Abstract
Intraspecific rearrangements of mitochondrial genomes are rarely reported in reptiles, even in vertebrates. The sunwatcher toad-headed agama, Phryncoephalus helioscopus, can serve as an excellent model for investigating the dynamic mitogenome structure at intraspecific level. To date, seven subspecies of P. helioscopus are well recognized, but little is known about the mitogenomic evolution among different subspecies. In this study, complete mitogenomes of subspecies P. helioscopus varius II and P. helioscopus cameranoi were determined by next-generation sequencing, and another P. helioscopus varius I retrieved from GenBank was compiled for comparative analysis. The nucleotide composition and the codon usage are similar to those previously published from toad-headed agamas. P. helioscopus varius II and P. helioscopus cameranoi have 23 tRNA genes, including standard 22 tRNA genes and one extra tRNA-Phe (tRNA-Phe duplication). Gene order and phylogenetic analyses in the genus Phrynocephalus support prevalent intraspecific gene rearrangement in P. helioscopus and other congener species including P. erythrurus, P. vlangalii, and P. forsythii. Six different mitochondrial gene arrangements are observed in Phrynocephalus. Overall, the occurrence of rearrangements may result from multiple independent structural dynamic events. The split of the two subspecies in P. helioscopus was dated at approximately 2.34 million years ago (Ma). Two types of gene rearrangements are found in the three mitogenomes of P. helioscopus, and this intraspecific rearrangement phenomenon can be explained by the tandem duplication/random loss (TDRL) model. Post duplication, the alternative loss types can occur in 0.23–0.72 Ma, suggesting that the duplication and fixation of these rearrangements can occur quite quickly. These findings highlight the need for more mitogenomes at the population level in order to better understand the potentially rampant intraspecific mitogenomic reorganization in Phrynocephalus.
1. Introduction
It is well known that the structure of the vertebrate mitochondrial genome (mitogenome) is compact and relatively conservative, containing 37 genes (13 protein-coding genes, two ribosomal RNA genes and 22 transfer RNA genes) as well as a control region (CR; also called D-loop) [1,2,3]. The advancement of sequencing technology including next-generation sequencing has facilitated rapid availability of mitogenome of animals from various groups [4,5]. Accordingly, gene rearrangement phenomena have been more and more discovered in various vertebrate lineages [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. Nevertheless, intraspecific gene rearrangements are not commonly found through comparison of all mitochondrial DNA records of the squamate reptiles [15]. Two cases occur in the squamates, one in asexual geckos with multiple origins of duplication [16] and another in an amphisbaenian (worm lizard) with alternative loss types varying among populations [17]. Thus, investigations at intraspecific level may be necessary to understand the evolution of mitochondrial gene rearrangements.
The tandem duplication followed by the random loss (TDRL) is the most frequently invoked model to understand the diversity of gene rearrangements in vertebrate mitogenomes [7]. According to the TDRL model, random deletion of redundant duplicated genes results in novel gene orders [6,7]. The agamid genus Phrynocephalus, known as toad-headed agama or toad-headed lizard, is one of the most speciose reptile genera in arid central Asia. As of 31 July 2021, a total of 23 mitogenomes representing 14 species in the genus Phrynocephalus have been released in GenBank. Several cases of gene rearrangements in the mitogenomes of the genus Phrynocephalus have been reported. Liu et al. [18] summarized five rearrangement types (V, VI, VII, VIII, and IX) of mitogenomes among 12 species in Phrynocephalus. The mitogenome structures of P. przewalskii, P. versicolor, and P. frontalis have been reported to have tRNA genes duplication [19,20,21]. However, as for the mitogenomics of Phrynocephalus, exploration of the potential mechanism of gene rearrangements is still lacking.
The sunwatcher toad-headed agama, P. helioscopus (Pallas, 1771), is one of the most taxonomically complex taxa within the toad-headed agamas [22,23,24]. As one of the most typical and widespread desert lizards in the arid central Asia, P. helioscopus occurs in a variety of habitats from sand dunes and gravel deserts to steppe deserts [23,24,25,26,27,28]. It is now widely recognized that P. helioscopus constitutes a complex assembly of more or less separated populations and subspecies. In combination with mitochondrial DNA and morphological characters, P. helioscopus was classified into seven subspecies [22,23], i.e., P. helioscopus helioscopus, P. helioscopus cameranoi Bedriaga, 1907, P. helioscopus meridionalis Dunayev, Soloveyeva, and Poyarkov, 2012, P. helioscopus saidalievi Sattorov, 1981, P. helioscopus sergeevi Dunayev, Soloveyeva, and Poyarkov, 2012, P. helioscopus turcomanus Dunayev, Soloveyeva, and Poyarkov, 2012, and P. helioscopus varius Eichwald, 1831. Among these subspecies, two are permeated in Northwest China, i.e., P. helioscopus varius from eastern Kazakhstan through Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China to western Mongolia, and P. helioscopus cameranoi from east Kazakhstan to the Chinese part of the Ily River Valley. Thus, P. helioscopus can serve as an excellent model for investigating the dynamic mitogenome structure at intraspecific level.
As such, the starting point of this study is to investigate whether there is intraspecific rearrangement in the mitogenomes of P. helioscopus. If so, we will further explore the underlying arrangement process. We used next-generation sequencing to produce complete mitognomes of two subspecies, i.e., P. helioscopus varius and P. helioscopus cameranoi. Specifically, we aimed to (i) document the conservation or variation between the two subspecies’ mitogenomes in genome size, genomic features, and gene content; (ii) determine the structure of the rearranged region at subspecies level, and infer the steps resulting in observed gene rearrangements; and (iii) estimate the time of intraspecific gene rearrangements by Bayesian phylogenetic dating. The findings will provide clues to understand the multiple independent structural dynamic events in the mitogenomic evolution of the toad-headed agamas.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and DNA Extraction
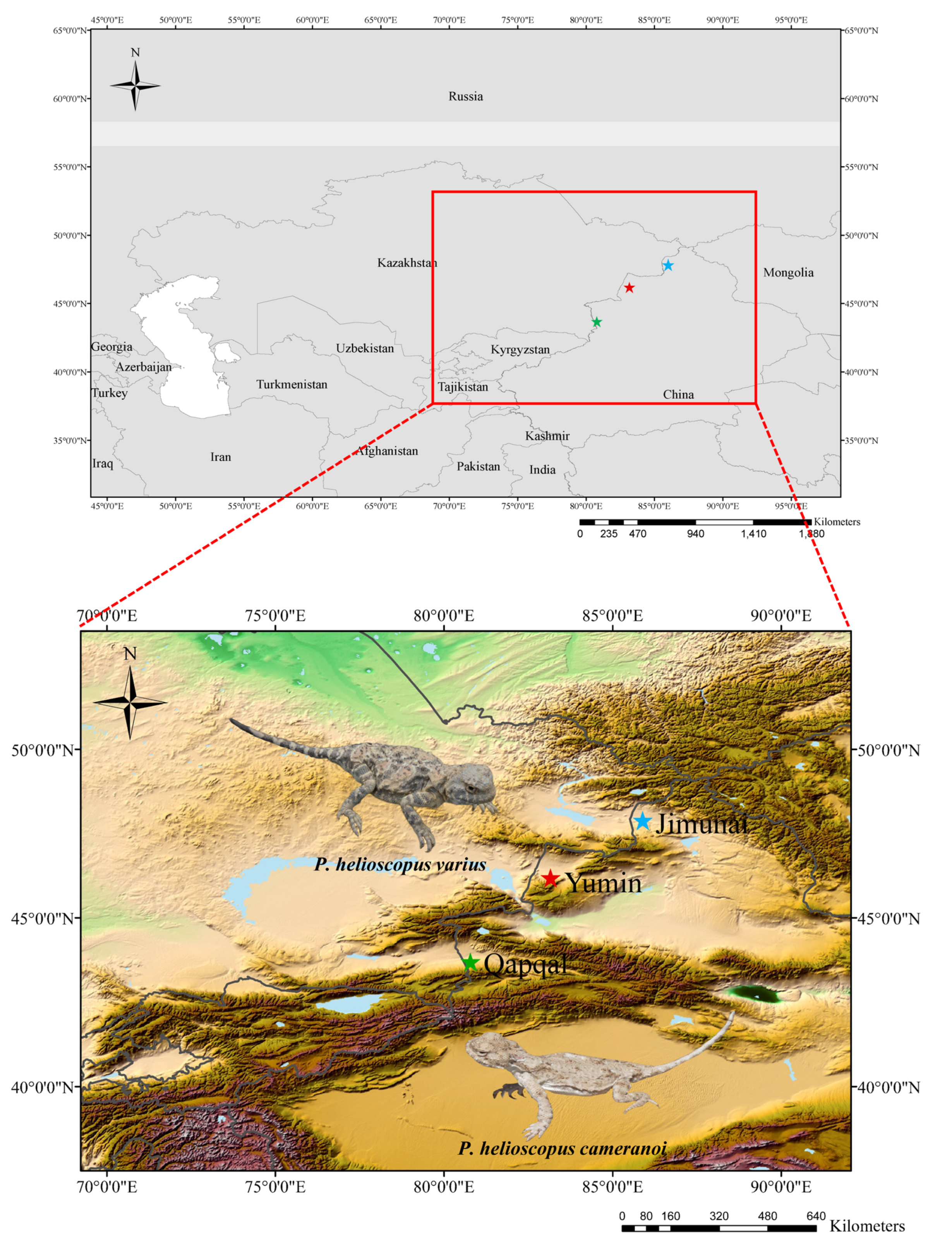
The specimen of P. helioscopus varius was captured from Yumin County (43.69313° N; 80.78233° E), Tacheng Prefecture, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China (voucher no. GXG345, called P. helioscopus varius II in this paper) on 1 July 2017, and the specimen of P. helioscopus cameranoi (voucher no. Guo6379) was captured from Qapqal Xibe Autonomous County (46.18425° N; 83.16024° E), Yili Kazak Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China on 14 July 2019 (Figure 1). Specimens were identified by their morphological characteristics [23]. A liver sample was dissected from the euthanized lizard with an overdose of sodium pentobarbital delivered by intraperitoneal injection. Both the liver samples and voucher specimens were fixed in 95% ethanol and deposited in the Chengdu Institute of Biology (CIB), Chinese Academy of Sciences. All animal procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of CIB (Permit Number: CIB-20121220A).
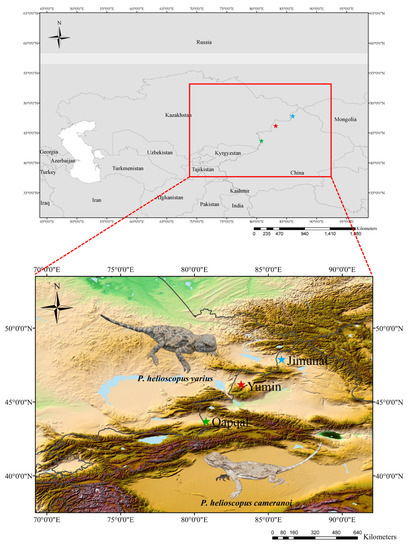
Figure 1.
Sampling sites for the specimens of P. helioscopus in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China.  , P. helioscopus cameranoi, from Qapqal (Ily River Valley; sequenced in this study).
, P. helioscopus cameranoi, from Qapqal (Ily River Valley; sequenced in this study).  , P. helioscopus varius II, from Yumin (Tacheng Prefecture, north of the Tianshan; sequenced in this study).
, P. helioscopus varius II, from Yumin (Tacheng Prefecture, north of the Tianshan; sequenced in this study).  , P. helioscopus varius I, from Jimunai [29] (Altay Prefecture, north of the Tianshan; retrieved from GenBank under accession number KM093858). Photos were taken by Jinlong Liu.
, P. helioscopus varius I, from Jimunai [29] (Altay Prefecture, north of the Tianshan; retrieved from GenBank under accession number KM093858). Photos were taken by Jinlong Liu.
 , P. helioscopus cameranoi, from Qapqal (Ily River Valley; sequenced in this study).
, P. helioscopus cameranoi, from Qapqal (Ily River Valley; sequenced in this study).  , P. helioscopus varius II, from Yumin (Tacheng Prefecture, north of the Tianshan; sequenced in this study).
, P. helioscopus varius II, from Yumin (Tacheng Prefecture, north of the Tianshan; sequenced in this study).  , P. helioscopus varius I, from Jimunai [29] (Altay Prefecture, north of the Tianshan; retrieved from GenBank under accession number KM093858). Photos were taken by Jinlong Liu.
, P. helioscopus varius I, from Jimunai [29] (Altay Prefecture, north of the Tianshan; retrieved from GenBank under accession number KM093858). Photos were taken by Jinlong Liu.
Total genomic DNA was extracted from the liver tissue. The integrity of DNA samples was measured using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and by the HiPure Universal DNA Kit (Magen Biotech, Guangzhou, China) following the manufacturer’s protocol for UV spectroscopy. DNA concentration and purity were measured by NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Wilmington, NC, USA) and Qubit 2.0 Flurometer (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Qualified DNA samples were stored at −20 °C for the next experiment.
2.2. Library Construction and High-Troughput Sequencing
High-quality DNA samples were randomly fragmented with a size of 350 bp for paired-end sequencing, and DNA libraries were constructed according to the standard procedure of Illumina DNA library construction in the Genepioneer Biotechnologies Co. Ltd. (Nanjing, China). The library (inserted size of 350 bp) was constructed using the VAHTS® Universal DNA Library Prep Kit. The quality of the library was control by qPCR method and Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The quality-qualified DNA library was run on an Illumina NovaSeq (Illumina, , San Diego, CA, USA) with paired-end reads of 150 bp in the Genepioneer Biotechnologies Co. Ltd. (Nanjing, China).
2.3. Sequence Assembly, Annotation, and Analysis
The raw data obtained by Illumina NovaSeq sequencing were filtered to get high-quality sequences with fastp v.0.20.0 [30], by trimming adapters and primers, filtering reads with phred quality < Q5 and N base number > 5. The obtained high-quality fragments were aligned with P. helioscopus mtiogenome in GenBank (accession no. KM093858) to remove sequence repeats and inaccurate sequencing, and then assembled by SPAdes v.3.10.1 [31] to obtain the complete circular mitogenome. The preliminary annotations of mitochondrial genome were performed in the MITOS Web Server [32,33]. The protein-coding genes and ribosomal genes were determined by alignment with the reported mitochondrial genomes of the congeners based on the methods of Blastn [34]. Twenty-two transfer RNAs (tRNAs) genes and their potential secondary structures were verified using tRNA scan-SE software [35,36].
Mitochondrial gene structure maps were drawn using the online tool OGDRAW v.1.3.1 [37,38]. In order to conduct comparative analysis of the mitochondrial genomes of two subspecies of P. helioscopus, another published sequence of P. helioscopus (accession no. KM093858, from Jimunai County, Altay Prefecture, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, called P. helioscopus varius I in this paper) was also included. The nucleotide composition, codon distribution, and relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) of PCGs values were analyzed with MEGA v.7.0 [39]. Composition skew values were calculated using the formulae: AT-skew = (A% − T%) / (A% + T%); GC-skew = (G% − C%) / (G% + C%) [40].
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
Phylogenetic analyses were performed based on 27 available mitogenomes, including P. helioscopus cameranoi and P. helioscopus varius II, 23 published sequences of Phrynocephalus, and two outgroups (Table S1). Pseudotrapelus sinaitus and Xenagama taylori were selected as outgroup taxa based on current understanding of the phylogenetic relationship among agamid lizards and the available data in GeneBank [41,42,43,44]. The 13 PCGs were used with a total length of 11,028 bp in our analyses. The 13 PCGs were aligned in MAFFT v.7.313 [45] with the default parameters and were concatenated by the plug-in concatenate sequence option in PhyloSuite v.1.2.2 [46]. The optimal partitioning scheme for nucleotide substitution models for each gene were determined by PartitionFinder v.2.0 [47] implemented in the PhyloSuite under a greedy search algorithm with linked branch lengths based on the Bayesian information criterion (BIC). The best-fit substitution models and partitioning schemes for each gene are listed in Table S2.
Phylogenetic trees were reconstructed using Maximum Likelihood (ML) and Bayesian Inference (BI) methods. The ML analyses were implemented in IQ-TREE v.1.6.8 [48] under the models selected for each identified partition. Branch support analyses were conducted under 5000 ultrafast-bootstrap replicates (UFBoot) [49]. Nodes with UFBoot ≥ 95 were considered to be well-supported [49]. Partitioned Bayesian analyses were performed in MrBayes v.3.2.6 [50] based on the optimal model of each partition. Two independent runs of four Monte Carlo Markov chains (MCMCs) were simultaneously run for two million generations, with sampling conducted every 100 generations. The convergence of the independent runs was indicated by a standard deviation of split frequencies < 0.01, and the effective sample size (ESS) > 200 calculated in Tracer v.1.7.1 [51]. A 50% majority-rule consensus tree and posterior probability (PP) of clades were assessed from the trees after the initial 25% trees of each MCMC run were discarded as burn-in. The phylogenetic trees were viewed and edited with FigTree v.1.4.4 [52] and PowerPoint.
2.5. Molecular Dating Analyses
Given that different species usually had different molecular substitution rates, a relaxed molecular clock method was used within the program BEAST v.1.8.4 [53] to estimate divergence time among Phrynocephalus species, specifically the three P. helioscopus individuals. This was performed using a concatenated dataset of 13 protein-coding genes. Best partition schemes and corresponding models were inferred using PartitionFinder v.2.0 [47] under the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) (Table S2). All mitochondrial data sets were run with linked trees, clock models, and unlinked sites. Due to a lack of reliable fossil evidence, two calibration points described in a previous study were employed in the divergence time estimation [21]. The first calibration point, C1, representing the divergence time of genus Phrynocephalus was set at 9.78 million years ago (Ma; 95% credible interval: 6.49–13.07 Ma). The second calibration point, C2, based on the result of Jin and Brown [21] on the MRCA of viviparous species, was dated to 5.04 Ma (95% credible interval: 2.57–7.51 Ma). Two independent runs of 20 million generations were performed with birth-death speciation tree prior and a sampling frequency of 2000 generations. Convergence for all model parameters was assessed by examining trace plots and histograms in Tracer v.1.7.1 [51] after obtaining an effective sample size (ESS) > 200. Runs were combined using LogCombiner (discarding 25% of the initial runs), and maximum credibility trees with divergence time means and 95% highest posterior densities (HPDs) were produced using TreeAnnotator (both part of the BEAST package).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Genome Organization and Composition
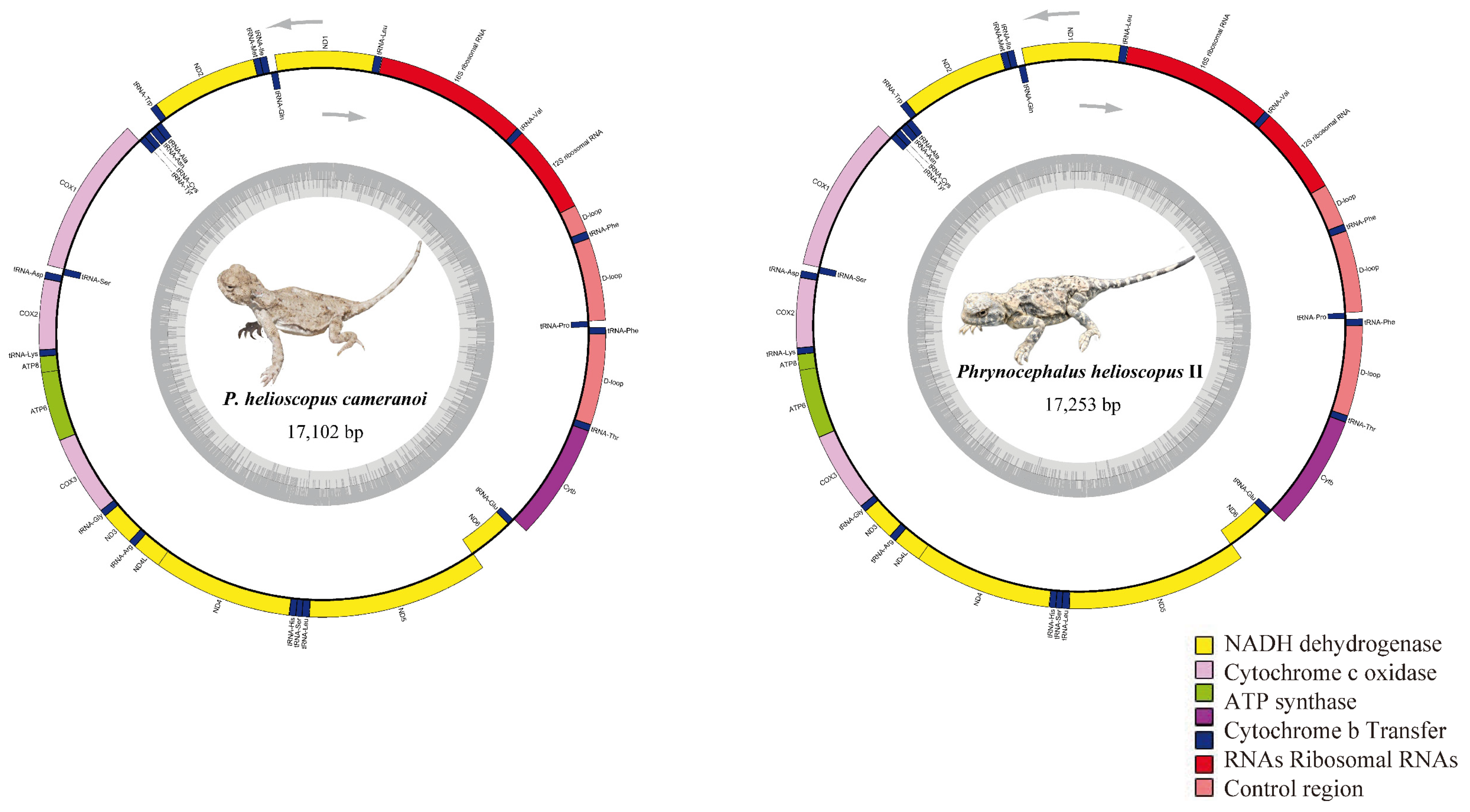
The complete mitogenomes of P. helioscopus varius II and P. helioscopus cameranoi, 17,253 bp and 17,102 bp in size, respectively, were circular DNA molecules (Figure 2; Table S3b,c). Notably, by re-annotating the mitogenome of P. helioscopus varius I (accession number KM093858), we found that the originally annotated tRNA-Pro did belong to part of the CR. Meanwhile, the alignment of KM093858 only resulted in a 16 bp length of tRNA-Pro gene (the position can be determined), so KM093858 was recognized as a nearly complete mitogenome, with a length of 16,249 bp (Table S3a). The three mitogenomes have genetic content typical of most vertebrate mitogenomes [2,54], including 13 protein coding genes (PCGs) and two rRNA genes (12S and 16S). In addition to the typical 22 tRNA genes commonly found in the mitogenomes of both P. helioscopus varius II and P. helioscopus cameranoi, an additional tRNA-Phe was identified in them. However, only 21 tRNA genes were recognized in P. helioscopus varius I—an incomplete tRNA-Pro (only 16 bp) and no tRNA-Phe duplication (Table S3a). Most of the mtDNA genes are encoded on the H-strand, except for ND6 and eight tRNA genes (tRNA-Pro, tRNA-Gln, tRNA-Ala, tRNA-Asn, tRNA-Cys, tRNA-Tyr, tRNA-Ser (UCN), and tRNA-Glu), which are encoded on the L-strand (Table S3). Gene overlaps were observed at eight locations, and the longest overlap involved 13 bp between ND5 and ND6. Overall, nine intergenic/non-coding regions are present, ranging in length from 1 to 16 bp.
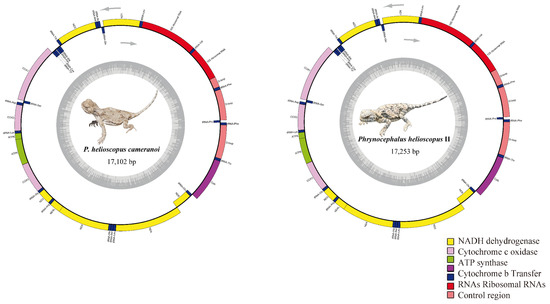
Figure 2.
Mitochondrial genome map of P. helioscopus cameranoi and P. helioscopus varius II. Genes encoded on the heavy or light strand are indicated on the outside or inside of the circular mitogenome map, respectively, showing the direction of transcription. The tRNAs are denoted by color and labeled according to the three-letter amino acid codes. Lizard photos were taken by Jinlong Liu.
Nucleotide composition analysis indicated that the three mitogenomes displayed a significant bias toward adenine (A)/thymine (T), with overall A + T content of 62.3% in P. helioscopus varius I, 62.4% in P. helioscopus varius II, and 62.3% in P. helioscopus cameranoi (Table S4). This base pattern is congruent with most previously reported mitogenomes in Phrynocephalus [55,56,57,58,59]. The PCGs, rRNAs, and tRNAs were also A/T-biased in nucleotide composition. The A + T content composition in regions of P. helioscopus varius I was 62.7% (PCGs), 61.3% (tRNAs), and 59.7% (rRNAs); 62.8% (PCGs), 61.4% (tRNAs), and 59.7% (rRNAs) in P. helioscopus varius II; and 62.9% (PCGs), 61.4% (tRNAs), and 59.3% (rRNAs) in P. helioscopus cameranoi. In addition, the skew metrics of the three mitogenomes showed AT-skew value of each region (except for the CRs) was positive (0.055 to 0.275), which implied that A had more content than T. In contrast, except for tRNA genes region of P. helioscopus varius II and P. helioscopus cameranoi, the CG-skew value of each region was negative (−0.002 to −0.354), indicating a higher content of C than G (see Table S4 for details).
3.2. Protein-Coding Genes (PCGs) and Codon Usage
In the mitogenome of P. helioscopus varius I, P. helioscopus varius II, and P. helioscopus cameranoi, the total length of PCGs was 11,249 bp, 11,252 bp, and 11,246 bp, accounting for 69.2%, 65.2%, and 65.8% of the whole mitogenome, respectively (Table S4). The initiation codon of PCGs of the three mitogenomes are mostly ATN (ATG, ATT, ATA, and ATC), except for ATP8, ND4L, and ND6 genes, which have GTG as the initiation codon (Table S3). Most of the PCGs terminate with TAA or TAG stop codons, except that termination codons of ND2, COX1, and ND6 genes are AGA, AGA, and AGG, respectively. In addition, five mitochondrial genes (COX2, ATP6, COX3, ND3, Cytb) in P. helioscopus are terminated with an incomplete stop codon T--.
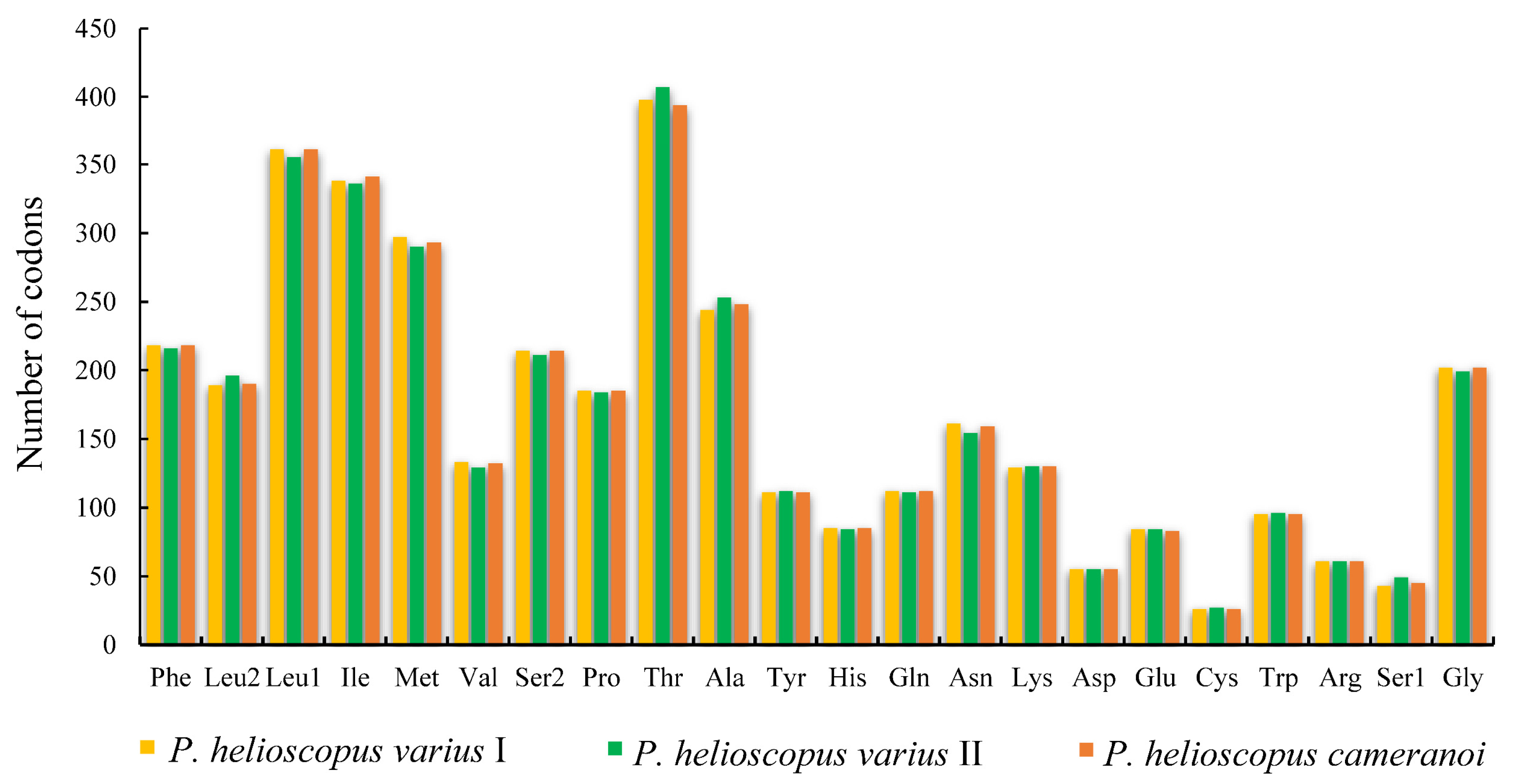
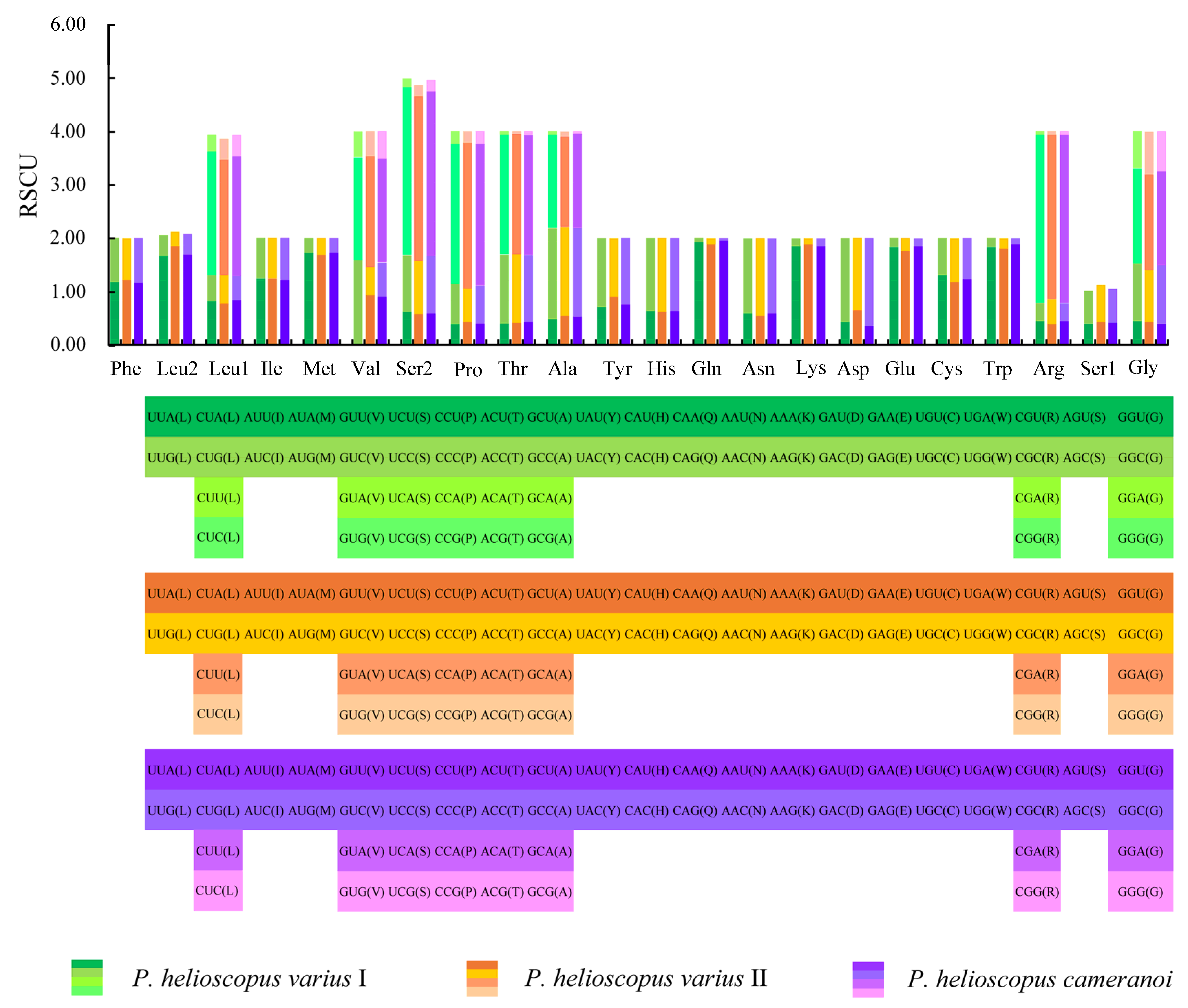
The total number of codons in PCGs is 3748 in P. helioscopus varius I, 3749 in P. helioscopus varius II, and 3747 in P. helioscopus cameranoi. Comparative analysis showed that codon usage patterns of three mitogenomes were highly conserved. The most frequently encoded amino acid by codons are Threonine (Thr), Leucine-CUN (Leu1), and Isoleucine (Ile), while those encoding Cys, Ser-AGY (Ser1), and Asp are rare (Figure 3; Table S5). Meanwhile, the relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) values of three mitogenomes were calculated and are summarized in Figure 4 and Table S5. Comparative analysis found that the relative synonymous codon usages (RSCU) of the three P. helioscopus mitochondrial PCGs were basically similar. Among them, UCA-Ser2, CGA-Arg, and CCA-Pro were the most frequently used codons.
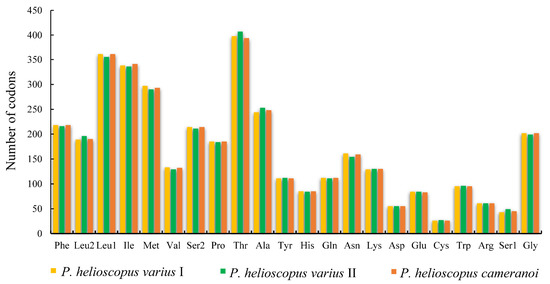
Figure 3.
Amino acid frequency in the mitogenomes of P. helioscopus varius I, P. helioscopus varius II, and P. helioscopus cameranoi. Numbers on the Y-axis refer to the total number of the codons and codon families are provided on the X-axis.
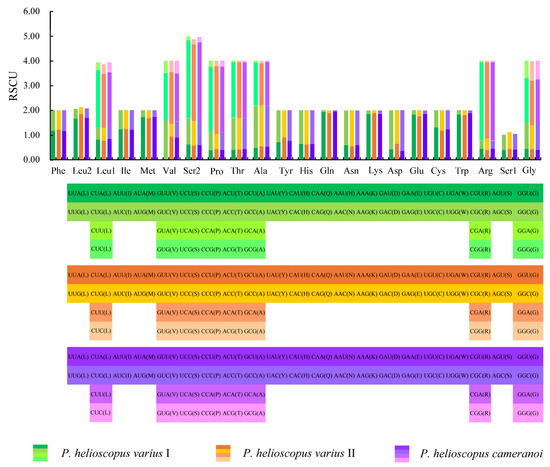
Figure 4.
The relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) in the mitogenomes of P. helioscopus varius I, P. helioscopus varius II, and P. helioscopus cameranoi. The codons are shown on the X-axis and the RSCU values are shown on the Y-axis.
3.3. Transfer RNAs and Ribosomal RNAs
The typical 22 tRNA genes and the additional tRNA-Phe were detected in P. helioscopus varius II and P. helioscopus cameranoi (Figure S1, Table S3). In contrast, only 21 tRNA genes were observed in P. helioscopus varius I, with an incomplete tRNA-Pro and without tRNA-Phe duplication. The total length of tRNAs of the three mitogenomes is 1428 bp in P. helioscopus varius I, 1542 bp in P. helioscopus varius II, 1546 bp in P. helioscopus cameranoi, respectively. Most of the tRNAs are able to fold into a typical cloverleaf secondary structure, but with a few exceptions. Overall, tRNA-Ser1AGY and tRNA-Cys lack a dihydrouridine (DHU) stem-loop structure, tRNA-Thr lacked TΨC loop (Figure S1, Table S3). Specifically, in P. helioscopus varius I, tRNA-Pro fails to form a cloverleaf secondary structure due to its incompleteness.
Both 12S rRNA and 16S rRNA genes are encoded from the H-strand in the three P. helioscopus mitogenomes (Table S3). The two rRNAs of P. helioscopus are located between the control region (CR) and tRNA-Leu (UUR) and separated by tRNA-Val. The length of 12S rRNA is 865 bp for P. helioscopus varius I, 867 bp for P. helioscopus varius II, and 868 bp for P. helioscopus cameranoi. The length of 16S rRNA is 1484 bp for P. helioscopus varius I, 1485 bp for P. helioscopus varius II, and 1484 bp for P. helioscopus cameranoi (Table S3).
3.4. Control Region
The control region is the largest functional non-coding entity in the mitogenome and is heavily biased to A+T nucleotides. The CRs of Phrynocephalus species vary in number and location within the genome due to duplications and gene rearrangements. In the three mitogenomes of P. helioscopus, three CRs are observed in the P. helioscopus varius II and P. helioscopus cameranoi, two in P. helioscopus varius I. The CRI is located between tRNA-Thr and tRNA-Phe in the three P. helioscopus mitogenomes with a length of 892 bp, 893 bp, and 889 bp, respectively. This is similar to the typical position of the CR of vertebrate mitogenomes known to date. The CRII of P. helioscopus varius II and P. helioscopus cameranoi are located between tRNA-Pro and tRNA-Phe with a length of 804 bp and 806 bp, respectively; while the CRII of P. helioscopus varius I is located between tRNA-Phe and 12S rRNA with a length of 334 bp. The CRIII of P. helioscopus varius II and P. helioscopus cameranoi are located between tRNA-Phe and 12S rRNA with a length of 417 bp and 272 bp, respectively. It is notable that the sequences of the CRI of the three mitogenomes are highly similar, and the sequences of CRII and CRI are also very similar (except for P. helioscopus varius I), while the CRII of P. helioscopus varius I is similar to the CRIII of P. helioscopus varius II and P. helioscopus cameranoi. In addition, we observed a conserved motif (CSB1: CTTTTCATGCTCAGTAGACATA) in the CRI of the three mitogenomes and in the CRII of P. helioscopus varius II and P. helioscopus cameranoi.
3.5. Gene Rearrangement
Mitogenomes of vertebrates are generally compact and relatively conserved [2]. With the massive increase of the whole mitogenome data of vertebrates, the gene rearrangement phenomena were commonly encountered in mitogenomes of vertebrates [6,9,60,61,62]. By investigating the mitogenomes of 27 Agamidae species, Liu et al. [18] summarized nine types of mitochondrial gene rearrangement (Type I−IX) and listed the rearrangement patterns of the mitogenomes of 12 Phrynocephalus species. Liu and colleagues provided fundamental information for us to assess the mitochondrial gene rearrangement phenomena in Phrynocephalus.
In this study, the investigation of gene rearrangement events among 25 mitogenomes from 14 Phrynocephalus species revealed that there are six types of gene rearrangements (Figure 5, Table S6). Except for P. frontalis (GenBank accession no. MF039064), the rearrangement types of other 24 other mitogenomes are consistent with those of Phrynocephalus mitogenomes reported by Liu et al. [18]; while P. frontalis represents a novel rearrangement type (Type X). In the arrangement of mitochondrial genes, relative position variation of tRNA genes is more common than PCGs and rRNA genes [54]. Three types of tRNA gene position variation are observed in 25 mitogenomes of Phrynocephalus. The first is the gene rearrangement from IQM gene cluster (tRNAIle-tRNAGln-tRNAMet) to QIM, which supported the previous studies that the rearrangement of QIM gene cluster took place in an ancestral lineage of Agamidae + Chamaeleonidae [6,18,63]. The second is the change of tRNA-Pro location in Phrynocephalus mitogenomes, which exhibits extensive variations (Figure 5), including the translocation of the tRNA-Pro from the 5′ or 3′ end of tRNA-Phe, or the location of the tRNA-Pro between the two CRs. In the three P. helioscopus mitogenomes, tRNA-Pro of P. helioscopus varius II and P. helioscopus cameranoi is translocated to the upstream of tRNA-Phe and tRNA-Pro of P. helioscopus varius I is translocated to the downstream of tRNA-Phe. The third is the duplication of the tRNA-Phe occurring in P. helioscopus (except P. helioscopus varius I), P. przewalskii, P. frontalis, and P. versicolor. Interestingly, there are phenomena of intraspecific gene rearrangements in P. helioscopus, P. erythrurus, P. vlangalii, and P. forsythii. Intraspecific rearrangements of mitogenomes are rarely reported in reptiles, even in vertebrates [15], so it is necessary to further explore the mechanism of intraspecies rearrangements in P. helioscopus.

Figure 5.
Type of the gene arrangements of the Phrynocephalus spp. mitogenomes. Genes encoded by the heavy and light strands are denoted at the top and bottom of each gene rectangle box, respectively. The sizes of the boxes do not reflect the actual gene length. OL, light strand replication origin. CR, control region (D-loop). Assignment of the rearrangement type number corresponds to that in Liu et al. [18].
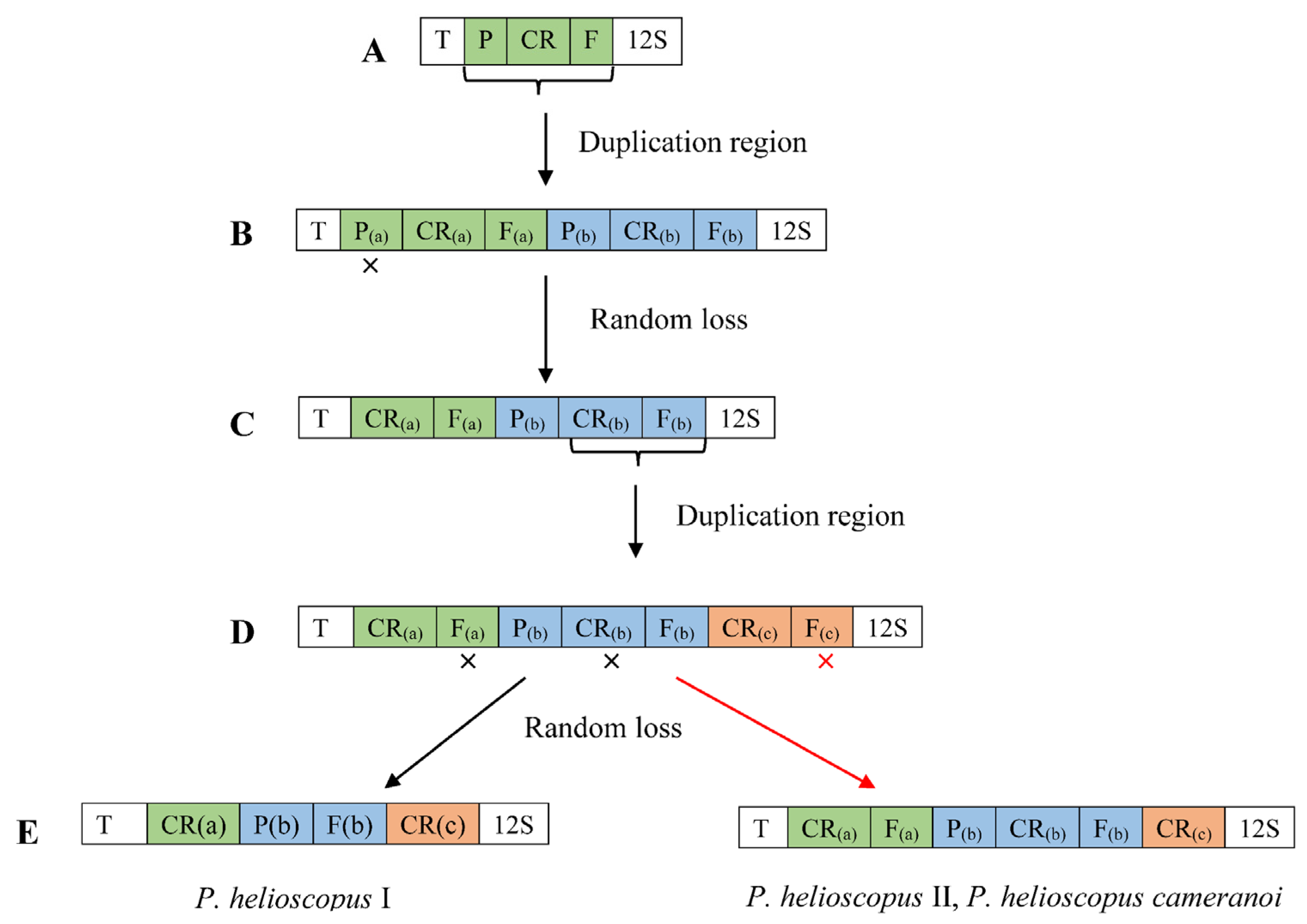
At present, the most widely invoked model is tandem duplication of mitogenome genes followed by the random loss of copy (TDRL). Therefore, we hypothesize the gene rearrangement of mitogenomes of P. helioscopus based on the TDRL model. The steps of the TDRL are as follows (Figure 6). Firstly, the tRNA-Pro—CR—tRNA-Phe gene cluster was tandemly duplicated and generated two sets of the same gene cluster (tRNA-Pro(a)—CR(a)—tRNA-Phe(a)—tRNA-Pro(b)—CR(b)—tRNA-Phe(b)). Secondly, the tRNA-Pro(a) gene was randomly eliminated, and the new order CR(a)—tRNA-Phe(a)—tRNA-Pro(b)—CR(b)—tRNA-Phe(b) was generated. After that, the CR(b)—tRNA-Phe(b) gene cluster duplicated again to form CR(a)—tRNA-Phe(a)—tRNA-Pro(b)—CR(b)—tRNA-Phe(b)—CR(c)—tRNA-Phe(c) of the gene order. Finally, randomly eliminated tRNA-Phe(a) and CR(b) genes were generated the arrangement of P. helioscopus varius I (tRNA-Thr—CR(a)—tRNA-Pro(b)—tRNA-Phe(b)—CR(c)—12S rRNA), random eliminating tRNA-Phe(c) gene, the arrangements of P. helioscopus varius II and P. helioscopus cameranoi were formed (tRNA-Thr—CR(a)—tRNA-Phe(a)—tRNA-Pro(b)—CR(b)—tRNA-Phe(b)—CR(c)—12S rRNA).
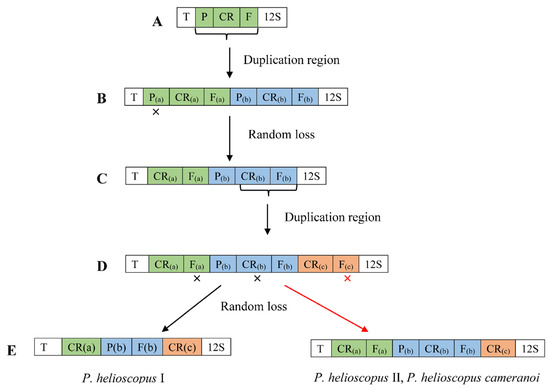
Figure 6.
The hypothetical process of gene rearrangement in the model of tandem duplication/random loss: (A) the ancestral gene order in vertebrate; (B) the tandem duplication of P/CR/F; (C) the random loss of P(a); (D) the tandem duplication of CR(b)/F(b); (E) random loss of F(a) and CR(b), the formation of P. helioscopus varius I arrangement type; random loss of F(c), the formation of P. helioscopus varius II and P. helioscopus cameranoi arrangement type. “x” indicates the random loss of the genes; T, P, F, 12S and CR stand for Threonine, Proline, Phenylalanine, 12S rRNA, control region, respectively.
3.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
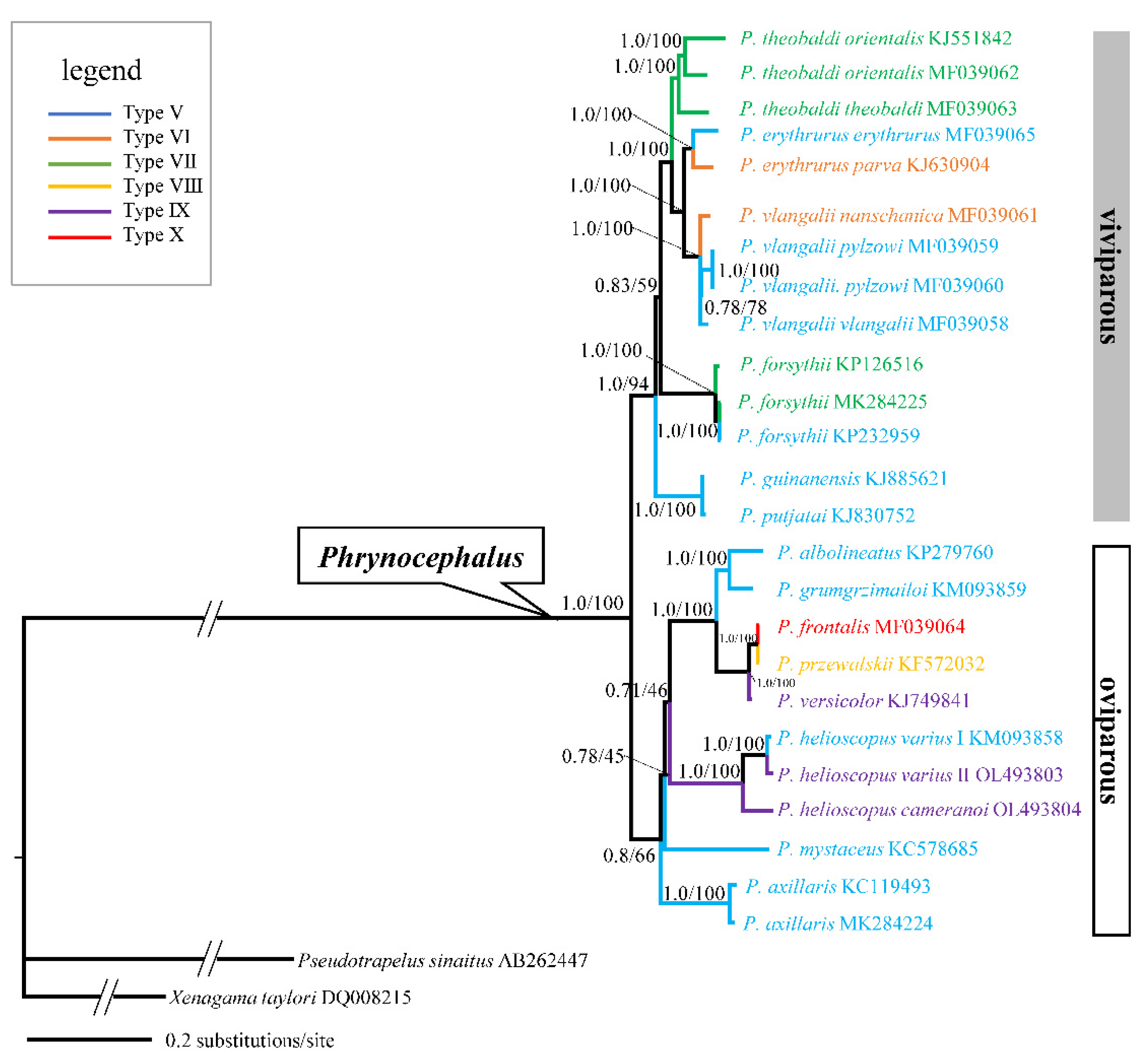
To further investigate the phylogenetic relationships of P. helioscopus, we constructed ML and BI trees based on the complete mitogenome of P. helioscopus varius II and P. helioscopus cameranoi along with 25 other Agamidae mitogenomes retrieved from GenBank. Both BI and ML approaches provided identical and well-supported tree topologies. Thus, only the BI tree is presented, which includes PP as well as UFBoot from ML (Figure 7). The phylogenetic tree strongly supports the monophyly of the viviparous group, which is consistent with previous studies [41,64,65,66,67]. The three individuals of P. helioscopus form a monophyletic group with strong support (PP = 1.0; UFBoot = 100), with the two individuals of P. helioscopus varius clustering together with strong support (PP = 1.0; UFBoot = 100). There is a relatively considerable p-distance between P. helioscopu varius and P. helioscopu cameranoi (7.1% and 6.9%). In contrast, P. helioscopus varius I and II only show a shallow divergence with p-distance of 1.5%. These results, in support of Solovyeya et al. [22], indicated that there is a deep genetic differentiation between P. helioscopus cameranoi distributed in the Ily River Valley and P. helioscopus varius distributed in the northern Junggar Basin.
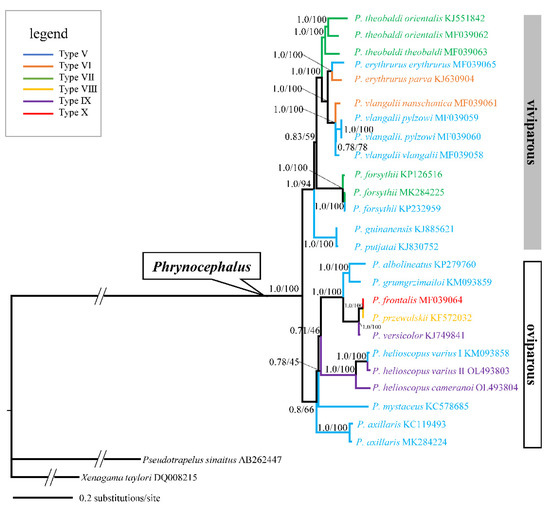
Figure 7.
A majority-rule consensus tree inferred from Bayesian inference using MrBayes with the best models for each partition, based on the PCGs of 25 mitogenomes of Phrynocephalus and two outgroups. Node numbers show Bayesian posterior probabilities and ML ultrafast bootstrap values (UFBoot), respectively. Branch lengths represent means of the posterior distribution. GenBank accession numbers are given with species names, genus/group assignments are listed. Types V to X follow the types of mitochondrial gene arrangement patterns as designated in Liu et al. [18].
A total of six types of mitochondrial gene rearrangements are observed in Phrynocephalus. As shown in Figure 7, multiple intraspecific gene rearrangements exist in P. helioscopus and other congeners including P. erythrurus, P. vlangalii, and P. forsythii. Overall, the occurrence of rearrangements may result from multiple independent tandem duplications and random loss events. However, the presence of extra tRNA gene is a rare event in the genus Phrynocephalus, even in reptiles. Phylogenetic analysis showed that species with tRNA duplication (P. versicolor, P. przewalskii, P. helioscopus varius II, and P. helioscopus cameranoi) are closely or far related oviparous species. Meanwhile, the existence of two types of gene rearrangements (Type V, IX) in P. helioscopus suggests that the duplication of tRNA may result from multiple independent structural dynamic events.
3.7. Divergence Time Estimation
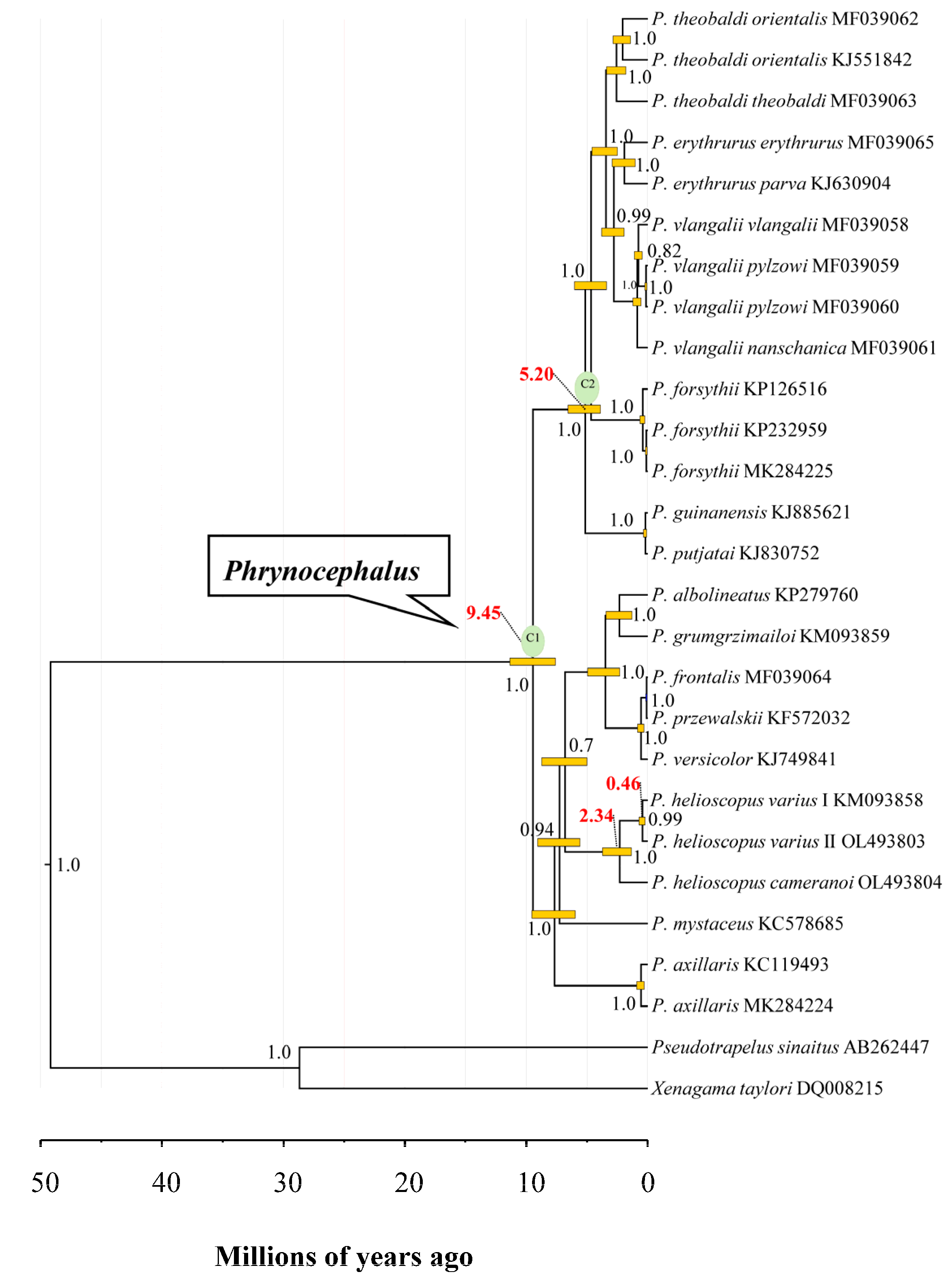
The most recent common ancestor of analyzed Phrynocephalus species was dated at approximately 9.45 Ma (95% HPD: 7.61–11.37 Ma) (Figure 8), which is consistent with previous studies [41,65,66]. The estimated splitting time between P. helioscopus varius I and P. helioscopus varius II was dated to approximately 0.46 Ma (95% HPD: 0.23–0.72 Ma), and P. helioscopus cameranoi diverged from P. helioscopus varius at approximately 2.34 Ma (95% HPD: 1.35–3.73 Ma). This implied that the differentiation of these two subspecies may be related to the rapid uplift event of the northern Tian Shan since 7–2.58 Ma [68,69]. The initiation of mitogenomic rearrangements in P. helioscopus possibly dates to about 2.34 Ma and divergence between the two types (Type V and IX) ranges from 0.23 to 0.72 Ma, suggesting that the duplication and fixation of these rearrangements can occur quite quickly. Combing interspecific rearrangement data, we may infer that post duplication, the alternative loss types could occur in 0.1–2 Ma.
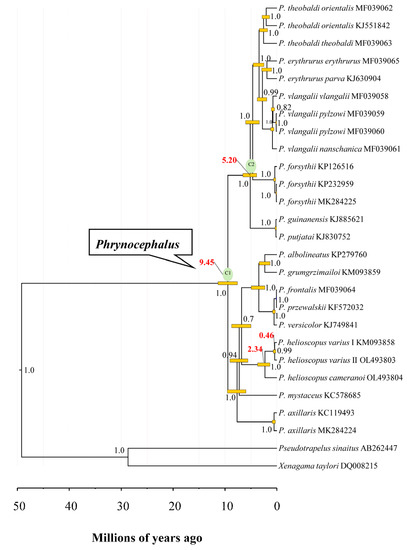
Figure 8.
Timetree of Phrynocephalus spp. and two outgroup taxa estimated using BEAST based on 13 concatenated PCGs. Numbers on nodes (in black) are posterior probability values, while those in red highlight the mean divergence times in the P. helioscopus and Phrynocephalus. The yellow boxes indicate the 95% HPD of the node age in Phrynocephalus.
4. Conclusions
In this study, by comparing the characteristics of mitogenomes of two subspecies P. helioscopus cameranoi and P. helioscopus varius, we observed the duplication of tRNA-Phe and the phenomenon of intraspecific rearrangements. We further speculate the rearrangement processes based on the TDRL model. Gene order and phylogenetic analyses support prevalent intraspecific gene rearrangement in P. helioscopus and other congener species including P. erythrurus, P. vlangalii, and P. forsythii. The split of the two subspecies was dated at approximately 2.34 Ma; this may be triggered by the rapid uplift event of the northern Tian Shan since 7–2.58 Ma. However, post duplication, the alternative loss types can occur in 0.72–0.23 Ma, suggesting that the duplication and fixation of these rearrangements can occur quite quickly. In addition, six types of mitochondrial gene rearrangements are observed in Phrynocephalus. Overall, the occurrence of rearrangements may result from multiple independent structural dynamic events. Our observation will provide clues to the investigations of intraspecific mitogenomic reorganization in Phrynocephalus. Further study is necessary to shed light on the evolutionary dynamics of the rearrangements in Phryncephalus by using intraspecific and population level investigations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/genes13020203/s1, Figure S1: Putative secondary structures of the tRNAs identified in the mitogenomes of P. helioscopus, (a), P. helioscopus varius I; (b), P. helioscopus varius II; (c), P. helioscopus cameranoi. Table S1: Phrynocephalus and two outgroup species analyzed in this study with their GenBank accession numbers. Table S2: Data partitions, their estimated models of sequence evolution, and total number of characters of each partition used in phylogenetic analysis and molecular dating. Table S3: Characteristics of the three mitochondrial genomes of P. helioscopus. Table S4: Comparison of the composition and skew values of three mitogenomes for P. helioscopus. Table S5: Comparison of the codon usage in mitochondrial protein-coding genes for P. helioscopus varius I, P. helioscopus varius II and P. helioscopus cameranoi. Table S6: Twenty-five Phrynocephalus mitogenomes analyzed in gene rearrangement with their GenBank accession numbers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.G.; methodology, N.W., J.L. and S.W.; software, N.W.; validation, J.L., S.W. and X.G.; formal analysis, N.W., J.L. and S.W.; investigation, N.W., J.L. and X.G.; resources, X.G.; data curation, J.L. and X.G.; writing—original draft preparation, N.W.; writing—review and editing, N.W., J.L., S.W. and X.G.; visualization, X.G.; supervision, X.G.; project administration, X.G.; funding acquisition, J.L. and X.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant no. XDA20050201), the Third Xinjiang Scientific Expedition Program (Grant No. 2021xjkk0600), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 32070433, 32000288).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Illumina raw reads are deposited at NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under accession no. SRR16925449 for P. helioscopus varius II in the BioProject PRJNA779875 and SRR16927567 for P. helioscopus cameranoi in the BioProject PRJNA779912. The mitochondrial genomes are deposited at GenBank with accession no. OL493803 for P. helioscopus varius II and OL493804 for P. helioscopus cameranoi.
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to Dali Chen, Qi Song, Minli Chen, Tianhe Zhou, and Xiong Gong who participated in the fieldwork. We would like to thank two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments on an earlier draft of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Avise, J.C.; Ellis, D. Mitochondrial DNA and the evolutionary genetics of higher animals. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 1986, 312, 325–342. [Google Scholar]
- Boore, J.L. Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saccone, C.; Giorgi, C.D.; Gissi, C.; Pesole, G.; Reyes, A. Evolutionary genomics in Metazoa: The mitochondrial DNA as a model system. Gene 1999, 238, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, C.; Bachmann, L.; Chevreux, B. Reconstructing mitochondrial genomes directly from genomic next-generation sequencing reads—A baiting and iterative mapping approach. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, D.R. The past, present and future of mitochondrial genomics: Have we sequenced enough mtDNAs? Brief Funct. Genomics 2016, 15, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macey, J.R.; Larson, A.; Ananjeva, N.B.; Fang, Z.; Papenfuss, T.J. Two novel gene orders and the role of light-strand replication in rearrangement of the vertebrate mitochondrial genome. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1997, 14, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boore, J.L. The duplication/random loss model for gene rearrangement exemplified by mitochondrial genomes of deuterostome animals. In Comparative Genomics; Sankoff, D., Nadeau, J., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, S.L. Mitochondrial genome organization and vertebrate phylogenetics. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2000, 23, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavrov, D.V.; Boore, J.L.; Brown, W.M. Complete mtDNA sequences of two millipedes suggest a new model for mitochondrial gene rearrangements: Duplication and nonrandom loss. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mauro, D.S.; Gower, D.J.; Zardoya, R.; Wilkinson, M. A hotspot of gene order rearrangement by tandem duplication and random loss in the vertebrate mitochondrial genome. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhao, S. New progress in snake mitochondrial gene rearrangement. Mitochondrial DNA 2009, 20, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, D.A.; Gower, D.J. Snake mitochondrial genomes: Phylogenetic relationships and implications of extended taxon sampling for interpretations of mitogenomic evolution. BMC Genomics 2010, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qian, L.; Wang, H.; Yan, J.; Pan, T.; Jiang, S.; Rao, D.; Zhang, B. Multiple independent structural dynamic events in the evolution of snake mitochondrial genomes. BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.L.; Liu, J.L.; Li, J.; Wu, N.; Guo, X.G. Complete mitochondrial genome of the steppe ribbon racer (Psammophis lineolatus): The first representative from the snake family Psammophiidae and its phylogenetic implications. Asian Herpetol. Res. 2021, 12, 295–307. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Murphy, R.W.; Zeng, X. Intraspecific rearrangement of mitochondrial genome suggests the prevalence of the tandem duplication-random loss (TDLR) mechanism in Quasipaa boulengeri. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujita, M.K.; Boore, J.L.; Moritz, C. Multiple origins and rapid evolution of duplicated mitochondrial genes in parthenogenetic geckos (Heteronotia binoei; Squamata, Gekkonidae). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 2775–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macey, J.R.; Papenfuss, T.J.; Kuehl, J.V.; Fourcade, H.M.; Boore, J.L. Phylogenetic relationships among amphisbaenian reptiles based on complete mitochondrial genomic sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2004, 33, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Yu, J.; Zhou, M.; Yang, J. Complete mitochondrial genome of Japalura flaviceps: Deep insights into the phylogeny and gene rearrangements of Agamidae species. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Song, S.; Chen, T.; Zhang, C.; Chang, C. Complete mitochondrial genome of the desert toad-headed agama, Phrynocephalus przewalskii (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae), a novel gene organization in vertebrate mtDNA. Mitochondrial DNA 2013, 26, 696–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, D.; Chang, C. The complete mitochondrial genome of the color changeable toad-headed agama, Phrynocephalus versicolor (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae). Mitochondrial DNA 2014, 27, 1121–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Brown, R. Partition number, rate priors and unreliable divergence times in Bayesian phylogenetic dating. Cladistics 2017, 34, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solovyeva, E.N.; Poyarkov, N.A.; Dunaev, E.A.; Duysebayevac, T.N.; Bannikovaa, A.A. Molecular differentiation and taxonomy of the sunwatcher toad-headed agama species complex Phrynocephalus superspecies helioscopus (Pallas 1771) (Reptilia: Agamidae). Russ. J. Genet. 2011, 47, 842–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyeva, E.N.; Dunayev, E.A.; Poyarkov, N.A. Interspecific taxonomy of sunwatcher toadhead agama species complex (Phrynocephalus helioscopus, Squamata). Zoologicheskiy Zhurnal 2012, 91, 1377–1396, (In Russian with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Uetz, P.; Freed, P.; Aguilar, R.; Hošek, J. The Reptile Database. Available online: http://www.reptile-database.org (accessed on 19 November 2021).
- Zhao, E.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, K. Fauna Sinica, Reptilia, Vol 2: Squamata, Lacertilia; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1999. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Szczerbak, N.N. Guide to the Reptiles of the Eastern Palearctic; Krieger Publishing Company: Malabar, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ananjeva, N.B.; Orlov, N.L.; Khalikov, R.G.; Darevsky, I.S.; Ryabov, S.A.; Barabanov, A.V. The Reptiles of Northern Eurasia: Taxonomic Diversity, Distribution, Conservation Status; Pensoft Publishers: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sindaco, R.; Jeremčnko, V.K. The Reptiles of the Western Palearctic. 1. Annotated Checklist and Distributional Atlas of the Turtles, Crocodiles, Amphisbaenians and Lizards of Europe, North Africa, Middle East and Central Asia; Edizioni Belvedere: Latina, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Guo, J.; Zhou, X.; Chang, C.; Zhang, S. The complete mitochondrial genome of Phrynocephalus helioscopus (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2014, 27, 1846–1847. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one fastq preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MITOS Web Server. Available online: http://mitos.bioinf.uni-leipzig.de/index.py (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- Web BLAST. Available online: https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- tRNAscan-SE Search Server. Available online: http://lowelab.ucsc.edu/tRNAscan-SE/ (accessed on 21 September 2021).
- Lowe, T.M.; Chan, P.P. tRNAscan-SE On-line: Integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W54–W57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OGDRAW. Available online: https://chlorobox.mpimp-golm.mpg.de/OGDraw.html (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3.1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perna, N.T.; Kocher, T.D. Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 41, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyeva, E.N.; Lebedev, V.S.; Dunayev, E.A.; Nazarov, R.A.; Bannikova, A.A.; Che, J.; Murphy, R.W.; Poyarkov, N.A. Cenozoic aridization in Central Eurasia shaped diversification of toad-headed agamas (Phrynocephalus; Agamidae, Reptilia). PeerJ 2018, 6, e4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macey, J.R.; Schulte, J.A.; Fong, J.J.; Das, I.; Papenfuss, T.J. The complete mitochondrial genome of an agamid lizard from the Afro-Asian subfamily Agaminae and the phylogenetic position of Bufoniceps and Xenagama. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 39, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyron, R.; Burbrink, F.T.; Wiens, J.J. A phylogeny and revised classification of Squamata, including 4161 species of lizards and snakes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, L.L.; Peng, L.F.; Gong, Y.A.; Huang, L.S.; Lu, S.Q. The complete mitochondrial genomes of Laudakia papenfussi (Iguania; Agamidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2019, 4, 2708–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kazutaka, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Li, W.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; Haeseler, A.V. Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Dong, X.; Guy, B.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarisation in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- FigTree. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolstenholme, D.R. Animal mitochondrial DNA: Structure and evolution. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1992, 141, 173–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Chen, W.; Jin, Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of Phrynocephalus guinanensis (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2014, 27, 1103–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.; Jin, Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of an agama, Phrynocephalus putjatia (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2014, 27, 1028–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, P.; Jin, Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of the toad-headed lizard subspecies, Phrynocephalus theobaldi orientalis (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2014, 27, 559–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Guo, X. Next-generation sequencing yields a nearly complete mitochondrial genome of the Yarkand toad-headed agama (Phrynocephalus axillaris) from the Turpan Depression. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2019, 4, 1198–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liao, P.; Tong, H.; Jin, Y. The complete mitochondrial genome of the subspecies, Phrynocephalus erythrurus parva (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae), a toad-headed lizard dwell at highest elevations of any reptile in the world. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2014, 27, 703–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, S.A.; Kumazawa, Y. The mitochondrial genome of the lizard Calotes versicolor and a novel gene inversion in south Asian draconine agamids. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, M.; Li, B.; Ouyang, B. Three new Ranidae mitogenomes and the evolution of mitochondrial gene rearrangements among Ranidae species. Asian Herpetol. Res. 2018, 9, 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Pääbo, S.; Thomas, W.K.; Whitfield, K.M.; Kumazawa, Y.; Wilson, A.C. Rearrangements of mitochondrial transfer RNA genes in marsupials. J. Mol. Evol. 1991, 33, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okajima, Y.; Kumazawa, Y. Mitochondrial genomes of acrodont lizards: Timing of gene rearrangements and phylogenetic and biogeographic implications. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Rus Hoelzel, A.; Papenfuss, T.J.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, Y. A phylogeny of Chinese species in the genus Phrynocephalus (Agamidae) inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 27, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, Y. Partitioned Bayesian analyses, dispersal-vicariance analysis, and the biogeography of Chinese toad-headed lizards (Agamidae: Phrynocephalus): A re-evaluation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 45, 643–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Brown, R. Species history and divergence times of viviparous and oviparous Chinese toad-headed sand lizards (Phrynocephalus) on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 68, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Li, J.; Guo, X. Next-generation sequencing yields a nearly complete mitochondrial genome of the Forsyth’s toad-headed agama, Phrynocephalus forsythii (Reptilia, Squamata, Agamidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2019, 4, 817–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Zhu, R.; Bowler, J. Timing of the Tianshan Mountains uplift constrained by magnetostratigraphic analysis of molasse deposits. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 2004, 219, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Lv, H.; Lv, Y.; Xiong, J. Signatures of tectonic limatic interaction during the Late Cenozoic orogenesis along the northern Chinese Tian Shan. Basin Res. 2021, 33, 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).