Penaeid Shrimp Chromosome Studies Entering the Post-Genomic Era
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Chromosome Number, Morphology, and Evolution in Penaeid Shrimp
| Species [13] | Alternative Species Name [14,15] | Number of Chromosomes | Karyotype | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| black tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon | Penaeus monodon | 2n = 88 | [11] | |
| 2n = 88 | 18A + 70B * | [16] | ||
| 2n = 88 | 16M + 20SM + 10ST + 42T | [17] | ||
| brown tiger shrimp, Penaeus esculentus | Penaeus esculentus | 2n = 88 | [18] | |
| green tiger shrimp, Penaeus semisulcatus | Penaeus semisulcatus | 2n = 90 | [11] | |
| 2n = 90 | [7] | |||
| brown shrimp, Farfantepenaeus aztecus | Penaeus aztecus | 2n = 88 | [19] | |
| 2n = 88 | 18 M + 18 SM + 52A ** | [20] | ||
| 2n = 88 | [21] | |||
| 2n = 88 | [11] | |||
| Pacific brown shrimp, Farfantepenaeus californiensis | Penaeus californiensis | 2n = 92 | 14M + 78ST | [22] |
| 2n = 88 | 4M + l0SM + 52ST + 22T | [23] | ||
| pink shrimp, Farfantepenaeus duorarum | Penaeus duorarum | 2n = 88 | [19] | |
| 2n = 88 | [21] | |||
| 2n = 88 | [11] | |||
| Chinese shrimp, Fenneropenaeus chinensis | Penaeus chinensis | 2n = 88 | 26A + 15B + 3C *** | [24] |
| 2n = 88 | 54M + 20(M, SM) + 10SM + 4(SM, ST) | [25] | ||
| Indian white shrimp, Fenneropenaeus indicus | Penaeus indicus | 2n = 88 | 27M + 13SM + 4ST | [12] |
| banana shrimp, Fenneropenaeus merguiensis | Penaeus merguiensis | 2n = 88 | [18] | |
| 2n = 88 | 21(M, SM) + 23(T, A **) | [8] | ||
| redtail shrimp, Fenneropenaeus penicillatus | Penaeus penicillatus | 2n = 88 | [11] | |
| Western white shrimp, Litopenaeus occidentalis | Penaeus occidentalis | 2n = 92 | 14M + 78ST | [22] |
| white shrimp, Litopenaeus setiferus | Penaeus setiferus | 2n = 90 | [19] | |
| 2n = 90 | [21] | |||
| 2n = 88 | [11] | |||
| blue shrimp, Litopenaeus stylirostris | Penaeus stylirostris | 2n = 88 | [26] | |
| 2n = 92 | 14M + 78ST | [22] | ||
| Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei | Penaeus vannamei | 2n = 92 | 14M + 78ST | [22] |
| 2n = 88 | [21] | |||
| 2n = 88 | 4M + l0SM + 56ST + 18T | [23] | ||
| 2n = 88 | [26] | |||
| Kuruma shrimp, Marsupenaeus japonicus | Penaeus japonicus | 2n = 92 | [6] | |
| 2n = 86 | [27] | |||
| 2n = 86 | [11] |
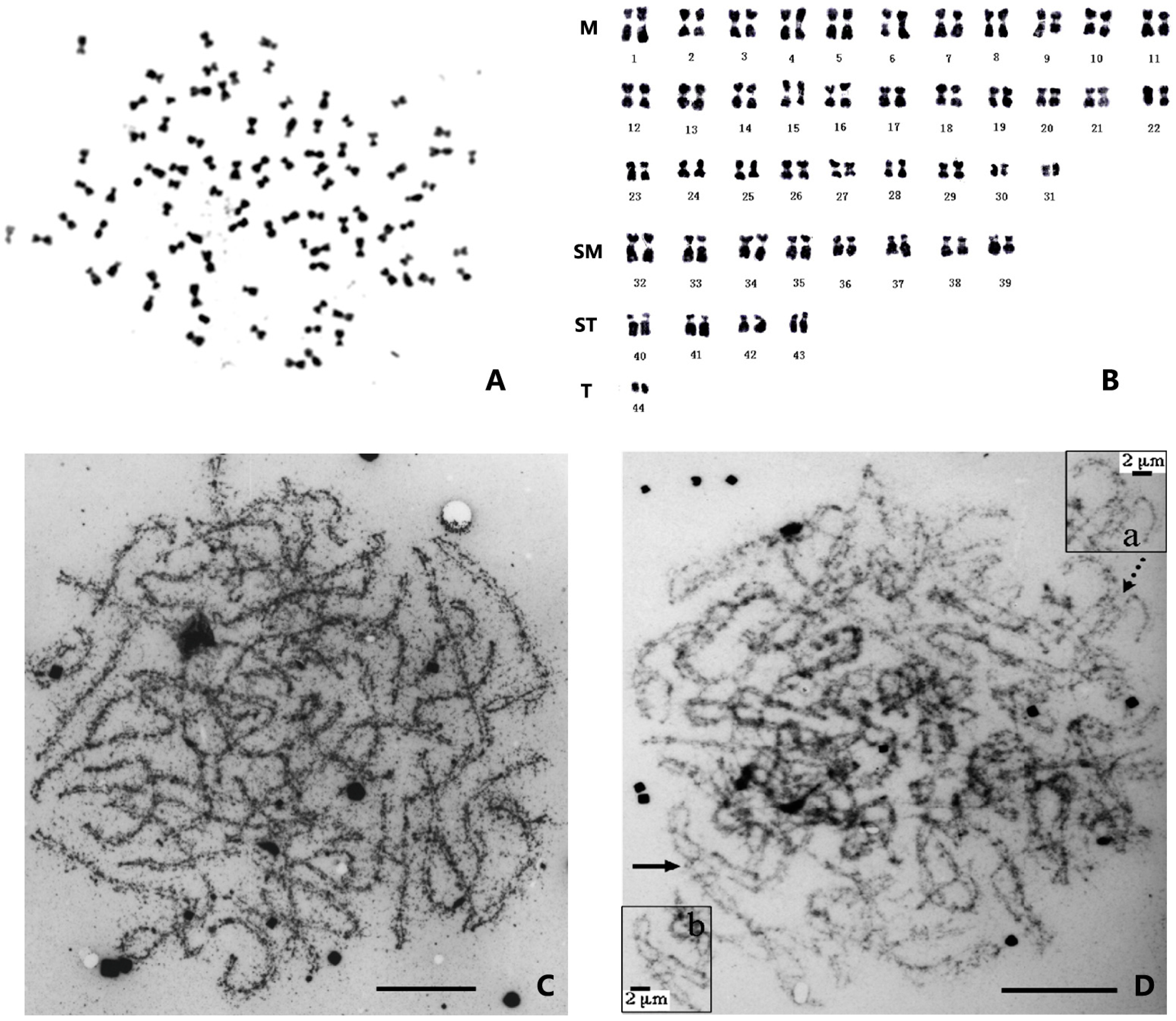
3. Ploidy and Chromosome Manipulation in Penaeid Shrimp
4. Gene Mapping
5. Whole Genome Assembly and Structure Analysis of Shrimp
5.1. Genome Assembly at Chromosome Level
5.2. Shrimp Genome Structure Analyses
6. Sex Chromosomes of Penaeid Shrimp
7. Chromosome Structure and Gene Regulation
8. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.J.; Yuan, J.B.; Sun, Y.M.; Li, S.H.; Gao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, C.Z.; Wang, Q.C.; Lv, X.J.; Zhang, X.X.; et al. Penaeid shrimp genome provides insights into benthic adaptation and frequent molting. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, I.C. A brief review of the larval rearing techniques of penaeid prawns. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on the Culture of Penaeid Prawns/Shrimps, Iloilo City, Philippines, 4–7 December 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Xiang, J. Recent advances in researches on the innate immunity of shrimp in China. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 39, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J. Disease Occurrence and Control Strategies of Mariculture Organisms; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, H.; Machii, A.; Wada, K.; Awaji, M.; Townsley, S. A check list of decapod chromosomes (Crustacea). Bull. Natl. Res. Inst. Aquac. 1988, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, S.J.; Elahi, E.; Raie, R.M. The chromosome number of the Persian gulf shrimp Penaeus semisulcatus. Iran. Int. J. Sci. 2004, 5, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri, S.M.; Farahmand, H.; Khalilabadi, F. Chromosome studies on the marine shrimp Penaeus (Fenneropenaeus) merguiensis from the Persian Gulf. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2011, 10, 734–741. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.B.; Zhang, X.J.; Wang, M.; Sun, Y.M.; Liu, C.Z.; Li, S.H.; Yu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, X.X.; et al. Simple sequence repeats drive genome plasticity and promote adaptive evolution in penaeid shrimp. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uengwetwanit, T.; Pootakham, W.; Nookaew, I.; Sonthirod, C.; Angthong, P.; Sittikankaew, K.; Rungrassamee, W.; Arayamethakorn, S.; Wongsurawat, T.; Jenjaroenpun, P.; et al. A chromosome-level assembly of the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) genome facilitates the identification of growth-associated genes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 1620–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Liu, R.; Zhou, L. Chromosomes of marine shrimps with special reference to different techniques. Aquaculture 1994, 111, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, M.; Le Déan, L.; Vonau, V.; Diter, A. Karyotype of the marine shrimp (Crustacea, Decapoda) established by using an image analysis system. Ophelia 1998, 49, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfante, I.P.; Kensley, B. Penaeids and Sergestoid Shrimps and Prawns of the World: Keys and Diagnoses for the Families and Genera; Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle: Paris, France, 1997; 233p. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.-H.; Ma, K.Y.; Chu, K.H.; Chan, T.-Y. Making sense of the taxonomy of the most commercially important shrimps Penaeus Fabricius, 1798 s.l. (Crustacea: Decapoda: Penaeidae), a way forward. Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.-Y. New subgeneric names for the most commercially important shrimp genus Penaeus Fabricius, 1798 (Crustacea, Decapoda, Penaeidae). ZooKeys 2023, 1141, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Zhang, D. The karyutype of tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon. J. Fish. China 1993, 17, 83–84. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Lakra, W.S. Somatic chromosomes of the black tiger prawn, Penaeus monodon (Penaeidae: Crustacea). B Mar. Sci. 1996, 59, 556–559. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.H.; Courtrey, A.; Zhou, L. Chromosome complements in the spermatogenesis of two Penaeid prawns, Penaeus merguiensis and P. esculentus. Cytologia 1996, 61, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, D.J. A method for obtaining metaphase spreads from marine shrimp with notes on the karyotypes of Penaeus aztecus, P. setiferus and P. duorarum. J. World Aquac. Soc. 1976, 7, 327–332. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, U. Chromosomal studies in Penaeus aztecus Ives larvae. Mahasagar-Bull. Natl. Inst. Oceanogr. 1985, 18, 75–77. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, S.; Dougherty, W.; Sandifer, P. Meiotic chromosome complements and nuclear DNA contents of four species of shrimps of the genus Penaeus. J. Crustac. Biol. 1990, 10, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayorga, Z. Genetica de crustaceos. Documenta 1982, 10, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- CamposRamos, R. Chromosome studies on the marine shrimps Penaeus vannamei and P. californiensis (Decapoda). J. Crustac. Biol. 1997, 17, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J. Chromosomc studies on Penaeus orientalis. Oceanol. Limnol. 1988, 19, 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.X.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Bao, Z.M. Karyotype studies on Penaeus orientalis. J. Ocean Univ. Qingdao 1989, 19, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, L.; Xiang, J. Studies on the chromosome of marine shrimps with special reference to different techniques. In Plant, Animal and Microbe Genomes X; Town & Country Convention Center: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; p. 642. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, K.; Fujiwara, Y. A New Method for Obtaining Metaphase Chromosomes from the Regeneration Blastema of Penaeus (Marsupenaeus) Japonicus. Nippon. Suisan Gakk. 1988, 54, 1563–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhou, L.; Xiang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhu, J. Triploidy induction with heat shocks to Penaeus chinensis and their effects on gonad development. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 1999, 17, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S. Karyotype Analysis and Gene Localization on Chromosomes of Fenneropenaeus chinensis and Ciona Intestinalis by fish. Master’s Thesis, Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (GUCAS), Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.S.; Li, F.H.; Zhang, C.S.; Yu, K.J.; Xiang, J.H. Synaptonemal complex analysis in spermatocytes of diploid and triploid Chinese shrimp. Tissue Cell. 2008, 40, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, P.D.; Patel, H.R.; Ruiz-Herrera, A.; Alvarez-Gonzalez, L.; Lister, N.C.; Simakov, O.; Ezaz, T.; Kaur, P.; Frere, C.; Grutzner, F.; et al. Microchromosomes are building blocks of bird, reptile, and mammal chromosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2112494118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson Pokorna, M.; Reifova, R. Evolution of B chromosomes: From dispensable parasitic chromosomes to essential genomic players. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 727570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachvaroff, T.R.; McDonald, R.C.; Plough, L.V.; Chung, J.S. Chromosome-level genome assembly of the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus. G3 2021, 11, jkab212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simakov, O.; Bredeson, J.; Berkoff, K.; Marletaz, F.; Mitros, T.; Schultz, D.T.; O’Connell, B.L.; Dear, P.; Martinez, D.E.; Steele, R.E.; et al. Deeply conserved synteny and the evolution of metazoan chromosomes. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabi5884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahajpal, N.S.; Barseghyan, H.; Kolhe, R.; Hastie, A.R.; Chaubey, A. Optical genome mapping as a next-generation cytogenomic tool for detection of structural and copy number variations for prenatal genomic analyses. Genes 2021, 12, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janíček, T.; Hobza, R.; Hudzieczek, V. Laser capture microdissection: From genomes to chromosomes, from complex tissue to single-cell analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2672, 163–175. [Google Scholar]
- Liehr, T. Overview of currently available approaches used in cytogenomics. In Cytogenomics; Liehr, T., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- De Resende, K.F.M. Karyotype Evolution: Concepts and Applications. In Chromosome Structure and Aberrations; Bhat, T.A., Wani, A.A., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2017; pp. 181–200. [Google Scholar]
- Murofushi, M.; Deguchi, Y. Karyotype evolution in Decapoda crustacean. In Proceedings of the Second Asian Fisheries Forum, Tokyo, Japan, 17–22 April 1989; pp. 549–553. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.H.; Li, F.H.; Zhang, C.S.; Zhang, X.J.; Yu, K.J.; Zhou, L.H.; Wu, C.G. Evaluation of induced triploid shrimp Penaeus (Fenneropenaeus) chinensis cultured under laboratory conditions. Aquaculture 2006, 259, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakra, W.S.; Das, P. Genetic engineering in aquaculture. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 1998, 68, 873–879. [Google Scholar]
- Pandian, T.J.; Koteeswaran, R. Ploidy induction and sex control in fish. Hydrobiologia 1998, 384, 167–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, M.; Trudeau, V.; Lakra, W. Chapter 1—Biotechnology in modern aquaculture: Innovations, advancements, and challenges. In Frontiers in Aquaculture Biotechnology; Wazir, S.L., Mukunda, G., Vance, L.T., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Coman, F.E.; Sellars, M.J.; Norris, B.J.; Coman, G.J.; Preston, N.P. The effects of triploidy on Penaeus (Marsupenaeus) japonicus (Bate) survival, growth and gender when compared to diploid siblings. Aquaculture 2008, 276, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellars, M.J.; Li, F.; Preston, N.P.; Xiang, J. Penaeid shrimp polyploidy: Global status and future direction. Aquaculture 2010, 310, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, R.; Yu, D. The chromosomes of three shrimps, Penaeus penicillatus, P. semisulcatus and P. japonicus. Mar. Sci. 1991, 4, 72–73. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.H.; Xiang, J.H.; Zhou, L.H.; Wu, C.G.; Zhang, X.J. Optimization of triploid induction by heat shock in Chinese shrimp. Aquaculture 2003, 219, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H. Cytochalasin B induced triploidy in Penaeus chinensis. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 1993, 13, 261–267. [Google Scholar]
- Sellars, M.J.; Wood, A.T.; Dixon, T.J.; Dierens, L.M.; Coman, G.J. A comparison of heterozygosity, sex ratio and production traits in two classes of triploid Penaeus (Marsupenaeus) japonicus (Kuruma shrimp). Aquaculture 2009, 296, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zúñiga-Panduro, M.D.; Casillas-Hernández, R.; Garza-Torres, R.; Guerrero-Tortolero, D.A.; Grijalva-Chon, J.M.; Campos-Ramos, R. Abnormalities and Possible Mosaicism during Embryonic Cell Division after Cold Shock in Zygotes of the Pacific White Shrimp, Related to Failure of Induction of Tetraploidy and Triploidy. J. Crustac. Biol. 2014, 34, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.H.; Xiang, J.H.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhou, L.H.; Zhang, C.S.; Wu, C.G. Gonad development characteristics and sex ratio in triploid Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Mar. Biotechnol. 2003, 5, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pongtippatee, P.; Laburee, K.; Thaweethamsewee, P.; Hiranphan, R.; Asuvapongpatana, S.; Weerachatyanukul, W.; Srisawat, T.; Withyachumnarnkul, B. Triploid Penaeus monodon: Sex ratio and growth rate. Aquaculture 2012, 356, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellars, M.J.; Wood, A.; Murphy, B.; McCulloch, R.M.; Preston, N.P. Triploid Black Tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) performance from egg to harvest age. Aquaculture 2012, 324, 242–249. [Google Scholar]
- Alfaro-Montoya, J.; Braga, A.; Umaña-Castro, R. Research frontiers in penaeid shrimp reproduction: Future trends to improve commercial production Aquaculture. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.S.; Wang, B.; Li, F.H.; Jiang, H.; Xiang, J.H. Molecular cloning and characterization of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) from Chinese shrimp. Comp. Biochem. Phys. B 2008, 151, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foote, A.R.; Mair, G.C.; Wood, A.T.; Sellars, M.J. Tetraploid inductions of Penaeus monodon using cold shock. Aquacult. Int. 2012, 20, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.H.; Zhou, L.H.; Liu, R.Y.; Zhu, J.Z.; Li, F.H.; Liu, X.D. Induction of the tetraploids of the Chinese shrimp, Penaeus chinensis. In Proceedings of the Asia Pacific Conference on Agricultural Biotechnology, Beijing, China, 20–24 August 1992; pp. 841–846. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhou l Yu, K. Tetraploid Induction by heatshocks in Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis. J. Shellfish Res. 2003, 22, 541–545. [Google Scholar]
- Alcivar-Warren, A.; Xu, Z.K.; Meehan, D.; Fan, Y.J.; Song, L.S. Shrimp genomics: Development of a genetic map to identify QTLs responsible for economically important traits in Litopenaeus vannamei. In Aquatic Genomics; Shimizu, N., Aoki, T., Hirono, I., Takashima, F., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2003; pp. 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, S.S.; Lehnert, S. Advances in gene mapping in Penaeid shrimp. In Advances in Shrimp Biotechnology; Flegel, T.W., Ed.; National Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology: Bangkok, Thailand, 1998; pp. 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Baranski, M.; Gopikrishna, G.; Robinson, N.A.; Katneni, V.K.; Shekhar, M.S.; Shanmugakarthik, J.; Jothivel, S.; Gopal, C.; Ravichandran, P.; Kent, M.; et al. The development of a high density linkage map for black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) based on cSNPs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Sun, X.; Yuan, J.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Whole Transcriptome Analysis Provides Insights into Molecular Mechanisms for Molting in Litopenaeus vannamei. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Luan, S.; Hu, L.Y.; Mao, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhong, S.P.; Kong, J. High-resolution genetic linkage mapping, high-temperature tolerance and growth-related quantitative trait locus (QTL) identification in Marsupenaeus japonicus. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2016, 291, 1391–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.B.; Jerry, D.R.; Khatkar, M.S.; Raadsma, H.W.; van der Steen, H.; Prochaska, J.; Forêt, S.; Zenger, K.R. A comparative integrated gene-based linkage and locus ordering by linkage disequilibrium map for the Pacific white shrimp. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Xu, Y.H.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, F.L.; Huang, J.H.; Liu, B.S.; Jiang, S.G.; Zhang, D.C. A high-density genetic linkage map and QTL mapping for sex in black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.H.; Fu, Q.; Luan, S.; Luo, K.; Sui, J.; Kong, J. Genome survey and high-resolution genetic map provide valuable genetic resources for Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, P.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, F.H.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, C.S.; Xiang, J.H. Chromosomal localization of 5S rDNA in Chinese shrimp (Fenneropenaeus chinensis): A chromosome-specific marker for chromosome identification. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2010, 28, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcivar-Warren, A.; Meehan-Meola, D.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhou, L.; Xiang, J.; Moss, S.; Arce, S.; Warren, W.; Xu, Z.; et al. Isolation and mapping of telomeric pentanucleotide (TAACC)n repeats of the Pacific whiteleg shrimp, Penaeus vannamei, using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, C.T.; Yao, N.; Huang, J.X.; Sun, X.S.; Zhao, B.R.; Li, H.D. Construction of a high-density linkage map and detection of sex-specific markers in Penaeus japonicus. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.J.; Chen, W.; Liu, F.K.; Huang, M.W.; Peng, K.; Zhao, J.C.; Chen, X.Y.; Sun, Y.P.; Li, C.Z.; Chen, Y.H.; et al. A genetic linkage map of the Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei): QTL mapping for low-temperature tolerance and growth-related traits and identification of the candidate genes. Aquaculture 2023, 562, 738834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Xiang, J.; Li, F. Recent advances in crustacean genomics and their potential application in aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 1501–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.X.; Sha, X.X.; Shi, Q. Research advances in the genomics and applications for molecular breeding of aquaculture animals. Aquaculture 2020, 526, 735357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, H.; ElHady, M.; Alcivar-Warren, A.; Allen, S.; Al-Tobasei, R.; Bao, L.S.; Beck, B.; Blackburn, H.; Bosworth, B.; Buchanan, J.; et al. Aquaculture genomics, genetics and breeding in the United States: Current status, challenges, and priorities for future research. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 191. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.B.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, F.H.; Xiang, J.H. Genome Sequencing and Assembly Strategies and a Comparative Analysis of the Genomic Characteristics in Penaeid Shrimp Species. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 658619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Yu, Y.; Wei, J.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Genomic resources and comparative analyses of two economical penaeid shrimp species, Marsupenaeus japonicus and Penaeus monodon. Mar. Genom. 2018, 39, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerlimann, R.; Cowley, J.A.; Wade, N.M.; Wang, Y.A.; Kasinadhuni, N.; Chan, C.K.K.; Jabbari, J.; Siemering, K.; Gordon, L.; Tinning, M.; et al. Genome assembly of the Australian black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) reveals a novel fragmented IHHNV EVE sequence. G3 2022, 12, jkac034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, S.H.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, F.H. Analysis of a sex-biased sequence in sex determination region and exploitation of a fast sex detection method in Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2021, 543, 736922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katneni, V.K.; Shekhar, M.S.; Jangam, A.K.; Krishnan, K.; Prabhudas, S.K.; Kaikkolante, N.; Baghel, D.S.; Koyadan, V.K.; Jena, J.; Mohapatra, T. A Superior Contiguous Whole Genome Assembly for Shrimp (Penaeus indicus). Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 808354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.Y.; Lv, J.J.; Liu, M.; Shao, H.X.; Liu, P.; Li, J. A chromosome-level genome of the kuruma shrimp (Marsupenaeus japonicus) provides insights into its evolution and cold-resistance mechanism. Genomics 2022, 114, 110373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawato, S.; Nishitsuji, K.; Arimoto, A.; Hisata, K.; Kawamitsu, M.; Nozaki, R.; Kondo, H.; Shinzato, C.; Ohira, T.; Satoh, N.; et al. Genome and transcriptome assemblies of the kuruma shrimp, Marsupenaeus japonicus. G3 2021, 11, jkab268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, J.; Li, H. Fast and accurate long-read assembly with wtdbg2. Nat. Methods 2019, 17, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Sun, S.; Liu, K.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Deagle, B.E.; Seim, I.; Biscontin, A.; Wang, Q.; et al. The enormous repetitive Antarctic krill genome reveals environmental adaptations and population insights. Cell 2023, 186, 1279–1294.e1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Duan, H.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Convergent evolution of the osmoregulation system in decapod shrimps. Mar. Biotechnol. 2017, 19, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A reference standard for genome biology. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 1121. [CrossRef]
- Zhiteneva, A.; Bonfiglio, J.J.; Makarov, A.; Colby, T.; Vagnarelli, P.; Schirmer, E.C.; Matic, I.; Earnshaw, W.C. Mitotic post-translational modifications of histones promote chromatin compaction in vitro. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 170076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeshima, K.; Matsuda, T.; Shindo, Y.; Imamura, H.; Tamura, S.; Imai, R.; Kawakami, S.; Nagashima, R.; Soga, T.; Noji, H.; et al. A transient rise in free Mg(2+) ions released from ATP-Mg hydrolysis contributes to mitotic chromosome condensation. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickeral, O.K.; Makalowski, W.; Boguski, M.S.; Boeke, J.D. Frequent human genomic DNA transduction driven by LINE-1 retrotransposition. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrader, L.; Schmitz, J. The impact of transposable elements in adaptive evolution. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 1537–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagi, A.; Aflalo, E.D. The androgenic gland and monosex culture in prawns—A biotechnological perspective. Aquac. Res. 2005, 36, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, L.J.; Saoud, P.I.; Rouse, D.B. The effects of monosex culture and stocking density on survival, growth and yield of redclaw crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus) in earthen ponds. Aquaculture 2006, 259, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.Q.; Bishop, T.; Wang, Y.H.; Shahriari, R.; Lynch, M. Evolution of sex determination in crustaceans. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2023, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunham, R.A. Aquaculture and Fisheries Biotechnology: Genetic Approaches; CABI Publisher: Wallingford, UK, 2004; p. 367. [Google Scholar]
- Manan, H.; Ikhwanuddin, M. Triploid induction in penaeid shrimps aquaculture: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 13, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Ramos, R.; Garza-Torres, R.; Guerrero-Tortolero, D.A.; Maeda-Martínez, A.M.; Obregón-Barboza, H. Environmental sex determination, external sex differentiation and structure of the androgenic gland in the Pacific white shrimp (Boone). Aquac. Res. 2006, 37, 1583–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Yuan, J.B.; Wang, Q.C.; Li, S.H.; Huang, H.; Li, F.H.; Xiang, J.H. Identification of sex-determining loci in Pacific white shrimp Litopeneaus vannamei using linkage and association analysis. Mar. Biotechnol. 2017, 19, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, J.; He, Y. Preliminary investigation of sex-linked loci of Chinese shrimp (Fenneropenaeus chinensis) based on the reference genome of two Penaeus shrimps. J. Fish. China 2023, 47, 039610. [Google Scholar]
- Bergero, R.; Charlesworth, D. The evolution of restricted recombination in sex chromosomes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.E.; Dean, R.; Zimmer, F.; Mank, J.E. How to make a sex chromosome. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, J.J.; Legrandhamelin, E.; Juchault, P. Sex Determination in Crustacea. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1987, 62, 439–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigaud, T. Déterminisme Extrachromosomique du Sexe Chez Armadillidium Vulgare Latr. (Crustacé, Isopode: Modification du SEX RAtio par une Bactérie Endocytobiotique et Conséquences sur L’évolution des Génotypes sexuels Dans les Populations. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Tours, Tours, France, 1991; 138p. [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann, R.M.; Schweitzer, C.E. The oldest shrimp (Devonian: Famennian) and remarkable preservation of soft tissue. J. Crustacean Biol. 2010, 30, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman-Aiden, E.; van Berkum, N.L.; Williams, L.; Imakaev, M.; Ragoczy, T.; Telling, A.; Amit, I.; Lajoie, B.R.; Sabo, P.J.; Dorschner, M.O.; et al. Comprehensive mapping of long-range interactions reveals folding principles of the human genome. Science 2009, 326, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.W.; Wang, X.J. Chromatin higher-order structure: An important form of genome regulation. Chin. Bull. Life Sci. 2015, 27, 336–343. [Google Scholar]
- Lohia, R.; Fox, N.; Gillis, J. A global high-density chromatin interaction network reveals functional long-range and trans-chromosomal relationships. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhimulev, I.F.; Zykova, T.Y.; Goncharov, F.P.; Khoroshko, V.A.; Demakova, O.V.; Semeshin, V.F.; Pokholkova, G.V.; Boldyreva, L.V.; Demidova, D.S.; Babenko, V.N.; et al. Genetic organization of interphase chromosome bands and interbands in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eagen, K.P.; Hartl, T.A.; Kornberg, R.D. Stable Chromosome Condensation Revealed by Chromosome Conformation Capture. Cell 2015, 163, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
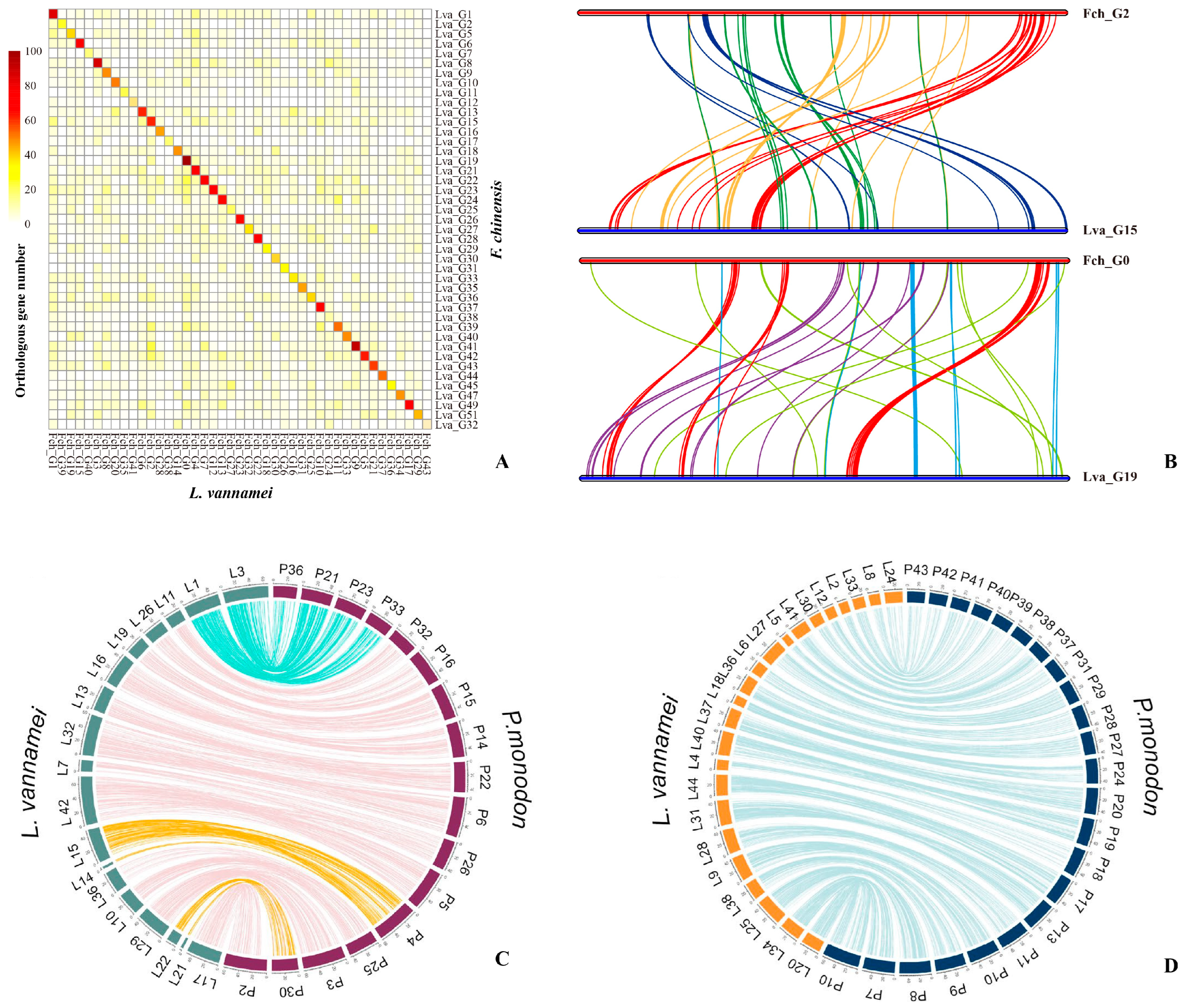
| Species | Chr Level | Assembled Genome Size (Gb) | Contig N50 (Kb) | Scaffold N50 (Kb) | Gene Number | Repeat/SSR Content (%) | Sequencing Platform | Publication Year | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. vannamei | N | 1.63 | 57.65 | 606 | 25,596 | 51.7/23.93 | Illumina + PacBio + HiC | 2019 | [1] |
| F. chinensis | Y | 1.58 | 58.996 | 28,916 | 26,343 | 48.58/19.5 | Illumina + PacBio + HiC | 2021 | [9] |
| F. chinensis | Y | 1.47 | 472.84 | 36,871 | 25,026 | 57.73/- | Illumina + PacBio + HiC | 2021 | [77] |
| P. monodon | Y | 2.39 | 79 | 44,862 | 31,640 | 62.5/27.1 | Illumina + PacBio + Chicago + HiC | 2021 | [10] |
| P. monodon | N | 1.89 | 78 | 496 | 25, 809 | 61.8/30 | Illumina + PacBio + 10×Genomics + HiC | 2022 | [76] |
| M. japonicus | N | 1.70 | 113.13 | 235 | 26,381 | 49.76/27.44 | Illumina + PacBio + HiC | 2021 | [80] |
| M. japonicus | Y | 1.54 | 229.97 | 38,270 | 24,317 | 61.56/43.13 | Illumina + PacBio + HiC | 2022 | [79] |
| F. indicus | Y | 1.93 | 1,462,103 | 34,406 | 28,720 | 49.31/31.99 | Illumina + PacBio + HiC | 2022 | [78] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Xiang, J.; Yuan, J.; Li, F. Penaeid Shrimp Chromosome Studies Entering the Post-Genomic Era. Genes 2023, 14, 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14112050
Zhang X, Xiang J, Yuan J, Li F. Penaeid Shrimp Chromosome Studies Entering the Post-Genomic Era. Genes. 2023; 14(11):2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14112050
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaojun, Jianhai Xiang, Jianbo Yuan, and Fuhua Li. 2023. "Penaeid Shrimp Chromosome Studies Entering the Post-Genomic Era" Genes 14, no. 11: 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14112050
APA StyleZhang, X., Xiang, J., Yuan, J., & Li, F. (2023). Penaeid Shrimp Chromosome Studies Entering the Post-Genomic Era. Genes, 14(11), 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14112050





