GNAI2 Promotes Proliferation and Decreases Apoptosis in Rabbit Melanocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. Overexpression Vector Construction
2.4. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.5. Indirect Immunofluorescence Staining Assay
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) Analysis
2.7. Protein Preparation and Western Blotting
2.8. Melanin Content Measurement
2.9. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.10. Apoptosis Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
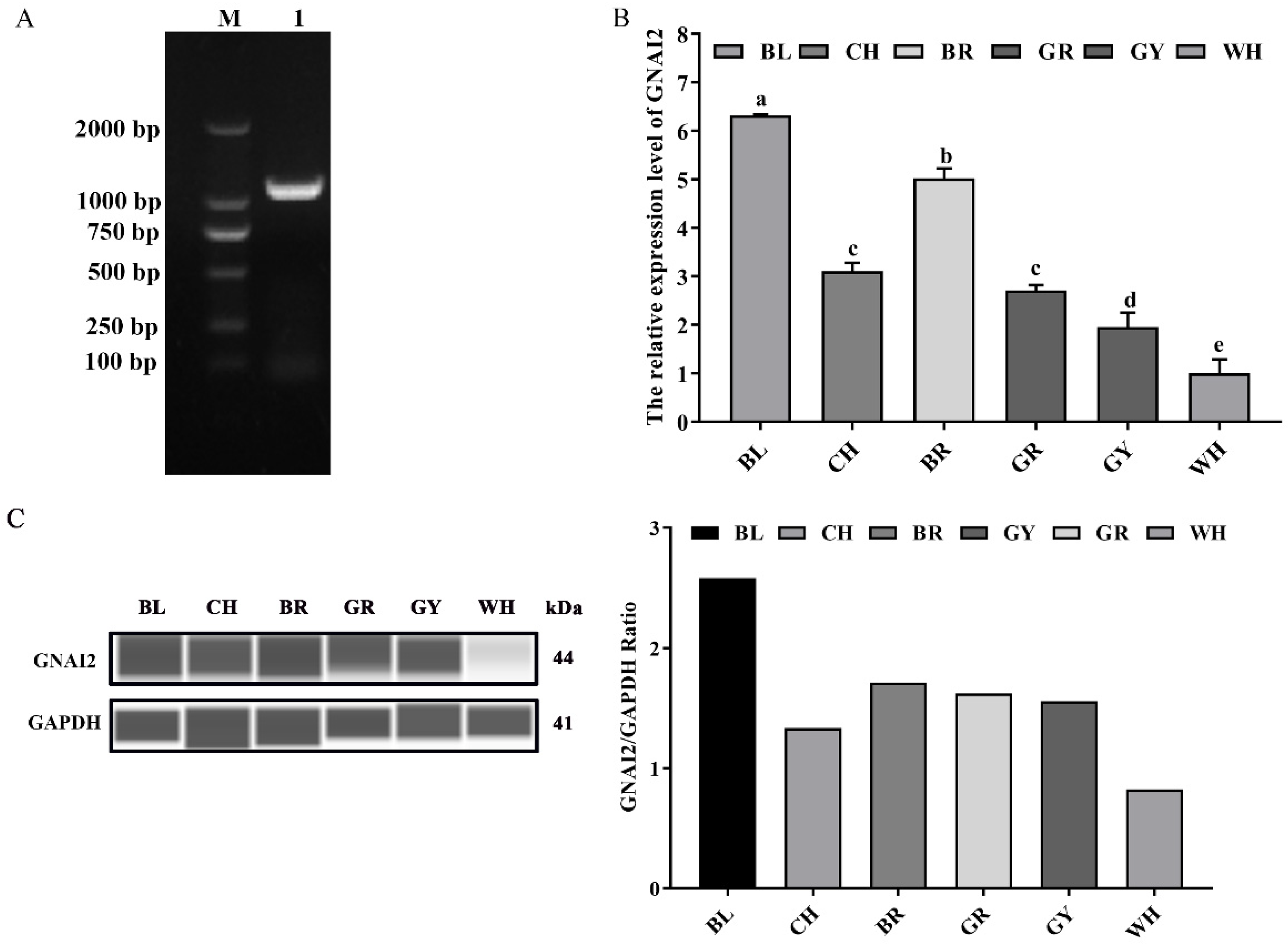
3.1. GNAI2 Was Differentially Expressed in the Skin of Rabbits with Different Coat Colors
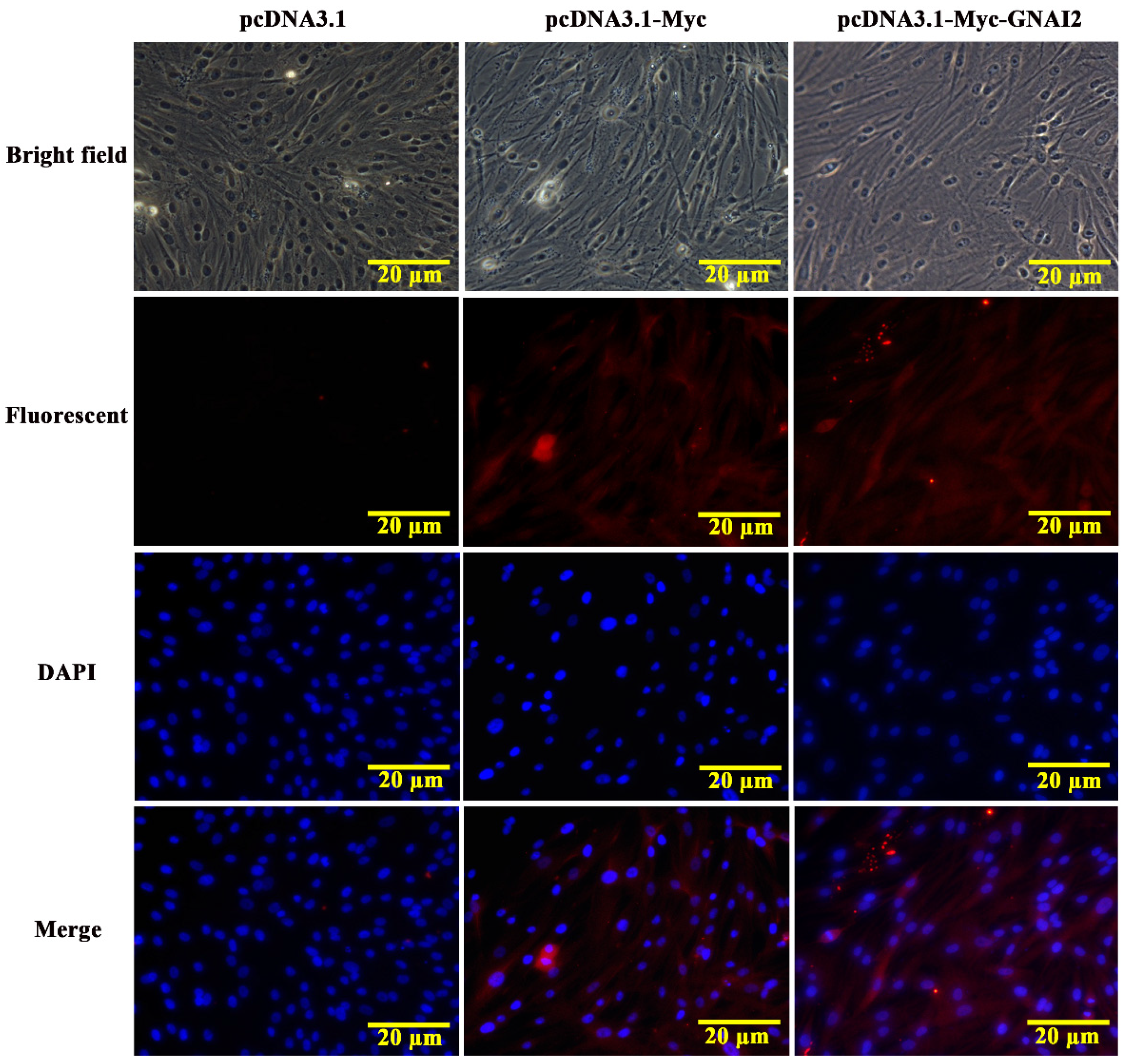
3.2. GNAI2 Protein Was Mainly Localized in the Cytoplasm of Melanocytes
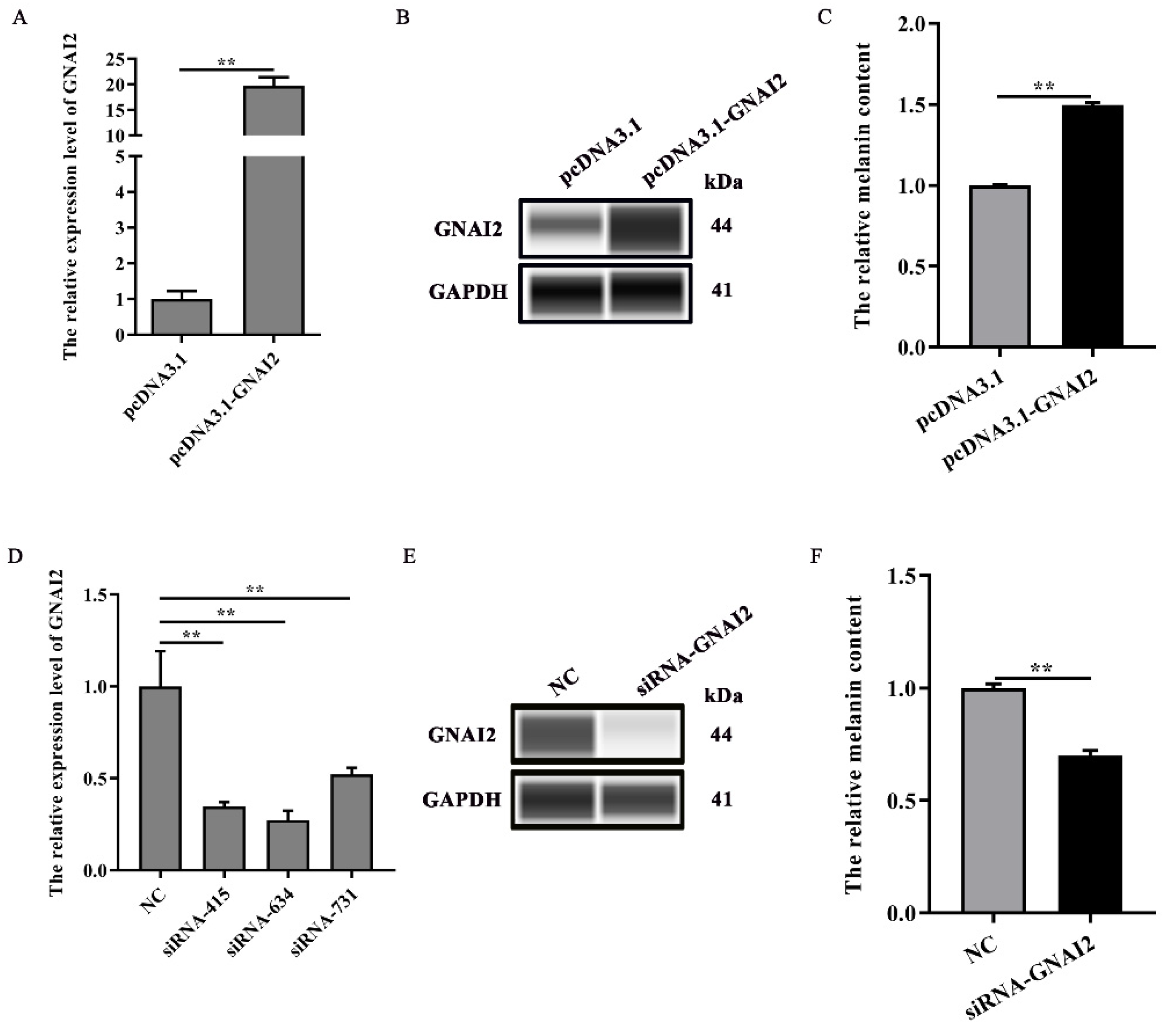
3.3. GNAI2 Promoted Melanogenesis
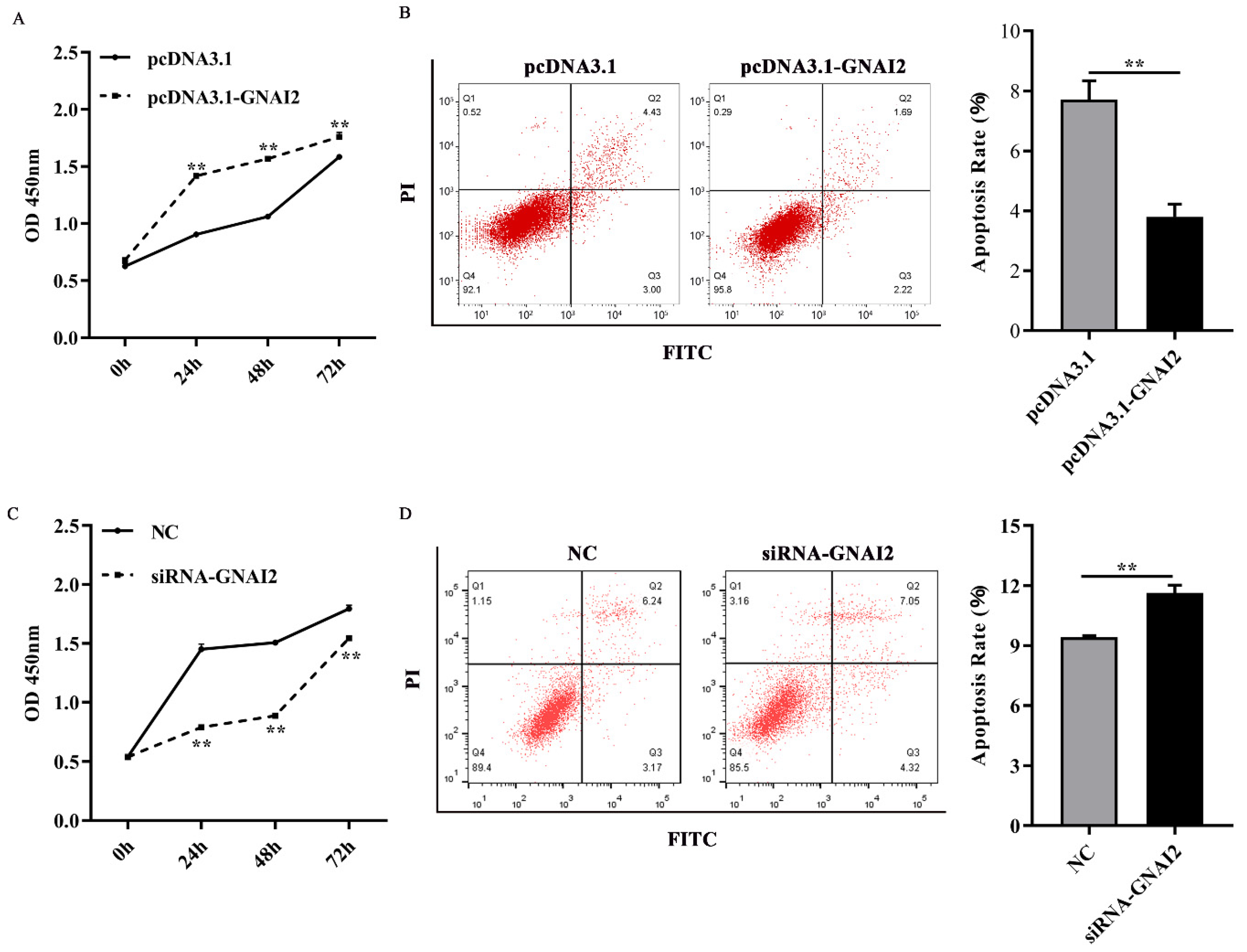
3.4. GNAI2 Improved Melanocyte Proliferation and Apoptosis
3.5. GNAI2 Overexpression and Knockdown Regulated the Expression of Melanin-Related Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Videira, I.F.D.S.; Moura, D.F.L.; Magina, S. Mechanisms regulating melanogenesis. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2013, 88, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naysmith, L.; Waterston, K.; Ha, T.; Flanagan, N.; Bisset, Y.; Ray, A.; Wakamatsu, K.; Ito, S.; Rees, J.L. Quantitative measures of the effect of the melanocortin 1 receptor on human pigmentary status. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.; Tobin, D.J.; Shibahara, S.; Wortsman, J. Melanin pigmentation in mammalian skin and its hormonal regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1155–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K.; Ozeki, H. Chemical analysis of melanins and its application to the study of the regulation of melanogenesis. Pigment Cell Res. 2000, 13 (Suppl. S8), 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Wakamatsu, K. Quantitative Analysis of Eumelanin and Pheomelanin in Humans, Mice, and Other Animals: A Comparative Review. Pigment. Cell Res. 2003, 16, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bino, S.; Ito, S.; Sok, J.; Nakanishi, Y.; Bastien, P.; Wakamatsu, K.; Bernerd, F. Chemical analysis of constitutive pigmentation of human epidermis reveals constant eumelanin to pheomelanin ratio. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2015, 28, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Panthier, J.J.; Arnheiter, H. Signaling and transcriptional regulation in the neural crest-derived melanocyte lineage: Interactions between KIT and MITF. Development 2000, 127, 5379–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Mello, S.A.; Finlay, G.J.; Baguley, B.C.; Askarian-Amiri, M.E. Signaling pathways in melanogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wen, H.; Hailer, F.; Dong, F.; Yang, Z.; Liu, T.; Han, L.; Shi, F.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, J. Pseudogenization of Mc1r gene associated with transcriptional changes related to melanogenesis explains leucistic phenotypes in Oreonectes cavefish (Cypriniformes, Nemacheilidae). J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2019, 57, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, P.; Healy, E.; Jackson, I.; Rees, J.L.; Thody, A.J. Variants of the melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor gene are associated with red hair and fair skin in humans. Nat. Genet. 1995, 11, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wang, G.; Liao, J.; Tang, M. Five alternative splicing variants of the TYR gene and their different roles in melanogenesis in the Muchuan black-boned chicken. Br. Poult. Sci. 2019, 60, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibert, S.; Girardot, M.; Leveziel, H.; Julien, R.; Oulmouden, A. Pheomelanin coat colour dilution in French cattle breeds is not correlated with the TYR, TYRP1 and DCT transcription levels. Pigment Cell Res. 2004, 17, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-L.; Mao, H.-M.; Shu, W.; Deng, W.-D. Melanin traits of Yunnan black bone sheep and TYR gene polymorphism. Hereditas 2006, 28, 291–298. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, E.M.; Gilman, A.G. Biochemical properties of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1980, 49, 533–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootten, D.; Christopoulos, A.; Marti-Solano, M.; Babu, M.M.; Sexton, P.M. Mechanisms of signalling and biased agonism in G protein-coupled receptors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 638–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, M.I.; Strathmann, M.P.; Gautam, N.J.S. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science 1991, 252, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Xi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, F.; Li, C.; Wang, Z. SNHG1 Inhibits ox-LDL-Induced Inflammatory Response and Apoptosis of HUVECs via Up-Regulating GNAI2 and PCBP1. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-W.; Sun, B.; Gong, T.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Sugawara, A.; Jiang, M.; Yan, J.; Gurary, A.J.G. GNAI1 and GNAI3 reduce colitis-associated tumorigenesis in mice by blocking IL6 signaling and down-regulating expression of GNAI2. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2297–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; He, Q.; Xu, J.; Liu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Sun, B.J.T.F.J. Guanine nucleotide–binding protein G (i) α2 aggravates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by regulating MLK3 signaling. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 7049–7060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dela Cruz, R.; Ji, F.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Feng, G.S.; Birnbaumer, L.; Jiang, M.; Chu, W.M. G(i)α proteins exhibit functional differences in the activation of ERK1/2, Akt and mTORC1 by growth factors in normal and breast cancer cells. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2014, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jung, K.S.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, J.T. Production, Differential Methylation of Melanin-related Epigenetic Genes during Brindle Cattle Growth. J. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 8, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, S.; Mu, L.; Zhao, B.; Wang, M.; Yang, N.; Bao, G.; Zhu, C.; Wu, X. Slc7a11 Modulated by POU2F1 is Involved in Pigmentation in Rabbit. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, V.M. Protein Detection by Simple Western™ Analysis. In Western Blotting; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1312, pp. 465–468. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Zhao, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Dong, C. MITF-M regulates melanogenesis in mouse melanocytes. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 90, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Zhai, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, B.; Yang, N.; Wang, M.; Xiao, Y.; Bao, G.; Wu, X. Morphological Characterization and Gene Expression Patterns for Melanin Pigmentation in Rex Rabbit. Biochem. Genet. 2019, 57, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, B.; Yang, N.; Chen, S.; Shen, J.; Bao, G.; Wu, X. KIT is involved in melanocyte proliferation, apoptosis and melanogenesis in the Rex Rabbit. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, W.; Wu, S.; Ma, T.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Q. Differential expression of MC1R gene in Liaoning Cashmere goats with different coat colors. Anim. Biotechnol. 2019, 30, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, T.; Yang, K.; Wang, R.; Yang, J.; Guo, H. Wnt5a inhibits the proliferation and melanogenesis of melanocytes. Int. J. Med Sci. 2013, 10, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Lu, F.; Qu, J.; Hou, L.J.J. Sox10 regulates skin melanocyte proliferation by activating the DNA replication licensing factor MCM5. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 85, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Fan, R.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Hu, S.; Liu, X.; Dong, C. MicroRNA 143-5p regulates alpaca melanocyte migration, proliferation and melanogenesis. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lan, Y.; Lu, H. Opsin3 Downregulation Induces Apoptosis of Human Epidermal Melanocytes via Mitochondrial Pathway. Photochem. Photobiol. 2020, 96, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primers | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| GNAI2-F | tagtccagtgtggtggaattcGCCACCATGGGCTGCACGGTGAGC |
| GNAI2-R | ttgttcgaagggccctctagaGAAGAGGCCGCAGTCCTTCA |
| Primers | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| Negative Control | Forward: UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT |
| Reverse: ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT | |
| siRNA-GNAI2-415 | Forward: GCAACCUGCAGAUUGACUUTT |
| Reverse: AAGUCAAUCUGCAGGUUGCTT | |
| siRNA-GNAI2-634 | Forward: GCAUCGCACAGAGUGACUATT |
| Reverse: UAGUCACUCUGUGCGAUGCTT | |
| siRNA-GNAI2-731 | Forward: CCUGCACUUCAAGAUGUUUTT |
| Reverse: AAACAUCUUGAAGUGCAGGTT |
| Primers | Sequence (5′→3′) | Product Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| GNAI2 | Forward: ACGACTCAGCCGCCTAC | 119 |
| Reverse: GTGCGTCTCCACGATCC | ||
| TYR | Forward: CTCTTCTTGTTGCTGTGGG | 156 |
| Reverse: GCTGAGTAGGTTAGGGTTTTC | ||
| DCT (TYRP2) | Forward: ATTCTGCTGCCAATGACCC | 154 |
| Reverse: AACGGCACCATGTTATACCTG | ||
| PMEL | Forward: GTCAGCACCCAGCTTGTCA | 130 |
| Reverse: GCTTCATTAGTCTGCGCCTGT | ||
| GPNMB | Forward: TCCAGATTGCAGAAGTCCCGAT | 173 |
| Reverse: GCAGCTCTCAGTCTCGTCCA | ||
| GAPDH | Forward: CACCAGGGCTGCTTTTAACTCT | 141 |
| Reverse: CTTCCCGTTCTCAGCCTTGACC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, S.; Dai, Y.; Bai, S.; Zhao, B.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y. GNAI2 Promotes Proliferation and Decreases Apoptosis in Rabbit Melanocytes. Genes 2021, 12, 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12081130
Hu S, Dai Y, Bai S, Zhao B, Wu X, Chen Y. GNAI2 Promotes Proliferation and Decreases Apoptosis in Rabbit Melanocytes. Genes. 2021; 12(8):1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12081130
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Shuaishuai, Yingying Dai, Shaocheng Bai, Bohao Zhao, Xinsheng Wu, and Yang Chen. 2021. "GNAI2 Promotes Proliferation and Decreases Apoptosis in Rabbit Melanocytes" Genes 12, no. 8: 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12081130
APA StyleHu, S., Dai, Y., Bai, S., Zhao, B., Wu, X., & Chen, Y. (2021). GNAI2 Promotes Proliferation and Decreases Apoptosis in Rabbit Melanocytes. Genes, 12(8), 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12081130






