TWIST1 Plays Role in Expression of Stemness State Markers in ESCC
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. In Silico Sequence Analysis
2.2. Cell Lines and Culture Condition
2.3. Retroviral Production and Enforced TWIST1 Overexpression
2.4. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, Comparative Real-Time PCR, and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Analysis of Cancer Stem Cell Self-Renewal Genes Promoter
3.2. Upregulation of TWIST1 in ESCC Cell Line KYSE-30
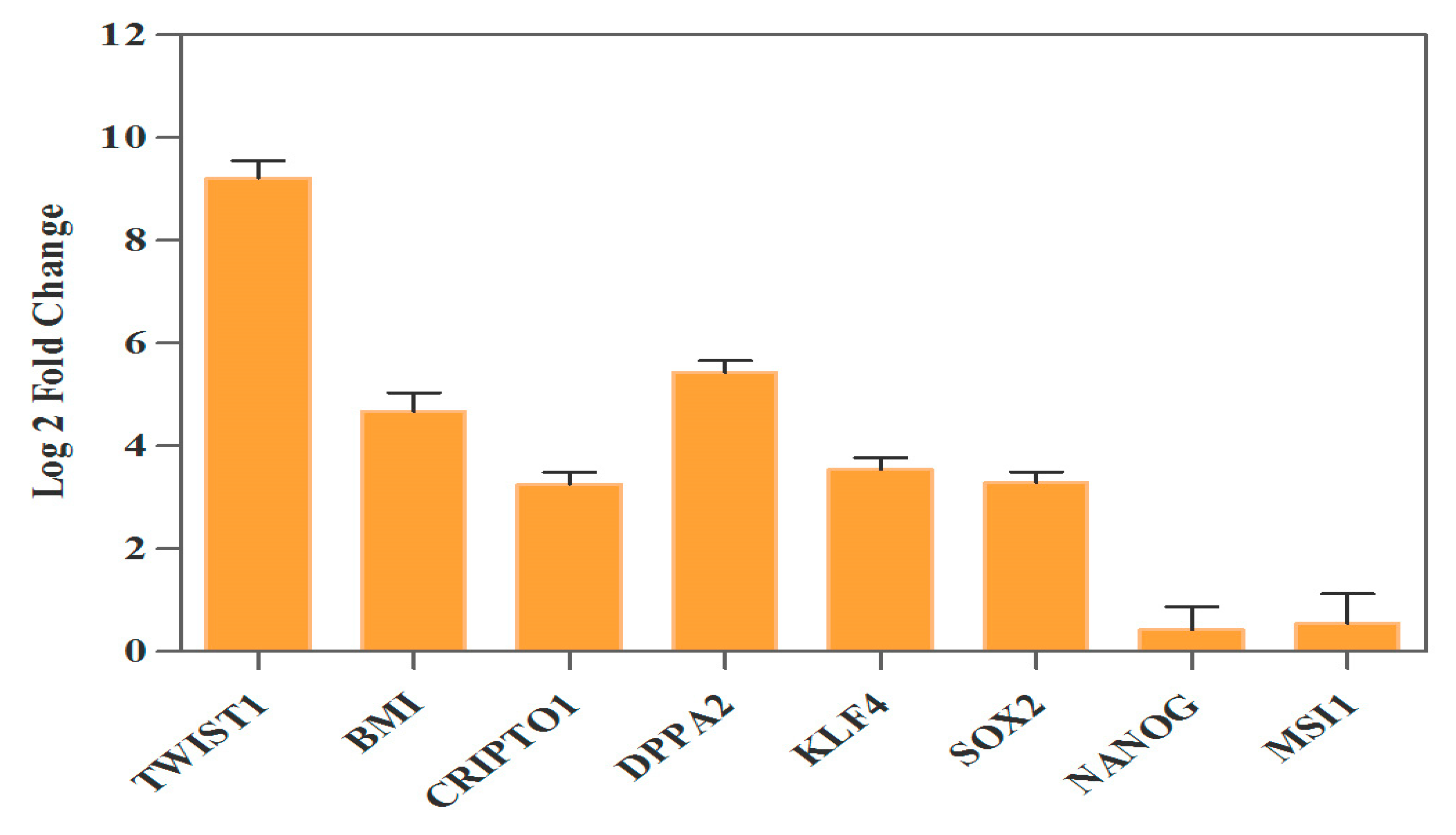
3.3. Ectopic Expression of TWIST1 Increased Expression of Cancer Stem Cell Self-Renewal Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, Y.-L.; Wang, S.-S.; Jiang, J.; Liang, X.-H. Links between cancer stem cells and epithelial– mesenchymal transition. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 2973–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valastyan, S.; Weinberg, R.A. Tumor Metastasis: Molecular Insights and Evolving Paradigms. Cell 2011, 147, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savagner, P. The epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) phenomenon. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, vii89–vii92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, A.; Cano, A. Tumorigenesis: Twist1 links EMT to self-renewal. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 924–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Settleman, J. EMT, cancer stem cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4741–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.-M.; Hu, S.-Q.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.-L.; Feng, J.-H.; Chen, Z.-Q.; Wen, K.-M. OCT4B1 Promoted EMT and Regulated the Self-Renewal of CSCs in CRC: Effects Associated with the Balance of miR-8064/PLK1. Mol. Ther.-Oncolytics 2019, 15, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidenfeld, K.; Barkan, D. EMT and Stemness in Tumor Dormancy and Outgrowth: Are They Intertwined Processes? Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Li, B.; Liu, F.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, D. The epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) and cancer stem cells: Implication for treatment resistance in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abell, A.N.; Johnson, G.L. Implications of Mesenchymal Cells in Cancer Stem Cell Populations: Relevance to EMT. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2014, 2, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phi, L.T.H.; Sari, I.N.; Yang, Y.-G.; Lee, S.-H.; Jun, N.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Kwon, H.Y. Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) in Drug Resistance and their Therapeutic Implications in Cancer Treatment. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 5416923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khales, S.A.; Abbaszadegan, M.R.; Majd, A.; Forghanifard, M.M. Linkage between EMT and stemness state through molecular association between TWIST1 and NY-ESO1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biochimie 2019, 163, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forghanifard, M.M.; Rad, A.; Farshchian, M.; Khaleghizadeh, M.; Gholamin, M.; Moghbeli, M.; Abbaszadegan, M.R. TWIST1 upregulates the MAGEA4 oncogene. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 56, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forghanifard, M.M.; Khales, S.A.; Farshchian, M.; Rad, A.; Homayouni-Tabrizi, M.; Abbaszadegan, M.R. Negative Regulatory Role of TWIST1 on SNAIL Gene Expression. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2016, 23, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudian, R.A.; Bahadori, B.; Rad, A.; Abbaszadegan, M.R.; Forghanifard, M.M. MEIS1 knockdown may promote differentiation of esophageal squamous carcinoma cell line KYSE-30. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e00746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izadpanah, M.H.; Abbaszadegan, M.R.; Fahim, Y.; Forghanifard, M.M. Ectopic expression of TWIST1 upregulates the stemness marker OCT4 in the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell line KYSE30. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2017, 22, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayachandran, A.; Dhungel, B.; Steel, J.C. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal plasticity of cancer stem cells: Therapeutic targets in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Rahman, M.A.; Chen, Z.G.; Shin, D.M. Multiple biological functions of Twist1 in various cancers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 20380–20393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Du, P.; Ge, Z.; Jin, Y.; Ding, D.; Liu, X.; Zou, Q. TWIST1 and BMI1 in Cancer Metastasis and Chemoresistance. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.-Y.; Liu, X.-Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.-N.; Yang, B.-X.; Ren, Q.; Liang, H.-Y.; Ma, X.-T. Twist-1, A Novel Regulator of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Myeloid Lineage Development. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 3173–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudian, R.A.; Abbaszadegan, M.R.; Forghanifard, M.M.; Moghbeli, M.; Moghbeli, F.; Chamani, J.; Gholamin, M. Biological and Clinicopathological Significance of Cripto-1 Expression in the Progression of Human ESCC. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 5, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghbeli, M.; Forghanifard, M.M.; Aarabi, A.; Mansourian, A.; Abbaszadegan, M.R. Clinicopathological Sex- Related Relevance of Musashi1 mRNA Expression in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2013, 20, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forghanifard, M.M.; Khales, S.A.; Javdani-Mallak, A.; Rad, A.; Farshchian, M.; Abbaszadegan, M.R. Stemness state regulators SALL4 and SOX2 are involved in progression and invasiveness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forghanifard, M.M.; Moaven, O.; Farshchian, M.; Montazer, M.; Raeisossadati, R.; Abdollahi, A.; Moghbeli, M.; Nejadsattari, T.; Parivar, K.; Abbaszadegan, M.R. Expression Analysis Elucidates the Roles of MAML1 and Twist1 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Aggressiveness and Metastasis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 19, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Noh, K.H.; Lee, Y.-H.; Song, K.-H.; Oh, S.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, T.W. NANOG signaling promotes metastatic capability of immunoedited tumor cells. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2015, 32, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranjape, A.N.; Balaji, S.A.; Mandal, T.; Krushik, E.V.; Nagaraj, P.; Mukherjee, G.; Rangarajan, A. Bmi1 regulates self-renewal and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in breast cancer cells through Nanog. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawlik-Rzemieniewska, N.; Bednarek, I.A. The role of NANOG transcriptional factor in the development of malignant phenotype of cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.-H.; Hsu, D.S.-S.; Wang, H.-W.; Wang, H.-J.; Lan, H.-Y.; Yang, W.-H.; Huang, C.-H.; Kao, S.-Y.; Tzeng, C.-H.; Tai, S.-K.; et al. Bmi1 is essential in Twist1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Nature 2010, 12, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.-H.; Dimri, M.; Dimri, G.P. A Positive Feedback Loop Regulates the Expression of Polycomb Group Protein BMI1 via WNT Signaling Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 3406–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamijo, T. Role of stemness-related molecules in neuroblastoma. Pediatr. Res. 2012, 71, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjimichael, C.; Chanoumidou, K.; Papadopoulou, N.; Arampatzi, P.; Papamatheakis, J.; Kretsovali, A. Common stemness regulators of embryonic and cancer stem cells. World J. Stem Cells 2015, 7, 1150–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siu, M.K.Y.; Wong, E.S.Y.; Kong, D.S.H.; Chan, H.Y.; Jiang, L.; Wong, O.G.W.; Lam, E.W.-F.; Chan, K.K.L.; Ngan, H.Y.S.; Le, X.-F.; et al. Stem cell transcription factor NANOG controls cell migration and invasion via dysregulation of E-cadherin and FoxJ1 and contributes to adverse clinical outcome in ovarian cancers. Oncogene 2012, 32, 3500–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-F.; Wu, K.-J. Endothelial Transdifferentiation of Tumor Cells Triggered by the Twist1-Jagged1-KLF4 Axis: Relationship between Cancer Stemness and Angiogenesis. Stem Cells Int. 2015, 2016, 6439864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Katz, J.P. KLF4 is downregulated but not mutated during human esophageal squamous cell carcinogenesis and has tumor stage-specific functions. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-F.; Huang, C.-H.; Liu, C.-J.; Hung, J.-J.; Hsu, C.-C.; Teng, S.-C.; Wu, K.-J. Twist1 induces endothelial differentiation of tumour cells through the Jagged1-KLF4 axis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaleb, A.M.; Yang, V.W. Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4): What we currently know. Gene 2017, 611, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Ye, X.; Wang, P.; Jung, K.; Wu, C.; Douglas, D.; Kneteman, N.; Bigras, G.; Ma, Y.; Lai, R. Sox2 suppresses the invasiveness of breast cancer cells via a mechanism that is dependent on Twist1 and the status of Sox2 transcription activity. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velpula, K.K.; Dasari, V.R.; Tsung, A.J.; Dinh, D.H.; Rao, J.S. Cord blood stem cells revert glioma stem cell EMT by down regulating transcriptional activation of Sox2 and Twist1. Oncotarget 2011, 2, 1028–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liang, J.; Ni, S.; Zhou, T.; Qing, X.; Li, H.; He, W.; Chen, J.; Li, F.; Zhuang, Q.; et al. A Mesenchymal-to-Epithelial Transition Initiates and Is Required for the Nuclear Reprogramming of Mouse Fibroblasts. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, M.C.; Karasawa, H.; Castro, N.P.; Nagaoka, T.; Salomon, D.S.; Bianco, C. Role of Cripto-1 during Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Development and Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 2188–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cui, X.; Yu, X.; Bian, B.-S.; Qian, F.; Hu, X.-G.; Ji, C.-D.; Yang, L.; Ren, Y.; Cui, W.; et al. Cripto-1 acts as a functional marker of cancer stem-like cells and predicts prognosis of the patients in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Guo, Y.-Z.; Yue, X.; Zhang, G.-P.; Zhang, Y.; Kuang, M.; Peng, B.-G.; Li, S.-Q. Cripto-1 promotes tumor invasion and predicts poor outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2019, 41, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.-J.; Chen, S.-N.; Chen, W.-G.; Wu, G.-Q.; Liao, Y.-F.; Xu, J.-B.; Tang, H.; Yang, S.-H.; He, S.-Y.; Luo, Y.-F.; et al. Cripto-1 expression in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma is associated with poor disease outcome. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.S.; Salem, A.M.; Ahmed, R.Z.; Amer, S.A.; Abozaid, M.M. Prognostic and predictive values of Twist-1 and Cripto-1 expressions in non-small cell carcinoma of lung: An immunohistochemical study. Egypt. J. Pathol. 2018, 38, 190–198. [Google Scholar]
- Khaleghizadeh, M.; Forghanifard, M.M.; Rad, A.; Farshchian, M.; Hejazi, Z.; Gholamin, M.; Memar, B.; Abbaszadegan, M.R. Ectopic Expression of Human DPPA2 Gene in ESCC Cell Line Using Retroviral System. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2018, 10, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Shabestarian, H.; Ghodsi, M.; Mallak, A.J.; Jafarian, A.H.; Montazer, M.; Forghanifard, M.M. DPPA2 Protein Expression is Associated with Gastric Cancer Metastasis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 16, 8461–8465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, C.; Wang, Z.; Ramazanov, B.; Tang, Y.; Mehta, S.; Dambrot, C.; Lee, Y.-W.; Tessema, K.; Kumar, I.; Astudillo, M. Dppa2/4 facilitate epigenetic remodeling during reprogramming to pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 23, 396–411.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, T.; Caballero, O.L.; Svobodová, S.J.; Kong, A.; Chua, R.; Browning, J.; Fortunato, S.; Deb, S.; Hsu, M.; Gedye, C.A.; et al. ECSA/DPPA2 is an Embryo-Cancer Antigen that Is Coexpressed with Cancer-Testis Antigens in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 3291–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchabo, N.E.; Mhawech-Fauceglia, P.; Caballero, O.L.; Villella, J.; Beck, A.F.; Miliotto, A.J.; Liao, J.; Andrews, C.; Lele, S.; Old, L.J.; et al. Expression and serum immunoreactivity of developmentally restricted differentiation antigens in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Immun. 2009, 9, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Li, S.; Peng, B.; Ye, Y.; Deng, X.; Yao, K. Embryonic stem cells markers SOX2, OCT4 and Nanog expression and their correlations with epithelial-mesenchymal transition in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56324. [Google Scholar]
- Moghbeli, M.; Sadrizadeh, A.; Forghanifard, M.M.; Mozaffari, H.M.; Golmakani, E.; Abbaszadegan, M.R. Role of Msi1 and PYGO2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma depth of invasion. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2015, 10, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghbeli, M.; Forghanifard, M.M.; Sadrizadeh, A.; Mozaffari, H.M.; Golmakani, E.; Abbaszadegan, M.R. Role of Msi1 and MAML1 in Regulation of Notch Signaling Pathway in Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2015, 46, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Primer Sequence | Annealing T, °C | Amplicon Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BMI1 | F: CGTGTATTGTTCGTTACCTGGAGAC R: CATTGGCAGCATCAGCAGAAGG | 63 | 204 |
| CRIPTO1 | F: GGGATACAGCACAGTAAGGAG R: ACGGTGGTAGTTGTCGAGTC | 61 | 295 |
| DPPA2 | F: AGAAATACAATCCAGGTCATCTACTTC R: GCATATCTTGCCGTTGTTCAGG | 62 | 237 |
| KLF4 | F: TCTTCTCTTCGTTGACTTTG R: GCCAGCGGTTATTCGG | 55 | 210 |
| NANOG | F: GGCAATGGTGTGACGCAGAAGGC R:GCTCCAGGTTGAATTGTTCCAGGTC | 65 | 137 |
| MSI1 | F: TGAGCAGTTTGGGAAGGTG R: TCACACACTTTCTCCACGATG | 62 | 117 |
| SOX2 | F: AACAGCCCGGACCGCGTCAA R: TCGCAGCCGCTTAGCCTCGT | 62 | 189 |
| TWIST1 | F: GGAGTCCGCAGTCTTACGAG R: TCTGGAGGACCTGGTAGAGG | 58 | 201 |
| GAPDH | F: GGAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTCA R: GTCATTGATGGCAACAATATCCACT | 60 | 101 |
| Sequence | Number | Positions |
| CACTTG | 4 | 1294-99, 1731-36, 1825-30, 4914-19 |
| CAGGTG | ||
| CAAGTG | 6 | 1125-30, 1942-47, 6084-89, 8852-57 |
| CATCTG | 2 | 6458-63, 6811-16 |
| CAGCTG | 1 | 5220-25 |
| CACCTG | 1 | 5394-99 * |
| CATTTG | 8 | 1356-61, 1668-73, 2111-16, 2495-2500, 3853-58, 7739-44, 7809-14, 10114-19 |
| CATATG | 1 | 1715-20 |
| CAGATG | 3 | 6641-46, 6888-93 *, 9107-12 |
| CAGTTG | 5 | 1334-39, 2046-51, 3434-39-4183-88, 4620-25 |
| CAAATG | 5 | 1936-41, 5040-45, 6279-75, 6614-19, 8194-99 |
| CACATG | 3 | 998-03-3923-28, 5774-79 |
| CAACTG | 3 | 2476-81-2611-16, 9243-48, |
| CATGTG | 4 | 2971-76, 7219-24, 8530-35, 8597-8602 |
| CAATTG | 1 | 9351-56 |
| Sequence | Number | Positions |
|---|---|---|
| CAGGTG | 2 | 4940-45, 6478-83 |
| CAAGTG | 2 | 6447-52, 7838-43 * |
| CATCTG | 4 | 2312-17, 5186-91, 6687-92 *, 7493-98 * |
| CAGCTG | 1 | 2565-70 |
| CACCTG | 11 | 636-41, 1493-98, 2009-14, 2604-09, 3144-49, 3542-47, 3961-66, 4048-53, 4920-25, 5442-47 *, 6103-08 |
| CATTTG | 6 | 2143-48, 3549-54, 4760-65 *, 6312-17, 6531-36, 6815-20 * |
| CATATG | ||
| CAGATG | 2 | 2062-2067, 6596-6601 |
| CAAATG | 2 | 324-329, 1339-1344 |
| CACATG | 2 | 2246-51, 3626-31 |
| CAACTG | 730-735, 1546-1551, 7263-7268 * | |
| CATGTG | 5 | 1646-1651, 1977-1982, 4274-4279, 4874-4879, 7121-71268 * |
| CACGTG | 1 | 7255-60 * |
| Sequence | Number | Positions |
|---|---|---|
| CACTTG | 8 | 1070-75, 1454-59, 4400-05, 5478-83, 5613-18, 10561-66, 16659-64, 20675-80 |
| CAGGTG | 20 | 4994-99, 6239-44, 6505-10, 8682-87, 9174-79-9768-73, 15373-78, 10959-64, 11852-57 *, 12504-09, 15912-17, 16955-60, 17376-81, 17665-70, 18194-99, 18530-35, 19210-15, 19551-56, 20059-64, 21256-61 |
| CAAGTG | 7 | 705-10, 1385-90, 7490-95, 15082-87, 19075-80, 19646-51, 22042-47 |
| CATCTG | 11 | 1855-60, 4637-42, 10316-21, 12695-700, 13351-56, 19349-54, 20068-73, 20688-93, 20992-97, 22177-82, 22367-72 |
| CAGCTG | 4 | 7701-06, 12359-64, 19869-74, 19954-59 |
| CACCTG | 14 | 980-85, 6429-34, 9608-13, 9777-82, 11186-91, 12911-16, 13324-29, 13786-91, 15389-94, 16617-22, 16704-09, 17385-90, 21127-32, 21272-77 |
| CATTTG | 10 | 1883-85, 2193-98, 2914-19, 7956-61, 8216-21, 8575-80, 12762-67, 20541-46, 21034-39, 21448-53 |
| CATATG | 1 | 6471-76 |
| CAGATG | 3 | 1980-85 *, 1440-45, 15296-301 |
| CAGTTG | 6 | 5328-33, 7712-17, 8349-54 *, 13242-47, 13293-98, 22140-45 |
| CAAATG | 6 | 2501-06, 3792-97, 3907-12 *, 7203-08 *, 15645-50, 16308-13, 18294-99 |
| CACATG | 5 | 4534-39, 8006-11, 8611-16, 12999-13004, 22124-29 |
| CAACTG | 1 | 15259-64 |
| CATGTG | 10 | 2171-76, 3457-62, 6417-22, 11499-504, 11708-13, 13915-20, 14636-41, 17135-40, 18799-804, 19970-74 |
| CAATTG | 6 | 2446-51, 10305-10, 11738-43, 16200-05, 16583-88, 22717-22 * |
| CACGTG | 1 | 9599-604 |
| Sequence | Number | Positions |
|---|---|---|
| CACTTG | 2 | 2948-53 *, 3379-84 * |
| CAGGTG | 4 | 1259-64 *, 1537-42 *, 2751-56 *, 4554-59 |
| CAGCTG | 3 | 489-94, 1268-73 *, 1715-20 * |
| CACCTG | 5 | 950-55 *, 1438-43 *, 2527-32 *, 3437-42 *, 4146-51 |
| CAGATG | 4 | 3152-57 *, 4611-16 *, 4923-28 *, 5401-06 * |
| CAAATG | 3 | 1988-93, 4255-60, 5455-60 * |
| CAACTG | 1 | 4856-61 * |
| CACGTG | 2 | 557-62, 2905-10 * |
| Sequence | Number | Positions |
|---|---|---|
| CAGCTG | 965-70 *, 1548-53 *, 1972-77 * | |
| CAGATG | 1013-18 * | |
| CAGTTG | 1988-93 * | |
| CAAATG | 1541-46 * | |
| CACATG | 737-42 *, 920-25 *, 1313-18 *, 1382-87 * | |
| CATGTG | 1384-89 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Izadpanah, M.H.; Forghanifard, M.M. TWIST1 Plays Role in Expression of Stemness State Markers in ESCC. Genes 2022, 13, 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122369
Izadpanah MH, Forghanifard MM. TWIST1 Plays Role in Expression of Stemness State Markers in ESCC. Genes. 2022; 13(12):2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122369
Chicago/Turabian StyleIzadpanah, Mohammad Hossein, and Mohammad Mahdi Forghanifard. 2022. "TWIST1 Plays Role in Expression of Stemness State Markers in ESCC" Genes 13, no. 12: 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122369
APA StyleIzadpanah, M. H., & Forghanifard, M. M. (2022). TWIST1 Plays Role in Expression of Stemness State Markers in ESCC. Genes, 13(12), 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122369






