Molecular Characterization of Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.) Miers Using Novel g-SSR Markers and Their Comparison with EST-SSR and SCoT Markers for Genetic Diversity Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Genomic DNA Extraction
2.2. g-SSR PCR Amplification
2.3. EST-SSR Amplification
2.4. SCoT Marker Amplification
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Diversity Assessment in Tinospora Species Using g-SSR
3.2. Genetic Relatedness Analysis
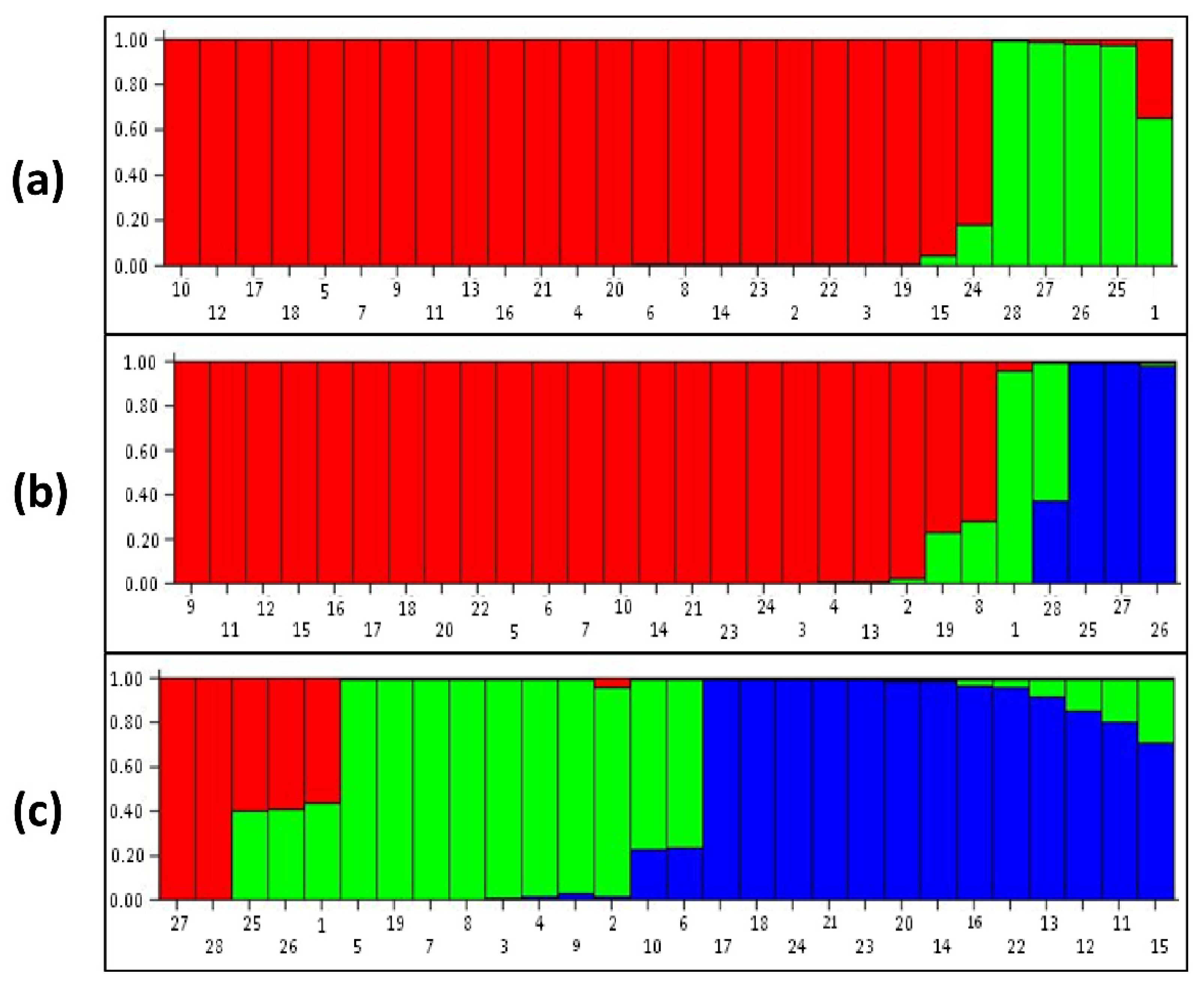
3.3. Population Structure Analysis
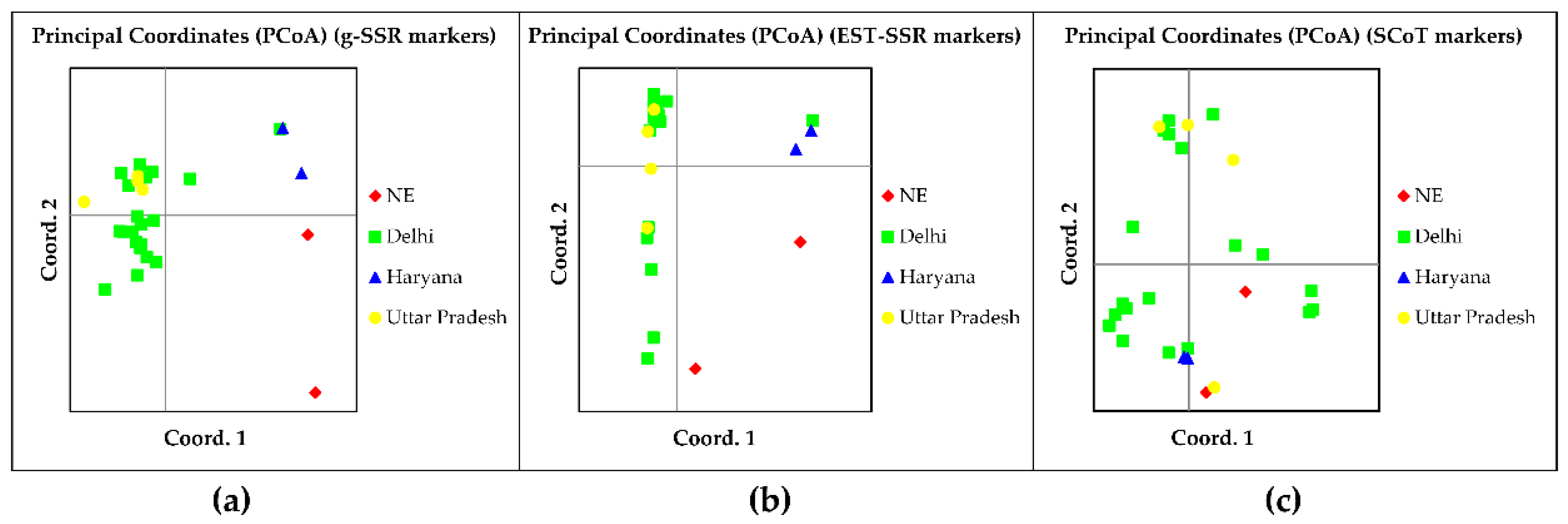
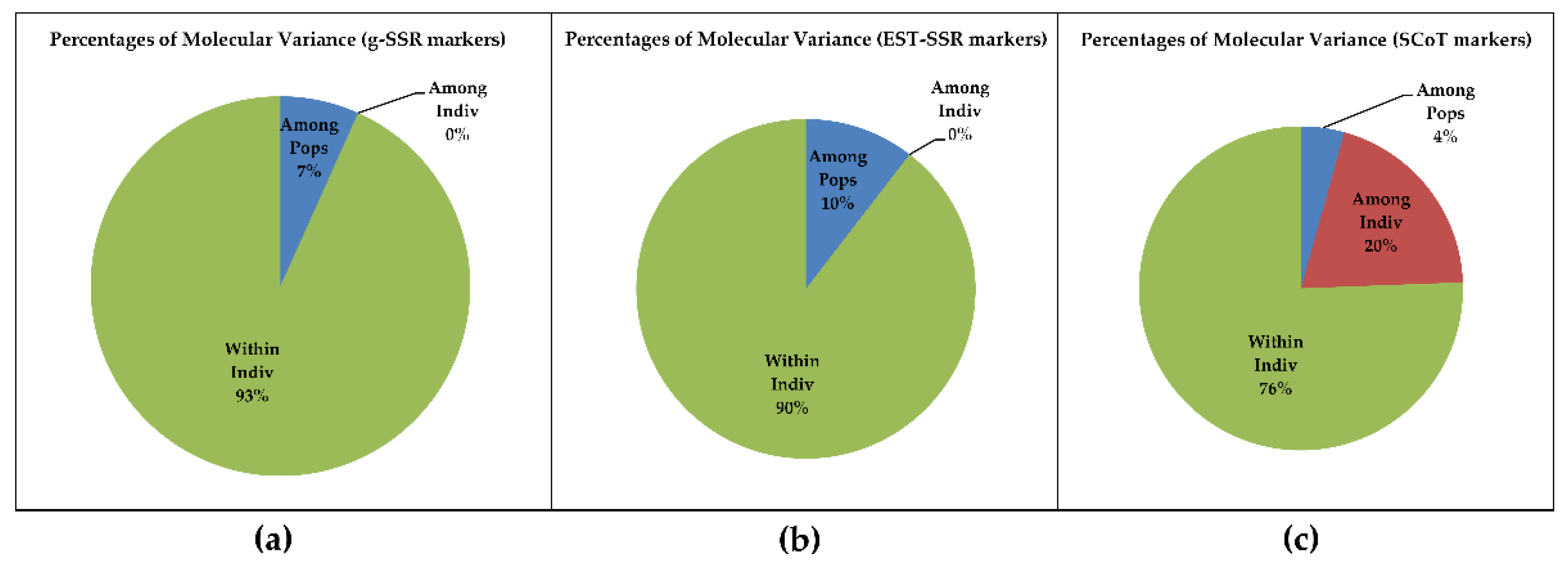
3.4. Principal Coordinate and AMOVA Analysis
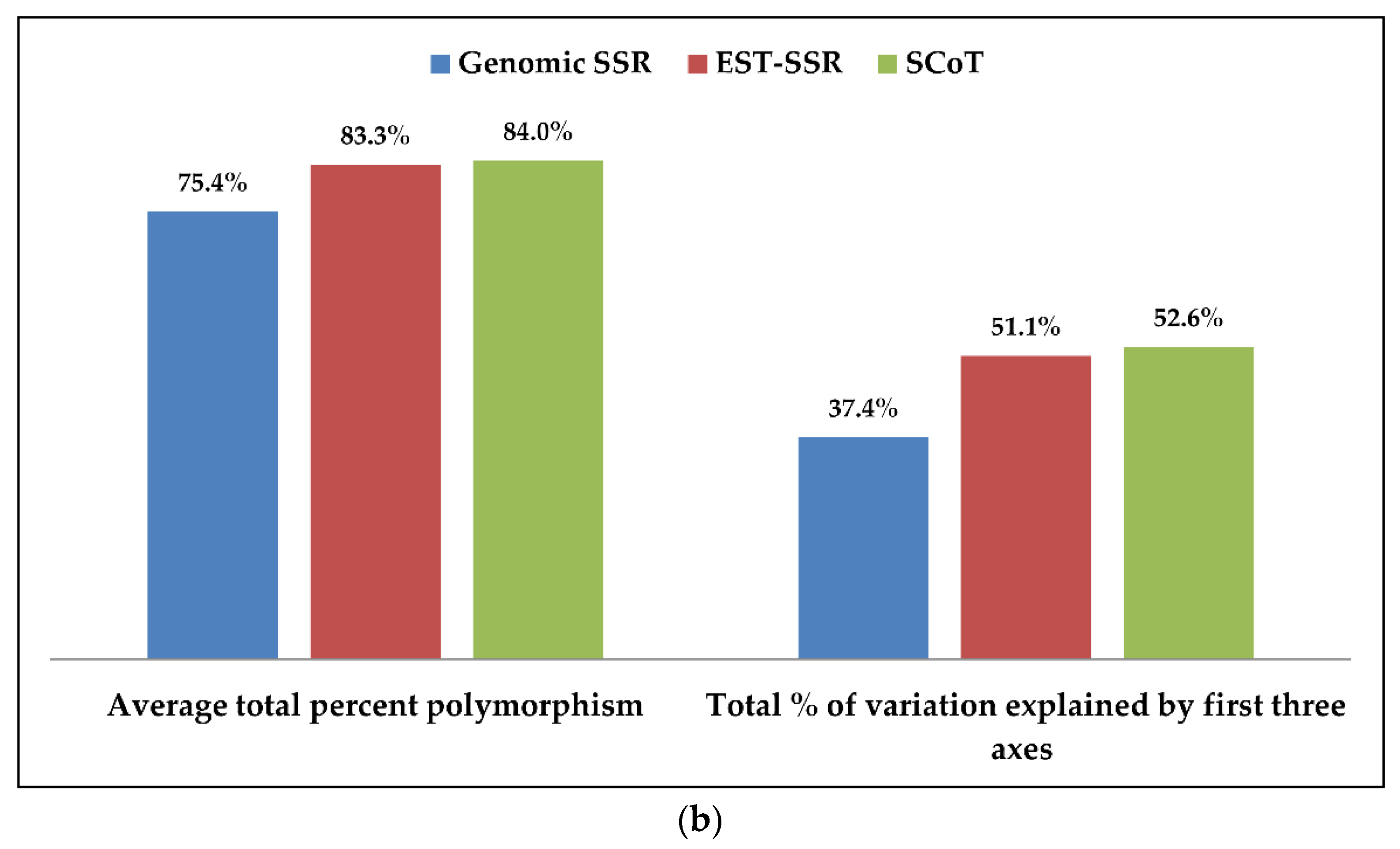
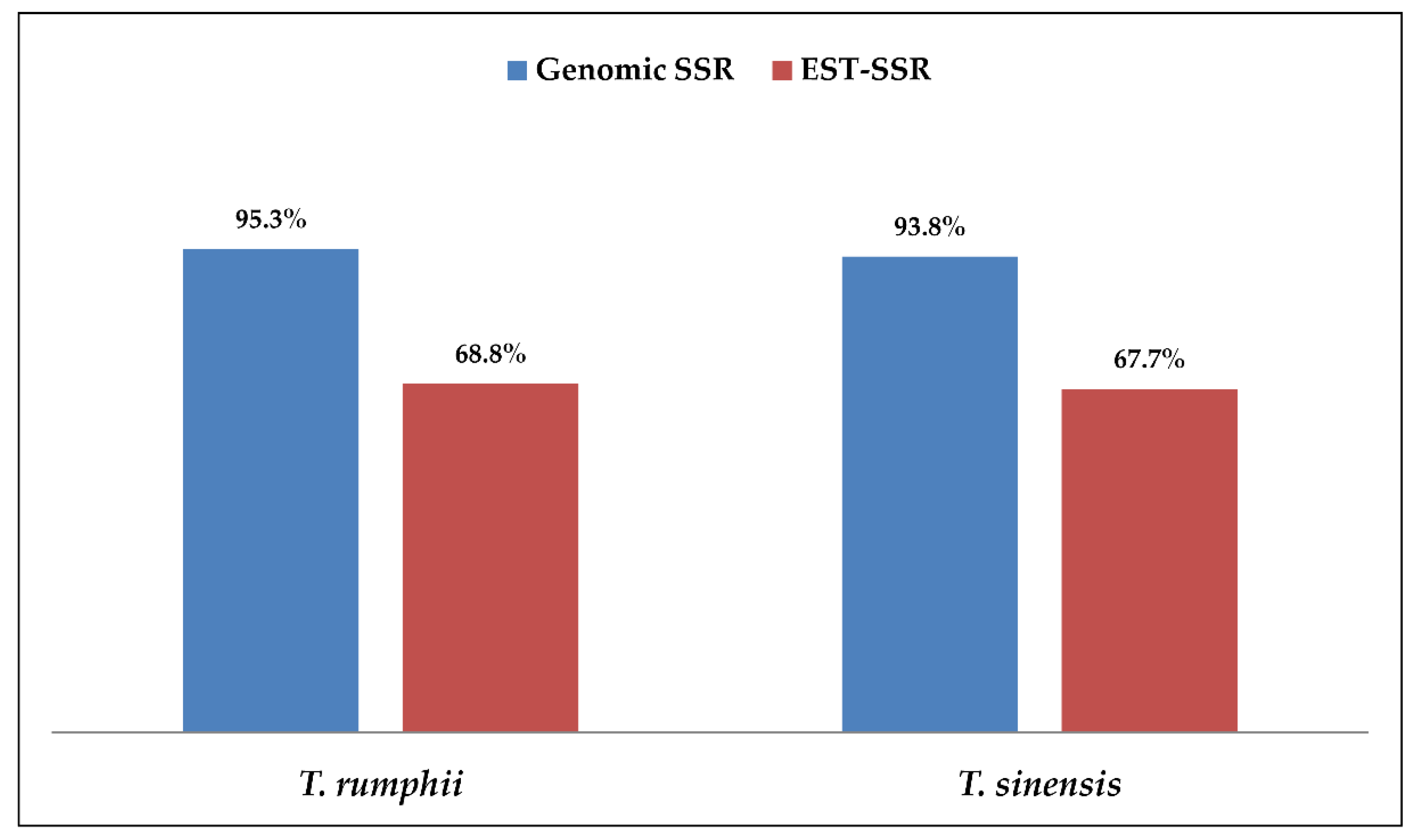
3.5. Comparison of g-SSR, EST-SSR and SCoT Markers in Genetic Diversity Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glaszmann, J.C.; Fautret, A.; Noyer, J.L.; Feldmann, P.; Lanaud, C. Biochemical Genetic-Markers in Sugarcane. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1989, 78, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Gupta, V.K.; Misra, A.K.; Modi, D.R.; Pandey, B.K. Potential of molecular markers in plant biotechnology. Plant Omics J. 2009, 2, 141–162. [Google Scholar]
- Lister, C.; Dean, C. Recombinant inbred lines for mapping RFLP and phenotypic markers in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1993, 4, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litt, M.; Luty, J.A. A hypervariable microsatellite revealed by in vitro amplification of a dinucleotide repeat within the cardiac muscle actin gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1989, 44, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tautz, D.; Renz, M. Simple sequences are ubiquitous repetitive components of eukaryotic genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984, 12, 4127–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gur-Arie, R.; Cohen, C.J.; Eitan, Y.; Shelef, L.; Hallerman, E.M.; Kashi, Y. Simple sequence repeats in Escherichia coli: Abundance, distribution, composition, and polymorphism. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zane, L.; Bargelloni, L.; Patarnello, T. Strategies for microsatellite isolation: A review. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Yang, J.M.; Zhu, J.H.; Jia, Q.J.; Tao, Y.Z. Assessment of genetic diversity by simple sequence repeat markers among forty elite varieties in the germplasm for malting barley breeding. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B. 2010, 11, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, H.; Jiang, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Xu, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. Genetic variation, population structure and linkage disequilibrium in Switchgrass with ISSR, SCoT and EST-SSR markers. Hereditas 2016, 153, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethi, P.; Rahman, S.; Naganeeswaran, S.; Sabana, A.A.; Gangaraj, K.P.; Jerard, B.A.; Niral, V.; Rajesh, M.K. Development of EST-SSR markers for genetic diversity analysis in coconut (Cocos nucifera L.). Mol. Biol. 2020, 47, 9385–9397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zuo, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, Y. The and germplasm collection for cultivated Dendrobium officinale K. Kimura & Migo individuals revealed by EST-SSR markers. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2020, 67, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervishi, A.; Jakše, J.; Ismaili, H.; Javornik, B.; Štajner, N. Genetic structure and core collection of olive germplasm from albania revealed by microsatellite markers. Genes 2021, 12, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, S.; Shaikh, N. Gaduchi-the best ayurvedic herb. Pharma Innov. -J. 2013, 2, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Nagral, A.; Adhyaru, K.; Rudra, O.S.; Gharat, A.; Bhandare, S. Herbal immune booster-induced liver injury in the COVID-19 pandemic-a case series. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devarbhavi, H. Response to Tinospora cordifolia (giloy)-induced liver injury during the COVID-19 pandemic—Multicenter nationwide study from India. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 2995–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, A.V.; Geetha, S.P.; Martin, G.; Balachandran, I.; Ravindran, P.N. In vitro propagation through mature nodes of Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.) Hook. F. & Thoms.: An important ayurvedic medicinal plant. Vitr. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006, 42, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, K.; Mishra, N.P.; Singh, J.; Khanuja, S.P.S. Tinospora cordifolia (Guduchi), a reservoir plant for therapeutic applications: A review. Indian J. Tradit. Know. 2004, 3, 257–270. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V.; Pandey, D. Beneficial effects of Tinospora cordifolia on blood profiles in male mice exposed to lead. Toxicol. Int. 2010, 17, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spandana, U.; Ali, S.L.; Nirmala, T.; Santhi, M.; Babu, S.D.S. A Review on Tinospora cordifolia. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2013, 4, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Kalpesh, I.; Mohan, J.S.S. Assessment of genetic diversity in the medicinal climber Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.) Miers (Menispermaceae) from Gujarat, India. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 6499–6505. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.M.; Verma, V.; Qazi, P.H.; Ganaie, M.M.; Bakshi, S.K.; Qazi, G.N. Molecular phylogeny in Indian Tinospora species by DNA based molecular markers. Plant Syst. Evol. 2006, 256, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.M.; Verma, V.; Qazi, P.H.; Hoot, S.B. Phylogenetic patterns and genetic diversity of Indian Tinospora species based on chloroplast sequence data and cytochrome P450 polymorphisms. Plant Syst. Evol. 2009, 281, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, R.; Singh, R.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S. Molecular characterization of Giloe (Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.) Miers ex Hook F & Thoms.) accessions using Start Codon Targeted (ScoT) markers. Int. J. Med. Arom. Plants. 2013, 3, 413–422. [Google Scholar]
- Rout, G.R. Identification of Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.) Miers ex Hook F & Thoms using RAPD markers. Z. Nat. C 2006, 61, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Arya, A.; Kaushik, V.; Sindhu, A. Studies on genetic variability of Tinospora cordifolia collected from different agroclimatic zones of Haryana using RAPD markers. Res. Crop. 2019, 1, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, V.; Thakur, K.; Sood, R.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, T.R. Genetic diversity analysis of Tinospora cordifolia germplasm collected from north-western Himalayan region of India. J. Genet. 2012, 9, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, V.M.; Dhalwal, K. DNA Fingerprinting of Tinospora cordifolia using RAPD analysis. J. Glob. Pharma Technol. 2010, 2, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Paliwal, R.; Kumar, R.; Choudhury, D.R.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, A.; Bhatt, K.C.; Singh, R.; Mahato, A.K.; Singh, N.K.; et al. Development of genomic simple sequence repeats (g-SSR) markers in Tinospora cordifolia and their application in diversity analyses. Plant Gene 2016, 5, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lade, S.; Pande, V.; Rana, T.S.; Yadav, H.K. Estimation of genetic diversity and population structure in Tinospora cordifolia using SSR markers. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Kumar, R.; Mahato, A.K.; Paliwal, R.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Marla, S.S.; Kumar, A.; Singh, N.K. De novo transcriptome sequencing facilitates genomic resource generation in Tinospora cordifolia. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2016, 16, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 1990, 12, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Muse, S.V. PowerMarker: An integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2128–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A. FigTreev1.4.2. A Graphical Viewer of Phylogenetic Trees. 2014. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peakall, R.O.; Smouse, P.E. GENALEX 6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol. Ecol. Notes. 2006, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.X.; Wang, P.; Gao, P.; Li, X.N.; Zhu, G.P. Microsatellite markers for assessing genetic diversity of the medicinal plant Paris polyphylla var. chinensis (Trilliaceae). Genet. Mol. Res. 2012, 11, 1975–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, M.; Banerjee, S.; Dhariwal, R.; Vyas, S.; Mir, R.R.; Topdar, N.; Kundu, A.; Khurana, J.P.; Tyagi, A.K.; Sarkar, D.; et al. Development of SSR markers and construction of a linkage map in jute. J. Genet. 2012, 91, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautami, B.; Ravi, K.; Narasu, M.L.; Hoisington, D.A.; Varshney, R.K. Novel set of groundnuts SSR markers for germplasm analysis and interspecific transferability. Int. J. Integr. Biol. 2009, 7, 100–106. [Google Scholar]
- Hvarleva, T.; Bakalova, A.; Chepinski, I.; Hristova-Cherbadji, M.; Hristov, M.; Atanasov, A. Characterization of Bulgarian sunflower cultivars and inbred lines with microsatellite markers. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2007, 21, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Botstein, D.; White, R.L.; Skolnick, M.; Davis, R. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1980, 32, 314–331. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Kim, C.-H.; Shin, D.-I.; Kim, S.-M.; Koo, H.M.; Park, Y. Development of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers to study diversity in the herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora). J. Med. Plant Res. 2011, 5, 6744–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.C.; Zhao, L.L.; Mo, B.T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.B. Genetic diversity of Ceratoides arborescens, a species endemic to China, detected by inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR). Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 5658–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.R.; Abreu, A.G.; Bajay, M.M.; Villela, P.M.; Batista, C.E.; Monteiro, M.; Alves-Pereira, A.; Figueira, G.M.; Pinheiro, J.B.; Appezzato-da-Glória, B.; et al. Development and Characterization of Microsatellite markers for the Medicinal Plant Smilax brasiliensis (Smilacaceae) and related species. Appl. Plant Sci. 2013, 1, 1200507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Ganesan, S.; Singh, R.; Choudhury, D.R.; Bharadwaj, J.; Gupta, V.; Singode, A. Genetic diversity and population structure study of drumstick (Moringa oleifera Lam.) using morphological and SSR markers. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 60, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.; Gepts, P. Structure of genetic diversity in the two major gene pools of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L., Fabaceae). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Wujisguleng, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Long, C. Isolation and characterization of polymorphic microsatellite loci for the valuable medicinal plant Astragalus Mongholicus. Open J. Genet. 2013, 3, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, C.; Paliwal, R.; Choudhury, D.R.; Singh, I.; Kumar, A.; Kumari, A.; Singh, R. Development of novel genomic simple sequence repeat (g-SSR) markers and their validation for genetic diversity analyses in Kalmegh [Andrographis paniculata (Burm. F.) Nees]. Plants 2020, 9, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.G.; Lin, Q.; Feng, Y.Z.; Hu, X.Y.; Tan, X.F.; Shao, F.G.; Zhang, L. Development and cross-species transferability of unigene-derived microsatellite markers in an edible oil woody plant, Camellia oleifera (Theaceae). Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 6906–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, V.; Kumar, V.; Bhardwaj, P.; Ahuja, P.S.; Sharma, R.K. Identification and cross-species transferability of 112 novel unigene-derived microsatellite markers in tea (Camellia sinensis). Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, e1–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Kumar, U.; Yadav, H.K. Identification of EST-SSRs and molecular diversity analysis in Mentha piperita. Crop. J. 2015, 3, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Gilmore, S.; Keys, W.; Morgante, M.; Rafalski, A. Cross-species amplification of soybean (Glycine max) simple sequence repeats (SSRs) within the genus and other legume genera: Implications for the transferability of SSRs in plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1998, 15, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Bai, Z.; Wang, F.; Zou, M.; Wang, X.; Xie, J.; Zhang, F. Analysis of the genetic diversity and population structure of Monochasma savatieri Franch. ex Maxim using novel EST-SSR markers. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, D.D.; Shah, S.N.M.; Pham, M.P.; Bui, V.T.; Nguyen, M.T.; Nguyen, T.P.T. De novo assembly and Transcriptome characterization of an endemic species of Vietnam, Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv., including the development of EST-SSR markers for population genetics. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Iqbal, R. SCoT molecular markers and population differentiation in Hedera helix L. Genetika 2021, 53, 739–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikendra, L.; Potshangbam, A.M.; Amom, T.; Dey, A.; Nongdam, P. Understanding the genetic diversity and population structure of Dendrobium chrysotoxum Lindl.-An endangered medicinal orchid and implication for its conservation. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 138, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, J.; Dwivedi, M.D.; Singh, N.; Uniyal, P.L.; Goel, S.; Pandey, A.K. Applicability of Start Codon Targeted (SCoT) and Inter Simple Sequence Repeat (ISSR) markers in assessing genetic diversity in Crepidium acuminatum (D. Don) Szlach. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2021, 23, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apana, N.; Amom, T.; Tikendra, L.; Potshangbam, A.M.; Dey, A.; Nongdam, P. Genetic diversity and population structure of Clerodendrum serratum (L.) Moon using CBDP, iPBS and SCoT markers. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2021, 25, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthiban, S.; Govindaraj, P.; Senthilkumar, S. Comparison of relative efficiency of genomic SSR and EST-SSR markers in estimating genetic diversity in sugarcane. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| S. No. | IC Number | Status | Source | District | State |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IC-281970 | Wild | Disturbed wild | Outer Delhi | Delhi |
| 2 | IC-281966 | Wild | Disturbed wild | Central Delhi | Delhi |
| 3 | IC-281965 | Wild | Disturbed wild | Central Delhi | Delhi |
| 4 | IC-281969 | Wild | Disturbed wild | West Delhi | Delhi |
| 5 | IC-281952 | Wild | Disturbed wild | Central Delhi | Delhi |
| 6 | IC-281973 | Wild | Disturbed wild | West Delhi | Delhi |
| 7 | IC-417323 | Wild | Natural wild | Balrampur | Uttar Pradesh |
| 8 | IC-471321 | Wild | Disturbed wild | Balrampur | Uttar Pradesh |
| 9 | IC-281955 | Wild | Natural wild | Central Delhi | Delhi |
| 10 | IC-417328 | Wild | Natural wild | Faizabad | Uttar Pradesh |
| 11 | IC-281960 | Wild | Disturbed wild | Outer Delhi | Delhi |
| 12 | IC-281963 | Wild | Disturbed wild | Central Delhi | Delhi |
| 13 | IC-417327 | Wild | Natural wild | Basti | Uttar Pradesh |
| 14 | IC-281967 | Wild | Disturbed wild | West Delhi | Delhi |
| 15 | IC-281954 | Wild | Disturbed wild | Central Delhi | Delhi |
| 16 | IC-281962 | Wild | Disturbed wild | North Delhi | Delhi |
| 17 | IC-281961 | Wild | Disturbed wild | North Delhi | Delhi |
| 18 | IC-281972 | Wild | Disturbed wild | Outer Delhi | Delhi |
| 19 | IC-281968 | Wild | Disturbed wild | West Delhi | Delhi |
| 20 | IC-281959 | Wild | Disturbed wild | West Delhi | Delhi |
| 21 | IC-281958 | Wild | Disturbed wild | North Delhi | Delhi |
| 22 | IC-281957 | Wild | Disturbed wild | Central Delhi | Delhi |
| 23 | IC-281971 | Wild | Disturbed wild | Outer Delhi | Delhi |
| 24 | IC-281953 | Wild | Garden | Central Delhi | Delhi |
| 25 | KCOP/41 | Wild | Garden | Sirsa | Haryana |
| 26 | KCOP/18 | Wild | Disturbed wild | Mahendragarh | Haryana |
| 27 | KCB/38 a | Wild | Disturbed wild | North Cachar Hills | Assam |
| 28 | KC/NS/GD-42/14 b | Wild | Disturbed wild | East Siang | Arunachal Pradesh |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paliwal, R.; Singh, R.; Choudhury, D.R.; Tiwari, G.; Kumar, A.; Bhat, K.C.; Singh, R. Molecular Characterization of Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.) Miers Using Novel g-SSR Markers and Their Comparison with EST-SSR and SCoT Markers for Genetic Diversity Study. Genes 2022, 13, 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112042
Paliwal R, Singh R, Choudhury DR, Tiwari G, Kumar A, Bhat KC, Singh R. Molecular Characterization of Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.) Miers Using Novel g-SSR Markers and Their Comparison with EST-SSR and SCoT Markers for Genetic Diversity Study. Genes. 2022; 13(11):2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112042
Chicago/Turabian StylePaliwal, Ritu, Rakesh Singh, Debjani Roy Choudhury, Gunjan Tiwari, Ashok Kumar, K. C. Bhat, and Rita Singh. 2022. "Molecular Characterization of Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.) Miers Using Novel g-SSR Markers and Their Comparison with EST-SSR and SCoT Markers for Genetic Diversity Study" Genes 13, no. 11: 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112042
APA StylePaliwal, R., Singh, R., Choudhury, D. R., Tiwari, G., Kumar, A., Bhat, K. C., & Singh, R. (2022). Molecular Characterization of Tinospora cordifolia (Willd.) Miers Using Novel g-SSR Markers and Their Comparison with EST-SSR and SCoT Markers for Genetic Diversity Study. Genes, 13(11), 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112042








