The Sex-Specific Splicing of Doublesex in Brine Shrimp Artemia franciscana
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Culture
2.2. Total RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.3. Identification of Putative of Dsx/Dmrt Transcripts
2.4. Isolation Full-Length of Dsx/Dmrt Transcript
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.6. Transcription Proof of Dsx/Dmrt Transcript
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Dsx/Dmrt Transcripts
3.2. Genome Mapping and Putative Protein Translation
3.3. Phylogenetic Tree
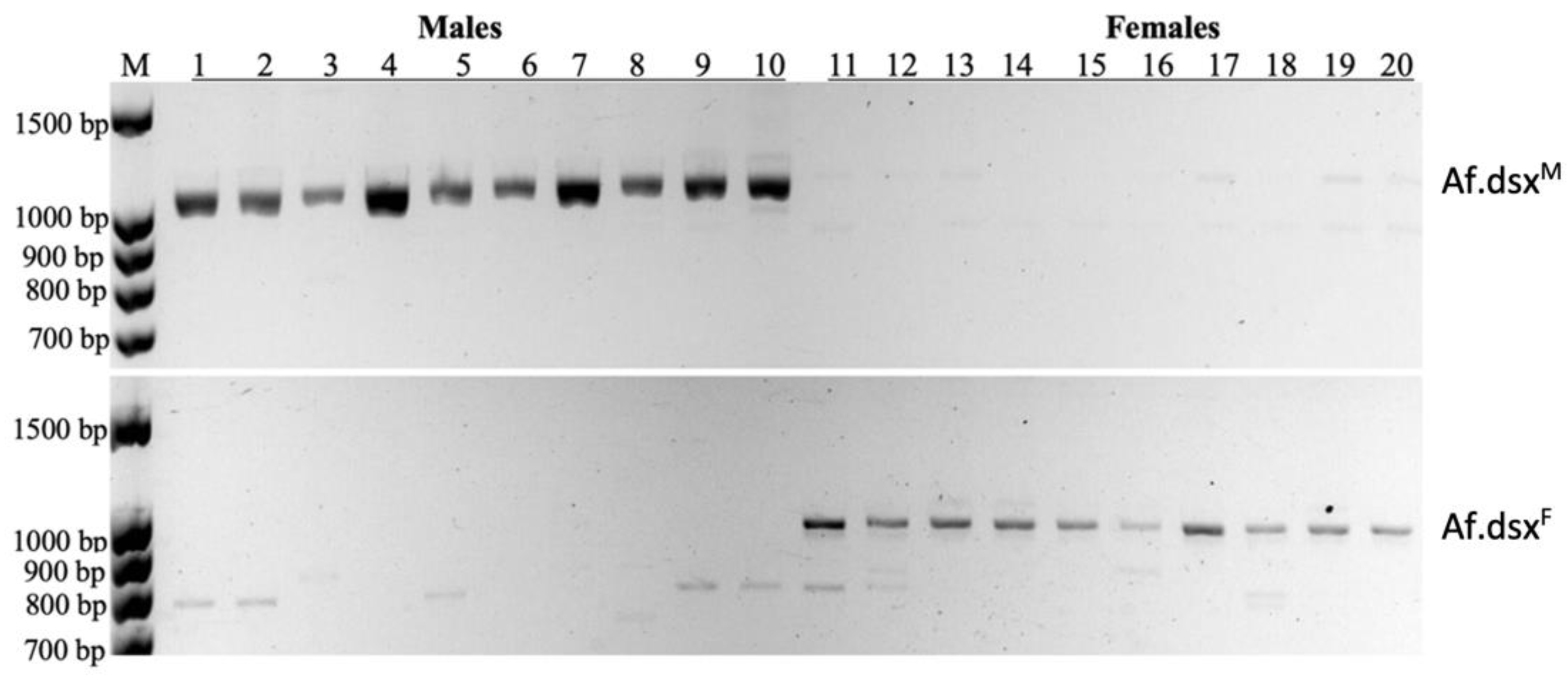
3.4. Sex-Specific Splicing of Doublesex Gene
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Vos, S.; Bossier, P.; Van Stappen, G.; Vercauteren, I.; Sorgeloos, P.; Vuylsteke, M. A First AFLP-Based Genetic Linkage Map for Brine Shrimp Artemia franciscana and Its Application in Mapping the Sex Locus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, S.T. The Genetics of Artemia salina. V. Crossing over between the X and Y Chromosomes. Genetics 1965, 52, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnes, S.; Khalaila, I.; Hulata, G.; Sagi, A. Sex Determination in Crayfish: Are Intersex Cherax quadricarinatus (Decapoda, Parastacidae) Genetically Females? Genet. Res. 2003, 82, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staelens, J.; Rombaut, D.; Vercauteren, I.; Argue, B.; Benzie, J.; Vuylsteke, M. High-Density Linkage Maps and Sex-Linked Markers for the Black Tiger Shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Genetics 2008, 179, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, T.; Sagi, A. The Insulin-like Androgenic Gland Hormone in Crustaceans: From a Single Gene Silencing to a Wide Array of Sexual Manipulation-Based Biotechnologies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Hui, M.; Liu, Y.; Song, C.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Shi, G.; Wang, S.; Li, F.; et al. High-Density Linkage Mapping Aided by Transcriptomics Documents ZW Sex Determination System in the Chinese Mitten Crab Eriocheir sinensis. Heredity 2015, 115, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huylmans, A.K.; Toups, M.A.; MacOn, A.; Gammerdinger, W.J.; Vicoso, B. Sex-Biased Gene Expression and Dosage Compensation on the Artemia Franciscana Z-Chromosome. Genome Biol Evol 2019, 11, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.; Lee, S.J.; Choi, E.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.H.; Park, H. Sex-Biased Gene Expression and Isoform Profile of Brine Shrimp Artemia Franciscana by Transcriptome Analysis. Animals 2021, 11, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-R.; Ye, H.-L.; Yang, J.-S.; Yang, F.; Wang, M.-R.; de Vos, S.; Vuylsteke, M.; Sorgeloos, P.; van Stappen, G.; Bossier, P.; et al. Identification and Characterization of a Masculinizer (Masc) Gene Involved in Sex Differentiation in Artemia. Gene 2017, 614, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhan, S.; Chen, S.; Zeng, B.; Li, Z.; James, A.A.; Tan, A.; Huang, Y. Sexually Dimorphic Traits in the Silkworm, Bombyx Mori, Are Regulated by Doublesex. Insect Biochem Mol. Biol 2017, 80, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawaribuchi, S.; Ito, Y.; Ito, M. Independent Evolution for Sex Determination and Differentiation in the DMRT Family in Animals. Biol. Open 2019, 8, bio041962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burtis, K.C.; Baker, B.S. Drosophila Doublesex Gene Controls Somatic Sexual Differentiation by Producing Alterna-tively Spliced MRNAs Encoding Related Sex-Specific Polypeptides. Cell 1989, 56, 997–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhulst, E.C.; van de Zande, L. Double Nexus—Doublesex Is the Connecting Element in Sex Determination. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2015, 14, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Yoon, B.-H.; Kim, W.-J.; Kim, D.-W.; Hurwood, D.A.; Lyons, R.E.; Salin, K.R.; Kim, H.-S.; Baek, I.; Chand, V.; et al. Optimizing Hybrid de Novo Transcriptome Assembly and Extending Genomic Resources for Giant Freshwater Prawns (Macrobrachium Rosenbergii): The Identification of Genes and Markers Associated with Re-production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-Q.; Ma, W.-M.; Zeng, Q.-G.; Qian, Y.-Q.; Yang, J.-S.; Yang, W.-J. Molecular Cloning and Sexually Di-morphic Expression of Two Dmrt Genes in the Giant Freshwater Prawn, Macrobrachium Rosenbergii. Agric. Res. 2014, 3, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amterat Abu Abayed, F.; Manor, R.; Aflalo, E.D.; Sagi, A. Screening for Dmrt Genes from Embryo to Mature Macro-brachium Rosenbergii Prawns. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 282, 113205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, P.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yi, J.; Lin, W.; Guo, Z.; Xu, A.; Yang, S.; Chan, S.; et al. Potential Involvement of a DMRT Family Member (Mr-Dsx) in the Regulation of Sexual Differentiation and Moulting in the Giant River Prawn Macrobrachium Rosenbergii. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 3037–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Qiu, G.; Feng, J.; Li, J. Transcriptome Analysis of the Oriental River Prawn, Macrobrachium Nipponense Using 454 Pyrosequencing for Discovery of Genes and Markers. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, E.F.; Qiu, G.F. A Novel Dmrt Gene Is Specifically Expressed in the Testis of Chinese Mitten Crab, Eriocheir Sinensis. Dev. Genes. Evol. 2010, 220, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, F.; Yu, K.; Xiang, J. Identification and Characterization of a Doublesex Gene Which Regulates the Expression of Insulin-like Androgenic Gland Hormone in Fenneropenaeus Chinensis. Gene 2018, 649, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wei, P.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, D.; Chen, X.; Li, M.; Chen, X. Gonadal Transcriptomic Analysis and Dif-ferentially Expressed Genes in the Testis and Ovary of the Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus Vannamei). BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Watanabe, H.; Iguchi, T. Environmental Sex Determination in the Branchiopod Crustacean Daphnia Magna: Deep Consevation of a Doublesex Gene in the Sex-Determining Pathway. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, J.C.; Fitzgibbon, Q.P.; Smith, G.; Elizur, A.; Ventura, T. Y-Linked IDmrt1 Paralogue (IDMY) in the Eastern Spiny Lobster, Sagmariasus Verreauxi: The First Invertebrate Sex-Linked Dmrt. Dev. Biol. 2017, 430, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, S.; van Stappen, G.; Sorgeloos, P.; Vuylsteke, M.; Rombauts, S.; Bossier, P. Identification of Salt Stress Response Genes Using the Artemia Transcriptome. Aquaculture 2019, 500, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A New Generation of Protein Database Search Programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemoine, F.; Correia, D.; Lefort, V.; Doppelt-Azeroual, O.; Mareuil, F.; Cohen-Boulakia, S.; Gascuel, O. NGPhyloge-ny.Fr: New Generation Phylogenetic Services for Non-Specialists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W260–W265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, W.; Zarkower, D. Similarity of DNA Binding and Transcriptional Regulation by Caenorhabditis Elegans MAB-3 and Drosophila Melanogaster DSX Suggests Conservation of Sex Determining Mechanisms. Development 1999, 126, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrer, J.R.; Zhang, W.; Weiss, M.A. Dimerization of Doublesex Is Mediated by a Cryptic Ubiquitin-Associated Domain Fold: Implications for Sex-Specific Gene Regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 32989–32996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, W.; Cho, S.; Ishii, H.; Wensink, P.C. Sex-Specific and Non-Sex-Specific Oligomerization Domains in Both of the Doublesex Transcription Factors from Drosophila Melanogaster. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 3106–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, S. Genomic Tools and Sex Determination in the Extremophile Brine Shrimp Artemia franciscana. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Bioscience Engineering, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Oda, S.; Colbourn, J.K.; Tatarazako, N.; Watanabe, H.; Iguchi, T. Molecular Cloning and Sexually Dimorphic Expression of DM-Domain Genes in Daphnia Magna. Genomics 2008, 91, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuchi, T.; Koga, H.; Kawamoto, M.; Shoji, K.; Sakai, H.; Arai, Y. A Single Female-Specific PiRNA Is the Primary Determiner of Sex in the Silkworm. Nature 2014, 509, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nong, Q.D.; Matsuura, T.; Kato, Y.; Watanabe, H. Two Doublesex1 Mutants Revealed a Tunable Gene Network Underlying Intersexuality in Daphnia magna. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Singh, R.; Narendra, U.; Zhu, L.; Weiss, M.A. Regulation of Sexual Dimorphism: Mutational and Chemogenetic Analysis of the Doublesex DM Domain. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Xu, H.; Guo, H.; O’Brochta, D.A.; Wang, F.; Ma, S.; Zhang, L.; Zha, X.; Zhao, P.; Xia, Q. New Insights into the Genomic Organization and Splicing of the Doublesex Gene, a Terminal Regulator of Sexual Differ-entiation in the Silkworm Bombyx Mori. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, F.; Ma, S.; Zha, X.; Guo, H.; Zhao, P.; Xia, Q. Novel Female-Specific Trans-Spliced and Al-ternative Splice Forms of Dsx in the Silkworm Bombyx Mori. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 431, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Genes | Gene-Specific Primers (5′-3′) | Size in bp |
|---|---|---|
| Doublesex-1 (Dmrt93B) | For: ATCCTTTGGGACAATGGATGTTACACTC Rev: CTTTCATAGTGTTGTCAAAACGCGC | 903 |
| Doublesex-2 (Dmrt99B) | For: TGGGAGAGAGACAGGAATGTAAATACATAC Rev: GCAGCTCTGAGTGATACCAAAAAATTAAG | 1459 |
| Doublesex-3 | For: ATATGAAGTGAGCAATGGTGATACGC Rev CGAATTCGTTTAATCACACATTTAAGGCCAC | 1169 |
| Af.dsx-4 | Af.dsxF-For: TCTTCAACCATGAAAACAAACAGGCATCTACC Af.dsxF-Rev-A: ATGTTTTCTGGTGTCTTCTCTGTCACAAC | 920 |
| Af.dsx4-For: TCTTCAACCATGAAAACAAACAGGCATCTACC Af.dsx4-Rev-B: AGAAAGAGATGGTGGAAATTGC | 1010 | |
| Af.dsxM-For: AGTTCGGTTTGTGGTTCCTCACGG Af.dsxM-Rev-C: CAGGCCAATTTTTTGAATATTATCTAGAAGC | 1124 | |
| Doublesex-5 | For: CTACTATCTTACACCTAAGTGCGCCTGAG Rev: GCAACGATTGAAGAGAAATGGGAAAGGATC | 918 |
| Doublesex-6 (Dmrt11E) | For: GATTAAACGAACTAAGGCCAGAGAGA Rev: CACAAAGAACGAAAATAAGAAACTAACACAC | 966 |
| Tubulin | For: GCAGTGGTCTACAAGGTTTC | 605 |
| Rev: TGCATTGACGTCTTTTGGTACGACATCTC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viet, D.N.; Christiaens, O.; De Vos, S.; Smagghe, G.; Bossier, P. The Sex-Specific Splicing of Doublesex in Brine Shrimp Artemia franciscana. Genes 2022, 13, 1997. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13111997
Viet DN, Christiaens O, De Vos S, Smagghe G, Bossier P. The Sex-Specific Splicing of Doublesex in Brine Shrimp Artemia franciscana. Genes. 2022; 13(11):1997. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13111997
Chicago/Turabian StyleViet, Dung Nguyen, Olivier Christiaens, Stephanie De Vos, Guy Smagghe, and Peter Bossier. 2022. "The Sex-Specific Splicing of Doublesex in Brine Shrimp Artemia franciscana" Genes 13, no. 11: 1997. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13111997
APA StyleViet, D. N., Christiaens, O., De Vos, S., Smagghe, G., & Bossier, P. (2022). The Sex-Specific Splicing of Doublesex in Brine Shrimp Artemia franciscana. Genes, 13(11), 1997. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13111997






