Expression and Functional Characterization of c-Fos Gene in Chinese Fire-Bellied Newt Cynops orientalis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Sample Collection
2.2. PCR Amplification and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
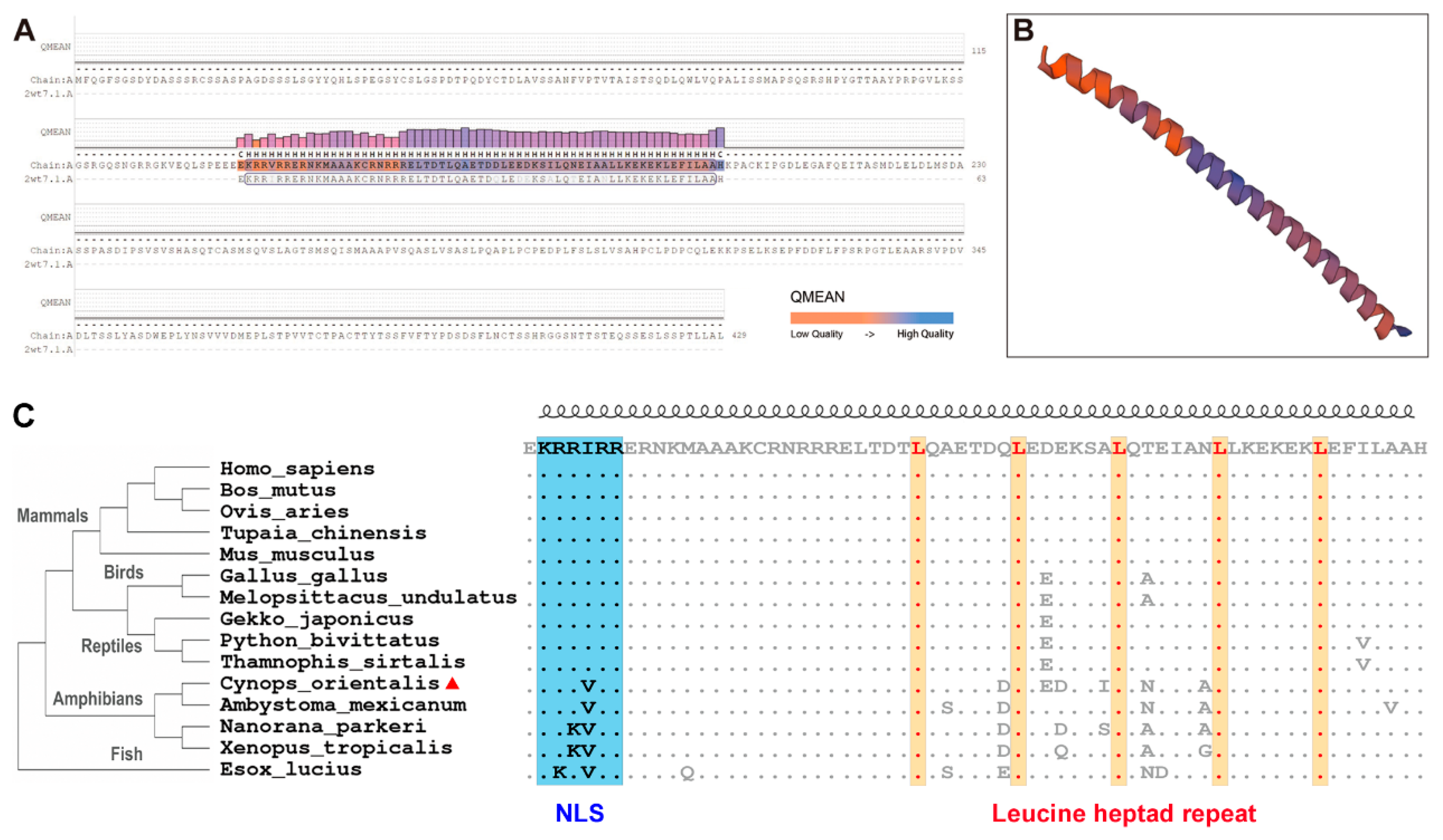
2.3. Bioinformatic Analyses
2.4. Sectioning and Histological Staining
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Co-c-Fos cDNA Cloning and Sequence Analyses
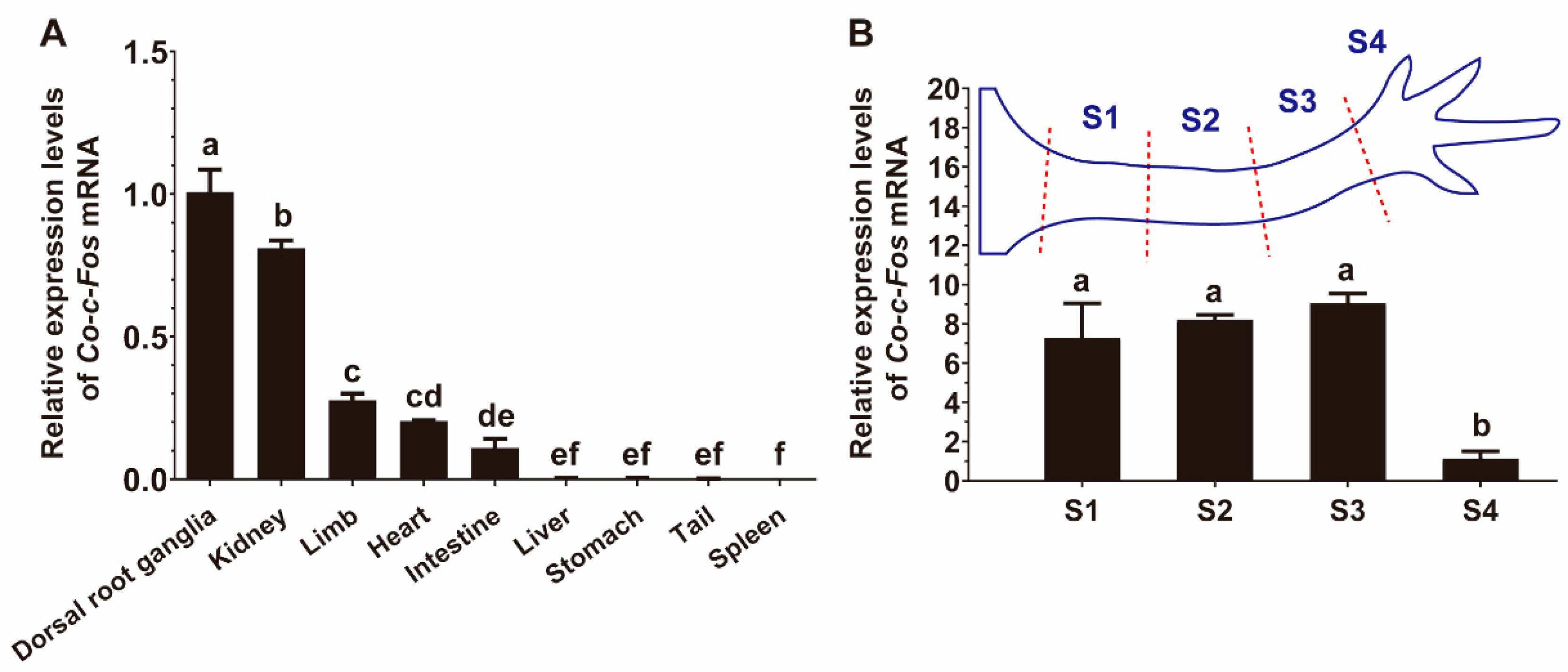
3.2. Distribution of Co-c-Fos mRNA Expression in Various Tissues of C. orientalis
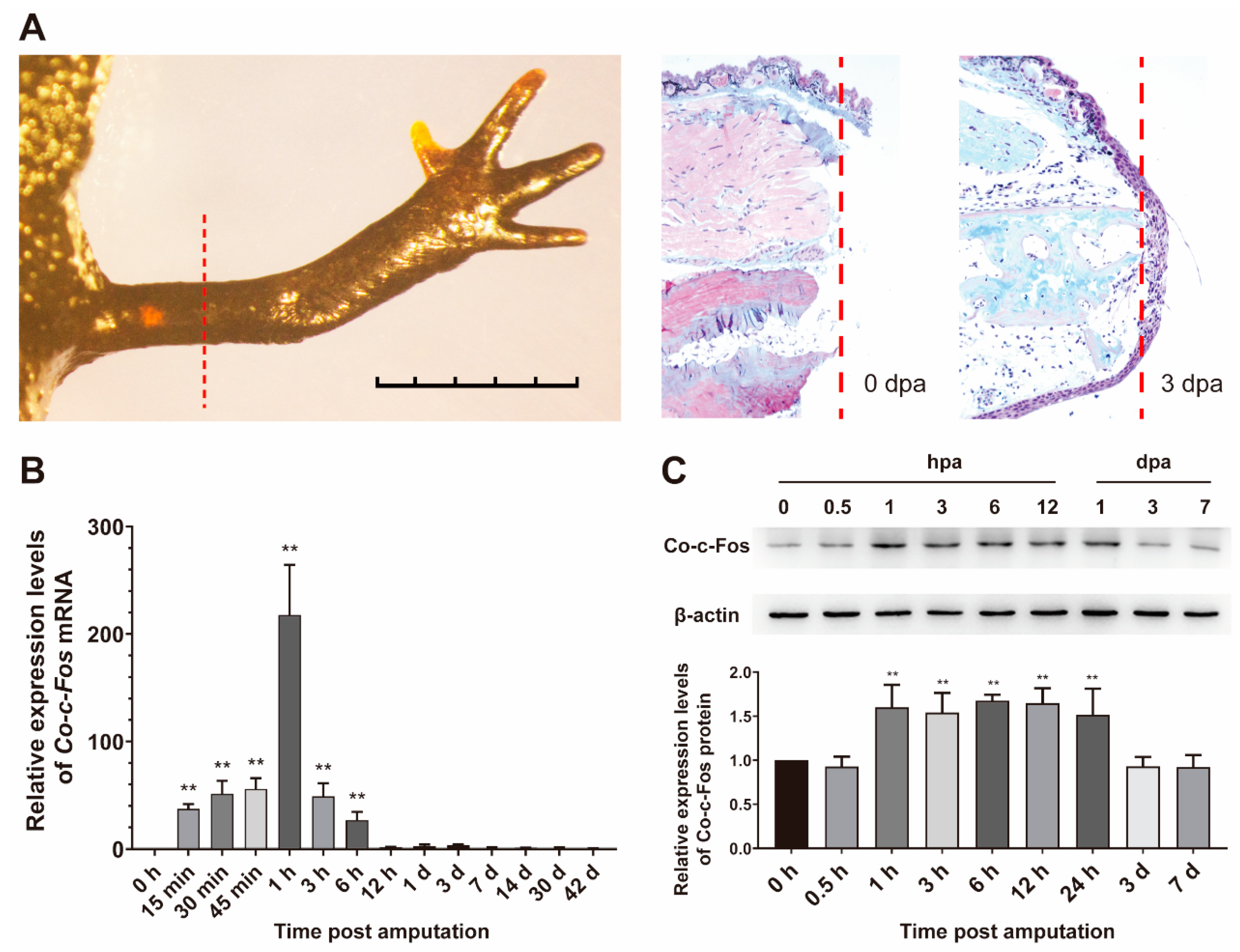
3.3. Expression Pattern of Co-c-Fos Gene during the Newt Limb Regeneration
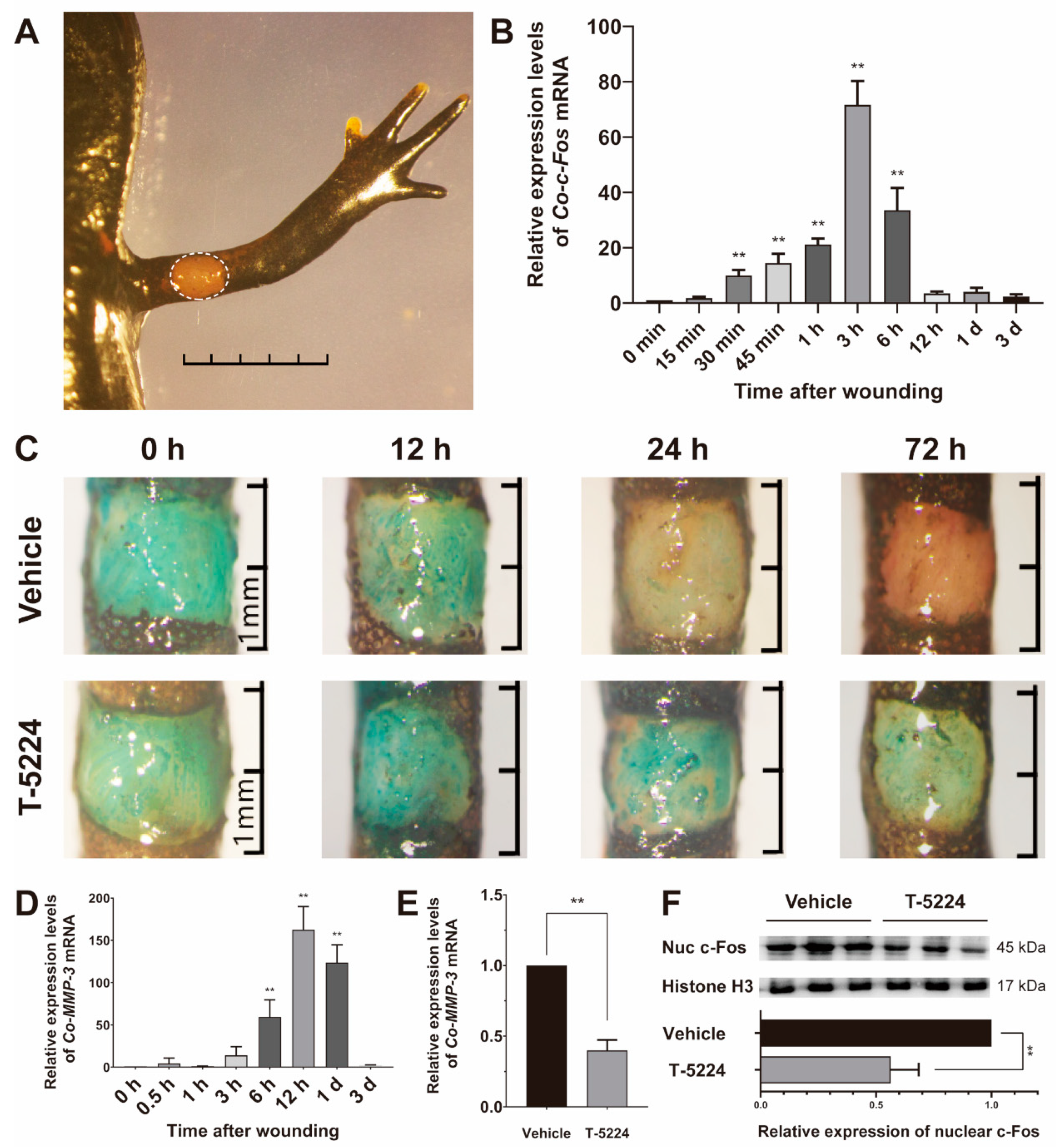
3.4. Role of Co-c-Fos in the Process of the Newt Wound Healing
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IEGs | immediate-early genes |
| AP-1 | activator protein 1 |
| bZIP | basic leucine zipper |
| NLS | Nuclear localization sequence |
| UTR | untranslated region |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| AEC | apical epithelial cap |
| dpa | days post-amputation |
| hpa | hours post-amputation |
References
- Brockes, J.P.; Kumar, A. Comparative aspects of animal regeneration. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 24, 525–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, H. Initiation of limb regeneration: The critical steps for regenerative capacity. Dev. Growth Differ. 2008, 50, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kragl, M.; Knapp, D.; Nacu, E.; Khattak, S.; Maden, M.; Epperlein, H.H.; Tanaka, E.M. Cells keep a memory of their tissue origin during axolotl limb regeneration. Nature 2009, 460, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, K.; Uchiyama, K.; Imokawa, Y.; Yoshizato, K. Cloning and characterization of cdnas for matrix metalloproteinases of regenerating newt limbs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 6819–6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.; Gardiner, D.; Carlson, M.; Nugas, C.; Bryant, S. Expression of mmp-9 and related matrix metalloproteinase genes during axolotl limb regeneration. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 1999, 216, 2–9. [Google Scholar]
- Vinarsky, V.; Atkinson, D.L.; Stevenson, T.J.; Keating, M.T.; Odelberg, S.J. Normal newt limb regeneration requires matrix metalloproteinase function. Dev. Biol. 2005, 279, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mescher, A. Effects on adult newt limb regeneration of partial and complete skin flaps over the amputation surface. J. Exp. Zool. 1976, 195, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niessen, N.; Balthazart, J.; Ball, G.F.; Charlier, T. C-fos down-regulation inhibits testosterone-dependent male sexual behavior and the associated learning. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2013, 38, 3325–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.E.; Hasan, M.; Bousso, P. A role for the immediate early gene product c-fos in imprinting t cells with short-term memory for signal summation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Straaten, F.; Muller, R.; Curran, T.; Van Beveren, C.; Verma, I.M. Complete nucleotide sequence of a human c-onc gene: Deduced amino acid sequence of the human c-fos protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 3183–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, T.; Gordon, M.B.; Rubino, K.L.; Sambucetti, L.C. Isolation and characterization of the c-fos (rat) cdna and analysis of post-translational modification in vitro. Oncogene 1987, 2, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, K.T.; Ashida, K.; Nishina, H.; Iba, H.; Miyajima, N.; Nishizawa, M.; Kawai, S. The chicken c-fos gene: Cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 4012–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kim, I.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, M.K.; Yoon, Y.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J. Cloning and sequence analysis of the self-fertilizing fish Rivulus marmoratus immediate early gene c-fos. Mar. Environ. Res. 2004, 58, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.H.; Xu, X.; Xu, F.; Meng, Y.; Sun, C.; Shi, L.; Zhao, E. Combined expression of c-jun, c-fos, and p53 improves estimation of prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Investig. 2016, 34, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Sans, M.D.; Hou, Y.; Ernst, S.A.; Williams, J.A. C-jun/ap-1 is required for cck-induced pancreatic acinar cell dedifferentiation and DNA synthesis in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. -Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G1381–G1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Florin, L.; Hummerich, L.; Dittrich, B.T.; Kokocinski, F.; Wrobel, G.; Gack, S.; Schorppkistner, M.; Werner, S.; Hahn, M.; Lichter, P. Identification of novel ap-1 target genes in fibroblasts regulated during cutaneous wound healing. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7005–7017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Liu, H.; Fu, X.; Sun, T.; Sheng, Z. Recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor enhanced dermal wound healing by a pathway involving erk and c-fos in diabetic rats. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2007, 45, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, S.; Knoll, B. Cns axon regeneration inhibitors stimulate an immediate early gene response via map kinase-srf signaling. Mol. Brain 2014, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, C.E.; Bauer, S.; Manke, T.; Ahrens, S.; Rodelsperger, C.; Grunhagen, J.; Kornak, U.; Duda, G.N.; Mundlos, S.; Robinson, P.N. Mechanical strain of osteoblasts induces promiscuous and depolarization-induced immediate-early response genes. Bone 2009, 44, S298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, T.; Mizuguchi, T.; Sugiyama, N.; Avital, I.; Rozga, J.; Demetriou, A.A. Immediate early genes and p21 regulation in liver of rats with acute hepatic failure. Am. J. Surg. 2002, 183, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabin, K.; Santosferreira, T.; Essig, J.; Rudasill, S.E.; Echeverri, K. Dynamic membrane depolarization is an early regulator of ependymoglial cell response to spinal cord injury in axolotl. Dev. Biol. 2015, 408, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Yin, L.; Sun, M.; Wang, W.; Cui, J.; Liu, W.; Xie, X.; Chen, F. Itraq-based quantitative proteomic analysis of Cynops orientalis limb regeneration. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Tang, J.; Su, J.; Cui, J.; Xie, X.; Chen, F. Integrative analysis of micrornaome, transcriptome, and proteome during the limb regeneration of Cynops orientalis. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, J.; Jia, L.; Feng, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Chen, F. Profiling of glycan alterations in regrowing limb tissues of Cynops orientalis. Wound Repair Regen. 2017, 25, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisenthal, L.M.; Marsden, J.A.; Dill, P.L.; Macaluso, C.K. A novel dye exclusion method for testing in vitro chemosensitivity of human tumors. Cancer Res. 1983, 43, 749–757. [Google Scholar]
- Bornberg-Bauer, E.; Rivals, E.; Vingron, M. Computational approaches to identify leucine zippers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 2740–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corpet, F. Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 10881–10890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Feng, J.; Zheng, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, F.; Yu, Y.; Cui, J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and expression analysis of the three cysteine and glycine-rich protein genes in the chinese fire-bellied newt Cynops orientalis. Gene 2018, 647, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikawa, Y.; Morimoto, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Chaki, H.; Hashiramoto, A.; Narita, H.; Hirono, S.; Shiozawa, S. Treatment of arthritis with a selective inhibitor of c-fos/activator protein-1. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reunanen, N.; Li, S.; Ahonen, M.; Foschi, M.; Han, J.; Kähäri, V. Activation of p38 α mapk enhances collagenase-1 (matrix metalloproteinase (mmp)-1) and stromelysin-1 (mmp-3) expression by mrna stabilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 32360–32368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Noh, E.; Song, H.; Lee, G.; Kwon, K.; Lee, Y. Reversine inhibits mmp-1 and mmp-3 expressions by suppressing of ros/mapk/ap-1 activation in uv-stimulated human keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts. Exp Derm. 2018, 27, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover, J.N.; Harrison, S.C. Crystal structure of the heterodimeric bzip transcription factor c-fos-c-jun bound to DNA. Nature 1995, 373, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M.; Liu, Z.; Zandi, E. Ap-1 function and regulation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingwall, C.; Laskey, R. Nuclear targeting sequences--a consensus? Trends Biochem. Sci. 1991, 16, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xie, P.; Li, G.; Hao, L.; Xiong, Q. In vivo study on the effects of microcystin extracts on the expression profiles of proto-oncogenes (c-fos, c-jun and c-myc) in liver, kidney and testis of male wistar rats injected i.V. With toxins. Toxicon 2009, 53, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatani, K.; Kawakami, M.; Weinstein, J.N.; Meller, S.T.; Gebhart, G.F. Characterization of thermal hyperalgesia, c-fos expression, and alterations in neuropeptides after mechanical irritation of the dorsal root ganglion. Spine 1995, 20, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Gates, P.B.; Brockes, J.P. Positional identity of adult stem cells in salamander limb regeneration. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2007, 330, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, M.E.; Ziff, E.B. Stimulation of 3t3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature 1984, 311, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, M.H.; Gates, P.B.; Brockes, J.P. Sustained erk activation underlies reprogramming in regeneration-competent salamander cells and distinguishes them from their mammalian counterparts. Stem Cell Rep. 2014, 3, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, A.; Makanae, A.; Hirata, A.; Satou, Y. Blastema induction in aneurogenic state and prrx-1 regulation by mmps and fgfs in ambystoma mexicanum limb regeneration. Dev. Biol. 2011, 355, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wu, C.; Chao, D.; Wu, C.; Li, C.; Chen, G.; Lan, C. High-glucose-cultivated peripheral blood mononuclear cells impaired keratinocyte function via reduced il-22 expression: Implications on impaired diabetic wound healing. Exp. Derm. 2015, 24, 639–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Chu, Y.; Chang, W.; Wang, J. Glycogen synthase kinase-3β-mediated ccaat/enhancer-binding protein delta phosphorylation in astrocytes promotes migration and activation of microglia/macrophages. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Hsu, J.; Ko, C.; Chiu, N.; Kan, W.; Lai, M.; Wang, J. Astrocytic ccaat/enhancer-binding protein delta contributes to glial scar formation and impairs functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 5912–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullard, K.; Lund, L.; Mudgett, J.; Mellin, T.; Hunt, T.; Murphy, B.; Ronan, J.; Werb, Z.; Banda, M. Impaired wound contraction in stromelysin-1-deficient mice. Ann. Surg. 1999, 230, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motomura, H.; Seki, S.; Shiozawa, S.; Aikawa, Y.; Nogami, M.; Kimura, T. A selective c-fos/ap-1 inhibitor prevents cartilage destruction and subsequent osteophyte formation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 497, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, H.; Seki, S.; Yahara, Y.; Shiozawa, S.; Aikawa, Y.; Motomura, H.; Nogami, M.; Watanabe, K.; Sainoh, T.; Ito, H.; et al. A selective inhibition of c-fos/activator protein-1 as a potential therapeutic target for intervertebral disc degeneration and associated pain. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, G.; Feng, Y.; Mi, Z.; Wang, D.; Lin, S.; Chen, F.; Cui, J.; Yu, Y. Expression and Functional Characterization of c-Fos Gene in Chinese Fire-Bellied Newt Cynops orientalis. Genes 2021, 12, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020205
Ye G, Feng Y, Mi Z, Wang D, Lin S, Chen F, Cui J, Yu Y. Expression and Functional Characterization of c-Fos Gene in Chinese Fire-Bellied Newt Cynops orientalis. Genes. 2021; 12(2):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020205
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Gang, Yalong Feng, Zhaoxiang Mi, Du Wang, Shuai Lin, Fulin Chen, Jihong Cui, and Yuan Yu. 2021. "Expression and Functional Characterization of c-Fos Gene in Chinese Fire-Bellied Newt Cynops orientalis" Genes 12, no. 2: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020205
APA StyleYe, G., Feng, Y., Mi, Z., Wang, D., Lin, S., Chen, F., Cui, J., & Yu, Y. (2021). Expression and Functional Characterization of c-Fos Gene in Chinese Fire-Bellied Newt Cynops orientalis. Genes, 12(2), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020205




