The Cannabis-Induced Epigenetic Regulation of Genes Associated with Major Depressive Disorder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Epigenomic Studies in Animal Models
3.2. Epigenomic Studies in Human Subjects
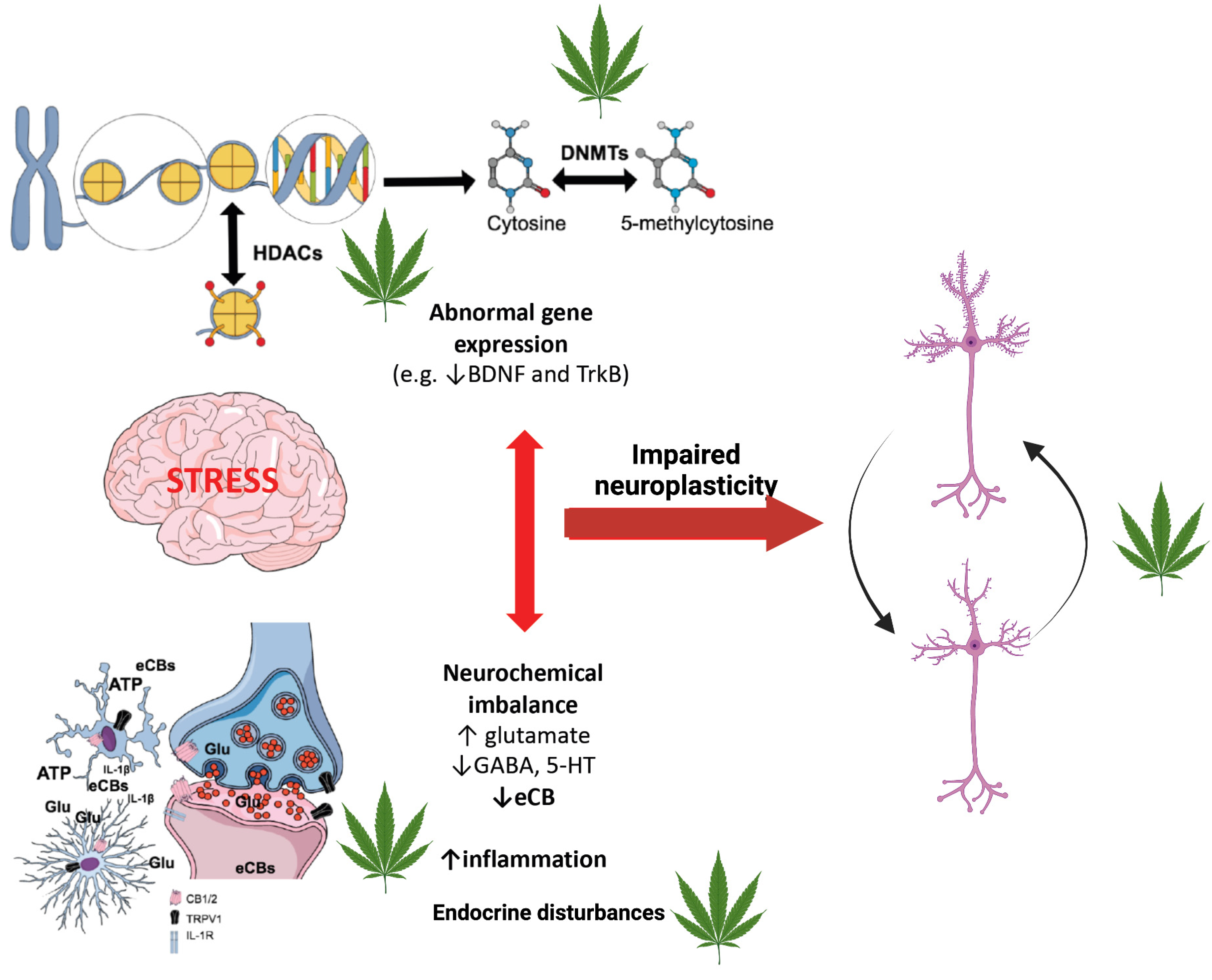
3.3. Cannabis-Associated Epigenetic Regulation of MDD Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ICD-10 Version:2016 [Internet]. Available online: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2016/en (accessed on 26 April 2018).
- World Health Organization (WHO). The Global Burden of Disease; 2004 Update; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, P.F.; de Geus, E.J.C.; Willemsen, G.; James, M.R.; Smit, J.H.; Zandbelt, T.; Arolt, V.; Baune, B.T.; Blackwood, D.; Cichon, S.; et al. Genome-wide association for major depressive disorder: A possible role for the presynaptic protein piccolo. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wray, N.R.; Sullivan, P.F. Genome-Wide Association Analyses Identify 44 Risk Variants and Refine the Genetic Architecture of Major Depression; bioRxiv; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41588-018-0090-3 (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- van Uffelen, J.G.Z.; van Gellecum, Y.R.; Burton, N.W.; Peeters, G.; Heesch, K.C.; Brown, W.J. Sitting-Time, Physical Activity, and Depressive Symptoms in Mid-Aged Women. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 45, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, R.A.; Tansey, K.E.; Buttenschøn, H.N.; Cohen-Woods, S.; Bigdeli, T.; Hall, L.S.; Kutalik, Z.; Lee, S.H.; Ripke, S.; Steinberg, S.; et al. Genome-wide Association for Major Depression Through Age at Onset Stratification: Major Depressive Disorder Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. In Biological Psychiatry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 81, pp. 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, J.; Kendler, K.S. The Genetics of Major Depression. In Neuron; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 81, pp. 484–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, M.J.; Harwood, R.H.; Blizard, R.A.; Thomas, A.; Mann, A.H. Social support deficits, loneliness and life events as risk factors for depression in old age. Psychol. Med. 1997, 27, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negele, A.; Kaufhold, J.; Kallenbach, L.; Leuzinger-Bohleber, M. Childhood Trauma and Its Relation to Chronic Depression in Adulthood. Depress. Res. Treat. 2015, 2015, 650804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.E.; Kaplan, G.A.; Shema, S.J.; Strawbridge, W.J. Prevalence and correlates of depression in an aging cohort: The Alameda County Study. J. Gerontol. B. Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 1997, 52, S252–S258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezuk, B.; Eaton, W.W.; Golden, S.H.; Ding, Y. The Influence of Educational Attainment on Depression and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes. Am. J. Public Health 2008, 98, 1480–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coryell, W.; Endicott, J.; Keller, M. Major depression in a nonclinical sample. Demographic and clinical risk factors for first onset. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1992, 49, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.S.S.; Asha, M.R.; Ramesh, B.N.; Rao, K.S.J. Understanding nutrition, depression and mental illnesses. Indian J. Psychiatry 2008, 50, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Farmer, A.; Harris, T.; Redman, K.; Sadler, S.; Mahmood, A.; McGuffin, P. Cardiff Depression Study. Br. J. Psychiatry 2000, 176, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, P.F.; Neale, M.C.; Kendler, K.S. Genetic Epidemiology of Major Depression: Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Psychiatry 2000, 157, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, I.; McGue, M.; Tan, Q.; Christensen, K.; Christiansen, L. Change in Depression Symptomatology and Cognitive Function in Twins: A 10-Year Follow-Up Study. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2016, 19, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wray, N.R.; Ripke, S.; Mattheisen, M.; Trzaskowski, M.; Byrne, E.M.; Abdellaoui, A.; Adams, M.J.; Agerbo, E.; Air, T.M.; Andlauer, T.M.F.; et al. Genome-wide association analyses identify 44 risk variants and refine the genetic architecture of major depression. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, D.F.; Stein, M.B.; Wendt, F.R.; Pathak, G.A.; Zhou, H.; Aslan, M.; Quaden, R.; Harrington, K.M.; Nuñez, Y.Z.; Overstreet, C.; et al. Bi-ancestral depression GWAS in the Million Veteran Program and meta-analysis in >1.2 million individuals highlight new therapeutic directions. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, D.F.; Mostafavi, S.; Milaneschi, Y.; Rivera, M.; Ripke, S.; Wray, N.R.; Sullivan, P.F. Genetic studies of major depressive disorder: Why are there no genome-wide association study findings and what can we do about it? In Biological Psychiatry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 510–512. [Google Scholar]
- Visscher, P.M.; Wray, N.R.; Zhang, Q.; Sklar, P.; McCarthy, M.I.; Brown, M.A.; Yang, J. 10 Years of GWAS Discovery: Biology, Function, and Translation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 101, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipriani, A.; Furukawa, T.A.; Salanti, G.; Chaimani, A.; Atkinson, L.Z.; Ogawa, Y.; Leucht, S.; Ruhe, H.G.; Turner, E.H.; Higgins, J.P.T.; et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs for the acute treatment of adults with major depressive disorder: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. In Lancet; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 391, pp. 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levkovitz, Y.; Tedeschini, E.; Papakostas, G.I. Efficacy of Antidepressants for Dysthymia: A Meta-Analysis of Placebo-Controlled Randomized Trials. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2011, 72, 5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fava, M. Diagnosis and definition of treatment-resistant depression. In Biological Psychiatry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 53, pp. 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.S.; Tian, C.; Hinds, D.; Agee, M.; Alipanahi, B.; Auton, A.; Bell, R.K.; Bryc, K.; Elson, S.L.; Fontanillas, P.; et al. Genome-wide association studies of antidepressant class response and treatment-resistant depression. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, D. Prevalence and clinical course of depression: A review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2011, 31, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blease, C.R.; O’neill, S.; Walker, J.; Hägglund, M.; Torous, J. Treatment outcomes for depression: Challenges and opportunities. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 925–927. [Google Scholar]
- Murillo-Rodriguez, E.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R.; Montii, J.M. Cannabinoids and Neuropsychiatric Disorders; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 1264. [Google Scholar]
- Sexton, M.; Cuttler, C.; Finnell, J.S.; Mischley, L.K. A Cross-Sectional Survey of Medical Cannabis Users: Patterns of Use and Perceived Efficacy. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2016, 1, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, L.A.; Freeman, T.; Gage, S.H.; Zammit, S.; Hickman, M.; Cannon, M.; Munafo, M.; Macleod, J.; Heron, J. Association of High-Potency Cannabis Use With Mental Health and Substance Use in Adolescence. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memedovich, K.A.; Dowsett, L.E.; Spackman, E.; Noseworthy, T.; Clement, F. The adverse health effects and harms related to marijuana use: An overview review. Can. Med. Assoc. Open Access J. 2018, 6, E339–E346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, E. Evolution and Classification of Cannabis sativa (Marijuana, Hemp) in Relation to Human Utilization. Bot. Rev. 2015, 81, 189–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, F.; Grandi, V.; Banerjee, A.; Trant, J.F. iScience Cannabinoids and Cannabinoid Receptors: The Story So Far; Cell Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Hempel, B.J.; Yang, H.-J.; Han, X.; Bi, G.-H.; Gardner, E.L.; Xi, Z.-X. Dissecting the role of CB1 and CB2 receptors in cannabinoid reward versus aversion using transgenic CB1- and CB2-knockout mice. In European Neuropsychopharmacology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 43, pp. 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joca, S.; Silote, G.P.; Sartim, A.; Sales, A.; Guimarães, F.; Wegener, G. Putative effects of cannabidiol in depression and synaptic plasticity. In The Neuroscience of Depression; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, A.J.; Guimarães, F.S.; Joca, S.R. CBD modulates DNA methylation in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of mice exposed to forced swim. In Behavioural Brain Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 388, p. 112627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milutinovic, S.; D’Alessio, A.C.; Detich, N.; Szyf, M. Valproate induces widespread epigenetic reprogramming which involves demethylation of specific genes. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, A.J.; Guimarães, F.S.; Joca, S.R.L. DNA methylation in stress and depression: From biomarker to therapeutics. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2021, 33, 217–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, A.J.; Maciel, I.S.; Suavinha, A.C.D.R.; Joca, S.R.L. Modulation of DNA Methylation and Gene Expression in Rodent Cortical Neuroplasticity Pathways Exerts Rapid Antidepressant-Like Effects. In Molecular Neurobiology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 58, pp. 777–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Taskesen, E.; van Bochoven, A.; Posthuma, D. Functional mapping and annotation of genetic associations with FUMA. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C.R. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2015. Available online: http://www.gbif.org/resource/81287 (accessed on 1 May 2016).
- Wanner, N.M.; Colwell, M.; Drown, C.; Faulk, C. Subacute cannabidiol alters genome-wide DNA methylation in adult mouse hippocampus. In Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; Volume 61, pp. 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, N.M.; Colwell, M.; Drown, C.; Faulk, C. Developmental cannabidiol exposure increases anxiety and modifies genome-wide brain DNA methylation in adult female mice. Clin. Epigenet. 2021, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, C.T.; Szutorisz, H.; Garg, P.; Martin, Q.; Landry, J.A.; Sharp, A.J.; Hurd, Y.L. Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Profiling Reveals Epigenetic Changes in the Rat Nucleus Accumbens Associated With Cross-Generational Effects of Adolescent THC Exposure. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 2993–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.L.; Chan, R.; Zhao, M.; Xie, L.Y.; Copeland, W.E.; Aberg, K.A.; Oord, E.J.V.D. Methylomic Investigation of Problematic Adolescent Cannabis Use and Its Negative Mental Health Consequences. In Child & Adolescent Psychiatry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 60, pp. 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, A.J.; Pearson, J.F.; Noble, A.J.; Gemmell, N.J.; Horwood, L.J.; Boden, J.M.; Benton, M.C.; Macartney-Coxson, D.P.; Kennedy, M.A. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of heavy cannabis exposure in a New Zealand longitudinal cohort. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markunas, C.A.; Hancock, D.; Xu, Z.; Quach, B.C.; Fang, F.; Sandler, D.P.; Johnson, E.O.; Taylor, J.A. Epigenome-wide analysis uncovers a blood-based DNA methylation biomarker of lifetime cannabis use. In American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; Volume 186, pp. 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, K.; Mitchell, J.T.; Visco, Z.; Grenier, C.; Murphy, S.K.; Schrott, R.; Hall, B.J.; Price, T.M.; McClernon, J.; Levin, E.D.; et al. Data from: Cannabinoid Exposure and Altered DNA Methylation in Rat and Human Sperm; Duke Research Data Repository: Online, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrott, R.; Murphy, S.K.; Modliszewski, J.L.; King, D.E.; Hill, B.; Itchon-Ramos, N.; Raburn, D.; Price, T.; Levin, E.D.; Vandrey, R.; et al. Refraining from use diminishes cannabis-associated epigenetic changes in human sperm. In Environmental Epigenetics; Oxford Academic: Oxford, UK, 2021; Volume 7, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mojtabai, R.; Olfson, M.; Han, B. National Trends in the Prevalence and Treatment of Depression in Adolescents and Young Adults. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20161878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, K.S. Treatment-resistant depression: Therapeutic trends, challenges, and future directions. In Patient Preference Adherence; Dove Press: Lincolnshire, UK, 2012; Volume 6, pp. 369–388. [Google Scholar]
- García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Navarrete, F.; Gasparyan, A.; Austrich-Olivares, A.; Sala, F.; Manzanares, J. Cannabidiol: A Potential New Alternative for the Treatment of Anxiety, Depression, and Psychotic Disorders. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustonen, A.; Hielscher, E.; Miettunen, J.; Denissoff, A.; Alakokkare, A.-E.; Scott, J.G.; Niemelä, S. Adolescent cannabis use, depression and anxiety disorders in the Northern Finland Birth Cohort 1986. In BJPsych Open; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; Volume 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.M.; Khardali, I.A.; Oraiby, M.E.; Hakami, A.F.; Shaheen, E.S.; Ageel, I.M.; Abutawil, E.H.; Abu-Taweel, G.M. Anxiety, depression-like behaviors and biochemistry disorders induced by cannabis extract in female mice. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 6097–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szutorisz, H.; Hurd, Y.L. Epigenetic Effects of Cannabis Exposure. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 79, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Misaki, A.; Liang, S.-B.; Tachibana, A.; Hayashi, N.; Sonobe, H.; Ohtsuki, Y. Expression of T-cadherin (CDH13, H-Cadherin) in human brain and its characteristics as a negative growth regulator of epidermal growth factor in neuroblastoma cells. J. Neurochem. 2002, 74, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GTEx Consortium. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.P.; Militello, L.; Hart, A.; Pierre, C.L.S.; Leung, E.; Versaggi, C.L.; Roberson, N.; Catlin, J.; Palmer, A.A.; Richards, J.B.; et al. Cdh13 and AdipoQ gene knockout alter instrumental and Pavlovian drug conditioning. Genes Brain Behav. 2017, 16, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredette, B.J.; Miller, J.; Ranscht, B. Inhibition of motor axon growth by T-cadherin substrata. Development 1996, 122, 3163–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, O.; Sich, S.; Popp, S.; Schmitt, A.; Franke, B.; Lesch, K.-P. Impact of the ADHD-susceptibility gene CDH13 on development and function of brain networks. In European Neuropsychopharmacology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 23, pp. 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiser, D.P.; Popp, S.; Schmitt-Böhrer, A.G.; Strekalova, T.; Hove, D.L.V.D.; Lesch, K.-P.; Rivero, O. Early-life stress impairs developmental programming in Cadherin 13 (CDH13)-deficient mice. In Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 89, pp. 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drgonova, J.; Walther, N.; Hartstein, G.L.; Bukhari, M.O.; Baumann, M.; Katz, J.; Hall, F.S.; Arnold, E.R.; Flax, S.; Riley, A.; et al. Cadherin 13: Human cis-Regulation and Selectively Altered Addiction Phenotypes and Cerebral Cortical Dopamine in Knockout Mice. Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Drgon, T.; Walther, N.; Uhl, G.R. Genomic Regions Identified by Overlapping Clusters of Nominally-Positive SNPs from Genome-Wide Studies of Alcohol and Illegal Substance Dependence. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drgon, T.; Montoya, I.; Johnson, C.; Liu, Q.-R.; Walther, D.; Hamer, D.; Uhl, G.R. Genome-Wide Association for Nicotine Dependence and Smoking Cessation Success in NIH Research Volunteers. Mol. Med. 2009, 15, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salatino-Oliveira, A.; Genro, J.P.; Polanczyk, G.V.; Zeni, C.; Schmitz, M.; Kieling, C.; Anselmi, L.; Menezes, A.M.B.; Barros, F.C.; Polina, E.R.; et al. Cadherin-13 gene is associated with hyperactive/impulsive symptoms in attention/deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am. J. Med Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2015, 168, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiihonen, J.; Rautiainen, M.-R.; Ollila, H.; Repotiihonen, E.; Virkkunen, M.; Palotie, A.; Pietilainen, O.; Kristiansson, K.; Joukamaa, M.; Lauerma, H.; et al. Genetic background of extreme violent behavior. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 20, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Børglum, A.D.; Demontis, D.; Grove, J.; Pallesen, J.; Hollegaard, M.V.; Pedersen, C.B.; Hedemand, A.; Mattheisen, M.; Uitterlinden, A.; Nyegaard, M.; et al. Genome-wide study of association and interaction with maternal cytomegalovirus infection suggests new schizophrenia loci. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Woo, H.G.; Choi, J.-H.; Greenwood, T.A.; Kelsoe, J.R. CDH13 and HCRTR2 May Be Associated with Hypersomnia Symptom of Bipolar Depression: A Genome-Wide Functional Enrichment Pathway Analysis. Psychiatry Investig. 2015, 12, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denzel, M.S.; Scimia, M.-C.; Zumstein, P.M.; Walsh, K.; Ruiz-Lozano, P.; Ranscht, B. T-cadherin is critical for adiponectin-mediated cardioprotection in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 4342–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebbard, L.W.; Garlatti, M.; Young, L.J.; Cardiff, R.D.; Oshima, R.G.; Ranscht, B. T-cadherin Supports Angiogenesis and Adiponectin Association with the Vasculature in a Mouse Mammary Tumor Model. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibille, E.; Wang, Y.; Joeyen-Waldorf, J.; Gaiteri, C.; Surget, A.; Oh, S.; Belzung, C.; Tseng, G.C.; Lewis, D. A Molecular Signature of Depression in the Amygdala. Am. J. Psychiatry 2009, 166, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.; Brennecke, A.; Mallat, S.; Brown, J.; Gomez-Rivadeneira, J.; Czepiel, N.; Londrigan, L. Genetic Associations between Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels and Psychiatric Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, Z.D.; Lee, A.S.; Burgdorf, C.E.; Fischer, D.K.; Rajadhyaksha, A.M.; Mok, E.; Rizzo, B.; Rice, R.C.; Singh, K.; Ota, K.T.; et al. Cacna1c in the Prefrontal Cortex Regulates Depression-Related Behaviors via REDD1. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 42, 2032–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, A.L.; Haan, N.; Wilkinson, L.S.; Thomas, K.L.; Hall, J. CACNA1C: Association With Psychiatric Disorders, Behavior, and Neurogenesis. Schizophr. Bull. 2018, 44, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royer-Bertrand, B.; Gygax, M.J.; Cisarova, K.; Rosenfeld, J.A.; Bassetti, J.A.; Moldovan, O.; O’Heir, E.; Burrage, L.C.; Allen, J.; Emrick, L.T.; et al. De novo variants in CACNA1E found in patients with intellectual disability, developmental regression and social cognition deficit but no seizures. Mol. Autism. 2021, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starnawska, A.; Demontis, D.; Pen, A.; Hedemand, A.; Nielsen, A.L.; Staunstrup, N.H.; Grove, J.; Als, T.D.; Jarram, A.; O’Brien, N.L.; et al. CACNA1C hypermethylation is associated with bipolar disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vysokov, N.V.; Silva, J.P.; Lelianova, V.G.; Ho, C.; Djamgoz, M.B.; Tonevitsky, A.G.; Ushkaryov, Y.A. The Mechanism of Regulated Release of Lasso/Teneurin-2. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vysokov, N.V.; Silva, J.P.; Lelianova, V.G.; Suckling, J.; Cassidy, J.; Blackburn, J.K. Proteolytically released Lasso/teneurin-2 induces axonal attraction by interacting with latrophilin-1 on axonal growth cones. Elife 2018, 7, e37935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.-P.; Lelianova, V.G.; Ermolyuk, Y.S.; Vysokov, N.; Hitchen, P.G.; Berninghausen, O.; Rahman, M.A.; Zangrandi, A.; Fidalgo, S.; Tonevitsky, A.G.; et al. Latrophilin 1 and its endogenous ligand Lasso/teneurin-2 form a high-affinity transsynaptic receptor pair with signaling capabilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12113–12118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, J.R.; Szeto, R.A.; Carvalho, V.M.A.; Muotri, A.R.; Papes, F. Transcription factor 4 and its association with psychiatric disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelernter, J.; Sun, N.; Polimanti, R.; Pietrzak, R.; Levey, D.; Bryois, J.; Lu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Li, B. Genome-wide association study of post-traumatic stress disorder reexperiencing symptoms in >165,000 US veterans. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1394–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessarin, G.W.L.; Michalec, O.M.; Torres-Da-Silva, K.R.; Da Silva, A.V.; Cruz-Rizzolo, R.J.; Gonçalves, A.; Gasparini, D.C.; Horta-Junior, J.D.A.; Ervolino, E.; Bittencourt, J.C.; et al. A Putative Role of Teneurin-2 and Its Related Proteins in Astrocytes. In Frontiers in Neuroscience; Frontiers Media S.A.: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 13, p. 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonyová, V.; Kejík, Z.; Brogyanyi, T.; Kaplánek, R.; Veselá, K.; Abramenko, N.; Ocelka, T.; Masařík, M.; Matkowski, A.; Gburek, J.; et al. Non-psychotropic cannabinoids as inhibitors of TET1 protein. In Bioorganic Chemistry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; Volume 124, p. 105793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusconi, F.; Rubino, T.; Battaglioli, E. Endocannabinoid-Epigenetic Cross-Talk: A Bridge toward Stress Coping. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusconi, F.; Battaglioli, E. Acute Stress-Induced Epigenetic Modulations and Their Potential Protective Role Toward Depression. In Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience; Frontiers Media S.A.: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11, p. 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanoski, C.E.; Glass, C.K.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; Wilson, L.; Almouzni, G. Epigenomics: Roadmap for regulation. Nature 2015, 518, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium, R.E.; Kundaje, A.; Meuleman, W.; Ernst, J.; Bilenky, M.; Yen, A.; Heravi-Moussavi, A.; Kheradpour, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Integrative analysis of 111 reference human epigenomes. Nature 2015, 518, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.K.; Kilaru, V.; Kocak, M.; Almli, L.M.; Mercer, K.B.; Ressler, K.J.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Conneely, K.N. Methylation quantitative trait loci (meQTLs) are consistently detected across ancestry, developmental stage, and tissue type. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.M.; Fry, R.C. Environmental Influences on the Epigenome: Exposure- Associated DNA Methylation in Human Populations. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2018, 39, 309–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, S. DNA methylation age of human tissues and cell types. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
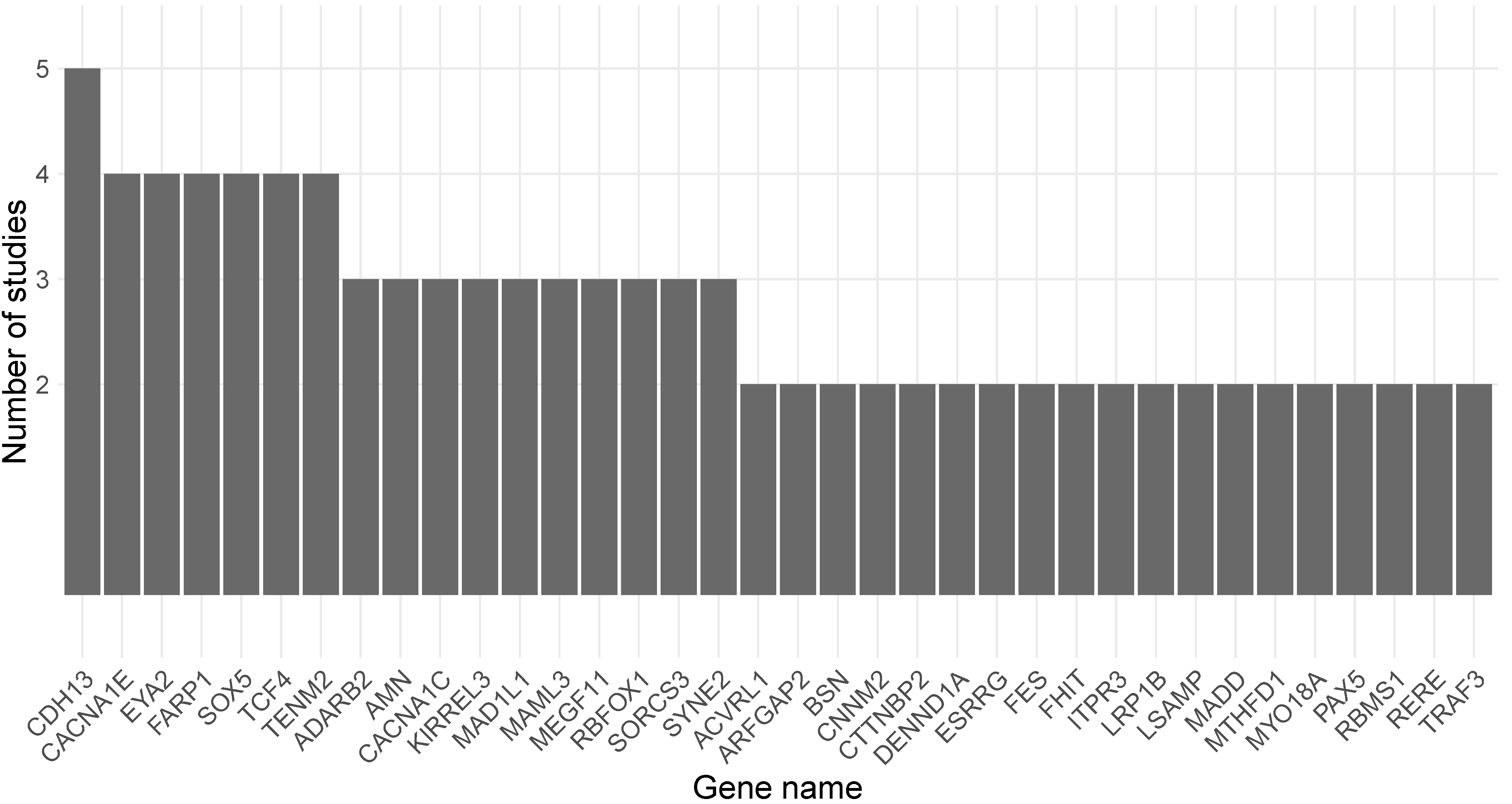
| Reference | Organism | Tissue | Exposure | DNAm Quantification Method | Genes Overlapping with MDD-Associated Loci |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [32] | Mouse | HPC | 20 mg/kg CBD daily for 2 weeks. | RRBS | ELAVL4, NEGR1, CACNA1E, CRB1, GALNT2, TGM4, LSAMP, MAML3, PCDHA8, TENM2, CTTNBP2, PAX5, PHF2, PTCH1, DENND1A, COMTD1, TRIM8, WBP1L, SORCS3, PRRG4, ARFGAP2, NCAM1, KIRREL3, CACNA1C, SOX5, FARP1, SYNE2, DLST, AMN, HERC1, MEGF11, FES, RBFOX1, CDH13, TCF4, EYA2 |
| [33] | Mouse | F0 cortex | F0: Adult female mice exposed to 0 mg/kg CBD daily for 9 weeks. | RRBS | RERE, CACNA1E, DENND1B, LRP1B, RBMS1, FHIT, LSAMP, NLGN1, MAML3, ADCY2, PCDHA1, PCDHA5, TENM2, MAD1L1, PAX5, DENND1A, CNNM2, MADD, MYBPC3, SPI1, FADS2, CACNA1C, ACVRL1, UNC119B, SPPL3, FARP1, MTHFD1, KLC1, FAM189A1, MEGF11, RBFOX1, CDH13, MYO18A, CELF4, TCF4, EYA2, ZMYND8 |
| F1cortex | F1: exposed to CBD during gestation and lactation. | CACNA1E, NRXN1, EFHD1, BSN, FHIT, PCDHA4, TENM2, ZSCAN12, MAD1L1, CTTNBP2, ADARB2, SORCS3, PAX6, KIRREL3, SOX5, GRASP, CABP1, OLFM4, SYNE2, RPS6KL1, AMN, FES, CDH13, MYO18A, TCF4, EYA2 | |||
| F1: HPC | F1: exposed to CBD during gestation and lactation. | CACNA1E, ESRRG, REEP1, LRP1B, RBMS1, BSN, RSRC1, MAML3, TMCO6, TENM2, ITPR3, PACRG, ADARB2, ARL3, SFXN2, NT5C2, INA, SORCS3, ARFGAP2, MADD, MYRF, FADS1, KIRREL3, CACNA1C, SOX5, ACVRL1, PCDH9, GPC5, FARP1, SYNE2, TRAF3, AMN, MEGF11, CD276, RBFOX1, SHISA9, CDH13, TCF4, EYA2, ARFGEF2 | |||
| [34] | Rat | F1: NAc | F0 exposed to 1.5 mg/kg THC every third day from postnatal day 28–49 and mated when no THC was detectable. | ERRBS | ESRRG, ITPR3, PARK2, CNNM2, NR1H3, SOX5, FARP1, MTHFD1, TRAF3, CDH13, CTC1 |
| [38] | Human | Sperm | Cannabis users with use frequency at least once weekly in the last 6 months compared with non-users. | RRBS | MAD1L1, ADARB2 |
| [39] | Human | Sperm | Cannabis users with a self-reported frequency of cannabis use at least once weekly over the prior 6 months compared to non-users. | WGBS | RERE, PCDH9, RBFOX1, ASXL3 |
| [36] | Human | Blood | Regular cannabis users, consumed cannabis via smoking compared to matched controls. | EPIC array | No overlap between the genes identified at p-value < 10−5 and the ones residing in MDD-associated loci. |
| [35] | Human | Blood | Problematic cannabis users compared with non-users. | MBD-seq | ESRRG, EYS, NKAIN2, CACNA1C, GPC5, FAM189A1 |
| [37] | Human | Blood | Lifetime cannabis use | 450K array | No overlap between the genes identified at p-value < 10−5 and the ones residing in MDD-associated loci. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohammad, G.S.; Joca, S.; Starnawska, A. The Cannabis-Induced Epigenetic Regulation of Genes Associated with Major Depressive Disorder. Genes 2022, 13, 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13081435
Mohammad GS, Joca S, Starnawska A. The Cannabis-Induced Epigenetic Regulation of Genes Associated with Major Depressive Disorder. Genes. 2022; 13(8):1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13081435
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohammad, Guldar Sayed, Sâmia Joca, and Anna Starnawska. 2022. "The Cannabis-Induced Epigenetic Regulation of Genes Associated with Major Depressive Disorder" Genes 13, no. 8: 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13081435
APA StyleMohammad, G. S., Joca, S., & Starnawska, A. (2022). The Cannabis-Induced Epigenetic Regulation of Genes Associated with Major Depressive Disorder. Genes, 13(8), 1435. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13081435






