The Connection between MicroRNAs and Oral Cancer Pathogenesis: Emerging Biomarkers in Oral Cancer Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
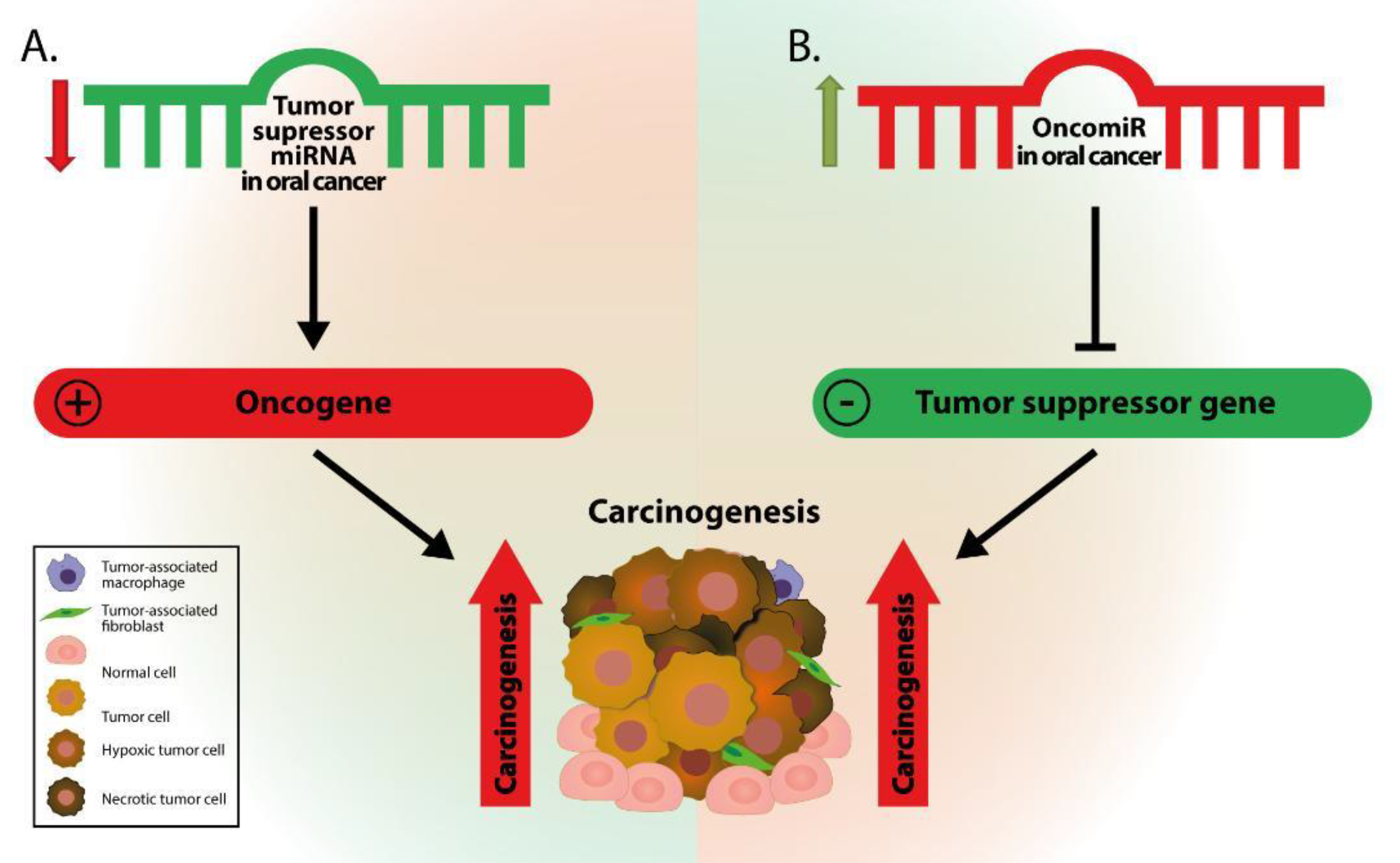
2. Altered miRNAs in Oral Cancer
3. Oncogenic miRNAs in Oral Cancer
4. Tumor Suppressor miRNAs in Oral Cancer
5. Modulation of Oral Cancer Tumor Microenvironment Components by miRNAs
6. miRNAs as Potential Biomarkers for Oral Cancer
7. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefner, M.F.; Lang, K.; Krug, D.; Koerber, S.A.; Uhlmann, L.; Kieser, M.; Debus, J.; Sterzing, F. Prognostic factors, patterns of recurrence and toxicity for patients with esophageal cancer undergoing definitive radiotherapy or chemo-radiotherapy. J. Radiat. Res. 2015, 56, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hendijani, F. Human mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for prevention and recovery of chemo/radiotherapy adverse reactions. Cytotherapy 2015, 17, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.; Wiesenfeld, D. Oral Cancer. Aust. Dent. J. 2018, 63 (Suppl. S1), S91–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanuthai, K.; Rojanawatsirivej, S.; Thosaporn, W.; Kintarak, S.; Subarnbhesaj, A.; Darling, M.; Kryshtalskyj, E.; Chiang, C.P.; Shin, H.I.; Choi, S.Y.; et al. Oral cancer: A multicenter study. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2018, 23, e23–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irimie, A.I.; Braicu, C.; Cojocneanu-Petric, R.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Campian, R.S. Novel technologies for oral squamous carcinoma biomarkers in diagnostics and prognostics. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2015, 73, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braicu, C.; Catana, C.; Calin, G.A.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. NCRNA combined therapy as future treatment option for cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 6565–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Calin, G.A. Molecular pathways: microRNAs, cancer cells, and microenvironment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6247–6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michlewski, G.; Caceres, J.F. Post-transcriptional control of miRNA biogenesis. RNA 2019, 25, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andres-Leon, E.; Gonzalez Pena, D.; Gomez-Lopez, G.; Pisano, D.G. miRGate: A curated database of human, mouse and rat miRNA-mRNA targets. Database 2015, 2015, bav035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.; Ayub, H.; Khan, T.; Wahid, F. MicroRNA biogenesis, gene silencing mechanisms and role in breast, ovarian and prostate cancer. Biochimie 2019, 167, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Yang, S. MicroRNA-146a regulates the transformation from liver fibrosis to cirrhosis in patients with hepatitis B via interleukin-6. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 4670–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, S.Y.; Chao, Y.X.; Dheen, S.T.; Tan, E.K.; Tay, S.S. Role of MicroRNAs in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karnati, H.K.; Panigrahi, M.K.; Gutti, R.K.; Greig, N.H.; Tamargo, I.A. miRNAs: Key Players in Neurodegenerative Disorders and Epilepsy. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 48, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, C.; Zhou, C.; Zhuang, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Liu, G.; Wei, J.; Sun, C. MicroRNA expression in cervical cancer: Novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 7080–7090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shi, Z.; Hong, Z.; Pan, J.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, C.; Zhuang, H.; Zheng, X. MicroRNA-1276 Promotes Colon Cancer Cell Proliferation by Negatively Regulating LACTB. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 12185–12195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Meng, W.; Huang, X.; Zhu, W.; Yin, C.; Wang, C.; Fassan, M.; Yu, Y.; Kudo, M.; Xiao, S.; et al. miR-196b-5p-mediated downregulation of TSPAN12 and GATA6 promotes tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 4347–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanjiao, Y.; Chunyan, C.; Xiaoxin, Q.; Youjian, H. MicroRNA-378a-3p contributes to ovarian cancer progression through downregulating PDIA4. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2021, 9, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Shi, P.; Tian, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, N. Overexpression of miR-1225 promotes the progression of breast cancer, resulting in poor prognosis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 21, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Yan, Y.; Guo, X.; Fang, Y.; Su, Y.; Wang, L.; Pathak, J.L.; Ge, L. miR-146a Overexpression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Potentiates Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion Possibly via Targeting HTT. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 585976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Ma, J.H. miR-105 Promotes the Progression and Predicts the Prognosis for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC). Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 11491–11499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, B.; Zhang, S.; Wu, S.; Zhu, Q.; Li, W. MiR-770 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma migration and invasion by regulating the Sirt7/Smad4 pathway. IUBMB Life 2021, 73, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimie, A.I.; Ciocan, C.; Gulei, D.; Mehterov, N.; Atanasov, A.G.; Dudea, D.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Current Insights into Oral Cancer Epigenetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manasa, V.G.; Kannan, S. Impact of microRNA dynamics on cancer hallmarks: An oral cancer scenario. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317695920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Huang, H.; Sun, L.; Yang, M.; Pan, C.; Chen, W.; Wu, D.; Lin, Z.; Zeng, C.; Yao, Y. MiR-21 indicates poor prognosis in tongue squamous cell carcinomas as an apoptosis inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3998–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.; Si, M.L.; Wu, H.; Mo, Y.Y. MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14328–14336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reis, P.P.; Tomenson, M.; Cervigne, N.K.; Machado, J.; Jurisica, I.; Pintilie, M.; Sukhai, M.A.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Grenman, R.; Gilbert, R.W.; et al. Programmed cell death 4 loss increases tumor cell invasion and is regulated by miR-21 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Hu, C.; Chi, J.; Li, J.; Peng, C.; Yun, X.; Li, D.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, M.; et al. miR-24 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma by targeting FBXW7. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Chi, J.; Gao, M.; Zhi, J.; Li, Y.; Zheng, X. Loss of PTEN Expression Is Associated with High MicroRNA 24 Level and Poor Prognosis in Patients With Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 75, 1449.e1–1449.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, A.; Heidbreder, C.E.; Jiang, L.; Yu, J.; Kolokythas, A.; Huang, L.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, X. MicroRNA-24 targeting RNA-binding protein DND1 in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 4115–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.C.; Liu, C.J.; Lin, J.A.; Chiang, W.F.; Hung, P.S.; Chang, K.W. miR-24 up-regulation in oral carcinoma: Positive association from clinical and in vitro analysis. Oral Oncol. 2010, 46, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.J.; Tsai, M.M.; Hung, P.S.; Kao, S.Y.; Liu, T.Y.; Wu, K.J.; Chiou, S.H.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, K.W. miR-31 ablates expression of the HIF regulatory factor FIH to activate the HIF pathway in head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.C.; Liu, C.J.; Tu, H.F.; Chung, Y.T.; Yang, C.C.; Kao, S.Y.; Chang, K.W.; Lin, S.C. miR-31 targets ARID1A and enhances the oncogenicity and stemness of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57254–57267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tseng, S.-H.; Yang, C.-C.; Yu, E.-H.; Chang, C.; Lee, Y.-S.; Liu, C.-J.; Chang, K.-W.; Lin, S.-C. K14-EGFP-miR-31 transgenic mice have high susceptibility to chemical-induced squamous cell tumorigenesis that is associating with Ku80 repression. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.-H.; Liu, H.; Chiang, W.-F.; Chen, T.-W.; Chu, L.J.; Yu, J.-S.; Chen, S.-J.; Chen, H.-C.; Tan, B.C.-M. MiR-31-5p-ACOX1 Axis Enhances Tumorigenic Fitness in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Via the Promigratory Prostaglandin E2. Theranostics 2018, 8, 486–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.Y.; Chou, C.H.; Yeh, L.Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Chang, K.W.; Liu, C.J.; Fan Chiang, C.Y.; Lin, S.C. MicroRNA miR-31 targets SIRT3 to disrupt mitochondrial activity and increase oxidative stress in oral carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2019, 456, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Xie, W.; Sun, Q.; Wang, H.; Qiao, B. LncRNA UCA1 promotes proliferation and cisplatin resistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma by sunppressing miR-184 expression. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 2897–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Yang, C.C.; Kao, S.Y.; Liu, C.J.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, K.W. MicroRNA-211 Enhances the Oncogenicity of Carcinogen-Induced Oral Carcinoma by Repressing TCF12 and Increasing Antioxidant Activity. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4872–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chu, T.H.; Yang, C.C.; Liu, C.J.; Lui, M.T.; Lin, S.C.; Chang, K.W. miR-211 promotes the progression of head and neck carcinomas by targeting TGFbetaRII. Cancer Lett. 2013, 337, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, J.; Jia, Y.; Liu, T.; Duan, Y.; Liang, X.; Liu, L. microRNA-211 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion ability of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via targeting the bridging integrator 1 protein. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 4644–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.J.; Shen, W.G.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, Y.W.; Lu, H.H.; Tsai, M.M.; Lin, S.C. miR-221 and miR-222 expression increased the growth and tumorigenesis of oral carcinoma cells. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2011, 40, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Jiang, F.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yu, D. Downregulation of miR-221/222 by a microRNA sponge promotes apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells through upregulation of PTEN. Oncol Lett. 2016, 12, 4419–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Ren, Y.; Tang, H.; Wang, W.; He, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, A. Deregulation of the miR-222-ABCG2 regulatory module in tongue squamous cell carcinoma contributes to chemoresistance and enhanced migratory/invasive potential. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 44538–44550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, F.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Yu, D. miR-222 regulates the cell biological behavior of oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting PUMA. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.M.; Shiah, S.G.; Huang, C.C.; Hsiao, J.R.; Chang, J.Y. Up-regulation of miR-455-5p by the TGF-β-SMAD signalling axis promotes the proliferation of oral squamous cancer cells by targeting UBE2B. J. Pathol. 2016, 240, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.A.; Kim, J.S.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Yu, S.K.; Kim, C.S.; Chun, H.S.; Kim, J.; Park, J.T.; Go, D.; et al. miR-203 downregulates Yes-1 and suppresses oncogenic activity in human oral cancer cells. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 120, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lin, Y.; Fan, L.; Kuang, W.; Zheng, L.; Wu, J.; Shang, P.; Wang, Q.; Tan, J. miR-203 inhibits cell proliferation and promotes cisplatin induced cell death in tongue squamous cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 473, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Choi, D.W.; Kim, C.S.; Yu, S.K.; Kim, H.J.; Go, D.S.; Lee, S.A.; Moon, S.M.; Kim, S.G.; Chun, H.S.; et al. MicroRNA-203 Induces Apoptosis by Targeting Bmi-1 in YD-38 Oral Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 3477–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.S.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, J.S.; Yu, S.K.; Go, D.S.; Lee, S.A.; Moon, S.M.; Chun, H.S.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, D.K. Suppression of Oral Carcinoma Oncogenic Activity by microRNA-203 via Down-regulation of SEMA6A. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 5425–5433. [Google Scholar]
- Henson, B.J.; Bhattacharjee, S.; O’Dee, D.M.; Feingold, E.; Gollin, S.M. Decreased expression of miR-125b and miR-100 in oral cancer cells contributes to malignancy. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2009, 48, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arunkumar, G.; Deva Magendhra Rao, A.K.; Manikandan, M.; Prasanna Srinivasa Rao, H.; Subbiah, S.; Ilangovan, R.; Murugan, A.K.; Munirajan, A.K. Dysregulation of miR-200 family microRNAs and epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.S.; Liu, X.B.; Chung-Wai Ho, A.; Po-Wing Yuen, A.; Wai-Man Ng, R.; Ignace Wei, W. Identification of pyruvate kinase type M2 as potential oncoprotein in squamous cell carcinoma of tongue through microRNA profiling. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutallip, M.; Nohata, N.; Hanazawa, T.; Kikkawa, N.; Horiguchi, S.; Fujimura, L.; Kawakami, K.; Chiyomaru, T.; Enokida, H.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. Glutathione S-transferase P1 (GSTP1) suppresses cell apoptosis and its regulation by miR-133alpha in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 27, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Dai, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, A.; Chen, Z.; Heidbreder, C.E.; Kolokythas, A.; Zhou, X. Identification and experimental validation of G protein α inhibiting activity polypeptide 2 (GNAI2) as a microRNA-138 target in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Hum. Genet. 2011, 129, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.; Sharma, S.; Teknos, T.N. RhoC regulates cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by overexpressing IL-6 and phosphorylation of STAT3. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lyu, M.; Zhang, C.; Meng, Z.; Gan, Y.; Yu, G. miR-375 inhibits cell growth and correlates with clinical outcomes in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2061–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Z.H.; Cheng, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Bo, C.X.; Li, Y.L. MicroRNA375 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma cell migration and invasion by targeting plateletderived growth factorA. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, A.B.; Bruce, J.P.; Alajez, N.M.; Shi, W.; Yue, S.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Xu, W.; O’Sullivan, B.; Waldron, J.; Cummings, B.; et al. Significance of dysregulated metadherin and microRNA-375 in head and neck cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 7539–7550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, X.; Song, B.; Qiu, X.; Zhao, J. MiR-375/SLC7A11 axis regulates oral squamous cell carcinoma proliferation and invasion. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.M.; Patel, R.S.; Phillips, B.L.; Wang, H.; Cohen, D.M.; Reinhold, W.C.; Chang, L.J.; Yang, L.J.; Chan, E.K. Tumor suppressor miR-375 regulates MYC expression via repression of CIP2A coding sequence through multiple miRNA-mRNA interactions. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 1638–1648, S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Jadhav, K.; Shah, V.; Gupta, N.; Dagrus, K. miRNA 21: Diagnostic Prognostic and Therapeutic Marker for Oral Cancer. Microrna 2016, 5, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoxhaj, G.; Manning, B.D. The PI3K-AKT network at the interface of oncogenic signalling and cancer metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Gu, L.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bai, X.; Li, L.; Wang, B.; Peng, Q.; Yao, Z.; et al. Tropomyosin-1 acts as a potential tumor suppressor in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, E.H.; Tu, H.F.; Wu, C.H.; Yang, C.C.; Chang, K.W. MicroRNA-21 promotes perineural invasion and impacts survival in patients with oral carcinoma. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2017, 80, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, Y.; Yanamoto, S.; Takahashi, H.; Yamada, S.; Naruse, T.; Sakamoto, Y.; Ikeda, H.; Shiraishi, T.; Fujita, S.; Ikeda, T.; et al. A clinicopathological study of perineural invasion and vascular invasion in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 44, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsuhashi, S.; Manirujjaman, M.; Hamajima, H.; Ozaki, I. Control Mechanisms of the Tumor Suppressor PDCD4: Expression and Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, W.; Shu, Y.; Liu, P. Prognostic value of miR-21 in various cancers: An updating meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; He, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, B.; Zhou, M.; Xu, X.J. Identification of Gene and MicroRNA Signatures for Oral Cancer Developed from Oral Leukoplakia. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 841956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, M.; Rodriguez-Barrueco, R.; Yu, J.; Do, C.; Silva, J.M.; Gautier, J. MYC is a critical target of FBXW. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3292–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Li, J.; Peng, C.; Zhao, J.; Chi, J.; Meng, X.; Yun, X.; Li, D.; Yu, Y.; Gao, M. MicroRNA-24 induces cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2015, 51, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siow, M.Y.; Ng, L.P.; Vincent-Chong, V.K.; Jamaludin, M.; Abraham, M.T.; Abdul Rahman, Z.A.; Kallarakkal, T.G.; Yang, Y.H.; Cheong, S.C.; Zain, R.B. Dysregulation of miR-31 and miR-375 expression is associated with clinical outcomes in oral carcinoma. Oral Dis. 2014, 20, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.S.; Liu, X.B.; Wong, B.Y.; Ng, R.W.; Yuen, A.P.; Wei, W.I. Mature miR-184 as Potential Oncogenic microRNA of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Tongue. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2588–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, K.W.; Liu, C.J.; Chu, T.H.; Cheng, H.W.; Hung, P.S.; Hu, W.Y.; Lin, S.C. Association between high miR-211 microRNA expression and the poor prognosis of oral carcinoma. J. Dent. Res. 2008, 87, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.L.; Luo, C.W.; Chou, C.L.; Yang, C.C.; Chen, T.J.; Li, C.F.; Pan, M.R. High Expression of UBE2B as a Poor Prognosis Factor in Patients With Rectal Cancer Following Chemoradiotherapy. Anticancer Res 2020, 40, 6305–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wu, K.; Liao, S.; Pan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J. MicroRNA-transcription factor network analysis reveals miRNAs cooperatively suppress RORA in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiklund, E.D.; Gao, S.; Hulf, T.; Sibbritt, T.; Nair, S.; Costea, D.E.; Villadsen, S.B.; Bakholdt, V.; Bramsen, J.B.; Sorensen, J.A. MicroRNA alterations and associated aberrant DNA methylation patterns across multiple sample types in oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, J.R., Jr.; Appleton, K.M.; Pierce, J.Y.; Peterson, Y.K. Suppression of GNAI2 message in ovarian cancer. J. Ovarian Res. 2014, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, D.; Xu, H.; Ji, N.; Li, J.; Zhou, M.; Dan, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, X.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Q. In situ measurement of miR-138 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue supports the role of this microRNA as a tumor suppressor. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2019, 48, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zhuang, X.; Lin, L.; Yu, P.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Hu, G.; Sun, Y. New horizons in tumor microenvironment biology: Challenges and opportunities. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arneth, B. Tumor Microenvironment. Medicina 2019, 56, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basanta, D.; Anderson, A.R.A. Homeostasis Back and Forth: An Ecoevolutionary Perspective of Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a028332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewis, C.; Murdoch, C. Macrophage responses to hypoxia: Implications for tumor progression and anti-cancer therapies. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedback, N.; Jensen, D.H.; Specht, L.; Fiehn, A.M.; Therkildsen, M.H.; Friis-Hansen, L.; Dabelsteen, E.; von Buchwald, C. MiR-21 expression in the tumor stroma of oral squamous cell carcinoma: An independent biomarker of disease free survival. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95193. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Q.; Cao, S.; Li, C.; Mengesha, A.; Kong, B.; Wei, M. Micro-RNA-21 regulates TGF-β-induced myofibroblast differentiation by targeting PDCD4 in tumor-stroma interaction. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sekhon, H.K.; Sircar, K.; Kaur, G.; Marwah, M. Evaluation of Role of Myofibroblasts in Oral Cancer: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2016, 9, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, A.; Zhu, C.; Peng, S.; Shuai, C.; Sun, L.; Han, Y.; Qian, Y.; Gao, S.; Su, T. Downregulation of Microrna-148a in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts from Oral Cancer Promotes Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion by Targeting Wnt10b. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2016, 30, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.W.; Liu, L.L.; Li, L.; Gao, F.; Zhuang, S.M.; Wang, L.P.; Li, Y.; Song, M. Cancer-associated fibroblasts provide a suitable microenvironment for tumor development and progression in oral tongue squamous cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalluri, R.; Zeisberg, M. Fibroblasts in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fan, Q.; Li, J.; Song, J.; Gu, Y. MiR-124 down-regulation is critical for cancer associated fibroblasts-enhanced tumor growth of oral carcinoma. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 351, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasahira, T.; Kurihara, M.; Bhawal, U.K.; Ueda, N.; Shimomoto, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Kirita, T.; Kuniyasu, H. Downregulation of miR-126 induces angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis by activation of VEGF-A in oral cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C.; Chen, P.C.; Lein, M.Y.; Tsao, C.W.; Huang, C.C.; Wang, S.W.; Tang, C.H.; Tung, K.C. WISP-1 promotes VEGF-C-dependent lymphangiogenesis by inhibiting miR-300 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 9993–10005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chuang, J.Y.; Chen, P.C.; Tsao, C.W.; Chang, A.C.; Lein, M.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Wang, S.W.; Lin, C.W.; Tang, C.H. WISP-1 a novel angiogenic regulator of the CCN family promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma angiogenesis through VEGF-A expression. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 4239–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Jao, Y.C.; Hsieh, I.S.; Chang, K.C.; Hong, T.M. miR-320 regulates tumor angiogenesis driven by vascular endothelial cells in oral cancer by silencing neuropilin 1. Angiogenesis 2014, 17, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.H.; He, Y.L.; Zuo, W.H.; Kang, Y.; Xue, H.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Meng, Y. Neuropilin1 silencing impairs the proliferation and migration of cells in pancreatic cancer. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.N.; He, L.H.; Bai, Z.T.; Li, X. NRP1 is a Prognostic Factor and Promotes the Growth and Migration of Cells in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 7021–7032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, B.; Khaled, Y.S.; Ammori, B.J.; Elkord, E. Neuropilin 1: Function and therapeutic potential in cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2014, 63, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Han, Z.; Wen, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Y. Niclosamide acts as a new inhibitor of vasculogenic mimicry in oral cancer through upregulation of miR-124 and downregulation of STAT3. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Folberg, R.; Maniotis, A.J. Vasculogenic mimicry. APMIS 2004, 112, 508–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.C.; Chen, P.N.; Peng, C.Y.; Yu, C.H.; Chou, M.Y. Suppression of miR-204 enables oral squamous cell carcinomas to promote cancer stemness, EMT traits, and lymph node metastasis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20180–20192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, P.Y.; Hsieh, P.L.; Wang, T.H.; Yu, C.C.; Lu, M.Y.; Liao, Y.W.; Lee, T.H.; Peng, C.Y. Andrographolide impedes cancer stemness and enhances radio-sensitivity in oral carcinomas via miR-218 activation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 4196–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, C.Y.; Chen, P.Y.; Ho, D.C.; Tsai, L.L.; Hsieh, P.L.; Lu, M.Y.; Yu, C.C.; Yu, C.H. miR-145 mediates the anti-cancer stemness effect of photodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) in oral cancer cells. J. Formos Med. Assoc. 2018, 117, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Z. Downregulation of miR-153 contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis in human epithelial cancer. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z.; Sun, L.; Chen, W.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Fan, S.; Li, Y.; Li, J. miR-639 regulates transforming growth factor β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human tongue cancer cells by targeting FOXC1. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bufalino, A.; Cervigne, N.K.; de Oliveira, C.E.; Fonseca, F.P.; Rodrigues, P.C.; Macedo, C.C.; Sobral, L.M.; Miguel, M.C.; Lopes, M.A.; Paes Leme, A.F. Low miR-143/miR-145 Cluster Levels Induce Activin A Overexpression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas, Which Contributes to Poor Prognosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
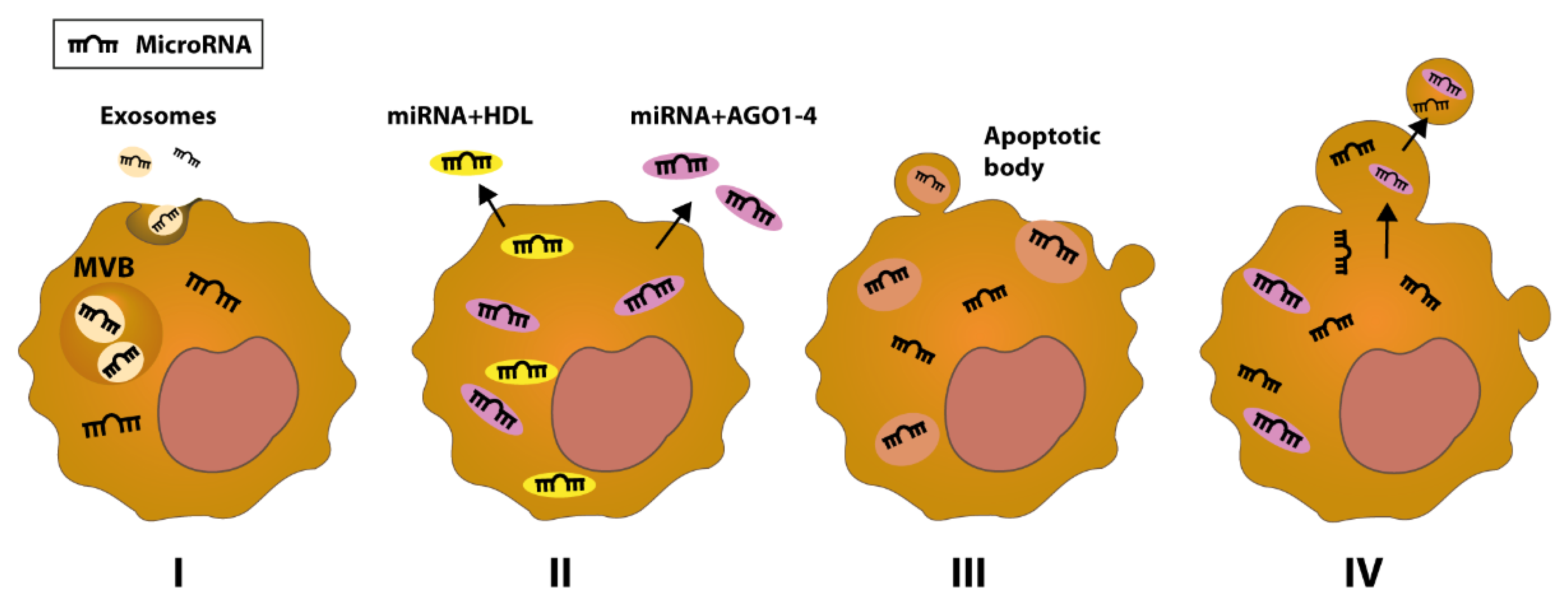
- Mazumder, S.; Datta, S.; Ray, J.G.; Chaudhuri, K.; Chatterjee, R. Liquid biopsy: miRNA as a potential biomarker in oral cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019, 58, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drula, R.; Ott, L.F.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Pantel, K.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs from Liquid Biopsy Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Recent Advances in Detection and Characterization Methods. Cancers 2020, 12, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Ping, F.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Deng, M.; Cheng, B.; Xia, J. Salivary exosomal miR-24-3p serves as a potential detective biomarker for oral squamous cell carcinoma screening. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Guo, C.; Yao, J.; Mi, S. Exosome and exosomal microRNA: Trafficking, sorting, and function. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arroyo, J.D.; Chevillet, J.R.; Kroh, E.M.; Ruf, I.K.; Pritchard, C.C.; Gibson, D.F.; Mitchell, P.S.; Bennett, C.F.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Stirewalt, D.L.; et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5003–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, J.; Riwanto, M.; Besler, C.; Knau, A.; Fichtlscherer, S.; Roxe, T.; Zeiher, A.M.; Landmesser, U.; Dimmeler, S. Characterization of levels and cellular transfer of circulating lipoprotein-bound microRNAs. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 1392–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turchinovich, A.; Weiz, L.; Burwinkel, B. Extracellular miRNAs: The mystery of their origin and function. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012, 37, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, K.; Katsuda, T.; Gailhouste, L.; Kosaka, N.; Ochiya, T. Commitment of Annexin A2 in recruitment of microRNAs into extracellular vesicles. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 4071–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Shen, W. Extracellular vesicle encapsulated microRNA-320a inhibits endometrial cancer by suppression of the HIF1alpha/VEGFA axis. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 394, 112113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zen, K.; Zhang, C.Y. Circulating microRNAs: A novel class of biomarkers to diagnose and monitor human cancers. Med. Res. Rev. 2012, 32, 326–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.; Lowry, M.C.; Corcoran, C.; Martinez, V.G.; Daly, M.; Rani, S.; Gallagher, W.M.; Radomski, M.W.; MacLeod, R.A.; O’Driscoll, L. miR-134 in extracellular vesicles reduces triple-negative breast cancer aggression and increases drug sensitivity. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 32774–32789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chong, Z.X.; Yeap, S.K.; Ho, W.Y. Roles of circulating microRNA(s) in human breast cancer. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 695, 108583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, K.; Li, C. Exosomes Derived from Hypoxic Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells Deliver miR-21 to Normoxic Cells to Elicit a Prometastatic Phenotype. Cancer Res 2016, 76, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, S.B.; Li, Z.L.; Luo, D.H.; Huang, B.J.; Chen, Y.S.; Zhang, X.S.; Cui, J.; Zeng, Y.X.; Li, J. Tumor-derived exosomes promote tumor progression and T-cell dysfunction through the regulation of enriched exosomal microRNAs in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 5439–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turchinovich, A.; Weiz, L.; Langheinz, A.; Burwinkel, B. Characterization of extracellular circulating microRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 7223–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Fu, H.; Wang, Q.; Shi, Y. Association of Decreased Expression of Serum miR-9 with Poor Prognosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yang, X.; Luo, Y.; Ren, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, N. Serum miR-483-5p: A novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, N.; Hanif, M.; Ahmed, A.; Jamal, Q.; Mushtaq, S.; Khan, A.; Saqib, M. Circulating miR-21 as a prognostic and predictive biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 35, 1408–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.J.; Lin, S.C.; Yang, C.C.; Cheng, H.W.; Chang, K.W. Exploiting salivary miR-31 as a clinical biomarker of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2012, 34, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristaldi, M.; Mauceri, R.; Di Fede, O.; Giuliana, G.; Campisi, G.; Panzarella, V. Salivary Biomarkers for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Diagnosis and Follow-Up: Current Status and Perspectives. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, C.; Nagadia, R.; Pandit, P.; Cooper-White, J.; Banerjee, N.; Dimitrova, N.; Coman, W.B.; Punyadeera, C. A novel saliva-based microRNA biomarker panel to detect head and neck cancers. Cell Oncol. 2014, 37, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Luo, R.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Qin, Y.; Zhou, D.; Liu, H.; Gong, X.; Chang, J. Paper-Based Strip for Ultrasensitive Detection of OSCC-Associated Salivary MicroRNA via CRISPR/Cas12a Coupling with IS-Primer Amplification Reaction. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 13336–13342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, W.Y.; Wang, H.J.; Chiu, C.W.; Chen, S.F. miR-27b-regulated TCTP as a novel plasma biomarker for oral cancer: From quantitative proteomics to post-transcriptional study. J Proteom. 2012, 77, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, C.; Roshan, V.G.D.; Khan, I.; Manasa, V.G.; Himal, I.; Kattoor, J.; Thomas, S.; Kondaiah, P.; Kannan, S. MiRNA expression profiling and emergence of new prognostic signature for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yu, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, Z.; Fletcher, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, D. Combined identification of three miRNAs in serum as effective diagnostic biomarkers for HNSCC. eBioMedicine 2019, 50, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomson, P.J. Perspectives on oral squamous cell carcinoma prevention-proliferation, position, progression and prediction. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2018, 47, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, D.; Sreenivasan, P.; Ohman, J.; Wallstrom, M.; Braz-Silva, P.H.; Giglio, D.; Kjeller, G.; Hasseus, B. Potentially Malignant Oral Disorders and Cancer Transformation. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 3223–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kramer, I.R.; Lucas, R.B.; Pindborg, J.J.; Sobin, L.H. Definition of leukoplakia and related lesions: An aid to studies on oral precancer. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1978, 46, 518–539. [Google Scholar]
- Speight, P.M.; Khurram, S.A.; Kujan, O. Oral potentially malignant disorders: Risk of progression to malignancy. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2018, 125, 612–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cervigne, N.K.; Reis, P.P.; Machado, J.; Sadikovic, B.; Bradley, G.; Galloni, N.N.; Pintilie, M.; Jurisica, I.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Gilbert, R.; et al. Identification of a microRNA signature associated with progression of leukoplakia to oral carcinoma. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 4818–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
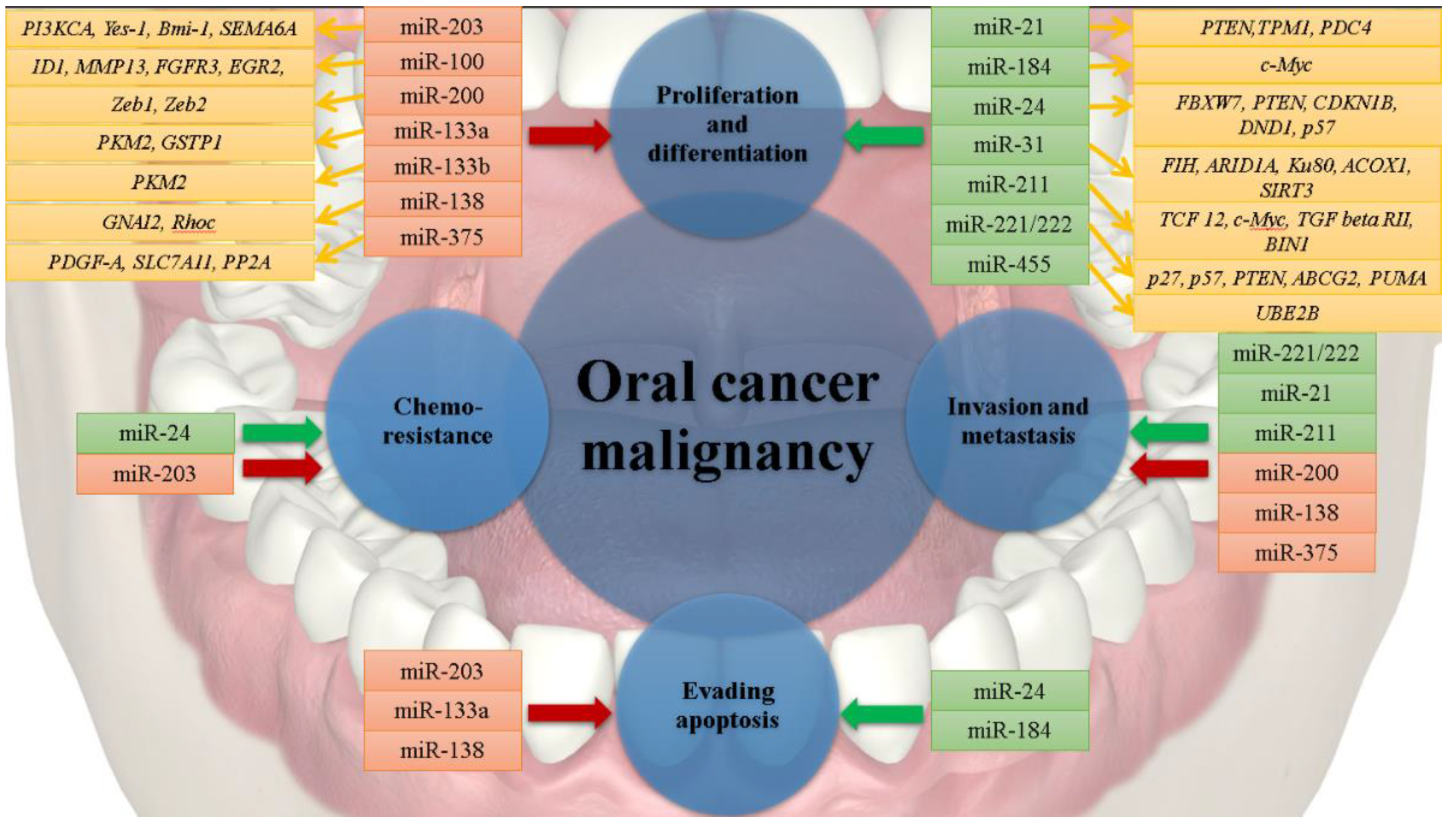
| microRNA | Level of Expression | Biological Influence on Cancerous Cells | Target Genes | Area of Assessment | Biomarker Role | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21 |  | Proliferation Invasion and Metastasis | PTEN, TPM1, PDC4 | Tumor tissue Saliva | Diagnostic and prognostic | [28,29,30] |
| miR-24 |  | Proliferation Resistance to chemotherapy Antiapoptotic | FBXW7, PTEN, CDKN1B, DND1, CDKN1C | Tumor tissue Plasma Saliva | Diagnostic | [31,32,33,34] |
| miR-31 |  | Proliferation and Differentiation Invasion and Metastasis | FIH, ARID1A, Ku80, ACOX1, SIRT3 | Tumor tissue Saliva | Diagnostic and prognostic | [35,36,37,38,39] |
| miR-184 |  | Proliferation Antiapoptotic | c-MYC | Tumor tissue Saliva | Diagnostic | [40] |
| miR-211 |  | Proliferation and Differentiation Invasion and Metastasis | TCF12, c-MYC, TGFBR2, BIN1 | Tumor tissue | Diagnostic and prognostic | [41,42,43] |
| miR-221, miR-222 |  | Proliferation Invasion and Metastasis | CDKN1B, CDKN1C, PTEN, ABCG2, PUMA | Tumor tissue Saliva (only miR-221) | Diagnostic | [44,45,46,47] |
| miR-455 |  | Proliferation and Differentiation | UBE2B | Tumor tissue | Diagnostic and prognostic | [48] |
| miR-203 |  | Proliferation Antiapoptotic Resistance to chemotherapy | PI3KCA, YES-1, BMI-1, SEMA6A | Tumor tissue Saliva (so far only in non-cancerous cells) | Diagnostic and prognostic | [49,50,51,52] |
| miR-100 |  | Proliferation and Differentiation | ID1, MMP13, EGR2, FGFR3 | Tumor tissue | Diagnostic | [53] |
| miR-200 |  | Differentiation Invasion and Metastasis | ZEB1, ZEB2 | Tumor tissue Saliva oral rinse | Diagnostic and prognostic | [54] |
| miR-133a |  | Proliferation and Differentiation Antiapoptotic | PKM2, GSTP1 | Tumor tissue | Diagnostic | [55] |
| miR-133b |  | Proliferation | PKM2 | Tumor tissue | Diagnostic | [55,56] |
| miR-138 |  | Proliferation Antiapoptotic Invasion and Metastasis | GNAI2, Rhoc | Tumor tissue | Diagnostic | [57,58] |
| miR-375 |  | Proliferation Invasion and Metastasis | PDGF-A, SLC7A11, CIP2A | Tumor tissue Saliva | Diagnostic | [59,60,61,62,63] |
| microRNA | Target Gene | Impact on Oral TME | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21 | TGFB1 | Myofibroblast differentiation | [88] |
| miR-148-a | WNT10B | Cancer-associated fibroblats (CAFs) proliferation | [90] |
| miR-124 | CCL2, IL8 | CAFs proliferation and migration | [93] |
| miR-126 | VEGF-A | Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis | [94] |
| miR 300 | VEGF-C | Lymphangiogenesis | [95] |
| miR-320 | NRP1 | Angiogenesis | [97] |
| miR-124 | STAT3 | Increase of Vasculogenic mimicry | [101] |
| miR-204 | SLUG, SOX4 | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), Stemness features | [103] |
| miR-218 | BMI1 | Stemness features | [104] |
| miR-145 | CD44 | Stemness features | [105] |
| miR-200 | ZEB1, ZEB2 | EMT | [54] |
| miR-153 | SNAI1, ZEB2 | EMT | [106] |
| miR-639 | FOXC1 | EMT | [107] |
| miR-143, miR-145 | Activin A | EMT | [108] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osan, C.; Chira, S.; Nutu, A.M.; Braicu, C.; Baciut, M.; Korban, S.S.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. The Connection between MicroRNAs and Oral Cancer Pathogenesis: Emerging Biomarkers in Oral Cancer Management. Genes 2021, 12, 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121989
Osan C, Chira S, Nutu AM, Braicu C, Baciut M, Korban SS, Berindan-Neagoe I. The Connection between MicroRNAs and Oral Cancer Pathogenesis: Emerging Biomarkers in Oral Cancer Management. Genes. 2021; 12(12):1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121989
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsan, Ciprian, Sergiu Chira, Andreea Mihaela Nutu, Cornelia Braicu, Mihaela Baciut, Schuyler S. Korban, and Ioana Berindan-Neagoe. 2021. "The Connection between MicroRNAs and Oral Cancer Pathogenesis: Emerging Biomarkers in Oral Cancer Management" Genes 12, no. 12: 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121989
APA StyleOsan, C., Chira, S., Nutu, A. M., Braicu, C., Baciut, M., Korban, S. S., & Berindan-Neagoe, I. (2021). The Connection between MicroRNAs and Oral Cancer Pathogenesis: Emerging Biomarkers in Oral Cancer Management. Genes, 12(12), 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121989










