A Machine Learning Approach to Parkinson’s Disease Blood Transcriptomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PPMI Data
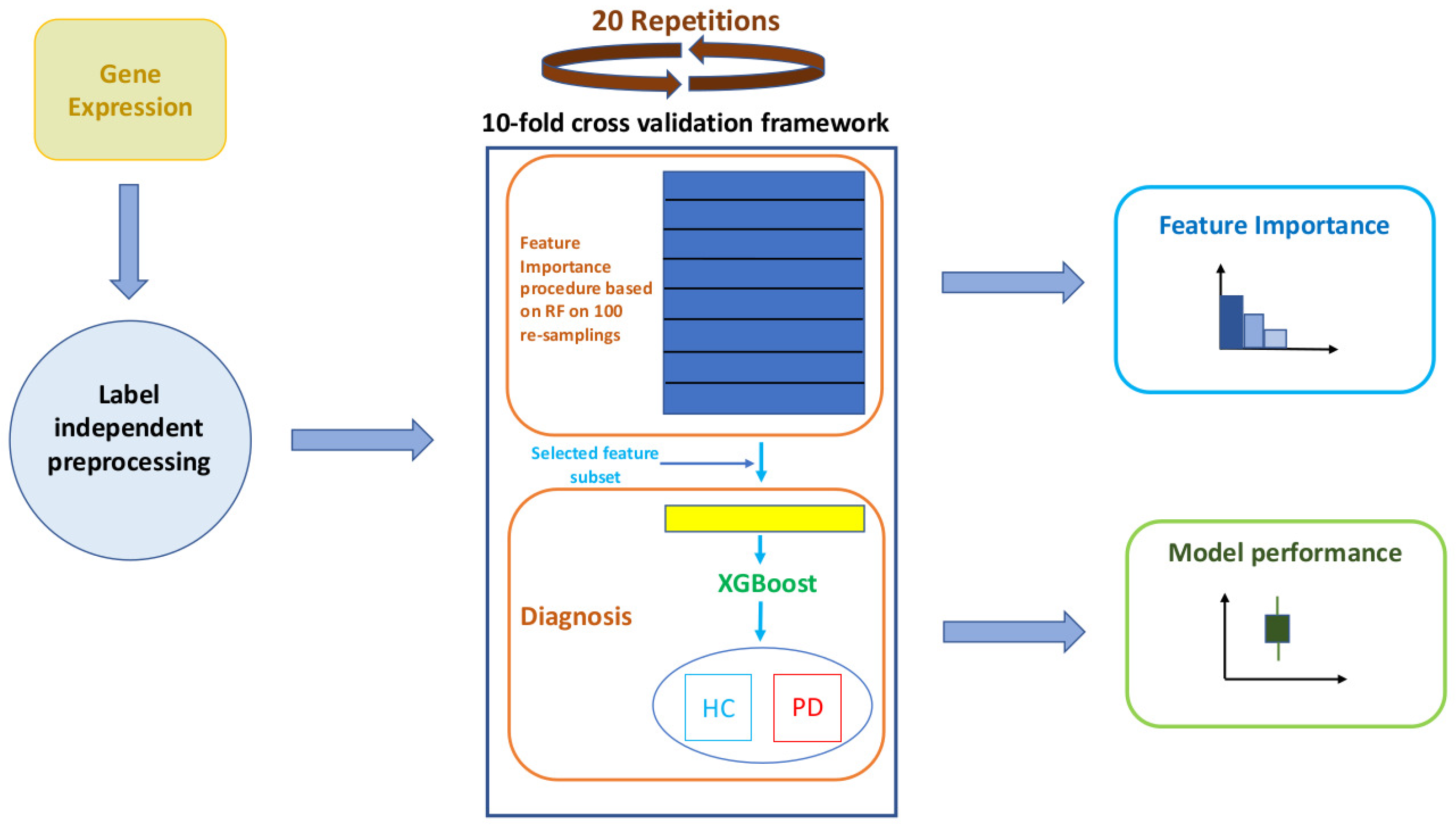
2.2. Overview of the Methodology
2.3. Empowering Informative Content of Gene Expression Values
2.4. Differential Expression Analysis
2.5. A Robust Learning Scheme
2.6. Performance Evaluation
- Accuracy
- Sensitivity
- Specificity
- Balanced Accuracy
- F1
- Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) Curve (AUC), which plots sensitivity against specificity by varying the decision threshold.
3. Results
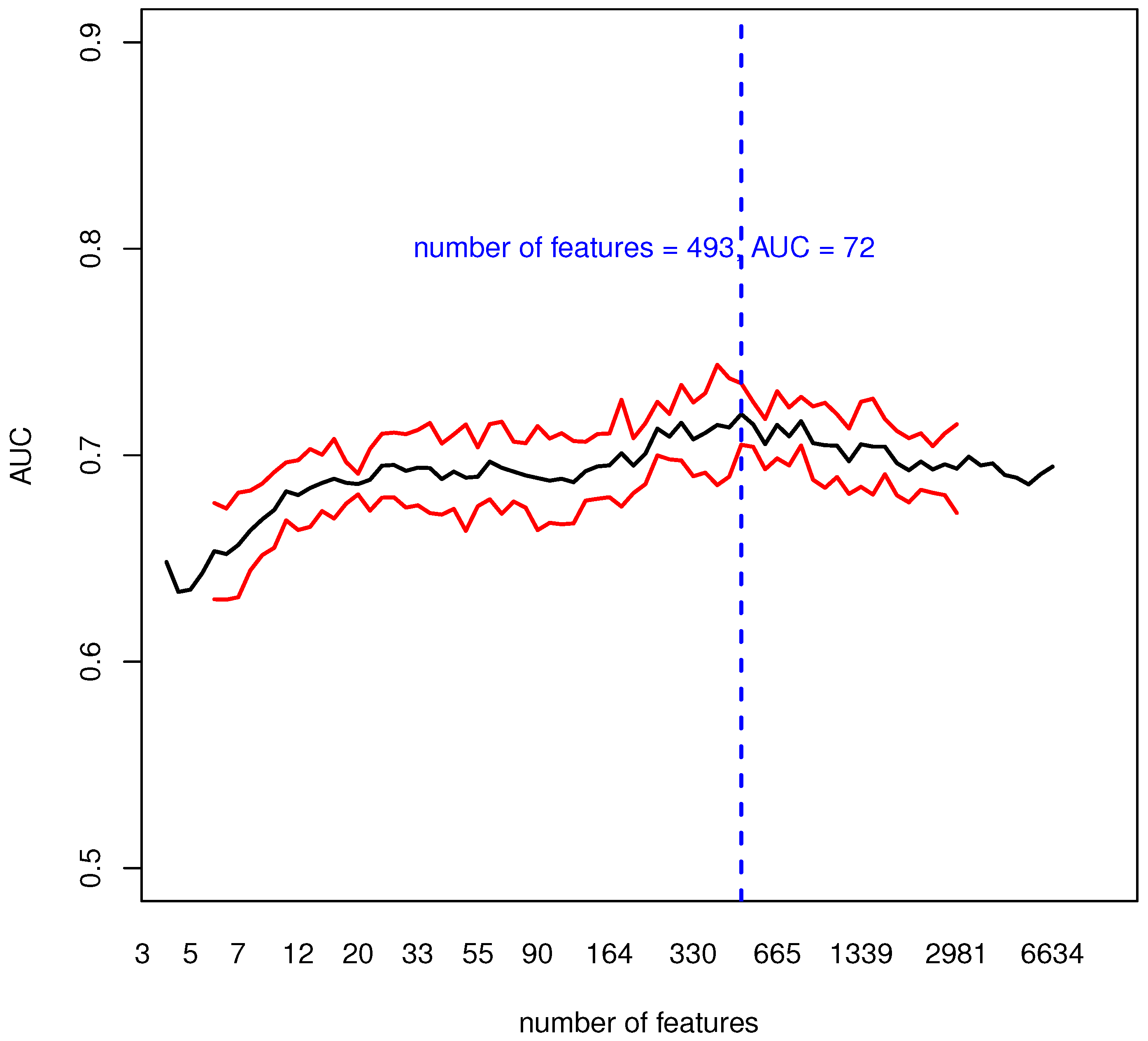
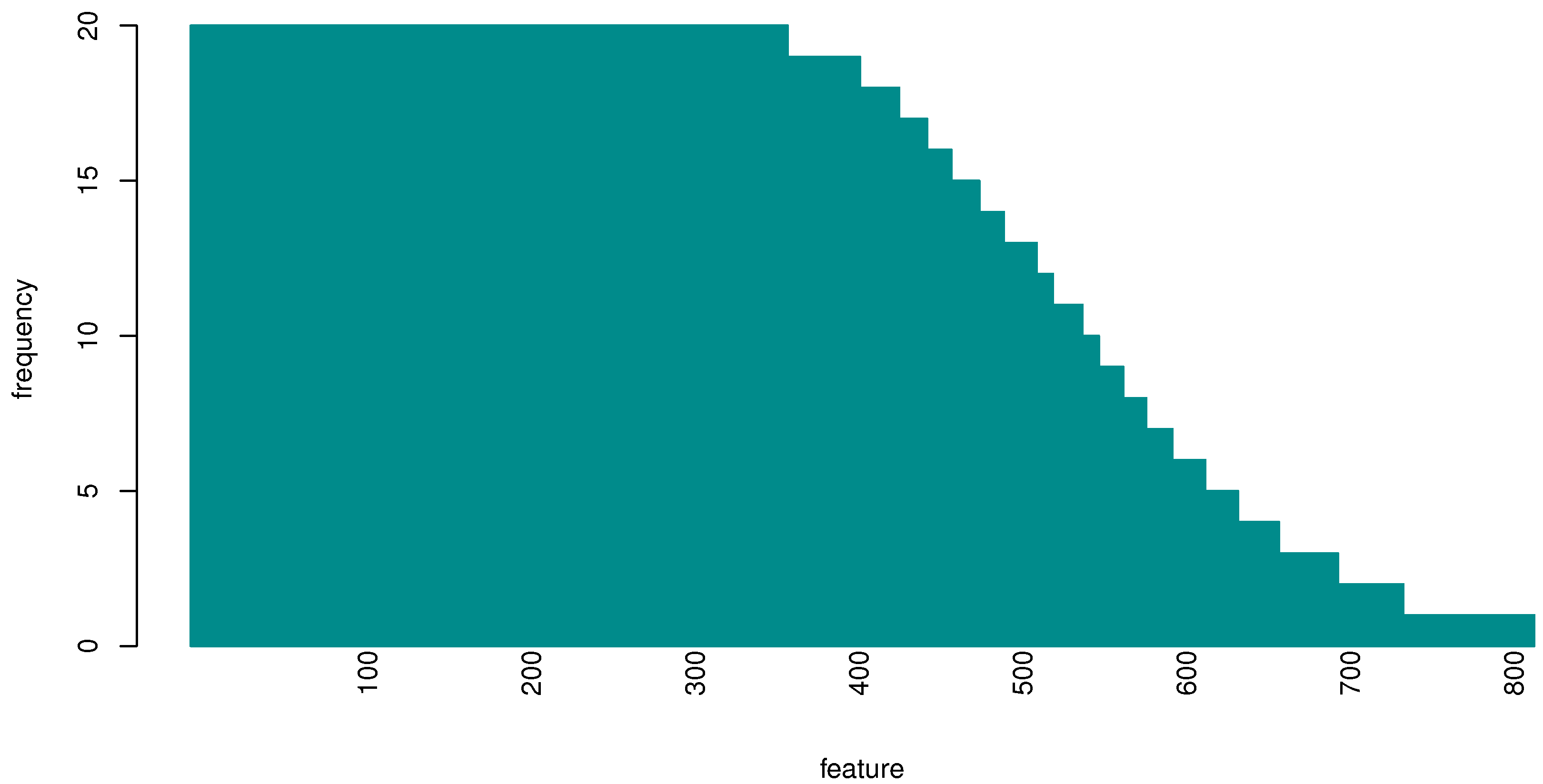
3.1. Evaluating the Informative Content of Transcriptomic Data
3.2. Evaluating Gene Importance
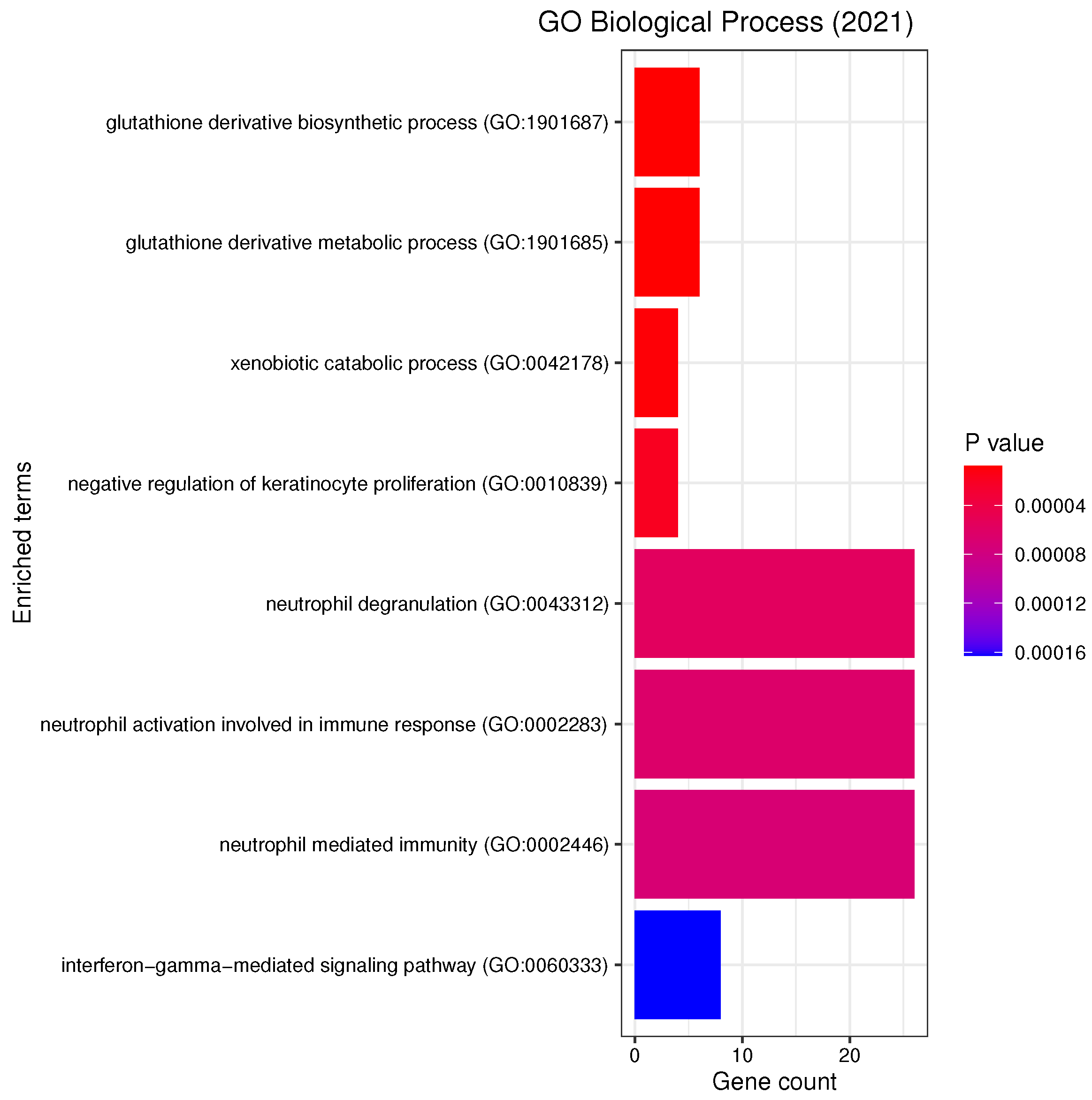
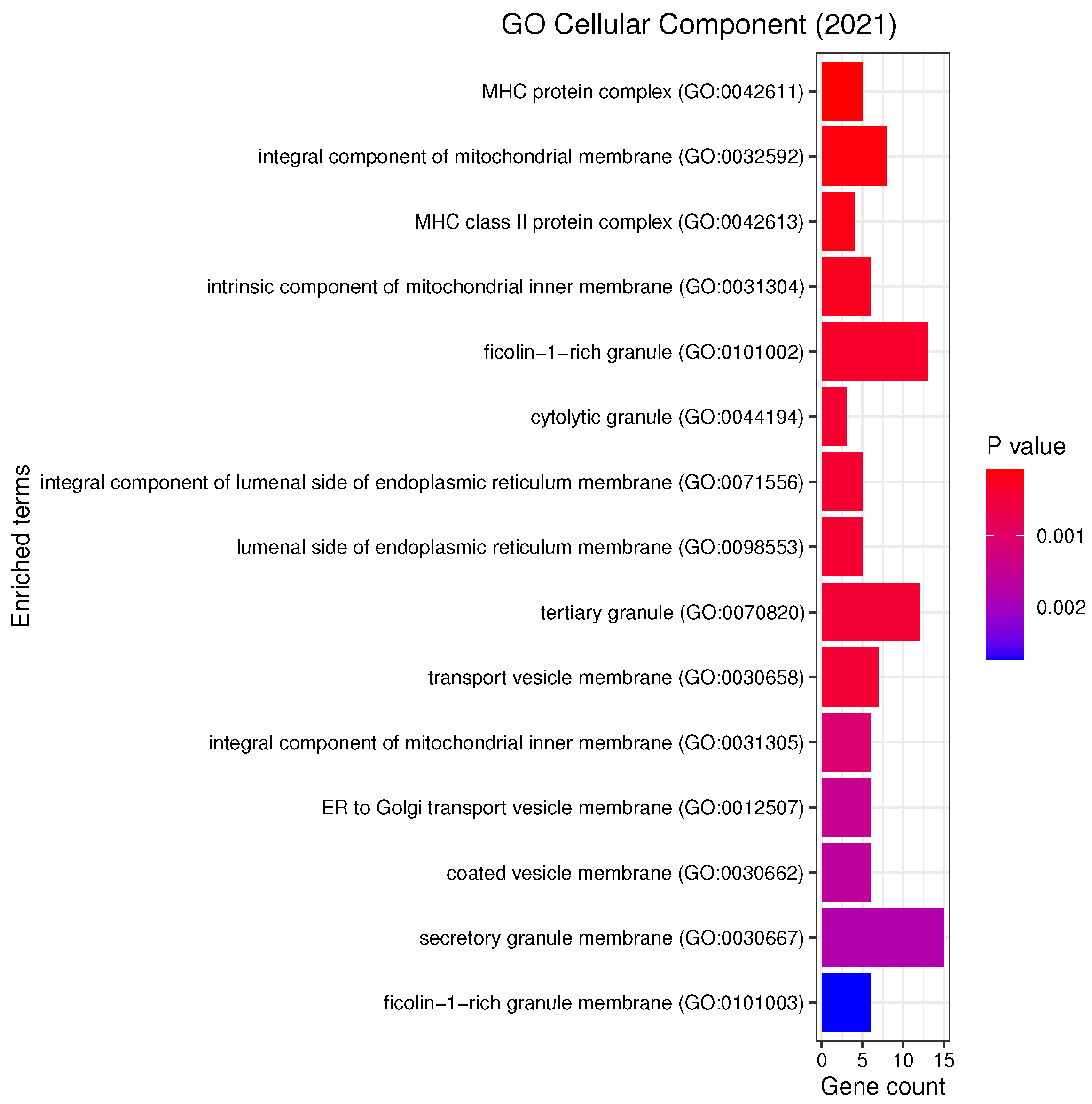
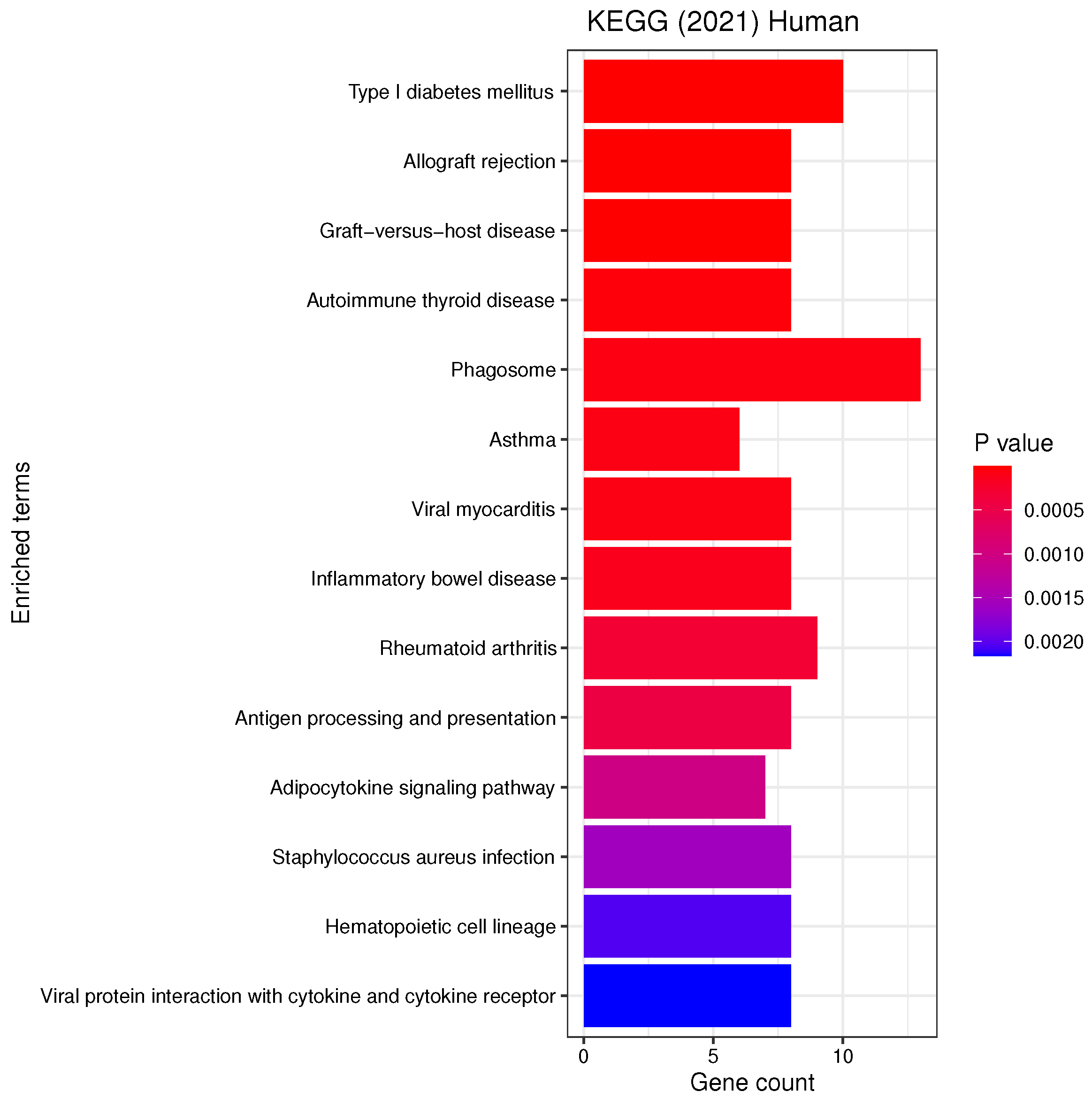
3.3. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. A Robust Machine Learning Model
4.2. Candidate Genes, GOs and KEGG Pathways
4.3. Final Considerations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Algorithm A1 Pseudocode. |
|
| e | Symbol | imp | f | e | Symbol | imp | f | e | Symbol | imp | f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ↑ | MYOM1 | 82.1 | 20 | ↑ | SLC25A20 | 62.7 | 20 | NRM | 46.4 | 20 | |
| ↓ | PHF7 | 45.9 | 20 | ↑ | ENSG00000277763 * | 39.4 | 20 | ICA1 | 36 | 20 | |
| ↑ | CPT1A | 33.8 | 20 | LINC02422 * | 33.3 | 20 | GSTM1 | 32.4 | 20 | ||
| PCDHGA6 | 31.6 | 20 | AK5 | 31.5 | 20 | ↓ | GCNT2 | 29.9 | 20 | ||
| CERS4 | 29.7 | 20 | ↓ | YJU2 | 29.4 | 20 | SURF6 | 27.7 | 20 | ||
| ENSG00000281181 * | 26.7 | 20 | ENSG00000285774 * | 26.7 | 20 | ↑ | ENSG00000272688 * | 26.2 | 20 | ||
| SERF1B | 25.8 | 20 | ENSG00000284773 | 25.7 | 20 | TREML4 | 25.7 | 20 | |||
| ANKRD34B | 25.1 | 14 | ↓ | NDUFB9 | 25 | 20 | ↓ | ERLIN2 | 24.6 | 20 | |
| ENSG00000276651 * | 24.4 | 20 | CCR4 | 23.9 | 20 | NFE2L3 | 23.9 | 20 | |||
| FGGY | 23.5 | 20 | ENSG00000234902 * | 23.3 | 20 | ↑ | ARRDC4 | 23.1 | 20 | ||
| TMTC4 | 21.6 | 20 | ↓ | BPHL | 20.1 | 20 | C2orf42 | 20 | 20 | ||
| BTBD19 | 19.8 | 15 | LOXHD1 | 19.4 | 20 | DHFR | 19.1 | 20 | |||
| LINC02470 * | 18.9 | 20 | SHISA4 | 18.8 | 20 | ↑ | FKBP5 | 18.4 | 20 | ||
| ENSG00000234426 * | 18.3 | 20 | ↑ | TKTL1 | 18.1 | 20 | ATP6V0A2 | 18 | 20 | ||
| GPR19 | 17.9 | 20 | ZNF584 | 17.4 | 20 | FAN1 | 17.4 | 20 | |||
| MRPS6 | 17.2 | 18 | TSPAN2 | 16.9 | 20 | ↓ | CRAT | 16.5 | 20 | ||
| CCRL2 | 16 | 20 | GTF2IRD2 | 15.9 | 20 | PUDP | 15.8 | 20 | |||
| ↓ | NOP16 | 15.7 | 20 | ↑ | LINC00243 * | 15.6 | 20 | ↑ | CEP19 | 15.6 | 20 |
| GAB3 | 15.6 | 20 | ↓ | ENSG00000269399 * | 15.5 | 20 | ↓ | YOD1 | 15.3 | 20 | |
| GET1 | 15.3 | 19 | ↓ | NREP | 15.2 | 20 | YES1 | 14.8 | 15 | ||
| ↑ | COL9A3 | 14.5 | 20 | NSUN4 | 14.4 | 20 | ↓ | FARSB | 14.3 | 20 | |
| ↑ | GZMB | 14.2 | 20 | B4GALNT3 | 14.1 | 20 | ↓ | TBL2 | 14.1 | 20 | |
| ↓ | RAP1GAP | 13.7 | 20 | ↑ | BASP1 | 13.5 | 20 | PRUNE2 | 13.5 | 19 | |
| FBN2 | 13.3 | 20 | VNN1 | 13.2 | 20 | ↑ | LSMEM1 | 13.2 | 20 | ||
| ZSCAN21 | 13.1 | 20 | CLEC12A | 13 | 20 | ↓ | COA4 | 13 | 20 | ||
| ↓ | DPY19L2 | 12.9 | 20 | ↑ | RNASET2 | 12.8 | 20 | DCXR | 12.4 | 20 | |
| WDR49 | 12.4 | 20 | CRYZ | 12.3 | 15 | ↑ | LINC00623 * | 12.2 | 20 | ||
| ↓ | ZNF714 | 12.2 | 20 | ↑ | TOR1B | 12 | 20 | ↑ | ADGRE5 | 11.9 | 20 |
| ↑ | SULF2 | 11.7 | 20 | MSH3 | 11.7 | 20 | PCDHGB3 | 11.6 | 20 | ||
| SPHK1 | 11.3 | 20 | ↓ | G6PC3 | 11 | 20 | ↓ | MASTL | 11 | 20 | |
| ↓ | LINC01806 * | 11 | 20 | ↓ | SQLE | 11 | 20 | PWP2 | 10.9 | 20 | |
| TXLNB | 10.8 | 20 | ZSWIM3 | 10.7 | 19 | SFXN4 | 10.6 | 20 | |||
| ↑ | RUBCNL | 10.6 | 20 | ↓ | PNO1 | 10.2 | 20 | SMIM12 | 10.2 | 18 | |
| TNFRSF10B | 10.2 | 20 | GPR162 | 10 | 16 | ↓ | KRT1 | 10 | 20 | ||
| B3GAT1 | 9.8 | 20 | PILRB | 9.8 | 20 | ↑ | TAP2 | 9.8 | 20 | ||
| MSR1 | 9.7 | 18 | LINC00482 * | 9.6 | 18 | OSER1-DT * | 9.4 | 15 | |||
| ASCC1 | 9.4 | 20 | ↑ | ZNF429 | 9.4 | 20 | SSPN | 9.3 | 20 | ||
| ↓ | GYPA | 9.3 | 20 | ↑ | FAT4 | 9.3 | 20 | ↓ | SLC18B1 | 9.2 | 20 |
| TIPIN | 9.1 | 20 | IL18RAP | 9 | 15 | GYPE | 8.9 | 20 | |||
| ↓ | HYAL3 | 8.7 | 20 | ↑ | PREX1 | 8.7 | 19 | KLRC2 | 8.6 | 20 | |
| FCER1A | 8.6 | 19 | ENDOG | 8.6 | 20 | GSTM3 | 8.6 | 20 | |||
| ↑ | TMEM252 | 8.6 | 20 | SRGAP2C | 8.5 | 17 | ↓ | ATP5MC1 | 8.5 | 20 | |
| FIS1 | 8.3 | 20 | ARRDC3-AS1 * | 8.3 | 19 | LINC01948 * | 8.3 | 16 | |||
| TPPP3 | 8.2 | 20 | HDHD3 | 8.2 | 19 | ↓ | LINC01560 * | 8.2 | 20 | ||
| ↓ | IFRD2 | 8.1 | 20 | ↓ | STK11 | 8.1 | 17 | ↓ | TARBP1 | 7.9 | 20 |
| LINC00299 * | 7.9 | 19 | XCL1 | 7.8 | 20 | ZNF491 | 7.6 | 20 | |||
| LINC00570 * | 7.4 | 20 | PARS2 | 7.4 | 20 | INPP1 | 7.4 | 20 | |||
| ↓ | TMEM245 | 7.4 | 20 | NECAP2 | 7.3 | 19 | PER3 | 7.3 | 20 | ||
| CDCA4 | 7.2 | 20 | NUP210L | 7.2 | 19 | GTF2H2 | 7.1 | 20 | |||
| APOLD1 | 7.1 | 20 | ETFDH | 7 | 20 | ↓ | GPX4 | 6.9 | 20 | ||
| ↓ | PPP1R14B | 6.9 | 20 | ↓ | GOLGA6L9 | 6.9 | 20 | ATP6AP1L | 6.9 | 20 | |
| ↓ | GFUS | 6.9 | 20 | ↑ | ENSG00000268240 * | 6.7 | 20 | MAST4 | 6.7 | 20 | |
| ↑ | ENSG00000225750 * | 6.7 | 20 | ↑ | BCL6 | 6.5 | 20 | DDO | 6.5 | 20 | |
| ↑ | TMEM185B | 6.4 | 20 | UPB1 | 6.4 | 20 | CCR3 | 6.4 | 20 | ||
| PLIN2 | 6.4 | 20 | ↓ | RALY-AS1 * | 6.3 | 20 | DDIT4 | 6.3 | 20 | ||
| FGFR2 | 6.3 | 20 | ↓ | PAICS | 6.3 | 20 | ENSG00000278384 | 6.2 | 19 | ||
| HLA-DRB5 | 6.2 | 16 | ↑ | VDR | 6.1 | 19 | ENSG00000254789 * | 6.1 | 20 | ||
| ENSG00000260077 * | 6.1 | 18 | CLEC18A | 6.1 | 15 | ↑ | LINC02193 * | 6.1 | 20 | ||
| ↑ | SBNO1 | 6.1 | 20 | ↑ | VAV1 | 6.1 | 17 | SCN3A | 6 | 20 | |
| CCL4L2 | 5.9 | 20 | ASB3 | 5.8 | 18 | GSTM2 | 5.8 | 20 | |||
| ↑ | KDM5B | 5.8 | 20 | GNAL | 5.7 | 18 | KCNMB1 | 5.6 | 15 | ||
| CSGALNACT1 | 5.6 | 20 | ↓ | RNASEH1 | 5.6 | 20 | ENSG00000285476 | 5.5 | 20 | ||
| ↑ | FBXL13 | 5.4 | 20 | VLDLR | 5.4 | 20 | ↑ | FPR2 | 5.4 | 20 | |
| ↑ | PPP1R3B | 5.4 | 20 | ↓ | SRSF8 | 5.4 | 20 | APOO | 5.3 | 20 | |
| ↑ | TXNIP | 5.3 | 20 | ↓ | MPG | 5.3 | 19 | TAS2R43 | 5.2 | 20 | |
| FLVCR2 | 5.1 | 20 | SLC25A3 | 5.1 | 20 | ↓ | CD36 | 5.1 | 19 | ||
| CENPK | 5 | 18 | C5 | 5 | 14 | ↑ | PRRG4 | 5 | 20 | ||
| DYRK1B | 4.9 | 17 | ↑ | APTR * | 4.8 | 20 | ↓ | TMEM14C | 4.8 | 19 | |
| PF4V1 | 4.8 | 20 | ↓ | ZNF789 | 4.7 | 20 | UBR7 | 4.7 | 17 | ||
| HMOX2 | 4.6 | 19 | PID1 | 4.6 | 20 | LERFS * | 4.5 | 20 | |||
| ENSG00000266302 | 4.5 | 20 | AKAP5 | 4.5 | 20 | DPCD | 4.4 | 20 | |||
| TMTC2 | 4.4 | 20 | NKAP | 4.4 | 17 | ENSG00000276476 * | 4.4 | 20 | |||
| EDAR | 4.4 | 20 | VSTM1 | 4.4 | 20 | PDK4 | 4.3 | 20 | |||
| ↑ | HIF1A | 4.3 | 20 | ↓ | GRHPR | 4.3 | 20 | TUBB2A | 4.3 | 20 | |
| PALLD | 4.3 | 20 | ↑ | LINC01303 * | 4.3 | 20 | FPR3 | 4.3 | 20 | ||
| ↑ | TMEM45B | 4.3 | 20 | RGMB | 4.3 | 20 | ↑ | CREM | 4.3 | 20 | |
| ↓ | LYRM9 | 4.3 | 18 | VSIG10 | 4.3 | 20 | ↓ | TSPAN17 | 4.2 | 20 | |
| BBLN | 4.1 | 16 | LTA4H | 4.1 | 20 | U2AF1 | 4.1 | 20 | |||
| PPAN | 4.1 | 20 | ARL17B | 4.1 | 20 | ENSG00000274922 * | 4.1 | 19 | |||
| TM9SF1 | 4 | 20 | EPPK1 | 4 | 20 | ↑ | THBD | 4 | 20 | ||
| DRAXIN | 4 | 14 | ↓ | USP12 | 3.9 | 20 | SLC11A2 | 3.9 | 19 | ||
| ENSG00000259071 * | 3.9 | 20 | ↑ | SPON2 | 3.8 | 20 | ENSG00000256427 * | 3.8 | 14 | ||
| FAM124B | 3.8 | 20 | ↓ | NBDY | 3.8 | 20 | ↓ | MBNL3 | 3.8 | 20 | |
| ↓ | COMMD9 | 3.7 | 20 | CTSK | 3.7 | 20 | ↓ | CYREN | 3.7 | 20 | |
| ↑ | LINC00654 * | 3.7 | 20 | ↑ | ENSG00000270972 * | 3.6 | 20 | ↓ | SVBP | 3.6 | 20 |
| TMEM185A | 3.6 | 18 | ↓ | CDK6 | 3.6 | 20 | MFSD9 | 3.6 | 20 | ||
| CRTAP | 3.5 | 14 | CSTB | 3.5 | 20 | ↓ | PTRHD1 | 3.5 | 20 | ||
| PPIE | 3.5 | 20 | HLA-DMB | 3.5 | 15 | DSC1 | 3.5 | 20 | |||
| ↓ | CEP85 | 3.4 | 20 | RNF182 | 3.4 | 20 | ↓ | HSD17B8 | 3.4 | 20 | |
| NKX3-1 | 3.4 | 20 | F2R | 3.4 | 20 | ENSG00000224635 * | 3.4 | 19 | |||
| ↓ | HDHD5 | 3.4 | 20 | ZKSCAN4 | 3.4 | 20 | ↑ | KPNB1 | 3.3 | 20 | |
| ↑ | LAMP1 | 3.3 | 20 | ↓ | ENSG00000277369 * | 3.3 | 20 | ↓ | SNHG4 * | 3.3 | 20 |
| MYG1 | 3.3 | 15 | ↓ | SLC25A25 | 3.3 | 18 | U2AF1L5 | 3.3 | 20 | ||
| ↓ | ETHE1 | 3.2 | 20 | KAT2B | 3.2 | 20 | ↓ | MIR378D2HG * | 3.2 | 16 | |
| ↓ | TLCD4 | 3.2 | 20 | ↑ | SPTY2D1 | 3.2 | 20 | MYOM2 | 3.2 | 20 | |
| ↑ | IL18R1 | 3.1 | 20 | ↓ | UBE2E2 | 3.1 | 20 | ↑ | KREMEN1 | 3.1 | 20 |
| ENSG00000227920 * | 3.1 | 19 | COX5A | 3 | 16 | ↓ | LINC00920 * | 3 | 20 | ||
| NRG1 | 3 | 17 | ↓ | GPR15 | 3 | 20 | ↓ | UROS | 3 | 20 | |
| LINC02520 * | 3 | 20 | ↑ | TGM3 | 3 | 20 | CCZ1B | 3 | 20 | ||
| S100B | 3 | 20 | NR4A2 | 2.9 | 20 | SULT1A1 | 2.9 | 19 | |||
| TMEM273 | 2.9 | 20 | LINC00381 * | 2.9 | 18 | FMN1 | 2.8 | 20 | |||
| CCDC144A | 2.8 | 20 | ↑ | LMTK2 | 2.8 | 20 | ↑ | HSDL2 | 2.8 | 20 | |
| ↑ | BMX | 2.8 | 20 | ZNF559 | 2.8 | 20 | ↑ | ELL | 2.8 | 17 | |
| ↑ | MIR646HG * | 2.8 | 20 | ↓ | CREG1 | 2.8 | 20 | DACT1 | 2.8 | 19 | |
| ↑ | TBC1D30 | 2.7 | 20 | JUN | 2.7 | 20 | CLEC4F | 2.7 | 20 | ||
| ENSG00000259652 * | 2.7 | 19 | ↓ | POMC | 2.6 | 14 | ↓ | THAP7 | 2.6 | 20 | |
| YDJC | 2.6 | 20 | ↑ | NFE4 | 2.6 | 20 | PDZD4 | 2.6 | 20 | ||
| FTCDNL1 | 2.6 | 20 | ↑ | GABARAPL1 | 2.6 | 20 | ↓ | TIMM9 | 2.6 | 20 | |
| ↓ | ANKRD9 | 2.6 | 19 | ↓ | RNF11 | 2.5 | 19 | ATP6V1F | 2.5 | 20 | |
| ↓ | MTCH2 | 2.5 | 20 | SCO1 | 2.5 | 19 | NOTCH2NLA | 2.5 | 20 | ||
| GATD3A | 2.5 | 20 | MAP3K7CL | 2.5 | 20 | ↑ | NCAM1 | 2.4 | 20 | ||
| LINC02273 * | 2.4 | 20 | PI16 | 2.4 | 14 | ↑ | CLCN4 | 2.4 | 20 | ||
| CTXN2-AS1 * | 2.4 | 19 | ↓ | MECR | 2.4 | 20 | ↑ | ENSG00000273243 * | 2.4 | 20 | |
| COL18A1 | 2.4 | 20 | ↑ | TLK2 | 2.3 | 20 | ↓ | HMBS | 2.3 | 17 | |
| CCDC102A | 2.3 | 15 | TTF2 | 2.3 | 19 | ↓ | C16orf91 | 2.3 | 16 | ||
| ↑ | HERPUD1 | 2.3 | 20 | ↑ | SLA | 2.2 | 20 | TMEM102 | 2.2 | 20 | |
| HLA-DQB1 | 2.2 | 20 | DUSP19 | 2.2 | 20 | ↓ | KCTD3 | 2.2 | 14 | ||
| FOLR3 | 2.2 | 20 | C1orf220 * | 2.1 | 15 | ↑ | PRDM8 | 2.1 | 19 | ||
| ↑ | KIF1B | 2.1 | 19 | LINC00298 * | 2.1 | 18 | LINC01410 * | 2.1 | 20 | ||
| ↑ | LINC02218 | 2.1 | 20 | ↑ | NKAPL | 2.1 | 20 | RAB34 | 2.1 | 20 | |
| ↓ | GSTZ1 | 2.1 | 19 | ↓ | ENSG00000267575 * | 2.1 | 16 | SYNM | 2 | 17 | |
| ↑ | RNF149 | 2 | 20 | ↑ | CSRNP1 | 2 | 17 | LSG1 | 2 | 19 | |
| ↑ | TOP1 | 2 | 20 | ↑ | IRF1 | 2 | 14 | ↑ | SYTL3 | 2 | 20 |
| ZNRD2 | 2 | 20 | ↓ | ICAM4 | 2 | 20 | CLEC12B | 1.9 | 20 | ||
| ↑ | NDRG3 | 1.9 | 20 | PAQR8 | 1.9 | 20 | ↓ | LGALS2 | 1.9 | 20 | |
| ↓ | WDR11 | 1.9 | 17 | ↓ | HDAC9 | 1.9 | 20 | RRS1 | 1.9 | 15 | |
| ANKRD55 | 1.9 | 16 | ↓ | NIT2 | 1.8 | 14 | ENSG00000272908 * | 1.8 | 20 | ||
| ↓ | PMVK | 1.8 | 20 | RFC5 | 1.8 | 20 | ↓ | PRADC1 | 1.8 | 18 | |
| ↑ | HSD17B13 | 1.8 | 18 | ↑ | ZNF487 | 1.8 | 20 | ↑ | NUP50-DT * | 1.8 | 20 |
| TOR3A | 1.7 | 20 | ADAM15 | 1.7 | 20 | ENSG00000285492 * | 1.7 | 20 | |||
| ↑ | CA4 | 1.7 | 20 | PARN | 1.7 | 18 | ↓ | AKR1A1 | 1.7 | 20 | |
| ↑ | DOCK4 | 1.7 | 20 | ↑ | IRS2 | 1.7 | 20 | CHST2 | 1.7 | 20 | |
| ↓ | C3orf18 | 1.6 | 20 | ZNF69 | 1.6 | 20 | ↑ | CCN3 | 1.6 | 20 | |
| CLMN | 1.6 | 20 | GCAT | 1.6 | 14 | ↓ | TXN2 | 1.6 | 15 | ||
| ↑ | TPST1 | 1.6 | 20 | ↑ | MIR3945HG * | 1.5 | 20 | PTPRN2 | 1.5 | 20 | |
| ADGRB3 | 1.5 | 18 | ENSG00000281831 * | 1.5 | 15 | ↓ | EIF2D | 1.5 | 20 | ||
| OAS1 | 1.5 | 14 | ↑ | ACSL1 | 1.5 | 20 | SRP19 | 1.5 | 20 | ||
| ↑ | NUP50 | 1.5 | 20 | ↓ | XK | 1.5 | 20 | ↑ | COA1 | 1.4 | 19 |
| KRT72 | 1.4 | 20 | ↑ | ROPN1L | 1.4 | 16 | SLC25A43 | 1.4 | 20 | ||
| ↑ | ENSG00000251093 * | 1.4 | 20 | ↑ | ABCA1 | 1.4 | 19 | AFDN | 1.4 | 18 | |
| TMEM176B | 1.3 | 20 | ↑ | SERINC3 | 1.3 | 18 | ↑ | CEMIP2 | 1.3 | 20 | |
| ↓ | NAXD | 1.3 | 20 | NFXL1 | 1.3 | 20 | ↓ | ALKBH7 | 1.3 | 19 | |
| ENSG00000259959 * | 1.3 | 20 | ↓ | ENSG00000275765 * | 1.3 | 15 | BSCL2 | 1.2 | 18 | ||
| ↓ | CISD2 | 1.2 | 20 | ↑ | DCAF4L1 | 1.2 | 19 | ↑ | CD93 | 1.2 | 19 |
| ↓ | APRT | 1.2 | 20 | CYBRD1 | 1.1 | 16 | ↑ | NBPF26 | 1.1 | 20 | |
| ↓ | MRPS27 | 1.1 | 18 | GIMAP1 | 1.1 | 20 | RRP7A | 1.1 | 20 | ||
| ISCA1 | 1.1 | 20 | FADS2 | 1.1 | 19 | ↑ | TRANK1 | 1.1 | 18 | ||
| ↑ | PHACTR1 | 1.1 | 20 | ↑ | VNN3 | 1 | 20 | ↑ | HLX | 1 | 20 |
| ↑ | JADE1 | 1 | 20 | ↓ | KNOP1 | 1 | 20 | HLA-DQA2 | 1 | 19 | |
| XKR3 | 1 | 20 | P2RX4 | 0.9 | 16 | CPA3 | 0.9 | 19 | |||
| ↓ | C8orf33 | 0.9 | 19 | MS4A4E | 0.9 | 20 | ENSG00000274979 * | 0.9 | 20 | ||
| ↑ | RPGRIP1 | 0.9 | 14 | ↑ | NCR1 | 0.9 | 20 | ↑ | PRF1 | 0.9 | 20 |
| PEA15 | 0.8 | 19 | S100A10 | 0.8 | 19 | ERO1A | 0.8 | 20 | |||
| ↑ | ADGRG3 | 0.8 | 16 | ↑ | BTNL8 | 0.8 | 20 | EMC9 | 0.8 | 20 | |
| LONRF3 | 0.8 | 20 | SLC38A11 | 0.7 | 20 | ↑ | BAZ1A | 0.7 | 17 | ||
| ↓ | ACAD11 | 0.7 | 15 | ↓ | C1orf109 | 0.7 | 20 | SUV39H1 | 0.7 | 14 | |
| PAAF1 | 0.7 | 18 | MGST3 | 0.7 | 20 | ↑ | PHTF1 | 0.7 | 20 | ||
| ↑ | CD55 | 0.6 | 20 | MTPAP | 0.6 | 20 | ZNF80 | 0.6 | 18 | ||
| ↑ | SIPA1L2 | 0.6 | 20 | PTGDS | 0.6 | 19 | ↓ | SNX3 | 0.6 | 20 | |
| KLF9 | 0.6 | 17 | ↑ | TGFA | 0.6 | 20 | HLA-DQA1 | 0.5 | 20 | ||
| AMACR | 0.5 | 20 | NCAPG2 | 0.5 | 14 | ↓ | CTSH | 0.5 | 15 | ||
| ↑ | ENSG00000282988 | 0.5 | 17 | PANX1 | 0.5 | 20 | HLA-A | 0.5 | 20 | ||
| ↑ | CPD | 0.5 | 20 | ↑ | NHS | 0.4 | 16 | KRT73 | 0.4 | 20 | |
| ↑ | METRNL | 0.3 | 17 | ↓ | PIGW | 0.3 | 16 | ↑ | AVIL | 0.3 | 20 |
| ↑ | ABCG1 | 0.2 | 20 | ↑ | RAB27A | 0.2 | 20 | ↑ | DNAJC3 | 0 | 20 |
References
- GBD Disease Incidence, Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapira, A.H.V.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Jenner, P. Non-motor features of Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelopoulou, E.; Paudel, Y.N.; Papageorgiou, S.G.; Piperi, C. Environmental Impact on the Epigenetic Mechanisms Underlying Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis: A Narrative Review. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nido, G.S.; Dick, F.; Toker, L.; Petersen, K.; Alves, G.; Tysnes, O.B.; Jonassen, I.; Haugarvoll, K.; Tzoulis, C. Common gene expression signatures in Parkinson’s disease are driven by changes in cell composition. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, P.F.; Fan, C.; Perou, C.M. Evaluating the comparability of gene expression in blood and brain. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2006, 141, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soreq, L.; Salomonis, N.; Bronstein, M.; Greenberg, D.S.; Israel, Z.; Bergman, H.; Soreq, H. Small RNA sequencing-microarray analyses in Parkinson leukocytes reveal deep brain stimulation-induced splicing changes that classify brain region transcriptomes. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, R.H.; Nasirian, F.; Nakano, K.; Ward, D.; Pay, M.; Hill, R.; Shults, C.W. Low platelet mitochondrial complex I and complex II/III activity in early untreated Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 1995, 37, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbanti, P.; Fabbrini, G.; Ricci, A.; Cerbo, R.; Bronzetti, E.; Caronti, B.; Calderaro, C.; Felici, L.; Stocchi, F.; Meco, G.; et al. Increased expression of dopamine receptors on lymphocytes in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 1999, 14, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soreq, L.; Guffanti, A.; Salomonis, N.; Simchovitz, A.; Israel, Z.; Bergman, H.; Soreq, H. Long non-coding RNA and alternative splicing modulations in Parkinson’s leukocytes identified by RNA sequencing. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grünblatt, E.; Zehetmayer, S.; Jacob, C.P.; Müller, T.; Jost, W.H.; Riederer, P. Pilot study: Peripheral biomarkers for diagnosing sporadic Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2010, 117, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehadeh, L.A.; Yu, K.; Wang, L.; Guevara, A.; Singer, C.; Vance, J.; Papapetropoulos, S. SRRM2, a potential blood biomarker revealing high alternative splicing in Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molochnikov, L.; Rabey, M.R.; Dobronevsky, E.; Bonuccelli, U.; Ceravolo, R.; Frosini, D.; Grünblatt, E.; Riederer, P.; Jacob, C.; Aharon-Peretz, J.; et al. A molecular signature in blood identifies early Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2012, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Tong, J.; Wang, F. Mining genetic and transcriptomic data using machine learning approaches in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2020, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, N.; La Rocca, M.; Monaco, A.; Bellotti, R.; Tangaro, S. Complex networks reveal early MRI markers of Parkinson’s disease. Med. Image Anal. 2018, 48, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalls, M.A.; McLean, C.Y.; Rick, J.; Eberly, S.; Hutten, S.J.; Gwinn, K.; Sutherland, M.; Martinez, M.; Heutink, P.; Williams, N.M.; et al. Parkinson’s Disease Biomarkers Program and Parkinson’s Progression Marker Initiative investigators. Diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease on the basis of clinical and genetic classification: A population-based modelling study. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, A.; Pantaleo, E.; Amoroso, N.; Bellantuono, L.; Lombardi, A.; Tateo, A.; Tangaro, S.; Bellotti, R. Identifying potential gene biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease through an information entropy based approach. Phys. Biol. 2020, 18, 016003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamir, R.; Klein, C.; Amar, D.; Vollstedt, E.J.; Bonin, M.; Usenovic, M.; Wong, Y.C.; Maver, A.; Poths, S.; Safer, H.; et al. Analysis of blood-based gene expression in idiopathic Parkinson disease. Neurology 2017, 89, 1676–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen-Plotkin, A. Blood transcriptomics for Parkinson disease? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, G.S.; Suresh, S. Parkinson’s disease prediction using gene expression—A projection based learning meta-cognitive neural classifier approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, M.K.; Sharma, P.; Aasly, J.; Toft, M.; Skogar, O.; Sæbø, S.; Lönneborg, A. Found in transcription: Accurate Parkinson’s disease classification in peripheral blood. J. Park. Dis. 2013, 3, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, K.; Chowdhury, S.; Siderowf, A.; Lasch, S.; Coffey, C.S.; Caspell-Garcia, C.; Simuni, T.; Jennings, D.; Tanner, C.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative. The Parkinson’s progression markers initiative (PPMI)—Establishing a PD biomarker cohort. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 1460–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchins, E.; Craig, D.; Violich, I.; Alsop, E.; Casey, B.; Hutten, S.; Reimer, A.; Whitsett, T.G.; Crawford, K.L.; Toga, A.W.; et al. Quality Control Metrics for Whole Blood Transcriptome Analysis in the Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI). medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, S.M.; Duvallet, C.; Alm, E.J. Correcting for batch effects in case-control microbiome studies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, A.; Pantaleo, E.; Amoroso, N.; Lacalamita, A.; Lo Giudice, C.; Fonzino, A.; Fosso, B.; Picardi, E.; Tangaro, S.; Pesole, G.; et al. A primer on machine learning techniques for genomic applications. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 4345–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A Comprehensive Gene Set Enrichment Analysis Web Server 2016 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarious, M.B.; Leonard, H.L.; Vitale, D.; Iwaki, H.; Sargent, L.; Dadu, A.; Violich, I.; Hutchins, E.; Saffo, D.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; et al. Multi-Modality Machine Learning Predicting Parkinson’s Disease. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaki, G.S.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Oxidative stress-induced signaling pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Neuromol. Med. 2014, 16, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, Y. Oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, A.; León-Martinez, R.; Blanco-Lezcano, L.; Pavón-Fuentes, N.; Lorigados-Pedre, L. Transient glutathione depletion in the substantia nigra compacta is associated with neuroinflammation in rats. Neuroscience 2016, 335, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufekci, K.U.; Meuwissen, R.; Genc, S.; Genc, K. Inflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2012, 88, 69–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Delgado, L.; Macías-García, D.; Jesús, S.; Martín-Rodríguez, J.F.; Labrador-Espinosa, M.Á.; Jiménez-Jaraba, M.V.; Adarmes-Gómez, A.; Carrillo, F.; Mir, P. Peripheral Immune Profile and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 2426–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzer, D.; Alcalay, R.N.; Garretti, F.; Cote, L.; Kanter, E.; Agin-Liebes, J.; Liong, C.; McMurtrey, C.; Hildebr, W.H.; Mao, X.; et al. T cells from patients with Parkinson’s disease recognize α-synuclein peptides. Nature 2017, 546, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.S.Y.; Chao, Y.X.; Rötzschke, O.; Tan, E.K. New Insights into Immune-Mediated Mechanisms in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, K.; Hishikawa, N.; Sawada, M.; Nagatsu, T.; Yoshida, M.; Hashizume, Y. Distribution of major histocompatibility complex class II-positive microglia and cytokine profile of Parkinson’s disease brains. Acta Neuropathol. 2003, 106, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malpartida, A.B.; Williamson, M.; Narendra, D.P.; Wade-Martins, R.; Ryan, B.J. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Mitophagy in Parkinson’s Disease: From Mechanism to Therapy. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2021, 46, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebanks, K.; Lewis, P.A.; Bandopadhyay, R. Vesicular Dysfunction and the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease: Clues From Genetic Studies. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, X.; Li, H.; Yan, H.; Zhang, P.; Chang, L.; Li, T. Risk of Parkinson Disease in Diabetes Mellitus: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Population-Based Cohort Studies. Medicine 2016, 95, e3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villumsen, M.; Aznar, S.; Pakkenberg, B.; Jess, T.; Brudek, T. Inflammatory bowel disease increases the risk of Parkinson’s disease: A Danish nationwide cohort study 1977–2014. Gut 2019, 68, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grünblatt, E.; Mandel, S.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Zeligson, S.; Amariglo, N.; Rechavi, G.; Li, J.; Ravid, R.; Roggendorf, W.; Riederer, P.; et al. Gene expression profiling of parkinsonian substantia nigra pars compacta; alterations in ubiquitin-proteasome, heat shock protein, iron and oxidative stress regulated proteins, cell adhesion/cellular matrix and vesicle trafficking genes. J. Neural Transm. 2004, 111, 1543–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Wu, Q.; Sun, S.; Bi, G.; Guo, L. Identification of potential diagnostic biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. FEBS Open Bio. 2019, 9, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherzer, C.R.; Eklund, A.C.; Morse, L.J.; Liao, Z.; Locascio, J.L.; Fefer, D.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Schlossmacher, M.G.; Hauser, M.A.; Vance, J.M.; et al. Molecular markers of early Parkinson’s disease based on gene expression in blood. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calligaris, R.; Banica, M.; Roncaglia, P.; Robotti, E.; Finaurini, S.; Vlachouli, C.; Antonutti, L.; Iorio, F.; Carissimo, A.; Cattaruzza, T.; et al. Blood transcriptomics of drug-naive sporadic Parkinson’s disease patients. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayka, A.; Şehirli, A.Ö. The Role of the SLC Transporters Protein in the Neurodegenerative Disorders. Clin Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2020, 18, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, K.; Chen, J.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, R. The integral nuclear membrane protein nurim plays a role in the suppression of apoptosis. Curr. Mol. Med. 2012, 12, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erekat, N.S. Apoptosis and its Role in Parkinson’s Disease. In Parkinson’s Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects; Stoker, T.B., Greenl, J.C., Eds.; Codon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2018; Chapter 4. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, D.; Nalls, M.A.; Hallgrímsdóttir, I.B.; van der Brug, M.; Cai, F.; International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics Consortium; 23andMe Research Team; Kerchner, G.A.; Ayalon, G.; Bingol, B.; et al. A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies 17 new Parkinson’s disease risk loci. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custodia, A.; Aramburu-Núñez, M.; Correa-Paz, C.; Posado-Fernández, A.; Gómez-Larrauri, A.; Castillo, J.; Gómez-Muñoz, A.; Sobrino, T.; Ouro, A. Ceramide Metabolism and Parkinson’s Disease Therapeutic Targets. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabjerg, M.S.; Mørkholt, A.S.; Lichota, J.; Oklinski, M.K.E.; Andersen, D.C.; Jønsson, K.; Mørk, K.; Skjønnemand, M.N.; Kroese, L.J.; Pritchard, C.E.J.; et al. Dysregulation of metabolic pathways by carnitine palmitoyl-transferase 1 plays a key role in central nervous system disorders: Experimental evidence based on animal models. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paratcha, G.; Ledda, F. The GTPase-activating protein Rap1GAP: A new player to modulate Ret signaling. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pagano, G.; Ferrara, N.; Brooks, D.J.; Pavese, N. Age at onset and Parkinson disease phenotype. Neurology 2016, 86, 1400–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
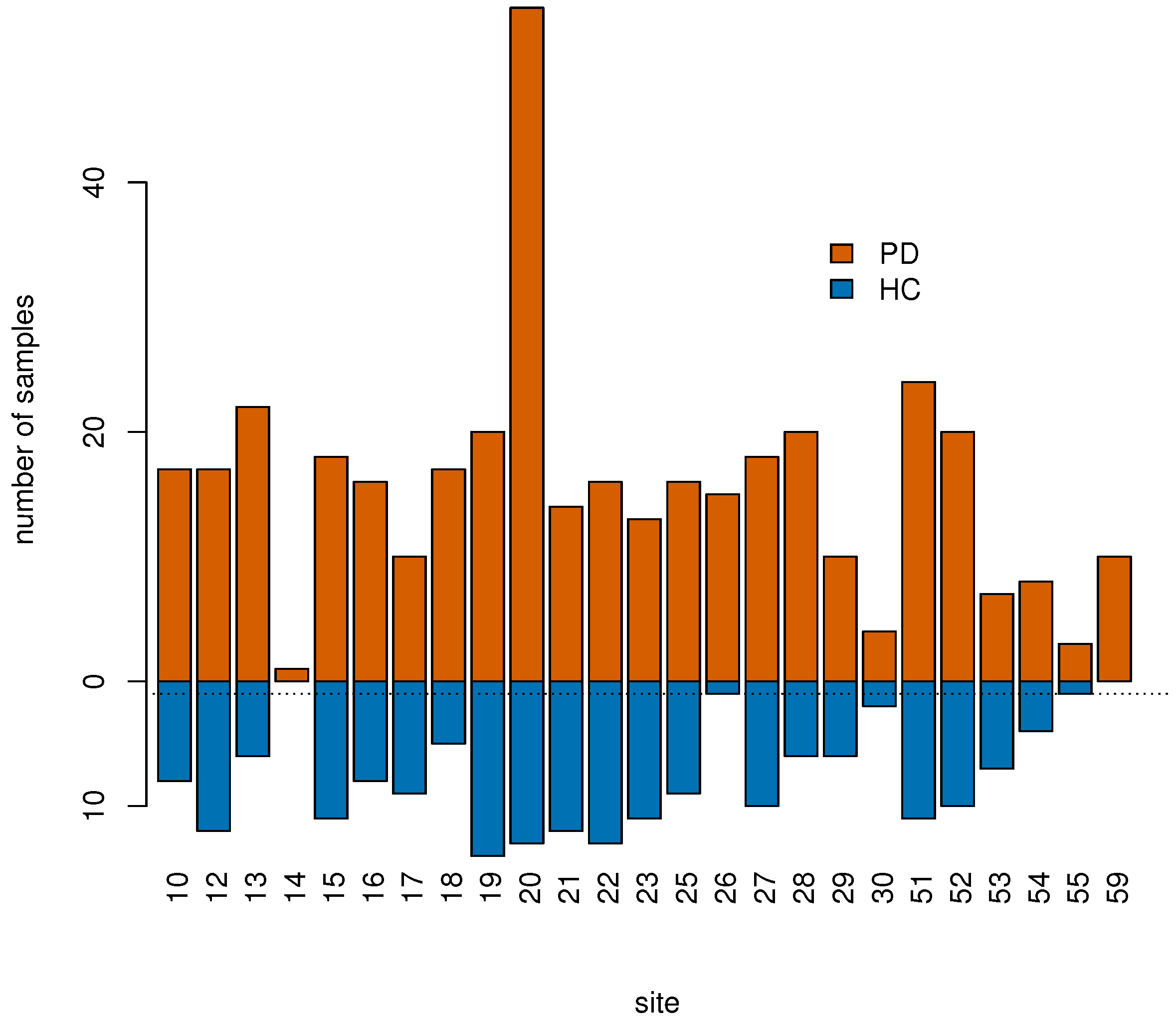
| Variable | PD | HC |
|---|---|---|
| Gender (male %) | 252/390 (64%) | 123/189 (65%) |
| Age at enrollment | 62 ± 10 | 61 ± 11 |
| Disease duration | 2 ± 2 | - |
| RBD | 37% | 20% |
| TD | 70% | 13% |
| Number of sites | 25 | 23 |
| MoCA (CI-adjusted for education) | 33% | 0.5% |
| RIN | 8 ± | 8 ± 1.7 |
| Mean | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|
| AUC | 71.3 | 1.2 |
| Accuracy | 69.3 | 1.2 |
| Sensitivity | 81.7 | 1.6 |
| Specificity | 45.5 | 2.3 |
| Balanced Accuracy | 63.6 | 1.3 |
| F1 | 77.8 | 0.9 |
| e | Symbol | imp | f | e | Symbol | imp | f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ↑ | MYOM1 | 82.1 | 20 | ↑ | SLC25A20 | 62.7 | 20 |
| NRM | 46.4 | 20 | ↓ | PHF7 | 45.9 | 20 | |
| ↑ | ENSG00000277763 * | 39.4 | 20 | ICA1 | 36 | 20 | |
| ↑ | CPT1A | 33.8 | 20 | LINC02422 * | 33.3 | 20 | |
| GSTM1 | 32.4 | 20 | PCDHGA6 | 31.6 | 20 | ||
| AK5 | 31.5 | 20 | ↓ | GCNT2 | 29.9 | 20 | |
| CERS4 | 29.7 | 20 | ↓ | YJU2 | 29.4 | 20 | |
| SURF6 | 27.7 | 20 | ENSG00000281181 * | 26.7 | 20 | ||
| ENSG00000285774 * | 26.7 | 20 | ↑ | ENSG00000272688 * | 26.2 | 20 | |
| SERF1B | 25.8 | 20 | ENSG00000284773 | 25.7 | 20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pantaleo, E.; Monaco, A.; Amoroso, N.; Lombardi, A.; Bellantuono, L.; Urso, D.; Lo Giudice, C.; Picardi, E.; Tafuri, B.; Nigro, S.; et al. A Machine Learning Approach to Parkinson’s Disease Blood Transcriptomics. Genes 2022, 13, 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050727
Pantaleo E, Monaco A, Amoroso N, Lombardi A, Bellantuono L, Urso D, Lo Giudice C, Picardi E, Tafuri B, Nigro S, et al. A Machine Learning Approach to Parkinson’s Disease Blood Transcriptomics. Genes. 2022; 13(5):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050727
Chicago/Turabian StylePantaleo, Ester, Alfonso Monaco, Nicola Amoroso, Angela Lombardi, Loredana Bellantuono, Daniele Urso, Claudio Lo Giudice, Ernesto Picardi, Benedetta Tafuri, Salvatore Nigro, and et al. 2022. "A Machine Learning Approach to Parkinson’s Disease Blood Transcriptomics" Genes 13, no. 5: 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050727
APA StylePantaleo, E., Monaco, A., Amoroso, N., Lombardi, A., Bellantuono, L., Urso, D., Lo Giudice, C., Picardi, E., Tafuri, B., Nigro, S., Pesole, G., Tangaro, S., Logroscino, G., & Bellotti, R. (2022). A Machine Learning Approach to Parkinson’s Disease Blood Transcriptomics. Genes, 13(5), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050727












