Performance Evaluation of SpliceAI for the Prediction of Splicing of NF1 Variants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
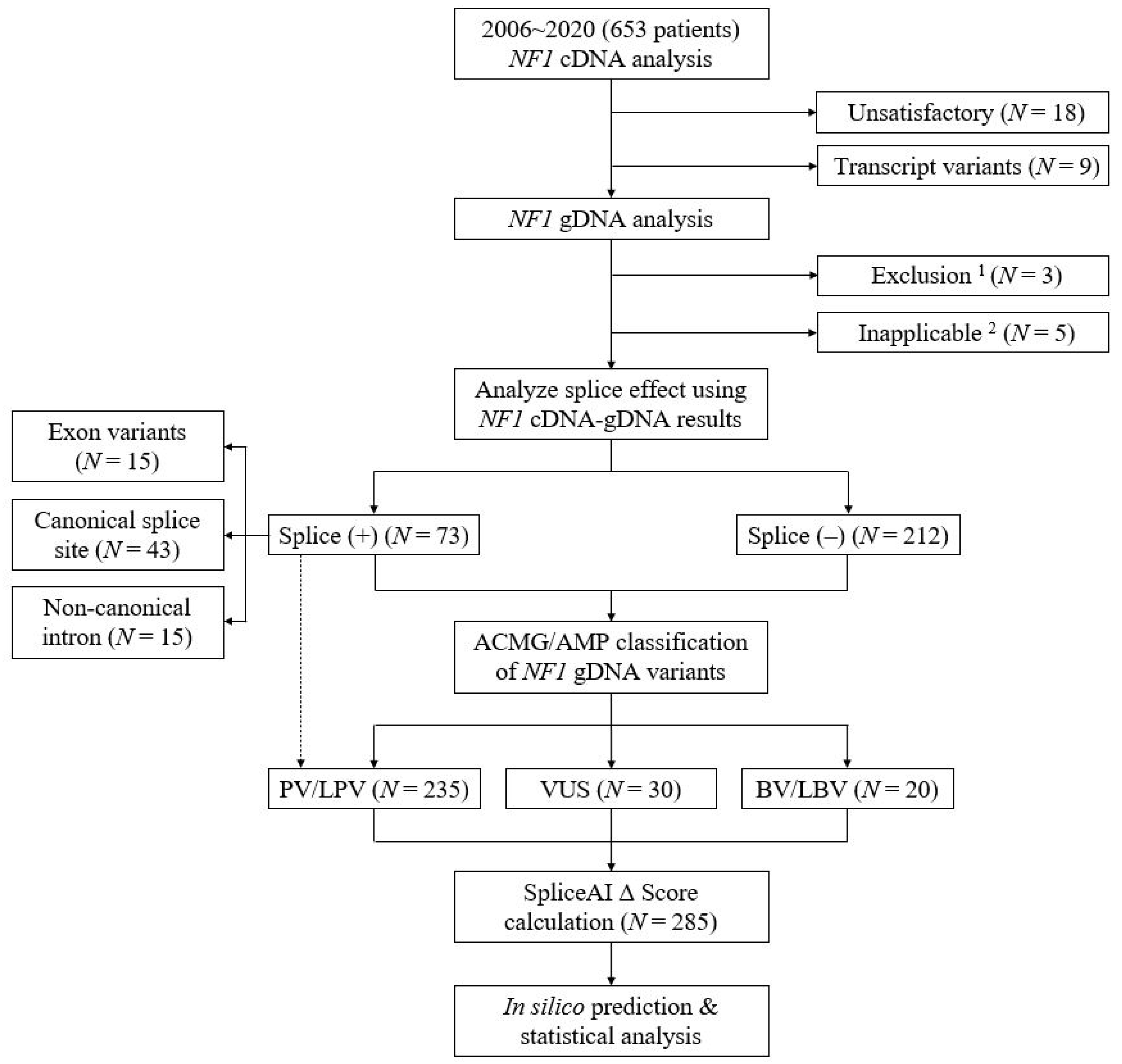
2.1. Characteristics of Variants
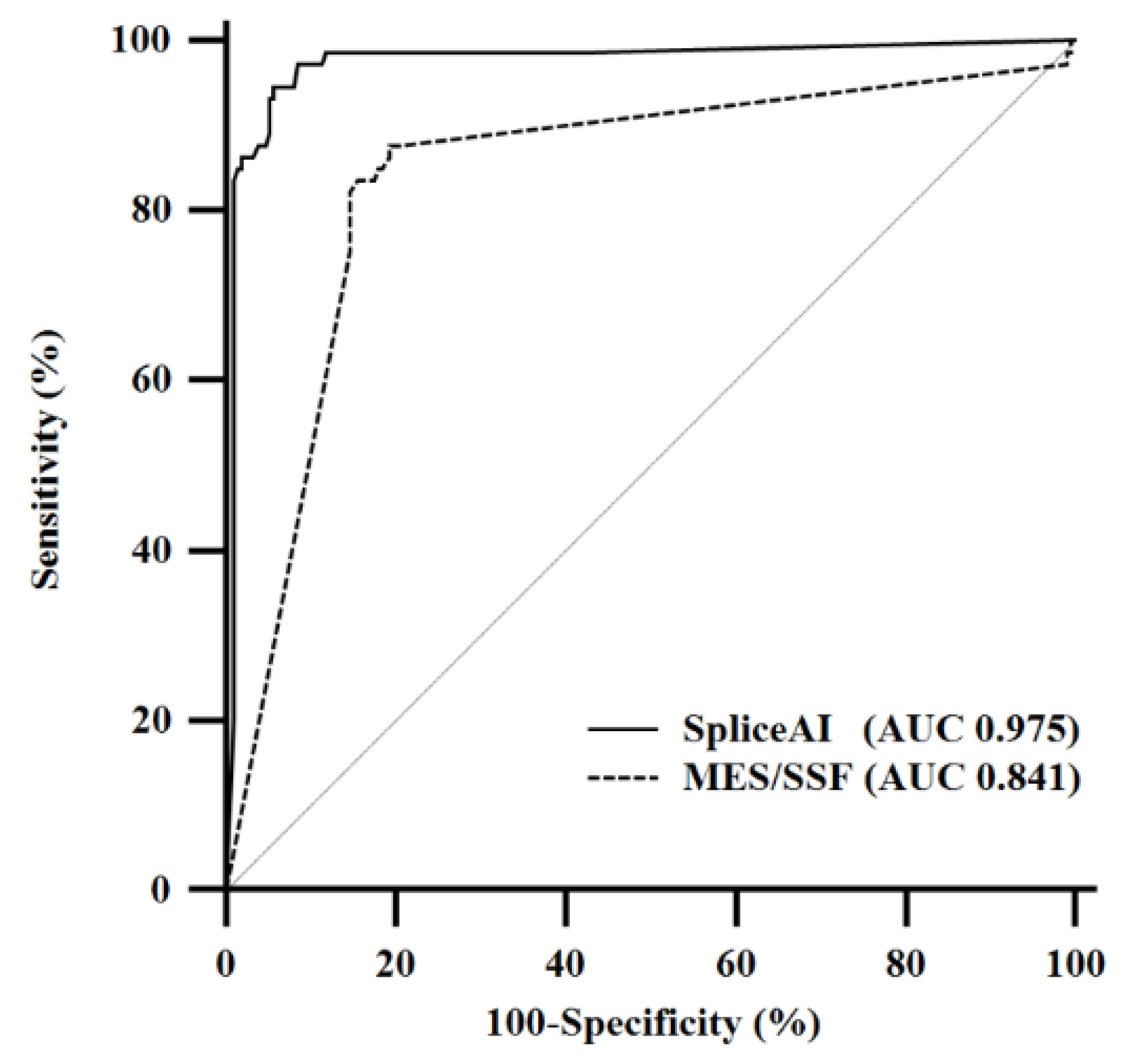
2.2. Sensitivity and Specificity
2.3. Pairwise Comparison of Receiver Operating Characteristic Curves
2.4. Concordance Rate
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Subjects
4.2. Complementary DNA and Genomic DNA Sequencing
4.3. Splicing Prediction
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutmann, D.H.; Ferner, R.E.; Listernick, R.H.; Korf, B.R.; Wolters, P.L.; Johnson, K.J. Neurofibromatosis type 1. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutmann, D.H.; Wood, D.L.; Collins, F.S. Identification of the neurofibromatosis type 1 gene product. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 9658–9662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabbagh, A.; Pasmant, E.; Imbard, A.; Luscan, A.; Soares, M.; Blanché, H.; Laurendeau, I.; Ferkal, S.; Vidaud, M.; Pinson, S.; et al. NF1 molecular characterization and neurofibromatosis type I genotype-phenotype correlation: The French experience. Hum. Mutat. 2013, 34, 1510–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferner, R.E. Neurofibromatosis 1 and neurofibromatosis 2: A twenty first century perspective. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenson, P.D.; Mort, M.; Ball, E.V.; Shaw, K.; Phillips, A.; Cooper, D.N. The Human Gene Mutation Database: Building a comprehensive mutation repository for clinical and molecular genetics, diagnostic testing and personalized genomic medicine. Hum. Genet. 2014, 133, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Messiaen, L.M.; Callens, T.; Mortier, G.; Beysen, D.; Vandenbroucke, I.; Van Roy, N.; Speleman, F.; Paepe, A.D. Exhaustive mutation analysis of the NF1 gene allows identification of 95% of mutations and reveals a high frequency of unusual splicing defects. Hum. Mutat. 2000, 15, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ars, E.; Kruyer, H.; Morell, M.; Pros, E.; Serra, E.; Ravella, A.; Estivill, X.; Lázaro, C. Recurrent mutations in the NF1 gene are common among neurofibromatosis type 1 patients. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wimmer, K.; Roca, X.; Beiglböck, H.; Callens, T.; Etzler, J.; Rao, A.R.; Krainer, A.R.; Fonatsch, C.; Messiaen, L. Extensive in silico analysis of NF1 splicing defects uncovers determinants for splicing outcome upon 5’ splice-site disruption. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, M.C.; Martín, Y.; Hernández-Imaz, E.; Marina Hernández, A.; Meleán, G.; Valero, A.M.; Javier Rodríguez-Álvarez, F.; Tellería, D.; Hernández-Chico, C. A highly sensitive genetic protocol to detect NF1 mutations. J. Mol. Diagn. 2011, 13, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Su, Y.N.; You, H.L.; Chiou, S.C.; Lin, L.C.; Yang, C.C.; Lee, W.C.; Hwu, W.L.; Hsieh, F.J.; Stephenson, D.A.; et al. Identification of forty-five novel and twenty-three known NF1 mutations in Chinese patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. Hum. Mutat. 2006, 27, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahsold, R.; Hoffmeyer, S.; Mischung, C.; Gille, C.; Ehlers, C.; Kücükceylan, N.; Abdel-Nour, M.; Gewies, A.; Peters, H.; Kaufmann, D.; et al. Minor lesion mutational spectrum of the entire NF1 gene does not explain its high mutability but points to a functional domain upstream of the GAP-related domain. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 66, 790–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallego Romero, I.; Pai, A.A.; Tung, J.; Gilad, Y. RNA-seq: Impact of RNA degradation on transcript quantification. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garneau, N.L.; Wilusz, J.; Wilusz, C.J. The highways and byways of mRNA decay. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, K.; Panagiotopoulou, S.K.; McRae, J.F.; Darbandi, S.F.; Knowles, D.; Li, Y.I.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Arbelaez, J.; Cui, W.; Schwartz, G.B.; et al. Predicting Splicing from Primary Sequence with Deep Learning. Cell 2019, 176, 535–548.e524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanley, J.A.; McNeil, B.J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeo, G.; Burge, C.B. Maximum entropy modeling of short sequence motifs with applications to RNA splicing signals. J. Comput. Biol. J. Comput. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 11, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, M.B.; Senapathy, P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: Sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 7155–7174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houdayer, C.; Caux-Moncoutier, V.; Krieger, S.; Barrois, M.; Bonnet, F.; Bourdon, V.; Bronner, M.; Buisson, M.; Coulet, F.; Gaildrat, P.; et al. Guidelines for splicing analysis in molecular diagnosis derived from a set of 327 combined in silico/in vitro studies on BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leman, R.; Gaildrat, P.; Le Gac, G.; Ka, C.; Fichou, Y.; Audrezet, M.P.; Caux-Moncoutier, V.; Caputo, S.M.; Boutry-Kryza, N.; Léone, M.; et al. Novel diagnostic tool for prediction of variant spliceogenicity derived from a set of 395 combined in silico/in vitro studies: An international collaborative effort. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 7913–7923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Houdayer, C.; Dehainault, C.; Mattler, C.; Michaux, D.; Caux-Moncoutier, V.; Pagès-Berhouet, S.; d’Enghien, C.D.; Laugé, A.; Castera, L.; Gauthier-Villars, M.; et al. Evaluation of in silico splice tools for decision-making in molecular diagnosis. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moles-Fernández, A.; Duran-Lozano, L.; Montalban, G.; Bonache, S.; López-Perolio, I.; Menéndez, M.; Santamariña, M.; Behar, R.; Blanco, A.; Carrasco, E.; et al. Computational Tools for Splicing Defect Prediction in Breast/Ovarian Cancer Genes: How Efficient Are They at Predicting RNA Alterations? Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wai, H.A.; Lord, J.; Lyon, M.; Gunning, A.; Kelly, H.; Cibin, P.; Seaby, E.G.; Spiers-Fitzgerald, K.; Lye, J.; Ellard, S.; et al. Blood RNA analysis can increase clinical diagnostic rate and resolve variants of uncertain significance. Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joynt, A.T.; Evans, T.A.; Pellicore, M.J.; Davis-Marcisak, E.F.; Aksit, M.A.; Eastman, A.C.; Patel, S.U.; Paul, K.C.; Osorio, D.L.; Bowling, A.D.; et al. Evaluation of both exonic and intronic variants for effects on RNA splicing allows for accurate assessment of the effectiveness of precision therapies. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1009100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Yang, S.; Lim, K.H.; Ko, E.; Jang, H.J.; Kang, M.; Suh, P.G.; Joo, J.Y. Prediction of Alzheimer’s disease-specific phospholipase c gamma-1 SNV by deep learning-based approach for high-throughput screening. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2011250118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, X.; Boerwinkle, E.; Liu, X. In silico prediction of splice-altering single nucleotide variants in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 13534–13544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrow, J.; Frankish, A.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Tapanari, E.; Diekhans, M.; Kokocinski, F.; Aken, B.L.; Barrell, D.; Zadissa, A.; Searle, S.; et al. GENCODE: The reference human genome annotation for The ENCODE Project. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1760–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frankish, A.; Diekhans, M.; Jungreis, I.; Lagarde, J.; Loveland, J.E.; Mudge, J.M.; Sisu, C.; Wright, J.C.; Armstrong, J.; Barnes, I.; et al. GENCODE 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D916–D923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonsdale, J.; Thomas, J.; Salvatore, M.; Phillips, R.; Lo, E.; Shad, S.; Hasz, R.; Walters, G.; Garcia, F.; Young, N.; et al. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GTEx Consortium. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) pilot analysis: Multitissue gene regulation in humans. Science 2015, 348, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, M.A.; Kim, Y.E.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, J.W.; Ki, C.S. Identification and characterization of NF1 splicing mutations in Korean patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 61, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Prosser, D.O.; Love, D.R. Evaluation of Bioinformatic Programmes for the Analysis of Variants within Splice Site Consensus Regions. Adv. Bioinform. 2016, 2016, 5614058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wappenschmidt, B.; Becker, A.A.; Hauke, J.; Weber, U.; Engert, S.; Köhler, J.; Kast, K.; Arnold, N.; Rhiem, K.; Hahnen, E.; et al. Analysis of 30 putative BRCA1 splicing mutations in hereditary breast and ovarian cancer families identifies exonic splice site mutations that escape in silico prediction. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50800. [Google Scholar]
- Reese, M.G.; Eeckman, F.H.; Kulp, D.; Haussler, D. Improved splice site detection in Genie. J. Comput. Biol. J. Comput. Mol. Cell Biol. 1997, 4, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmet, F.O.; Hamroun, D.; Lalande, M.; Collod-Béroud, G.; Claustres, M.; Béroud, C. Human Splicing Finder: An online bioinformatics tool to predict splicing signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stella, A.; Lastella, P.; Loconte, D.C.; Bukvic, N.; Varvara, D.; Patruno, M.; Bagnulo, R.; Lovaglio, R.; Bartolomeo, N.; Serio, G.; et al. Accurate Classification of NF1 Gene Variants in 84 Italian Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Genes 2018, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.M.; Lin, J.H.; Masson, E.; Liao, Z.; Férec, C.; Cooper, D.N.; Hayden, M. The Experimentally Obtained Functional Impact Assessments of 5’ Splice Site GT’GC Variants Differ Markedly from Those Predicted. Curr. Genom. 2020, 21, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Igelman, A.D.; Jones, K.D.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Goetz, K.E.; Birch, D.G.; Yang, P.; et al. Identification of Deep-Intronic Splice Mutations in a Large Cohort of Patients With Inherited Retinal Diseases. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 647400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Dunnen, J.T.; Dalgleish, R.; Maglott, D.R.; Hart, R.K.; Greenblatt, M.S.; McGowan-Jordan, J.; Roux, A.F.; Smith, T.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Taschner, P.E. HGVS Recommendations for the Description of Sequence Variants: 2016 Update. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best Practice Guidelines—Association for Clinical Genomic Science (ACGS Best Practice Guidelines for Variant Classification in Rare Disease 2020 v4.01). Available online: https://www.acgs.uk.com/quality/best-practice-guidelines/#VariantGuidelines (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Cartegni, L.; Chew, S.L.; Krainer, A.R. Listening to silence and understanding nonsense: Exonic mutations that affect splicing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variant Classification | Number of Different Variants | SpliceAI Δ Score 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Total variants | 285 | 0.01 (0.00–0.36) |
| Splice variants | 73 | 0.98 (0.80–0.99) |
| Variant location | ||
| Canonical splice-site | 43 | 0.99 (0.95–1.00) |
| Non-canonical intronic region | 15 | 0.91 (0.55–0.98) |
| Exon | 15 | 0.54 (0.13–0.99) |
| Splicing classification 2 | ||
| Type I | 35 | 0.97 (0.87–1.00) |
| Type II | 3 | 0.76 (0.72–0.93) |
| Type III | 5 | 0.99 (0.97–1.00) |
| Type IV | 20 | 0.99 (0.98–1.00) |
| Type V | 10 | 0.30 (0.12–0.62) |
| Non-splice variants | 212 | 0.00 (0.00–0.02) |
| Frameshift | 68 | 0.00 (0.00–0.04) |
| Nonsense | 68 | 0.01 (0.00–0.03) |
| Missense | 48 | 0.00 (0.00–0.01) |
| Synonymous | 22 | 0.00 (0.00–0.01) |
| In-frame deletion | 5 | 0.00 (0.00–0.01) |
| Start loss | 1 | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) |
| Method | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|
| N/Total N% (95% CI) | N/Total N% (95% CI) | |
| SpliceAI | 69/73 | 200/212 |
| 94.5% (86.6–98.5%) | 94.3% (90.3–97.0%) | |
| MES/SSF | 61/73 | 175/212 |
| 83.6% (73.1–91.2%) | 82.5% (76.8–87.4%) |
| Method | MES/SSF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Total | ||
| Positive | 67 | 14 | 80 | |
| SpliceAI | Negative | 31 | 173 | 205 |
| Total | 98 | 187 | 285 | |
| Positive percent agreement = 68.4% (95% CI, 58.6–76.7) Negative percent agreement = 92.5% (95% CI, 87.8–95.5) Kappa value = 0.64 (95% CI, 0.54–0.73) | ||||
| Variant Region | Discrepant Prediction SpliceAI/MES/SSF | Number of Variants | Splice +/− Identified by cDNA and gDNA Seq 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exon | −/+ | 31 | 0/31 |
| +/− | 9 | 3/6 | |
| Canonial splice-site | −/+ | 0 | 0/0 |
| +/− | 3 | 3/0 | |
| Non-canonical intronic region | −/+ | 0 | 0/0 |
| +/− | 2 | 2/0 | |
| Total | −/+ | 31 | 0/31 |
| +/− | 14 | 8/6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ha, C.; Kim, J.-W.; Jang, J.-H. Performance Evaluation of SpliceAI for the Prediction of Splicing of NF1 Variants. Genes 2021, 12, 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12091308
Ha C, Kim J-W, Jang J-H. Performance Evaluation of SpliceAI for the Prediction of Splicing of NF1 Variants. Genes. 2021; 12(9):1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12091308
Chicago/Turabian StyleHa, Changhee, Jong-Won Kim, and Ja-Hyun Jang. 2021. "Performance Evaluation of SpliceAI for the Prediction of Splicing of NF1 Variants" Genes 12, no. 9: 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12091308
APA StyleHa, C., Kim, J.-W., & Jang, J.-H. (2021). Performance Evaluation of SpliceAI for the Prediction of Splicing of NF1 Variants. Genes, 12(9), 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12091308






