Estimation of Complex-Trait Prediction Accuracy from the Different Holo-Omics Interaction Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Methodology
2.1. Real Data Analysis
2.2. Evaluation of the Models
2.3. Noninteractive Models
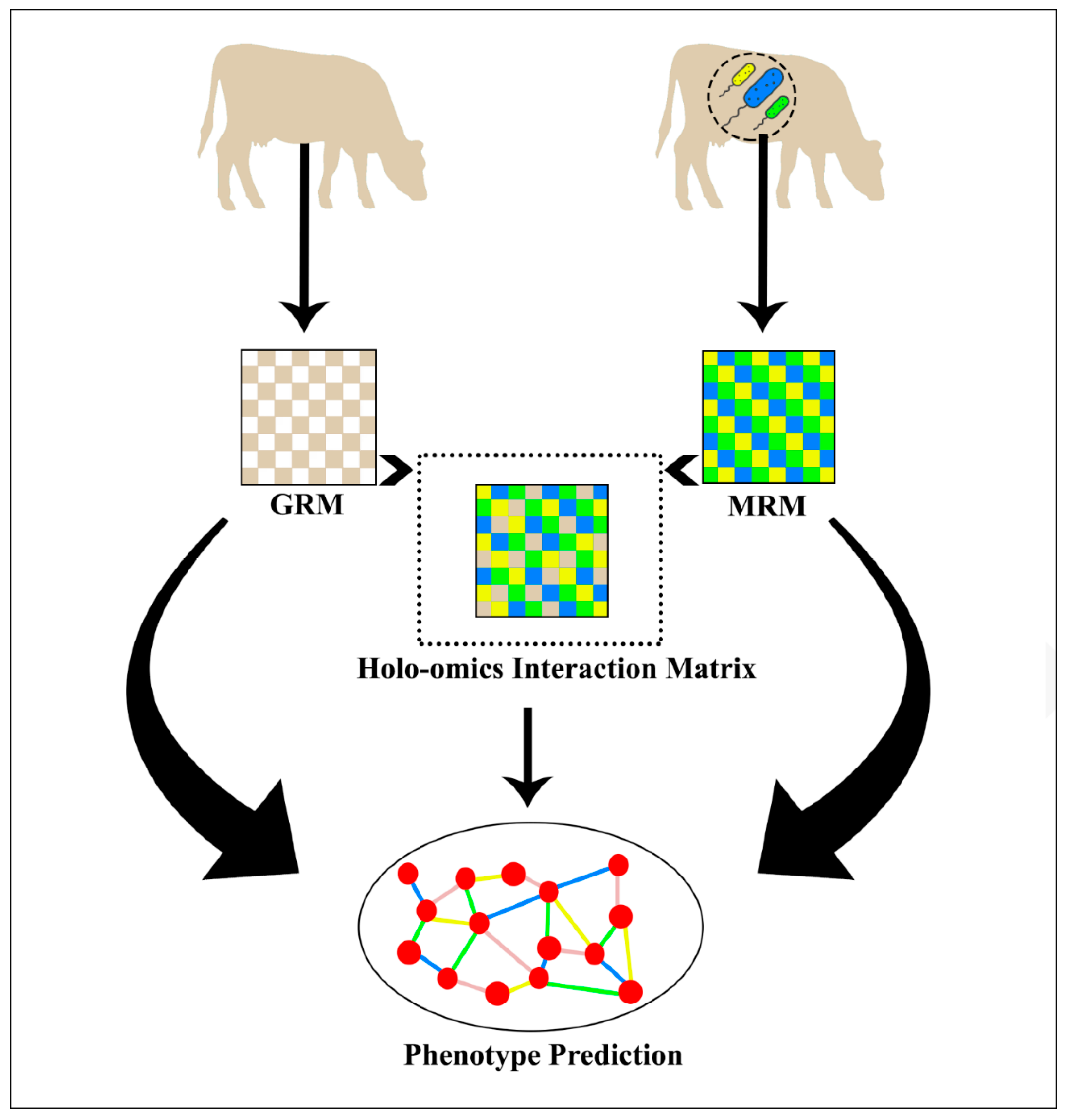
2.4. Holo-Omics Interactive Models
2.5. Prediction Accuracy Evaluation
3. Results
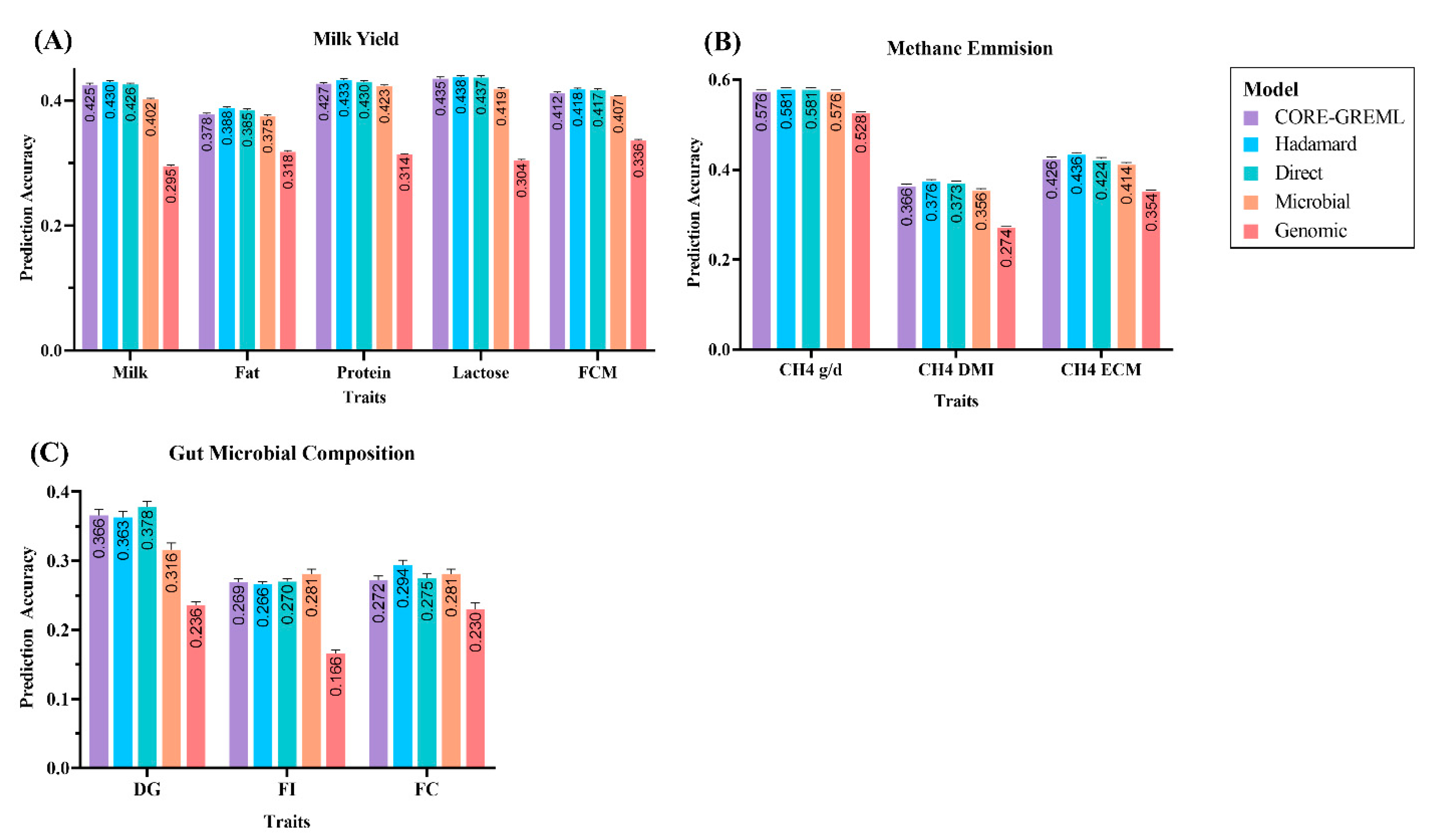
3.1. Prediction Accuracy of Complex Traits from the Ruminomics—1000 Cow’s Study
3.2. Prediction Accuracy of Complex Traits from the Gut Microbial Composition Study
4. Discussion
4.1. Modeling the Non-Interactive Interaction
4.2. Modeling the Interactive Interaction
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Georges, M.; Charlier, C.; Hayes, B. Harnessing genomic information for livestock improvement. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacquard, S.; Garrido-Oter, R.; González, A.; Spaepen, S.; Ackermann, G.; Lebeis, S.; McHardy, A.C.; Dangl, J.L.; Knight, R.; Ley, R. Microbiota and host nutrition across plant and animal kingdoms. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodhams, D.C.; Bletz, M.C.; Becker, C.G.; Bender, H.A.; Buitrago-Rosas, D.; Diebboll, H.; Huynh, R.; Kearns, P.J.; Kueneman, J.; Kurosawa, E. Host-associated microbiomes are predicted by immune system complexity and climate. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, J.A.; Blaser, M.J.; Caporaso, J.G.; Jansson, J.K.; Lynch, S.V.; Knight, R. Current understanding of the human microbiome. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Estellé, J.; Kiilerich, P.; Ramayo-Caldas, Y.; Xia, Z.; Feng, Q.; Liang, S.; Pedersen, A.Ø.; Kjeldsen, N.J.; Liu, C. A reference gene catalogue of the pig gut microbiome. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, M.E.; Hayes, B.J.; Meuwissen, T.H. Using the genomic relationship matrix to predict the accuracy of genomic selection. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2011, 128, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, E.M.; Moate, P.J.; Marett, L.C.; Cocks, B.G.; Hayes, B.J. Metagenomic predictions: From microbiome to complex health and environmental phenotypes in humans and cattle. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Irving, B.; Fitzsimmons, C.; Plastow, G.; Guan, L.L. Host genetics influence the rumen microbiota and heritable rumen microbial features associate with feed efficiency in cattle. Microbiome 2019, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmar, S.; Wellmann, R.; Borda-Molina, D.; Rodehutscord, M.; Camarinha-Silva, A.; Bennewitz, J. The gut microbial architecture of efficiency traits in the domestic poultry model species Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica) assessed by mixed linear models. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2020, 10, 2553–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, P.; Maltecca, C.; Schwab, C.; Fix, J.; Tiezzi, F. Microbiability of meat quality and carcass composition traits in swine. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2021, 138, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, D.; Leviatan, S.; Hanemann, A.; Cohen, Y.; Weissbrod, O.; Segal, E. An atlas of robust microbiome associations with phenotypic traits based on large-scale cohorts from two continents. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camarinha-Silva, A.; Maushammer, M.; Wellmann, R.; Vital, M.; Preuss, S.; Bennewitz, J. Host genome influence on gut microbial composition and microbial prediction of complex traits in pigs. Genetics 2017, 206, 1637–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramayo-Caldas, Y.; Zingaretti, L.; Popova, M.; Estellé, J.; Bernard, A.; Pons, N.; Bellot, P.; Mach, N.; Rau, A.; Roume, H. Identification of rumen microbial biomarkers linked to methane emission in Holstein dairy cows. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2020, 137, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusev, A.; Lee, S.H.; Trynka, G.; Finucane, H.; Vilhjálmsson, B.J.; Xu, H.; Zang, C.; Ripke, S.; Bulik-Sullivan, B.; Stahl, E. Partitioning heritability of regulatory and cell-type-specific variants across 11 common diseases. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 95, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Enciso, M.; Zingaretti, L.M.; Ramayo-Caldas, Y.; de Los Campos, G. Opportunities and limits of combining microbiome and genome data for complex trait prediction. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2021, 53, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.J.; Sasson, G.; Garnsworthy, P.C.; Tapio, I.; Gregson, E.; Bani, P.; Huhtanen, P.; Bayat, A.R.; Strozzi, F.; Biscarini, F. A heritable subset of the core rumen microbiome dictates dairy cow productivity and emissions. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, P.; de Los Campos, G. Genome-wide regression and prediction with the BGLR statistical package. Genetics 2014, 198, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Ghosh, M.; Mallick, B.K. Bayesian nonlinear regression for large p small n problems. J. Multivar. Anal. 2012, 108, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanRaden, P.M. Efficient methods to compute genomic predictions. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 4414–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Im, H.K.; Lee, S.H. CORE GREML for estimating covariance between random effects in linear mixed models for complex trait analyses. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitezica, Z.G.; Legarra, A.; Toro, M.A.; Varona, L. Orthogonal estimates of variances for additive, dominance, and epistatic effects in populations. Genetics 2017, 206, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Lai, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, P.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, Y. Applications of Support Vector Machine in Genomic Prediction in Pig and Maize Populations. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 598318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, M. Genomic selection: Prediction of accuracy and maximisation of long term response. Genetica 2009, 136, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.V.; Littman, D.R.; Macpherson, A.J. Interactions between the microbiota and the immune system. Science 2012, 336, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, S.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Palanichamy, P.; Marudhamuthu, M. Role of Gut Microbiome in Neuromodulation. In Understanding Host-Microbiome Interactions-An Omics Approach; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 105–122. [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild, D.; Weissbrod, O.; Barkan, E.; Kurilshikov, A.; Korem, T.; Zeevi, D.; Costea, P.I.; Godneva, A.; Kalka, I.N.; Bar, N. Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping human gut microbiota. Nature 2018, 555, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.; Johansen, R.; Dunbar, J.; Munsky, B. Machine learning to predict microbial community functions: An analysis of dissolved organic carbon from litter decomposition. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Refaey, M.M.; Xu, W.; Tang, R.; Li, L. Host age affects the development of southern catfish gut bacterial community divergent from that in the food and rearing water. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.C.; Brennan, J.R.; Wagner, N.E.; Egizi, A.M. Comparative hologenomics of two Ixodes scapularis tick populations in New Jersey. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Sánchez, S.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; de la Fuente, J. Evolutionary insights into the tick hologenome. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, E.; Koren, O.; Reshef, L.; Efrony, R.; Zilber-Rosenberg, I. The role of microorganisms in coral health, disease and evolution. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, E.; Zilber-Rosenberg, I. Microbes drive evolution of animals and plants: The hologenome concept. mBio 2016, 7, e01395-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Difford, G.F.; Plichta, D.R.; Løvendahl, P.; Lassen, J.; Noel, S.J.; Højberg, O.; Wright, A.-D.G.; Zhu, Z.; Kristensen, L.; Nielsen, H.B. Host genetics and the rumen microbiome jointly associate with methane emissions in dairy cows. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weishaar, R.; Wellmann, R.; Camarinha-Silva, A.; Rodehutscord, M.; Bennewitz, J. Selecting the hologenome to breed for an improved feed efficiency in pigs—A novel selection index. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2020, 137, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyholm, L.; Koziol, A.; Marcos, S.; Botnen, A.B.; Aizpurua, O.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Limborg, M.T.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Alberdi, A. Holo-omics: Integrated host-microbiota multi-omics for basic and applied biological research. Iscience 2020, 23, 101414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-H.; On, K.-W.; Lim, W.; Kim, J.; Ha, J.-W.; Zhang, B.-T. Hadamard product for low-rank bilinear pooling. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.04325. [Google Scholar]
- Merrick, L.F.; Herr, A.W.; Sandhu, K.S.; Lozada, D.N.; Carter, A.H. Optimizing plant breeding programs for genomic selection. Agronomy 2022, 12, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, J.W.; Crossa, J.; Toledo, F.H.; Cuevas, J. On Hadamard and Kronecker products in covariance structures for genotype× environment interaction. Plant Genome 2020, 13, e20033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, I. Life’s Other Secret: The New Mathematics of the Living World; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
| Name | Subject | Sample size | No. of SNPs | No. of OTUs | Fixed Effects | Traits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ruminomics—1000 cows study | Cattle | 795 * | 120,321 | 734 | Animal farm | Milk Fat Protein Lactose FCM CH4 g/d CH4 DMI CH4 ECM |
| Gut microbial composition study | Pig | 207 | 51,970 | 1870 | Slaughter weight, weight and age at the test station | Daily Gain Feed Intake Feed Conversion |
| Holo-omics Indirect Prediction | Holo-omics Direct Prediction | Microbial Prediction | Genomic Prediction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | rc | rh | rd | rm | rg |
| Milk | 0.425 ± 0.003 | 0.430 ± 0.002 | 0.426 ± 0.002 | 0.402 ± 0.002 | 0.295 ± 0.002 |
| Fat | 0.378 ± 0.002 | 0.388 ± 0.002 | 0.385 ± 0.002 | 0.375 ± 0.002 | 0.318 ± 0.002 |
| Protein | 0.427 ± 0.002 | 0.433 ± 0.002 | 0.430 ± 0.002 | 0.423 ± 0.002 | 0.314 ± 0.001 |
| Lactose | 0.435 ± 0.003 | 0.438 ± 0.002 | 0.437 ± 0.003 | 0.419 ± 0.002 | 0.304 ± 0.002 |
| FCM | 0.412 ± 0.002 | 0.418 ± 0.002 | 0.417 ± 0.002 | 0.407 ± 0.001 | 0.336 ± 0.001 |
| CH4 g/d | 0.576 ± 0.001 | 0.581 ± 0.001 | 0.581 ± 0.002 | 0.576 ± 0.001 | 0.528 ± 0.002 |
| CH4 DMI | 0.366 ± 0.002 | 0.376 ± 0.002 | 0.373 ± 0.002 | 0.356 ± 0.002 | 0.274 ± 0.001 |
| CH4 ECM | 0.426 ± 0.002 | 0.436 ± 0.002 | 0.424 ± 0.003 | 0.414 ± 0.002 | 0.354 ± 0.001 |
| Holo-Omics Indirect Prediction | Holo-Omics Direct Prediction | Microbial Prediction | Genomic Prediction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | rc | rh | rd | rm | rg |
| DG | 0.366 ± 0.009 | 0.363 ± 0.009 | 0.378 ± 0.008 | 0.316 ± 0.01 | 0.236 ± 0.005 |
| FI | 0.269 ± 0.005 | 0.266 ± 0.004 | 0.270 ± 0.004 | 0.281 ± 0.007 | 0.166 ± 0.005 |
| FC | 0.272 ± 0.006 | 0.294 ± 0.007 | 0.275 ± 0.006 | 0.281 ± 0.007 | 0.230 ± 0.009 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qadri, Q.R.; Zhao, Q.; Lai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Q. Estimation of Complex-Trait Prediction Accuracy from the Different Holo-Omics Interaction Models. Genes 2022, 13, 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091580
Qadri QR, Zhao Q, Lai X, Zhang Z, Zhao W, Pan Y, Wang Q. Estimation of Complex-Trait Prediction Accuracy from the Different Holo-Omics Interaction Models. Genes. 2022; 13(9):1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091580
Chicago/Turabian StyleQadri, Qamar Raza, Qingbo Zhao, Xueshuang Lai, Zhenyang Zhang, Wei Zhao, Yuchun Pan, and Qishan Wang. 2022. "Estimation of Complex-Trait Prediction Accuracy from the Different Holo-Omics Interaction Models" Genes 13, no. 9: 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091580
APA StyleQadri, Q. R., Zhao, Q., Lai, X., Zhang, Z., Zhao, W., Pan, Y., & Wang, Q. (2022). Estimation of Complex-Trait Prediction Accuracy from the Different Holo-Omics Interaction Models. Genes, 13(9), 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091580






