Abstract
Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological disorders with diverse phenotypic characteristics and high genetic heterogeneity. Epilepsy often occurs in childhood, so timely diagnosis and adequate therapy are crucial for preserving quality of life and unhindered development of a child. Next-generation-sequencing (NGS)-based tools have shown potential in increasing diagnostic yield. The primary objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of genetic testing and to investigate the diagnostic utility of targeted gene panel sequencing. This retrospective cohort study included 277 patients aged 6 months to 17 years undergoing NGS with an epilepsy panel covering 142 genes. Of 118 variants detected, 38 (32.2%) were not described in the literature. We identified 64 pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants with an overall diagnostic yield of 23.1%. We showed a significantly higher diagnostic yield in patients with developmental delay (28.9%). Furthermore, we showed that patients with variants reported as pathogenic presented with seizures at a younger age, which led to the conclusion that such children should be included in genomic diagnostic procedures as soon as possible to achieve a correct diagnosis in a timely manner, potentially leading to better treatment and avoidance of unnecessary procedures. Describing and discovering the genetic background of the disease not only leads to a better understanding of the mechanisms of the disorder but also opens the possibility of more precise and individualized treatment based on stratified medicine.
1. Introduction
Epilepsy is a heterogeneous disease with numerous clinical manifestations and various causes underlying the disease [1]. Part of the fundamental disease pathways is known, but many epilepsy cases remain of unclear etiology. With the development of genomic approaches, there has been a shift towards a more precise and accurate diagnosis of epilepsy by primarily researching the genetic background of symptom development [2]. Clinicians are trying to shift away from the “one size fits all” approach to the treatment of epilepsies. It has been shown that treatment based on symptoms and semiology of seizures is not always successful and that the percentage of refractory epilepsies is still high [3]. This was also recognized by the ILAE, and a shift can be seen in the classification of diseases, leading to the disease etiology being divided into six categories, one of which is genetic [4]. This underlines the importance of an etiology-based management approach.
For decades, it has been perceived that at least some people with epilepsy have a genetic background, and this was first confirmed in families with epileptic syndromes [5]. Today, it is estimated that 70–80% of epilepsy cases have genetic variants underlying the disease that are at least partly responsible for the onset of symptoms. Moreover, 20–30% can be considered secondary forms due to acquired conditions such as stroke, brain trauma, and tumors [6]. As with other complex diseases, a smaller proportion can be explained by monogenic changes while the remaining cases are caused by a complex interplay of environmental and multiple genetic factors. The application of genomic tests in children with epilepsy has led to the identification of new causative genes and expanded knowledge about the biological basis of epilepsy, which may also lead to therapeutic implications [1].
This study aimed to investigate the genetic etiology of pediatric epilepsy cases and to show the importance of targeted genomic tests in the diagnostic workflow of epilepsy.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
We retrospectively collected data from 277 cases of epilepsy patients aged 6 months to 17 years referred to the Department for Functional Genomics, Center for Translational and Clinical Research, University Hospital Center Zagreb, and University of Zagreb, School of Medicine, from 2016 to 2020. Exclusion criteria included seizures caused by acquired brain injury (including traumatic brain injury and neoplasm).
All patients were examined and diagnosed by a neurologist and/or pediatrician. We analyzed clinical data, including age at the onset of the disease, frequency, and type of seizures, as well as the presence of developmental delay and cranial malformations, if present. Seizure types and epileptic syndromes have been diagnosed and classified according to the guidelines of the International League Against Epilepsy (2014, 2017) [4]. We also assessed whether the patients had refractory epilepsy and whether epilepsy was present as part of a syndrome. All procedures were in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments, or comparable ethical standards.
2.2. Sample and Data Collection
Blood samples (3 mL) were collected in EDTA-containing tubes from all patients and control subjects. DNA was extracted from whole blood samples following the manufacturer’s specifications using the Quick DNA Kit (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA). A NanoDrop 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) spectrophotometer and a Qubit 4 (Invitrogen) fluorometer were used to determine the quality and concentration of genomic DNA samples. Only DNA of OD (optical density coefficient, 260/280) 1.80 ± 20% was used for further experiments.
2.3. Next-Generation Sequencing
The data for this study was obtained by next-generation sequencing of the custom epilepsy gene panel consisting of 142 genes (listed in Supplementary Table S1). The genes were selected through a comprehensive search of the literature (PubMed), and clinical databases of human genes and genetic disorders (OMIM, Clin-Var, and HGMD), and the genes associated with epilepsy were included. The panel included the coding DNA sequences, except for the CSTB gene, where the 5′UTR region was included, and for the TSC1, TSC2, NF1, and NF2 genes, where all introns were also covered, libraries for next-generation sequencing were prepared using Nextera XT DNA Library Prep Kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) according to manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, each DNA sample was diluted, fragmented, and amplified. The amplified samples were re-purified with magnetic particles, and the quality and quantification of the samples were evaluated via a DNA 1000 Kit using Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Next, the fragments were hybridized and amplified, and the regions of interest were separated using streptavidin magnetic particles. The next step was to add double indexes to name each sample for further recognition, and finally, they were diluted to a concentration of 12 pM.
The libraries prepared were sequenced on a MiSeq (Illumina) and NextSeq 550 (Illumina) next-generation sequencing platform according to the manufacturer’s instructions, generating approximately 5 million of the 150 bp paired-end reads for each sample (Q30 ≥ 96%, average passing filter 89.30%) with a mean region coverage depth of minimum 80.0 (median 125.5) and a median target coverage at 20× of 93%, and at 50× of 83.4%. After sequencing, the FASTQ files were imported to Variant Interpreter (Illumina), which was used for further analysis of the sequencing data. After sequencing data submission, the pipeline included the following steps: quality checks and filter of the reads; alignment on the reference genome, coverage statistics, and metrics; and variant calling and annotation. We focused on two variant types; single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and short insertions and deletions (indels). Alignment mapping and variant calling in our analysis pipelines were performed with the Variant Interpreter (Illumina) and DRAGEN (Illumina) platforms. Annotation was followed by the filtering and classification of variants depending on phenotype and clinical indication for testing. All variants were classified according to the guidelines jointly established by the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) and the Association for Molecular Pathology for the interpretation of sequence variants [7]. The final interpretation of the variant was ultimately guided by the phenotype of the case. Variants were reported based on relevance to the primary indication for testing. All likely pathogenic and pathogenic variants are listed in the supplement data (Supplementary Table S2).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Differences between different patient characteristics and the rate of reported variants were compared through Chi-squared or ANOVA tests depending on the data. All statistical analyses were performed with the Statistica 10 software (StatSoft, Tulsa, AK, USA), and a p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
Our cohort consisted of 277 participants with unexplained pediatric-onset epilepsy referred to our Department for Functional Genomics from 2016 to 2020. The majority of cases were without identifiable genetic syndrome (n = 231; 83%). For the remainder of the cohort, almost half of the participants presented with craniofacial malformations and/or developmental delay (n = 115; 49.8%). Age at enrollment was 4 weeks to 17 years, with seizure onset at birth to 16 years of age (median = 2 years, 30% < 1 year). Fifty-two percent of participants were male (144/277). All participants were Caucasians of Croatian origin. The main demographic data are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics.
We detected 118 variants in 38.6% of our study participants (107/277). Of those 118 variants, 54 were described as variants of unknown significance (VUS), 47 were described as likely pathogenic (LP), and 17 were described as pathogenic (P). The overall yield of pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants from our cohort was 23.1% (n = 64). The highest diagnostic rate achieved in our study was among participants with epilepsy accompanied by developmental delay with pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants in 28.9% (n = 42/146) (Table 1). Further analysis showed that developmental delay can be related to the presence or absence of a mutation (chi-square, 4.538, p = 0.03315) but not how the mutation is reported (chi-square, 3.43, p = 0.179962.). On the other hand, there was no correlation between craniofacial malformations, and the presence or absence of a mutation (chi-square, 1.9736, p = 0.16007). Furthermore, there was a significant difference in the odds of having a developmental delay between patients with a negative NGS panel result and patients with variants. This was reported as VUS, LP, or P (OD 1.6963; 95% CI 1.0414 to 2.7629; p = 0.0337), but there is no significant difference in the odds for craniofacial malformations (95% CI 0.8299 to 3.0415; p = 0.1623) or for refractory epilepsy (95% CI 0.9579 to 1.2999; p = 0.1593) (Figure 1).
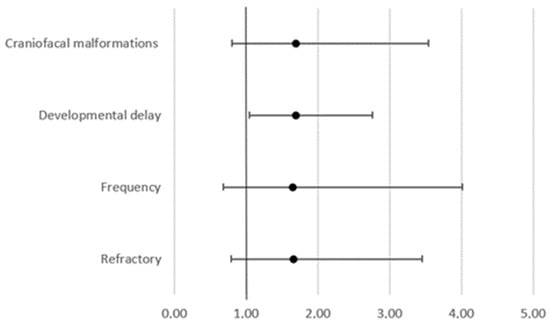
Figure 1.
Odds ratio for patient’s characteristics between patients with a negative NGS panel result and patients with variants reported as VUS, LP, or P.
The overall rate of reported variants did not differ significantly between participants divided according to the frequency of symptoms (chi-square, 1.984, p = 0.370842) or the presence of refractory epilepsy (chi-square, 1.8533, p = 0.173402). There was also no significant difference in the overall rate of reported variants depending on epilepsy type (chi-square, 5.1893, p = 0.158447).
As previously mentioned, the age at enrollment was 4 weeks to 17 years, with seizure onset between birth and 16 years of age (median = 2 years, 30% < 1 year). Interestingly, pathogenicity report significantly correlated with age at onset (one-way ANOVA F (2.77) = 3.7887, p = 0.02695), meaning that patients with variants reported as pathogenic had a younger age of onset than patients with variants described as VUS (Figure 2).
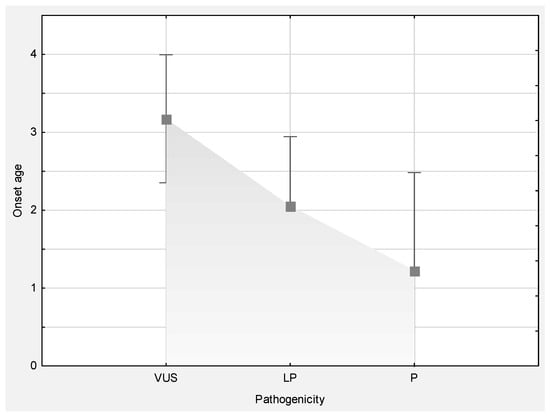
Figure 2.
Significantly different age at onset between groups of patients stratified according to variant annotation.
Although variants were analyzed with a panel consisting of 142 genes, variants in only 47 genes have been detected in this group of 277 patients. Of 118 variants described, 38 (32.2%) were not described in the literature. Those 38 variants were present in 25 genes. One novel variant in the ALDH7A1 gene, 1566-1G>T, rs140845195) was present in four patients. The genes with repeated novel variants were ADGRV1, ALDH7A1, KCNT1, MBD5, SCN2A, SCN8A, TBC1D24, and TSC2.
The most clinically interesting group of variants were the ones described as pathogenic and likely pathogenic. There were altogether 47 variants described as LP and 17 as P. These 64 variants were related to 32 genes, and the gene with the most frequent variants was CNTNAP2 (Figure 3). Most genetic changes (34.38%) have been identified in genes encoding ion channels (CACNA1A, GABRA1, SCN1B, SCN5A, SCN1A, HCN4, KCNQ2, SCN9A, SCN2A, and SCN8A), but variants have also been reported in genes encoding enzymes and/or enzyme modulators (18.75%) (TSC2, NDUFA1, ALDH7A1, TPP1, ADSL, and CDKL5) as well as in genes associated with membrane trafficking(18.75%) (CNTNAP2, ABCB1, ADGRV1, STXBP1, EFHC1, and PRRT2) (Figure 4).
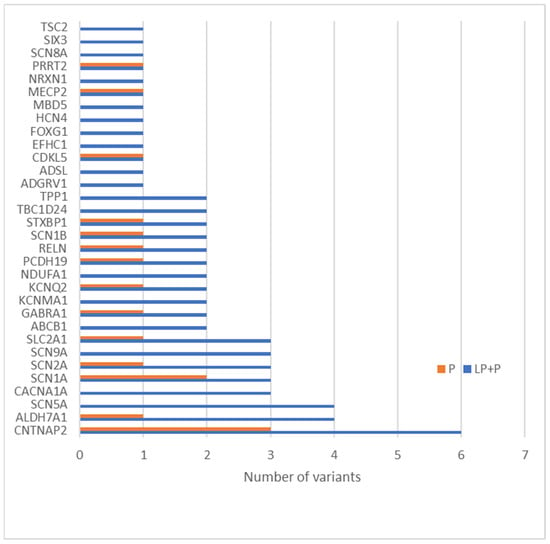
Figure 3.
Sixty-four candidate variants classified as LP or P in 32 genes in our group.
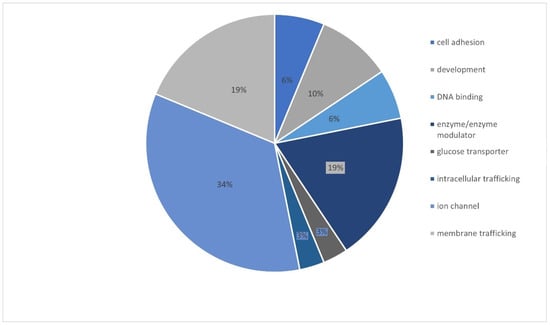
Figure 4.
Functional classification of the mutated pathogenic or likely pathogenic genes.
4. Discussion
In the recent decade, the development and greater availability of advanced genomic methods have led to a major shift towards etiological diagnostics of epilepsy. The number of causal genes is increasing daily, which has led to an increase in diagnostic yield [8]. The overall yield of pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants from our cohort was 23.1%. Miao and colleagues had a slightly higher yield of 27% but included only pathogenic variants [9]. It is important to note that they had comparable inclusion and exclusion criteria but used a larger panel of 480 genes compared to ours consisting of 142 genes [9]. On the other hand, Rochtus and colleagues achieved a higher yield and identified pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants in 40% (50/125) of their study participants [10]. The difference in yield can be explained by the use of WES in this study, but perhaps an even more important difference is that the profile of patients was slightly different and that the cohort consisted of as many as 70% of patients with developmental delay and epileptic encephalopathy [10]. On the other hand, Hoelz and colleagues showed a diagnostic yield of 18% reporting LP and P variants [11]. The importance of the number and selection of genes included in the panel was shown by Parrini and colleagues. They showed that a 95-gene panel allowed for a genetic diagnosis in 6.3% of patients that would have otherwise been missed using a 30-gene panel [12]. Ortega-Moreno found disease-causing variants in 19.5% of analyzed patients using two panels of 83 and 106 genes [13]. Another study that showed the importance of a good selection of suitable patients but also the importance of a purposeful diagnostic course was conducted by Patel et al. [14]. They showed that patients with genetic causes of epileptic encephalopathy were diagnosed by clinical features, metabolic investigations, MRI, or microarray in 44% of cases, targeted next-generation sequencing epilepsy panels in another 44% of cases, and whole exome sequencing in 12% of cases [14]. Our data together with the results of other studies show that the diagnostic yield depends on the adequate selection of patients and the number of genes analyzed. An increase in the number of genes analyzed is not proportionally linked to an increase in the diagnostic yield; thus, for the majority of patients, it would not be cost-effective to perform WES. Parrini and colleagues concluded that panels with about 100 genes represent the best cost-effective diagnostic method in drug-resistant pediatric epilepsy [12].
It is crucial to understand the great importance of including advanced genomic methods in the diagnostic process of pediatric epilepsy. Identifying genetic causes can help select appropriate pharmacotherapeutic approaches, may lead to fewer (often invasive) diagnostic methods required, and may lead to timely use of other non-AED therapies. Hoelz et al. showed that 63% of patients with reported LP or P variants experienced changes in clinical management and avoided further diagnostic evaluation after genomic testing [11]. Our study showed a significantly higher diagnostic yield in patients with developmental delay as well as in patients with disease onset at a very young age, which leads to the conclusion that such children should be included in genomic diagnostics as soon as possible to achieve the correct diagnosis in a timely manner, to potentially improve treatment, and to prevent unnecessary diagnostic procedures.
Miao and colleagues found the largest number of variants in the SCN1A gene, followed by KCNQ2, KCNT1, and PCDH19 [9]. Parrini and colleagues found that SCN2A was the most frequently mutated gene, followed by SCN1A, KCNQ2, STXBP1, SCN8A, CDKL5, and MECP2 [12]. Variants found by Ortega-Moreno were all in known epilepsy-associated genes (KCNQ2, CDKL5, STXBP1, SCN1A, PCDH19, POLG, SLC2A1, ARX, ALG13, CHD2, SYNGAP1, and GRIN1) [13]. All listed genes were among the most prevalent genes in our cohort, but the gene with the largest number of variants in our cohort was CNTNAP2, which was not present in the large epi panel of Miao and colleagues [9], or in other smaller aforementioned panels [10,11,12,13]. This shows that not only the size of the panel but also the careful selection of the genes included in the panel that are important. Around a third of genetic changes (34.38%) have been identified in genes encoding ion channels (CACNA1A, GABRA1, SCN1B, SCN5A, SCN1A, HCN4, KCNQ2, SCN9A, SCN2A, and SCN8A), but variants have also been reported in genes encoding enzymes and/or enzyme modulators (TSC2, NDUFA1, ALDH7A1, TPP1, ADSL, and CDKL5) as well as in genes associated with membrane trafficking (CNTNAP2, ABCB1, ADGRV1, STXBP1, EFHC1, and PRRT2) and cell divisions and processes (SIX3, FOXG1, and RELN), which is in accordance with other studies [2]. Furthermore, this study confirmed that mutations in one gene can lead to a spectrum of epilepsy phenotypes and that the same variants can exhibit different phenotypes. For instance, variant 1566-1G>T in the ALDH7A1 gene is a novel variant and was present in four patients with different symptoms. Interestingly we found some more novel variants present in more patients. Variant c.1361_1362delAT in CNTNAP2 was also present in four patients. The CNTNAP2 gene encodes for a neuronal transmembrane protein member of the neurexin superfamily, Contactin-associated protein-like 2 (CASPR2), which clusters voltage-gated potassium channels at the nodes of Ranvier and is involved in neuron–glia interactions [15]. Mutations in the CNTNAP2 disrupt the expression of CASPR2, causing abnormalities in cortical histogenesis. Such mutations have been identified in neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism, intellectual disability, and epilepsy [16]. In a study from 2006, Strauss et al. showed that homozygous mutation in CNTNAP2 causes cortical dysplasia-focal epilepsy (CDFE), a disorder that results in epileptic seizures, intellectual disability; hyperactivity; speech regression; and in most cases, autism [17].
Pathogenic variants were identified in several genes, with SCN1A, SCN2A, and KCNQ2, being the most significant ones. The SCN1A and SCN2A mutations result in truncated sodium channels, which alter the transmission of depolarizing impulses throughout the neurons. SCN1A mutations are associated with developmental and epileptic encephalopathy, Dravet syndrome, febrile seizures, and generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus (GEFS+) [18,19,20]. SCN2A mutations are associated with developmental and epileptic encephalopathy [21,22], episodic ataxia [23], and benign familial infantile seizures [24]. The mechanism of pathogenicity of these mutations remains unknown, but it is suggested that gain-of-function and loss-of-function defects contribute to abnormal neuronal network excitability [21]. On the other hand, KCNQ2 encodes voltage-gated potassium channel subunit, which together with the KCNQ3 subunit can form neuronal M channels that carry slowly activating and non-inactivating potassium currents. These currents contribute to resting membrane potential and regulate excitability in central and peripheral neurons. KCNQ2 mutations are associated with developmental and epileptic encephalopathy, benign neonatal seizures, and myokymia [25]. Loss-of-function mutations in either subunit cause neuronal hyperexcitability and can lead to benign familial neonatal convulsions. Even though the underlying pathogenetic mechanism of epileptic encephalopathy remains unclear, it is believed that a combination of defects in voltage-dependent activation and axonal expression causes a decrease in potassium current and its ability to inhibit neuronal excitability in the brain [26]. The limitations of our study are that we did not perform genotype–phenotype correlations and parental DNA analysis. By performing complex and precise genotype–phenotype correlations after the NGS epilepsy gene panel, Horák and colleagues increased their diagnostic yield by 53.33% [27]. Furthermore, we did not perform re-testing of samples. Salinas and colleagues detected pathogenic variants initially in 38% of subjects with developmental and epileptic encephalopathies. However, after an average time of 29 months, 25% of the subjects without a genetic diagnosis were re-categorized and diagnosed [8]. Finally, patients were not monitored throughout the study, and we cannot access data from the diagnostic test to monitor the impact on therapeutic management.
5. Conclusions
This research has shown the importance of including advanced genomic methods in the diagnostic process of pediatric epilepsy. This study has presented that at least a quarter of pediatric epilepsy patients previously classified as patients with unknown etiology has a clear genetic etiology. We have shown that a good selection of patients who would benefit the most from genetic diagnostics is extremely important because patients who developed epilepsy at a younger age and who have a developmental delay in addition to epilepsy are most likely to have a causal genetic variant detected by advanced genomic methods. We have also shown the importance of the proper selection of genes to be included in the panel. However, from a diagnostic point of view, it should be noted that not every genomic method is good for every patient and the choice of the most appropriate genetic test can play a pivotal role. In conclusion, an ideal diagnostic pipeline would consist of a good clinical examination by a pediatrician and a clinical geneticist who, if necessary, refer the patient to a well-designed epilepsy panel. If a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant is detected, genotypic–phenotypic tests should also be performed, and it is recommended to include them in the diagnostic workflow. Furthermore, in an ideal situation, an analysis of the parents (the so-called case-parent triad) should also be carried out.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/genes13081466/s1, Table S1: List of genes included in the custom epilepsy gene panel; Table S2: Variants classified as likely pathogenic or pathogenic.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B. and F.B.; methodology, A.B.; validation, F.B., formal analysis, A.B. and S.M. (Sarah Meglaj); investigation, A.B. and K.G.J.; resources, V.D., I.P., B.L., M.M., S.M. (Silvana Markovic), L.L., R.G.J., N.B., I.B., Z.P.G. and F.B.; writing—original draft preparation, A.B. and S.M. (Sarah Meglaj); writing—review and editing, F.B.; visualization, A.B.; supervision, F.B.; project administration, A.B. and F.B.; funding acquisition, F.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Croatian Science Foundation, grant HRZZ-8475.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted according to the guidelines of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments, or comparable ethical standards and approved by the ethical committee of University of Zagreb School of Medicine and University Hospital Centre Zagreb.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Scala, M.; Bianchi, A.; Bisulli, F.; Coppola, A.; Elia, M.; Trivisano, M.; Pruna, D.; Pippucci, T.; Canafoglia, L.; Lattanzi, S.; et al. Advances in genetic testing and optimization of clinical management in children and adults with epilepsy. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2020, 20, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symonds, J.D.; Zuberi, S.M.; Johnson, M.R. Advances in epilepsy gene discovery and implications for epilepsy diagnosis and treatment. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2017, 30, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalilani, L.; Sun, X.; Pelgrims, B.; Noack-Rink, M.; Villanueva, V. The epidemiology of drug-resistant epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 2179–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falco-Walter, J.J.; Scheffer, I.E.; Fisher, R.S. The new definition and classification of seizures and epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2018, 139, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annegers, J.F.; Hauser, W.A.; Anderson, V.E.; Kurland, L.T. The risks of seizure disorders among relatives of patients with childhood onset epilepsy. Neurology 1982, 32, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, C.T.; Mefford, H.C. Advancing epilepsy genetics in the genomic era. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, V.; Martínez, N.; Maturo, J.P.; Rodriguez-Quiroga, S.A.; Zavala, L.; Medina, N.; Amartino, H.; Sfaello, I.; Agosta, G.; Serafín, E.M.; et al. Clinical next generation sequencing in developmental and epileptic encephalopathies: Diagnostic relevance of data re-analysis and variants re-interpretation. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 64, 104363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, P.; Feng, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, L.; Zheng, C.; Cheng, H. Genotype and phenotype analysis using an epilepsy-associated gene panel in Chinese pediatric epilepsy patients. Clin. Genet. 2018, 94, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochtus, A.; Olson, H.E.; Smith, L.; Keith, L.G.; El Achkar, C.; Taylor, A.; Mahida, S.; Park, M.; Kelly, M.; Shain, C.; et al. Genetic diagnoses in epilepsy: The impact of dynamic exome analysis in a pediatric cohort. Epilepsia 2020, 61, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelz, H.; Herdl, C.; Gerstl, L.; Tacke, M.; Vill, K.; von Stuelpnagel, C.; Rost, I.; Hoertnagel, K.; Abicht, A.; Hollizeck, S.; et al. Impact on Clinical Decision Making of Next-Generation Sequencing in Pediatric Epilepsy in a Tertiary Epilepsy Referral Center. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2020, 51, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrini, E.; Marini, C.; Mei, D.; Galuppi, A.; Cellini, E.; Pucatti, D.; Chiti, L.; Rutigliano, D.; Bianchini, C.; Virdò, S.; et al. Diagnostic Targeted Resequencing in 349 Patients with Drug-Resistant Pediatric Epilepsies Identifies Causative Mutations in 30 Different Genes: HUMAN MUTATION. Hum. Mutat. 2017, 38, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Moreno, L.; Giráldez, B.G.; Soto-Insuga, V.; Losada-Del Pozo, R.; Rodrigo-Moreno, M.; Alarcón-Morcillo, C.; Sánchez-Martín, G.; Díaz-Gómez, E.; Guerrero-López, R.; Serratosa, J.M.; et al. Molecular diagnosis of patients with epilepsy and developmental delay using a customized panel of epilepsy genes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.; Cordeiro, D.; Hewson, S.; Cohn, R.; Kannu, P.; Kobayashi, J.; Mahmutoglu, S. Diagnostic yield of genetic testing in epileptic encephalopathy in childhood. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 357, e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñagarikano, O.; Abrahams, B.S.; Herman, E.I.; Winden, K.D.; Gdalyahu, A.; Dong, H.; Sonnenblick, L.I.; Gruver, R.; Almajano, J.; Bragin, A.; et al. Absence of CNTNAP2 Leads to Epilepsy, Neuronal Migration Abnormalities, and Core Autism-Related Deficits. Cell 2011, 147, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Martin, M.; Joubert, B.; Pellier-Monnin, V.; Pascual, O.; Noraz, N.; Honnorat, J. Contactin-associated protein-like 2, a protein of the neurexin family involved in several human diseases. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 48, 1906–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, K.A.; Puffenberger, E.G.; Huentelman, M.J.; Gottlieb, S.; Dobrin, S.E.; Parod, J.M.; Stephan, D.A.; Morton, D.H. Recessive Symptomatic Focal Epilepsy and Mutant Contactin-Associated Protein-like 2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutational analysis of the SCN1A, SCN1B and GABRG2 genes in 150 Italian patients with idiopathic childhood epilepsies. Clin. Genet. 2009, 75, 579–581. [CrossRef]
- Carranza Rojo, D.; Hamiwka, L.; McMahon, J.M.; Dibbens, L.M.; Arsov, T.; Suls, A.; Stodberg, T.; Kelley, K.; Wirrell, E.; Appleton, B.; et al. De novo SCN1A mutations in migrating partial seizures of infancy. Neurology 2011, 77, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadleir, L.G.; Mountier, E.I.; Gill, D.; Davis, S.; Joshi, C.; DeVile, C.; Kurian, M.A.; For the DDD Study; Mandelstam, S.; Wirrell, E.; et al. Not all SCN1A epileptic encephalopathies are Dravet syndrome: Early profound Thr226Met phenotype. Neurology 2017, 89, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogiwara, I.; Ito, K.; Sawaishi, Y.; Osaka, H.; Mazaki, E.; Inoue, I.; Montal, M.; Hashikawa, T.; Shike, T.; Fujiwara, T.; et al. De novo mutations of voltage-gated sodium channel II gene SCN2A in intractable epilepsies. Neurology 2009, 73, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, M.; Johannesen, K.M.; Hedrich, U.B.S.; Masnada, S.; Rubboli, G.; Gardella, E.; Lesca, G.; Ville, D.; Milh, M.; Villard, L.; et al. Genetic and phenotypic heterogeneity suggest therapeutic implications in SCN2A-related disorders. Brain 2017, 140, 1316–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, N.; Hahn, A.; Bast, T.; Müller, S.; Löffler, H.; Maljevic, S.; Gaily, E.; Prehl, I.; Biskup, S.; Joensuu, T.; et al. Mutations in the sodium channel gene SCN2A cause neonatal epilepsy with late-onset episodic ataxia. J. Neurol. 2016, 263, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkovic, S.F.; Heron, S.E.; Giordano, L.; Marini, C.; Guerrini, R.; Kaplan, R.E.; Gambardella, A.; Steinlein, O.K.; Grinton, B.E.; Dean, J.T.; et al. Benign familial neonatal-infantile seizures: Characterization of a new sodium channelopathy. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Yamagata, T.; Kubota, M.; Arai, H.; Yamashita, S.; Nakagawa, T.; FujII, T.; Sugai, K.; Imai, K.; Uster, T.; et al. Clinical spectrum of early onset epileptic encephalopathies caused by KCNQ2 mutation. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1282–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kim, E.C.; Chen, C.; Procko, E.; Pant, S.; Lam, K.; Patel, J.; Choi, R.; Hong, M.; Joshi, D.; et al. Identifying mutation hotspots reveals pathogenetic mechanisms of KCNQ2 epileptic encephalopathy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horák, O.; Burešová, M.; Kolář, S.; Španělová, K.; Jeřábková, B.; Gaillyová, R.; Česká, K.; Réblová, K.; Šoukalová, J.; Zídková, J.; et al. Next-generation sequencing in children with epilepsy: The importance of precise genotype–phenotype correlation. Epilepsy Behav. 2022, 128, 108564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).