Comparative Genetic Association Analysis of Human Genetic Susceptibility to Pulmonary and Lymph Node Tuberculosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. SNP Selection
2.3. SNP Genotyping
2.4. ELISA for Serum Cytokine Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. SNP Targeted Pathway Analysis
3. Results
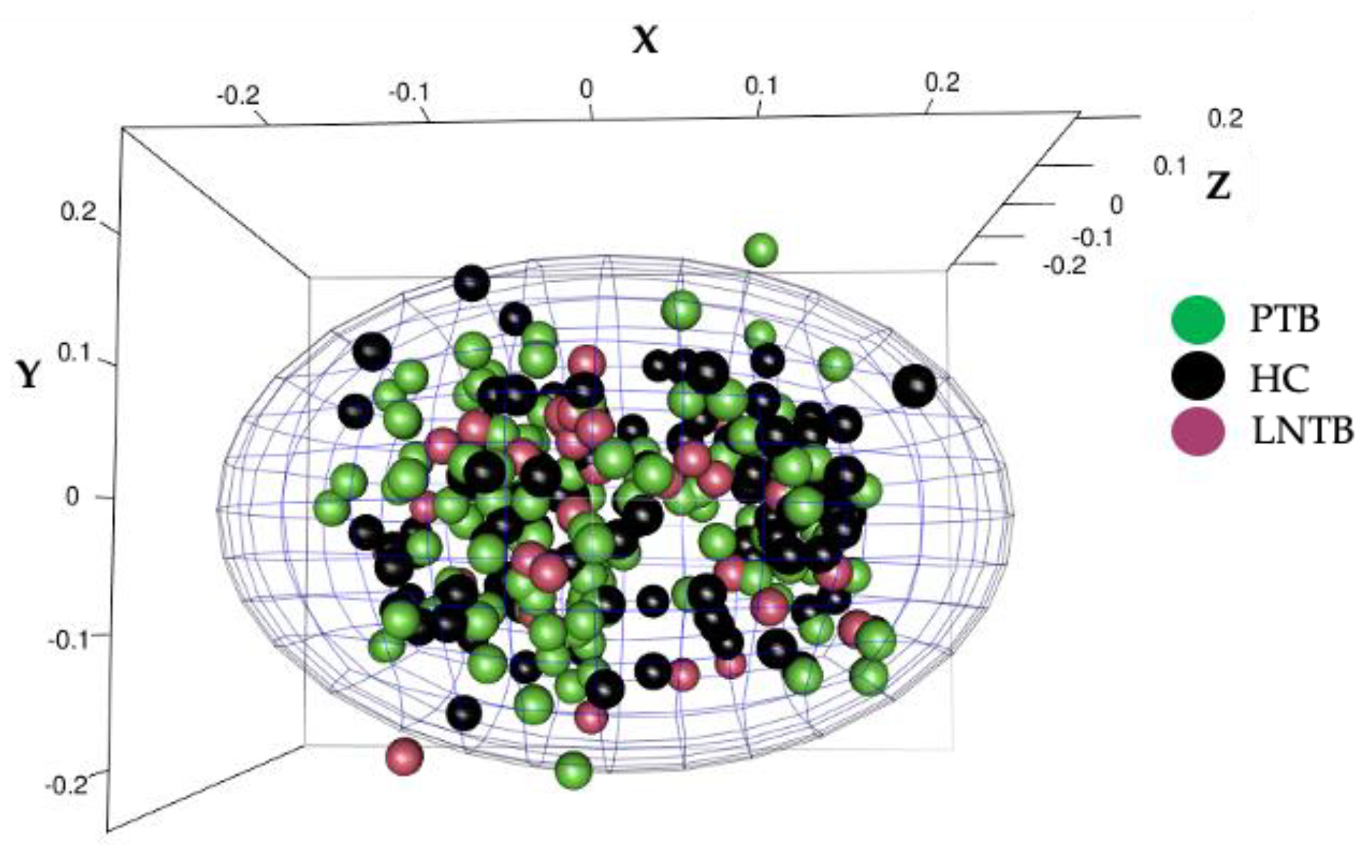
3.1. The Study Population Was Devoid of Population Stratification
3.2. Cytokine Genetic Variants Show Significant Allelic and Haplotypic Association in PTB and Not in LNTB
3.3. Gene-Gene Epistatic Interaction Analysis Reveals a Higher Risk for Cytokine Genes Majorly in PTB and Not LNTB
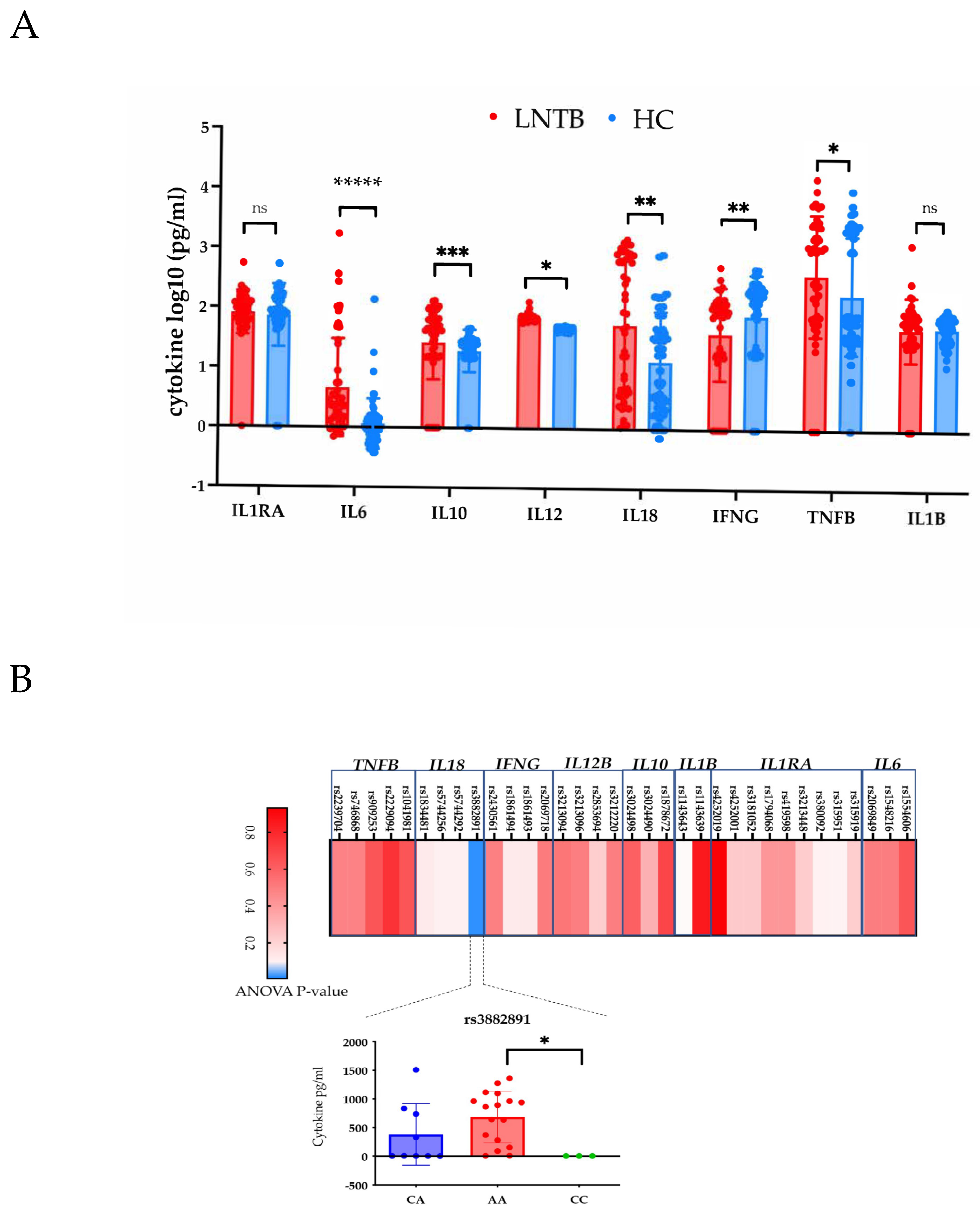
3.4. Lack of Major Association of Cytokine Levels with Genotypes in LNTB
3.5. Innate Immunity Related Genes Are Majorly Associated with LNTB and Not PTB
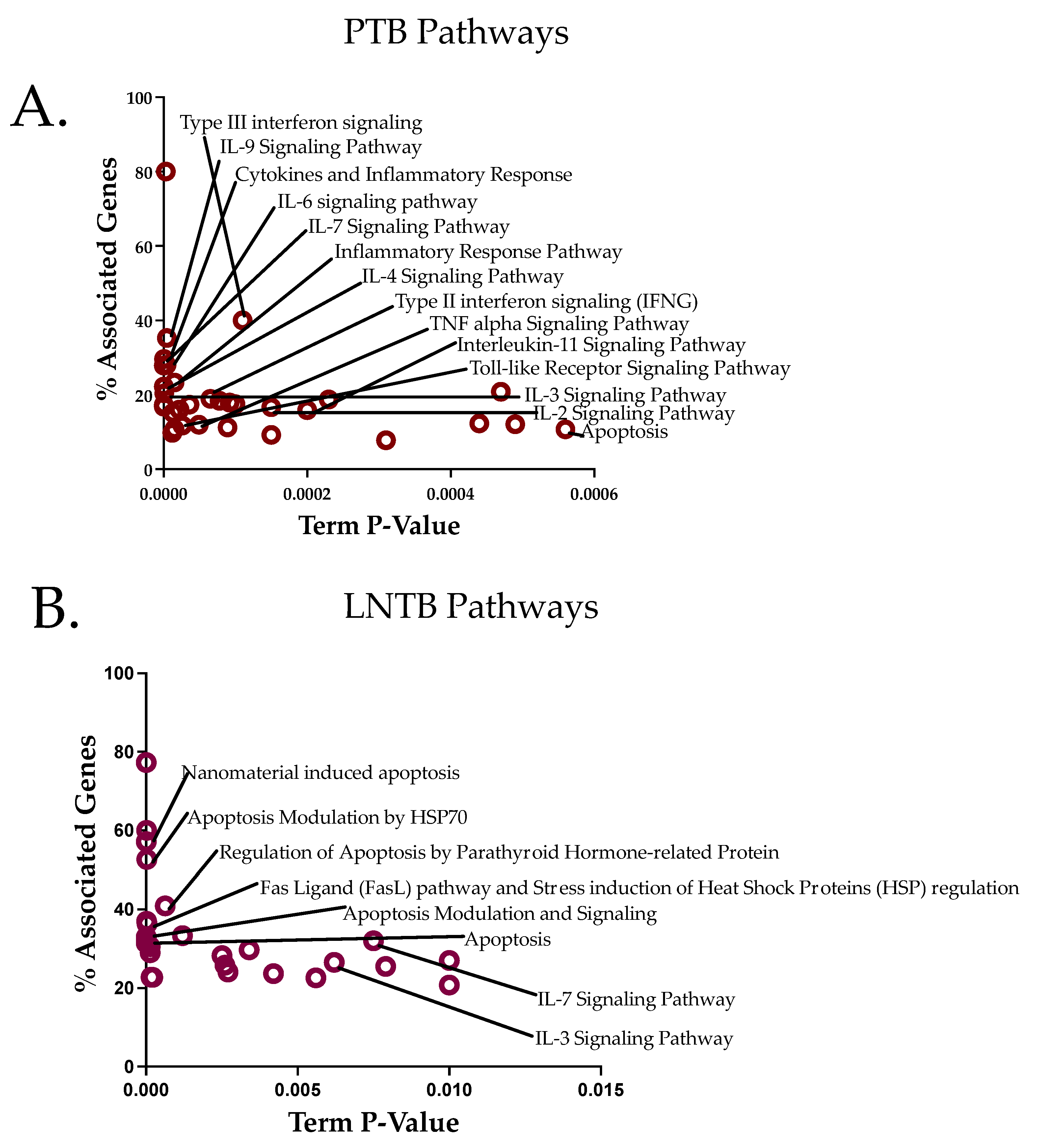
3.6. Pathway Analysis Reveals an Apoptotic Axis for LNTB and a Cytokine Axis for PTB
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2017; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.K.; Mohan, A. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Indian J. Med. Res. 2004, 120, 316–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Polesky, A.; Grove, W.; Bhatia, G. Peripheral tuberculous lymphadenitis: Epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment, and outcome. Medicine 2005, 84, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia de Viedma, D.L.G.; Cardona, P.J.; Rodriguez, N.A.; Gordillo, S.; Serrano, M.J.; Bouza, E. Association between the infectivity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains and their efficiency for extrarespiratory infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 12, 2059–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yun, Y.J.; Kqueen, C.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, Y.R.; Kook, Y.H.; Lee, K.H. pncA Mutations in the Specimens from Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. (Seoul) 2012, 72, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, D.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Marrs, C.F.; Foxman, B.; Bates, J.H.; Wilson, F.; Cave, M.D. Clinical Relevance ofMycobacterium tuberculosis plcDGene Mutations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 1436–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma-Basill, M.; Nair, D. Molecular epidemiology of tuberculosis: Opportunities & challenges in disease control. Indian J. Med. Res. 2017, 146, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruesen, C.; Chaidir, L.; van Laarhoven, A.; Dian, S.; Ganiem, A.R.; Nebenzahl-Guimaraes, H.; Huynen, M.A.; Alisjahbana, B.; Dutilh, B.E.; van Crevel, R. Large-scale genomic analysis shows association between homoplastic genetic variation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis genes and meningeal or pulmonary tuberculosis. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caws, M.; Thwaites, G.; Dunstan, S.; Hawn, T.R.; Lan, N.T.; Thuong, N.T.; Stepniewska, K.; Huyen, M.N.; Bang, N.D.; Loc, T.H.; et al. The influence of host and bacterial genotype on the development of disseminated disease with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, A.K.; Wilkinson, R.J.; Nikolayevskyy, V.; Elkington, P.T.; Hanifa, Y.; Islam, K.; Timms, P.M.; Bothamley, G.H.; Claxton, A.P.; Packe, G.E.; et al. Ethnic variation in inflammatory profile in tuberculosis. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuong, N.T.; Hawn, T.R.; Thwaites, G.E.; Chau, T.T.; Lan, N.T.; Quy, H.T.; Hieu, N.T.; Aderem, A.; Hien, T.T.; Farrar, J.J.; et al. A polymorphism in human TLR2 is associated with increased susceptibility to tuberculous meningitis. Genes Immun. 2007, 8, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, D.M.; Vary, J.C., Jr.; Ray, J.P.; Walsh, G.S.; Dunstan, S.J.; Bang, N.D.; Hagge, D.A.; Khadge, S.; King, M.C.; Hawn, T.R.; et al. The lta4h locus modulates susceptibility to mycobacterial infection in zebrafish and humans. Cell 2010, 140, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, Z.; Jamil, B.; Khan, J.; Ali, R.; Khan, M.A.; Nasir, N.; Yusuf, M.S.; Jamil, S.; Irfan, M.; Hussain, R. Relationship between circulating levels of IFN-gamma, IL-10, CXCL9 and CCL2 in pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis is dependent on disease severity. Scand. J. Immunol. 2009, 69, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, R.J.; Llewelyn, M.; Toossi, Z.; Patel, P.; Pasvol, G.; Lalvani, A.; Wright, D.; Latif, M.; Davidson, R.N. Influence of vitamin D deficiency and vitamin D receptor polymorphisms on tuberculosis among Gujarati Asians in west London: A case-control study. Lancet 2000, 355, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motsinger-Reif, A.A.; Antas, P.R.; Oki, N.O.; Levy, S.; Holland, S.M.; Sterling, T.R. Polymorphisms in IL-1beta, vitamin D receptor Fok1, and Toll-like receptor 2 are associated with extrapulmonary tuberculosis. BMC Med. Genet. 2010, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.L.; Saunders, B.M.; Sluyter, R.; Skarratt, K.K.; Goldberg, H.; Marks, G.B.; Wiley, J.S.; Britton, W.J. A Polymorphism in the P2X7Gene Increases Susceptibility to Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shandera, W.; Webster, A. The extrapulmonary dissemination of tuberculosis: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2014, 3, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tailleux, L.; Fox, G.J.; Sy, D.N.; Nhung, N.V.; Yu, B.; Ellis, M.K.; Van Hung, N.; Cuong, N.K.; Thi Lien, L.; Marks, G.B.; et al. Polymorphisms of SP110 Are Associated with both Pulmonary and Extra-Pulmonary Tuberculosis among the Vietnamese. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhimanyu; Jha, P.; Jain, A.; Arora, K.; Bose, M. Genetic association study suggests a role for SP110 variants in lymph node tuberculosis but not pulmonary tuberculosis in north Indians. Hum. Immunol. 2011, 72, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, R.J.; Patel, P.; Llewelyn, M.; Hirsch, C.S.; Pasvol, G.; Snounou, G.; Davidson, R.N.; Toossi, Z. Influence of polymorphism in the genes for the interleukin (IL)-1 receptor antagonist and IL-1beta on tuberculosis. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1863–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, N.O.; Motsinger-Reif, A.A.; Antas, P.R.; Levy, S.; Holland, S.M.; Sterling, T.R. Novel human genetic variants associated with extrapulmonary tuberculosis: A pilot genome wide association study. BMC Res. Notes 2011, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, M.; Hoal, E.G. Current findings, challenges and novel approaches in human genetic susceptibility to tuberculosis. Tuberculosis 2010, 90, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Liu, F.; Yao, K.; Gao, M.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y. Sp110 enhances macrophage resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis via inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress and inhibiting anti-apoptotic factors. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 64050–64065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, J.S.; Sluyter, R.; Gu, B.J.; Stokes, L.; Fuller, S.J. The human P2X7 receptor and its role in innate immunity. Tissue Antigens 2011, 78, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indian Genome Variation, C. The Indian Genome Variation database (IGVdb): A project overview. Hum. Genet. 2005, 118, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abhimanyu; Bose, M.; Jha, P.; Indian Genome Variation Consortium. Footprints of genetic susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis: Cytokine gene variants in north Indians. Indian J. Med. Res. 2012, 135, 763–770. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, S.; Dhillon, S.; Ke, X.; Collins, A.R.; Day, I.N. An efficient procedure for genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, S.B.; Schaffner, S.F.; Nguyen, H.; Moore, J.M.; Roy, J.; Blumenstiel, B.; Higgins, J.; DeFelice, M.; Lochner, A.; Faggart, M.; et al. The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science 2002, 296, 2225–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakir-Gungor, B.; Egemen, E.; Sezerman, O.U. PANOGA: A web server for identification of SNP-targeted pathways from genome-wide association study data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1287–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakir-Gungor, B.; Sezerman, O.U. Identification of SNP Targeted Pathways from Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) Data. Protoc. Exch. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ideker, T.; Ozier, O.; Schwikowski, B.; Siegel, A.F. Discovering regulatory and signalling circuits in molecular interaction networks. Bioinformatics 2002, 18 (Suppl. S1), S233–S240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Hackl, H.; Charoentong, P.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Fridman, W.H.; Pages, F.; Trajanoski, Z.; Galon, J. ClueGO: A Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, M.; Ammar, A.; Riutta, A.; Waagmeester, A.; Slenter, D.N.; Hanspers, K.; R, A.M.; Digles, D.; Lopes, E.N.; Ehrhart, F.; et al. WikiPathways: Connecting communities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D613–D621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhimanyu; Bose, M. Reporting genetic association studies: The roadblocks and guiding rules for robust results. Lung 2012, 190, 587–588, author reply 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, W.; Plummer, W.J. PS: Power and Sample Size Calculation. Available online: http://biostat.mc.vanderbilt.edu/wiki/Main/PowerSampleSize (accessed on 23 March 2017).
- Abhimanyu; Mangangcha, I.R.; Jha, P.; Arora, K.; Mukerji, M.; Banavaliker, J.N.; Indian Genome Variation, C.; Brahmachari, V.; Bose, M. Differential serum cytokine levels are associated with cytokine gene polymorphisms in north Indians with active pulmonary tuberculosis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brites, D.; Gagneux, S. Co-evolution of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Homo sapiens. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 264, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, J.J.; Selvaraj, P. Genetic susceptibility in tuberculosis. Respirology 2010, 15, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza De Lima, D.; Bomfim, C.C.B.; Leal, V.N.C.; Reis, E.C.; Soares, J.L.S.; Fernandes, F.P.; Amaral, E.P.; Loures, F.V.; Ogusku, M.M.; Lima, M.R.D.; et al. Combining Host Genetics and Functional Analysis to Depict Inflammasome Contribution in Tuberculosis Susceptibility and Outcome in Endemic Areas. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 550624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhimanyu; Bose, M.; Komal; Varma-Basil, M. Lack of association between IL17A and IL17F polymorphisms and related serum levels in north Indians with tuberculosis. Gene 2013, 529, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Yue, J.; Liu, L.; Han, M.; Wang, H. Relationship between human LTA4H polymorphisms and extra-pulmonary tuberculosis in an ethnic Han Chinese population in Eastern China. Tuberculosis 2014, 94, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, D.M.; Roca, F.J.; Oh, S.F.; McFarland, R.; Vickery, T.W.; Ray, J.P.; Ko, D.C.; Zou, Y.; Bang, N.D.; Chau, T.T.; et al. Host genotype-specific therapies can optimize the inflammatory response to mycobacterial infections. Cell 2012, 148, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Q.; Wang, W.F.; Zhu, C.Z.; Zhang, K.H.; Chen, X.C.; Chen, J.Y. The Polymorphism rs17525495 of LTA4H Is Associated with Susceptibility of Crohn’s Disease instead of Intestinal Tuberculosis in a Chinese Han Population. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 9537050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, L.; Ponnana, M.; Sivangala, R.; Chelluri, L.K.; Nallari, P.; Penmetsa, S.; Valluri, V.; Gaddam, S. Evaluation of TNF-alpha, IL-10 and IL-6 Cytokine Production and Their Correlation with Genotype Variants amongst Tuberculosis Patients and Their Household Contacts. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peresi, E.; Oliveira, L.R.; da Silva, W.L.; da Costa, E.A.; Araujo, J.P., Jr.; Ayres, J.A.; Fortes, M.R.; Graviss, E.A.; Pereira, A.C.; Calvi, S.A. Cytokine Polymorphisms, Their Influence and Levels in Brazilian Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis during Antituberculosis Treatment. Tuberc. Res. Treat. 2013, 2013, 285094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Yadav, A.B.; Garg, R.; Misra, A. Single nucleotide polymorphic macrophage cytokine regulation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and drug treatment. Pharmacogenomics 2014, 15, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soare, A.Y.; Freeman, T.L.; Min, A.K.; Malik, H.S.; Osota, E.O.; Swartz, T.H. P2RX7 at the Host-Pathogen Interface of Infectious Diseases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2021, 85, e00055-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugo-Villarino, G.; Troegeler, A.; Balboa, L.; Lastrucci, C.; Duval, C.; Mercier, I.; Benard, A.; Capilla, F.; Al Saati, T.; Poincloux, R.; et al. The C-Type Lectin Receptor DC-SIGN Has an Anti-Inflammatory Role in Human M(IL-4) Macrophages in Response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tailleux, L.; Pham-Thi, N.; Bergeron-Lafaurie, A.; Herrmann, J.L.; Charles, P.; Schwartz, O.; Scheinmann, P.; Lagrange, P.H.; de Blic, J.; Tazi, A.; et al. DC-SIGN induction in alveolar macrophages defines privileged target host cells for mycobacteria in patients with tuberculosis. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tailleux, L.; Schwartz, O.; Herrmann, J.L.; Pivert, E.; Jackson, M.; Amara, A.; Legres, L.; Dreher, D.; Nicod, L.P.; Gluckman, J.C.; et al. DC-SIGN is the major Mycobacterium tuberculosis receptor on human dendritic cells. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.J.; Xia, X.; Tang, S.D.; Wang, J.; Deng, X.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yue, M. Meta-analysis on the associations of TLR2 gene polymorphisms with pulmonary tuberculosis susceptibility among Asian populations. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, D.; Singh, S.; Sinha, E.; Mohanty, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Kumar Barik, S.; Patil, S.A.; Katara, P. Systematic review and meta-analysis of human Toll-like receptors genetic polymorphisms for susceptibility to tuberculosis infection. Cytokine 2022, 152, 155791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, M. Associations between genetic polymorphisms of TLRs and susceptibility to tuberculosis: A meta-analysis. Innate Immun. 2020, 26, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davila, S.; Hibberd, M.L.; Hari Dass, R.; Wong, H.E.; Sahiratmadja, E.; Bonnard, C.; Alisjahbana, B.; Szeszko, J.S.; Balabanova, Y.; Drobniewski, F.; et al. Genetic association and expression studies indicate a role of toll-like receptor 8 in pulmonary tuberculosis. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | SNP (rsID) | Risk Allele | Case, Control Frequencies | Odds Ratio (CI) | p-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTB (n = 110) | LNTB (n = 35) | Combined (n = 145) | PTB | LNTB | Combined | PTB | LNTB | Combined | |||
| TNFB | rs746868 | C/C/C | 0.650, 0.543 | 0.589, 0.543 | 0.637, 0.543 | 1.6 (1.0–2.4) | NA | NA | 0.0442 | 0.5545 | 0.0647 |
| IL10 | rs1878672 | C/G/C | 0.937, 0.812 | 0.250, 0.188 | 0.894, 0.812 | 3.4 (1.6–7.2) | NA | 2.0 (1.1–3.6) | 0.0007 | 0.3487 | 0.0271 |
| IL1B | rs1143643 | G/A/G | 0.935, 0.817 | 0.286, 0.183 | 0.887, 0.817 | 3.2 (1.6–6.6) | NA | NA | 0.001 | 0.1174 | 0.0635 |
| IL1RA | rs419598 | C/T/C | 0.418, 0.264 | 0.796, 0.736 | 0.369, 0.264 | 2 (1.2–3.4) | NA | NA | 0.0079 | 0.401 | 0.054 |
| IL6 | rs1548216 | G/C/C | 0.985, 0.978 | 0.089, 0.022 | 0.031, 0.022 | NA | 4.4 (1.0–19) | NA | 0.6447 | 0.032 | 0.5846 |
| Gene | Block | Haplotype | Case, Control Frequencies | p-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTB | LNTB | Combined | PTB | LNTB | Combined | PTB | LNTB | Combined | ||
| IL18 | Block 1 | |||||||||
| TG | 0.907 | 0.884 | 0.905 | 0.926, 0.880 | 0.893, 0.880 | 0.919, 0.880 | 0.153 | 0.8036 | 0.211 | |
| CC | 0.093 | 0.116 | 0.095 | 0.074, 0.120 | 0.107, 0.120 | 0.081, 0.120 | 0.153 | 0.8036 | 0.211 | |
| TNFB | Block 2 | |||||||||
| GC/GCC | 0.609 | 0.281 | 0.601 | 0.650, 0.549 | 0.313, 0.268 | 0.629, 0.548 | 0.0568 | 0.5305 | 0.1146 | |
| TG/GTC | 0.383 | 0.269 | 0.387 | 0.343, 0.441 | 0.241, 0.280 | 0.358, 0.442 | 0.0637 | 0.5736 | 0.098 | |
| TTC | 0.011 | 0.036, 0.001 | 0.0303 | |||||||
| TTG | 0.433 | 0.411, 0.442 | 0.6911 | |||||||
| Gene | SNP (rsID) | Risk Allele | Case, Control Frequencies | Odds Ratio (CI) | p-Value | P-Bonferroni | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTB | LNTB | Combined | PTB | LNTB | Combined | PTB | LNTB | Combined | PTB | LNTB | Combined | |||
| IFNG | rs1861493 | A | 0.935, 0.858 | 0.148, 0.142 | 0.912, 0.858 | 2.4 (1.3 –4.2) | 1.1 (0.62–1.8) | 1.7 (1.1–2.7) | 0.002 | 0.853 | 0.0197 | 0.013 | 1 | 0.138 |
| IL1RA | rs4252019 | C | 0.974, 0.934 | 0.090, 0.066 | 0.962, 0.934 | 2.6 (1.1–6.0) | 1.4 (0.72–2.7) | 1.8 (0.93–3.4) | 0.018 | 0.314 | 0.078 | 0.159 | 1 | 0.71 |
| IL4 | rs2070874 | T | 0.306, 0.239 | 0.847, 0.761 | 0.280, 0.239 | 1.4 (1.0–2.0) | 1.7 (1.1–2.9) | 1.2 (0.90–1.7) | 0.048 | 0.027 | 0.194 | 0.303 | 0.2436 | 1 |
| IL12 | rs2853694 | A | 0.624, 0.508 | 0.620, 0.508 | 0.608, 0.508 | 1.6 (1.2–2.2) | 1.6 (1.1–2.3) | 1.5 (1.1–2.0) | 0.002 | 0.018 | 0.004 | 0.017 | 0.1624 | 0.032 |
| rs3212220 | T | 0.409, 0.297 | 0.355, 0.297 | 0.394, 0.297 | 1.6 (1.2–2.2) | 1.3 (0.8–1.9) | 1.5 (1.2–2.1) | 0.002 | 0.186 | 0.003 | 0.017 | 1 | 0.031 | |
| CHR1 | Gene | SNP1 | CHR2 | Gene | SNP2 | OR_INT | STAT | p-Value | TB Form |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | IL1RA | rs1794068 | 2 | IL1RA | rs3213448 | 0.07834 | 21.47 | 3.60 × 10−6 | PTB |
| 2 | IL1RA | rs1794068 | 2 | IL1RA | rs3181052 | 0.08759 | 22.68 | 1.92 × 10−6 | PTB |
| 2 | IL1RA | rs1794068 | 5 | IL12 | rs3213119 | 0.04328 | 24.7 | 6.69 × 10−7 | PTB |
| 2 | IL1RA | rs1794068 | 5 | IL12 | rs3213096 | 0.06435 | 25.68 | 4.03 × 10−7 | PTB |
| 2 | IL1RA | rs1794068 | 6 | TNFB | rs3093542 | 0.05699 | 26.41 | 2.76 × 10−7 | PTB |
| 2 | IL1RA | rs315951 | 2 | IL1RA | rs9005 | 8.265 | 17.38 | 3.07 × 10−5 | PTB |
| 2 | IL1RA | rs315951 | 5 | IL4 | rs2243266 | 0.1028 | 17.66 | 2.64 × 10−5 | PTB |
| 2 | IL1RA | rs315951 | 5 | IL12 | rs3213119 | 0.008753 | 31.27 | 2.25 × 10−8 | PTB |
| 2 | IL1RA | rs315951 | 5 | IL12 | rs3213096 | 0.007691 | 32.86 | 9.92 × 10−9 | PTB |
| 2 | IL1RA | rs315951 | 6 | TNFB | rs3093542 | 0.008263 | 32.32 | 1.31 × 10−8 | PTB |
| 5 | IL4 | rs2070874 | 5 | IL12 | rs3213119 | 18.18 | 29.85 | 4.66 × 10−8 | PTB |
| 5 | IL4 | rs2070874 | 5 | IL12 | rs3213096 | 18.33 | 30.69 | 3.03 × 10−8 | PTB |
| 5 | IL4 | rs2070874 | 6 | TNFB | rs3093542 | 18.86 | 31.75 | 1.76 × 10−8 | PTB |
| 5 | IL4 * | rs2070874 | 5 | IL12 | rs3213096 | 16.71 | 37.64 | 8.52 × 10−10 | PTB |
| 5 | IL4 * | rs2070874 | 5 | IL12 | rs730690 | 5.056 | 16.02 | 6.26 × 10−5 | PTB |
| 5 | IL4 * | rs2070874 | 5 | IL4 | rs2243266 | 5.007 | 23.61 | 1.18 × 10−6 | LNTB |
| Gene | db SNP rsID/Other Name | Gene Location | Risk Allele | Case, Control Frequencies | Chi Square | p-Value | Odds Ratio | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (CI) | |||||||||||
| PTB | LNTB | PTB | LNTB | PTB | LNTB | PTB | LNTB | ||||
| P2RX7 | rs2393799/−762T/C | Exon | C | 0.707, 0.611 | 0.917, 0.611 | 3.892 | 19.23 | 0.048 | 1.15 × 10−5 | 1.5 (1–2.4) | 7 (2.6–18.4) |
| rs3751143/1513 A/C | Exon | C | 0.574, 0.525 | 0.574, 0.525 | 0.816 | 0.079 | 0.3664 | 0.7791 | 1.2 (0.79–1.7) | 1.1 (0.5–2.2) | |
| VDR | rs2228570/FokI | Exon | G | 0.505, 0.472 | 0.552, 0.472 | 0.436 | 1.151 | 0.5 | 0.288 | ND | ND |
| rs731236/TaqI | Exon | C | 0.893, 0.861 | 0.895, 0.525 | 0.849 | 0.298 | 0.357 | 0.5849 | ND | ND | |
| rs1544410/BsmI | Exon | Only GG Genotype observed | |||||||||
| IRGM | rs9637876/−261T/C | Alu sequence | C | 0.306, 0.255 | 0.272, 0.255 | 1.53 | 1.2 | 0.2161 | 0.515 | ND | ND |
| TLR2 | rs6265786/Arg 299 Trp | intron | G | 1.000, 0.958 | 0.979, 0.958 | 9.53 | 0.471 | 0.002 | 0.4925 | 20.92 (1.2–369.3) | 2.1 (0.25–17.25) |
| TLR4 | rs498670/Asp 299 Gly | Intron | G | 0.223, 0.125 | 0.05, 0.125 | 6.09 | 2.622 | 0.0135 | 0.1054 | 2.1 (1.2–2.5) | 0.11 (0.10–1.3) |
| NOS2A | rs7215373 | Intron | T | 0.481, 0.405 | 0.514, 0.400 | 2.732 | 2.914 | 0.0983 | 0.0878 | 1.3 (0.94–1.95) | 1.6 (0.94–2.65) |
| rs2274894 | 3’UTR | T/G | 0.213, 0.171 | 0.05, 0.125 | 1.348 | 0.45 | 0.2456 | 0.5022 | 1.3 (0.83–2.06) | 1.3 (0.63–2.6) | |
| SLC11A1/NRAMP1 | rs3731865 | Exon | Only CC genotype observed | ||||||||
| 17235409 | Intron | Only AG genotype observed | |||||||||
| SP110 | rs6436915 | Intron | T | 0.421, 0.347 | 0.417, 0.350 | 2.766 | 1.038 | 0.0963 | 0.3082 | ND | ND |
| rs1346311 | Intron | T | 0.105, 0.104 | 0.959, 0.900 | 0.001 | 2.516 | 0.9701 | 0.1127 | ND | ND | |
| rs7580900 | Intron | T | 0.531, 0.473 | 0.554, 0.472 | 1.613 | 1.471 | 0.204 | 0.2252 | ND | ND | |
| DCSIGN (CD209) | rs4804803/−336 A/G | Promoter | A | 0.745, 0.380 | 0.534, 0.380 | 55.47 | 4.52 | 9.48 × 10−14 | 3.34 × 10−2 | 4.0 (2.6–6.0) | 1.9 (1.0–3.4) |
| SNP | Groups | N | Genotype Frequencies | Allele Frequencies | Without Heterozygosity Model | Heterozygosity Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (01 vs. 00 + 11) | ||||||||||||
| 00 | 01 | 11 | 0 | 1 | OR (CI ) | p-Value | OR (CI) | p-Value | Padj | |||
| rs1978331 | All TB | 185 | 0.26 | 0.44 | 0.30 | 0.48 | 0.52 | 1.02 (0.73–1.41) | 0.9209 | 0.55 (0.34–0.87) | 0.013 | 0.039 |
| T = 0, C = 1 | PTB | 135 | 0.25 | 0.46 | 0.29 | 0.48 | 0.52 | 1 (0.70–1.43) | 0.9738 | 0.60 (0.36–0.99) | 0.076 | 0.168 |
| LNTB | 50 | 0.3 | 0.38 | 0.32 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 1.04 (0.65–1.66) | 0.8533 | 0.43 (0.22–0.85) | 0.018 | 0.037 | |
| Control | 120 | 0.18 | 0.59 | 0.23 | 0.47 | 0.52 | ||||||
| rs2660898 | TT | TG | GG | |||||||||
| T = 0, G = 1 | All TB | 185 | 0.17 | 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.38 | 0.63 | 1.21 (0.85–1.7) | 0.2761 | 0.76(0.48–1.2) | 0.283 | 0.849 |
| PTB | 135 | 0.15 | 0.42 | 0.44 | 0.36 | 0.64 | 1.1 (0.76–1.61) | 0.5822 | 0.77(0.46–1.3) | 0.309 | 0.927 | |
| LNTB | 50 | 0.22 | 0.4 | 0.36 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 1.5(0.93–2.44) | 0.093 | 0.75(0.38–1.5) | 0.496 | 1.488 | |
| Control | 120 | 0.09 | 0.48 | 0.43 | 0.33 | 0.67 | ||||||
| TT | TC | CC | ||||||||||
| rs17525495 | All TB | 185 | 0.06 | 0.24 | 0.69 | 0.19 | 0.82 | 1.33(0.83–2.1) | 0.238 | 0.95(0.53–1.7) | 0.8827 | 2.6481 |
| T = 0, C = 1 | PTB | 135 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.65 | 0.19 | 0.81 | 1.31(0.78–2.2) | 0.298 | 1.1(0.60–2.1) | 0.753 | 2.259 |
| LNTB | 50 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.62 | 0.19 | 0.80 | 1.38(0.72–2.65) | 0.329 | 0.82(0.35–1.9) | 0.831 | 2.493 | |
| Control | 120 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 0.73 | 0.15 | 0.85 | ||||||
| db SNP rsID | Risk Allele | Males (Case = 75; Control = 70) | Female (Case = 50; Control = 54) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case, Control Frequencies | p-Value | P Bonferroni | Odds Ratio (CI) | Case, Control Frequencies | p-Value | P Bonferroni | Odds Ratio (CI) | ||
| rs3788935 | A | 0.1102, 0.01 | 0.0072 | 0.0288 | 17 (0.94–300) | 0.160, 0.106 | 0.1673 | 0.6692 | 1.6 (0.82–3.2) |
| rs3761624 | A | 0.2, 0.05 | 0.012 | 0.048 | 4.3 (1.2–16) | 0.356, 0.244 | 0.0423 | 0.1692 | 1.7 (1.0–2.9) |
| rs3764880 | A | 0.107, 0.029 | 0.1012 | 0.4048 | 3.9 (0.81–19) | 0.229, 0.149 | 0.0557 | 0.2228 | 1.7 (0.98–2.9) |
| rs3764879 | C | 0.558, 0.482 | 0.5934 | 2.3736 | 1.3 (0.61–2.6) | 0.489, 0.440 | 0.3981 | 1.5924 | 1.2 (0.77–1.9) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abhimanyu; Bose, M.; Giri, A.; Varma-Basil, M. Comparative Genetic Association Analysis of Human Genetic Susceptibility to Pulmonary and Lymph Node Tuberculosis. Genes 2023, 14, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010207
Abhimanyu, Bose M, Giri A, Varma-Basil M. Comparative Genetic Association Analysis of Human Genetic Susceptibility to Pulmonary and Lymph Node Tuberculosis. Genes. 2023; 14(1):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010207
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbhimanyu, Mridula Bose, Astha Giri, and Mandira Varma-Basil. 2023. "Comparative Genetic Association Analysis of Human Genetic Susceptibility to Pulmonary and Lymph Node Tuberculosis" Genes 14, no. 1: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010207
APA StyleAbhimanyu, Bose, M., Giri, A., & Varma-Basil, M. (2023). Comparative Genetic Association Analysis of Human Genetic Susceptibility to Pulmonary and Lymph Node Tuberculosis. Genes, 14(1), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010207







