A Genome-Wide Association Study of Genetic Variants of Apolipoprotein A1 Levels and Their Association with Vitamin D in Korean Cohorts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Biochemical Measurements
2.3. Genotyping
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.5. Functional Annotation Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Participants
3.2. GWAS Meta-Analysis of ApoA1, ApoB, and ApoB/ApoA1
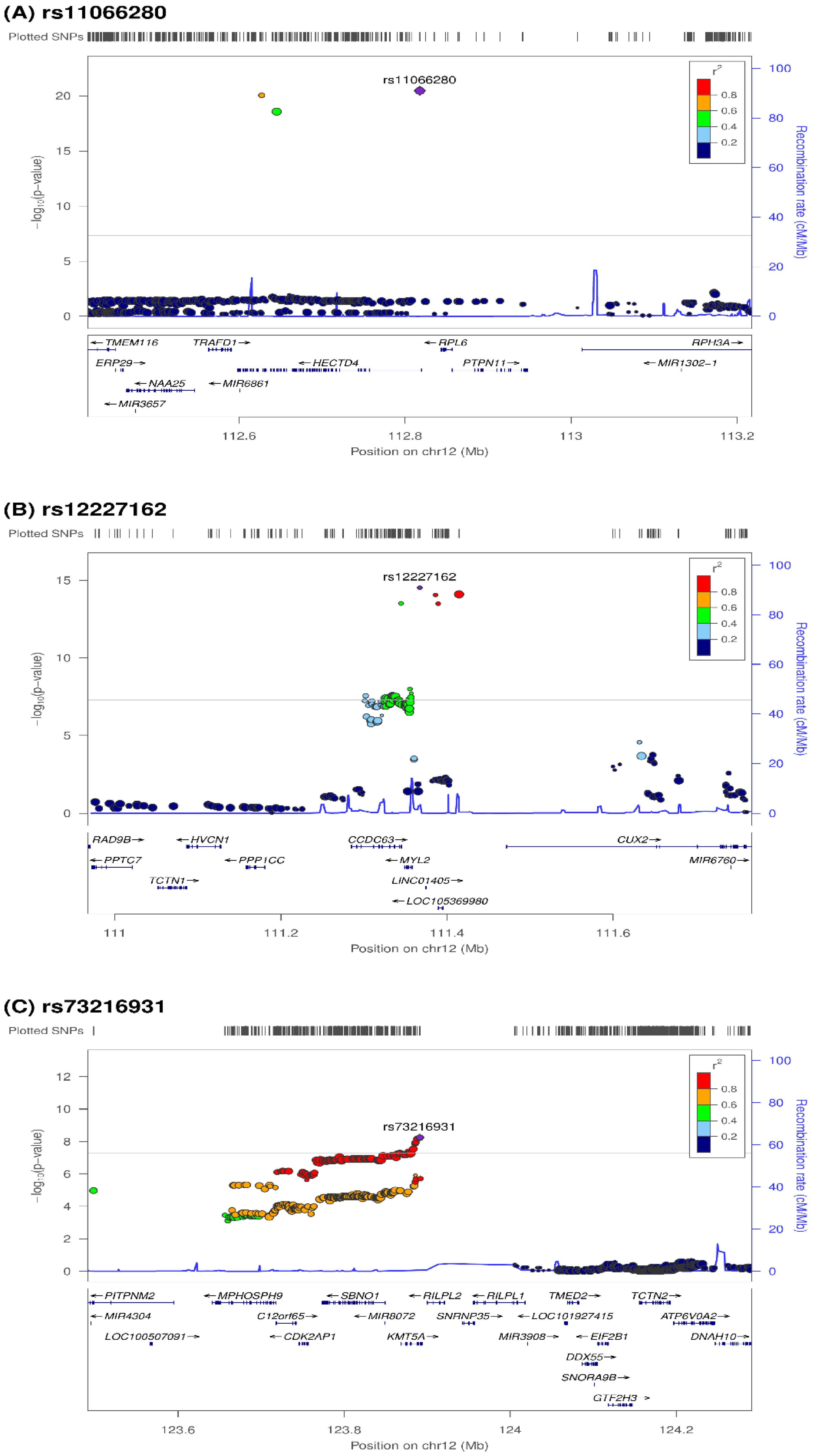
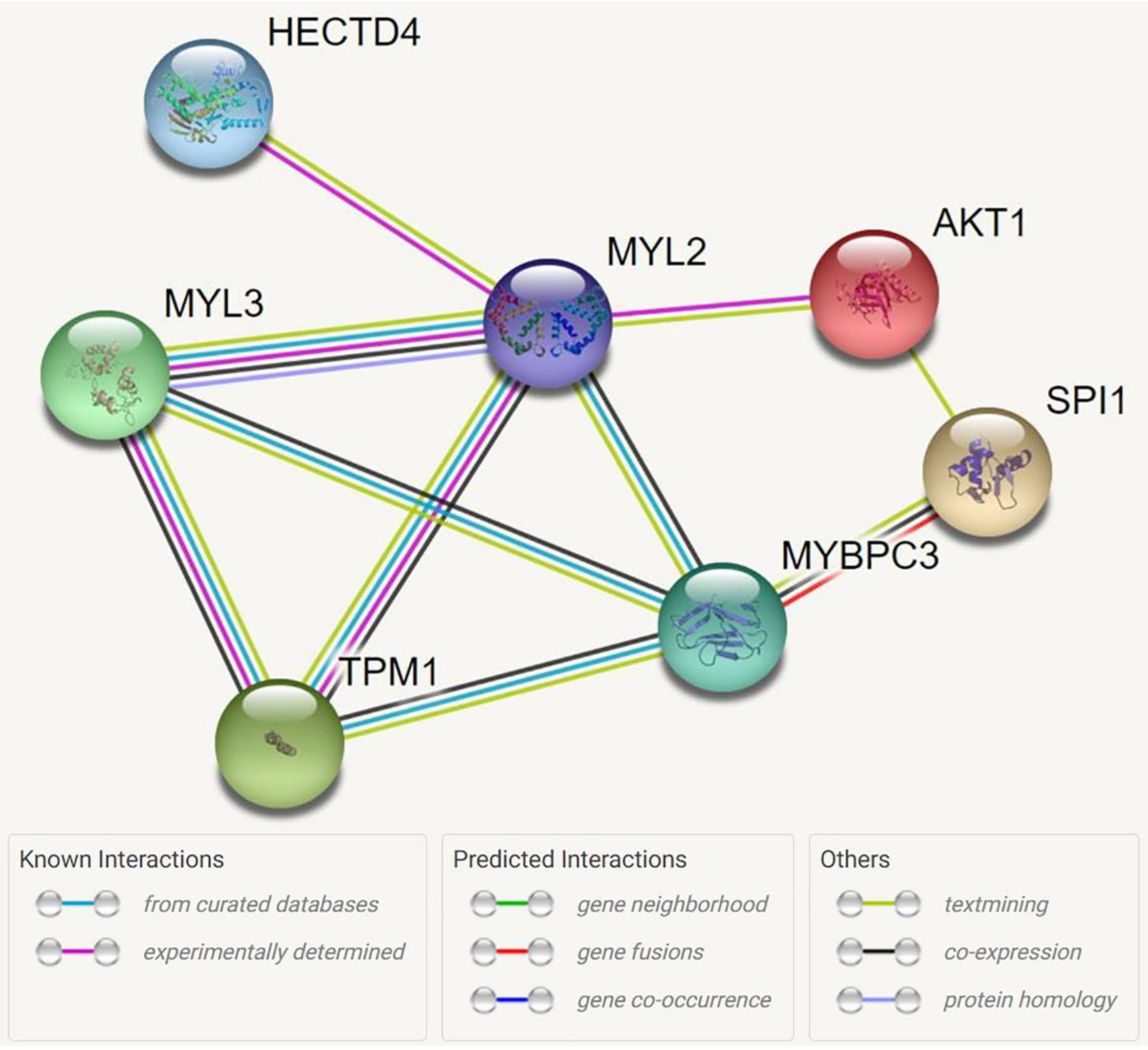
3.3. Regional Analysis and Functional Annotation
3.4. Association between Vitamin D and ApoA1, ApoB, and ApoB/ApoA1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The WHO CVD Risk Chart Working Group. World Health Organization cardiovascular disease risk charts: Revised models to estimate risk in 21 global regions. Lancet Glob Health 2019, 7, e1332–e1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathiresan, S.; Melander, O.; Anevski, D.; Guiducci, C.; Burtt, N.P.; Roos, C.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; Berglund, G.; Hedblad, B.; Groop, L.; et al. Polymorphisms associated with cholesterol and risk of cardiovascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willer, C.J.; Sanna, S.; Jackson, A.U.; Scuteri, A.; Bonnycastle, L.L.; Clarke, R.; Heath, S.C.; Timpson, N.J.; Najjar, S.S.; Stringham, H.M.; et al. Newly identified loci that influence lipid concentrations and risk of coronary artery disease. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhainds, D.; Brodeur, M.R.; Tardif, J.C. Lipids, Apolipoproteins, and Inflammatory Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Risk: What Have We Learned? Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 104, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenendijk, M.; Cantor, R.M.; de Bruin, T.W.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M. The apoAI-CIII-AIV gene cluster. Atherosclerosis 2001, 157, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, J.S.; Cuchel, M. ApoA-I-Directed Therapies for the Management of Atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2015, 17, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneva, A.M.; Potolitsyna, N.N.; Bojko, E.R.; Odland, J.O. The apolipoprotein B/apolipoprotein A-I ratio as a potential marker of plasma atherogenicity. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 591454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Tan, W.; Chen, X.; Ye, S. Serum apolipoprotein B-to-apolipoprotein A1 ratio is independently associated with disease severity in patients with acute pancreatitis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalani, R.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Deepa, D.; Gopala, S.; Prabhakaran, D.; Tirschwell, D.; Sylaja, P.N. Apolipoproteins B and A1 in Ischemic Stroke Subtypes. J. Stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 104670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, X.; Chen, Y.; Yan, C.; Liu, S.; Deng, L.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, P.; Pan, D.; Zeng, B.; Chen, Q. Apolipoprotein B/apolipoprotein A1 ratio and mortality among incident peritoneal dialysis patients. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathiresan, S.; Melander, O.; Guiducci, C.; Surti, A.; Burtt, N.P.; Rieder, M.J.; Cooper, G.M.; Roos, C.; Voight, B.F.; Havulinna, A.S.; et al. Six new loci associated with blood low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol or triglycerides in humans. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathiresan, S.; Willer, C.J.; Peloso, G.M.; Demissie, S.; Musunuru, K.; Schadt, E.E.; Kaplan, L.; Bennett, D.; Li, Y.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Common variants at 30 loci contribute to polygenic dyslipidemia. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teslovich, T.M.; Musunuru, K.; Smith, A.V.; Edmondson, A.C.; Stylianou, I.M.; Koseki, M.; Pirruccello, J.P.; Ripatti, S.; Chasman, D.I.; Willer, C.J.; et al. Biological, clinical and population relevance of 95 loci for blood lipids. Nature 2010, 466, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willer, C.J.; Schmidt, E.M.; Sengupta, S.; Peloso, G.M.; Gustafsson, S.; Kanoni, S.; Ganna, A.; Chen, J.; Buchkovich, M.L.; Mora, S.; et al. Discovery and refinement of loci associated with lipid levels. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhang, X.; Shuai, P.; Miao, Y.; Ye, Z.; Lin, Y. Genetic variants influencing lipid levels and risk of dyslipidemia in Chinese population. J. Genet. 2017, 96, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; He, M.; Mo, Z.; Wu, C.; Yang, H.; Yu, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; et al. A genome wide association study identifies common variants associated with lipid levels in the Chinese population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, M.; Akiyama, M.; Takahashi, A.; Matoba, N.; Momozawa, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Iwata, N.; Ikegawa, S.; Hirata, M.; Matsuda, K.; et al. Genetic analysis of quantitative traits in the Japanese population links cell types to complex human diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ober, C.; Abney, M.; McPeek, M.S. The genetic dissection of complex traits in a founder population. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 69, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kraft, H.G.; Kochl, S.; Menzel, H.J.; Sandholzer, C.; Utermann, G. The apolipoprotein (a) gene: A transcribed hypervariable locus controlling plasma lipoprotein (a) concentration. Hum. Genet. 1992, 90, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainwater, D.L.; Kammerer, C.M.; VandeBerg, J.L.; Hixson, J.E. Characterization of the genetic elements controlling lipoprotein(a) concentrations in Mexican Americans. Evidence for at least three controlling elements linked to LPA, the locus encoding apolipoprotein(a). Atherosclerosis 1997, 128, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasman, D.I.; Pare, G.; Zee, R.Y.; Parker, A.N.; Cook, N.R.; Buring, J.E.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Rose, L.M.; Smith, J.D.; Williams, P.T.; et al. Genetic loci associated with plasma concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, apolipoprotein A1, and Apolipoprotein B among 6382 white women in genome-wide analysis with replication. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2008, 1, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, T.G.; Sanderson, E.; Palmer, T.M.; Ala-Korpela, M.; Ference, B.A.; Davey Smith, G.; Holmes, M.V. Evaluating the relationship between circulating lipoprotein lipids and apolipoproteins with risk of coronary heart disease: A multivariable Mendelian randomisation analysis. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaaby, T.; Thuesen, B.H.; Linneberg, A. Vitamin D, Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Factors. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 996, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.A.; Yoon, J.W.; Lee, Y.; Choi, H.J.; Yun, J.W.; Bae, E.; Kwon, S.H.; Ahn, S.E.; Do, A.R.; Jin, H.; et al. Unveiling Genetic Variants Underlying Vitamin D Deficiency in Multiple Korean Cohorts by a Genome-Wide Association Study. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 36, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, B.W.; Shin, H.T.; Seo, J. Risk Allele Frequency Analysis of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms for Vitamin D Concentrations in Different Ethnic Group. Genes 2021, 12, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Han, S.; Hwang, M.Y.; Shin, D.M.; Park, M.Y.; Lu, Y.; Yoon, K.; Jang, H.M.; Kim, Y.K.; et al. The Korea Biobank Array: Design and Identification of Coding Variants Associated with Blood Biochemical Traits. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.S.; Go, M.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Heo, J.Y.; Oh, J.H.; Ban, H.J.; Yoon, D.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, D.J.; Park, M.; et al. A large-scale genome-wide association study of Asian populations uncovers genetic factors influencing eight quantitative traits. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaneau, O.; Marchini, J.; Zagury, J.F. A linear complexity phasing method for thousands of genomes. Nat. Methods 2011, 9, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini, J.; Howie, B.; Myers, S.; McVean, G.; Donnelly, P. A new multipoint method for genome-wide association studies by imputation of genotypes. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, M.; Venturi, S.; Del Bo, C.; Moller, P.; Riso, P.; Porrini, M. Vitamin D Counteracts Lipid Accumulation, Augments Free Fatty Acid-Induced ABCA1 and CPT-1A Expression While Reducing CD36 and C/EBPbeta Protein Levels in Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochran, W.G. The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics 1954, 10, 101–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, J.P. Interpretation of tests of heterogeneity and bias in meta-analysis. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2008, 14, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, B.; Roeder, K.; Wasserman, L. Genomic control, a new approach to genetic-based association studies. Theor. Popul. Biol. 2001, 60, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruim, R.J.; Welch, R.P.; Sanna, S.; Teslovich, T.M.; Chines, P.S.; Gliedt, T.P.; Boehnke, M.; Abecasis, G.R.; Willer, C.J. LocusZoom: Regional visualization of genome-wide association scan results. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2336–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabet, F.; Vickers, K.C.; Cuesta Torres, L.F.; Wiese, C.B.; Shoucri, B.M.; Lambert, G.; Catherinet, C.; Prado-Lourenco, L.; Levin, M.G.; Thacker, S.; et al. HDL-transferred microRNA-223 regulates ICAM-1 expression in endothelial cells. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG: Integrating viruses and cellular organisms. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2021, 49, D545–D551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangaraj, M.; Nanda, R.; Panda, S. Apolipoprotein A-I: A Molecule of Diverse Function. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 31, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Tabet, F.; Cochran, B.J.; Cuesta Torres, L.F.; Wu, B.J.; Barter, P.J.; Rye, K.A. Apolipoprotein A-I enhances insulin-dependent and insulin-independent glucose uptake by skeletal muscle. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Khanbabapour Sasi, A.; Hussen, B.M.; Shoorei, H.; Siddiq, A.; Taheri, M.; Ayatollahi, S.A. Interplay between PI3K/AKT pathway and heart disorders. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, A.; Dubuis, G.; Ferreira, C.S.M.; Petremand, J.; Vanli, G.; Widmann, C. The PI3K/Akt pathway is not a main driver in HDL-mediated cell protection. Cell Signal. 2019, 62, 109347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karjalainen, M.K.; Holmes, M.V.; Wang, Q.; Anufrieva, O.; Kahonen, M.; Lehtimaki, T.; Havulinna, A.S.; Kristiansson, K.; Salomaa, V.; Perola, M.; et al. Apolipoprotein A-I concentrations and risk of coronary artery disease: A Mendelian randomization study. Atherosclerosis 2020, 299, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zittermann, A.; Pilz, S. Vitamin D and Cardiovascular Disease: An Update. Anticancer. Res. 2019, 39, 4627–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zittermann, A.; Trummer, C.; Theiler-Schwetz, V.; Lerchbaum, E.; Marz, W.; Pilz, S. Vitamin D and Cardiovascular Disease: An Updated Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration/EPIC-CVD/Vitamin D Studies Collaboration. Estimating dose-response relationships for vitamin D with coronary heart disease, stroke, and all-cause mortality: Observational and Mendelian randomisation analyses. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Total (N = 12,924) | KARE Cohort (N = 4938) | CAVAS Cohort (N = 7986) | p | Number of Missing KARE/CAVAS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 58.05 ± 8.70 | 57.48 ± 8.46 | 58.40 ± 8.82 | <0.001 | 0/0 |
| Sex (male %) | 5313 (41.1%) | 2309 (46.8%) | 3004 (37.6%) | <0.001 | 0/0 |
| Weight (kg) | 62.00 ± 9.95 | 62.90 ± 10.01 | 61.45 ± 9.88 | <0.001 | 0/1 |
| Height (cm) | 158.78 ± 8.53 | 159.96 ± 8.77 | 158.06 ± 8.29 | <0.001 | 0/1 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 24.53 ± 3.03 | 24.53 ± 3.02 | 24.54 ± 3.04 | 0.935 | 0/1 |
| Current smoking n (%) | 1571 (14.7%) | 804 (16.3%) | 767 (13.4%) | <0.001 | 5/2251 |
| Current drinking n (%) | 5522 (42.8%) | 2286 (46.3%) | 3236 (40.6%) | <0.001 | 5/9 |
| History of hypertension n (%) | 2375 (18.4%) | 218 (4.42%) | 2157 (27%) | <0.001 | 6/7 |
| History of diabetes n (%) | 752 (5.82%) | 90 (1.83%) | 662 (8.3%) | <0.001 | 7/7 |
| Systemic blood pressure (mmHg) | 122.16 ± 17.17 | 118.34 ± 16.17 | 124.52 ± 17.34 | <0.001 | 0/6 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 78.19 ± 10.40 | 77.61 ± 9.65 | 78.56 ± 10.83 | <0.001 | 0/6 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 196.48 ± 34.94 | 195.74 ± 34.29 | 196.94 ± 35.32 | 0.056 | 0/1 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 123.91 ± 31.28 | 124.23 ± 30.68 | 123.71 ± 31.64 | 0.36 | 109/170 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 44.74 ± 10.76 | 44.10 ± 10.51 | 45.14 ± 10.90 | <0.001 | 0/1 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 144.61 ± 93.73 | 141.68 ± 91.74 | 146.42 ± 94.90 | 0.005 | 0/3 |
| Log Triglycerides | 4.83 ± 0.52 | 4.80 ± 0.53 | 4.84 ± 0.52 | <0.001 | 0/3 |
| HbA1C (%) | 5.75 ± 0.89 | 5.76 ± 0.90 | 5.70 ± 0.81 | 0.004 | 0/6471 |
| Vitamin D (ng/mL) | 21.25 ± 8.90 | 17.35 ± 7.22 | 23.67 ± 8.98 | <0.001 | 0/20 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 99.05 ± 25.27 | 100.34 ± 30.48 | 98.1 ± 20.6 | <0.001 | 0/1 |
| ApoA1 (mg/dL) | 151.11 ± 26.26 | 145.24 ± 24.52 | 154.74 ± 26.64 | <0.001 | 0/0 |
| ApoB (mg/dL) | 108.33 ± 24.90 | 106.79 ± 24.26 | 109.28 ± 25.24 | <0.001 | 0/0 |
| ApoB/ApoA1 ratio | 0.74 ± 0.22 | 0.76 ± 0.22 | 0.73 ± 0.21 | <0.001 | 0/0 |
| HOMA-IR | 2.28 ± 2.56 | 2.50 ± 3.18 | 1.98 ± 1.29 | <0.001 | 0/4290 |
| HOMA-beta cell | 107.40 ± 80.43 | 110.26 ± 76.84 | 103.57 ± 84.86 | <0.001 | 0/4290 |
| Chr | SNP | Position | Allele | Independent Study | Meta-Analysis | Mapped Genes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort | Effect | SE | MAF | p | Effect | SE | p | |||||
| (HetPVal) | ||||||||||||
| 12 | rs11066280 | 112817783 | A/T | KARE | −4.123 | 0.646 | 0.17 | 1.89 × 10−10 | −4.002 | 0.424 | 3.46 × 10−21 | HECTD4 (intronic) |
| CAVAS | −3.91 | 0.561 | 0.16 | 3.45 × 10−12 | (0.8034) | |||||||
| 15 | rs16940212 | 58694020 | T/G | KARE | 3.37 | 0.513 | 0.34 | 5.79 × 10−11 | 3.09 | 0.336 | 3.62 × 10−20 | AQP9;LIPC (intergenic) |
| CAVAS | 2.88 | 0.444 | 0.34 | 9.37 × 10−11 | (0.4704) | |||||||
| 9 | rs2740488 | 107661742 | C/A | KARE | −4.192 | 0.558 | 0.26 | 6.59 × 10−14 | 3.341 | 0.369 | 1.49 × 10−19 | ABCA1 (intronic) |
| CAVAS | −2.676 | 0.493 | 0.25 | 5.90 × 10−8 | (0.0417) | |||||||
| 11 | rs75198898 | 116649806 | A/G | KARE | −5.302 | 0.931 | 0.07 | 1.31 × 10−8 | −5.327 | 0.599 | 5.64 × 10−19 | ZPR1 (intronic) |
| CAVAS | −5.345 | 0.782 | 0.08 | 8.54 × 10−12 | (0.9718) | |||||||
| 15 | rs6494007 | 58734645 | T/C | KARE | 3.196 | 0.572 | 0.25 | 2.44 × 10−8 | 3.197 | 0.37 | 5.17 × 10−18 | LIPC-AS1 (ncRNA_intronic) |
| CAVAS | 3.197 | 0.484 | 0.26 | 4.29 × 10−11 | (0.9989) | |||||||
| 11 | rs61905084 | 116610294 | C/T | KARE | 2.94 | 0.554 | 0.27 | 1.15 × 10−7 | −3.03 | 0.36 | 4.32 × 10−17 | LINC02702;BUD13 (intergenic) |
| CAVAS | 3.096 | 0.475 | 0.26 | 7.49 × 10−11 | (0.8307) | |||||||
| 8 | rs35495249 | 19865509 | A/C | KARE | 2.97 | 0.596 | 0.21 | 6.33 × 10−7 | 3.088 | 0.389 | 1.93 × 10−15 | LPL;SLC18A1 (intergenic) |
| CAVAS | 3.175 | 0.513 | 0.21 | 6.27 × 10−10 | (0.7942) | |||||||
| 12 | rs12227162 | 111367244 | T/C | KARE | −4.421 | 0.722 | 0.13 | 1.01 × 10−9 | −3.823 | 0.484 | 2.98 × 10−15 | MYL2;LINC01405 (intergenic) |
| CAVAS | −3.334 | 0.653 | 0.12 | 3.36 × 10−7 | (0.2643) | |||||||
| 15 | rs11858164 | 58742731 | G/T | KARE | −2.2 | 0.558 | 0.26 | 8.06 × 10−5 | 2.64 | 0.362 | 3.06 × 10−13 | LIPC-AS1 (ncRNA_intronic) |
| CAVAS | −2.962 | 0.476 | 0.26 | 5.26 × 10−10 | (0.2987) | |||||||
| 7 | rs146148222 | 80304855 | G/T | KARE | 5.099 | 1.115 | 0.05 | 4.88 × 10−6 | −4.728 | 0.665 | 1.16 × 10−12 | CD36 (intronic) |
| CAVAS | 4.523 | 0.829 | 0.07 | 4.93 × 10−8 | (0.6783) | |||||||
| 15 | rs62001712 | 58653911 | A/G | KARE | −2.043 | 0.551 | 0.28 | 2.08 × 10−4 | −2.473 | 0.358 | 4.73 × 10−12 | AQP9;LIPC (intergenic) |
| CAVAS | −2.788 | 0.471 | 0.28 | 3.30 × 10−9 | (0.3037) | |||||||
| 18 | rs12458441 | 47122158 | C/A | KARE | 2.075 | 0.563 | 0.27 | 2.29 × 10−4 | −2.361 | 0.363 | 7.42 × 10−11 | LIPG (UTR3) |
| CAVAS | 2.565 | 0.474 | 0.28 | 6.57 × 10−8 | (0.5055) | |||||||
| 16 | rs1800775 | 56995236 | C/A | KARE | −1.796 | 0.489 | 0.46 | 2.40 × 10−4 | 1.95 | 0.319 | 9.68 × 10−10 | CETP (upstream) |
| CAVAS | −2.065 | 0.421 | 0.45 | 9.57 × 10−7 | (0.6766) | |||||||
| 15 | rs539901 | 58674669 | G/T | KARE | 3.339 | 0.805 | 0.1 | 3.43 × 10−5 | −3.113 | 0.525 | 2.95 × 10−9 | AQP9;LIPC (intergenic) |
| CAVAS | 2.947 | 0.692 | 0.1 | 2.06 × 10−5 | (0.7119) | |||||||
| 12 | rs73216931 | 123891209 | C/T | KARE | 2.282 | 0.556 | 0.29 | 4.13 × 10−5 | −2.059 | 0.353 | 5.62 × 10−9 | KMT5A (intronic) |
| CAVAS | 1.908 | 0.458 | 0.3 | 3.08 × 10−5 | (0.6035) | |||||||
| 11 | rs1076485 | 116772441 | C/T | KARE | −1.339 | 0.497 | 0.45 | 7.11 × 10−3 | 1.778 | 0.323 | 3.64 × 10−8 | SIK3 (intronic) |
| CAVAS | −2.099 | 0.425 | 0.45 | 7.87 × 10−7 | (0.2451) | |||||||
| Chr | SNP | Position | Allele | Independent Study | Meta-Analysis | Mapped Genes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort | Effect | SE | MAF | p | Effect | SE | p | |||||
| (HetPVal) | ||||||||||||
| 1 | rs611917 | 109815252 | G/A | KARE | −7.6 | 1.057 | 0.05 | 7.66 × 10−13 | 6.643 | 0.657 | 4.69 × 10−24 | CELSR2 (intronic) |
| CAVAS | −6.042 | 0.838 | 0.06 | 6.02 × 10−13 | (0.2482) | |||||||
| 2 | rs3817588 | 27731212 | C/T | KARE | −2.961 | 0.516 | 0.32 | 9.86 × 10−9 | 2.45 | 0.326 | 5.71 × 10−14 | GCKR (intronic) |
| CAVAS | −2.11 | 0.421 | 0.32 | 5.51 × 10−7 | (0.2011) | |||||||
| 2 | rs11901649 | 21250223 | A/G | KARE | 3.038 | 0.826 | 0.09 | 2.38 × 10−4 | 3.32 | 0.516 | 1.24 × 10−10 | APOB (intronic) |
| CAVAS | 3.501 | 0.661 | 0.1 | 1.20 × 10−7 | (0.6617) | |||||||
| 5 | rs10474433 | 74616843 | C/T | KARE | 2.396 | 0.518 | 0.33 | 3.87 × 10−6 | −2.073 | 0.326 | 2.03 × 10−10 | ANKRD31;HMGCR (intergenic) |
| CAVAS | 1.861 | 0.419 | 0.33 | 9.19 × 10−6 | (0.4222) | |||||||
| 19 | rs404935 | 45372794 | A/G | KARE | 2.2 | 0.716 | 0.14 | 2.14 × 10−3 | 2.799 | 0.452 | 5.78 × 10−10 | NECTIN2 (intronic) |
| CAVAS | 3.195 | 0.582 | 0.13 | 4.21 × 10−8 | (0.281) | |||||||
| 8 | rs2954029 | 126490972 | A/T | KARE | 2.163 | 0.483 | 0.44 | 7.76 × 10−6 | 1.767 | 0.305 | 6.99 × 10−9 | TRIB1;LINC00861 (intergenic) |
| CAVAS | 1.504 | 0.393 | 0.44 | 1.32 × 10−4 | (0.2902) | |||||||
| 2 | rs72788559 | 21195522 | T/G | KARE | −2.938 | 0.711 | 0.13 | 3.62 × 10−5 | −2.609 | 0.467 | 2.28 × 10−8 | LDAH;APOB (intergenic) |
| CAVAS | −2.359 | 0.619 | 0.12 | 1.39 × 10−4 | (0.5389) | |||||||
| 11 | rs75198898 | 116649806 | A/G | KARE | 3.078 | 0.916 | 0.07 | 7.81 × 10−4 | 3.132 | 0.57 | 3.87 × 10−8 | ZPR1 (intronic) |
| CAVAS | 3.166 | 0.728 | 0.08 | 1.38 × 10−5 | (0.94) | |||||||
| Gene Symbol | Log FC | AveExpr | p Value | Adj p Value | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCL20 | −0.841 | 0.354 | 1.29 × 10−8 | 3.70 × 10−4 | 6.470 |
| PTGS2 | −0.694 | −0.058 | 9.83 × 10−7 | 1.42 × 10−2 | 4.253 |
| TNIP3 | −0.587 | 0.156 | 1.97 × 10−6 | 1.90 × 10−2 | 3.829 |
| SLC7A2 | −0.499 | 0.180 | 3.86 × 10−6 | 2.36 × 10−2 | 3.406 |
| VCAM1 | −0.626 | 0.302 | 4.09 × 10−6 | 2.36 × 10−2 | 3.368 |
| TNFAIP6 | −0.791 | 0.349 | 5.17 × 10−6 | 2.49 × 10−2 | 3.215 |
| CYP1A1 | 0.861 | −0.529 | 8.87 × 10−6 | 3.55 × 10−2 | 2.858 |
| DLL4 | −0.570 | 0.174 | 9.84 × 10−6 | 3.55 × 10−2 | 2.788 |
| SDF2L1 | 0.594 | 0.012 | 1.17 × 10−5 | 3.75 × 10−2 | 2.670 |
| TNIP1 | −0.472 | 0.033 | 1.32 × 10−5 | 3.79 × 10−2 | 2.590 |
| TNFRSF9 | −0.516 | 0.025 | 1.69 × 10−5 | 4.42 × 10−2 | 2.419 |
| Term ID | Term Description | Count in Network | Strength | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Biological process | ||||
| GO:0030049 | Muscle filament sliding | 4/38 | 2.47 | 8.20 × 10−6 |
| GO:0055010 | Ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis | 4/48 | 2.37 | 8.20 × 10−6 |
| GO:0060048 | Cardiac muscle contraction | 4/79 | 2.15 | 1.67 × 10−5 |
| GO:0008015 | Blood circulation | 5/394 | 1.55 | 5.47 × 10−5 |
| GO:0006937 | Regulation of muscle contraction | 4/162 | 1.84 | 1.00 × 10−4 |
| GO:1903522 | Regulation of blood circulation | 4/292 | 1.58 | 7.30 × 10−4 |
| GO:0006942 | Regulation of striated muscle contraction | 3/93 | 1.96 | 1.40 × 10−3 |
| GO:0051146 | Striated muscle cell differentiation | 3/200 | 1.62 | 1.20 × 10−2 |
| GO:0008016 | Regulation of heart contraction | 3/245 | 1.53 | 2.00 × 10−2 |
| 2. Molecular function | ||||
| GO:0008307 | Structural constituent of muscle | 4/43 | 2.41 | 3.29 × 10−6 |
| 3. Cellular component | ||||
| GO:0030017 | Sarcomere | 4/207 | 1.73 | 5.00 × 10−4 |
| GO:0016459 | Myosin complex | 2/55 | 2.01 | 4.05 × 10−2 |
| 4. KEGG | ||||
| hsa05410 | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | 4/89 | 2.1 | 5.56 × 10−6 |
| hsa05414 | Dilated cardiomyopathy | 4/95 | 2.07 | 5.56 × 10−6 |
| hsa04261 | Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | 4/147 | 1.88 | 1.31 × 10−5 |
| hsa04260 | Cardiac muscle contraction | 3/87 | 1.98 | 2.70 × 10−4 |
| KARE | CAVAS | KARE + CAVAS | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome Variable | Beta | SE | p Value | Beta | SE | p Value | Beta | SE | p Value |
| ApoA1 | 0.235 | 0.056 | <0.001 | 0.447 | 0.038 | <0.001 | 0.387 | 0.031 | <0.001 |
| ApoB | −0.138 | 0.055 | 0.013 | 0.083 | 0.036 | 0.022 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.325 |
| ApoB/ApoA1 | −0.002 | 0.000 | <0.001 | −0.001 | 0.000 | <0.001 | −0.002 | 0.000 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.; Yoon, J.W.; Kim, Y.A.; Choi, H.J.; Yoon, B.W.; Seo, J.H. A Genome-Wide Association Study of Genetic Variants of Apolipoprotein A1 Levels and Their Association with Vitamin D in Korean Cohorts. Genes 2022, 13, 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091553
Lee Y, Yoon JW, Kim YA, Choi HJ, Yoon BW, Seo JH. A Genome-Wide Association Study of Genetic Variants of Apolipoprotein A1 Levels and Their Association with Vitamin D in Korean Cohorts. Genes. 2022; 13(9):1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091553
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Young, Ji Won Yoon, Ye An Kim, Hyuk Jin Choi, Byung Woo Yoon, and Je Hyun Seo. 2022. "A Genome-Wide Association Study of Genetic Variants of Apolipoprotein A1 Levels and Their Association with Vitamin D in Korean Cohorts" Genes 13, no. 9: 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091553
APA StyleLee, Y., Yoon, J. W., Kim, Y. A., Choi, H. J., Yoon, B. W., & Seo, J. H. (2022). A Genome-Wide Association Study of Genetic Variants of Apolipoprotein A1 Levels and Their Association with Vitamin D in Korean Cohorts. Genes, 13(9), 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091553






