement of hippocampal volume in posttraumatic stress disorder related to childhood physical and sexual abuse—A preliminary report. Biol. Psychiatry 1997, 41, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, S.; Iacoviello, B.M.; Charney, D.S. Risk Factors for the Development of Psychopathology Following Trauma. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2015, 17, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milan, S.; Zona, K.; Acker, J.; Turcios-Cotto, V. Prospective Risk Factors for Adolescent PTSD: Sources of Differential Exposure and Differential Vulnerability. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2013, 41, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, M.; Bouthillier, D.; Moss, E.; Rousseau, C.; Brunet, A. Emotion regulation strategies as mediators of the association between level of attachment security and PTSD symptoms following trauma in adulthood. Anxiety Stress Coping 2010, 23, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daviss, W.B.; Mooney, D.; Racusin, R.; Ford, J.D.; Fleischer, A.; McHUGO, G.J. Predicting Posttraumatic Stress After Hospitalization for Pediatric Injury. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2000, 39, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrasher, S.; Power, M.; Morant, N.; Marks, I.; Dalgleish, T. Social Support Moderates Outcome in a Randomized Controlled Trial of Exposure Therapy and (or) Cognitive Restructuring for Chronic Posttraumatic Stress Disorder. Can. J. Psychiatry 2010, 55, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herringa, R.J. Trauma, PTSD and the Developing Brain. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2017, 19, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.J.; Dalvie, S.; Cuzen, N.L.; Cardenas, V.; Fein, G.; Stein, D.J. Childhood adversity is linked to differential brain volumes in adolescents with alcohol use disorder: A voxel-based morphometry study. Metab. Brain Dis. 2014, 29, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Paquola, C.; Bennett, M.R.; Lagopoulos, J. Understanding heterogeneity in grey matter research of adults with childhood maltreatment-A meta-analysis and review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 69, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luby, J.L.; Belden, A.C.; Jackson, J.J.; Lessov-Schlaggar, C.N.; Harms, M.P.; Tillman, R.; Botteron, K.; Whalen, D.; Barch, D.M. Early Childhood Depression and Alterations in the Trajectory of Gray Matter Maturation in Middle Childhood and Early Adolescence. JAMA Psychiatry 2016, 73, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neshat Doost, H.T.; Yule, W.; Kalantari, M.; Rezvani, S.R.; Dyregrov, A.; Jobson, L. Reduced autobiographical memory specificity in bereaved Afghan adolescents. Memory 2014, 22, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasik, A.E.; Saigh, P.A.; Oberfield, R.A.; Halamandaris, P.V. Posttraumatic stress disorder: Memory and learning performance in children and adolescents. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.L.; Nacewicz, B.M.; Sutterer, M.J.; Cayo, A.A.; Schaefer, S.M.; Rudolph, K.D.; Shirtcliff, E.A.; Pollak, S.D.; Davidson, R.J. Behavior Problems after Early Life Stress: Contributions of the Hippocampus and Amygdala. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malejko, K.; Tumani, V.; Rau, V.; Neumann, F.; Plener, P.L.; Fegert, J.M.; Abler, B.; Straub, J. Neural correlates of script-driven imagery in adolescents with interpersonal traumatic experiences: A pilot study. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2020, 303, 111131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sun, H.; Su, X.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, S.; Xia, C.; Li, L.; Kemp, G.J.; Yue, Q.; Gong, Q. Increased right amygdala metabolite concentrations in the absence of atrophy in children and adolescents with PTSD. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2019, 28, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannlowski, U.; Kugel, H.; Huber, F.; Stuhrmann, A.; Redlich, R.; Grotegerd, D.; Dohm, K.; Sehlmeyer, C.; Konrad, C.; Baune, B.T.; et al. Childhood maltreatment is associated with an automatic negative emotion processing bias in the amygdala. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2012, 34, 2899–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ousdal, O.T.; Milde, A.M.; Hafstad, G.S.; Hodneland, E.; Dyb, G.; Craven, A.R.; Melinder, A.; Endestad, T.; Hugdahl, K. The association of PTSD symptom severity with amygdala nuclei volumes in traumatized youths. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, M.; Sepede, G.; Mingoia, G.; Catani, C.; Ferretti, A.; Merla, A.; Del Gratta, C.; Romani, G.L.; Babiloni, C. Elevated response of human amygdala to neutral stimuli in mild post traumatic stress disorder: Neural correlates of generalized emotional response. Neuroscience 2010, 168, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickie, E.W.; Brunet, A.; Akerib, V.; Armony, J.L. An fMRI investigation of memory encoding in PTSD: Influence of symptom severity. Neuropsychologia 2008, 46, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickie, E.W.; Brunet, A.; Akerib, V.; Armony, J.L. Neural correlates of recovery from post-traumatic stress disorder: A longitudinal fMRI investigation of memory encoding. Neuropsychologia 2011, 49, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, L.M.; Rauch, S.L.; Pitman, R.K. Amygdala, medial prefrontal cortex, and hippocampal function in PTSD. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1071, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, K.; Qi, R.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Lu, G. Altered cortical and subcortical local coherence in PTSD: Evidence from resting-state fMRI. Acta Radiol. 2015, 56, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, G.; Luu, P.; Posner, M.I. Cognitive and emotional influences in anterior cingulate cortex. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2000, 4, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Z.W.; Yip, S.W.; Lacadie, C.M.; Sinha, R.; Mayes, L.C.; Potenza, M.N. Childhood trauma moderates inhibitory control and anterior cingulate cortex activation during stress. NeuroImage 2019, 185, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Doherty DC, M.; Ryder, W.; Paquola, C.; Tickell, A.; Chan, C.; Hermens, D.F.; Bennett, M.R.; Lagopoulos, J. White matter integrity alterations in post-traumatic stress disorder. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, R.D. Neuroscience. Change in the brain’s white matter. Science 2010, 330, 768–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornari, E.; Knyazeva, M.G.; Meuli, R.; Maeder, P. Myelination shapes functional activity in the developing brain. NeuroImage 2007, 38, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, B.; Garver, K.E.; Urban, T.A.; Lazar, N.A.; Sweeney, J.A. Maturation of cognitive processes from late childhood to adulthood. Child Dev. 2004, 75, 1357–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gvozdanovic, G.; Stämpfli, P.; Seifritz, E.; Rasch, B. Structural brain differences predict early traumatic memory processing. Psychophysiology 2020, 57, e13354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viard, A.; Mutlu, J.; Chanraud, S.; Guenolé, F.; Egler, P.-J.; Gérardin, P.; Baleyte, J.-M.; Dayan, J.; Eustache, F.; Guillery-Girard, B. Altered default mode network connectivity in adolescents with post-traumatic stress disorder. NeuroImage. Clin. 2019, 22, 101731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, R.; Lei, D.; Chen, F.; Chen, Y.; Suo, X.; Li, L.; Lui, S.; Huang, X.; Sweeney, J.A.; Gong, Q. Disrupted grey matter network morphology in pediatric posttraumatic stress disorder. NeuroImage. Clin. 2018, 18, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; He, M.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Huang, X.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, L. Mapping structural covariance networks in children and adolescents with post-traumatic stress disorder after earthquake. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 923572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhle, J.T.; Silvers, J.A.; Wager, T.D.; Lopez, R.; Onyemekwu, C.; Kober, H.; Weber, J.; Ochsner, K.N. Cognitive reappraisal of emotion: A meta-analysis of human neuroimaging studies. Cereb. Cortex 2014, 24, 2981–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Van Duijvenvoorde AC, K.; Koolschijn PC, M.P.; Crone, E.A. Longitudinal development of frontoparietal activity during feedback learning: Contributions of age, performance, working memory and cortical thickness. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, M.C.; Sartin-Tarm, A.S.; Letkiewicz, A.M.; Crombie, K.M.; Cisler, J.M. Distinct cortical thickness correlates of early life trauma exposure and posttraumatic stress disorder are shared among adolescent and adult females with interpersonal violence exposure. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 46, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinne-Albers, M.A.; Boateng, C.P.; Van Der Werff, S.J.; Lamers-Winkelman, F.; Rombouts, S.A.; Vermeiren, R.R.; Van Der Wee, N.J. Preserved cortical thickness, surface area and volume in adolescents with PTSD after childhood sexual abuse. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, D.A.; Turner, R.J. Cumulative Adversity and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: Evidence from a Diverse Community Sample of Young Adults. Am. J. Orthopsychiatry 2003, 73, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chahal, R.; Miller, J.G.; Yuan, J.P.; Buthmann, J.L.; Gotlib, I.H. An exploration of dimensions of early adversity and the development of functional brain network connectivity during adolescence: Implications for trajectories of internalizing symptoms. Dev. Psychopathol. 2022, 34, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Haswell, C.C.; Morey, R.A.; De Bellis, M.D. Brain structural covariance network centrality in maltreated youth with PTSD and in maltreated youth resilient to PTSD. Dev. Psychopathol. 2019, 31, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.J.; Lin, C.; Talmasov, D.; Ferguson, M.A.; Schaper FL WV, J.; Jiang, J.; Goodkind, M.; Grafman, J.; Etkin, A.; Siddiqi, S.H.; et al. A transdiagnostic network for psychiatric illness derived from atrophy and lesions. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2023, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasin, D.S.; O’Brien, C.P.; Auriacombe, M.; Borges, G.; Bucholz, K.; Budney, A.; Compton, W.M.; Crowley, T.; Ling, W.; Petry, N.M.; et al. DSM-5 Criteria for Substance Use Disorders: Recommendations and Rationale. Am. J. Psychiatry 2013, 170, 834–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dube, S.R.; Felitti, V.J.; Dong, M.; Chapman, D.P.; Giles, W.H.; Anda, R.F. Childhood abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction and the risk of illicit drug use: The adverse childhood experiences study. Pediatrics 2003, 111, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, N.N. Adolescent Adversity and Concurrent Tobacco, Alcohol, and Marijuana Use. Am. J. Health Behav. 2018, 42, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, M.; Grigsby, T.J.; Rogers, C.J.; Benjamin, S.M. The relationship between family-based adverse childhood experiences and substance use behaviors among a diverse sample of college students. Addict. Behav. 2018, 76, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensley, L.S.; Spieker, S.J.; Van Eenwyk, J.; Schoder, J. Self-reported abuse history and adolescent problem behaviors. II. Alcohol and drug use. J. Adolesc. Health Off. Publ. Soc. Adolesc. Med. 1999, 24, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.H.; Edwards, E.M.; Heeren, T. Child abuse and neglect: Relations to adolescent binge drinking in the national longitudinal study of Adolescent Health (AddHealth) Study. Addict. Behav. 2009, 34, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.; Uezato, A.; Newell, J.M.; Frazier, E. Major depression and comorbid substance use disorders. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2008, 21, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, D.; Weinstein, A. Cannabis and Depression. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1264, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D. The reality of comorbidity: Depression and drug abuse. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 56, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffner, J.L.; Blom, T.J.; Anthenelli, R.M. Gender differences in trauma history and symptoms as predictors of relapse to alcohol and drug use. Am. J. Addict. 2011, 20, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaycox, L.H.; Ebener, P.; Damesek, L.; Becker, K. Trauma exposure and retention in adolescent substance abuse treatment. J. Trauma. Stress 2004, 17, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, N.T.; Rando, K.; Potenza, M.N.; Tuit, K.; Sinha, R. Childhood maltreatment, altered limbic neurobiology, and substance use relapse severity via trauma-specific reductions in limbic gray matter volume. JAMA Psychiatry 2014, 71, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.H.; Jiskrova, G.K.; Yoon, S.H.; Kobulsky, J.M. Childhood maltreatment, motives to drink and alcohol-related problems in young adulthood. Child Abus. Negl. 2020, 108, 104657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Wise, R.A.; Baler, R. The dopamine motive system: Implications for drug and food addiction. Nat. Reviews. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez de Fonseca, F.; Navarro, M. Role of the limbic system in dependence on drugs. Ann. Med. 1998, 30, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, C.E.; Pommy, J.M.; Adinoff, B. Neural Circuitry of Impaired Emotion Regulation in Substance Use Disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 2016, 173, 344–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.B.; Chung, T.; Pajtek, S.; Zhai, Z.; Long, E.; Hasler, B. Neuroimaging Methods for Adolescent Substance Use Disorder Prevention Science. Prev. Sci. 2013, 14, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squeglia, L.M.; Tapert, S.F.; Sullivan, E.V.; Jacobus, J.; Meloy, M.J.; Rohlfing, T.; Pfefferbaum, A. Brain development in heavy-drinking adolescents. Am. J. Psychiatry 2015, 172, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.A.; Nagel, B.J. Altered frontostriatal white matter microstructure is associated with familial alcoholism and future binge drinking in adolescence. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 44, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, T.M.; Barker, L.A. The Frontal Lobes and Executive Functioning. In Handbook of Executive Functioning; Goldstein, S., Naglieri, J.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squire, L.R.; Zola-Morgan, S. The medial temporal lobe memory system. Science 1991, 253, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarcho, J.M.; Wyngaarden, J.B.; Johnston, C.R.; Quarmley, M.; Smith, D.V.; Cassidy, C.M. Substance Abuse in Emerging Adults: The Role of Neuromelanin and Ventral Striatal Response to Social and Monetary Rewards. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squeglia, L.M.; Pulido, C.; Wetherill, R.R.; Jacobus, J.; Brown, G.G.; Tapert, S.F. Brain response to working memory over three years of adolescence: Influence of initiating heavy drinking. J. Stud. Alcohol Drugs 2012, 73, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetherill, R.R.; Squeglia, L.M.; Yang, T.T.; Tapert, S.F. A longitudinal examination of adolescent response inhibition: Neural differences before and after the initiation of heavy drinking. Psychopharmacology 2013, 230, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrion, V.G.; Weems, C.F.; Eliez, S.; Patwardhan, A.; Brown, W.; Ray, R.D.; Reiss, A.L. Attenuation of frontal asymmetry in pediatric posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 50, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bellis, M.D. Developmental traumatology part II: Brain development. Biol. Psychiatry 1999, 45, 1271–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bellis, M.D.; Keshavan, M.S.; Frustaci, K.; Shifflett, H.; Iyengar, S.; Beers, S.R.; Hall, J. Superior temporal gyrus volumes in maltreated children and adolescents with ptsd. Biol. Psychiatry 2002, 51, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrion, V.G.; Wong, S.S.; Kletter, H. Update on Neuroimaging and Cognitive Functioning in Maltreatment-Related Pediatric PTSD: Treatment Implications. J. Fam. Violence 2013, 28, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkman, M.N.; Gebarski, S.S.; Berent, S.; Schteingart, D.E. Hippocampal formation volume, memory dysfunction, and cortisol levels in patients with Cushing’s syndrome. Biol. Psychiatry 1992, 32, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.C.; Maheu, F.S.; Dozier, M.; Peloso, E.; Mandell, D.; Leibenluft, E.; Pine, D.S.; Ernst, M. Early-life stress is associated with impairment in cognitive control in adolescence: An fMRI study. Neuropsychologia 2010, 48, 3037–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsolini, L.; Chiappini, S.; Volpe, U.; De Berardis, D.; Latini, R.; Papanti, G.D.; Corkery, J.M. Use of Medicinal Cannabis and Synthetic Cannabinoids in Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): A Systematic Review. Medicina 2019, 55, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borne, J.; Riascos, R.; Cuellar, H.; Vargas, D.; Rojas, R. Neuroimaging in Drug and Substance Abuse Part II: Opioids and Solvents. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2005, 16, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, M. Behavioral and Functional Neuroimaging Evidence for Prefrontal Dysfunction in Methamphetamine-Dependent Subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology 2002, 26, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, M.P.; Hozack, N.; Frank, L.; Brown, G.G.; Schuckit, M.A. Decision making by methamphetamine-dependent subjects is associated with error-rate-independent decrease in prefrontal and parietal activation. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 53, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langenecker, S.A.; Kling, L.R.; Crane, N.A.; Gorka, S.M.; Nusslock, R.; Damme KS, F.; Weafer, J.; De Wit, H.; Phan, K.L. Anticipation of monetary reward in amygdala, insula, caudate are predictors of pleasure sensitivity to d-Amphetamine administration. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020, 206, 107725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, J. DNA Methylation and Epigenetics. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 41–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, L.N.; Lattal, K.M. Histone-Mediated Epigenetics in Addiction. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 128, pp. 51–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwapis, J.L.; Wood, M.A. Epigenetic mechanisms in fear conditioning: Implications for treating post-traumatic stress disorder. Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 706–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenson, J.M.; Roth, T.L.; Lubin, F.D.; Miller, C.A.; Huang, I.-C.; Desai, P.; Malone, L.M.; Sweatt, J.D. Evidence That DNA (Cytosine-5) Methyltransferase Regulates Synaptic Plasticity in the Hippocampus. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 15763–15773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzimenti, C.L.; Lattal, K.M. Epigenetics and memory: Causes, consequences and treatments for post-traumatic stress disorder and addiction: Epigenetics and memory. Genes Brain Behav. 2015, 14, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Choi, K.-H.; Renthal, W.; Tsankova, N.M.; Theobald DE, H.; Truong, H.-T.; Russo, S.J.; LaPlant, Q.; Sasaki, T.S.; Whistler, K.N.; et al. Chromatin Remodeling Is a Key Mechanism Underlying Cocaine-Induced Plasticity in Striatum. Neuron 2005, 48, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renthal, W.; Maze, I.; Krishnan, V.; Covington, H.E.; Xiao, G.; Kumar, A.; Russo, S.J.; Graham, A.; Tsankova, N.; Kippin, T.E.; et al. Histone Deacetylase 5 Epigenetically Controls Behavioral Adaptations to Chronic Emotional Stimuli. Neuron 2007, 56, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, S.; Vanhoutte, P.; Arnold FJ, L.; Huang, C.L.-H.; Bading, H. Neuronal activity-dependent nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of HDAC4 and HDAC5. J. Neurochem. 2003, 85, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, P.O.; Sasaki, A.; D’Alessio, A.C.; Dymov, S.; Labonté, B.; Szyf, M.; Turecki, G.; Meaney, M.J. Epigenetic regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor in human brain associates with childhood abuse. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, T.L.; Lubin, F.D.; Funk, A.J.; Sweatt, J.D. Lasting Epigenetic Influence of Early-Life Adversity on the BDNF Gene. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Etami, Y.; Lildharrie, C.; Manza, P.; Wang, G.-J.; Volkow, N.D. Neuroimaging in Adolescents: Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Risk for Substance Use Disorders. Genes 2023, 14, 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122113
Etami Y, Lildharrie C, Manza P, Wang G-J, Volkow ND. Neuroimaging in Adolescents: Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Risk for Substance Use Disorders. Genes. 2023; 14(12):2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122113
Chicago/Turabian StyleEtami, Yasameen, Christina Lildharrie, Peter Manza, Gene-Jack Wang, and Nora D. Volkow. 2023. "Neuroimaging in Adolescents: Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Risk for Substance Use Disorders" Genes 14, no. 12: 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122113
APA StyleEtami, Y., Lildharrie, C., Manza, P., Wang, G.-J., & Volkow, N. D. (2023). Neuroimaging in Adolescents: Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Risk for Substance Use Disorders. Genes, 14(12), 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122113





