Isolation of High Molecular Weight DNA from the Model Beetle Tribolium for Nanopore Sequencing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- Insects: Laboratory culture of the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum; highly inbred Georgia 2 (GA2) strain, T. freemani and T. confusum routinely reared in whole wheat flour at 28 °C and 40% relative humidity in the dark. For the collection of a larger amount of different life stages, 0.71 mm sieve was used for sifting and individual beetles were picked with tweezers.
- Liquid nitrogen.
- Sterilized mortar with pestle and metal spatula.
- 100 µm cell strainer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cat. No. 22363549, Waltham, MA, USA).
- 1000 µL wide bore filtered pipette tips (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cat. No. 2079G, Waltham, MA, USA).
- 1.5 mL DNA LoBind tubes (Eppendorf, Cat. No. 0030108051, Hamburg, Germany).
- Glass rod (Pasteur pipette heated at the end to form thin hook).
- NIB buffer: 10 mM Tris pH 9.4, 60 mM NaCl, 10 mM EDTA pH 8.0, 0.15 mM spermidine, 0.15 mM spermine, 0.5% v/v Triton X-100, 0.1% v/v β-mercaptoethanol.
- Blood and Cell Culture DNA Midi Kit (Qiagen, Cat. No. 13343, Hilden, Germany) or Genomic-Tip 100/G columns (Qiagen, Cat. No. 10243) with prepared G2 (800 mM guanidine HCl, 30 mM Tris-Cl pH 8.0, 30 mM EDTA pH 8.0; 5% Tween-20, 0.5% Triton X-100), QBT (750 mM NaCl, 50 mM MOPS pH 7.0, 15% isopropanol, 0.15% triton X-100), QC (1 M NaCl, 50 mM MOPS pH 7.0, 15% isopropanol) and QF (1.25 M NaCl, 50 mM Tris-Cl pH 8.5, 15% isopropanol) buffers according to recipes of manufacturer’s kit handbook.
- RNase A solution (100 mg/mL, Qiagen, Cat. No. 1007885).
- Proteinase K from Tritirachium album (Sigma-Aldrich, Cat. No. SRE0047, St. Louis, MO, USA) or Protease (7.5 AU, Qiagen, Cat. No. 19155), prepared as 20 mg/mL solution in miliQ water.
- Isopropyl alcohol.
- TE buffer pH 8.0: 10 mM Tris, 1 mM EDTA.
- Nuclease-free water (Invitrogen, Cat. No. AM9937, Waltham, MA, USA).
- Pulsed Field Certified Agarose (BioRad, Cat. No. 1620137, Hercules, CA, USA).
- 0.5× TBE buffer: 45 mM Tris-borate, 1 mM EDTA.
- Quick-Load 1 kb Extend DNA Ladder (New England Biolabs, Cat. No. N3239S, Ipswich, MA, USA).
- Lambda PFG Ladder (New England Biolabs, Cat.No. N0341S).
- Syringe and G30 needle.
- Short Read Eliminator XS Kit (Circulomics, Cat. No. SKU SS-100-121-01, Baltimore, MD, USA).
- Qubit dsDNA BR Assay kit (Invitrogen, Cat. No. Q32850).
- Agencourt AMPure XP beads (Beckman Coulter, Cat. No. A63880, Brea, CA, USA).
- Ligation Sequencing Kit (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, Cat. No. LSK-110, Oxford, UK).
- NEBNext Companion Module for Oxford Nanopore Technologies Ligation Sequencing (New England BioLabs, Cat. No. E7180S).
- MinION flow cell (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, Cat. No. FLO-MIN111).
2.2. Equipment
2.2.1. Necessary Equipment
- Fume hood.
- Centrifuge with cooling option (Centrifuge 5424 R, Eppendorf).
- Thermomixer (ThermoMixer C with SmartBlock 1.5 mL and ThermoTop, Eppendorf).
- Shaker (Vibramax 100, Heidolph, Schwabach, Germany).
- Qubit 4 Fluorometer (Invitrogen).
- Spectrophotometer (BioSpec-nano, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan).
2.2.2. Optional Equipment (for DNA Length Assessment, Library Preparation and Sequencing)
- Magnetic separator for 1.5 mL tubes (MagnaRack Magnetic Separation Rack, Invitrogen).
- Pulsed field gel electrophoresis system (CHEF-DR III system, Bio-Rad).
- Thermal cycler (2720 Thermal cycler, Thermo Fisher Scientific).
- Rotator mixer (Programmable Rotator Multi Bio RS-24, Biosan, Riga, Latvia).
- MinION device (Oxford Nanopore Technologies).
2.3. Procedure
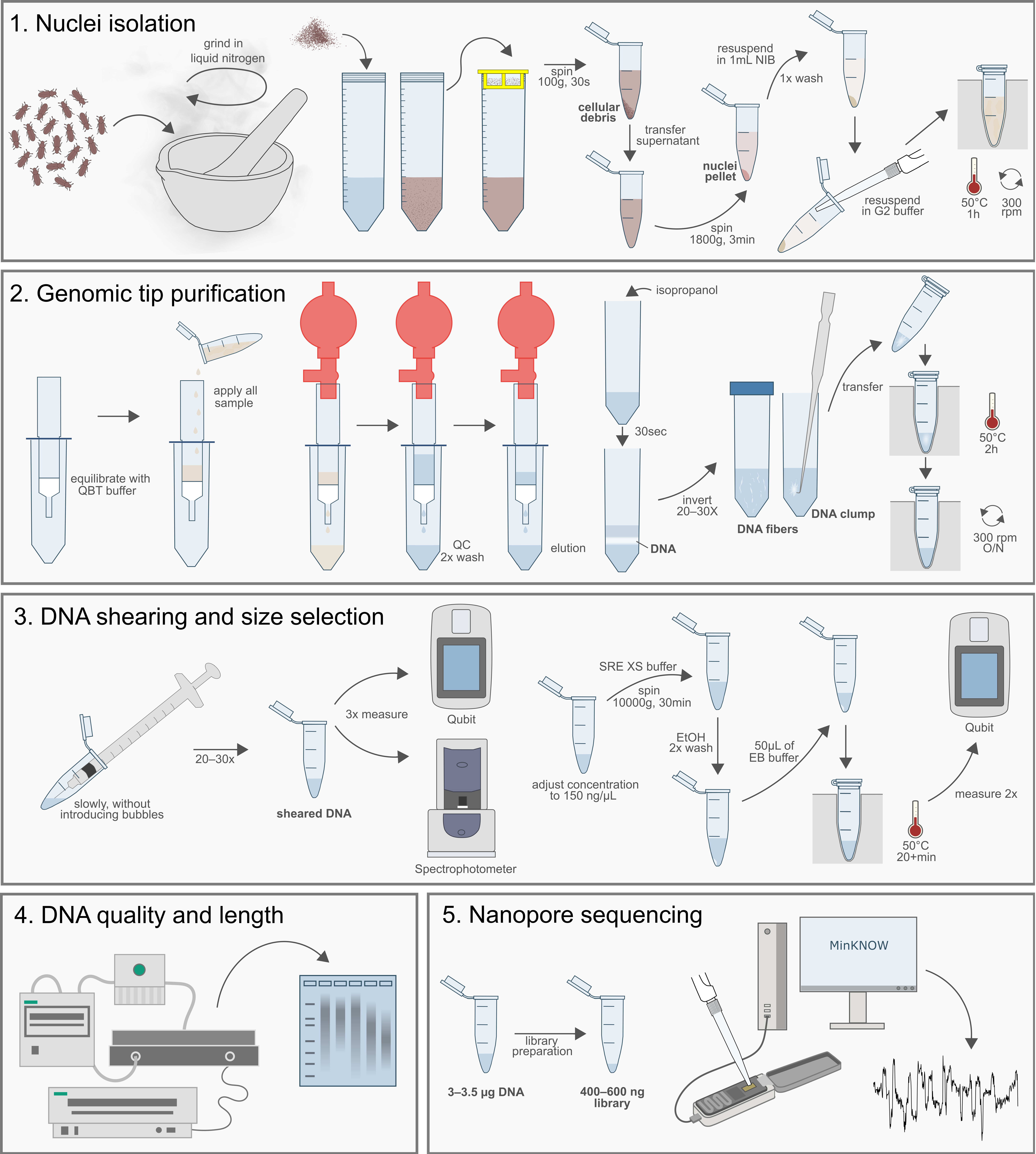
2.3.1. Nuclei Isolation
2.3.2. Genomic Tip Purification
2.3.3. DNA Shearing and Size Selection
2.3.4. Assessment of DNA Quality and Length
2.3.5. Nanopore Sequencing
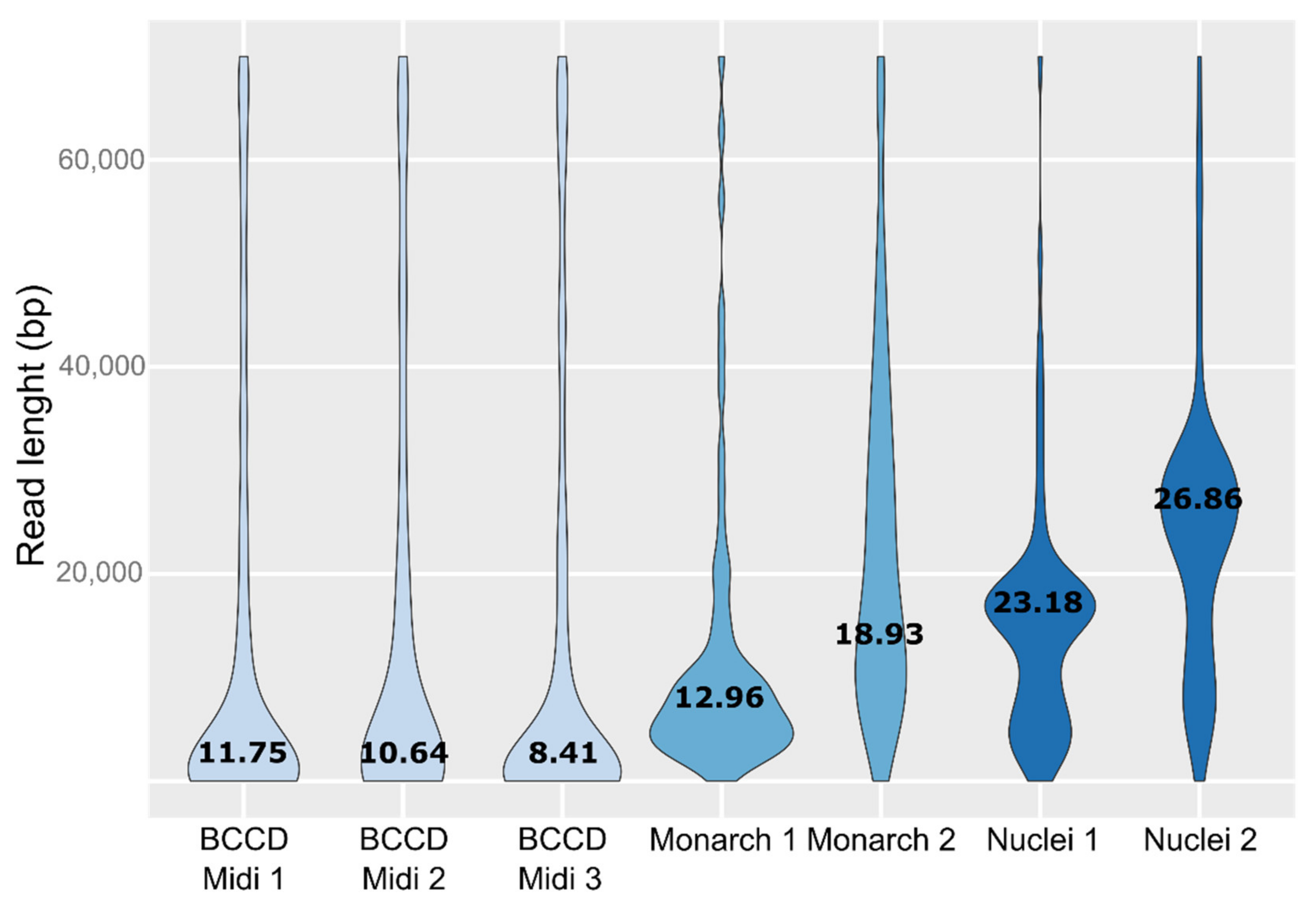
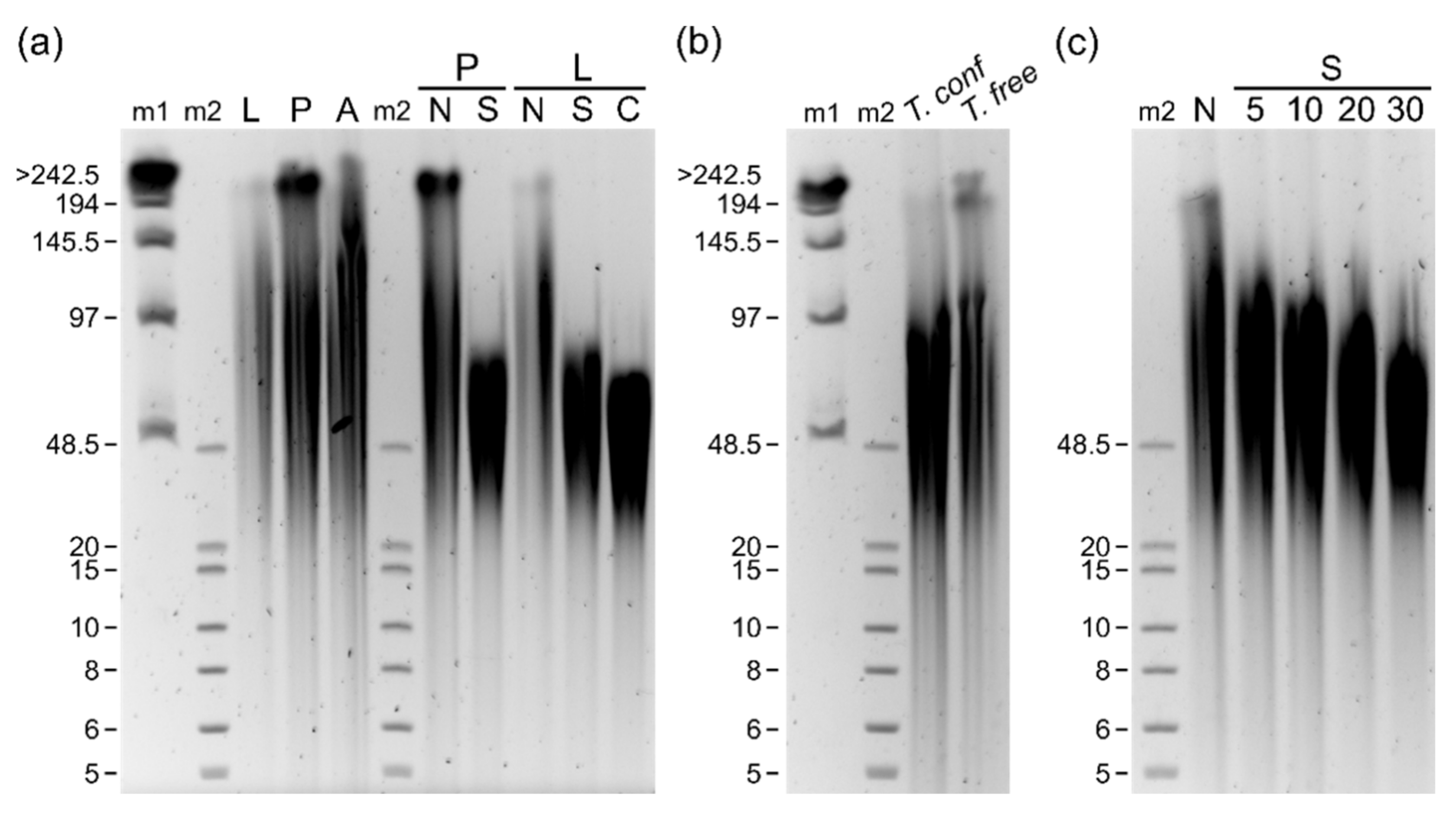
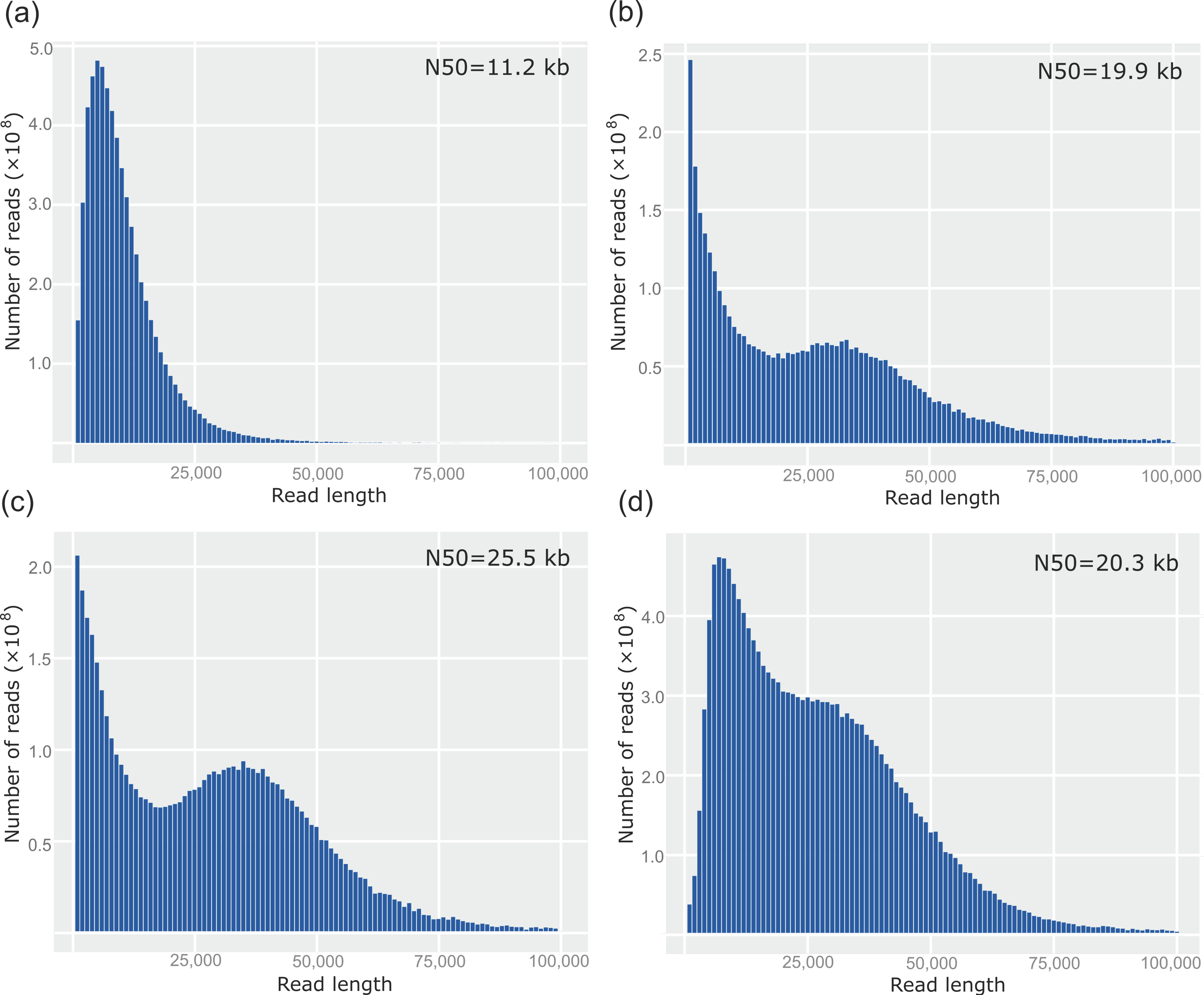
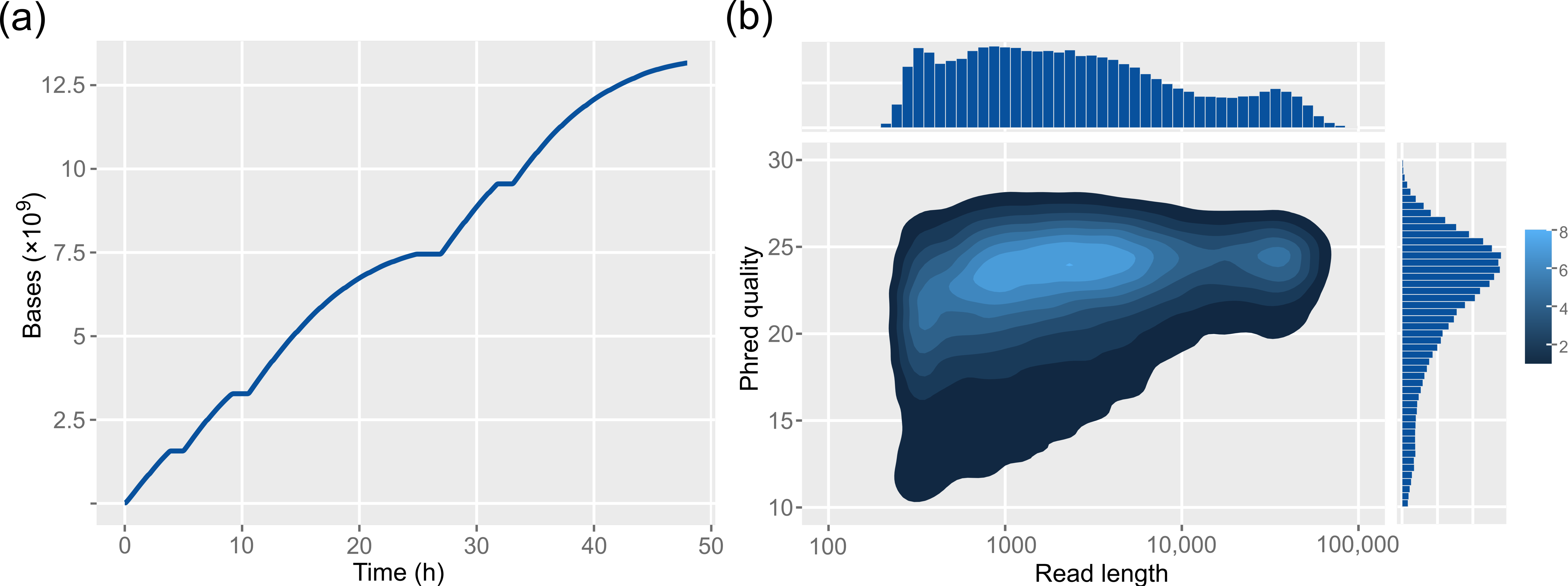
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klingler, M. Tribolium. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, R639–R640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richards, S.; Gibbs, R.A.; Weinstock, G.M.; Brown, S.; Denell, R.; Beeman, R.W.; Gibbs, R.; Bucher, G.; Friedrich, M.; Grimmelikhuijzen, C.J.P.; et al. The Genome of the Model Beetle and Pest Tribolium Castaneum. Nature 2008, 452, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herndon, N.; Shelton, J.; Gerischer, L.; Ioannidis, P.; Ninova, M.; Dönitz, J.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Liang, C.; Damm, C.; Siemanowski, J.; et al. Enhanced Genome Assembly and a New Official Gene Set for Tribolium Castaneum. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Lorenzen, M.D.; Beeman, R.W.; Brown, S.J. Analysis of Repetitive DNA Distribution Patterns in the Tribolium Castaneum Genome. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ugarković, D.; Podnar, M.; Plohl, M. Satellite DNA of the Red Flour Beetle Tribolium Castaneum—Comparative Study of Satellites from the Genus Tribolium. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1996, 13, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pavlek, M.; Gelfand, Y.; Plohl, M.; Meštrović, N. Genome-Wide Analysis of Tandem Repeats in Tribolium Castaneum Genome Reveals Abundant and Highly Dynamic Tandem Repeat Families with Satellite DNA Features in Euchromatic Chromosomal Arms. DNA Res. 2015, 22, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miga, K.H.; Koren, S.; Rhie, A.; Vollger, M.R.; Gershman, A.; Bzikadze, A.; Brooks, S.; Howe, E.; Porubsky, D.; Logsdon, G.A.; et al. Telomere-to-Telomere Assembly of a Complete Human X Chromosome. Nature 2020, 585, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, M.; Olsen, H.E.; Turner, D.J.; Stoddart, D.; Bulazel, K.V.; Paten, B.; Haussler, D.; Willard, H.F.; Akeson, M.; Miga, K.H. Linear Assembly of a Human Centromere on the Y Chromosome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Logsdon, G.A.; Vollger, M.R.; Hsieh, P.H.; Mao, Y.; Liskovykh, M.A.; Koren, S.; Nurk, S.; Mercuri, L.; Dishuck, P.C.; Rhie, A.; et al. The Structure, Function and Evolution of a Complete Human Chromosome 8. Nature 2021, 593, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rang, F.J.; Kloosterman, W.P.; de Ridder, J. From Squiggle to Basepair: Computational Approaches for Improving Nanopore Sequencing Read Accuracy. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Rosikiewicz, W.; Pan, Z.; Jillette, N.; Taghbalout, A.; Foox, J.; Mason, C.; Carroll, M.; Cheng, A.; Li, S. DNA Methylation Calling Tools for Oxford Nanopore Sequencing: A Survey and Human Epigenome-Wide Evaluation. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayjonade, B.; Gouzy, J.; Donnadieu, C.; Pouilly, N.; Marande, W.; Callot, C.; Langlade, N.; Muños, S. Extraction of High-Molecular-Weight Genomic DNA for Long-Read Sequencing of Single Molecules. Biotechniques 2016, 61, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angthong, P.; Uengwetwanit, T.; Pootakham, W.; Sittikankaew, K.; Sonthirod, C.; Sangsrakru, D.; Yoocha, T.; Nookaew, I.; Wongsurawat, T.; Jenjaroenpun, P.; et al. Optimization of High Molecular Weight DNA Extraction Methods in Shrimp for a Long-Read Sequencing Platform. PeerJ 2020, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Rangasamy, M.; Tan, S.Y.; Wang, H.; Siegfried, B.D. Evaluation of Five Methods for Total DNA Extraction from Western Corn Rootworm Beetles. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, S.J.; Coleman, M. Isolation of High Molecular Weight DNA from Insects. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1858, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, S. Beads Free ONT Ligation Kit Library Preparation for Ultra-Long Read Sequencing. Available online: https://gih.uq.edu.au/research/long-read-sequencing/beads-free-ont-ligation-kit-library-preparation-ultra-long-read-sequencing (accessed on 3 March 2021).
- Tyson, J. Rocky Mountain Adventures in Genomic DNA Sample Preparation, Ligation Protocol Optimisation/Simplification and Ultra Long Read Generation. protocols.io 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppert, B.; Stoss, S.; Monk, A.; Smith, T. Optimized Extraction of Insect Genomic DNA for Long-Read Sequencing. Methods Protoc. 2019, 2, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mravinac, B.; Plohl, M. Parallelism in Evolution of Highly Repetitive DNAs in Sibling Species. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 1857–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Starting Material (mg) | DNA Concentration (ng/µL) | DNA Yield (µg) | A220/260 | A260/280 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Larvae | 1100 | 512 | 51.2 | 1.87 | 2.35 |
| Pupae | 200 | 172 | 17.2 | 1.87 | 2.25 |
| Adults | 1000 | 643 | 64.3 | 1.85 | 2.14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Volarić, M.; Veseljak, D.; Mravinac, B.; Meštrović, N.; Despot-Slade, E. Isolation of High Molecular Weight DNA from the Model Beetle Tribolium for Nanopore Sequencing. Genes 2021, 12, 1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12081114
Volarić M, Veseljak D, Mravinac B, Meštrović N, Despot-Slade E. Isolation of High Molecular Weight DNA from the Model Beetle Tribolium for Nanopore Sequencing. Genes. 2021; 12(8):1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12081114
Chicago/Turabian StyleVolarić, Marin, Damira Veseljak, Brankica Mravinac, Nevenka Meštrović, and Evelin Despot-Slade. 2021. "Isolation of High Molecular Weight DNA from the Model Beetle Tribolium for Nanopore Sequencing" Genes 12, no. 8: 1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12081114
APA StyleVolarić, M., Veseljak, D., Mravinac, B., Meštrović, N., & Despot-Slade, E. (2021). Isolation of High Molecular Weight DNA from the Model Beetle Tribolium for Nanopore Sequencing. Genes, 12(8), 1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12081114






