Synthetic Lethality Targeting Polθ
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Polθ: Structure and Functions
3. The Role of Polθ in Normal Cells
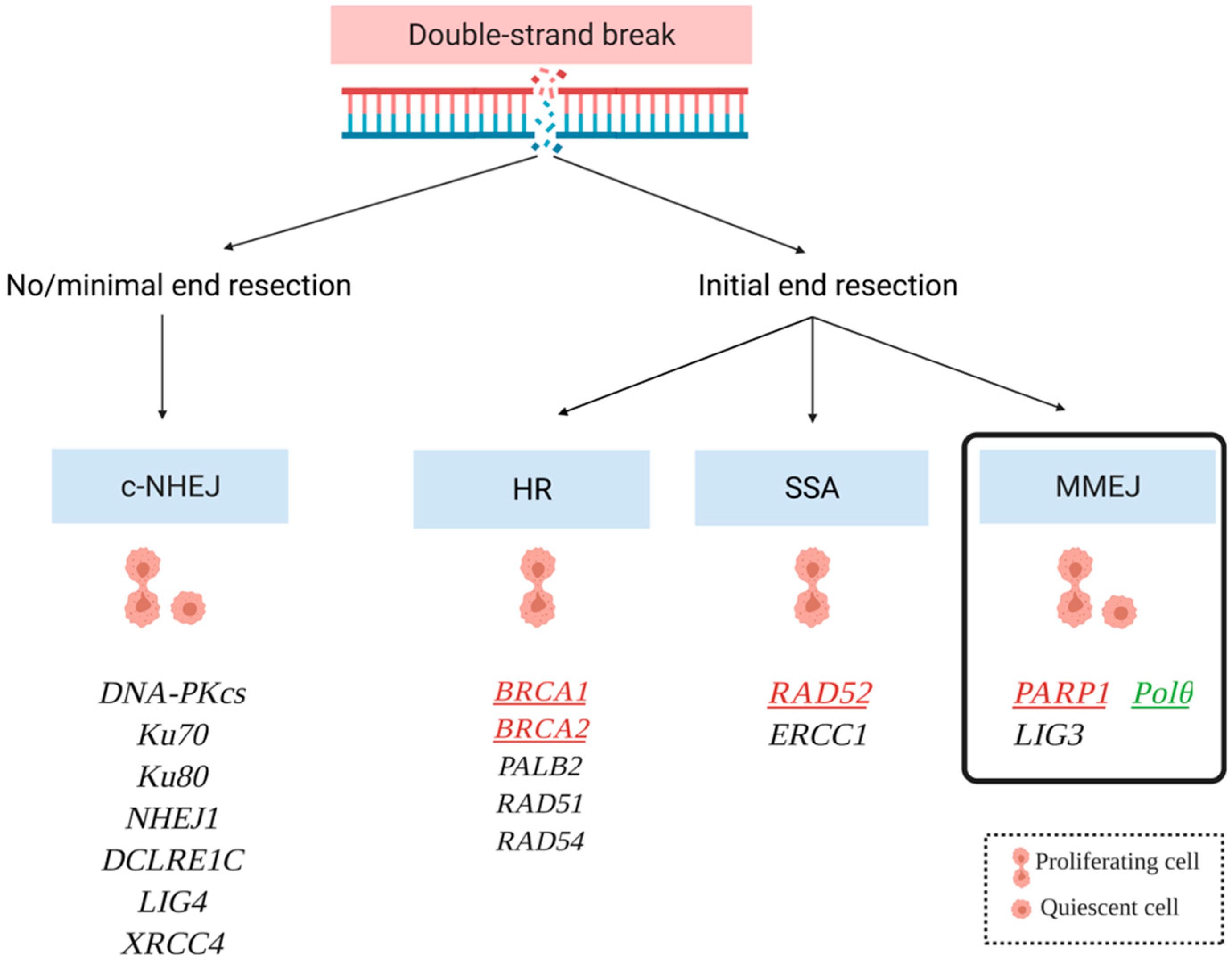
3.1. Mechanisms of DNA Double Strand Break Repair: Where Is Polθ?
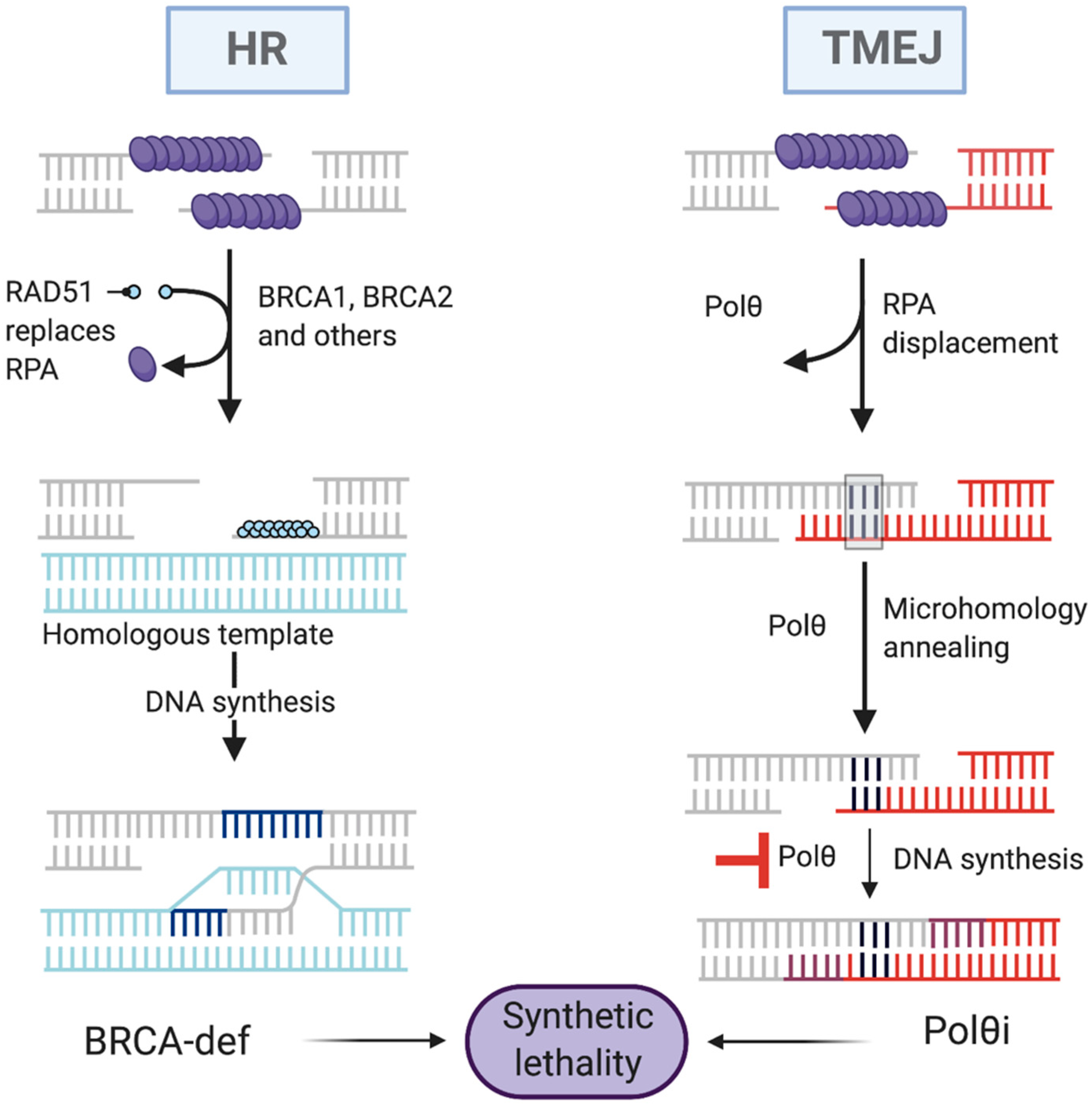
3.1.1. Homologous Recombination Repair (HRR)
3.1.2. Single Strand Annealing (SSA)
3.1.3. Nonhomologous End Joining (NHEJ)
3.1.4. Polymerase Theta-Mediated End Joining (TMEJ)
4. The Role of Polθ in Malignant Cells
4.1. Expression of Polθ in Cancer Cells
4.2. HR-Deficient Tumors
4.3. Synthetic Lethality Targeting Polθ
5. Polθ—A Therapeutic Target for Cancer Therapy
5.1. Why Target Polθ to Trigger Synthetic Lethality?
5.2. Polθ Inhibition as a Potential Target for Synthetic Lethality-Based Anticancer Therapy
Novobiocin and ART558
5.3. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATM | Ataxia telangiectasia mutated |
| alt-NHEJ | Alternative non-homologous end joining |
| B-NHEJ | Backup nonhomologous end-joining |
| BER | Base excision repair |
| 51BP1 | P51 binging protein 1 |
| c-NHEJ | Canonical non-homologous end joining |
| CtIP | BRCA1 C-terminal Interacting Protein |
| D-NHEJ | DNA-PK-mediated nonhomologous end-joining |
| DDR | DNA damage response |
| DSB | DNA double strand break |
| ESCC | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma |
| FDA | Food and drug administration |
| HR | Homologous recombination |
| MMEJ | Microhomology-mediated end-joining |
| NHEJ | Nonhomologous end-joining |
| PARPi | Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 inhibitor |
| Polθ | Polymerase theta |
| Polθi | Polymerase theta inhibitor |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RBBP8 | Retinoblastoma binding protein 8 |
| RPA | Replication protein A |
| RIF1 | Replication timing regulatory factor 1 |
| SSA | Single strand annealing |
| SSB | Single strand break |
| ssDNA | Single stranded DNA |
| SL | Synthetic lethality |
| XPF | Xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group F |
References
- Beagan, K.; Armstrong, R.L.; Witsell, A.; Roy, U.; Renedo, N.; Baker, A.E.; Schärer, O.D.; McVey, M. Drosophila DNA Polymerase Theta Utilizes Both Helicase-like and Polymerase Domains during Microhomology-Mediated End Joining and Interstrand Crosslink Repair. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobzhansky, T. Genetics of Natural Populations. xiii. Recombination and Variability in Populations of Drosophila Pseudoobscura. Genetics 1946, 31, 269–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Jeng, E.E.; Hess, G.T.; Morgens, D.W.; Li, A.; Bassik, M.C. Synergistic Drug Combinations for Cancer Identified in a CRISPR Screen for Pairwise Genetic Interactions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, C.J.; Ashworth, A. Mechanisms of Resistance to Therapies Targeting BRCA-Mutant Cancers. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Song, Y.; Li, S.; Kurian, S.; Xiang, R.; Chiba, T.; Wu, X. DNA Polymerase θ (POLQ) Is Important for Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks Caused by Fork Collapse. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 3909–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ko, J.M.-Y.; Dai, W.; Yu, V.Z.; Ng, H.Y.; Hoffmann, J.-S.; Lung, M.L. Depletion of DNA Polymerase Theta Inhibits Tumor Growth and Promotes Genome Instability through the CGAS-STING-ISG Pathway in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goullet de Rugy, T.; Bashkurov, M.; Datti, A.; Betous, R.; Guitton-Sert, L.; Cazaux, C.; Durocher, D.; Hoffmann, J.S. Excess Polθ Functions in Response to Replicative Stress in Homologous Recombination-Proficient Cancer Cells. Biol. Open 2016, 5, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeoka, S.; Nakahara, T.; Iwahashi, H.; Mizushina, Y. The Establishment of an Assay to Measure DNA Polymerase-Catalyzed Repair of UVB-Induced DNA Damage in Skin Cells and Screening of DNA Polymerase Enhancers from Medicinal Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, M. POLQ (Pol), a DNA Polymerase and DNA-Dependent ATPase in Human Cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 6117–6126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, S.J.; Ozdemir, A.Y.; Kashkina, E.; Kent, T.; Rusanov, T.; Ristic, D.; Shin, Y.; Suma, A.; Hoang, T.; Chandramouly, G.; et al. Molecular Basis of Microhomology-Mediated End-Joining by Purified Full-Length Polθ. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos-Gomez, P.A.; Kent, T.; Deng, S.K.; McDevitt, S.; Kashkina, E.; Hoang, T.M.; Pomerantz, R.T.; Sfeir, A. The Helicase Domain of Polθ Counteracts RPA to Promote Alt-NHEJ. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2017, 24, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzzini, D.M.; Plevani, P.; Boulton, S.J.; Cassata, G.; Marini, F. Caenorhabditis Elegans POLQ-1 and HEL-308 Function in Two Distinct DNA Interstrand Cross-Link Repair Pathways. DNA Repair 2008, 7, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Vidal, A.; Guitton-Sert, L.; Cadoret, J.-C.; Drac, M.; Schwob, E.; Baldacci, G.; Cazaux, C.; Hoffmann, J.-S. A Role for DNA Polymerase θ in the Timing of DNA Replication. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, T.; Mateos-Gomez, P.A.; Sfeir, A.; Pomerantz, R.T. Polymerase θ Is a Robust Terminal Transferase That Oscillates between Three Different Mechanisms during End-Joining. eLife 2016, 5, e13740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, S.; Kashkina, E.; Kent, T.; Pomerantz, R. DNA Polymerase θ: A Unique Multifunctional End-Joining Machine. Genes 2016, 7, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasiak, J. Single-Strand Annealing in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Levine, A.S.; Lan, L. Transcription-Coupled Homologous Recombination after Oxidative Damage. DNA Repair 2016, 44, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.J.; DiDomenico, S.F.; Patel, M.; Mazin, A.V. RAD52: Paradigm of Synthetic Lethality and New Developments. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 780293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koole, W.; van Schendel, R.; Karambelas, A.E.; van Heteren, J.T.; Okihara, K.L.; Tijsterman, M. A Polymerase Theta-Dependent Repair Pathway Suppresses Extensive Genomic Instability at Endogenous G4 DNA Sites. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, M.; Masutani, C.; Yang, L.W.; Schuffert, A.; Iwai, S.; Bahar, I.; Wood, R.D. High-Efficiency Bypass of DNA Damage by Human DNA Polymerase Q. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 4484–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjha, L.; Howard, S.M.; Cejka, P. Main Steps in DNA Double-Strand Break Repair: An Introduction to Homologous Recombination and Related Processes. Chromosoma 2018, 127, 187–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunting, S.F.; Callén, E.; Wong, N.; Chen, H.-T.; Polato, F.; Gunn, A.; Bothmer, A.; Feldhahn, N.; Fernandez-Capetillo, O.; Cao, L.; et al. 53BP1 Inhibits Homologous Recombination in Brca1-Deficient Cells by Blocking Resection of DNA Breaks. Cell 2010, 141, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noordermeer, S.M.; Adam, S.; Setiaputra, D.; Barazas, M.; Pettitt, S.J.; Ling, A.K.; Olivieri, M.; Álvarez-Quilón, A.; Moatti, N.; Zimmermann, M.; et al. The Shieldin Complex Mediates 53BP1-Dependent DNA Repair. Nature 2018, 560, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symington, L.S. Mechanism and Regulation of DNA End Resection in Eukaryotes. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 51, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, N.N.; Akagawa, R.; Yamasaki, T.; Hirota, K.; Sasa, K.; Natsume, T.; Kobayashi, J.; Sakuma, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Komatsu, K.; et al. Relative Contribution of Four Nucleases, CtIP, Dna2, Exo1 and Mre11, to the Initial Step of DNA Double-Strand Break Repair by Homologous Recombination in Both the Chicken DT40 and Human TK6 Cell Lines. Genes Cells 2015, 20, 1059–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVey, M.; Khodaverdian, V.Y.; Meyer, D.; Cerqueira, P.G.; Heyer, W.-D. Eukaryotic DNA Polymerases in Homologous Recombination. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2016, 50, 393–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez Sanchez-Rebato, M.; Bouatta, A.M.; Gallego, M.E.; White, C.I.; Da Ines, O. RAD54 Is Essential for RAD51-Mediated Repair of Meiotic DSB in Arabidopsis. PLOS Genet. 2021, 17, e1008919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallmyr, A.; Tomkinson, A.E. Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks by Mammalian Alternative End-Joining Pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 10536–10546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridounnia, M.; Folkers, G.; Boelens, R. Function and Interactions of ERCC1-XPF in DNA Damage Response. Molecules 2018, 23, 3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, A.; Dardillac, E.; Muhammad, A.; Chailleux, C.; Sesma-Sanz, L.; Ragu, S.; Le Cam, E.; Canitrot, Y.; Masson, J.Y.; Dupaigne, P.; et al. RAD51 Protects against Nonconservative DNA Double-Strand Break Repair through a Nonenzymatic Function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 2651–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Yang, S.; Hwang, G.-H.; Yu, J.; Bae, S. Analysis of NHEJ-Based DNA Repair after CRISPR-Mediated DNA Cleavage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnoult, N.; Correia, A.; Ma, J.; Merlo, A.; Garcia-Gomez, S.; Maric, M.; Tognetti, M.; Benner, C.W.; Boulton, S.J.; Saghatelian, A.; et al. Regulation of DNA Repair Pathway Choice in S and G2 Phases by the NHEJ Inhibitor CYREN. Nature 2017, 549, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, R.; Panday, A.; Elango, R.; Willis, N.A. DNA Double-Strand Break Repair-Pathway Choice in Somatic Mammalian Cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 698–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley, J. DNA Double Strand Break Repair in Human Bladder Cancer Is Error Prone and Involves Microhomology-Associated End-Joining. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 5249–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chang, H.H.Y.; Pannunzio, N.R.; Adachi, N.; Lieber, M.R. Non-Homologous DNA End Joining and Alternative Pathways to Double-Strand Break Repair. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, D.W.; Feng, W.; Conlin, M.P.; Yousefzadeh, M.J.; Roberts, S.A.; Mieczkowski, P.; Wood, R.D.; Gupta, G.P.; Ramsden, D.A. Essential Roles for Polymerase θ-Mediated End Joining in the Repair of Chromosome Breaks. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsek, D.; Brunet, E.; Wong, S.Y.-W.; Katyal, S.; Gao, Y.; McKinnon, P.J.; Lou, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Rebar, E.J.; et al. DNA Ligase III Promotes Alternative Nonhomologous End-Joining during Chromosomal Translocation Formation. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Deng, L.; Nguyen, S.C.; Zhao, X.; Maulion, C.D.; Shao, C.; Tischfield, J.A. Human DNA Ligases I and III, but Not Ligase IV, Are Required for Microhomology-Mediated End Joining of DNA Double-Strand Breaks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3297–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Duan, J.; Shu, S.; Wang, X.; Gao, L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y. Ligase I and Ligase III Mediate the DNA Double-Strand Break Ligation in Alternative End-Joining. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, M.; Kohzaki, M.; Nakamura, J.; Asagoshi, K.; Sonoda, E.; Hou, E.; Prasad, R.; Wilson, S.H.; Tano, K.; Yasui, A.; et al. Vertebrate POLQ and POLβ Cooperate in Base Excision Repair of Oxidative DNA Damage. Mol. Cell 2006, 24, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arana, M.E.; Seki, M.; Wood, R.D.; Rogozin, I.B.; Kunkel, T.A. Low-Fidelity DNA Synthesis by Human DNA Polymerase Theta. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3847–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, G.S.; Prevo, R.; Lee, Y.-F.; Helleday, T.; Muschel, R.J.; Taylor, S.; Yoshimura, M.; Hickson, I.D.; Bernhard, E.J.; McKenna, W.G. A Small Interfering RNA Screen of Genes Involved in DNA Repair Identifies Tumor-Specific Radiosensitization by POLQ Knockdown. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2984–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimmel, J.; van Schendel, R.; den Dunnen, J.T.; Tijsterman, M. Templated Insertions: A Smoking Gun for Polymerase Theta-Mediated End Joining. Trends Genet. 2019, 35, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, K.; Bahar, R.; Seimiya, M.; Chiyo, M.; Wada, A.; Okada, S.; Hatano, M.; Tokuhisa, T.; Kimura, H.; Watanabe, S.; et al. DNA Polymerase? Is Preferentially Expressed in Lymphoid Tissues and Upregulated in Human Cancers. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 109, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemee, F.; Bergoglio, V.; Fernandez-Vidal, A.; Machado-Silva, A.; Pillaire, M.-J.; Bieth, A.; Gentil, C.; Baker, L.; Martin, A.-L.; Leduc, C.; et al. DNA Polymerase Up-Regulation Is Associated with Poor Survival in Breast Cancer, Perturbs DNA Replication, and Promotes Genetic Instability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13390–13395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, G.S.; Harris, A.L.; Prevo, R.; Helleday, T.; McKenna, W.G.; Buffa, F.M. Overexpression of POLQ Confers a Poor Prognosis in Early Breast Cancer Patients. Oncotarget 2010, 1, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoncini, E.; Ricciardi, W.; Cadoni, G.; Arzani, D.; Petrelli, L.; Paludetti, G.; Brennan, P.; Luce, D.; Stucker, I.; Matsuo, K.; et al. Adult Height and Head and Neck Cancer: A Pooled Analysis within the INHANCE Consortium. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 29, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allera-Moreau, C.; Rouquette, I.; Lepage, B.; Oumouhou, N.; Walschaerts, M.; Leconte, E.; Schilling, V.; Gordien, K.; Brouchet, L.; Delisle, M.B.; et al. DNA Replication Stress Response Involving PLK1, CDC6, POLQ, RAD51 and CLASPIN Upregulation Prognoses the Outcome of Early/Mid-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Oncogenesis 2012, 1, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillaire, M.-J.; Selves, J.; Gordien, K.; Gouraud, P.-A.; Gentil, C.; Danjoux, M.; Do, C.; Negre, V.; Bieth, A.; Guimbaud, R.; et al. A ‘DNA Replication’ Signature of Progression and Negative Outcome in Colorectal Cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Gelot, C.; Pantelidou, C.; Li, A.; Yücel, H.; Davis, R.E.; Färkkilä, A.; Kochupurakkal, B.; Syed, A.; Shapiro, G.I.; et al. A First-in-Class Polymerase Theta Inhibitor Selectively Targets Homologous-Recombination-Deficient Tumors. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccaldi, R.; Liu, J.C.; Amunugama, R.; Hajdu, I.; Primack, B.; Petalcorin, M.I.R.; O’Connor, K.W.; Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; Elledge, S.J.; Boulton, S.J.; et al. Homologous-Recombination-Deficient Tumours Are Dependent on Polθ-Mediated Repair. Nature 2015, 518, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambati, A.; Barry, R.M.; Sfeir, A. DNA Polymerase Theta (Polθ)—An Error-Prone Polymerase Necessary for Genome Stability. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2020, 60, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinmura, K.; Kato, H.; Kawanishi, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Tsuchiya, K.; Takahara, Y.; Hosokawa, S.; Kawase, A.; Funai, K.; Sugimura, H. POLQ Overexpression Is Associated with an Increased Somatic Mutation Load and PLK4 Overexpression in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, W.; Deng, T.; Peng, M.-L.; Jiang, J.-Q.; Tang, J.; et al. Knockdown of POLQ Interferes the Development and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Regulating Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis and Migration. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathania, S.; Bade, S.; Le Guillou, M.; Burke, K.; Reed, R.; Bowman-Colin, C.; Su, Y.; Ting, D.T.; Polyak, K.; Richardson, A.L.; et al. BRCA1 Haploinsufficiency for Replication Stress Suppression in Primary Cells. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlacher, K.; Christ, N.; Siaud, N.; Egashira, A.; Wu, H.; Jasin, M. Double-Strand Break Repair-Independent Role for BRCA2 in Blocking Stalled Replication Fork Degradation by MRE11. Cell 2011, 145, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlacher, K.; Wu, H.; Jasin, M. A Distinct Replication Fork Protection Pathway Connects Fanconi Anemia Tumor Suppressors to RAD51-BRCA1/2. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kais, Z.; Rondinelli, B.; Holmes, A.; O’Leary, C.; Kozono, D.; D’Andrea, A.D.; Ceccaldi, R. FANCD2 Maintains Fork Stability in BRCA1/2-Deficient Tumors and Promotes Alternative End-Joining DNA Repair. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 2488–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Guo, M. Synthetic Lethality Strategies: Beyond BRCA1/2 Mutations in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 3111–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, M.; Witusik-Perkowska, M.; Szwed, M.; Stawski, R.; Szemraj, J.; Drzewiecka, M.; Nieborowska-Skorska, M.; Radek, M.; Kolasa, P.; Matlawska-Wasowska, K.; et al. Eradication of LIG4-Deficient Glioblastoma Cells by the Combination of PARP Inhibitor and Alkylating Agent. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 36867–36877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Czyż, M.; Toma, M.; Gajos-Michniewicz, A.; Majchrzak, K.; Hoser, G.; Szemraj, J.; Nieborowska-Skorska, M.; Cheng, P.; Gritsyuk, D.; Levesque, M.; et al. PARP1 Inhibitor Olaparib (Lynparza) Exerts Synthetic Lethal Effect against Ligase 4-Deficient Melanomas. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 75551–75560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, R.; Al-Kawaz, A.; Toss, M.S.; Green, A.R.; Miligy, I.M.; Mesquita, K.A.; Seedhouse, C.; Mirza, S.; Band, V.; Rakha, E.A.; et al. Targeting PARP1 in XRCC1-Deficient Sporadic Invasive Breast Cancer or Preinvasive Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Induces Synthetic Lethality and Chemoprevention. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6818–6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatreanu, D.; Robinson, H.M.R.; Alkhatib, O.; Boursier, M.; Finch, H.; Geo, L.; Grande, D.; Grinkevich, V.; Heald, R.A.; Langdon, S.; et al. Polθ Inhibitors Elicit BRCA-Gene Synthetic Lethality and Target PARP Inhibitor Resistance. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Simpson, D.A.; Carvajal-Garcia, J.; Price, B.A.; Kumar, R.J.; Mose, L.E.; Wood, R.D.; Rashid, N.; Purvis, J.E.; Parker, J.S.; et al. Genetic Determinants of Cellular Addiction to DNA Polymerase Theta. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shima, N.; Hartford, S.A.; Duffy, T.; Wilson, L.A.; Schimenti, K.J.; Schimenti, J.C. Phenotype-Based Identification of Mouse Chromosome Instability Mutants. Genetics 2003, 163, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, J.M.; Aguirre, A.J.; Shapiro, G.I.; D’Andrea, A.D. Biomarker-Guided Development of DNA Repair Inhibitors. Mol. Cell 2020, 78, 1070–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Scott, S.P.; Bussen, W.; Sharma, G.G.; Guo, G.; Pandita, T.K.; Powell, S.N. Rad52 Inactivation Is Synthetically Lethal with BRCA2 Deficiency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizdar, O.; Arslan, C.; Altundag, K. Advances in PARP Inhibitors for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2015, 16, 2751–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.S.; Algouneh, A.; Hakem, R. Exploiting Synthetic Lethality to Target BRCA1/2-Deficient Tumors: Where We Stand. Oncogene 2021, 40, 3001–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, G.S.; Boulton, S.J. Beyond PARP—POLθ as an Anticancer Target. Science 2018, 359, 1217–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefzadeh, M.J.; Wyatt, D.W.; Takata, K.; Mu, Y.; Hensley, S.C.; Tomida, J.; Bylund, G.O.; Doublié, S.; Johansson, E.; Ramsden, D.A.; et al. Mechanism of Suppression of Chromosomal Instability by DNA Polymerase POLQ. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourley, C.; Balmaña, J.; Ledermann, J.A.; Serra, V.; Dent, R.; Loibl, S.; Pujade-Lauraine, E.; Boulton, S.J. Moving From Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Inhibition to Targeting DNA Repair and DNA Damage Response in Cancer Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2257–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caracciolo, D.; Riillo, C.; Di Martino, M.T.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P. Alternative Non-Homologous End-Joining: Error-Prone DNA Repair as Cancer’s Achilles’ Heel. Cancers 2021, 13, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnie, N.J.; Gottlieb, T.M.; Blunt, T.; Jeggo, P.A.; Jackson, S.P. DNA-Dependent Protein Kinase Activity Is Absent in Xrs-6 Cells: Implications for Site-Specific Recombination and DNA Double-Strand Break Repair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Wu, N.; Chen, Y.-C.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, J. PARP Inhibitor Resistance: The Underlying Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrempf, A.; Slyskova, J.; Loizou, J.I. Targeting the DNA Repair Enzyme Polymerase θ in Cancer Therapy. Trends Cancer 2021, 7, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Topatana, W.; Juengpanich, S.; Cao, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, B.; Ma, D.; Cai, X.; Chen, M. Development of Synthetic Lethality in Cancer: Molecular and Cellular Classification. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelso, A.A.; Lopezcolorado, F.W.; Bhargava, R.; Stark, J.M. Distinct Roles of RAD52 and POLQ in Chromosomal Break Repair and Replication Stress Response. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Schendel, R.; van Heteren, J.; Welten, R.; Tijsterman, M. Genomic Scars Generated by Polymerase Theta Reveal the Versatile Mechanism of Alternative End-Joining. PLOS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, J.-H.; Shim, E.Y.; Lee, S.E. Microhomology-Mediated End Joining: Good, Bad and Ugly. Mutat. Res./Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2019, 809, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos-Gomez, P.A. Mammalian Polymerase θ Promotes Alternative NHEJ and Suppresses Recombination. Nature 2015, 518, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.-H.; Chen, P.; Li, J.; Lan, T.; Chen, Y.-C.; Qian, H.; Chen, K.; Li, M.-Y. Co-Inhibition of Pol θ and HR Genes Efficiently Synergize with Cisplatin to Suppress Cisplatin-Resistant Lung Cancer Cells Survival. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 65157–65170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, M.J. Targeting the DNA Damage Response in Cancer. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, G.; Forsberg, L.K.; Zhao, H.; Blagg, B.S.J. Development of Phenyl Cyclohexylcarboxamides as a Novel Class of Hsp90 C-terminal Inhibitors. HHS Public Access. 2018, 23, 16574–16585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, G.; Forsberg, L.K.; Zhao, H.; Blagg, B.S.J. Development of Phenyl Cyclohexylcarboxamides as a Novel Class of Hsp90 C-Terminal Inhibitors. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 16574–16585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shima, N.; Munroe, R.J.; Schimenti, J.C. The Mouse Genomic Instability Mutation Chaos1 Is an Allele of Polq That Exhibits Genetic Interaction with Atm. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 10381–10389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drzewiecka, M.; Barszczewska-Pietraszek, G.; Czarny, P.; Skorski, T.; Śliwiński, T. Synthetic Lethality Targeting Polθ. Genes 2022, 13, 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061101
Drzewiecka M, Barszczewska-Pietraszek G, Czarny P, Skorski T, Śliwiński T. Synthetic Lethality Targeting Polθ. Genes. 2022; 13(6):1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061101
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrzewiecka, Małgorzata, Gabriela Barszczewska-Pietraszek, Piotr Czarny, Tomasz Skorski, and Tomasz Śliwiński. 2022. "Synthetic Lethality Targeting Polθ" Genes 13, no. 6: 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061101
APA StyleDrzewiecka, M., Barszczewska-Pietraszek, G., Czarny, P., Skorski, T., & Śliwiński, T. (2022). Synthetic Lethality Targeting Polθ. Genes, 13(6), 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13061101





