MiR-375 and miR-21 as Potential Biomarkers of Prostate Cancer: Comparison of Matching Samples of Plasma and Exosomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients: Clinical Data and Sample Collection
2.2. Plasma Exosome Isolation
2.3. Flow Cytometry
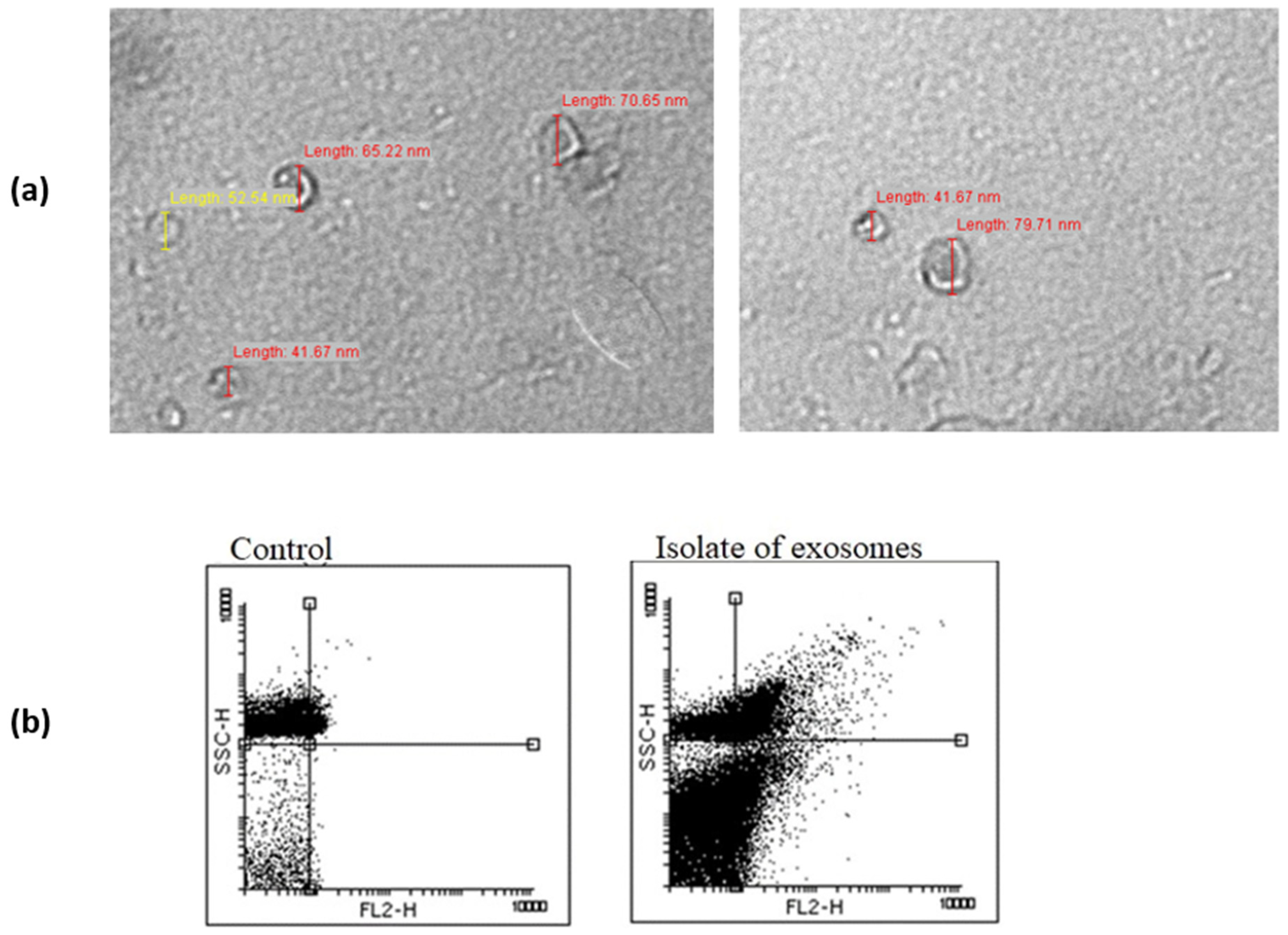
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.5. RNA Extraction
2.6. Reverse Transcription and RT-qPCR Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellinger, J.; Alajati, A.; Kubatka, P.; Giordano, F.A.; Ritter, M.; Costigliola, V.; Golubnitschaja, O. Prostate cancer treatment costs increase more rapidly than for any other cancer—How to reverse the trend? EPMA J. 2022, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marhold, M.; Kramer, G.; Krainer, M.; Le Magnen, C. The prostate cancer landscape in Europe: Current challenges, future opportunities. Cancer Lett. 2022, 526, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.; Valbuena, G.N.; Curry, E.; Bevan, C.L.; Keun, H.C. MicroRNAs as biomarkers for prostate cancer prognosis: A systematic review and a systematic reanalysis of public data. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, H.N.; Lin, H.-Y.; Sørensen, K.D.; Ogunwobi, O.O.; Kumar, N.; Chornokur, G.; Phelan, C.; Jones, D.; Kidd, L.; Batra, J.; et al. miRNAs associated with prostate cancer risk and progression. BMC Urol. 2017, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanacore, D.; Boccellino, M.; Rossetti, S.; Cavaliere, C.; D’Aniello, C.; Di Franco, R.; Romano, F.J.; Montanari, M.; La Mantia, E.; Piscitelli, R.; et al. Micrornas in prostate cancer: An overview. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 50240–50251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramovic, I.; Ulamec, M.; Katusic Bojanac, A.; Bulic-Jakus, F.; Jezek, D.; Sincic, N. miRNA in prostate cancer: Challenges toward translation. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, X.; Foj, L. miRNAs as novel biomarkers in the management of prostate cancer. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 715–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Deng, J.J.; Gowda, P.S.; Rao, M.K.; Lin, C.-L.; Chen, C.L.; Huang, T.; Sun, L.-Z. Androgen receptor and microRNA-21 axis downregulates transforming growth factor β receptor II (TGFBR2) expression in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4097–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Pinheiro, P.; Ramalho-Carvalho, J.; Vieira, F.Q.; Torres-Ferreira, J.; Oliveira, J.; Gonçalves, C.S.; Costa, B.M.; Henrique, R.; Jerónimo, C. MicroRNA-375 plays a dual role in prostate carcinogenesis. Clin. Epigenetics 2015, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, L.; Spasojević, M.; Prodanović, R.; Korać, A.; Matijaševic, S.; Brajušković, G.; de Marco, A.; Popović, M. Affinity-based isolation of extracellular vesicles by means of single-domain antibodies bound to macroporous methacrylate-based copolymer. New Biotechnol. 2022, 69, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolić, Z.Z.; Savić Pavićević, D.; Vukotić, V.D.; Tomović, S.M.; Cerović, S.J.; Filipović, N.; Romac, S.P.; Brajušković, G.N. Association between genetic variant in hsa-miR-146a gene and prostate cancer progression: Evidence from Serbian population. Cancer Causes Control 2014, 25, 1571–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolić, Z.; Savić Pavićević, D.; Vučić, N.; Cidilko, S.; Filipović, N.; Cerović, S.; Vukotić, V.; Romac, S.; Brajušković, G. Assessment of association between genetic variants in microRNA genes hsa-miR-499, hsa-miR-196a2 and hsa-miR-27a and prostate cancer risk in Serbian population. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2015, 99, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolić, Z.; Savić Pavićević, D.; Vučić, N.; Cerović, S.; Vukotić, V.; Brajušković, G. Genetic variants in RNA-induced silencing complex genes and prostate cancer. World J. Urol. 2017, 35, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotarac, N.; Dobrijevic, Z.; Matijasevic, S.; Savic-Pavicevic, D.; Brajuskovic, G. Analysis of association of potentially functional genetic variants within genes encoding miR-34b/c, miR-378 and miR-143/145 with prostate cancer in Serbian population. EXCLI J. 2019, 18, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotarac, N.; Dobrijevic, Z.; Matijasevic, S.; Savic-Pavicevic, D.; Brajuskovic, G. Association of KLK3, VAMP8 and MDM4 Genetic Variants within microRNA Binding Sites with Prostate Cancer: Evidence from Serbian Population. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020, 26, 2409–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, T.L. The emerging role of plasma exosomes in diagnosis, prognosis and therapies of patients with cancer. Contemp. Oncol. 2018, 2018, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Chen, Q.; Lin, L.; Sha, C.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Yin, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; Gao, W.; et al. Regulation of exosome production and cargo sorting. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endzeliņš, E.; Berger, A.; Melne, V.; Bajo-Santos, C.; Soboļevska, K.; Ābols, A.; Rodriguez, M.; Šantare, D.; Rudņickiha, A.; Lietuvietis, V.; et al. Detection of circulating miRNAs: Comparative analysis of extracellular vesicle-incorporated miRNAs and cell-free miRNAs in whole plasma of prostate cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, D.; Sha, J.; Sun, P.; Huang, Y. MicroRNA-21 directly targets MARCKS and promotes apoptosis resistance and invasion in prostate cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 383, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, J.; Ni, X.; Haffner, M.; Wentzel, E.A.; Salmasi, A.H.; Chowdhury, W.H.; Kudrolli, T.A.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Luo, J.; Rodriguez, R.; et al. miR-21: An Androgen Receptor–Regulated MicroRNA that Promotes Hormone-Dependent and Hormone-Independent Prostate Cancer Growth. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7165–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, S.T.; Pontes-Junior, J.; Antunes, A.A.; Dall’Oglio, M.F.; Dip, N.; Passerotti, C.C.; Rossini, G.A.; Morais, D.R.; Nesrallah, A.J.; Piantino, C.B.; et al. miR-21 may acts as an oncomir by targeting RECK, a matrix metalloproteinase regulator, in prostate cancer. BMC Urol. 2012, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, V.; Musumeci, M.; Patrizii, M.; Cannistraci, A.; Addario, A.; Maugeri-Saccà, M.; Biffoni, M.; Francescangeli, F.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S.; et al. BTG2 loss and miR-21 upregulation contribute to prostate cell transformation by inducing luminal markers expression and epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1843–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, J.-X.; Shao, Z.-Q. miR-21 targets and inhibits tumor suppressor gene PTEN to promote prostate cancer cell proliferation and invasion: An experimental study. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arisan, E.D.; Rencuzogullari, O.; Freitas, I.L.; Radzali, S.; Keskin, B.; Kothari, A.; Warford, A.; Uysal-Onganer, P. Upregulated Wnt-11 and miR-21 Expression Trigger Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Aggressive Prostate Cancer Cells. Biology 2020, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonov, R.; Shtam, T.; Burdakov, V.; Glotov, A.; Tsyrlina, E.; Berstein, L.; Nosov, A.; Evtushenko, V.; Filatov, M.; Malek, A. Lectin-induced agglutination method of urinary exosomes isolation followed by mi-RNA analysis: Application for prostate cancer diagnostic. Prostate 2016, 76, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppers-Lalic, D.; Hackenberg, M.; de Menezes, R.; Misovic, B.; Wachalska, M.; Geldof, A.; Zini, N.; de Reijke, T.; Wurdinger, T.; Vis, A.; et al. Non-invasive prostate cancer detection by measuring miRNA variants (isomiRs) in urine extracellular vesicles. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 22566–22578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamvirdizadeh, A.; Jamshidian, F.; Entezari, M.; Nooraei, S.; Hashemi, M. Non-invasive Prostate Cancer Detection by Measuring Expression Level of miR-21 and miR-214 in Urine. Int. J. Cancer Manag. 2021, 14, e110014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Bai, L.; Liao, R.; Zhao, J.; Guo, M.; Jiang, W.; Li, J.; et al. MicroRNA-375 is a therapeutic target for castration-resistant prostate cancer through the PTPN4/STAT3 axis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1290–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Shi, J.; Mao, J.; Luo, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, R.; Yang, F. The expression of miR-375 in prostate cancer: A study based on GEO, TCGA data and bioinformatics analysis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, R.-S.; Li, Y.-H.; Zhong, S.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Zhang, C.-M.; Hu, M.-M.; Shen, Z.-J. miR-21 as an Independent Biochemical Recurrence Predictor and Potential Therapeutic Target for Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 2012, 187, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melbø-Jørgensen, C.; Ness, N.; Andersen, S.; Valkov, A.; Dønnem, T.; Al-Saad, S.; Kiselev, Y.; Berg, T.; Nordby, Y.; Bremnes, R.M.; et al. Stromal Expression of MiR-21 Predicts Biochemical Failure in Prostate Cancer Patients with Gleason Score 6. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, K.R.M.; Reis, S.T.; Viana, N.; Morais, D.R.; Moura, C.M.; Silva, I.A.; Pontes, J., Jr.; Katz, B.; Srougi, M. Controlling RECK miR21 Promotes Tumor Cell Invasion and Is Related to Biochemical Recurrence in Prostate Cancer. J. Cancer 2015, 6, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Hruby, G.W.; McKiernan, J.M.; Gurvich, I.; Lipsky, M.J.; Benson, M.C.; Santella, R.M. Dysregulation of circulating microRNAs and prediction of aggressive prostate cancer. Prostate 2012, 72, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramovic, I.; Vrhovec, B.; Skara, L.; Vrtaric, A.; Nikolac Gabaj, N.; Kulis, T.; Stimac, G.; Ljiljak, D.; Ruzic, B.; Kastelan, Z.; et al. MiR-182-5p and miR-375-3p Have Higher Performance Than PSA in Discriminating Prostate Cancer from Benign Prostate Hyperplasia. Cancers 2021, 13, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaman Agaoglu, F.; Kovancilar, M.; Dizdar, Y.; Darendeliler, E.; Holdenrieder, S.; Dalay, N.; Gezer, U. Investigation of miR-21, miR-141, and miR-221 in blood circulation of patients with prostate cancer. Tumor Biol. 2011, 32, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yuan, T.; Liang, M.; Du, M.; Xia, S.; Dittmar, R.; Wang, D.; See, W.; Costello, B.A.; Quevedo, F.; et al. Exosomal miR-1290 and miR-375 as Prognostic Markers in Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedan, A.H.; Osther, P.J.S.; Assenholt, J.; Madsen, J.S.; Hansen, T.F. Circulating miR-141 and miR-375 are associated with treatment outcome in metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.J.; Pawlowski, T.; Catto, J.W.; Marsden, G.; Vessella, R.L.; Rhees, B.; Kuslich, C.; Visakorpi, T.; Hamdy, F.C. Changes in circulating microRNA levels associated with prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidarra, D.; Constâncio, V.; Barros-Silva, D.; Ramalho-Carvalho, J.; Moreira-Barbosa, C.; Antunes, L.; Maurício, J.; Oliveira, J.; Henrique, R.; Jerónimo, C. Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Detection and Metastasis Development Prediction. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wach, S.; Al-Janabi, O.; Weigelt, K.; Fischer, K.; Greither, T.; Marcou, M.; Theil, G.; Nolte, E.; Holzhausen, H.-J.; Stöhr, R.; et al. The combined serum levels of miR-375 and urokinase plasminogen activator receptor are suggested as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1406–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Fei, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Song, Y. Circulating miRNAs as Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis in Subjects with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 5873056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Standard Prognostic Parameter | PCa Patients—n (%) |
|---|---|
| PSA at diagnosis | |
| <10 ng/mL | 15 (42.8) |
| 10–20 ng/mL | 10 (28.6) |
| >20 ng/mL | 8 (22.8) |
| Biopsy Gleason score | |
| <7 | 7 (20) |
| =7 | 22 (62.8) |
| >7 | 4 (11.4) |
| TNM stage | |
| T1/T2 | 13 (37.1) |
| T3/T4 | 16 (45.7) |
| Metastases | |
| Distant (M+) | 3 (8.6) |
| Regional (N+) or not detected | 26 (74.3) |
| Risk of progression | |
| Less aggressive | 10 (28.6) |
| Aggressive | 18 (51.4) |
| Groups of Participants | r Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| miR-375 | ||
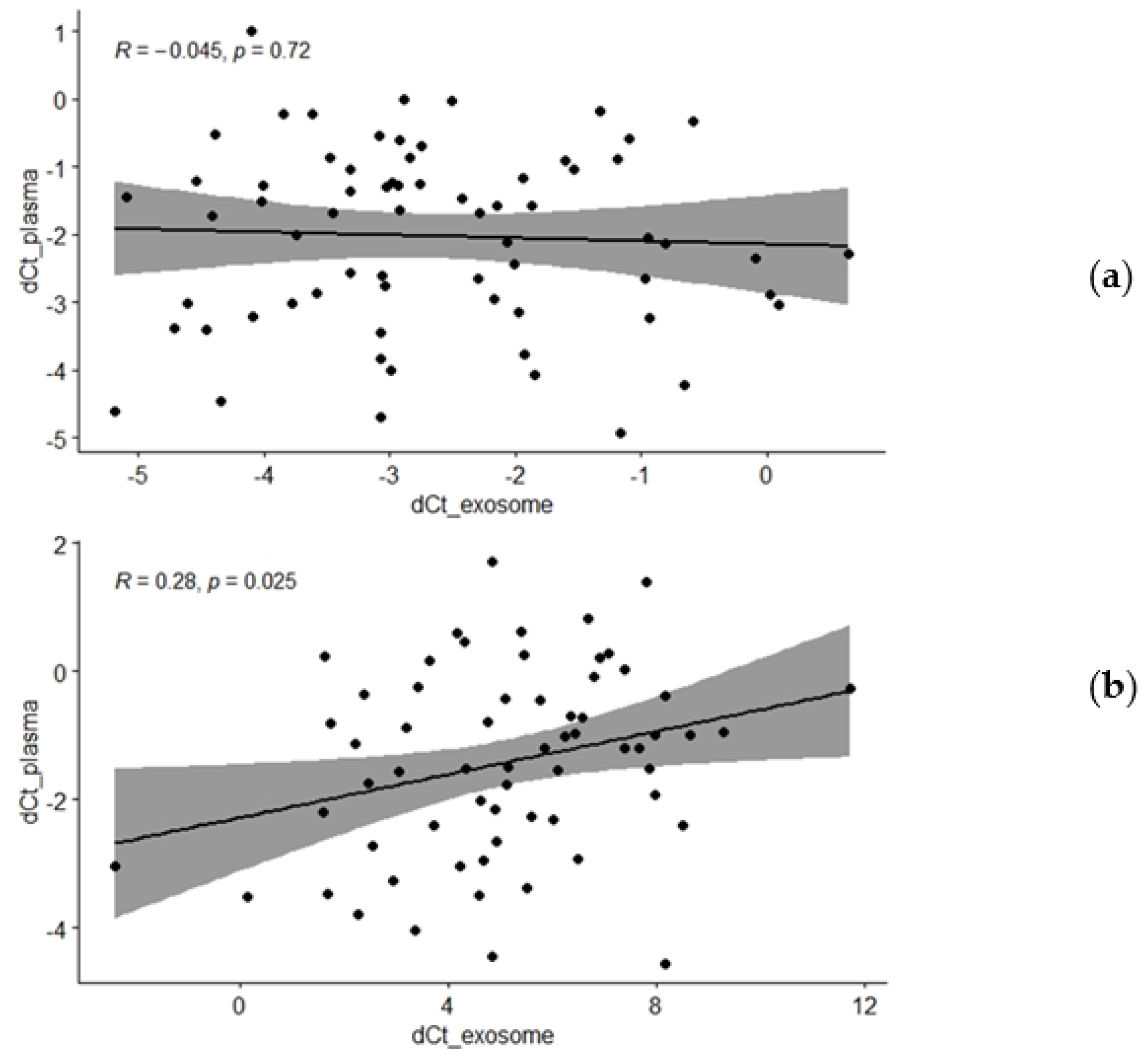
| All participants | −0.045 | 0.722 |
| BPH | −0.341 | 0.049 |
| PCa | 0.139 | 0.438 |
| miR-21 | ||
| All participants | 0.281 | 0.025 |
| BPH | 0.386 | 0.032 |
| PCa | 0.228 | 0.209 |
| Groups of Participants | dCt Mean ± SD | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| exosomal miR-375 | ||
| PSA ≤ 20/PSA > 20 | −2.57 ± 2.58/−3.02 ± 0.99 | 0.453 |
| T1T2 stage/T3T4 stage | −2.68 ± 1.59/−3.27 ± 1.03 | 0.271 |
| GS < 7/GS ≥ 7 | −2.36 ± 3.28/−2.89 ± 1.84 | 0.395 |
| less aggressive/aggressive | −2.95 ± 1.58/−2.66 ± 3.08 | 0.615 |
| exosomal miR-21 | ||
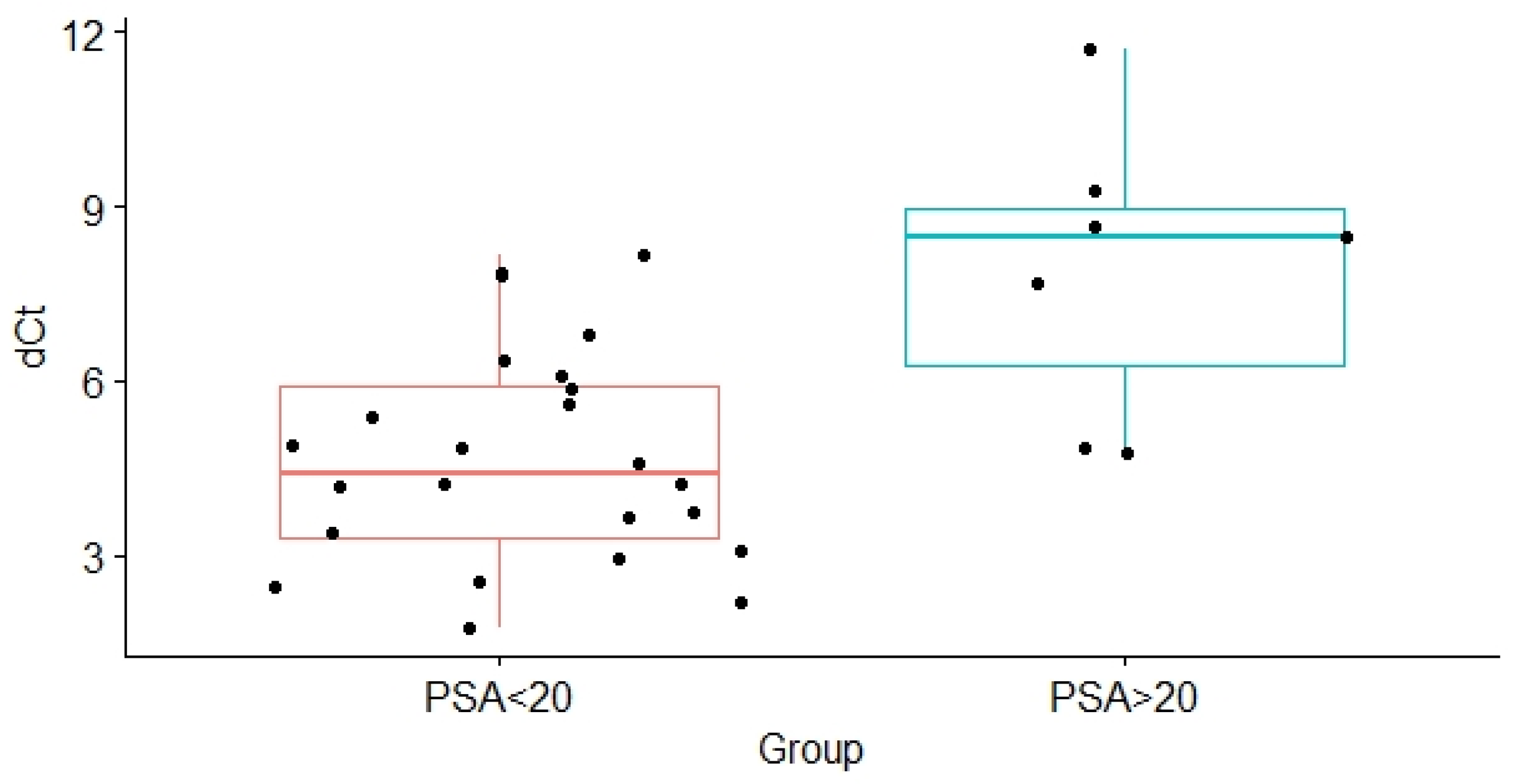
| PSA ≤ 20/PSA > 20 | 4.69 ± 1.84/7.92 ± 2.47 | 0.012 |
| T1T2 stage/T3T4 stage | 4.67 ± 2.15/6.08 ± 2.43 | 0.124 |
| GS < 7/GS ≥ 7 | 5.26 ± 2.03/5.07 ± 2.43 | 0.852 |
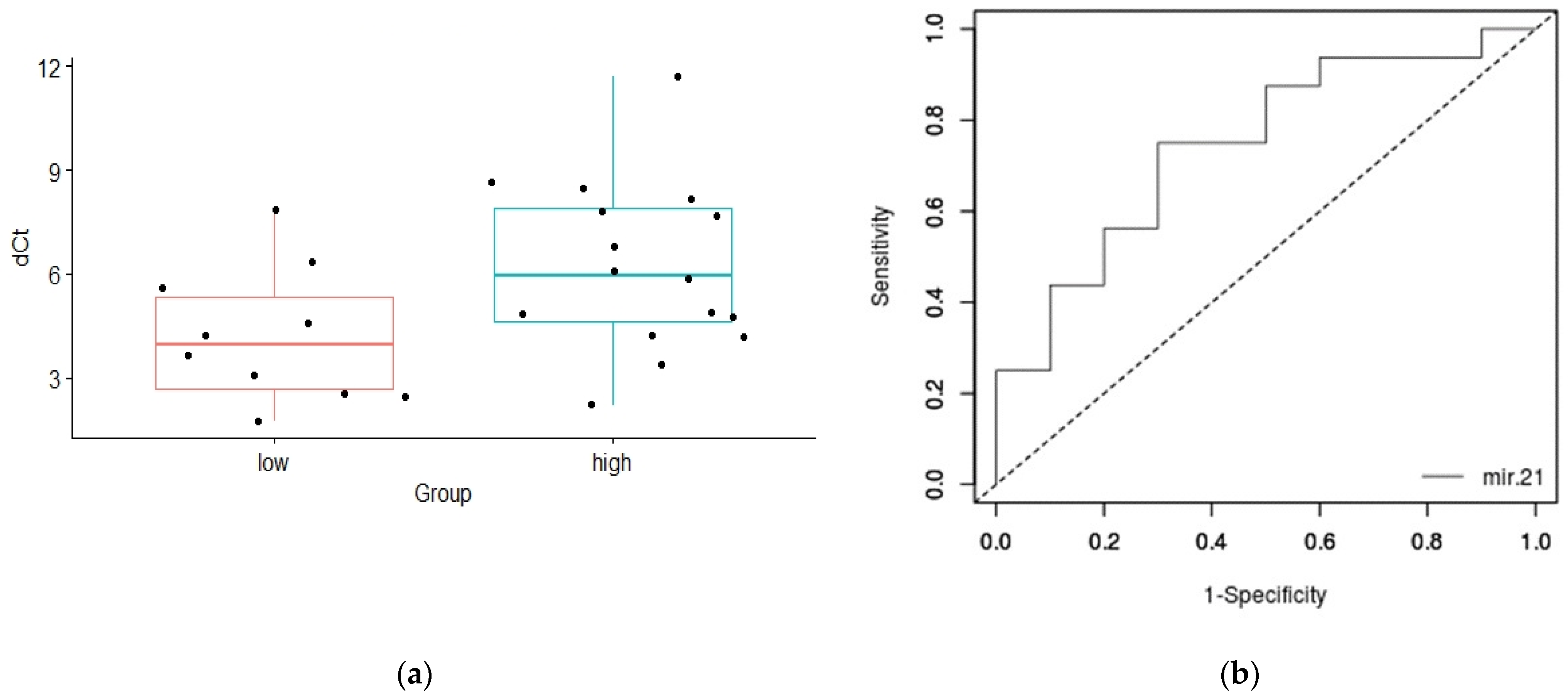
| less aggressive/aggressive | 4.21 ± 1.93/6.23 ± 2.43 | 0.028 |
| plasma miR-375 | ||
| PSA ≤ 20/PSA > 20 | −3.15 ± 2.31/−2.88 ± 0.34 | 0.486 |
| T1T2 stage/T3T4 stage | −2.22 ± 1.45/1.82 ± 1.48 | 0.476 |
| GS < 7/GS ≥ 7 | −1.95 ± 1.56/−1.87 ± 1.44 | 0.905 |
| less aggressive/aggressive | −1.84 ± 1.96/−2.59 ± 1.46 | 0.172 |
| plasma miR-21 | ||
| PSA ≤ 20/PSA > 20 | −1.34 ± 3.05/−1.89 ± 1.89 | 0.426 |
| T1T2 stage/T3T4 stage | −2.04 ± 1.13/−1.49 ± 1.74 | 0.333 |
| GS < 7/GS ≥ 7 | −1.68 ± 1.49/−0.89 ± 2.13 | 0.926 |
| less aggressive/aggressive | −1.64 ± 2.84/−1.77 ± 1.30 | 0.836 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Joković, S.M.; Dobrijević, Z.; Kotarac, N.; Filipović, L.; Popović, M.; Korać, A.; Vuković, I.; Savić-Pavićević, D.; Brajušković, G. MiR-375 and miR-21 as Potential Biomarkers of Prostate Cancer: Comparison of Matching Samples of Plasma and Exosomes. Genes 2022, 13, 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122320
Joković SM, Dobrijević Z, Kotarac N, Filipović L, Popović M, Korać A, Vuković I, Savić-Pavićević D, Brajušković G. MiR-375 and miR-21 as Potential Biomarkers of Prostate Cancer: Comparison of Matching Samples of Plasma and Exosomes. Genes. 2022; 13(12):2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122320
Chicago/Turabian StyleJoković, Suzana Matijašević, Zorana Dobrijević, Nevena Kotarac, Lidija Filipović, Milica Popović, Aleksandra Korać, Ivan Vuković, Dušanka Savić-Pavićević, and Goran Brajušković. 2022. "MiR-375 and miR-21 as Potential Biomarkers of Prostate Cancer: Comparison of Matching Samples of Plasma and Exosomes" Genes 13, no. 12: 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122320
APA StyleJoković, S. M., Dobrijević, Z., Kotarac, N., Filipović, L., Popović, M., Korać, A., Vuković, I., Savić-Pavićević, D., & Brajušković, G. (2022). MiR-375 and miR-21 as Potential Biomarkers of Prostate Cancer: Comparison of Matching Samples of Plasma and Exosomes. Genes, 13(12), 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122320






